Regional Disparities and Influencing Factors of Eco-Efficiency of Arable Land Utilization in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
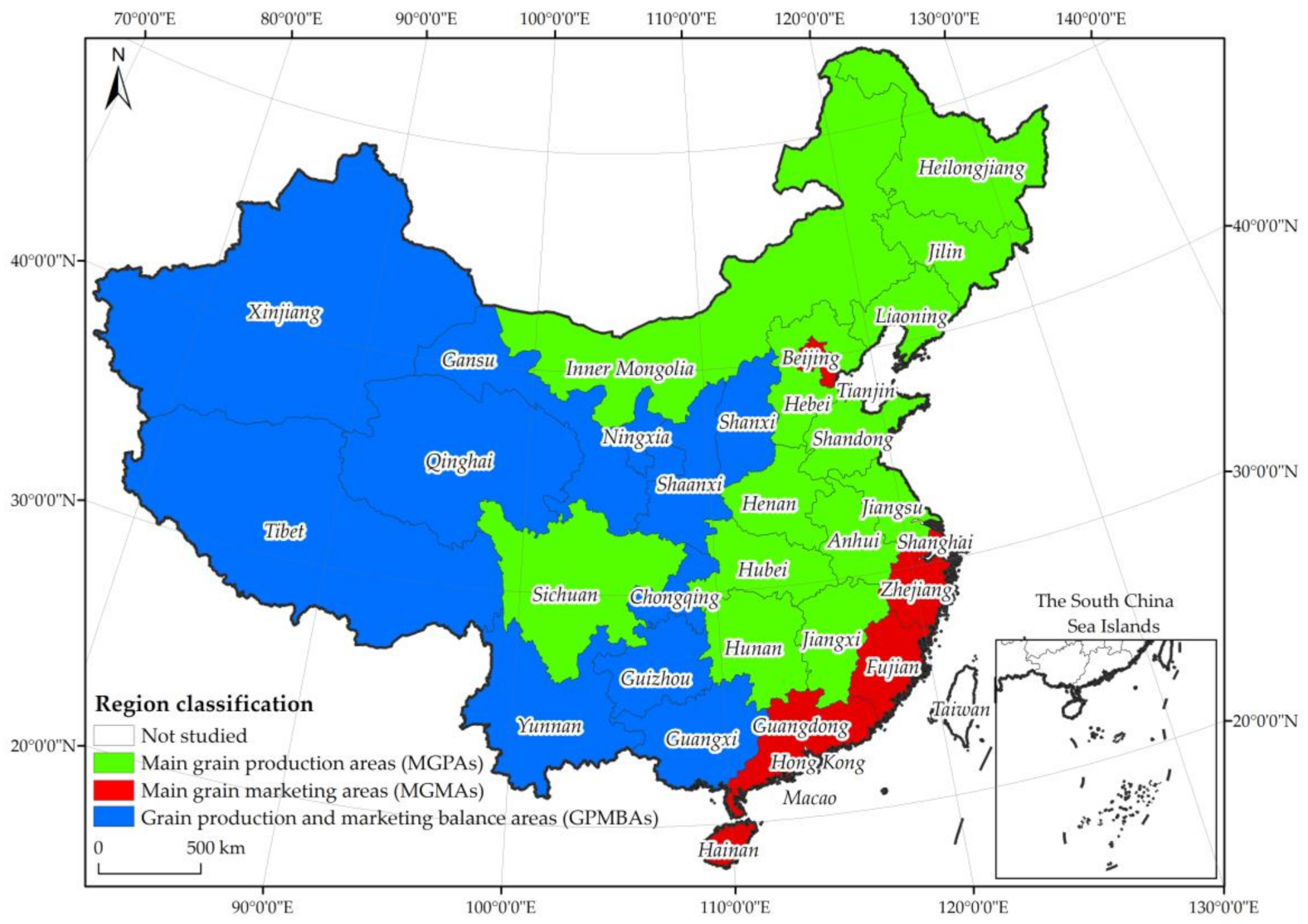
2.1. Research Area
2.2. Empirical Methods
2.2.1. The Super-SBM Model
2.2.2. Kernel Density Estimation
2.2.3. Tobit Regression Model
2.3. Selection of Indicators and Data Description
2.3.1. Indicators Used to Measure EALU
2.3.2. Indicators of Influence Factors of EALU
2.3.3. Data Sources and Description
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Measurement and Comparison of EALU
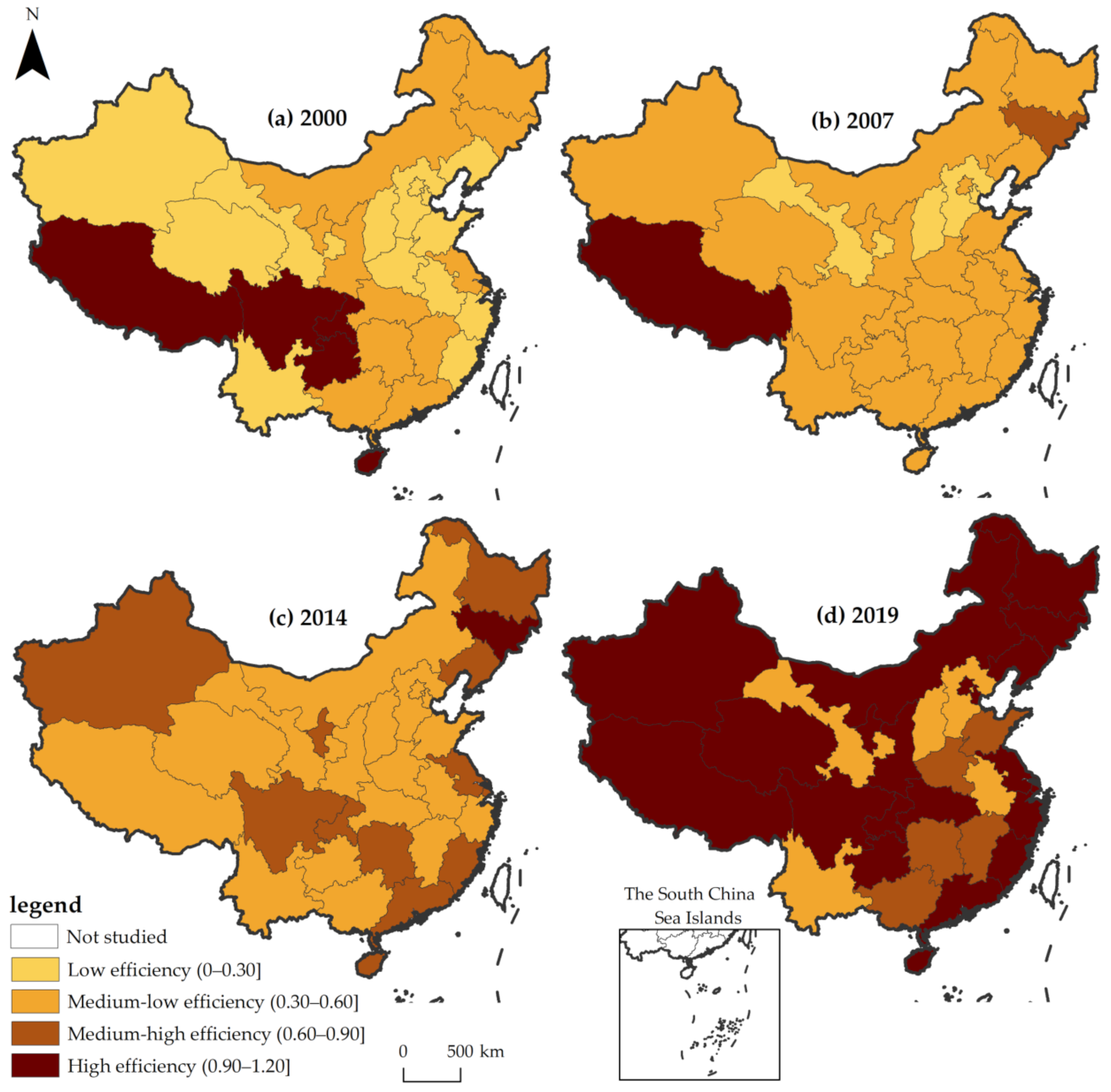
3.2. Spatial-Temporal Disparity of EALU
3.3. Dynamic Evolution of EALU
3.4. Influencing Factors of EALU
4. Conclusions and Policy Implications
4.1. Conclusions
4.2. Policy Implications
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bommarco, R.; Vico, G.; Hallin, S. Exploiting ecosystem services in agriculture for increased food security. Glob. Food Secur. 2018, 17, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Xie, H.L.; Lv, T.G.; Yao, G.R. Determinants of cultivated land recuperation in ecologically damaged areas in China. Land Use Policy 2019, 81, 160–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, R.M. The US farmland protection policy act: Another case of benign neglect. Land Use Policy 1991, 8, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichtenberg, E.; Ding, C.R. Assessing farmland protection policy in China. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.W.; Zhao, C.L.; Song, W. Review of the evolution of cultivated land protection policies in the period following China’s reform and liberalization. Land Use Policy 2017, 67, 660–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abass, K.; Adanu, S.K.; Agyemang, S. Peri-urbanisation and loss of arable land in Kumasi Metropolis in three decades: Evidence from remote sensing image analysis. Land Use Policy 2018, 72, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Z.H.; Du, X.J.; Castillo, C.S.Z. How does urbanization affect farmland protection? Evidence from China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 145, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, X.Z.; Huang, J.K.; Rozelle, S.; Zhang, J.P.; Li, Z.H. Impact of urbanization on cultivated land changes in China. Land Use Policy 2015, 45, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.S.; Wang, J.Y.; Long, H.L. Analysis of arable land loss and its impact on rural sustainability in Southern Jiangsu Province of China. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, Z.Z.; Li, Y.Y.; Fang, P.; Zhou, L. “One family, two systems”: Food safety crisis as a catalyst for agrarian changes in rural China. J. Rural Stud. 2019, 69, 87–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berihun, M.L.; Tsunekawa, A.; Haregeweyn, N.; Meshesha, D.T.; Adgo, E.; Tsubo, M.; Masunaga, T.; Fenta, A.A.; Sultan, D.; Yibeltal, M. Exploring land use/land cover changes, drivers and their implications in contrasting agro-ecological environments of Ethiopia. Land Use Policy 2019, 87, 104052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, B.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yan, J.Z.; Rai, R.J.; Li, L.H. Farmers’ perceptions of agricultural land use changes in Nepal and their major drivers. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 235, 432–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, L.R. Who Will Feed China?: Wake-Up Call for a Small Planet; W.W. Norton & Company: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Glendinning, A.; Xu, Y.Q. Land-use changes and land policies evolution in China’s urbanization processes. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Long, H.L.; Tu, S.S.; Zhang, Y.N.; Zheng, Y.H. Farmland transition in China and its policy implications. Land Use Policy 2020, 92, 104470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.B.; Zhang, X.Y. Static and dynamic cultivated land use efficiency in China: A minimum distance to strong efficient frontier approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 246, 119002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.L.; Chen, Q.R.; Wang, W.; He, Y.F. Analyzing the green efficiency of arable land use in China. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2018, 133, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.J.; Song, C.Q.; Shen, S.; Gao, P.C.; Cheng, C.X.; Cheng, F.; Wan, C.J.; Zhu, D.H. Spatial pattern of arable land-use intensity in China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 104845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, B.; Lu, X.H.; Zhou, M.; Chen, D.L. Provincial cultivated land use efficiency in China: Empirical analysis based on the SBM-DEA model with carbon emissions considered. Technol. Forecast. Soc. 2020, 151, 119874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skevas, T.; Stefanou, S.E.; Lansink, A.O. Pesticide use, environmental spillovers and efficiency: A DEA risk-adjusted efficiency approach applied on Dutch arable farming. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2014, 237, 658–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukuve, F.M.; Fenner, R.A. Scale variability of water, land, and energy resource interactions and their influence on the food system in Uganda. Sustain. Prod. Consumpt. 2015, 2, 79–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaltegger, S.; Sturm, A. Ökologische Rationalität: Ansatzpunkte zur Ausgestaltung von Ökologieorientierten Managementinstrumenten. Unternehmung 1990, 4, 117–131. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Y.P.; Deng, X.Z.; Jiang, S.J.