Glacial Debris Flow Blockage Event (2018) in the Sedongpu Basin of the Yarlung Zangbo River, China: Occurrence Factors and Its Implications
Abstract
:Highlights:
- The topography and climate background determine that the hazard happens periodically, and these factors are fundamental for the weak vulnerability in the Sedongpu basin;
- The dynamic glacier simulations with the Elmer/Ice model showed that the glacier surface velocity can reach 19 cm/d on the Dongpu glacier;
- Heavy rain and an earthquake were triggering factors of the ice avalanche that led to the glacial debris flow.
Abstract
1. Introduction
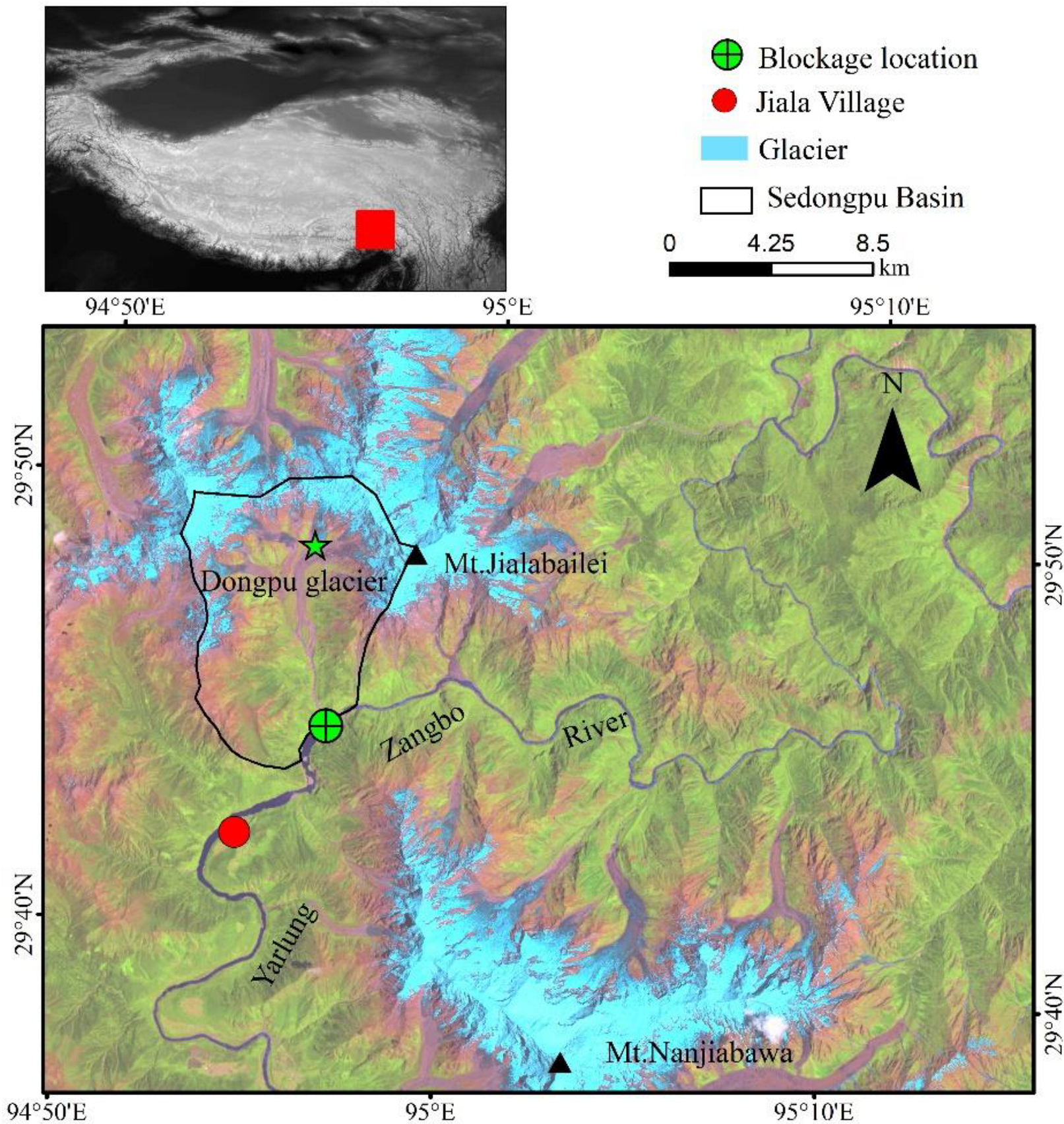
2. Study Area
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data and Processing
3.2. Methods
3.3. Uncertainties
4. Results and Discussion
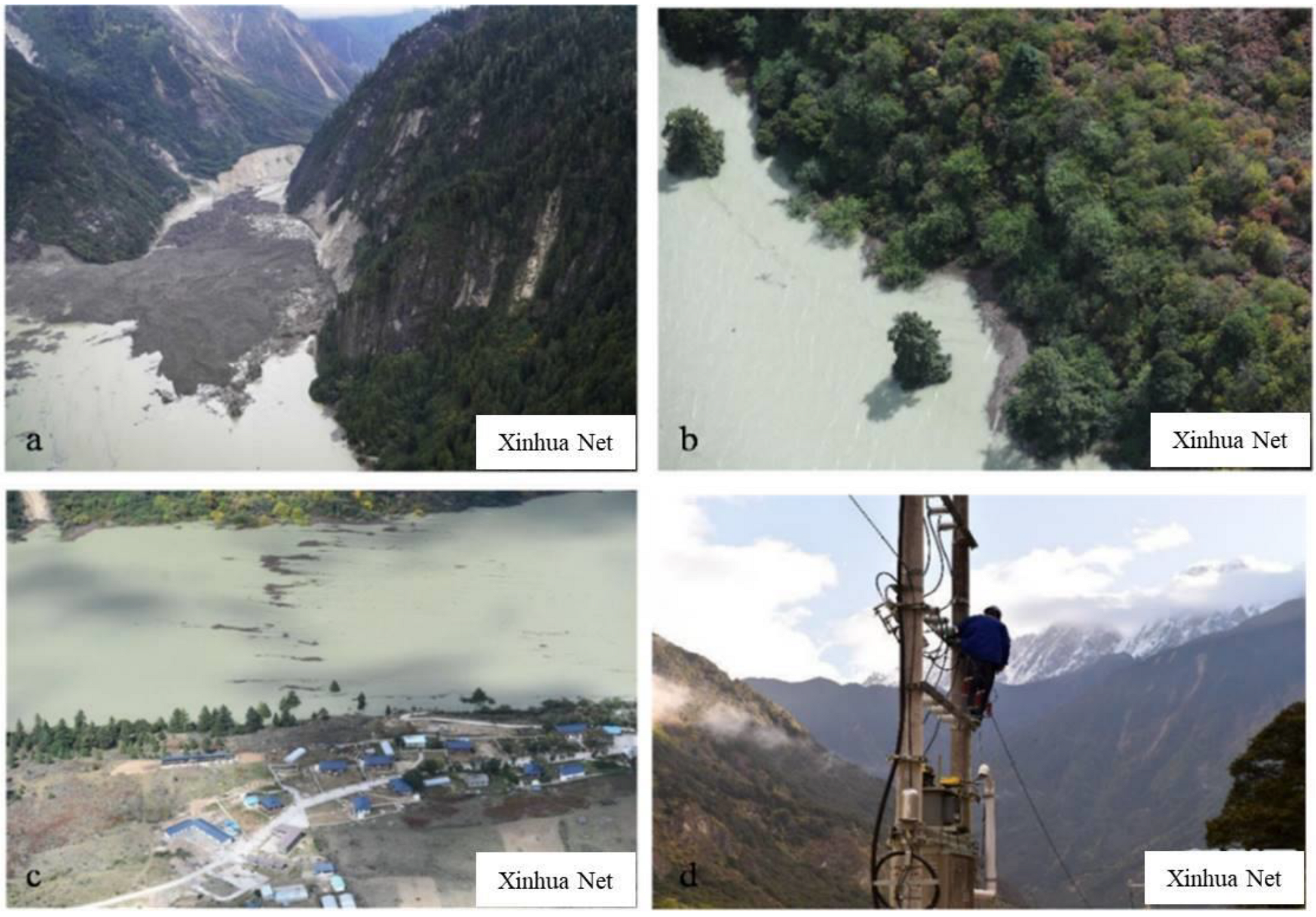
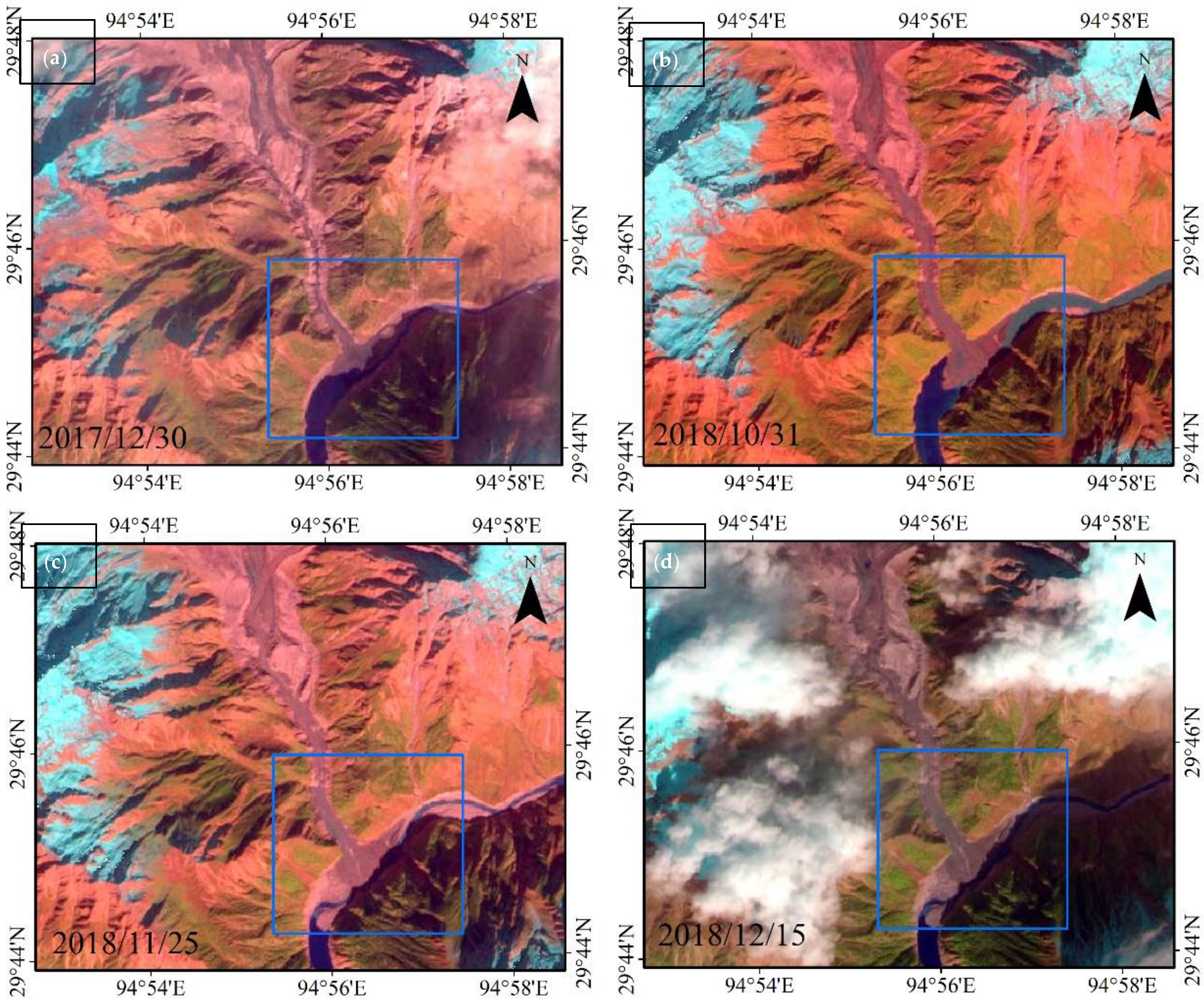
4.1. Blockage Event Process
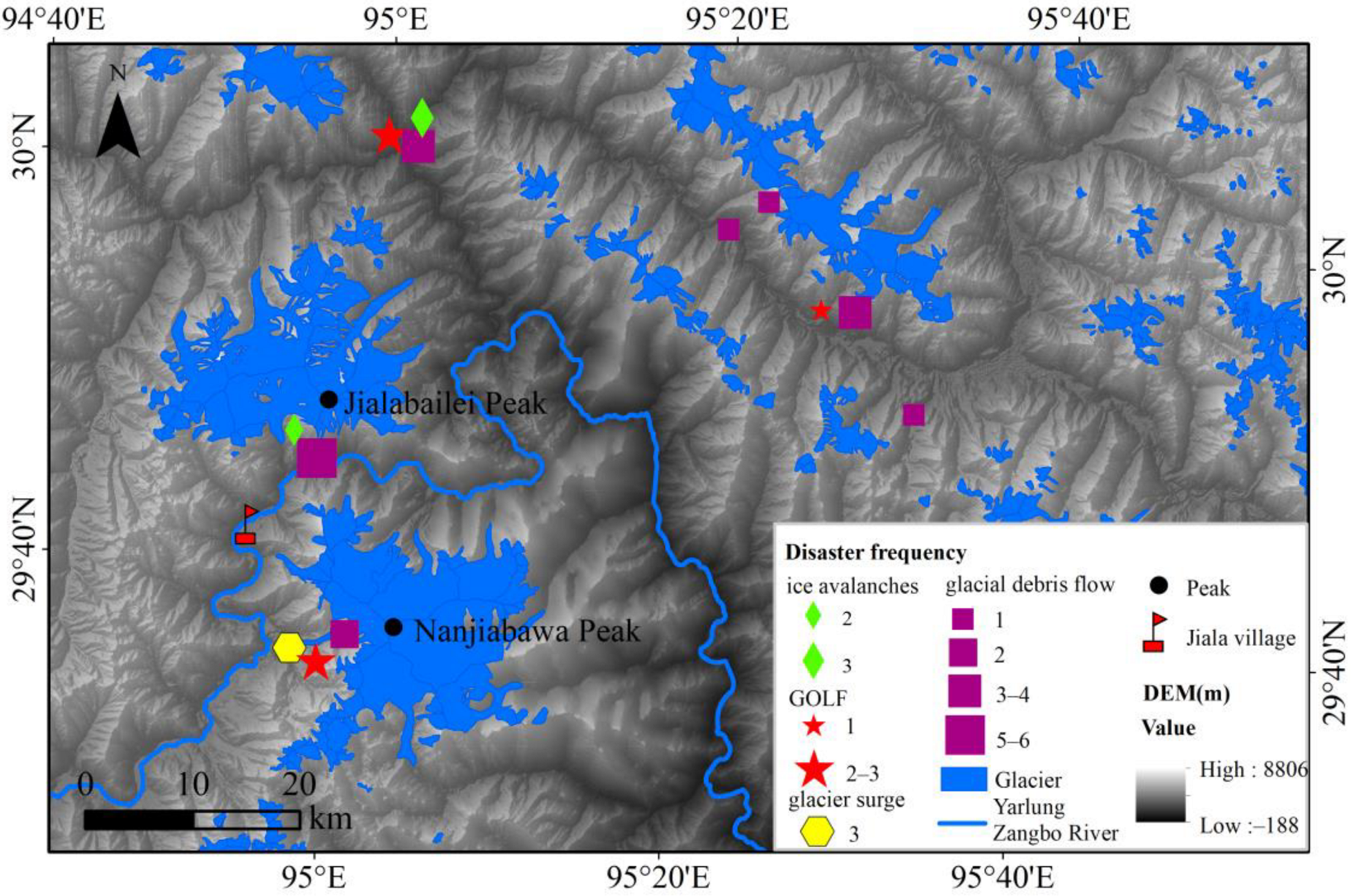
4.2. Historical Glacier Hazards
4.3. Diagnostic of Influencing Factors
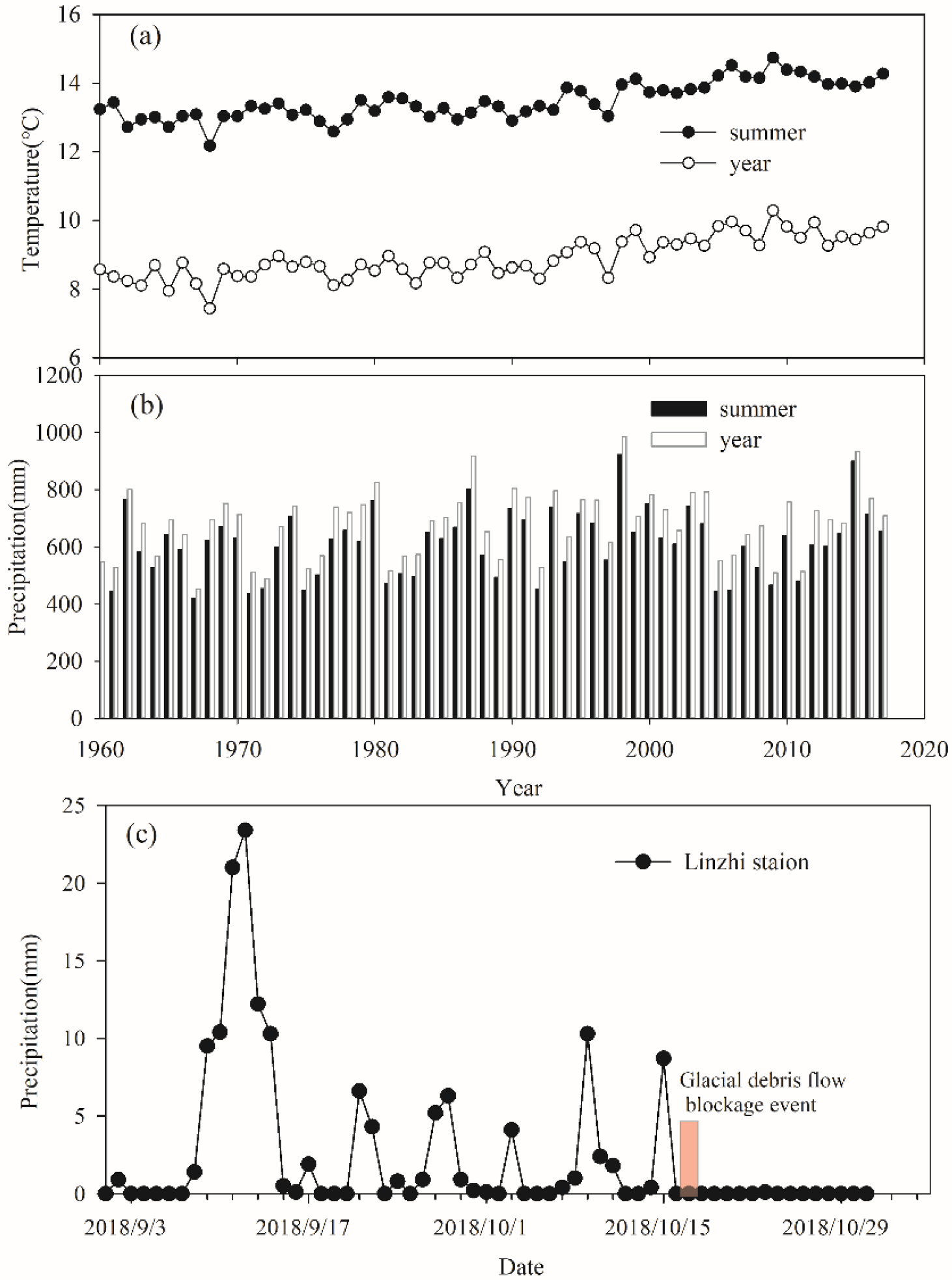
4.3.1. Climate Change
4.3.2. Topography
4.3.3. Glacier Dynamics
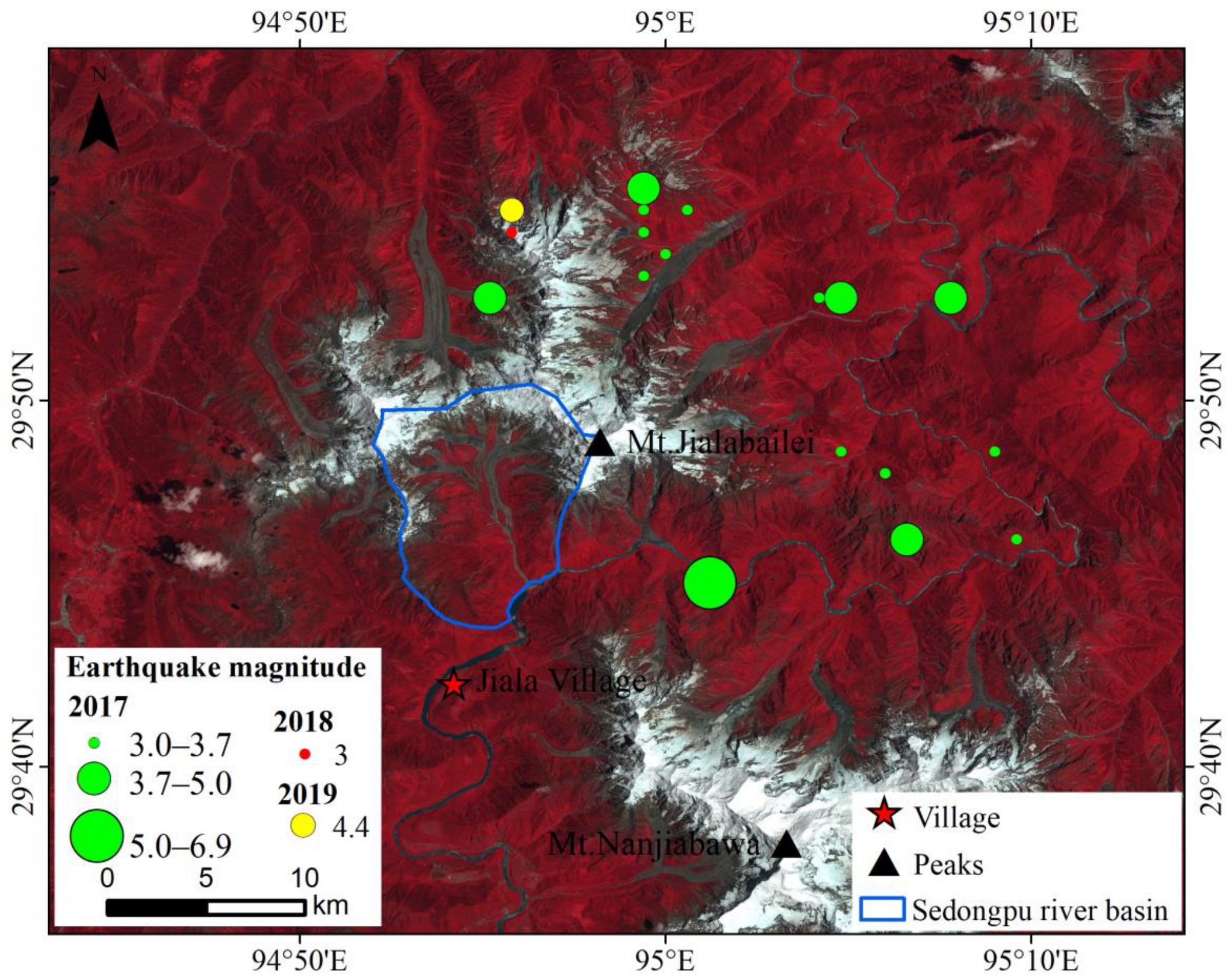
4.3.4. Earthquakes
4.3.5. Characteristics of Debris in the Glacier Ablation Area
5. Conclusions and Prospective
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Richardson, S.D.; Reynolds, J.M. An overview of glacial hazards in the Himalayas. Quat. Int. 2000, 65–66, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeberli, W. Frequency and characteristics of glacier floods in the Swiss Alps. Ann. Glaciol. 1983, 4, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrivick, J.L.; Tweed, F.S. A global assessment of the societal impacts of glacier outburst floods. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2016, 144, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, L.; Yao, T.; Gao, Y.; Thompson, L.; Mosley-Thompson, E.; Muhammad, S.; Zong, J.; Wang, C.; Jin, S.; Li, Z. Two glaciers collapse in western Tibet. J. Glaciol. 2017, 63, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chernomorets, S.S.; Tutubalina, O.V.; Seinova, I.B.; Petrakov, D.A.; Nosov, K.N.; Zaporozhchenko, E.V. Glacier and debris flow disasters around Mt. Kazbek, Russia/Georgia. In Debris-Flow Hazards Mitigation: Mechanics, Prediction, and Assessment; Chen, C.L., Major, J.J., Eds.; Millpress: Rotterdam, The Netherlands; Chendgu, China, 2007; pp. 691–702. [Google Scholar]
- Colgan, W.; Sommers, A.; Rajaram, H.; Abdalati, W.; Frahm, J. Considering thermal-viscous collapse of the Greenland ice sheet. Earth’s Future 2015, 3, 252–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Mu, C.; Wu, T.; Hu, G.; Zou, D.; Wang, D.; Li, W.; Wu, X. Increasing cryospheric hazards in a warming climate. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2021, 213, 103500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A.; Huggel, C.; Guex, S.; Paul, F.; Salzmann, N.; Schmutz, K.; Schneider, D.; Weidmann, Y. Glacier hazard assessment in mountains using satellite optical data. EARSeL eProc. 2005, 4, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Wen, J. Characteristics, influence of cryosphere disaster and prospect of discipline development. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 523–530. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, M.; Huai, B.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Guo, X.; Zhang, T. Surge-type glaciers in Karakoram Mountain and possible catastrophes alongside a portion of the Karakoram Highway. Nat. Hazards 2018, 90, 1017–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kääb, A.; Leinss, S.; Gilbert, A.; Bühler, Y.; Gascoin, S.; Evans, S.G.; Bartelt, P.; Berthier, E.; Brun, F.; Chao, W.; et al. Massive collapse of two glaciers in western Tibet in 2016 after surge-like instability. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, A.; Leinss, S.; Kargel, J.; Kaab, A.; Gascoin, S.; Leonard, G.; Berthier, E.; Karki, A.; Yao, T. Mechanisms leading to the 2016 giant twin glacier collapses, Aru Range, Tibet. Cryosphere 2018, 12, 2883–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, P.; Chen, X.Q.; Cheng, Z.L.; Chen, N.S.; Dang, C. Monitoring and prevent of debris-flows and landslides in Tibet. Chin. J. Nat. 2010, 32, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Shangguan, D.; Ding, Y.; Liu, S.; Xie, Z.; Pieczonka, T.; Xu, J.; Moldobekov, B. Quick release of internal water storage in a glacier leads to underestimation of the hazard potential of glacial lake qutburst floods from Lake Merzbacher in Central Tian Shan Mountains. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 9786–9795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Tu, J.; Pei, L.; Guo, Z.; Zheng, X.; Fan, J. Preliminary discussion of the frequently debris flow events in Sedongpu Basin at Gyalaperi peak, YarlungZangbo River. J. Eng. Geol. 2018, 26, 1552–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Lü, J.; Tong, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, R.; Tu, J. Research on glacial/rock fall-landslide-debris flows in Sedongpu basin along Yarlung Zangbo River in Tibet. Geol. China 2019, 46, 219–234, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Chen, F.; Cui, P.; Ma, Y.; Xu, B.; Zhu, L.; Yang, X. From Tibetan Plateau to Third Pole and Pan-Third Pole. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2017, 32, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, Q.; Kang, S.; Yan, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, J. Trends in daily temperature and precipitation extremes over the Yarlung Zangbo River basin during 1961–2005. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2009, 64, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Some features of the surge glacier in the Mt. Namjagbarwa. Mt. Res. 1985, 3, 234–238. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Xu, Z.; Li, F.; Su, L. Climate change scenarios in the Yarlung Zangbo river basin based on the ASD model. Plateau Meteorol. 2014, 33, 26–36. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Xu, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Y. The impact of climate change on runoff in the Yarlung Tsangpo River basin in the Tibetan Plateau. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, N.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Deng, C. Analysis of the characteristics of the glacier system and typical glacier change based on remote sensing in the Yarlung Zangbo River basin during the past 30 years. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2013, 35, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fineberg, S.J.; Nandyala, S.V.; Marquez-Lara, A.; Oglesby, M.; Patel, A.A.; Singh, K. Incidence and risk factors for postoperative delirium after lumbar spine surgery (Phila Pa 1976). Spine 2013, 38, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komori, J.; Koike, T.; Yamanokuchi, T.; Tshering, P. Glacial lake outburst events in the Bhutan Himalayas. Glob. Environ. Res. 2012, 16, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, T.; Ju, L.; Leng, W.; Price, S.; Gunzburger, M. Thermomechanically coupled modelling for land-terminating glaciers: A comparison of two-dimensional, first-order and three-dimensional, full-Stokes approaches. J. Glaciol. 