Abstract
Floods rarely occur in hyper-arid deserts and little is known about the magnitude and frequency of sediment delivery from their basins, despite their importance to changes to the landscape, infrastructures and engineering activities. Sediment yield from the Nahal Nehushtan watershed (11.9 km2) located in the Timna Valley in southern Israel was determined by assessing stratigraphic sections in its 60-year reservoir deposits. Stratigraphic correlation between event couplets allowed for quantification of sediment yields representing 13 former flow and flood events. Based on the sediment volume in the reservoir, the 29.8 t km−2 year−1 average specific sediment yield is one of the lowest among other studied warm deserts. Among the event layers, the thickest layer, deposited by a flash flood caused by a single short rain event, contributed 31% of the total sediment yield. Based on event reservoir sedimentation from watersheds located in several hyper-arid areas in the Middle East and North America, we demonstrate that sediment yield increases with drainage area as expected and mean annual sediment yield increases in hyper-arid areas with flood frequency. Our quantitative results, together with previous studies of hyper-arid areas, provide complementary evidence of fluvial sediment transport—the main landscape designer in hyper-arid fluvial landscapes.
1. Introduction
Drylands occupy about 41% of the global land area, with hyper-arid conditions prevailing by about 7% and defined by an aridity of less than 0.05—the ratio between mean annual precipitation and reference evapotranspiration [1]. Global change and human activity are expected to increase the risk of desertification in 29% of the global lands, whereas areas around deserts and barren land are at higher risk of desertification [2].
Flash floods, usually caused by short duration heavy rainfall, are a natural hydrological phenomenon, expected to increase in frequency worldwide as well as in ephemeral streams due to the effects of global change and extreme climatic events [3]. Although the benefits of flowing water in deserts are obvious, infrastructures, lives and (to some extent) ecological systems may be harmed by floods and transported sediments. Heavy convective rain and flash floods in deserts are spatiotemporally unpredictable [4,5], and over longer periods of time flash floods are highly variable in their intensity and frequency [6]. For instance, based on data obtained from the Israel Hydrological Service in the hyper-arid southern Negev desert, the frequency of flow events between 1991–2019 was 1.5 year−1, with event duration ranging between 11 h in small basins (<50 km2) and 25 h in larger basins (50–750 km2). With few exceptions, large floods are seldom monitored in arid areas. However, peak water discharge from unmonitored channels can be determined based on slack water deposits [7,8].
High intensity rain events generate flash floods [9] when runoff occurs on hillslopes and flows to the channel network. The geological and geomorphological characteristics of the drainage basin affect peak discharge and the runoff coefficient [10,11], required to model flash floods in arid terrains [12]. Flow duration and peak discharge determine the capacity and characteristics of the sediments transported by flash floods [13,14] originating from fluvial, and from aeolian sources [15]. Sediment characteristics are also affected by soil type and land use, vegetation cover, as well as by the interval between flood events, different scales of the watershed area and different stages of a flood [16,17].
Sediment particles move either as bedload near and in contact with the channel bed, or as suspended material, in trajectories determined by flow velocity and particle size and mass. In many humid and semiarid environments, bedload constitutes a small fraction of the total sediment yield, often <1% [18]. In arid environments, the bedload fraction is considerably higher (up to 10 %) than in humid environments, and increases with increased aridity [13,14].
Upon entering a standing body of water, sediment transported as bedload is deposited in deltaic deposits. The location of these deposits is in the upstream-proximal areas in lakes [19] and even in reservoirs that are empty most of the time [20]. However, in dry dammed areas, the coarser sediment deposition shifts proximally as water level rises. This environmental condition in dryland reservoirs allows coarser-grained deposits to be deposited even in distal locations, thereby forming a lower sedimentary singlet. As reservoir water depth increases during hydrograph rise, finer-grained sediments begin to settle from suspension [21], thereby forming an upper, finer-grained singlet. With the exception of very small inflows, and thus minute sediment deposits that are entrained by later floods, historic flood inputs are identified by event couplets. Quantitative differentiation between deposited suspended material and bedload relies on grain size distributions and whether laminae are cross-laminated, coarser-grained, and are thus deposited due to cessation of bedload, or planar and silty-clayey deposited from suspension [22,23]. The processes and extent of reservoir deposition are described elsewhere [24].
Sediment yield (t year−1) and specific sediment yield (t km−2 year−1) can be evaluated both by direct and indirect approaches. Indirect approaches are usually based on radioactive isotopes (e.g., 10Be and 26Al dating geomorphological processes [25]), remote sensing [26,27] and modeling [28]. However, sediment yields are often evaluated using direct approaches, based on mode of particle transport and deposition. The concentration of suspended sediments in flood waters is determined by manual or automatic sampling or by the use of turbidimeters [14,29]. Bedload transported along the riverbed is measured by manual sampling [30], automatic sampling using bedload traps [31,32] as well as by various surrogate methods [33,34,35]. All these methods either require measurements during the occurrence of floods or expensive monitoring installations unavailable in hyper-arid, flash flood settings.
Estimation of sediment yield is also carried out in studies of reservoir deposition [36,37,38], supplying an excellent indicator for total event yields, although these layers may lack dating resolution. Errors associated with determination of historic sediment yields require attention, but they are small when considering the spatial distribution of event layers [39,40]. Event sediment layers detected in reservoirs, and their derived specific event sediment yields, are very accurate for long-term assessments [41,42], as long as the trap efficiency is known [43,44].
In reservoirs, particle deposition depends on the deceleration and trajectories of water velocity wherelarge and heavy particles are deposited first [45]. Accordingly, at the entrance to a reservoir, water velocity decreases and the bedload (the coarser particles transported along the riverbed) is deposited, whereas the suspended, fine-grained particles are deposited throughout the entire reservoir area [24]. The rate of deposition depends on water depth and wind-induced movement [46,47]. Differentiation between the finest-grained, often clay-sized particles are clearly identified in sediment cores [48] and trenches [47].
Specific sediment yield depends on climate and geographic features [48,49]. Although it is widely accepted that specific sediment yield is higher in semiarid areas than in more humid locations [50,51], other studies show no effect of annual rainfall on specific sediment yield [52]. The high specific sediment yield in semiarid environments is due to insufficient cover of vegetation, unstable soils and high-intensity rain events [53]. The bedload is particularly high in semiarid and arid areas due to the lack of an armour layer [31] with the exception of bars [54].
Although sediment yields have been quantified in different drylands, especially semiarid and some arid zones (e.g., in China [15]; India [55]; Spain [37]; Sudan [26]; Arizona USA [16]; Australia [56]), results from hyper-arid environments are scarce. Whereas an increase in aridity has been documented in different parts of the world [57,58,59], hyper- arid areas are expected to expand, highlighting the necessity of further data from these areas.
Our research goals were:
- To study the sedimentary sequence deposited during the past 60 years in the Nehushtan Reservoir,
- To calculate the overall and the event sediment yields.
- To compare these values to the scant information available on specific sediment yields from hyper-arid watersheds worldwide.