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z. Exploring the relationship between urbanization and urban eco-efficiency: Evidence from prefecture-level cities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 195, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.W.; Tang, J.X.; Choi, G. A two-stage eco-efficiency evaluation of China’s industrial sectors: A dynamic network data envelopment analysis (DNDEA) approach. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2021, 148, 879–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zou, L.; Zou, L.L.; Zhang, H.W. Exploring the eco-efficiency of cultivated land utilization and its influencing factors in China’s Yangtze River Economic Belt, 2001–2018. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 294, 112939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coluccia, B.; Valente, D.; Fusco, G.; Leo, F.D.; Porrini, D. Assessing agricultural eco-efficiency in Italian Regions. Ecol. Ind. 2020, 116, 106483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mózner, Z.; Tabi, A.; Csutora, M. Modifying the yield factor based on more efficient use of fertilizer—The environmental impacts of intensive and extensive agricultural practices. Ecol. Ind. 2012, 16, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sabiha, N.-E.; Salim, R.; Rahman, S.; Rola-Rubzen, M.F. Measuring environmental sustainability in agriculture: A composite environmental impact index approach. J. Environ. Manag. 2016, 166, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Englund, O.; Börjesson, P.; Berndes, G.; Scarlat, N.; Dallemand, J.-F.; Grizzetti, B.; Dimitriou, I.; Mola-Yudego, B.; Fahl, F. Beneficial land use change: Strategic expansion of new biomass plantations can reduce environmental impacts from EU agriculture. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2020, 60, 101990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reith, C.C.; Guidry, M.J. Eco-efficiency analysis of an agricultural research complex. J. Environ. Manag. 2003, 68, 219–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, A.; Grovermann, C.; Kadzere, I.; Egyir, I.S.; Muriuki, A.; Bandanaa, J.; Clottey, J.; Ndungu, J.; Blockeel, J.; Muller, A.; et al. Sustainable intensification pathways in Sub-Saharan Africa: Assessing eco-efficiency of smallholder perennial cash crop production. Agric. Syst. 2022, 195, 103304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gancone, A.; Pubule, J.; Rosa, M.; Blumberga, D. Evaluation of agriculture eco-efficiency in Latvia. Energy Procedia 2017, 128, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassauer, F.; Herndl, M.; Nemecek, T.; Guggenberger, T.; Fritz, C.; Steinwidder, A.; Zollitsch, W. Eco-efficiency of farms considering multiple functions of agriculture: Concept and results from Austrian farms. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 297, 126662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, Y.Z. Utilization benefit of cultivated land and land institution reforms: Economy, society and ecology. Habitat Int. 2018, 77, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.H.; Wu, L.; Lin, H.L. Analysis of total-factor cultivated land efficiency in China’s agriculture. Agric. Econ. 2010, 56, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.X.; Zhu, D.L.; Xie, B.P.; Du, T.; Wang, X. Spatiotemporal pattern evolvement and driving factors of cultivated land utilization efficiency of the major grain producing area in China. Resour. Sci. 2017, 39, 608–619. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Luo, X.; Ao, X.H.; Zhang, Z.; Wan, Q.; Liu, X. Spatiotemporal variations of cultivated land use efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt based on carbon emission constraints. J. Geogr. Sci. 2020, 30, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, S.R.; Cheng, L. Evaluation of cultivated land use efficiency with environmental constraints in the Dongting Lake Eco-Economic Zone of Hunan province, China. Land 2020, 9, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, W.Y.; Chatterton, J.; Sim, S.; Kulak, M.; Beltran, A.M.; Huijbregts, M.A.J. Estimating greenhouse gas emissions from direct land use change due to crop production in multiple countries. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 755, 143338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajwang’Ondiek, R.; Hayes, D.S.; Kinyua, D.N.; Kitaka, N.; Lautsch, E.; Mutuo, P.; Hein, T. Influence of land-use change and season on soil greenhouse gas emissions from a tropical wetland: A stepwise explorative assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 787, 147701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babin, N.; Mullendore, N.D.; Prokopy, L.S. Using social criteria to select watersheds for non-point source agricultural pollution abatement projects. Land Use Policy 2016, 55, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.Z.; Su, Y.Y.; Yang, G.Q.; Chen, D.L.; Yang, R.X. Spatial-temporal characteristics of cultivated land use efficiency in major function-oriented zones: A case study of Zhejiang province, China. Land 2020, 9, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, J.H.; Xiao, P.N.; Wu, H. Spatial characteristics of cultivated land quality accounting for ecological environmental condition: A case study in hilly area of northern Hubei province, China. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 774, 145765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Geng, Y.; Viglia, S.; Bleischwitz, R.; Buonocore, E.; Ulgiati, S. Regional disparities in the Chinese economy: An emergy evaluation of provincial international trade. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2017, 126, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Peng, J.; Chen, X.; Lu, Z. Carbon emissions, energy consumption and economic growth: Evidence from the agricultural sector of China’s main grain-producing areas. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 665, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of super-efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2002, 143, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, S.U.; Cui, Y.; Khan, A.A.; Ali, M.A.S.; Khan, A.; Xia, X.L.; Liu, G.B.; Zhao, M.J. Tracking sustainable development efficiency with human-environmental system relationship: An application of DPSIR and super efficiency SBM model. Sci. Total. Environ. 2021, 783, 146959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.W.; Jiang, J.; Li, C.H. Ecological efficiency evaluation of marine ranching based on the Super-SBM model: A case study of Shandong. Ecol. Ind. 2021, 131, 108174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.J.; Zeng, L.E.; Lu, H.Y.; Zhou, Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Wei, X.Y. Green economic efficiency and its influencing factors in China from 2008 to 2017: Based on the super-SBM model with undesirable outputs and spatial Dubin model. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 741, 140026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkovnik, V.; Shmulevich, I. Kernel density estimation with adaptive varying window size. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2002, 23, 1641–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.L.; Li, W.Y.; Xiong, X.F. Estimating wind speed probability distribution using kernel density method. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2011, 81, 2139–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.D.; Li, J.C.; Guo, G.X.; Li, S.P.; Gong, Q.X. Evaluation for water resource system efficiency and influencing factors in western China: A two-stage network DEA-Tobit model. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 328, 129674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J. Estimation of relationships for limited dependent variables. Econometrica 1958, 26, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.R.; Zeng, W.H.; Shi, H. Regional environment efficiency in China: Analysis based on a regional slack-based measure with environmental undesirable outputs. Ecol. Ind. 2016, 71, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madu, I.A. Spatial impacts of rural population pressure on agricultural land use in Nigeria. Appl. Spat. Anal. Policy 2012, 5, 123–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.Y.; Zhang, W.G. Cross-provincial differences in determinants of agricultural eco-efficiency in China: An analysis based on panel data from 31 provinces in 1996-2015. Chin. Rural Econ. 2018, 