Exploring Development Trends of Terrestrial Ecosystem Health—A Case Study from China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
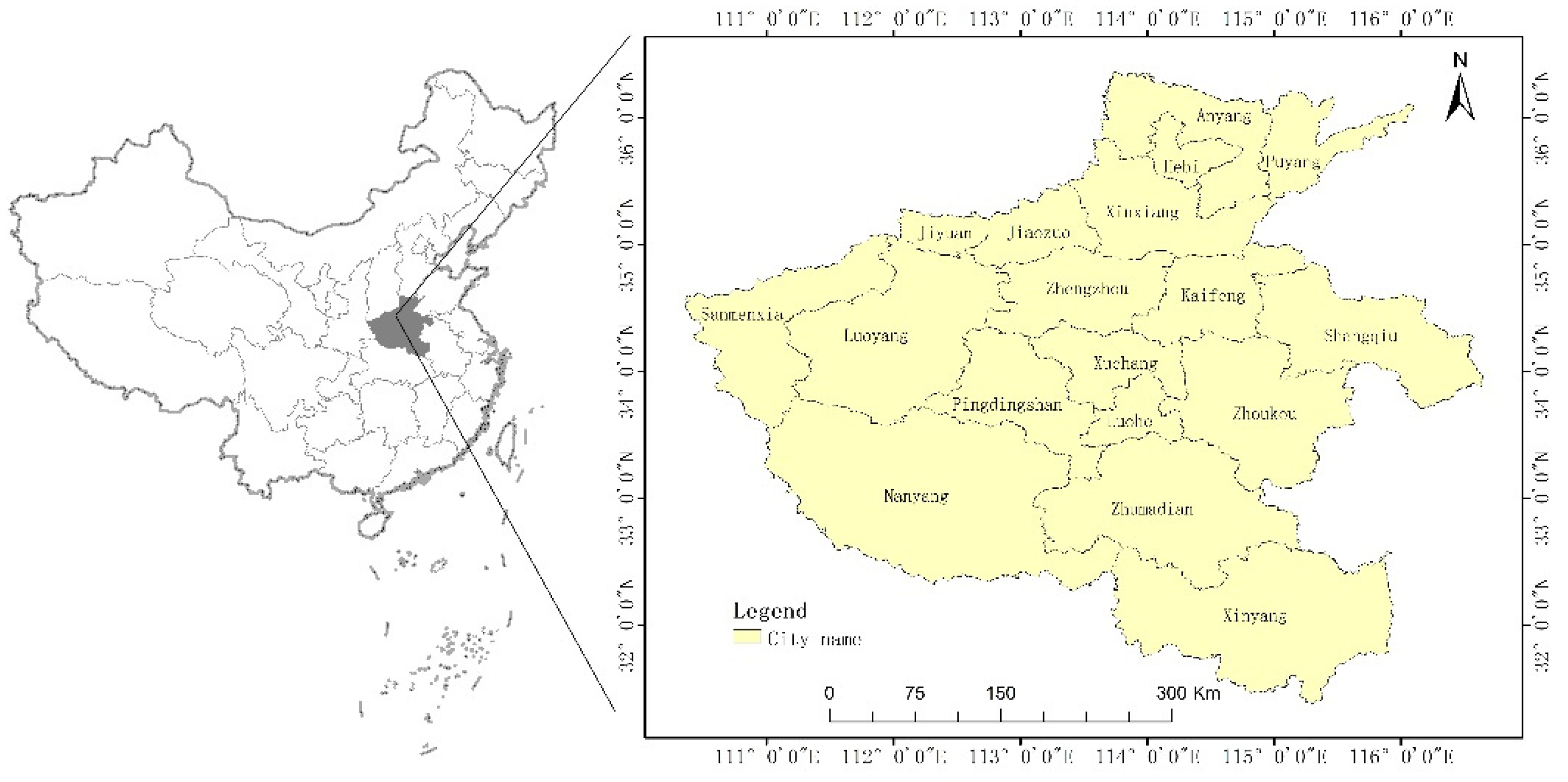