2015, 61, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, W.; Yao, T.; Yu, W.; Yang, W.; Gao, Y. Advances in the study of glacier avalanches in High Asia. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2018, 40, 1141–1152. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xu, Z.; Gong, T. Characteristics of runoff variationin the Yarlung Zangbo River basin. Geogr. Res. 2008, 27, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wang, G.; Wang, A.; Cao, S.; Cao, K. The morphology of the Yalung Zangbo River in the Great Canyon Region and its implications. Geol. Bull. China 2013, 32, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, N. The Study on Climate Change, Glacier Fluctuation and River Water Resource over Yarlung Zangbo River basin in Recent Years. Ph.D. Thesis, Nanjing University, Nanjing, China, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, T.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Guo, X.; Zhu, L.; Kang, S.; Wu, Y.; Yu, W. Glacial distribution and mass balance in the Yarlung Zangbo River and its influence on lakes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Xiao, C.; Colgan, W.; Qin, X.; Du, W.; Sun, W.; Ding, M. Observed and modelled ice temperature and velocity along themain flowline of East Rongbuk Glacier, Qomolangma (MountEverest), Himalaya. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 438–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabus, B.; Eineder, M.; Roth, A.; Bamler, R. The Shuttle radar topography mission-A new class of digital elevation models acquired by spaceborne radar. J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2003, 57, 241–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolch, T.; Buchroithner, M.F.; Kunert, A.; Kamp, U. Automated delineation of debris-covered glaciers based on ASTER data. In GeoInformation in Europe; Gomarasca, M.A., Ed.; Millpress: Rotterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 403–410. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, S.; Wang, Z.E.D.; Holmén, K.; Tan, Z.; Zhou, C.; Sun, W. Topography, ice thickness and ice volume of the glacier Pedersenbreen in Svalbard, using GPR and GPS. Polar Res. 2014, 33, 18533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paterson, W.S.B. The Physics of Glaciers; Pergamon: New York, NY, USA, 1981; 380p. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, D.; Feng, Q. Studies on Catastrophes of glacial debris flow and glacial lake outburst floods in China. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 1988, 10, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Zhou, H.; Hu, G. Development Rules of debris flow Under the Influence of Climate Change in Nyingchi. Adv. Clim. Chang. Res. 2011, 7, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, D.K.; Bayr, K.J.; Schöner, W.; Bindschadler, R.A.; Chien, J.Y. Consideration of the errors inherent in mapping historical glacier positions in Austria from ground and space (1893–2001). Remote Sens. Environ. 2003, 86, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverio, W.; Jaquet, J.-M. Glacial cover mapping (1987–1996) of the Cordillera Blanca (Peru) using satellite imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. Impact analysis of Gega glacier debris flow blocking of river at entrance of Brahmaputra bend. Sichuan Water Power 2015, 34, 81–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Zhu, P.; Dang, C.; Liu, J. Hazards of debris flow due to glacier-lake outburst in southeastern Tibet. J. Glaciol. Geocryol. 