Ecological Evaluation of Sponge City Landscape Design Based on Aquatic Plants Application
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Model Description
2.2. Aquatic Plants
2.3. Model Structure
3. Results
3.1. Optimal Landscape Design
3.2. Ecological Problems of Sponge City
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, H. Experimental investigation on the application of carbon dioxide adsorption for a shale reservoir. Energy Sci. Eng. 2021, 9, 2165–2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.P.; Ouyang, P.; Xing, S.M.; Qi, L.Y. Optimal structure design of a PV/FC HRES using amended Water Strider Algorithm. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 2057–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, S.; Ikeda, M.; Amano, M.; Sakayama, H.; Kadono, Y.; Kosuge, K. Erratum to: Loss of heterophylly in a quatic plants: Not aba-mediated stress but exogenous aba treatment induces stomatal leaves in potamogeton perfoliatus. J. Plant Res. 2017, 130, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feng, B.; Fang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xiang, C.; Zhao, H. Development of a new marker system for identification of spirodela polyrhiza and landoltia punctate. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Lambert, T.; Bouillon, S.; Darchambeau, F.; Morana, C.; Borges, A. Effects of human land use on the terrestrial and aquatic sources of fluvial organic matter in a temperate river basin (the Meuse River, Belgium). Biogeochemistry 2017, 136, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurbatova, S.; Mylnikova, Z.; Yershov, I.; Bykova, S.; Vinogradova, O. Influence of aquatic plants of different ecological groups on zooplankton distribution and abundance. Contemp. Probl. Ecol. 2018, 11, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, R.; Hill, J.; Coetzee, J.; Hill, M. The contributions of biological control to reduced plant size and biomass of water hyacinth populations. Hydrobiologia 2017, 807, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pickett, S.; Cadenasso, M. How many principles of urban ecology are there? Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.; Gao, H. A scheme for a sustainable urban water environmental system during the urbanization process in China. Engineering 2018, 4, 190–193. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Ma, J.; Li, W. An optimal configuration for hybrid SOFC, gas turbine, and Proton Exchange Membrane Electrolyzer using a developed Aquila Optimizer. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 8943–8955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Men, H.; Lu, H.; Jiang, W.; Xu, D. Mathematical optimization methods of low-impact development layout in the sponge city. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 20, 6734081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Deng, Y. Layout optimization of sponge facilities based on suitability evaluation of sponge city. In Innovative Computing; Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering; Yang, C.T., Pei, Y., Chang, J.W., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; Volume 675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawken, S.; Sepasgozar, S.M.E.; Prodanovic, V.; Jing, J.; Bakelmun, A.; Avazpour, B.; Che, S.; Zhang, K. What makes a successful Sponge City project? Expert perceptions of critical factors in integrated urban water management in the Asia-Pacific. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 75, 103317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Khayatnezhad, M. Evaluating the storm water management model to improve urban water allocation system in drought conditions. Water Supply 2021, 21, 1514–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, L.; Wei, M.; You, X.Y. Multi-objective layout optimization for sponge city by annealing algorithm and its environmental benefits analysis. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.J.; Xiao, M.; Li, Y.; Yan, R.; Zhang, Q.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, T. The optimization of low impact development placement considering life cycle cost using genetic algorithm. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 309, 114700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Qin, C.; Du, P. Optimization of China sponge city design: The case of Lincang technology innovation park. Water 2018, 10, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, J.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Xia, J.; Lv, P. A distribution optimization method of typical LID facilities for sponge city construction. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2021, 21, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, X.; Xiao, Y.; Chen, L.; Hou, X.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Fu, Y.; Chen, B.; Shen, Z. Integrating cost-effectiveness optimization and robustness analysis for low impact development practices design. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2022, 185, 106491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Xu, L.; Qi, Q.; Yang, H.; Zhou, Y. Building a multi-objective optimization model for Sponge City projects. Urban Clim. 2022, 43, 101171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauze, T.; Zieliński, J. Intrapersonal and interpersonal differences in results of quantitative winter studies on selected species of corvids in urban green areas. Russ. J. Ecol. 2019, 50, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Qi, L. Phylogenetic relatedness, ecological strategy, and stress determine interspecific interactions within a salt marsh community. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 79, 587–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deb, K.; Pratap, A.; Agarwal, S.; Meyarivan, T. A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 2002, 6, 181–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirjalili, S.; Lewis, A. The whale optimization algorithm. Adv. Eng. Softw. 2016, 95, 51–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Optimal model evaluation of the proton-exchange membrane fuel cells based on deep learning and modified African vulture optimization algorithm. Energy Sources A: Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 287–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwijendra, N.K.A.; Sharma, S.; Asary, A.R.; Majdi, A.; Muda, I.; Mutlak, D.A.; Hammid, A.T. Economic performance of a hybrid renewable energy system with optimal design of resources. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2022, 26, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Peng, K.; Zeng, J.; Marzouki, R.; Majdi, A.; Jan, A.; Assilzadeh, H. Effects of mining activities on nano-soil management using artificial intelligence models of ANN and ELM. Adv. Nano Res. 2022, 12, 549–566. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, R.; Li, S.; Wu, M.; Ren, G.; Gao, W. Assessing of impact climate parameters on the gap between hydropower supply and electricity demand by RCPs scenarios and optimized ANN by the improved Pathfinder (IPF) algorithm. Energy 2021, 237, 121621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shang, Y. Fuzzy stress-based modeling for probabilistic irrigation planning using Copula-NSPSO. Water Resour. Manag. 2021, 35, 4943–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.N.; She, C.; Kong, D.B.; Yan, S.L.; Xu, Y.P. Prediction of the effects of climate change on hydroelectric generation, electricity demand, and emissions of greenhouse gases under climatic scenarios and optimized ANN model. Energy Rep. 2021, 7, 5431–5445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Mu, X.; Zhao, X.; Xu, J. Developing the non-dimensional framework for water distribution formulation to evaluate sprinkler irrigation. Irri. Drain. 2021, 70, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Cui, Z.; Yu, J. Finite difference modeling of groundwater flow for constructing artificial recharge structures. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2022, 46, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Khayatnezhad, M.; Davarpanah, A. Statistical analysis of treated flow-back water measurements: An Industrial Insight for a Shale Reservoir. Geofluids 2022, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalehzari, R.; Boroomand-Nasab, S.; Moazed, H.; Haghighi, A. Multi-objective management of water allocation to sustainable irrigation planning and optimal cropping pattern. J. Irri. Drain. Eng. 2016, 142, 05015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.Y.; Chen, B.; Pan, D.; Lv, Z.A. Optimal wind energy generation considering climatic variables by Deep Belief network (DBN) model based on modified coot optimization algorithm (MCOA). Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 2022, 53, 102744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Saadati, H. Application of probability decision system and particle swarm optimization for improving soil moisture content. Water Supply 2021, 21, 4145–4152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasim, S.A.; Yasin, G.; Cartono, C.; Sevbitov, A.; Shichiyakh, R.A.; Al-Husseini, Y.; Iswanto, A. Survey of ground beetles inhabiting agricultural crops in south-east Kazakhstan. Braz. J. Biol. 2022, 84, e260092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, D.; Wang, J. Estimation of actual evapotranspiration using soil moisture balance and remote sensing. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 2021, 45, 2779–2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Khayatnezhad, M. Fuzzy-probabilistic modeling the flood characteristics using bivariate frequency analysis and α-cut decomposition. Water Supply. 2021, 21, 4391–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaraman, R.; Bharath Kumar, N.; Majdi, A.; Emad Izzat, S.; Muda, I.; Molana, A. A cascade energy cycle based on solid oxide fuel cell with electric energy storage option. Energy Sources A Recovery Util. Environ. Eff. 2022, 44, 8591–8610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Knox, R.G.; Medvigy, D.M.; Levine, N.M.; Dietze, M.C.; Kim, Y.; Moorcroft, P.R. The biophysics, ecology, and biogeochemistry of functionally diverse, vertically and horizontally heterogeneous ecosystems: The Ecosystem Demography model, version 2.2—Part 1: Model description. Geosci. Model Dev. 2019, 12, 4309–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Khayatnezhad, M.; Yousefi, N. Using an optimized soil and water assessment tool by deep belief networks to evaluate the impact of land use and climate change on water resources. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawee, W.H.; Abdullah, A.S.; Mohammed, S.A.; Majdi, A.; Omara, Z.M.; Younes, M.M. Testing a single slope solar still with copper heating coil, external condenser, and phase change material. J. Energy Storage 2022, 56, 106030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunawan, W.; Rudiansyah, M.; Sultan, M.Q.; Ansari, M.J.; Izzat, S.E.; Al Jaber, M.S.; Aravindhan, S. Effect of tomato consumption on inflammatory markers in health and disease status: A systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN. 2022. [CrossRef]

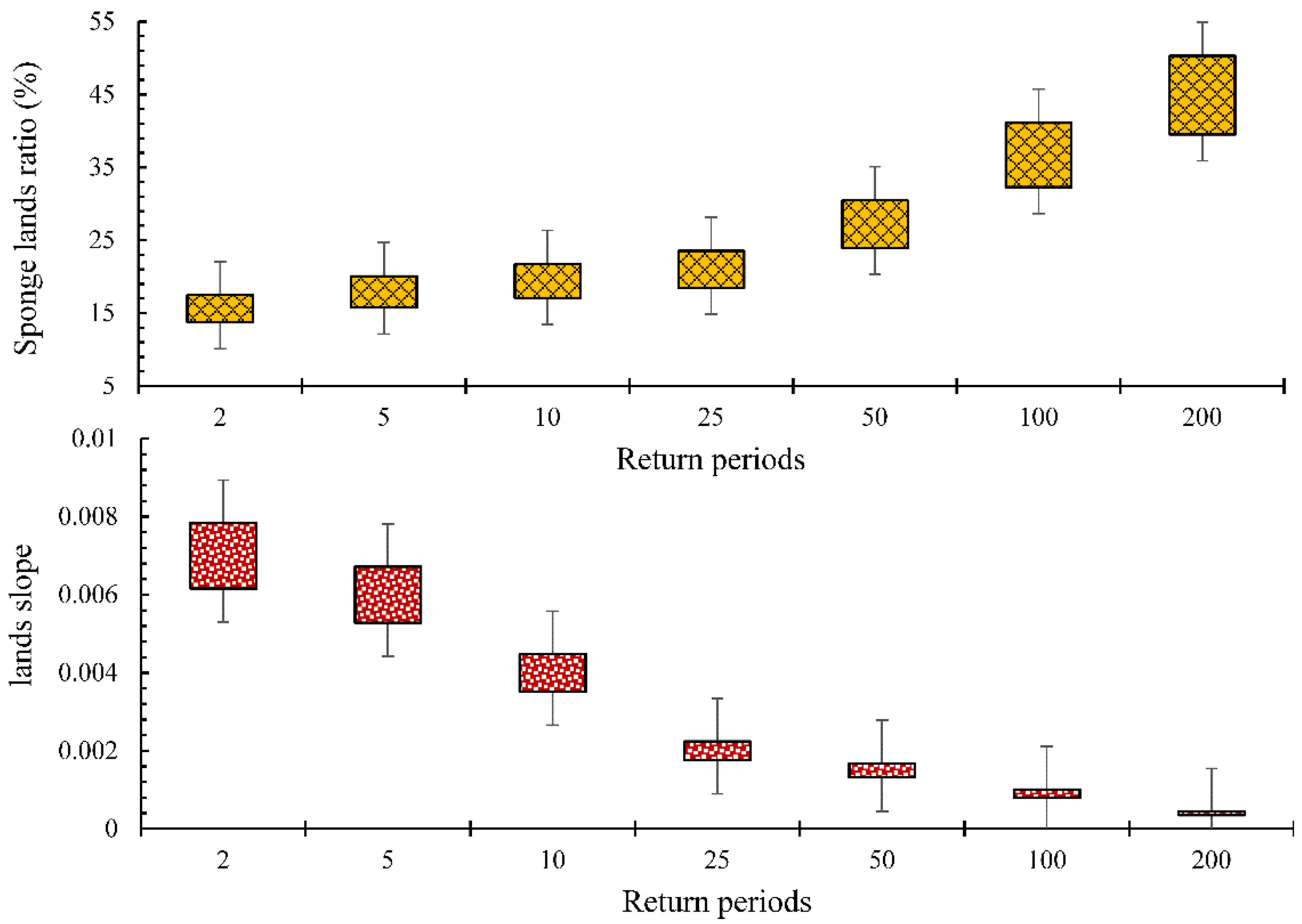
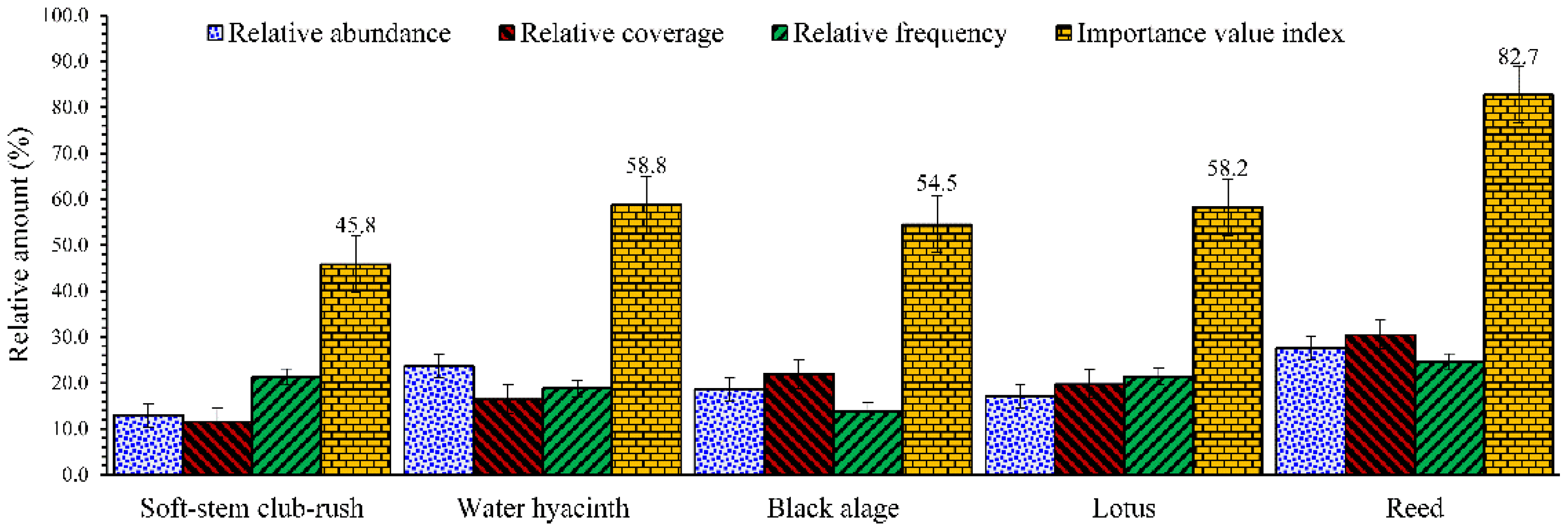

| Species | Return Period | Runoff | Urban Water Logging | Groundwater Storage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reed | 10 | 18 | 37 | 8 |
| 50 | 34 | 63 | 13 | |
| 100 | 58 | 94 | 19 | |
| Lotus | 10 | 14 | 31 | 6 |
| 50 | 26 | 56 | 9 | |
| 100 | 48 | 78 | 14 | |
| Black algae | 10 | 13 | 26 | 5 |
| 50 | 24 | 47 | 8 | |
| 100 | 49 | 69 | 13 | |
| Water hyacinth | 10 | 10 | 19 | 3 |
| 50 | 18 | 39 | 8 | |
| 100 | 32 | 58 | 12 | |
| Soft-stem club-rush | 10 | 7 | 14 | 1 |
| 50 | 21 | 23 | 4 | |
| 100 | 43 | 40 | 10 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, D.; Hua, R.; Shao, J. Ecological Evaluation of Sponge City Landscape Design Based on Aquatic Plants Application. Land 2022, 11, 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112081
Jiang D, Hua R, Shao J. Ecological Evaluation of Sponge City Landscape Design Based on Aquatic Plants Application. Land. 2022; 11(11):2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112081
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Dan, Rui Hua, and Jian Shao. 2022. "Ecological Evaluation of Sponge City Landscape Design Based on Aquatic Plants Application" Land 11, no. 11: 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112081
APA StyleJiang, D., Hua, R., & Shao, J. (2022). Ecological Evaluation of Sponge City Landscape Design Based on Aquatic Plants Application. Land, 11(11), 2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11112081