Our results shed light on various characteristics of sediment yield based on accumulation in reservoirs in local and regional hyper-arid environments.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Site
The Nehushtan basin, located in the Arava Valley, southern Israel (Figure 1a) is characterized by high temperatures and low annual rainfall of ca. 25 mm year−1 (Figure 1b). Precipitation in the region is highly variable in space and time, averaging 26.6 mm year−1, ranging between 2–97 mm year−1 (1949–2022) in the city of Eilat, located 23 km south of the study site (according to the Israel Meteorological Service [60]). The Nehushtan basin geological record is highly variable and includes the following lithologies (Figure 1c): plutonic rocks (granite and gabbro; ca. 17% cover), marine sedimentary rocks (limestone and dolomite; ca. 13% cover), sandstone formations (containing copper ore; ca. 41% cover) and alluvial terraces and ephemeral channels (30% cover) [61]. The international terminology for these channels is wadi, locally termed ‘nahal’.
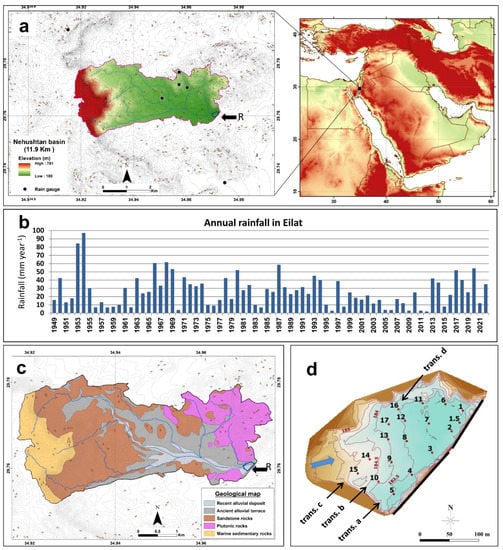
Figure 1.
The study area: (a) The Nahal Nehushtan study site is located in the southern Negev Desert of Israel, between the Arabian Peninsula and the deserts of northeastern Africa. The main tributaries of Nehushtan catchment area (11.9 km2) drain into the reservoir (“R”) and the location of six rain gauges inside and outside the basin (Black circles). (b) Annual rainfall in Eilat according to the Israel Meteorological Service [60]. The city of Eilat is located 23 km south of the study area. (c) The different lithologies in the Nahal Nehushtan drainage basin (modified from [61]). (d) Topographic map of the Nehushtan Reservoir following the 2015 flood event. Sediment was sampled in pits (1–17) along transects (trans. a-trans. d). The blue arrow indicates flow direction and the dam by a dashed line.
The Nehushtan Reservoir was constructed in 1958 as part of the infrastructure associated with the Timna copper mines, to prevent flooding of the mines during flash flood events. Since then, runoff and sediments have been transported into the reservoir by flood events. Because the reservoir never overflowed and sediments were never removed (i.e., 100% trap efficiency), the sediments in the reservoir are evidence of former floods and sediment yields.
2.2. Stratigraphic Characterization
To examine the stratigraphic sequence in the reservoir and calculate sediment yields, we characterized stratigraphic sections at 17 pits that were excavated to a depth of 60–225 cm throughout the entire reservoir area. The pits were dug to form four transects parallel to the dam, approximately 50 m apart, with a distance of 40 m between pits (Figure 1d). The stratigraphic sequence of pit 1 was found to be disturbed and, therefore, a close location was selected for another dug pit (1.5). The rest of the pits showed undisturbed horizontal stratified layers, indicating minimal disturbance.
Fieldwork was conducted during October, 2018 (Figure 2). Wide pits (Figure 2b) were excavated to a depth of the original riverbed (prior to dam construction) using a backhoe digger. The former riverbed, an alluvial substrate, is a thick layer of unstratified fine to coarse gravel within a fine-grained matrix. Stratigraphy was observed and measured following a gentle cleanup with subsequent measurements and sketching of the section.
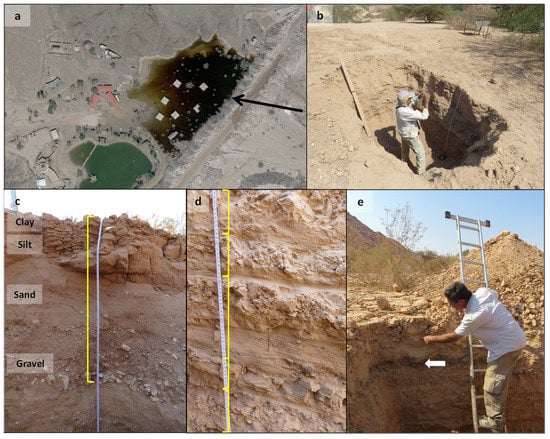

Figure 2.
Stratigraphic sections in the Nehushtan Reservoir. (a) The sediment-laden water in the Nehushtan Reservoir following the Oct. 2015 heavy flash flood event. (b) Stratigraphic documentation of pit 15. (c) Thick (89 cm) sedimentary layer deposited by the Oct. 2015 flood event; pit 15. The event layers consist of gravel, sand and silt overlain by a relatively thin layer of clay. (d) Sequence of five flood event couplets near the dam, part of the chronological sequence determined using stratigraphic sections. (e) The Oct. 2015 event layer (pit 3) was deposited above the artificial fill (white arrow) placed as part of local efforts to improve infrastructure.
The identified stratification included laminae to thicker interbedded layers of gravel, sand, silt and clay (Figure 2c). Due to cessation of bedload movement, gravel was deposited with sand to form a sand-gravel mixture denoted ‘sand and gravel’. Fine sand and silt gradually settled from suspension and were labelled ‘silt and sand’. Since sand is transported as bedload and also in suspension depending on local hydrodynamics, and since we could not differentiate between layers of gravel sand and silt, our calculated results (sediment yield) refer to event layers, i.e., we did not differentiate between bedload and suspended sediments. Identification of different layers (‘sand and gravel’, ‘silt and sand’ and clay) was used to obtain correlation of event layers between pits. To decrease uncertainty with regard to the separation between ‘silt and sand’ and clay singlets (the majority of sediment), we compared frequency distributions of grain size in the upper singlets (clay) and lower singlets (silt and sand) in 11 event layers sampled in pit 3 (a total of 22 samples). Ten grams of dried (40 °C) and sieved (<2 mm) soil samples were analysed using MASTERSIZER 3000 (Malvern Panalytical, Malvern, UK) and statistically tested (volume density of 50–2000 µm fractions of lower and upper singlets) using the non-parametric Mann-Whitney U test (using Statistica 13® statistical software, Statsoft Inc., Tulsa, OK, USA). As is common in desert reservoirs that are almost always empty, with short intervals during which hydrostatic pressures exist, we assume that the bulk density of the deposited shallow sediments does not increase with depth [13].
Differentiation between events was determined by considering the layers’ sequence according to the upper edge of a visible clay layer—the last to deposit from suspension distinguished by cohesion and a darker hue. Wherever a clay layer was not found, event layers were determined according to the boundary between a fine sand and silt layer deposited by a given event and a coarse-grained, sand and gravel layer deposited by the succeeding event (see Figure 2c,d) [47].
In all pits (except pits 4–5), a layer of artificial fill was discerned immediately beneath the layer deposited during the last flood event (‘artificial fill’; Figure 2e). The artificial fill was laid down after the major flood of winter 2010, prior to the October 2015 flood event, as part of an effort to ease land use by the park management (personal communication with Timna Park Operations staff). This layer contains a darker material, most likely granulated granite (arkose), formed from natural erosion of plutonic rocks typical of the nearby Timna Mountain. This layer was found in most pits and was used as a chronological marker to reduce uncertainty in the identification of the 2015 flood event layer.
