Cross-County Characteristics of Water–Ecology–Economy Coupling Coordination in the Wuding River Watershed, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Evaluation Index System and Data
2.3. Statistical Methods
2.3.1. Coupling Coordination Model
2.3.2. Grey Correlation Analysis Model
3. Results
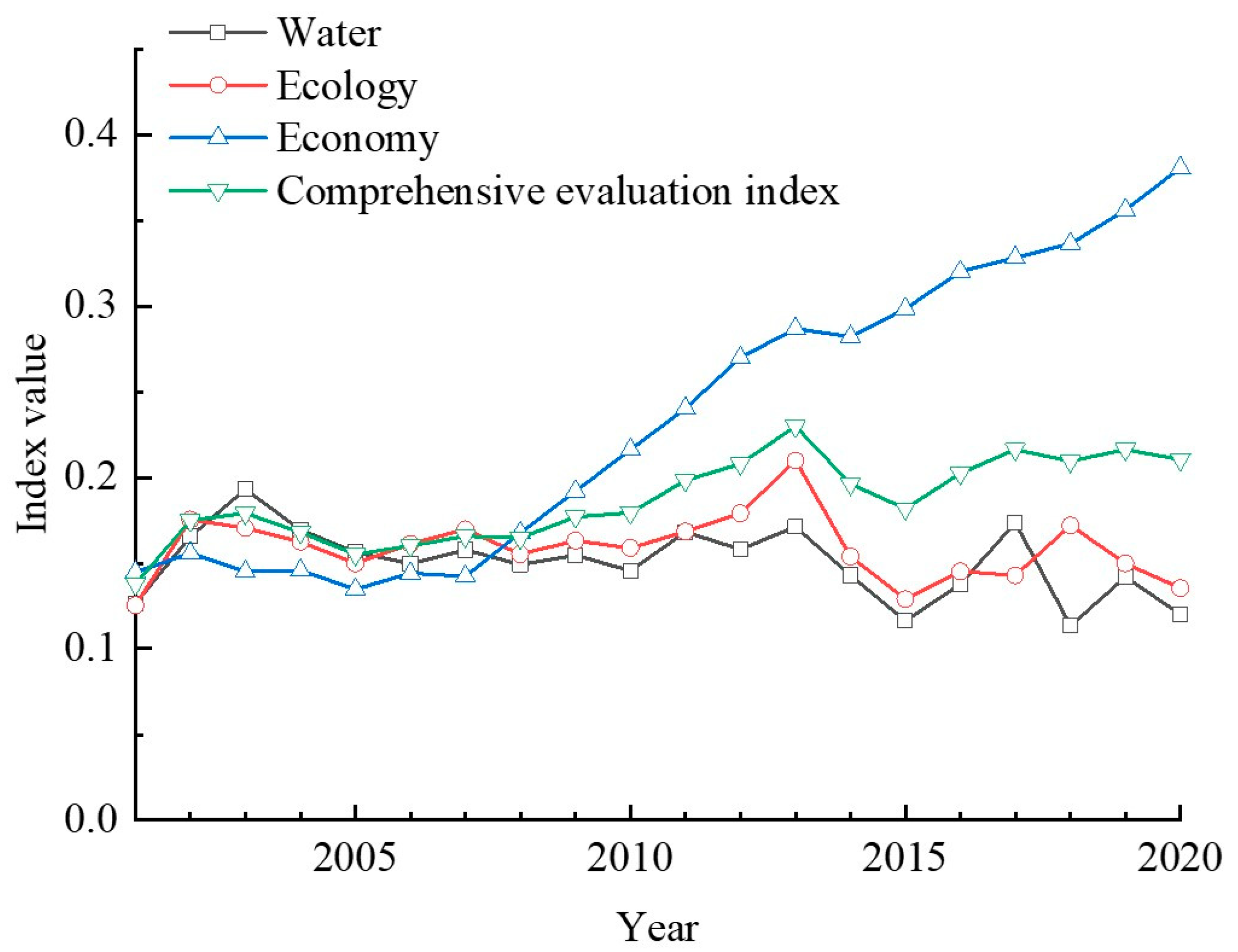
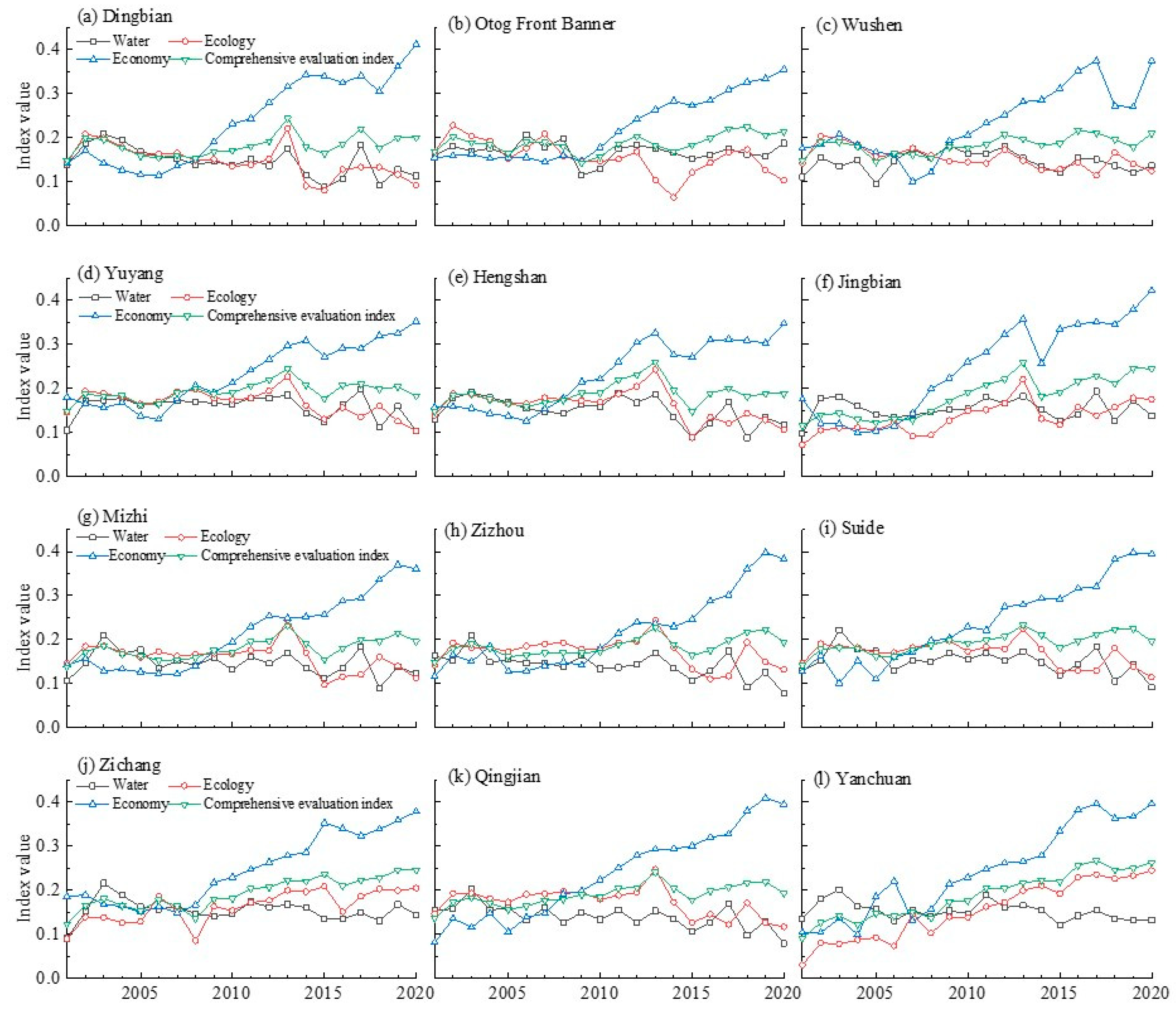
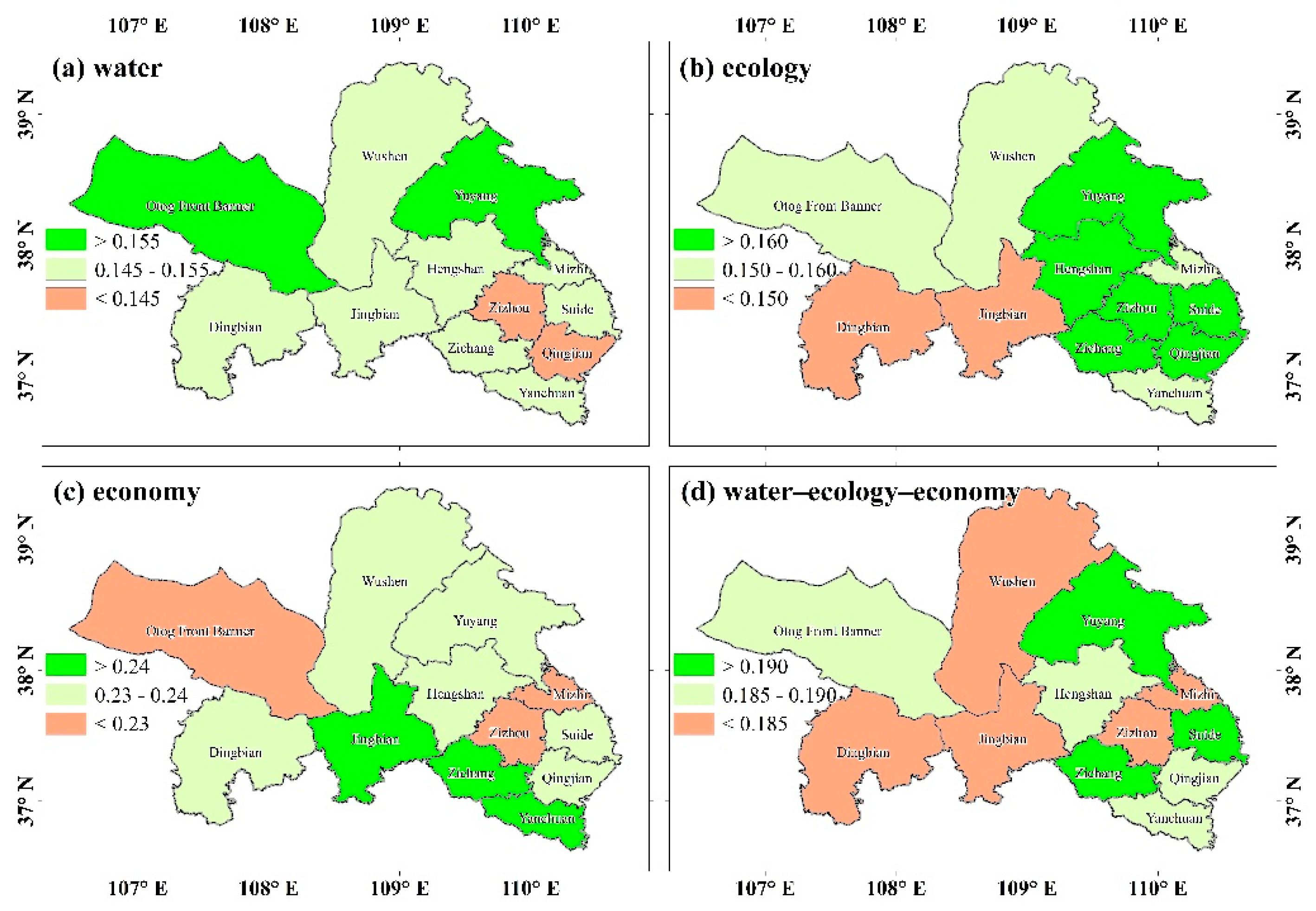
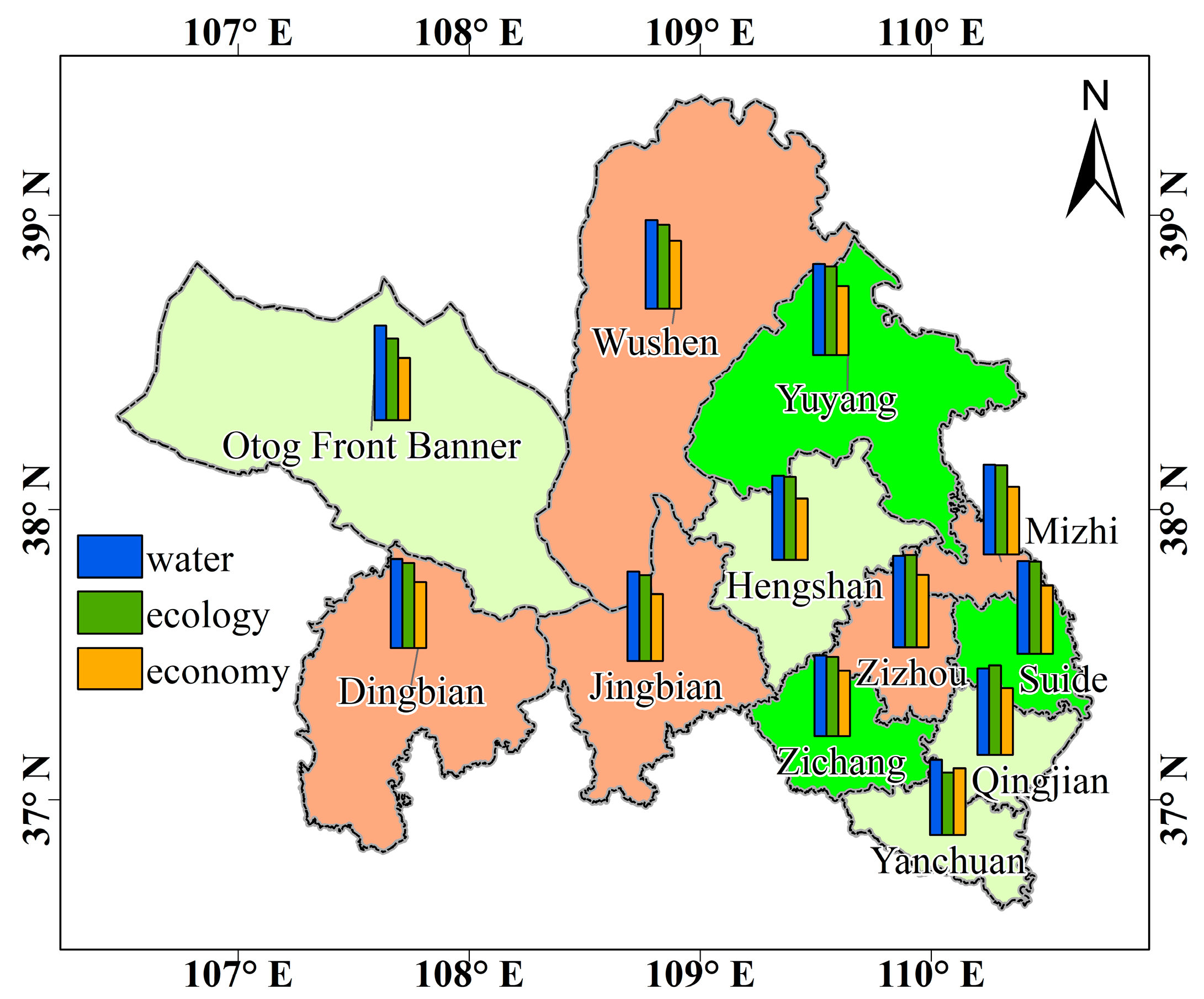
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of Evaluation Indices of Water Resource, Ecology and Economy Subsystems and Their Comprehensive Index
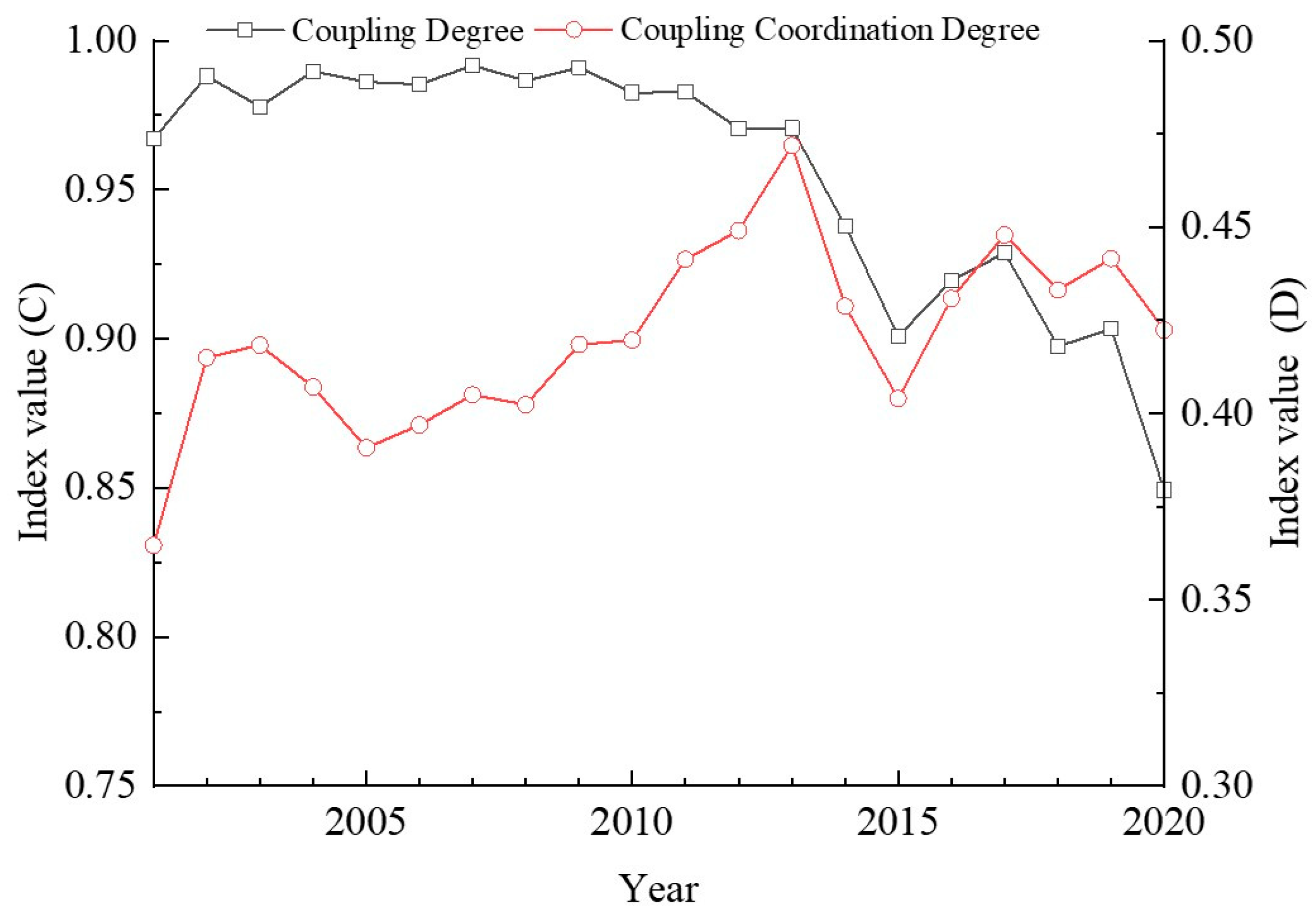
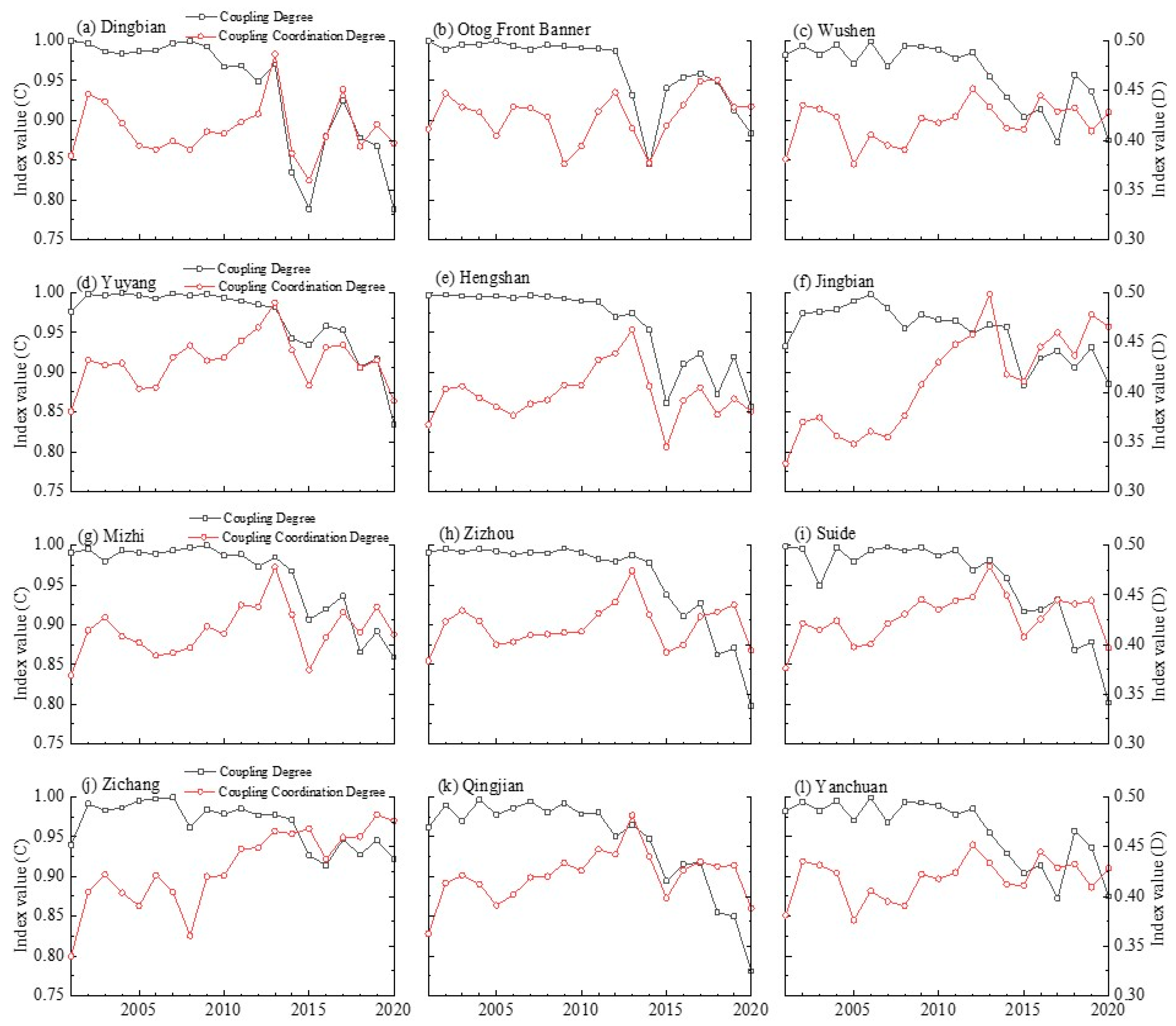
3.2. Spatio-Temporal Patterns of the Coupling Degree and Coupling Coordination Degree of the Water–Ecology–Economic System
3.3. Contributions of Water, Ecology, Economy Subsystems on Their Coupling Coordination Degree
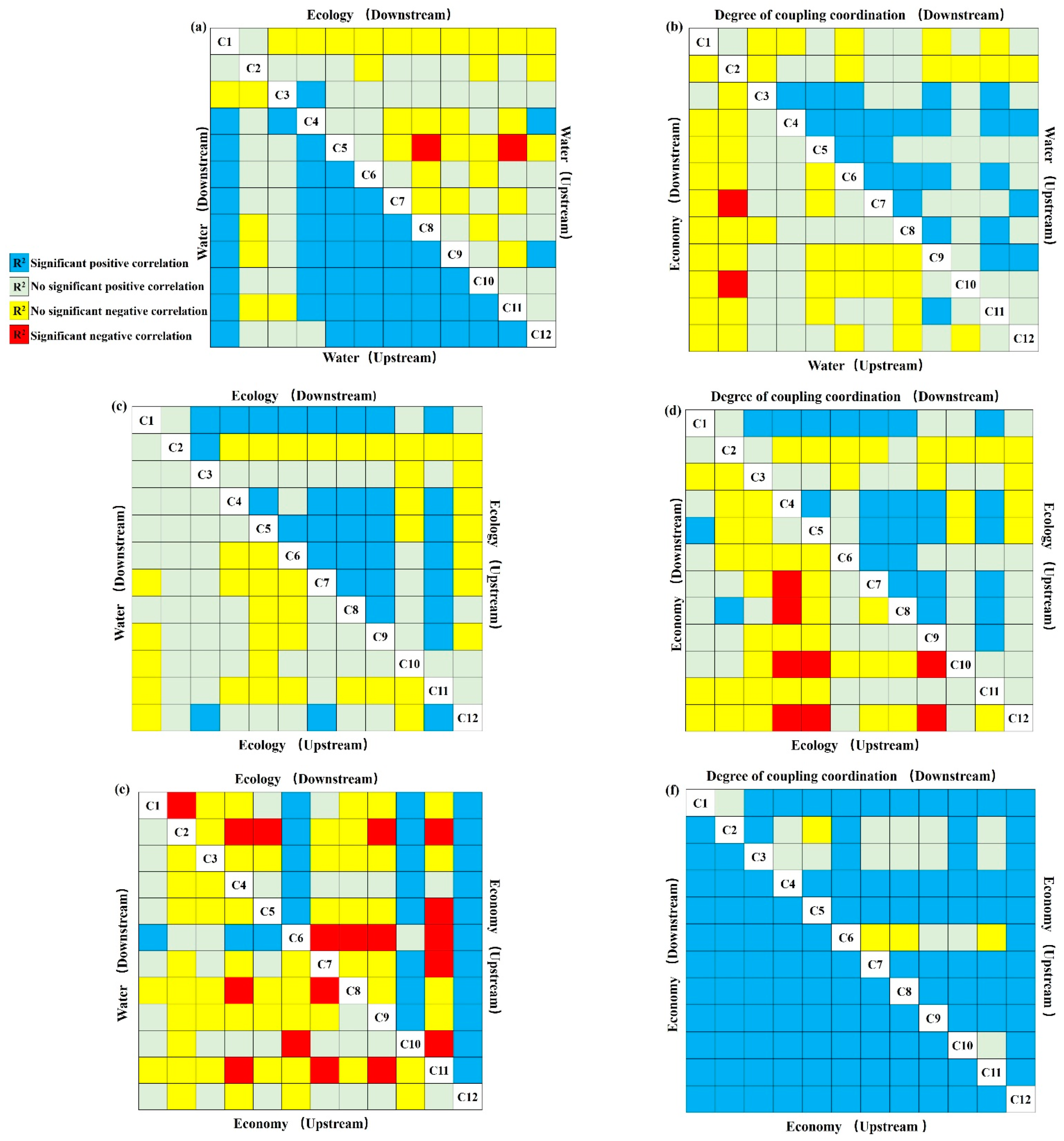
3.4. Cross-County Characteristic between Upstream and Downstream
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Shao, W.; Wang, H. The Relationship Between China’s Coal Resource Development and Water Resource. Energy Procedia 2015, 75, 2548–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Li, E.; Mu, X.; Wen, Z.; Rayburg, S.; Tian, P. Changing trends and regime shift of streamflow in the Yellow River basin. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 1331–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, R.I.; Weber, K.; Padowski, J.; Flörke, M.; Schneider, C.; Green, P.A.; Gleeson, T.; Eckman, S.; Lehner, B.; Balk, D.; et al. Water on an urban planet: Urbanization and the reach of urban water infrastructure. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2014, 27, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, R.I.; Weber, K.F.; Padowski, J.; Boucher, T.; Shemie, D. Estimating watershed degradation over the last century and its impact on water-treatment costs for the world’s large cities. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9117–9122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; Flörke, M.; Hanasaki, N.; Eisner, S.; Fischer, G.; Tramberend, S.; Satoh, Y.; van Vliet, M.T.H.; Yillia, P.; Ringler, C.; et al. Modeling global water use for the 21st century: The Water Futures and Solutions (WFaS) initiative and its approaches. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 175–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosling, S.N.; Arnell, N.W. A global assessment of the impact of climate change on water scarcity. Clim. Chang. 2016, 134, 371–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yang, H.; Gosling, S.N.; Kummu, M.; Flörke, M.; Pfister, S.; Hanasaki, N.; Wada, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, C.; et al. Water scarcity assessments in the past, present, and future. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, P.; Costa, L.; Rybski, D.; Lucht, W.; Kropp, J. A Systematic Study of Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) Interactions. Earth’s Future 2017, 5, 1169–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Best, J. Anthropogenic stresses on the world’s big rivers. Nat. Geosci. 2019, 12, 7–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veldkamp, T.; Wada, Y.; Aerts, J.; Döll, P.; Gosling, S.N.; Liu, J.; Masaki, Y.; Oki, T.; Ostberg, S.; Pokhrel, Y.; et al. Water scarcity hotspots travel downstream due to human interventions in the 20th and 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, K. Water Security: Research Challenges and Opportunities. Science 2012, 337, 914–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, T.; Sun, S.; Fu, G.; Hall, J.W.; Ni, Y.; He, L.; Yi, J.; Zhao, N.; Du, Y.; Pei, T.; et al. Pollution exacerbates China’s water scarcity and its regional inequality. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, W.E.; Unsworth, S.J. Do humans belong with nature? The influence of personal vs. abstract contexts on human–nature categorization at different stages of development. J. Environ. Psychol. 2013, 33, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.; Zuo, Q.; Shao, Q.; Ding, X. The impact of socioeconomic system on the river system in a heavily disturbed basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 660, 851–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, S.W.D.; Rice, J.S.; Nelson, K.D.; Vernon, C.R.; McManamay, R.; Dickson, K.; Marston, L. Comparison of potential drinking water source contamination across one hundred U.S. cities. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, M.G.; Frank, K.A.; Pokhrel, Y.; Dietz, T.; Liu, J. Natural infrastructure in sustaining global urban freshwater ecosystem services. Nat. Sustain. 2021, 4, 1068–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wickham, J.D.; Wade, T.G.; Riitters, K.H. An environmental assessment of United States drinking water watersheds. Landsc. Ecol. 2011, 26, 605–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Caldwell, P.V.; Dobbs, G.R.; Miniat, C.F.; Bolstad, P.V.; Nelson, S.A.C.; Sun, G. Forested lands dominate drinking water supply in the conterminous United States. Environ. Res. Lett. 2021, 16, 084008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, L.; Mackay, E.B.; Cardoso, A.C.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Birk, S.; Blackstock, K.L.; Borics, G.; Borja, A.; Feld, C.K.; Ferreira, M.T.; et al. Protecting and restoring Europe’s waters: An analysis of the future development needs of the Water Framework Directive. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 1228–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grizzetti, B.; Liquete, C.; Pistocchi, A.; Vigiak, O.; Zulian, G.; Bouraoui, F.; De Roo, A.; Cardoso, A.C. Relationship between ecological condition and ecosystem services in European rivers, lakes and coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 671, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, S.; Fang, J.; Ma, S.; Cai, Q.; Xiong, X.; Tian, D.; Zhao, X.; Fang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhu, J.; et al. Changes in China’s lakes: Climate and human impacts. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2019, 7, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Wei, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zou, S.; Ren, J.; Lyle, C. Trade-offs between midstream agricultural production and downstream ecological sustainability in the Heihe River basin in the past half century. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 152, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, S.; Fu, B.; Gao, G.; Shen, Q. Ecological effects and potential risks of the water diversion project in the Heihe River Basin. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 619–620, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, F.-L. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Xiao, S.; Xie, J.; Zou, S.; Yang, Q.; Si, J. The impacts of the ecological water diversion project on the ecology-hydrology-economy nexus in the lower reaches in an inland river basin. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 164, 105154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Syvitski, J.P.M.; Gao, S.; Overeem, I.; Kettner, A.J. Socio-economic Impacts on Flooding: A 4000-Year History of the Yellow River, China. AMBIO 2012, 41, 682–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhong, D.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H. Wide river or narrow river: Future river training strategy for Lower Yellow River under global change. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2018, 33, 271–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Song, C.; Wang, J.; Ke, L. China’s inland water dynamics: The significance of water body types. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 13876–13878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wei, Y.; Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Moran, E.F. Evolution and effects of the social-ecological system over a millennium in China’s Loess Plateau. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabc0276. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Gao, J.; Luo, H. Changes and implications of the relationship between rainfall, runoff and sediment load in the Wuding River basin on the Chinese Loess Plateau. CATENA 2019, 175, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-X.; Ji, S. Effect of erosion control measures on sediment delivery ratio. Adv. Water Sci. 2004, 15, 29. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, C.; Zhang, H.; Singh, V.P.; Yu, Y.; Shao, S. Investigating Hydrological Variability in the Wuding River Basin: Implications for Water Resources Management under the Water–Human-Coupled Environment. Water 2021, 13, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Wu, B.F.; Lue, Y.H.; Xu, Z.H.; Cao, J.H.; Niu, D.; Yang, G.S.; Zhou, Y.M. Three Gorges Project: Efforts and challenges for the environment. Prog. Phys. Geogr. Earth Environ. 2010, 34, 741–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Fan, Y.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yin, L. Earthquakes spatio–temporal distribution and fractal analysis in the Eurasian seismic belt. Rend. Lincei. Sci. Fis. E Naturali. 2020, 31, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, Z.; Yin, L.; Zheng, W. Statistical analysis of regional air temperature characteristics before and after dam construction. Urban Clim. 2022, 41, 101085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiongxin, X.U. Sediment Flux to the Sea as Influenced by Changing Human Activities and Precipitation: Example of the Yellow River, China. Environ. Manag. 2003, 31, 0328–0341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Zhang, L. Hydrological responses to conservation practices in a catchment of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 1885–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, L.; McVicar, T.R.; Chille, B.; Gau, P. Analysis of the impact of conservation measures on stream flow regime in catchments of the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 2124–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Shi, C.; Du, J.; Fan, X. Characteristics and causes of changes in annual runoff of the Wuding River in 1956–2009. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 69, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, W.; Bai, D.; Jin, Z.; You, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. A Study on the Streamflow Change and its Relationship with Climate Change and Ecological Restoration Measures in a Sediment Concentrated Region in the Loess Plateau, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2015, 29, 4045–4060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Ali, A.; Antonarakis, A.; Moghaddam, M.; Saatchi, S.; Tabatabaeenejad, A.; Chen, R.; Jaruwatanadilok, S.; Cuenca, R.; Crow, W.T.; et al. The Sensitivity of North American Terrestrial Carbon Fluxes to Spatial and Temporal Variation in Soil Moisture: An Analysis Using Radar-Derived Estimates of Root-Zone Soil Moisture. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2019, 124, 3208–3231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Knox, R.G.; Medvigy, D.M.; Levine, N.M.; Dietze, M.C.; Kim, Y.; Swann, A.L.S.; Zhang, K.; Rollinson, C.R.; Bras, R.L.; et al. The biophysics, ecology, and biogeochemistry of functionally diverse, vertically and horizontally heterogeneous ecosystems: The Ecosystem Demography model, version 2.2–Part 1: Model description. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 4309–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Mu, X.; Zhao, G.; Gao, P.; Sun, W. Effects of check dams on runoff and sediment load in a semi-arid river basin of the Yellow River. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2017, 31, 1791–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Li, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Huang, P. A hybrid runoff generation modelling framework based on spatial combination of three runoff generation schemes for semi-humid and semi-arid watersheds. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, M.F. Interpolating mean rainfall using thin plate smoothing splines. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Syst. 1995, 9, 385–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Save, H.; Bettadpur, S.; Tapley, B.D. High-resolution CSR GRACE RL05 mascons. J. Geophys. Res. Solid Earth 2016, 121, 7547–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Heinsch, F.A.; Nemani, R.R.; Running, S.W. Improvements of the MODIS terrestrial gross and net primary production global data set. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 95, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Park, T.; Yan, G.; Liu, Z.; Yang, B.; Chen, C.; Nemani, R.R.; Knyazikhin, Y.; Myneni, R.B. Evaluation of MODIS LAI/FPAR Product Collection 6. Part 1: Consistency and Improvements. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, C.; Wang, G.; Bao, S. An integrated sustainable development approach to modeling the eco-environmental effects from urbanization. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhu, X. Investigation of a coupling model of coordination between urbanization and the environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 98, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Gu, C.-L.; Gu, L.-W.; Zhang, Y. The evaluation of tourism destination competitiveness by TOPSIS & information entropy—A case in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Tour. Manag. 2011, 32, 443–451. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, N.; Liu, S. Research on evaluations of several grey relational models adapt to grey relational axioms. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2009, 20, 304–309. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, S.; Wu, Y.; Wong, S.W.; Shen, L. Provincial perspective analysis on the coordination between urbanization growth and resource environment carrying capacity (RECC) in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 730, 138964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Fang, C.; Zhang, Q. Coupling coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment in Chinese provincial capital cities-assessment and policy implications. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 229, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, R. Toward the Coordinated Sustainable Development of Urban Water Resource Use and Economic Growth: An Empirical Analysis of Tianjin City, China. Sustainability 2018, 10, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, C.; He, D. The Causal Relationship between Urbanization, Economic Growth and Water Use Change in Provincial China. Sustainability 2015, 7, 16076–16085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Baldassarre, G.; Sivapalan, M.; Rusca, M.; Cudennec, C.; Garcia, M.; Kreibich, H.; Konar, M.; Mondino, E.; Mård, J.; Pande, S.; et al. Sociohydrology: Scientific Challenges in Addressing the Sustainable Development Goals. Water Resour. Res. 2019, 55, 6327–6355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, M. Scale Independence and Spatial Uniformity of Specific Sediment Yield in Loess Areas of the Wuding River Basin, Northwest China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Mo, X.; Zhao, W.; Naeimi, V.; Dai, D.; Shu, C.; Mao, L. Temporal variation of soil moisture over the Wuding River basin assessed with an eco-hydrological model, in-situ observations and remote sensing. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1375–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Chiu, Y.-H.; Liu, F.-P. Measuring the Performance of Wastewater Treatment in China. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Mu, X.; Holden, J.; Wu, Y.; Irvine, B.; Wang, F.; Gao, P.; Zhao, G.; Sun, W. Comparison of soil erosion models used to study the Chinese Loess Plateau. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2017, 170, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Geng, Q.; Si, X.; Kan, L. Coupling and coordination analysis of urbanization, economy and environment of Shandong Province, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 10397–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Li, X.; Li, Q.; Wang, J. Temporal and Spatial Changes in Coupling and Coordinating Degree of New Urbanization and Ecological-Environmental Stress in China. Sustainability 2019, 11, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merz, L.; Yang, D.; Hull, V. A Metacoupling Framework for Exploring Transboundary Watershed Management. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenerette, G.D.; Larsen, L. A global perspective on changing sustainable urban water supplies. Glob. Planet. Chang. 2006, 50, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Jiang, X.; Shang, X.; Wei, C. Study on the Water Resource Carrying Capacity in the Middle Reaches of the Heihe River Based on Water Resource Allocation. Water 2018, 10, 1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, H. Capacity-Building for Ecological Modernization: Lessons From Cross-National Research. Am. Behav. Sci. 2002, 45, 1340–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, K. Integrated Water Resources Management: Global Theory, Emerging Practice, and Local Needs. Am. J. Agric. Econ. 2008, 90, 856–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Underdal, A. Complexity and challenges of long-term environmental governance. Globl Environ. Chang. Guildf. 2010, 20, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsang, S.; Burnett, M.; Hills, P.; Welford, R. Trust, public participation and environmental governance in Hong Kong. Environ. Policy Gov. 2009, 19, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckerberg, K.; Joas, M. Multi-level Environmental Governance: A concept under stress? Local Environ. 2004, 9, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopy, L.S.; Mullendore, N.; Brasier, K.; Floress, K. A Typology of Catalyst Events for Collaborative Watershed Management in the United States. Soc. Nat. Resour. 2014, 27, 1177–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Liu, W.; Chen, M. Study on the ecological compensation standard for river basin water environment based on total pollutants control. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 446–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, H.; Svensson, J. Joint analysis of water rights trading and water-saving management contracts in China. Int. J. Water Resour. Dev. 2020, 36, 716–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Target Layer | Guideline Layer | Index Layer | Unit | Data Sources | Property 1 | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water | Water resource situation | Annual total precipitation | mm | China Meteorological Data Network | + | 0.033 |
| Surface water storage | 108 m3 | Statistical yearbook NASA CSR GRACE data | + | 0.043 | ||
| Groundwater storage | cm | + | 0.065 | |||
| Water resource utilization | Water consumption per capita | m3 | Statistical yearbook | - | 0.051 | |
