Decoupling Relationship between Industrial Land Expansion and Economic Development in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Material and Methods
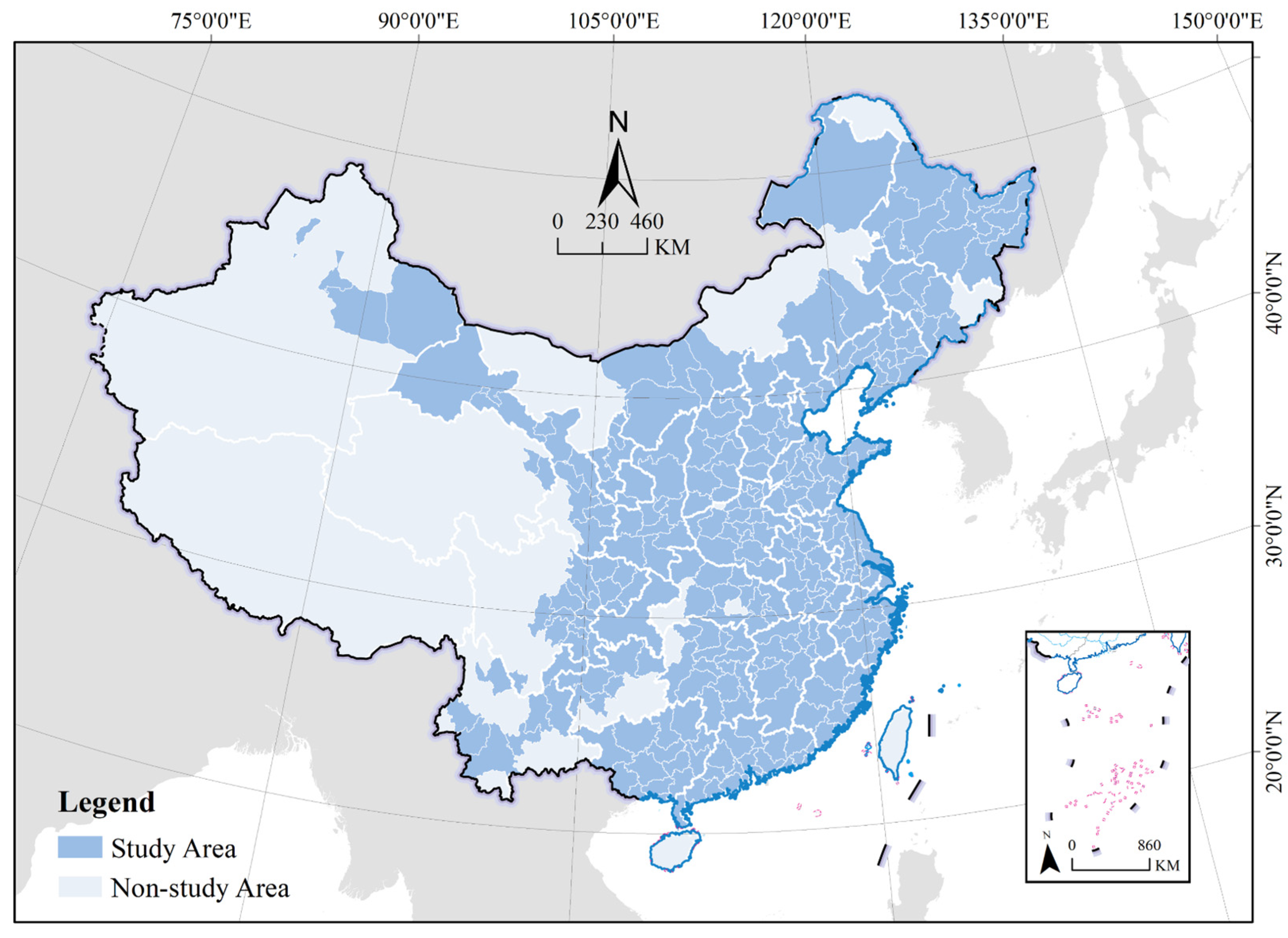
3.1. Study Area
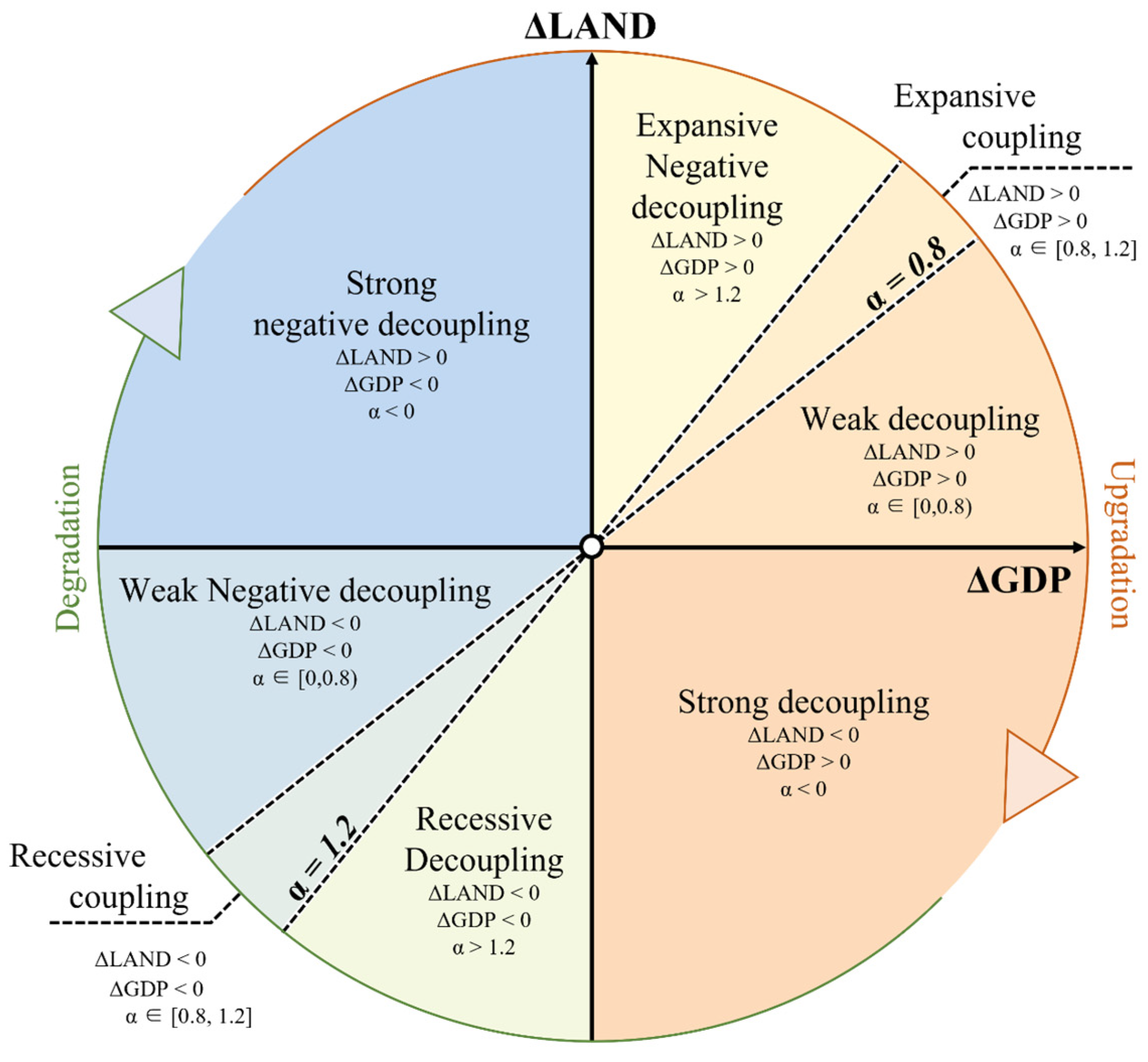
3.2. Method
3.3. Research Steps and Data Resource
4. Results
4.1. Pattern of Relationship between Industrial Land and Economy
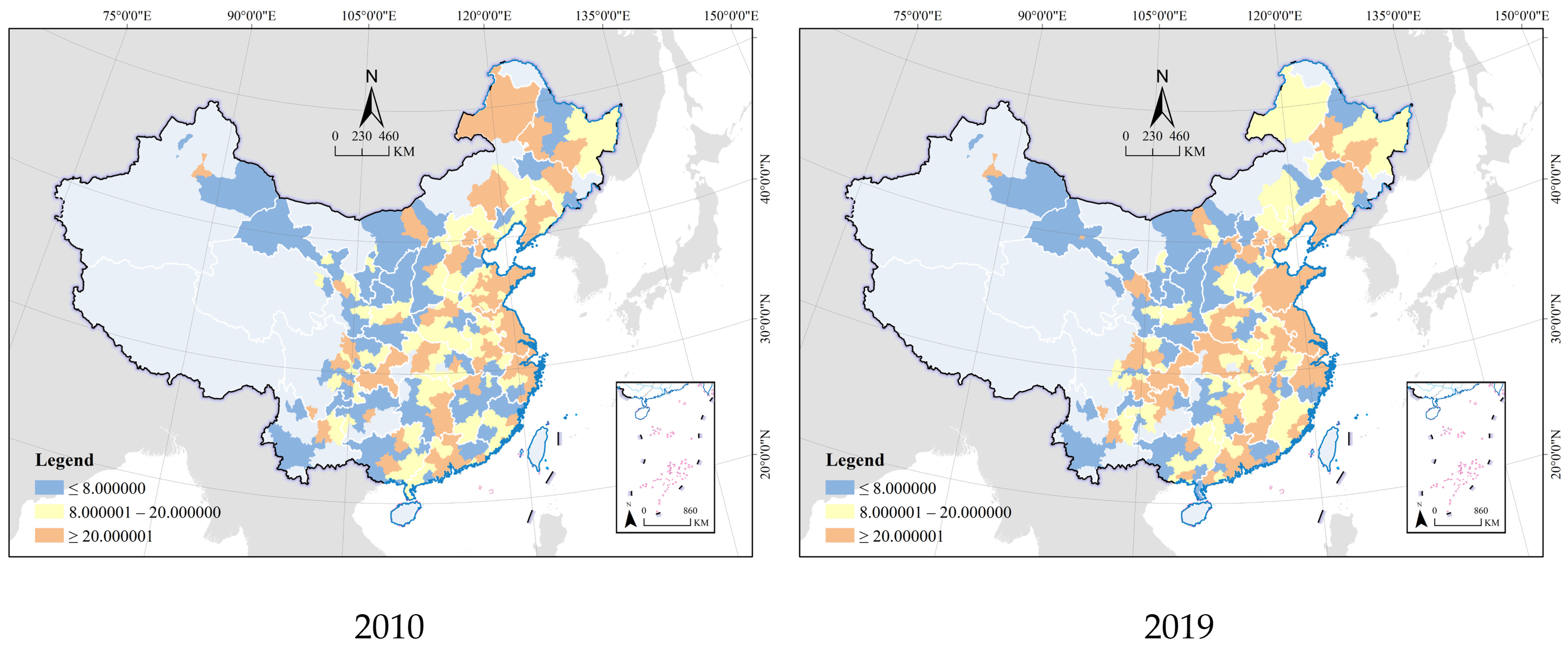
4.1.1. Scale of Industrial Land and Economy
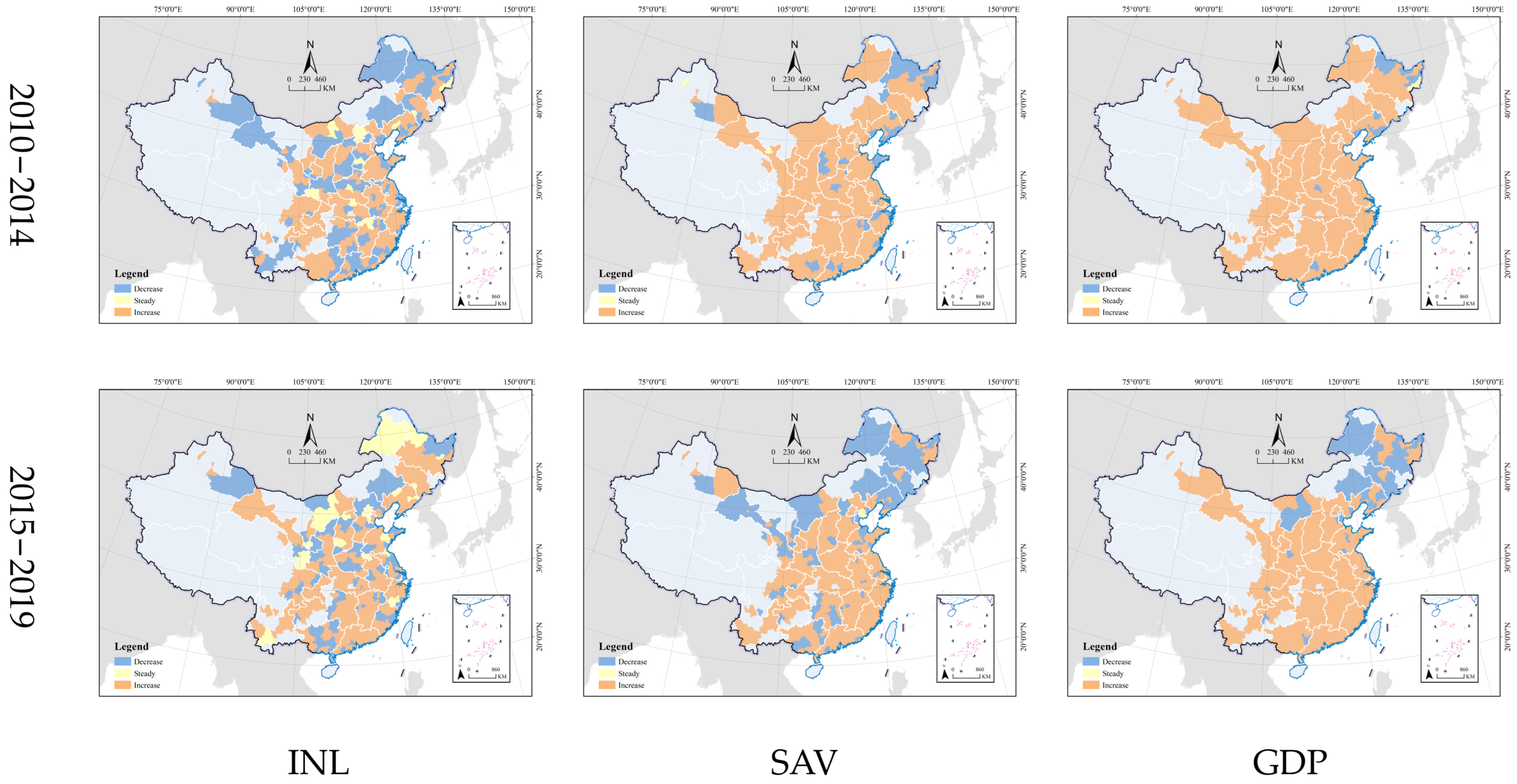
4.1.2. Growth Rate of Industrial Land and Economy
4.2. Decoupling Relationship between Industrial Land and Economy
4.2.1. Relationship between Industrial Land and Second-Industry Added Value
4.2.2. Relationship between Industrial Land and Gross Domestic Product
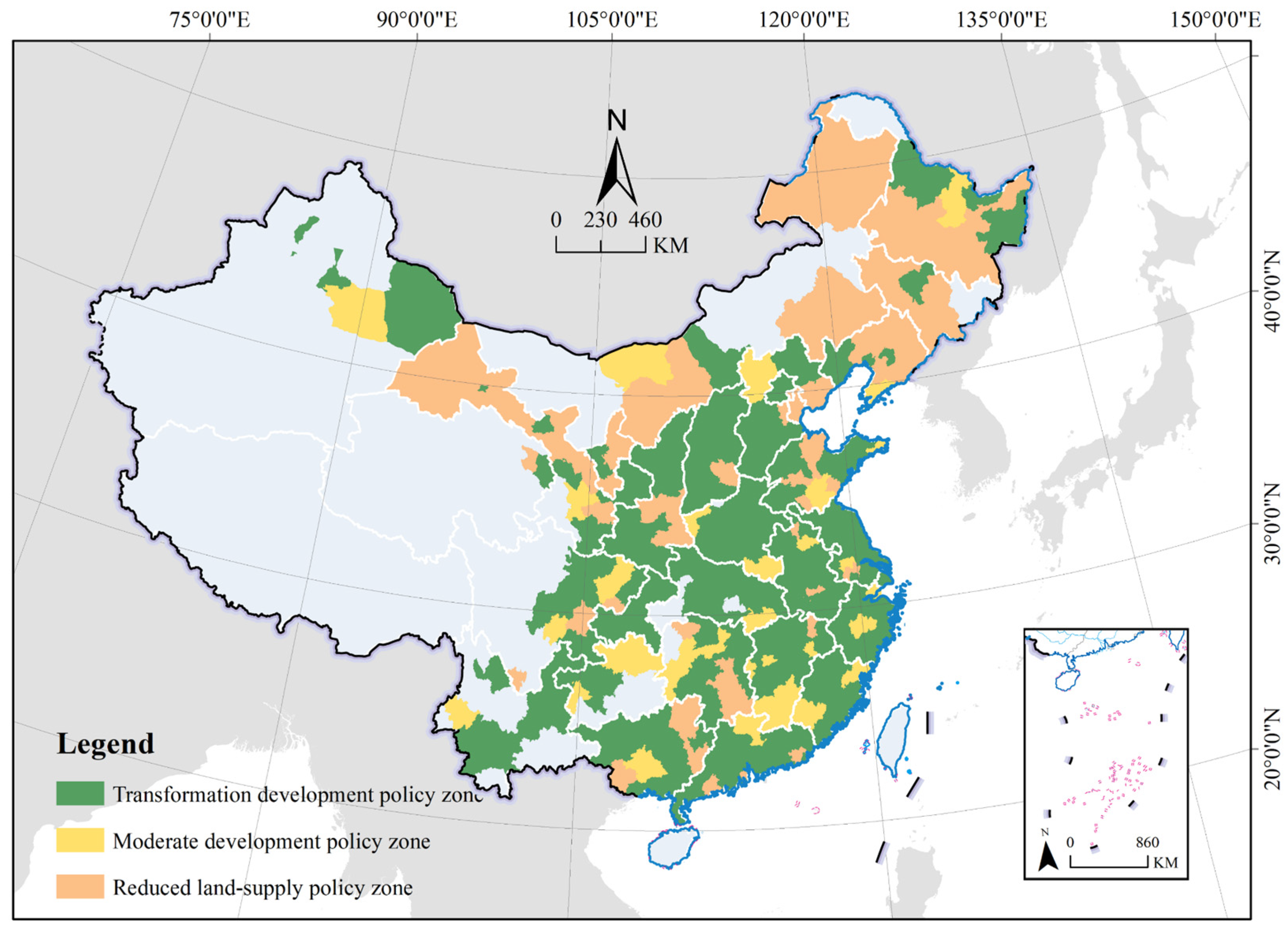
5. Policy Suggestion
5.1. Transformation Development Policy Zone
5.2. Moderate Development Policy Zone
5.3. Reduced Land-Supply Policy Zone
6. Discussion
6.1. Theoretical Value
6.2. Limitation and Future Implications
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Semova, N.G. Problems of reindustrialization: Approaches to its study at the beginning of the XXI century. Vopr. Istor. 2019, 10, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, B.; Lengyel, I.; Udvari, B. Reindustrialization patterns in the post-socialist EU members: A comparative study between 2000 and 2017. Eur. J. Comp. Econ. 2020, 17, 253–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, W.Q.; Jiao, L.M.; Xu, G. Understanding the urban scaling of urban land with an internal structure view to characterize China’s urbanization. Land Use Policy 2022, 112, 105781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obeng-Odoom, F. Industrial policy, economic theory, and ecological planning. Int. Rev. Appl. Econ. 2022, 36, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajinipriya, M.; Nagalakshmaiah, M.; Robert, M. Importance of Agricultural and Industrial Waste in the Field of Nanocellulose and Recent Industrial Developments of Wood Based Nanocellulose: A Review. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2018, 6, 2807–2828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.K.; Liu, Y.; Lin, S.J. Soil Pollution Management in China: A Brief Introduction. Sustainability 2019, 11, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abrantes, P.; Fontes, I.; Gomes, E.; Rocha, J. Compliance of land cover changes with municipal land use planning: Evidence from the Lisbon metropolitan region (1990–2007). Land Use Policy 2016, 51, 120–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.J. China Urban Construction Statistical Yearbook; Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019; pp. 48–83. [CrossRef]