2.3. Assessment of Sediment Yield
Spatial correlation between event layers in the 17 pits was undertaken to calculate event sediment yields. Event layers were correlated considering characteristics of the layers of each stratigraphic sequence: total number, sequence profile, total thickness and thicknesses ratio. The correlation between pits was based on topography, pit location in the reservoir (proximal, center and margins), pit depth (Figure 3) and the distance between pits. We used the deepest pits (1.5 and 2) to determine the maximum number of events and to estimate their magnitude, from small to large according to thickness. To reduce uncertainty and thereby validate the spatial correlation between event layers, maps were prepared for each chronological event showing the local deposited event layers.
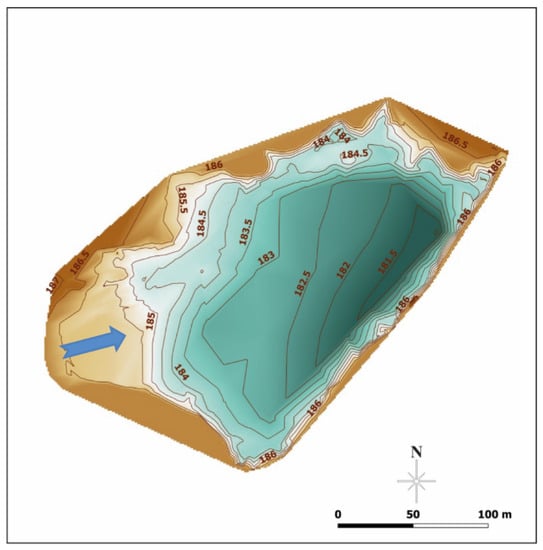
Figure 3.
Map showing the original topography of the reservoir area in 1958 following dam construction. Blue arrow indicates flow direction.
For calculating event sediment yields with GIS (ArcGIS10, QGIS 3) we used: (1) a 2018 high-resolution (1 × 1 m) digital elevation model (DEM) based on aerial LiDAR scanning representing the reservoir topography after the 2015 flood event; (2) the depth of the 17 pits from the surface to the alluvial riverbed representing the former riverbed depth; and (3) calculated elevation of 13 event layers in the 17 pits based on stratigraphic correlation and layer thicknesses. For each event layer, we prepared a DEM raster layer representing the topography in the reservoir area and its margins, using linear interpolation (considered accurate on moderate slopes—as appears in reservoir deposits). We assumed that the topography of most of the reservoir edges remained unchanged throughout the study period (1958–2018). Sediment volumes for each event layer were calculated by subtracting two adjoining DEM raster layers.
2.4. Characterization of the 2010 and 2015 Flood Events
Two significant flood events were recorded in Nahal Nehushtan, on 18 January 2010 and 25 October 2015. During these events, heavy rainfall generated runoff throughout the basin resulting in large floods in Nahal Nehushtan. As a result, water and sediment accumulated in the reservoir (Figure 2a). During these events, rainfall was measured at six locations inside and outside the basin as shown in Figure 1a (total rainfall in the rain event-rain depth). Water level was measured in the reservoir, allowing for calculation of event water volume (m3) in the reservoir—the volume between the water surface and the reservoir bed as determined by identification of event deposits in the pits. Sediment concentration of the 2010 and 2015 flood events was calculated as the mass ratio of event sediment deposits in reservoir water (sediment/water mass event). Sediment mass was calculated using an undisturbed bulk sediment density of 1.4 t m−3 [13]. Desert streams have considerable transmission losses (runoff loss by infiltration on hillslopes and channels) [62,63,64], but the reservoir infrastructure is coated by a series of clay layers that are deposited after each flow event. Therefore, water losses by infiltration are considered to be negligible, provided the water level is measured shortly after flooding.
3. Results
3.1. Reservoir Structure
The topographic structure of the reservoir area following dam construction in 1958 was reproduced using measurements of the former riverbed depth and GIS tools (Figure 3). The pre-reservoir topography is such that prior to dam construction the lowest elevation was located in the northeast corner. Water flowed northeast from the highest elevation in the southwest. The current topography is similar to the original topography. The deepest area lies in the northeastern corner and the shallowest in the southwestern corner of the reservoir. The sediment fill of the reservoir area is 225 cm thick in the deepest part and 60 cm in the margin (Figure 2). Sediment load that accumulated in the reservoir during the past 60 years between 1958 and 2018 was estimated to be 15,200 m3, equivalent to about 21,300 t. In terms of yield, this is 1800 t km−2 or a specific yield of 29.8 t km−2 year−1.
3.2. Sediment Deposition in the Reservoir
The columnar sections demonstrate that the coarse fraction gravel settled first, and finer-grained fractions later (Figure 2c). Above the gravel, the sand layers stratified according to grain size—first the coarser sand, above which the fine-grained sand was deposited. Gradually, within the fine-sand layers, silt particles also settled. Since deposition was gradual, it was impossible to differentiate between fine sand and silt. Above the silt and fine sand, layered clay deposits formed hard, thin, fragile laminae. Laboratory analysis of grain size frequency distributions in upper singlets (clay) and lower singlets (silt and sand) confirmed the field identification of event and singlet layers made. Frequency distributions of upper and lower singlets in 11 event layers sampled in pit 3 were found to be significantly different (Figure 4). Among eleven cumulative distributions sample, #10 (Figure 4d) is the only one that does not demonstrate a grain size difference between the singlets. A sampling error may be involved, or else local topography may have caused most of the coarser sediment to be transported down-reservoir. Overall, the stratigraphic sections of the 17 pits demonstrate a typical stratified structure of reservoir sediments.
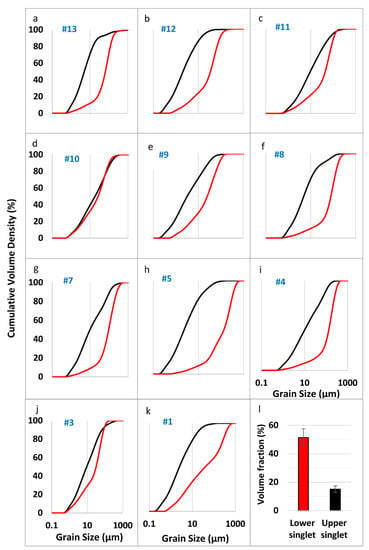
Figure 4.
Cumulative frequency distributions of grain size (presented as cumulative volume density) of the upper finer-grained singlet (black line) and the coarser silt and sand lower singlet (red line) of 11 event layers sampled in pit 3 (a–k; layer #1 is oldest). The volumetric fraction of sand (50–2000 µm) is significantly smaller (p-value < 0.01) in the upper singlet compared to that in the lower singlet (l).