1, 46–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, B.; Fu, S.Y.; Zhang, J.B.; Yu, H.S. Carbon functions of agricultural land use and economy across China: A correlation analysis. Energy Procedia 2011, 5, 1949–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- West, T.O.; Marland, G. A synthesis of carbon sequestration, carbon emissions, and net carbon flux in agriculture: Comparing tillage practices in the United States. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2002, 91, 217–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, W.M.; Kwon, K.C. Soil carbon sequestration and land-use change: Processes and potential. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2000, 6, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dubey, A.; Lal, R. Carbon footprint and sustainability of agricultural production systems in Punjab, India and Ohio, USA. J. Crop Improv. 2009, 23, 332–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Yang, H.R.; Wu, Q. The spatial and temporal differentiation of the farmland utilization efficiency in the Eastern Coastal Economic Zone. Res. Agric. Modern. 2020, 41, 321–330. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ji, Z.X.; Wang, X.L.; Li, L.; Guan, X.K.; Yu, L.; Xu, Y.Q. The evolution of cultivated land utilization efficiency and its influencing factors in Nanyang Basin. J. Nat. Resour. 2021, 36, 688–701. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, K.F.; Yang, Q.Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Sun, X.F. Mapping and evaluating cultivated land fallow in Southwest China using multisource data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2019, 654, 987–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.H.; Yang, G.Q.; Wang, G.; Song, Y.; Yang, F. How do different rural-land-consolidation modes shape farmers’ ecological production behaviors? Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, M.T.; Yu, Q.Y.; Wu, W.B. From multiple cropping index to multiple cropping frequency: Observing cropland use intensity at a finer scale. Ecol. Ind. 2019, 101, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.S.; Wang, H.M.; Cheng, Y.X.; Zheng, B.; Lu, Z.L. The impact of rural out-migration on arable land use intensity: Evidence from mountain areas in Guangdong, China. Land Use Policy 2016, 59, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.H.; Kuang, B.; Li, J. Regional differences and its influencing factors of cultivated land use efficiency under carbon emission constraint. J. Nat. Resour. 2018, 33, 657–668. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, X.W.; Chen, B.Y.; Shang, Y.P.; Song, M.L. Challenges toward carbon neutrality in China: Strategies and countermeasures. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 176, 105959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