| Water consumption per million yuan | m3 | - | 0.030 | |||
| Domestic water | 108 m3 | - | 0.046 | |||
| Ecology | Ecosystem function | Net primary productivity | kgC m−2 year−1 | NASA MODIS data | + | 0.045 |
| Water conservation capacity | m3 m−2 year−1 | + | 0.033 | |||
| Vegetation leaf area | m2 m−2 | + | 0.045 | |||
| Pollutant emission | Wastewater emission | 104 t | Statistical yearbook | - | 0.039 | |
| Solid waste emission | 104 t | - | 0.051 | |||
| Waste gas emission | 108 t | - | 0.056 | |||
| Economy | Economic and social situation | Gross domestic product per capita | Yuan | Statistical yearbook | + | 0.098 |
| Fixed investment per capita | Yuan | + | 0.116 | |||
| Disposable income | Yuan | + | 0.079 | |||
| Industrial structure | Proportion of primary industry | % | Statistical yearbook | + | 0.117 | |
| Proportion of secondary industry | % | + | 0.055 | |||
| Proportion of tertiary industry | % | + | 0.069 |
| Type | Coupling Coordination Degree | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Coordinated development | 0.90–1.00 | High-quality coordinated development |
| 0.80–0.89 | Good coordinated development | |
| 0.70–0.79 | Intermediate coordinated development | |
| 0.60–0.69 | Primary coordinated development | |
| Excessive status | 0.50–0.59 | Barely coordinated development |
| 0.40–0.49 | On the verge of dysfunctional decline | |
| Dysfunctional decline | 0.30–0.39 | Mild dysfunctional decline |
| 0.20–0.29 | Moderate dysfunctional decline | |
| 0.10–0.19 | Severe dysfunctional decline | |
| 0–0.09 | Extremely dysfunctional decline |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tao, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, G. Cross-County Characteristics of Water–Ecology–Economy Coupling Coordination in the Wuding River Watershed, China. Land 2022, 11, 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11122283
Tao J, Xie Y, Zhou H, Xu Y, Zhao G. Cross-County Characteristics of Water–Ecology–Economy Coupling Coordination in the Wuding River Watershed, China. Land. 2022; 11(12):2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11122283
Chicago/Turabian StyleTao, Jian, Yujie Xie, Haoyuan Zhou, Yuqian Xu, and Guangshuai Zhao. 2022. "Cross-County Characteristics of Water–Ecology–Economy Coupling Coordination in the Wuding River Watershed, China" Land 11, no. 12: 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11122283
APA StyleTao, J., Xie, Y., Zhou, H., Xu, Y., & Zhao, G. (2022). Cross-County Characteristics of Water–Ecology–Economy Coupling Coordination in the Wuding River Watershed, China. Land, 11(12), 2283. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11122283