At the entrance to the reservoir, the columnar sections mainly contain coarse-grained sand (e.g., pits 13–15), whereas in the lower topographic areas, adjacent to the dam (e.g., pits 1.5, 2 and 3), mostly fine-grained sediments—silt and clay—were deposited (Figure 5). Few flow events are recorded at the entrance to the reservoir, where sediment accumulation was low (<60 cm), whereas in the deep area adjacent to the dam, considerable (>200 cm) accumulation of sediment exhibits evidence of 13 flood events (Figure 5 and Figure 6). The shallow pits located in the reservoir margins (such as, pits 11 and 16) represent few flow events (Figure 6). The former alluvial riverbed was deep beneath the surface in the northeast corner of the reservoir (in pits 1.5, 2 and 3). The clay layers are very thick, especially those of the early flow events when the reservoir was deeper.
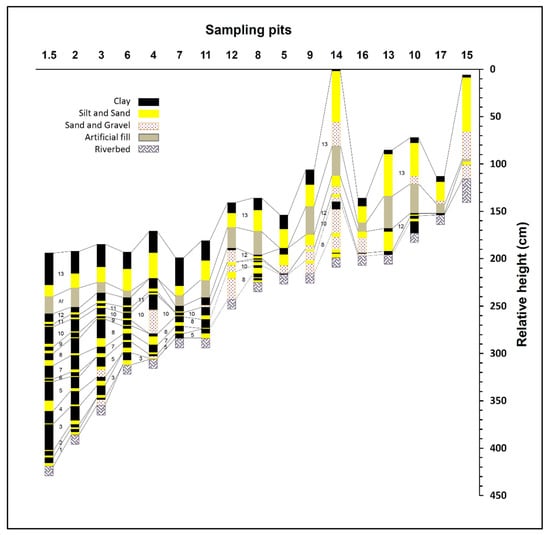
Figure 5.
Spatial correlation between reservoir event deposits. Event-layer thickness is marked relative to the highest topographic level in the reservoir (Y axis-elevation relative to surface). The pre-reservoir riverbed was identified in all pits. Event deposits were identified based on sequences of gravel, sand and silt layers underlying clay. An artificial layer was identified in most of the area, except in pits 4 and 5 located at the reservoir’s margin. Stratigraphic correlation between 13 event layers is marked by continuous lines (certain correlation) and dashed lines (uncertain correlation).
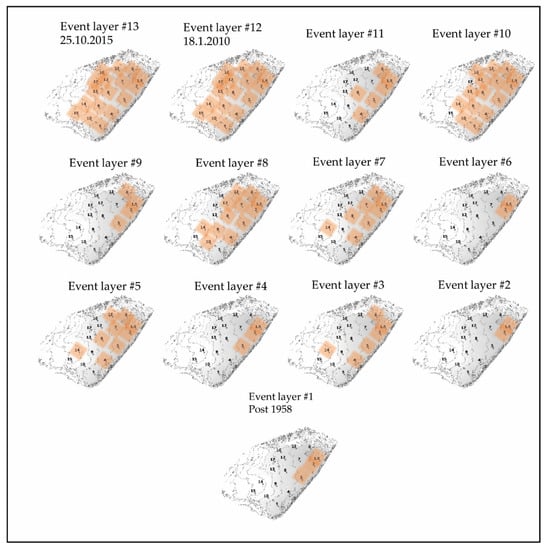
Figure 6.
Spatial layout of identified (highlighted in orange) event layers located in each of the pits, in accordance with the correlation shown in Figure 5.
Based on the chronological sequence of maps showing the spatial layout of each event (Figure 6), it is evident that with time, sediments were deposited throughout a larger area. Indeed, as the reservoir filled with sediment, the topography changed and became flatter. The flooded area increased, and thus the clay layers were deposited throughout a larger area and consequently became thinner.
3.3. Water Volume and Sediment in the 2010 and 2015 Flood Events
The flood events that occurred on 18 January 2010 and 25 October 2015 were well- documented. Data on rain depth, water level in the reservoir and sediment yields were available. In the 2010 flood event, 23–40 mm rainfall generated a flood that filled the reservoir with approximately 36,100 m3 of water. Altogether, a sediment volume of 2300 m3 was deposited in the reservoir during this event; its estimated mass is 3250 t. The sediment concentration of this event accounts for 9% of the water mass in the reservoir (calculated as the mass ratio of event sediment/water; Table 1). In the 2015 flood event, 32–50 mm rainfall generated a larger flood filling 77,100 m3 of water in the reservoir. The sediment volume deposited in the reservoir by this flood is 4770 m3 (6650 t)—indicating that the sediment concentration was on average 8.6% (Table 1). Although the 2015 flood event was larger than the 2010 event, with respect to different hydrological characteristics (Table 1), the sediment concentration in water was similar: 8.6 and 9%, respectively. Although the 2010 and 2015 event deposits were evident in all pits (Figure 5 and Figure 6), considerably larger amounts of sediment were deposited throughout the reservoir in 2015: on average 85 cm of sand near the entrance, 42 cm of clay near the dam and 26 cm in the margins.

Table 1.
Reservoir sedimentation and water input of two recent flood events. Sediment concentration was calculated as the mass ratio of event sediment/water using an undisturbed bulk sediment density of 1.4 t m−3.
3.4. Event Layer Correlation and Sediment Yield
Correlation between event layers in the 17 pits (Figure 5) was performed according to stratigraphic sequence character, pit location and reservoir topography as explained in the methods section. To express the level of confidence in the resulting correlation, certain stratigraphic correlations between 13 event layers are marked by continuous lines and uncertain correlations by dashed lines (Figure 5). Event layers 12 and 13 were evident throughout the entire reservoir. These event layers were recognized at a high level of certainty. Event layers 10, 8, 7, 5 and 3 were observed throughout a large area of the reservoir, whereas event layers 11, 9, 6, 4, 2 and 1 were recognized locally, mostly at the deepest part of the reservoir (Figure 5 and Figure 6). In general, the degree of uncertainty in the correlation of event layers is larger for earlier events than in chronologically late events and greater for smaller events compared to larger events.
Event layer correlation allowed for calculating sediment yields of the flow events throughout the reservoir area by comparing GIS raster layers and calculating volumes (m3). Sediment yield (t) and specific sediment yields (t km−2) were calculated from sediment volumes using an undisturbed bulk sediment density of 1.4 t m−3 (Figure 7).
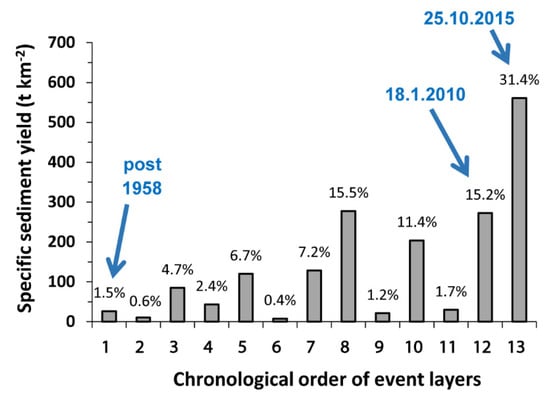
Figure 7.
Specific event sediment yield of the identified event layers. The proportion (%) of each event yield relative to total historical yield appears above the columns.