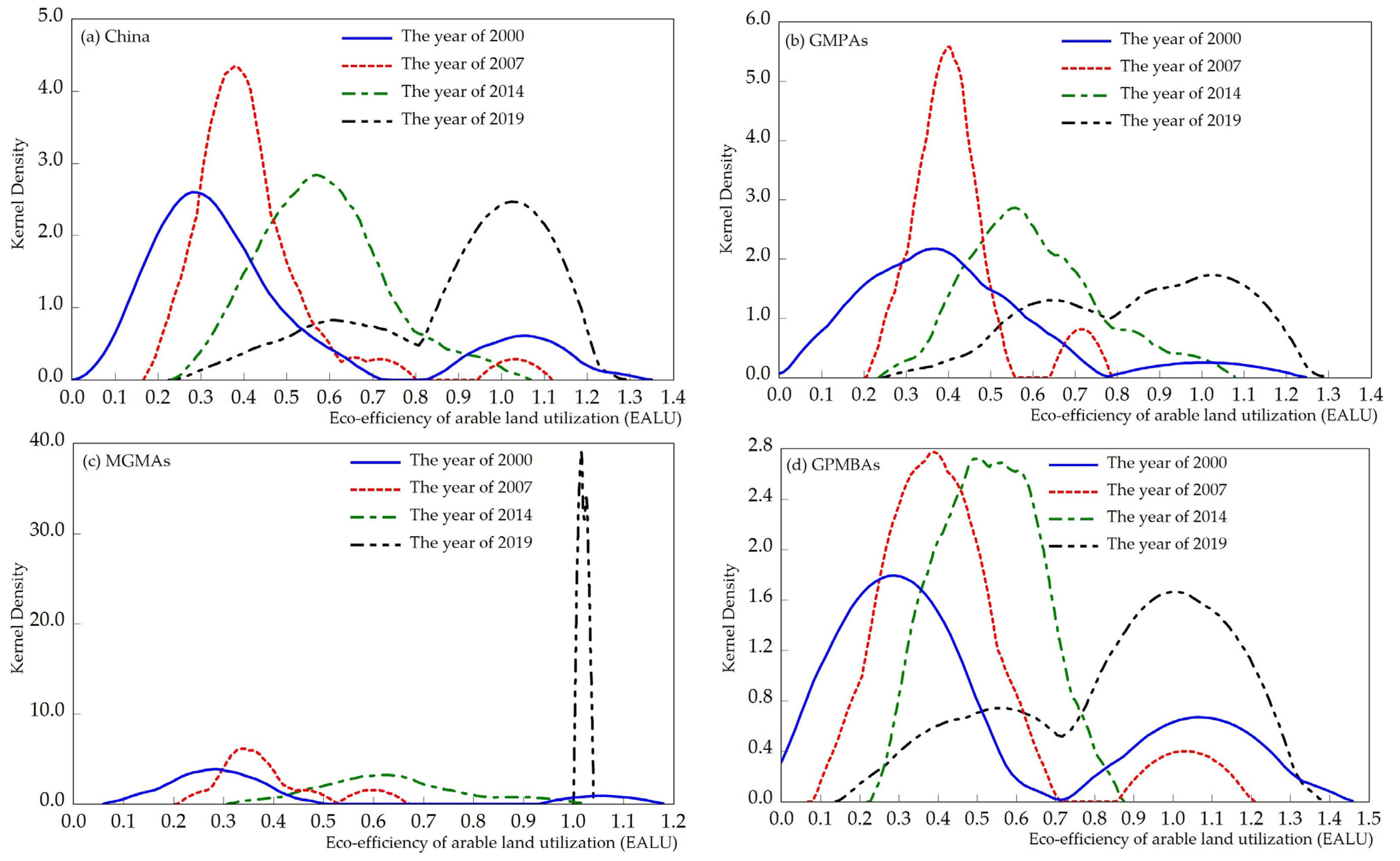
| Degree of Disparity | Height of the Peak | Width of the Peak | Position of the Peak | Number of Peaks |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Increase | Flat | Distensible | Move left | Increase |
| Decrease | Steep | Narrowed | Move right | Reduce |
| Indicators | Variables | Unit | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Input | Total sown area of farm crops (I1) | 103 hectares | Kuang et al. [19] |
| Number of rural population (I2) | 104 people | Madu [56] | |
| Effective irrigation area (I3) | 103 hectares | Chen et al. [38] | |
| Total power of agricultural machinery (I4) | 104 kW·h | Luo et al. [37] | |
| Consumption of chemical fertilizers (I5) | 104 t | Zhang et al. [36] | |
| Consumption of pesticides (I6) | 104 t | Kuang et al. [19] | |
| Consumption of agricultural film (I7) | 104 t | Chen et al. [38] | |
| Desirable output | Gross agricultural production (D1) | 108 Yuan | Kuang et al. [19] |
| Total grain production (D2) | 104 t | Zhang et al. [36] | |
| Undesirable output | Carbon emissions (U1) | 104 t | Zhang et al. [42] |
| Non-point source pollution (U2) | 104 t | Wang and Zhang [57] |
| Source | Coefficient | Unit | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tillage | 312.6 | kg/km2 | Zhang et al. [42] |
| Agricultural machinery | 0.18 | kg/kW | Li et al. [58] |
| Chemical fertilizer | 0.8956 | kg/kg | West and Marland [59] |
| Pesticide | 4.9341 | kg/kg | Post and Kwon [60] |
| Agricultural film | 5.18 | kg/kg | Wang and Zhang [57] |
| Irrigation | 25 | kg/hectares | Dubey and Lal [61] |
| Influencing Factors | Variables (Unit) | Abbreviation | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural conditions | Multiple cropping index (%) | MCI | Kuang et al. [19] |
| Financial support for agriculture | Ratio of agricultural expenditure to financial expenditure (%) | RAF | Jiang et al. [62] |
| Science and technology inputs | Ratio of science and technology expenditure in fiscal expenditure (%) | RSF | Zhang et al. [36] |
| Level of industrialization | Ratio of Industrial added value to GDP (%) | RIG | Wang and Zhang [57] |
| Agricultural mechanization | Agricultural machinery power per unit area (kW·h/hectares) | AMP | Wang and Zhang [57] |
| Living standard of farmers | Per capita disposable income of rural residents (Yuan/people) | PIR | Ji et al. [63] |
| Indicators | Variables | Mean | Median | Std. Dev. | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input | I1 | 3533.27 | 3122.05 | 2787.22 | 46.50 | 14,338.10 |
| I2 | 1188.28 | 1073.24 | 889.69 | 48.27 | 4510.90 | |
| I3 | 1946.50 | 1516.89 | 1523.85 | 109.20 | 6177.60 | |
| I4 | 2730.99 | 2017.90 | 2675.11 | 94.00 | 13,353.00 | |
| I5 | 169.63 | 133.30 | 138.68 | 2.50 | 716.10 | |
| I6 | 5.10 | 4.65 | 4.25 | 0.06 | 17.35 | |