2008, 30, 954–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Tian, J.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, B. Debris flow induced by glacial-lake break in Southeast Tibet. Earth Sci. Frontiers. 2009, 16, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, L.; Feng, Q. Analysis on the development characteristics and mechanism of the debris flow in the Zelongnong Glacier, NanjiaBawa. Inn. Mong. Sci. Technol. Econ. 2018, 4, 58–59. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P. Study on the Chronology of the Glaciers at the Entrance of the Yarlung Zangbo River and Its Tectonic-Environmental Evolution; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Yao, X.; Sun, J.; Li, L.; Ling, S. An overview on research development of glacier-related debris flow. J. Eng. Geol. 2014, 22, 459–495. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, D.; Yang, Y.; Chang, M. Cause analysis and preventive measures of debris flow disaster-chain due to glacier lake outburst in southeastern Tibet. Water Resour. Power 2003, 31, 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, M.; Chen, N.; Ding, H.; Zhou, C. The hydrothermal condition and formation mechanism of the group-occurring debris flows in the southeast Tibet in 2007. J. Nat. Hazards 2013, 22, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Chen, N.; Deng, M.; Wang, Y. Classification and initiation conditions of debris flows in Linzhi area, Tibet. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2011, 31, 193–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IPCC. IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Pörtner, H.O., Roberts, D.C., Masson-Delmotte, V., Zhai, P., Tignor, M., Poloczanska, E., Weyer, N.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019.