Event sediment yield during the past 60 years of sediment accumulation ranged between 92 and 6700 t. Accordingly, the specific sediment yield of the 13 flow events generated in the Nahal Nehushtan basin was 7.8–560 t km−2 (Figure 7). Among 13 event sediment yields, 12 were small and medium size events (n = 12), contributing 69% of the total sediment yield, and one flood contributed 31% of the total sediment yield (Figure 7). Due to uncertainty in the slope angle of the reservoir (between the former riverbed and margins), inaccuracy in sediment volume calculation is higher near the margins (±10%) than between the pits inside the reservoir (±4%). It is likely that during 1958–2018 additional insignificant small flow events (of low discharge) occurred, but did not deposit a traceable layer of sediment.
4. Discussion
4.1. Nahal Nehushtan Reservoir—60 Years of Sediment Record
When water enters reservoirs that are almost always dry, most of the coarse-grained sediments deposit in the proximal part of the reservoir (depending also on the magnitude of the flood), although some reach the distal, deepest part of the reservoir at the beginning of the event while the reservoir is still dry. The fine-grained particles are suspended in the water column during a period of time that depends on their size (Stokes Law), the depth of the water column and wind activity generating water movement; eventually they deposit throughout the entire reservoir area. The layer of fine-grained particles becomes thicker with an increase in depth of water [47].
The stratigraphic sections of the Nahal Nehushtan Reservoir show this characteristic pattern. The pits at the entrance to the reservoir are mainly comprised of thick layers of sand and gravel and the pits of the deeper distal area, close to the dam, exhibit mostly silt and clay (Figure 5). The pits at the reservoir entrance display a record of recent flow events, not earlier ones (Figure 6). We propose that when the flash floods enter the reservoir, some of the sediments deposited by previous events are removed, mainly from the shallow parts of the reservoir. Unlike the pits at the entrance of the reservoir that contain mainly deposited sediment from recent floods, the pits at the margins represent only the largest flow events, in which the flooded area reached the reservoir margin. Alternatively, they may represent floods that flowed through a lateral sub-channel (a small side channel that enters the reservoir from a side entrance) and accordingly, the sediments contain some gravel.
An interesting aspect is the relationship between frequency, size and efficiency of sediment transport. During these 60 years, most of the sediment (69%) was deposited by 12 small and medium flow events and 31% was deposited by the largest flood event recorded (estimated return period of 1:50 years). Although the largest flood event (2015) caused damage to the park’s infrastructure, in the long-term perspective, the higher sediment supply brought by small and intermediate events had a greater influence on the total output of sediment from the landscape [38,50].
Do intermediate flow events, the main source of sediment supply, play an important role in riverside landscape morphology? River sediment supply does not necessarily correspond with river landscape design. In semi-arid areas and especially in arid areas, the significance of large events in shaping river landscapes is larger in small drainage basins [65]. For example, a large event causes an irreversible expansion of channel width. The new expanded width will not return to its original width, but will continue expanding and subsequently dictate landscape formation [66].
Since sediment has the tendency to move in waves over time periods ranging from hours to centuries (reviewed by [67]), it is difficult to define a suitable time period over which to calculate a reference value for sediment yields. For various climate zones (except hyper-arid), it is generally accepted that evidence of sediment yield from databases covering 50 years provides a qualitative as well as a quantitative description of the drainage basin [50]. In hyper-arid areas due to low rainfall, low frequency of flow events and high temporal and spatial variability, we suggest that evaluating mean annual sediment yields requires a longer span of data collection (>50 years).
4.2. Sediment Yield in Arid Environments, the Role of Watershed Area and the Frequency of Flow Events
Specific sediment yield in arid environments is affected by watershed area and morphology [13], as well as soil characteristics and thickness [16]. In addition, specific sediment yields also vary between climatic zones [68] and different flood frequencies [49]. Due to the very low rainfall, low frequency of flow events and high temporal and spatial variability, evaluating annual and event sediment yields in hyper-arid settings is challenging, as data on sediment yields are limited. Searching the literature for data on sediment yields based on reservoir sedimentation in hyper-arid areas reveals few published studies, most of them conducted in the Negev Desert (Israel), others in Oman (Wadi Asserin) and in the Mojave Desert (Cal., USA). The relevant data are summarized in Table 2 and Figure 8.
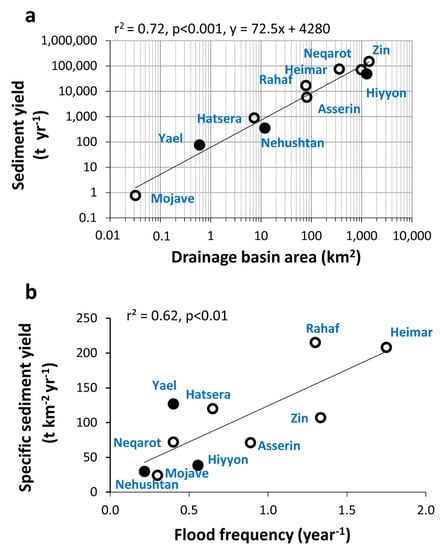
Figure 8.
Variation of mean annual sediment yield with respect to drainage area (a) and of specific sediment yield with flood frequency (b) in drainage basins draining hyper-arid areas, based on Table 2. Flood frequency is calculated based on the number of events documented in reservoir deposits. Black circles denote basins in arid areas (<50 mm year−1 rain).
As expected, the annual sediment yield (t year−1) of the monitored hyper-arid drainage basins is positively correlated with the drainage basin area (r2 = 0.72, p < 0.001, Y = 72.5X + 4280; Figure 8a). In large basins draining arid and semi-arid areas, where the width and the length of channels considerably increase with drainage area, it is generally assumed that specific sediment yield (t km−2 year−1) is reduced with an increase in drainage area due to considerable transmission losses and resultant deposition [64]. However, we found no obvious effect of watershed area on sediment yield (r2 = 0.02, p = 0.64), likely due to specific characteristics of basin lithology, slope and spatiotemporal patterns of rainfall intensity as suggested by [53].
Extremely low specific sediment yields (5.9 t km−2 year−1) were recorded in the cold Antarctic desert, the largest hyper-arid desert of our globe [69]. Upon comparison among warm deserts, Nahal Nehushtan has one of the lowest specific annual sediment yields, (Table 2) lower than expected when compared with other basins. Several characteristics can explain these low values.

Table 2.
Sediment yield (SY) of select watersheds in arid areas.
Table 2.
Sediment yield (SY) of select watersheds in arid areas.
| Watershed | Area | Mean Rain | Duration | # of Events | Mean Annual Specific SY | Specific Event SY | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | mm year−1 | years | t km−2 year−1 | t km−2 | |||
| † Mojave Desert | 0.05 | 65–190 | 90 | 25 | 24 | 3 | [70] |
| Yael | 0.5 | 25 | 10 | 4 | ‡ 127 | ‡ 318 | [48] |
| Hatsera | 7.3 | 80 | 25–30 | 18 | 110–130 | 180 | [49] |
| Nehushtan | 11.9 | 25 | 60 | 13 | 29.8 | 137 | current study |
| Rahaf | 78 | 50–130 | 10 | 13 | 215 | 165 | [71] |
| Wadi Asserin | 81.3 | 117 | 9 | 8 | 71 | 80 | [72,73] |
| Heimar | 360 | 50–110 | 4 | 7 | 208 | 119 | [74] |
| Neqarot- En Yahav reservoir | 984 | 40–100 | 20 | 8 | 71.8 | 180 | [13] |
| Hiyyon- Eshet reservoir | 1260 | 30–50 | 9 | 5 | 38.6 | 69.5 | [13] |
| Zin | 1400 | 50–100 | 3 | 4 | 107 | 21 | [75] |
† average values of 8 small catchments. ‡ calculation based on an estimated undisturbed bulk density of 1.5 t m−3.