- Industry (Including Construction), Value Added (Constant 2015 US$) World Development Indicators. Available online: www.data.worldbank.org/indicator/NV.IND.TOTL.KD (accessed on 15 April 2022).
- Taylor, P.J.; Ni, P.; Derudder, B. Measuring the world city network: New results and developments. GaWC Res. Bull. 2010, 300, 1–8. Available online: https://www.lboro.ac.uk/gawc/rb/rb300.html (accessed on 23 June 2022).
- Raźniak, P.; Dorocki, S.; Winiarczyk-Raźniak, A. Spatial changes in the command and control function of cities based on the corporate centre of gravity model. Misc. Geogr. 2020, 24, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Csomós, G. Cities as Command and Control Centres of the World Economy: An Empirical Analysis, 2006–2015. Bull. Geogr. 2017, 38, 7–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raźniak, P.; Csomós, G.; Dorocki, S.; Winiarczyk-Raźniak, A. Exploring the Shifting Geographical Pattern of the GLobal Command-and-Control Function of Cities. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derudder, B.; Cao, Z.; Liu, X. Changing Connectivities of Chinese Cities in the World City Network, 2010–2016. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 183–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, J.N.; Zhang, B. Can China Comply with Its 12th Five-Year Plan on Industrial Emissions Control: A Structural Decomposition Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4816–4824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.X.; Liu, Y.Z.; Zhu, X.N. The impacts of urban land expansion on ecosystem services in Wuhan, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 10635–10648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Gao, X.; Wu, J.Y. Demand prediction and regulation zoning of urban-industrial land: Evidence from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.S.; Liao, Q.P.; Liang, Y. Spatio-Temporal Heterogeneity of Urban Expansion and Population Growth in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 18, 13031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, F.B.E.; Koomen, E.; Diogo, V. Estimating Demand for Industrial and Commercial Land Use Given Economic Forecasts. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e91991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vandermeer, M.C.; Halleux, J.M. Evaluation of the Spatial and Economic Effectiveness of Industrial Land Policies in Northwest Europe. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2017, 25, 1454–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Louw, E.; van der Krabben, E.; van Amsterdam, H. The Spatial Productivity of Industrial Land. Reg. Stud. 2012, 46, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Folmer, E.; Risselada, A. Planning the Neighbourhood Economy: Land-Use Plans and the Economic Potential of Urban Residential Neighbourhoods in the Netherlands. Eur. Plan. Stud. 2013, 21, 1873–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, S.; Korzhenevych, A. The effect of industrial and commercial land consumption on municipal tax revenue: Evidence from Bavaria. Land Use Policy 2018, 77, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Chen, W.J. Exploring the industrial land use efficiency of China’s resource-based cities. Cities 2019, 93, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, E.; Lavalle, C. Examining lag effects between industrial land development and regional economic changes: The Netherlands experience. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0183285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shih, C.M.; Yen, S.Y. Transformation of the Sugar Industry and Land Use Policy in Taiwan. J. Asian Archit. Build. Eng. 2009, 8, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouoba, Y. Industrial mining land use and poverty in regions of Burkina Faso. Agric. Econ. 2018, 49, 511–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.F.; Zhang, L. Evolution of the Spatiotemporal Pattern of Urban Industrial Land Use Efficiency in China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.J.; Zhou, G.L.; Liu, D.G. The Interaction of Population, Industry and Land in Process of Urbanization in China: A Case Study in Jilin Province. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2018, 28, 529–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tu, F.; Yu, X.F.; Ruan, J.Q. Industrial land use efficiency under government intervention: Evidence from Hangzhou, China. Habitat Int. 2014, 43, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Huang, H.P. The Identification and Use Efficiency Evaluation of Urban Industrial Land Based on Multi-Source Data. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiong, C.; Lu, J.Y. Urban Industrial Land Expansion and Its Influencing Factors in Shunde: 1995–2017. Complexity 2020, 2020, 6769176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.X.; Gao, X.; He, B.J. Coupling Coordination Relationships between Urban-industrial Land Use Efficiency and Accessibility of Highway Networks: Evidence from Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration, China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, D.; Yang, L.; Lin, J. How industrial landscape affects the regional industrial economy: A spatial heterogeneity framework. Habitat Int. 2020, 100, 102187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shi, Y.Y.; Duan, W.K. Spatiotemporal Decoupling of Population, Economy, and Construction Land Changes in Hebei Province. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.D.; Zhao, K.X.; Yan, Y.R. Spatio-Temporal Evolution Characteristics, and Influencing Factors of Urban Service-Industry Land in China. Land 2022, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiedenhofer, D.; Virag, D.; Virag, D. A systematic review of the evidence on decoupling of GDP, resource use and GHG emissions, part I: Bibliometric and conceptual mapping. Environ. Res. Lett. 2020, 15, 65002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasmeen, H.; Tan, Q.M. Assessing Pakistan’s energy use, environmental degradation, and economic progress based on Tapio decoupling model. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 68364–68378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.D.; Wang, P.; Cui, L.B. Decomposition and decoupling analysis of CO2 emissions in OECD. Appl. Energy 2018, 231, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.P.; Pang, J.X.; Zhang, Z.L. Sustainability Assessment of Solid Waste Management in China: A Decoupling and Decomposition Analysis. Sustainability 2014, 6, 9268–9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, S.; Yan, Y.; Han, J. Industrial Land Change in Chinese Silk Road Cities and Its Influence on Environments. Land 2021, 10, 806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Chen, Q.R.; Lu, F.C. Spatial-temporal disparities and influencing factors of total-factor green use efficiency of industrial land in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 207, 1047–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.C.; Lin, Y.B. Spatial-temporal characteristics of industrial land use efficiency in provincial China based on a stochastic frontier production function approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 295, 126432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Wang, W. Spatiotemporal differences and convergence of urban industrial land use efficiency for China’s major economic zones. J. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 1183–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.Y.; Geng, M.Z. The effect of industrial relocations to central and Western China on urban construction land expansion. J. Land Use Sci. 2021, 16, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Tian, L. How did industrial land supply respond to transitions in state strategy? An analysis of prefecture-level cities in China from 2007 to 2016. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.J.; He, C.F. Local government intervention, firm-government connection, and industrial land expansion in China. J. Urban Aff. 2017, 41, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.N.; Cai, M.M.; Wu, K.Y.; Wei, J.C. Decoupling analysis of carbon emission from construction land in Shanghai. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 210, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Hu, B.Q.; Shi, K.F.; Su, K.C.; Yang, Q.Y. Exploring the dynamic, forecast and decoupling effect of land natural capital utilization in the hinterland of the Three Gorges Reservoir area, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 718, 134832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, M.; Li, Q. Spatial Threshold Effect of Industrial Land Use Efficiency on Industrial Carbon Emissions: A Case Study in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 9368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liang, S.K.; Li, Y.B. The spatial distribution of dissolved and particulate heavy metals and their response to land-based inputs and tides in a semi-enclosed industrial embayment: Jiaozhou Bay, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 10480–10495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ustaoglu, E.; Silva, F.B.E.; Lavalle, C. Quantifying and modelling industrial and commercial land-use demand in France. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2020, 22, 519–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.X.; Zhang, J.F.; Han, R. Two-stage development, allocation strategies’ effect, and industrial land policies’ adjustment, China. Growth Chang. 2022, 53, 890–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.F.; Mao, X.Y. Emerging Themes of Environmental Economic Geography in China. Sci. Geol. Sin. 2021, 41, 1497–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Indicators to Measure Decoupling of Environmental Pressure and Economic Growth; OECD: Paris, France, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Longhofer, W.; Jorgenson, A. Decoupling reconsidered: Does world society integration influence the relationship between the environment and economic development? Soc. Sci. Res. 2017, 65, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Ma, X.; Wang, Y.X. The increasing district heating energy consumption of the building sector in China: Decomposition and decoupling analysis. J. Clean Prod. 2020, 271, 122696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.Q.; Zhang, L.; Zha, D.L.; Wu, F.; Wang, Q.W. Decoupling and decomposing analysis of construction industry’s energy consumption in China. Nat. Hazards 2019, 95, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseem, S.; Mohsin, M.; Zia-UR-Rehman, M.; Baig, S.A.; Sarfraz, M. The influence of energy consumption and economic growth on environmental degradation in BRICS countries: An application of the ARDL model and decoupling index. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2021, 29, 13042–13055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, C.Z.; Wei, C. Decoupling economic and energy growth: Aspiration or reality? Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 044017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, F.; Li, J.Y.; Zhang, X.Y.; Zhu, J. Decoupling relationship between haze pollution and economic growth: A new decoupling index. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.L.; Ding, D.H.; He, J. Fiscal Decentralization, Economic Growth, and Haze Pollution Decoupling Effects: A Simple Model and Evidence from China. Comput. Econ. 2019, 54, 1423–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundquist, S. Explaining events of strong decoupling from CO2 and NOx emissions in the OECD 1994–2016. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 793, 148390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.; Shi, H.; Hu, Y. Coupling coordination degree for urbanization city-industry integration level: Sichuan case. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 58, 102136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, N.; Haase, D.; Seppelt, R. Omnipresent Sprawl? A Review of Urban Simulation Models with Respect to Urban Shrinkage. Environ. Plan. B Plan. Des. 2010, 37, 265–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hu, J.; Zhao, K.; Chen, H.; Zhao, S.; Li, W. Dynamics and Decoupling Analysis of Carbon Emissions from Construction Industry in China. Buildings 2022, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.L.; Wang, S.H.; Wu, K.Y. Environment-biased technological progress and industrial land-use efficiency in China’s new normal. Ann. Oper. Res. 2018, 268, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selvaggi, R.; Pappalardo, G.; Chinnici, G. Assessing land efficiency of biomethane industry: A case study of Sicily. Energy Policy 2018, 119, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.H.; Liu, J.Y.; Dong, J.W. The rapid and massive urban and industrial land expansions in China between 1990 and 2010: A CLUD-based analysis of their trajectories, patterns, and driver. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2016, 145, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.T.; Jiang, G.H.; Zheng, Q.Y. Does the land use structure change conform to the evolution law of industrial structure? An empirical study of Anhui Province, China. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.L. Spatial-temporal differences of industrial land use efficiency and its influencing factors for China’s central region: Analyzed by SBM model. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 22, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.Y.; Zhang, Z.F. Spatial differentiation characteristics and driving mechanism of rural-industrial Land transition: A case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, China. Land Use Policy 2021, 102, 105239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Su, Z.G. Spatial-Temporal Evolution of Sustainable Urbanization Development: A Perspective of the Coupling Coordination Development Based on Population, Industry, and Built-Up Land Spatial Agglomeration. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.M.; Hou, X.H. Study the effect of industrial structure optimization on urban land-use efficiency in China. Land Use Policy 2021, 105, 105390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Hu, S.G. Decoupling Relationship between China’s Construction Land Expansion and Economic Growth and Its Control Strategies. China Land Sci. 2019, 33, 68–76. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.Y.; Yue, W.Z. Decoupling Relationship between Urban Expansion and Economic Growth and Its Spatial Heterogeneity in the Yangtze Economic Belt. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 219–232. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.J.; Zang, B. On the Degree of Decoupling and Re- coupling of Spatial and Temporal Evolution of Urban Expansion Speed and Economic Development From 2000 to 2010: A Case Study of Chongqing City. Econ. Geogr. 2013, 33, 52–60. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.Y.; Gao, P.C. Decoupling Analysis between Urban Land Expansion and Economic Growth at the Different Scale: A Case Study of Shandong Province in China. Econ. Geogr. 2021, 41, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.Y.Z.; Li, Y.C.; Balland, P.A.; Zheng, S.Q. Industrial land policy and economic complexity of Chinese Cities. Ind. Innov. 2021, 29, 367–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Shi, M.J. Industrial land policy, firm heterogeneity and firm location choice: Evidence from China. Land Use Policy 2018, 76, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Needham, B.; Louw, E.; Metzemakers, P. An economic theory for industrial land policy. Land Use Policy 2013, 33, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

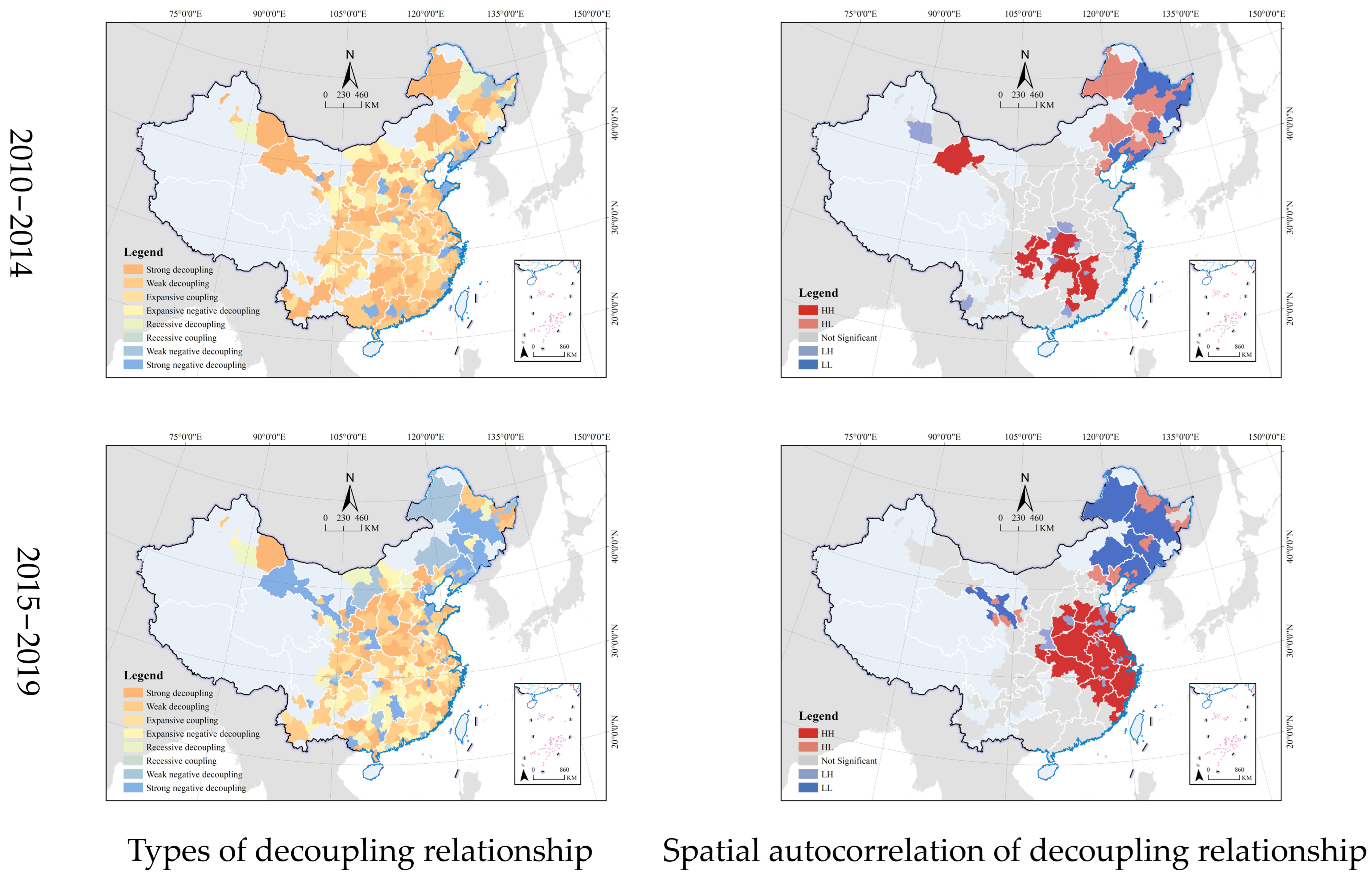
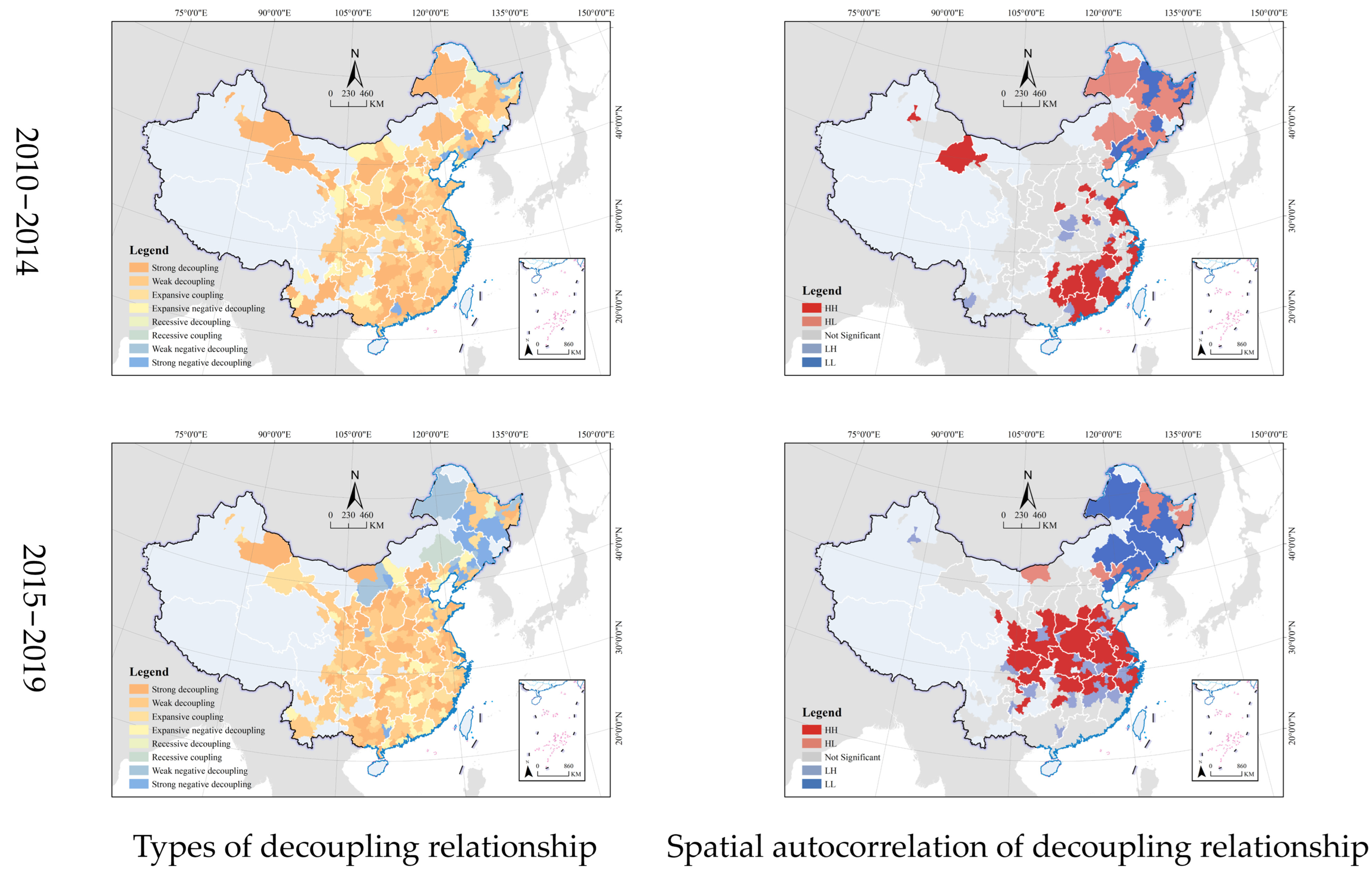
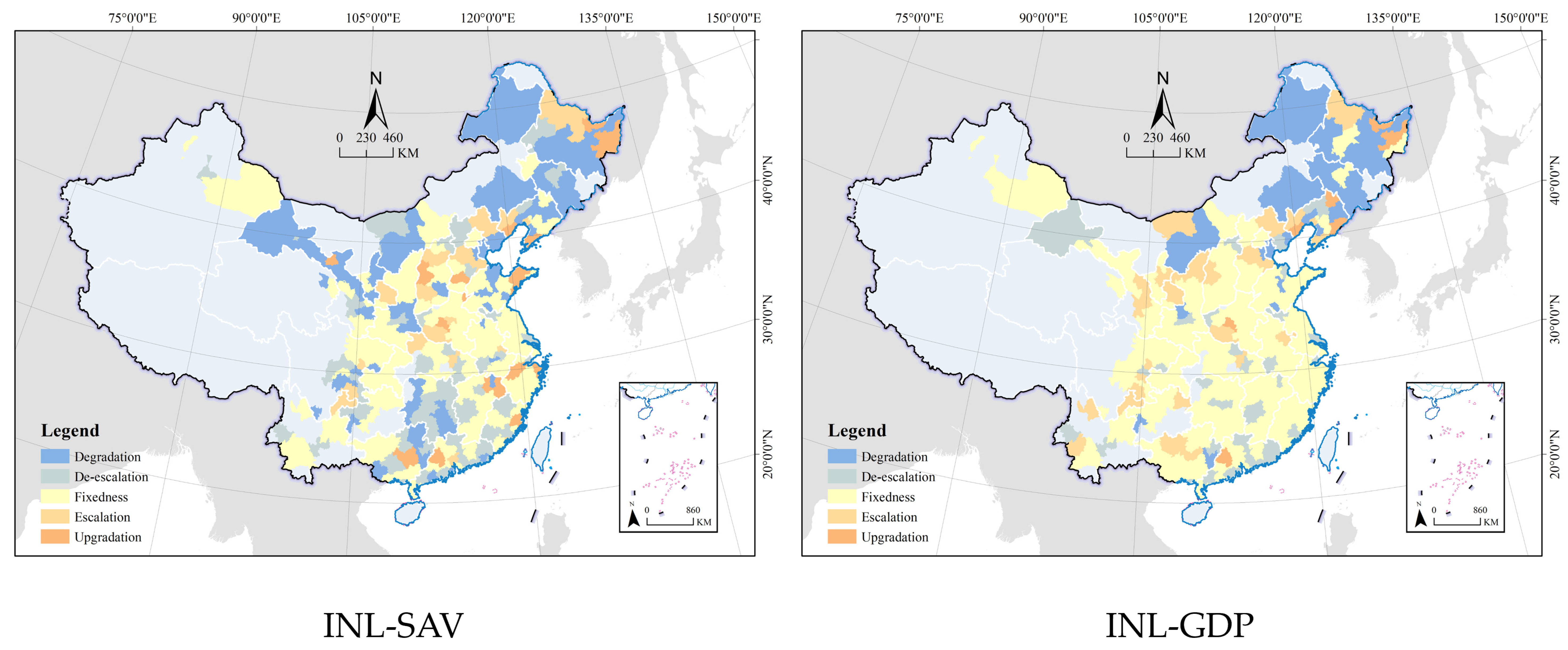