- Dou, T.; Xiao, C.; Liu, J.; Han, W.; Du, Z.; Mahoney, A.R.; Jones, J.; Eicken, H. A key factor initiating surface ablation of Arctic sea ice: Earlier and increasing liquid precipitation. Cryosphere 2019, 13, 1233–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, B.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wang, X. Glacier deformation inversion before disaster using SBAS-InSAR technology in Sedongpu basin along the Yarlung Zangbo River. Surv. Mapp. Bull. 2021, 11, 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, N.; Deng, M.; Hu, G.; Zhou, W.; Yang, C. Risk Characteristics and Prevention Strategy of Debris Flow Under the Seismic Influence in Mountainous Arid Area, Southwest China. J. Sichuan Univ. (Eng. Sci. Ed.) 2010, 41, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, X. Landslides triggered by the Ms 6.9 Nyingchi earthquake, China (18 November 2017): Analysis of the spatial distribution and occurrence factors. Landslides 2019, 16, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benn, D.I.; Bolch, T.; Hands, K.; Gulley, J.; Luckman, A.; Nicholson, L.I.; Quincey, D.; Thompson, S.; Toumi, R.; Wiseman, S. Response of debris-covered glaciers in the Mount Everest region to recent warming, and implications for outburst flood hazards. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2012, 114, 156–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scherler, D.; Bookhagen, B.; Strecker, M.R. Spatially variable response of Himalayan glaciersto climate change affected by debris cover. Nat. Geosci. 2011, 4, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobhal, D.P.; Mehta, M.; Srivastava, D. Influence of debris cover on terminus retreat and mass changes of Chorabari Glacier, Garhwal region, central Himalaya, India. J. Glaciol. 2013, 59, 961–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, L.; Benn, D.I. Calculating ice melt beneath a debris layer using meteorological data. J. Glaciol. 2006, 52, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]



| ID | Receive Date | Sensor | Resolution (m) | Path |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LC8135039_03920150725 | 2015-07-25 | OLI/TIRS | 30/15 | 135/039 |
| LC5135039_03920040507 | 2004-05-07 | TM | 30 | 135/039 |
| LC5135039_03919960415 | 1996-04-15 | TM | 30 | 135/039 |
| LC5135039_03919870407 | 1987-04-07 | TM | 30 | 135/039 |
| L1C_T46RFT_A004120 | 2017-12-20 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFT_A004263 | 2017-12-30 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFT_A008982 | 2018-11-25 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFT_A009268 | 2018-12-15 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFT_A017533 | 2018-10-31 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFT_A017962 | 2018-11-30 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A004120 | 2017-12-20 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A004263 | 2017-12-30 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A008982 | 2018-11-25 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A009268 | 2018-12-15 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A017533 | 2018-10-31 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A017533 | 2018-10-31 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A017819 | 2018-11-20 | MSI | 10 | T46RFT |
| L1C_T46RFU_A017962 | 2018-11-30 | MSI | 10 | T46RFU |
| Symbol | Description | Value and Unit |
|---|---|---|
| ρ | Ice density | 910 kg m−3 |
| g | Gravitational acceleration | 9.81 kg s−2 |
| n | Glen exponent | 3 |
| A0 | Rate factor | |
| When T ≤ −10 °C | 2.89 × 10−13 s−1 Pa−3 | |
| When T > −10 °C | 2.43 × 10−13 s−1 Pa−3 | |
| Q | Creep activation energy | |
| When T ≤ −10 °C | 60 kJ mol−1 | |
| When T > −10 °C | 115 kJ mol−1 | |
| R | Gas constant | 8.31 J kg−1 K−1 |
| Date | Location | Hazard Type | Reference | Village Affected |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950, 1968, 1984 | Zenong glacier | Glacier debris flows Glacier surge | [40] [43] [44] | Zhibai village Gega village |
| 1953, 1972, 2005 | Guxiang Valley | Glacier debris flows GLOF | [45] [36] [37] | Gu village |
| 1983–1985 | Peilong Valley | Glacier debris flows GLOF, ice avalanches | [42] [41] [46] | Pailong village |
| 2007 | Tianmo Valley | Glacier debris flows | [47] | Songrao village |
| 2007 | Bitong Valley | Glacier debris flows | [47] | Bitong village |
| 2007 | Baka Valley | Glacier debris flows | [47] | Baka village |
| Unknown | Layue | Glacier debris flows | [26] | Layue village |
| Unknown | Suotong Valley | Glacier debris flows | [48] | Suotong village |
| Unknown | Gelang Valley | Glacier debris flows | [48] | Galang village |
| 2017, 2018 | Sedongpu basin | Glacier debris flows Glacier avalanches | This study | Jiala village |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huai, B.; Ding, M.; Ai, S.; Sun, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J. Glacial Debris Flow Blockage Event (2018) in the Sedongpu Basin of the Yarlung Zangbo River, China: Occurrence Factors and Its Implications. Land 2022, 11, 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081217
Huai B, Ding M, Ai S, Sun W, Wang Y, Gao J. Glacial Debris Flow Blockage Event (2018) in the Sedongpu Basin of the Yarlung Zangbo River, China: Occurrence Factors and Its Implications. Land. 2022; 11(8):1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081217
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuai, Baojuan, Minghu Ding, Songtao Ai, Weijun Sun, Yetang Wang, and Jiajia Gao. 2022. "Glacial Debris Flow Blockage Event (2018) in the Sedongpu Basin of the Yarlung Zangbo River, China: Occurrence Factors and Its Implications" Land 11, no. 8: 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081217
APA StyleHuai, B., Ding, M., Ai, S., Sun, W., Wang, Y., & Gao, J. (2022). Glacial Debris Flow Blockage Event (2018) in the Sedongpu Basin of the Yarlung Zangbo River, China: Occurrence Factors and Its Implications. Land, 11(8), 1217. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081217