The frequency of flow events as recorded in the studied sedimentary sequence was influenced by a severe drought period recorded between 1995 to 2009 in the southern Arava Valley [76,77]. This may or may not be typical of longer time periods. The occurrence of low frequency flow events (as recorded by deposition layers of sediments in the reservoir) and low annual sediment yield in Nahal Nehushtan raises the assumption that event frequency may have a significant effect on annual sediment yields (Table 2). Indeed, sediment yield is positively correlated with frequency of flow events for various drainage basins (r2 = 0.62, p < 0.01, Figure 8b). The role of rainfall induced runoff in generating mechanical erosion in hyper-arid climates is suggested to act as a major mechanism driving carbonate mineral dissolution and denudation [78]. Unlike the nearby Nehushtan, Nahal Yael has high sediment yields, as its small drainage basin (0.5 km2) comprises plutonic rocks (gneissic granite, schist and amphibolite), steep slopes and narrow channels, which increase sediment erosion and transport [79]. Present day evacuation rates in Nahal Yael are much higher than past rates of sediment production from hillslopes [25].
Nahal Rahaf also exemplifies high levels of specific sediment yield; this is suggested to be caused by the highest frequency of flow events among all compared catchments as well as by the highest sediment yields. The explanatory situation for the Rahaf is its slightly more humid upstream area, an arid (average rainfall 129 mm year−1) rather than a hyper-arid setting. The Hiyyon exemplifies low levels of specific sediment yields, as the majority of its drainage basin covers the wide Uvda and Sayarim valleys, rather than a high coverage of rock formations that are the prime runoff producing areas in deserts [80]. Nahal Nehushtan has the lowest values of flow event frequency and specific sediment yield, whereas the ephemeral Nahal Rahaf [81], located 1000 m above its outlet to the Dead Sea, has the highest values. The Rahaf upland area near Arad is less arid than the rest of the basin. Among the compared catchments, Nahal Yael generates the highest specific sediment yields (except the Rahaf) and Nahal Nehushtan the lowest (except the Mojave Desert).
5. Conclusions
We examined the mean annual and the event specific sediment yields from the Nahal Nehushtan Reservoir in the Timna Valley under hyper-arid conditions (mean annual rainfall 25 mm). The dam constructed in 1958 allowed us to summarize 60 years of individual event sediment inputs, the longest period recorded by individual event reservoir sedimentation in hyper-arid watersheds in the Middle East. Nahal Nehushtan was found to have one of the lowest records of both mean annual specific sediment yield and frequency of flow events. Specific sediment yields increase with event frequency, highlighting the importance of rainfall leading to mechanical erosion.
As expected, the sediment yield (t year−1) of drainage basins in hyper-arid areas increases with drainage area. However, specific sediment yields (t km−2 year−1) do not necessarily decrease with an increase in hyper-arid drainage areas, as reported for arid and semiarid areas, possibly due to high geomorphological variability between individual watersheds. We suggest that the study periods reported in the literature (3–90 years; Table 2) are insufficient in determining a reliable mean annual sediment yield in hyper arid conditions. This is due to the high variability in the frequency and intensity of flood events.
Further contributions are needed on the role of various geomorphological variables (e.g., soil characteristics, hillslope topography) and their effects on fluvial erosion, transport and deposition in hyper-arid environments.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A.-Z., Y.S. and I.A.; methodology and investigation, R.A.-Z., Y.S., R.S.-T., I.A. and J.B.L.; software, R.S.-T.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A.-Z., Y.S. and I.A.; writing—review and editing, R.A.-Z. and J.B.L.; supervision, J.B.L.; funding acquisition, R.A.-Z. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded by the Arava Drainage Authority (Israel) and the Israel Ministry of Science and Technology, grant number alona17525.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank M. Silver for providing the Nahal Nehushtan DEM, H. Ginat for offering valuable comments on an earlier version of the manuscript, and M. Finzi for carefully editing this manuscript. We acknowledge the Timna Park Operations staff for helpful support during fieldwork. We thank the three reviewers for their helpful comments and suggestions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Moral, F.J.; Rebollo, F.J.; Paniagua, L.L.; García-Martín, A.; Honorio, F. Spatial distribution and comparison of aridity indices in Extremadura, southwestern Spain. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2016, 126, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guan, X.; Wei, Y.; Guo, R. Global desertification vulnerability to climate change and human activities. Land. Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1380–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pörtner, H.-O.; Roberts, D.C.; Masson-Delmotte, V.; Zhai, P.; Tignor, M.; Poloczanska, E.; Mintenbeck, K.; Nicolai, M.; Okem, A.; Petzold, J.; et al. IPCC Special Report on the Ocean and Cryosphere in a Changing Climate; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahana, R.; Ziv, B.; Enzel, Y.; Dayan, U. Synoptic climatology of major floods in the Negev Desert, Israel. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 867–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.A.; Baeck, M.L.; Yang, L.; Signell, J.; Morin, E.; Goodrich, D.C. The paroxysmal precipitation of the desert: Flash floods in the southwestern United States. Water. Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 10218–10247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayan, U.; Morin, E. Flash flood-producing rainstorms over the Dead Sea: A review. In New Frontiers in Dead Sea Paleoenvironmental Research; Enzel, Y., Agnon, A., Stein, M., Eds.; Special Paper of the Geological Society of America; Geological Society of America: McLean, VA, USA, 2006; Volume 401, pp. 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, P.K.; Baker, V.R. Paleohydrology of flash floods in small desert watersheds in western Arizona. Water. Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 1825–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zituni, R.; Greenbaum, N.; Porat, N.; Benito, G. Magnitude, frequency and hazard assessment of the largest floods in steep, mountainous bedrock channels of the Southern Judean Desert, Israel. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2021, 37, 100886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belachsen, I.; Marra, F.; Peleg, N.; Morin, E. Convective rainfall in a dry climate: Relations with synoptic systems and flash-flood generation in the Dead Sea region. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sc. 2017, 21, 5165–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yair, A.; Sharon, D.; Lavee, H. Trends in runoff and erosion processes over an arid limestone hillside, northern Negev, Israel. Hydrol. Sci. B. 1980, 25, 243–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zoccatelli, D.; Marra, F.; Armon, M.; Rinat, Y.; Smith, J.A.; Morin, E. Contrasting rainfall-runoff characteristics of floods in desert and Mediterranean basins. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 2665–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahat, Y.; Grodek, T.; Lekach, J.; Morin, E. Rainfall-runoff modeling in a small hyper-arid catchment. J. Hydrol. 2009, 373, 204–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laronne, J.B.; Wilhelm, R. Shifting stage-volume curves: Predicting event sedimentation rate based on reservoir stratigraphy. In Applying Geomorphology to Environmental Management; Anthony, D.J., Ethridge, F., Harvey, M., Laronne, J.B., Mosley, M.P., Eds.; Water Resources Publ.: Highlands Ranch, CO, USA, 2001; pp. 33–54. [Google Scholar]