| Index | Max. | Min. | Mean | COV | Moran’s I | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010–2014 | INL | 128.55 | −39.39 | 1.18 | 13.56 | 0.035 |
| SAV | 110.20 | −46.39 | 12.75 | 1.30 | 0.050 | |
| GDP | 61.88 | −10.40 | 13.23 | 0.59 | 0.109 | |
| 2015–2019 | INL | 68.10 | −39.14 | 3.18 | 4.14 | 0.042 |
| SAV | 37.50 | −36.00 | 4.09 | 2.39 | 0.215 | |
| GDP | 32.93 | −22.41 | 8.42 | 0.92 | 0.330 | |
| INL–GDP | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A 1 | B | C | D | E | F | G | H | ||
| INL–SAV | A | 55 2 (A 3) | 0 (B) | 0 (C) | 0 (D) | 0 (E) | 0 (F) | 0 (G) | 0 (H) |
| B | 0 (B) | 79 (B) | 1 (C) | 0 (D) | 0 (E) | 0 (F) | 0 (G) | 1 (H) | |
| C | 0 (C) | 14 (C) | 5 (C) | 2 (D) | 0 (E) | 0 (F) | 0 (G) | 1 (H) | |
| D | 0 (D) | 13 (D) | 10 (D) | 24 (D) | 0 (E) | 0 (F) | 0 (G) | 0 (H) | |
| E | 9 (E) | 0 (E) | 0 (E) | 0 (E) | 2 (E) | 0 (F) | 0 (G) | 0 (H) | |
| F | 2 (F) | 0 (F) | 0 (F) | 0 (F) | 2 (F) | 0 (F) | 0 (G) | 0 (H) | |
| G | 2 (G) | 2 (G) | 0 (G) | 0 (G) | 0 (G) | 2 (G) | 8 (G) | 0 (H) | |
| H | 0 (H) | 17 (H) | 4 (H) | 13 (H) | 0 (H) | 0 (H) | 0 (H) | 19 (H) | |
| Decoupling Type | Development Status | Policy Orientation |
|---|---|---|
| Strong decoupling, | Healthy development with less dependence on land expansion | Transformation development |
| weak decoupling, | ||
| and expansive negative decoupling | ||
| Expansive coupling | Basic equivalence between urban development and land expansion | Moderate development |
| and recessive decoupling | ||
| Recessive coupling, | Urban development does not need as much land, and the excess supply of land leads to waste of resources | Reduced land supply |
| weak negative decoupling, | ||
| and strong negative decoupling |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Hu, M.; Han, B.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H. Decoupling Relationship between Industrial Land Expansion and Economic Development in China. Land 2022, 11, 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081209
Qi J, Hu M, Han B, Zheng J, Wang H. Decoupling Relationship between Industrial Land Expansion and Economic Development in China. Land. 2022; 11(8):1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081209
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Junheng, Mingxing Hu, Bing Han, Jiemin Zheng, and Hui Wang. 2022. "Decoupling Relationship between Industrial Land Expansion and Economic Development in China" Land 11, no. 8: 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081209
APA StyleQi, J., Hu, M., Han, B., Zheng, J., & Wang, H. (2022). Decoupling Relationship between Industrial Land Expansion and Economic Development in China. Land, 11(8), 1209. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11081209