| I7 | 6.74 | 5.10 | 6.34 | 0.01 | 34.35 | |
| Desirable output | D1 | 1169.71 | 827.80 | 1108.73 | 11.40 | 5223.40 |
| D2 | 1766.44 | 1371.65 | 1488.03 | 28.8 | 7506.80 | |
| Undesirable output | U3 | 253.72 | 225.31 | 193.98 | 3.43 | 870.64 |
| U4 | 1.12 | 0.71 | 1.09 | 0.01 | 4.76 | |
| Influencing Factors | MCI | 125.83 | 118.86 | 37.56 | 41.46 | 230.90 |
| RAF | 9.69 | 9.64 | 3.57 | 2.13 | 20.34 | |
| RSF | 1.47 | 1.07 | 1.33 | 0.15 | 7.20 | |
| RIG | 45.07 | 46.60 | 8.45 | 16.16 | 61.50 | |
| AMP | 5.77 | 5.01 | 3.33 | 1.32 | 24.63 | |
| PIR | 7472.00 | 5775.55 | 5522.80 | 1330.81 | 33,195.20 |
| Research Scale | The Average of EALU | Average Annual Growth Rate | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2000 | 2019 | ||
| China | 0.4393 | 0.8929 | 4.01% |
| MGPAs | 0.4144 | 0.8504 | 4.07% |
| MGMAs | 0.3914 | 1.0195 | 5.34% |
| GPMBAs | 0.4991 | 0.8625 | 3.16% |
| Variables | China (Model 1) | MGPAs (Model 2) | MGMAs (Model 3) | GPMBAs (Model 4) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Std. Err. | Coefficient | Std. Err. | Coefficient | Std. Err. | Coefficient | Std. Err. | |
| MCI | −0.1398 *** | 0.0376 | −0.1852 *** | 0.0556 | −0.1473 *** | 0.0656 | 0.1966 ** | 0.0988 |
| RAF | −0.6121 ** | 0.2965 | −1.0831 *** | 0.4012 | −0.9026 | 1.0041 | −0.3851 *** | 0.4793 |
| RSF | 2.4757 *** | 0.6685 | 1.7679 * | 1.0172 | 0.1793 | 1.1151 | 2.1025 | 3.0921 |
| RIG | −0.7173 *** | 0.1068 | −0.6631 *** | 0.1156 | −0.5800 ** | 0.2470 | −0.7025 *** | 0.2423 |
| AMP | −0.1998 *** | 0.0289 | −0.1384 *** | 0.0365 | −0.2488 *** | 0.0620 | −0.2358 *** | 0.0620 |
| PIR | 0.2248 *** | 0.0169 | 0.2323 *** | 0.0224 | 0.3379 *** | 0.0382 | 0.1929 *** | 0.0328 |
| _cons | 1.5020 *** | 0.0798 | 1.5364 *** | 0.1052 | 1.5238 *** | 0.1657 | 1.1830 *** | 0.1600 |
| Obs. | 620 | 260 | 140 | 220 | ||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ke, N.; Zhang, X.; Lu, X.; Kuang, B.; Jiang, B. Regional Disparities and Influencing Factors of Eco-Efficiency of Arable Land Utilization in China. Land 2022, 11, 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020257
Ke N, Zhang X, Lu X, Kuang B, Jiang B. Regional Disparities and Influencing Factors of Eco-Efficiency of Arable Land Utilization in China. Land. 2022; 11(2):257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020257
Chicago/Turabian StyleKe, Nan, Xupeng Zhang, Xinhai Lu, Bing Kuang, and Bin Jiang. 2022. "Regional Disparities and Influencing Factors of Eco-Efficiency of Arable Land Utilization in China" Land 11, no. 2: 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020257
APA StyleKe, N., Zhang, X., Lu, X., Kuang, B., & Jiang, B. (2022). Regional Disparities and Influencing Factors of Eco-Efficiency of Arable Land Utilization in China. Land, 11(2), 257. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11020257