- Alexandrov, Y.; Laronne, J.B.; Reid, I. Suspended sediment concentration and its variation with water discharge in a dryland ephemeral channel, northern Negev, Israel. J. Arid. Environ. 2003, 53, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, W.; Wang, H.; Jia, X. The contribution of aeolian processes to fluvial sediment yield from a desert watershed in the Ordos Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, L.J.; Hernandez, M.; Nichols, M. Processes controlling sediment yield from watersheds as functions of spatial scale. Environ. Modell. Softw. 1997, 12, 355–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichols, M.H.; Nearing, M.A.; Polyakov, V.O.; Stone, J.J. A sediment budget for a small semiarid watershed in southeastern Arizona, USA. Geomorphology 2013, 180–181, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandrov, Y.; Cohen, H.; Laronne, J.B.; Reid, I. Suspended sediment load, bed load, and dissolved load yields from a semiarid drainage basin: A 15-year study. Water. Resour. Res. 2009, 45, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Håkanson, L. Sedimentation processes in lakes. In Encyclopedia of Lakes and Reservoirs. Encyclopedia of Earth Sciences Series; Bengtsson, L., Herschy, R.W., Fairbridge, R.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, R.S.; Chacko, E.; Kaur, D.; Viadero, R. Silting patterns in the reservoirs of small- and medium-sized earthen check dams in humid subtropical monsoon regions, Earth. Surf. Proc. Land. 2019, 44, 2638–2648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czymzik, M.; Dulski, P.; Plessen, B.; von Grafenstein, U.; Naumann, R.; Brauer, A. A 450 year record of spring-summer flood layers in annually laminated sediments from Lake Ammersee (southern Germany). Water. Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W11528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leeder, M.R. Sedimentology: Process and Product; Chapman and Hall: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, J.R.L. Principles of Physical Sedimentology; Blackburn Press: Caldwell, NJ, USA, 2001; p. 272. [Google Scholar]
- Annandale, G.W. Reservoir Sedimentation. In Encyclopedia of Hydrological Sciences; Anderson, M.G., McDonnell, J.J., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Clapp, E.M.; Bierman, P.R.; Schick, A.P.; Lekach, J.; Enzel, Y.; Caffee, M. Sediment yield exceeds sediment production in arid region drainage basins. Geology 2000, 28, 995–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haj El Tahir, M.; Kääb, A.; Xu, C.Y. Identification and mapping of soil erosion areas in the Blue Nile, Eastern Sudan using multispectral ASTER and MODIS satellite data and the SRTM elevation model. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1167–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrawi, J.A.; Elhag, M.; Aldhebiani, A.Y.; Galal, H.K.; Hegazy, A.K.; Alghailani, E. Soil erosion estimation using remote sensing techniques in Wadi Yalamlam basin, Saudi Arabia. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2016, 9585962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şen, Z. Sediment yield estimation formulations for arid regions. Arab. J. Geosci. 2014, 7, 1627–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekach, J.B.; Schick, P. Suspended sediment in desert floods in small catchments. Isr. J. Earth. Sci. 1982, 31, 144–156. [Google Scholar]
- Bunte, K.; Abt, S.R. Effect of sampling time on measured gravel bed load transport rates in a coarse-bedded stream. Water. Resour. Res. 2005, 41, W11405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.; Laronne, J.B.; Powell, D.M. Flood flows, sediment fluxes and reservoir sedimentation in upland desert rivers. In Hydrology in a Changing Environment; Wheater, H., Kirby, C., Eds.; John Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1998; pp. 377–386. [Google Scholar]
- Lucía, A.; Recking, A.; Martín-Duque, J.F.; Storz-Peretz, Y.; Laronne, J.B. Continuous monitoring of bedload discharge in a small, steep sandy channel. J. Hydrol. 2013, 497, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenmann, D.; Turowski, J.M.; Fritschi, B.; Wyss, C.; Laronne, J.; Barzilai, R.; Reid, I.; Kreisler, A.; Aigner, J.; Seitz, H.; et al. Bedload transport measurements with impact plate geophones: Comparison of sensor calibration in different gravel-bed streams. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2014, 39, 928–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geay, T.; Belleudy, P.; Gervaise, C.; Habersack, H.; Aigner, J.; Kreisler, A.; Seitz, H.; Laronne, J.B. Passive acoustic monitoring of bed load discharge in a large gravel bed river. J. Geophys. Res.-Earth. 2017, 122, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietze, M.; Lagarde, S.; Halfi, E.; Laronne, J.B.; Turowski, J.M. Joint sensing of bedload flux and water depth by seismic data inversion. Water. Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 9892–9904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, I.D.L.; Dearing, J.A.; Grew, R.; Orend, K. The sedimentary data base: An appraisal of lake and reservoir sediment-based studies of sediment yield. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 1990, 189, 19–43. [Google Scholar]
- Millares, A.; Moñino, A. Sediment yield and transport process assessment from reservoir monitoring in a semi-arid mountainous river. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 2990–3005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekach, J.; Enzel, Y. Flood-duration integrated stream power and frequency magnitude of >50- year-long sediment discharge out of a hyper arid watershed. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 2021, 46, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, M.; Church, M.A. Method for error analysis of sediment yields derived from estimates of lacustrine sediment accumulation. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2000, 25, 1257–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verstraeten, G.; Poesen, J. Using sediment deposits in small ponds to quantify sediment yield from small catchments: Possibilities and limitations. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2002, 27, 1425–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hereford, R. Sediment-yield history of a small basin in southern Utah, 1937-1976: Implications for land management and geomorphology. Geology 1987, 15, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geilhausen, M.; Otto, J.C.; Morche, D.; Schrott, L. Decadal sediment yield from an Alpine proglacial zone inferred from reservoir sedimentation (Pasterze, Hohe Tauern, Austria). In Erosion and Sediment Yields in the Changing Environment; Collins, A.L., Golosov, V., Horrowitz, A.J., Lu, X., Stone, M., Walling, D.E., Zhang, X., Eds.; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK, 2012; pp. 161–172. [Google Scholar]
- Brune, G.M. Trap efficiency of reservoirs. EOS 1953, 34, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinwarth, B.; Riddell, E.S.; Glotzbach, C.; Baade, J. Estimating the sediment trap efficiency of intermittently dry reservoirs: Lessons from the Kruger National Park, South Africa. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 2018, 43, 463–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.L.; Annandale, G.; Hotchkiss, R. Reservoir Sedimentation. In Sedimentation Engineering: Processes, Measurements, Modeling, and Practice; García, M.H., Ed.; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2008; pp. 579–612. [Google Scholar]
- Heinemann, H.G. A new sediment trap efficiency curve for small reservoirs. J. Am. Water. Resour. As. 1981, 17, 825–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laronne, J.B. Event-based deposition in the ever-emptying Yatir Reservoir, Israel. In The Hydrology-Geomorphology Interface: Rainfall, Floods, Sedimentation, Land Use; Hassan, M.A., Slaymaker, O., Berkowicz, S.M., Eds.; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK, 2000; pp. 285–302. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, A.; Hsu, K.J. Non-annual cycles of varve-like sedimentation in Walensee, Switzerland. Sedimentology 1979, 26, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schick, A.P.; Lekach, J. An evaluation of two ten-year sediment budgets, Nahal Yael, Israel. Phys. Geogr. 1993, 14, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, U.; Greenbaum, N. Extremely high sediment yield from a small arid catchment-Giv’at Hayil, northwestern Negev, Israel. Isr. J. Earth Sci. 2008, 57, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolman, M.G.; Miller, J.P. Magnitude and frequency of forces in geomorphic processes. J. Geol. 1960, 68, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laronne, J.B.; Reid, L. Very high rates of bedload sediment transport by ephemeral desert rivers. Nature 1993, 366, 148–150, (and 113). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, D.E.; Kleo, A.H.A. Sediment yields of rivers in areas of low precipitation: A global view. In The Hydrology of Areas of Low Precipitation; IAHS, Ed.; IAHS-AISH Publication 128: Wallingford, UK, 1979; pp. 479–493. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, K.D. Soil erosion and sediment yield in the Indian arid zone. In Erosion and Sediment Yield: Global and Regional Perspectives; Walling, D.E., Webb, B.W., Eds.; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK, 1996; pp. 175–182. [Google Scholar]
- Storz-Peretz, Y.; Laronne, J.B. The morpho-textural signature of large bedforms in ephemeral gravel-bed channels of various planforms. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 617–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, K.D.; Vangani, N.S.; Choudhari, J.S. Sediment transport characteristics of the desert streams in India. J. Hydrol. 1984, 67, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.A.; Loughran, R.J.; Elliott, G.L. Sedimentation in a semi-arid zone reservoir in Australia determined by 137Cs. Acta Geol. Hisp. 2000, 35, 329–338. [Google Scholar]
- Totin, H.S.V.; Zannou, A.; Amoussou, E.; Afouda, A.; Boko, M. Progressive aridity impact on the hydrological regime in the Volta River basin in Benin (West Africa). In Hydrology in a Changing World: Environmental and Human Dimensions; Daniell, T.M., Van Lanen, H.A.J., Demuth, S., Laaha, G., Servat, E., Mahé, G., Boyer, J.-F., Paturel, J.-E., Dezetter, A., Ruelland, D., Eds.; IAHS Press: Wallingford, UK, 2014; pp. 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, K.; Shahid, S.; Wang, X.; Nawaz, N.; Khan, N. Spatiotemporal changes in aridity of Pakistan during 1901–2016. Hydrol. Earth. Syst. Sci. 2019, 23, 3081–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdugo, M.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Soliveres, S.; Hernández-Clemente, R.; Zhao, Y.; Gaitán, J.J.; Gross, N.; Saiz, H.; Maire, V.; Lehman, A.; et al. Global ecosystem thresholds driven by aridity. Science 2020, 367, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Israel Meteorological Service Data Base, Eilat Station 1949–2022. Available online: https://ims.data.gov.il/he/ims-results (accessed on 4 July 2022).
- Beyth, M.; Segev, A.; Ginat, H. Stratigraphy and structure of the Timna Valley and adjacent ancient mining areas. In Mining for Ancient Copper: Essays in Memory of Beno Rothenberg; Ben-Yosef, E., Ed.; The Institute of Archaeology of Tel Aviv University: Tel Aviv, Israel, 2018; pp. 3–20. [Google Scholar]
- Abdulrazzak, M.J.; Sorman, A.U. Transmission losses from ephemeral streams in arid region. J. Irrig. Drain. E 1994, 120, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shentsis, I.; Meirovich, L.; Ben-Zvi, A.; Rosenthal, E. Assessment of transmission losses and groundwater recharge from runoff events in a wadi under shortage of data on lateral inflow, Negev, Israel. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 1649–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahan, O.; Tatarsky, B.; Enzel, Y.; Kulls, C.; Seely, M.; Benito, G. Dynamics of flood water infiltration and ground water recharge in hyperarid desert. Ground Water 2008, 46, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolman, M.G.; Gerson, R. Relative scales of time and effectiveness of climate in watershed geomorphology. Earth Surf. Process. 1978, 3, 189–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gellis, A.C.; Elliott, J.G.; Pavich, M. Geomorphic processes responsible for decadal-scale arroyo changes, Rio Puerco, New Mexico. GSA Bull. 2017, 129, 1660–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tooth, S. Dryland fluvial environments: Assessing distinctiveness and diversity from a global perspective. In Treatise on Geomorphology; Shroder, J.F., Ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; Volume 9, pp. 612–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbein, W.B.; Schumm, S.A. Yield of sediment in relation to mean annual precipitation. Eos 1958, 39, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosley, M.P. Bedload transport and sediment yield in the Onyx River, Antarctica. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 1988, 13, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.G.; Hereford, R.; Webb, R.H. Sediment yield and runoff frequency of small drainage basins in the Mojave Desert, U.S.A. Geomorphology 2006, 74, 232–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munwes, Y. Record of Event Sedimentation in a Mining Pit in Nahal Rahaf, South of the Dead Sea; Seminar Report Submitted to the Department of Geography & Environmental Development, Ben Gurion University; Ben Gurion University: Beer Sheva, Israel, 2008. (In Hebrew) [Google Scholar]
- Saber, M.; Kantoush, S.; Sumi, T.; Ogiso, Y. Reservoir sedimentation at Wadi System: Challenges and management strategies. Disaster Prev. Res. Inst. Annu. 2019, 62, 689–699. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Harrasi, T.; Kantoush, S.A.; Sumi, T.; Saber, M. Assessment of sedimentation using field investigation and UVA imaging at Asserin upstream dam, Wadi Mijlass, Oman. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Symposium on Flash Floods in Wadi Systems, ISFF 2020, Kyoto University, Kyoto, Japan, 25–28 February 2020; p. 70. [Google Scholar]
- Laronne, J.B.; Cohen, H. Optimization of Mining of Alluvial Material and Calculation of the Infilling of Reservoirs in the Southwestern Coast of the Dead Sea—A Summary of a 3-Year Research; Report submitted to the Dead Sea Works; Ben Gurion University: Beer Sheva, Israel, 1999. (In Hebrew) [Google Scholar]
- Taig, M. The use of sediment accumulating in flood reservoirs. In Reservoirs as a Source of Water to the Negev Desert; Laronne, J.B., Ed.; Ben-Gurion University: Beer Sheva, Israel, 1996; pp. 25–30. (In Hebrew) [Google Scholar]
- Ginat, H.; Shlomi, Y.; Batarseh, S.; Vogel, J. Reduction in precipitation levels in the Arava Valley (Southern Israel and Jordan), 1949–2009. J. Dead-Sea Arav. Res. 2011, 1, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Katz, T.; Ginat, H.; Eyal, G.; Steiner, Z.; Braun, Y.; Shalev, S.; Goodman-Tchernov, B.N. Desert flash floods form hyperpycnal flows in the coral-rich Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2015, 417, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryb, U.; Matmon, A.; Erel, Y.; Haviv, I.; Benedetti, L.; Hidy, A.J. Styles and rates of long-term denudation in carbonate terrains under a Mediterranean to hyper-arid climatic gradient. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2014, 406, 142–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yair, A.; Klein, M. The influence of surface properties on flow and erosion processes on debris covered slopes in an arid area. Catena 1973, 1, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, H.; Laronne, J.B. High rates of sediment transport by flashfloods in the southern Judean Desert, Israel. Hydrol. Process. 2005, 19, 1687–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).