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Resources
2.3. Index System Construction
2.4. Early Warning Methods
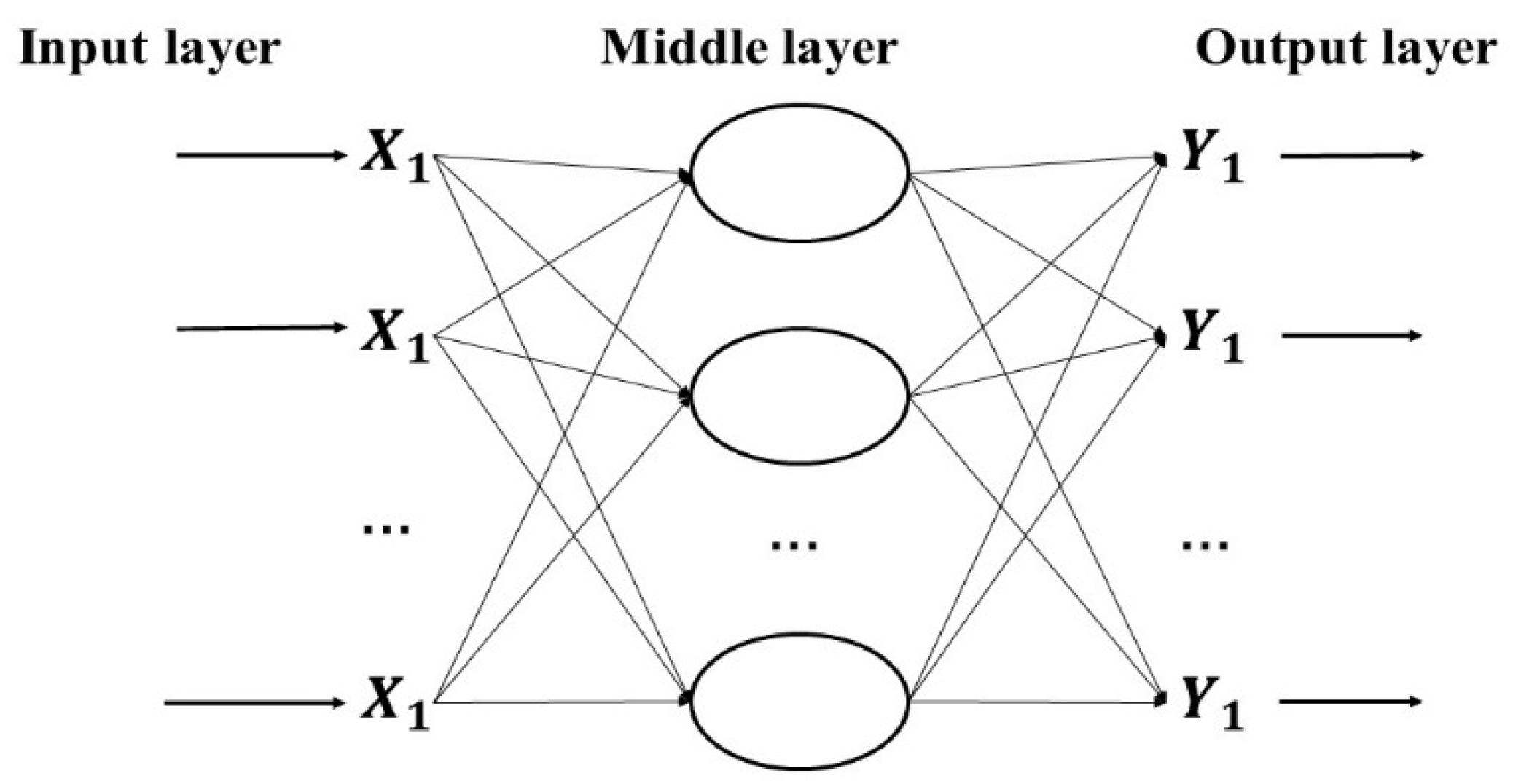
2.4.1. RBF Neural Network Model
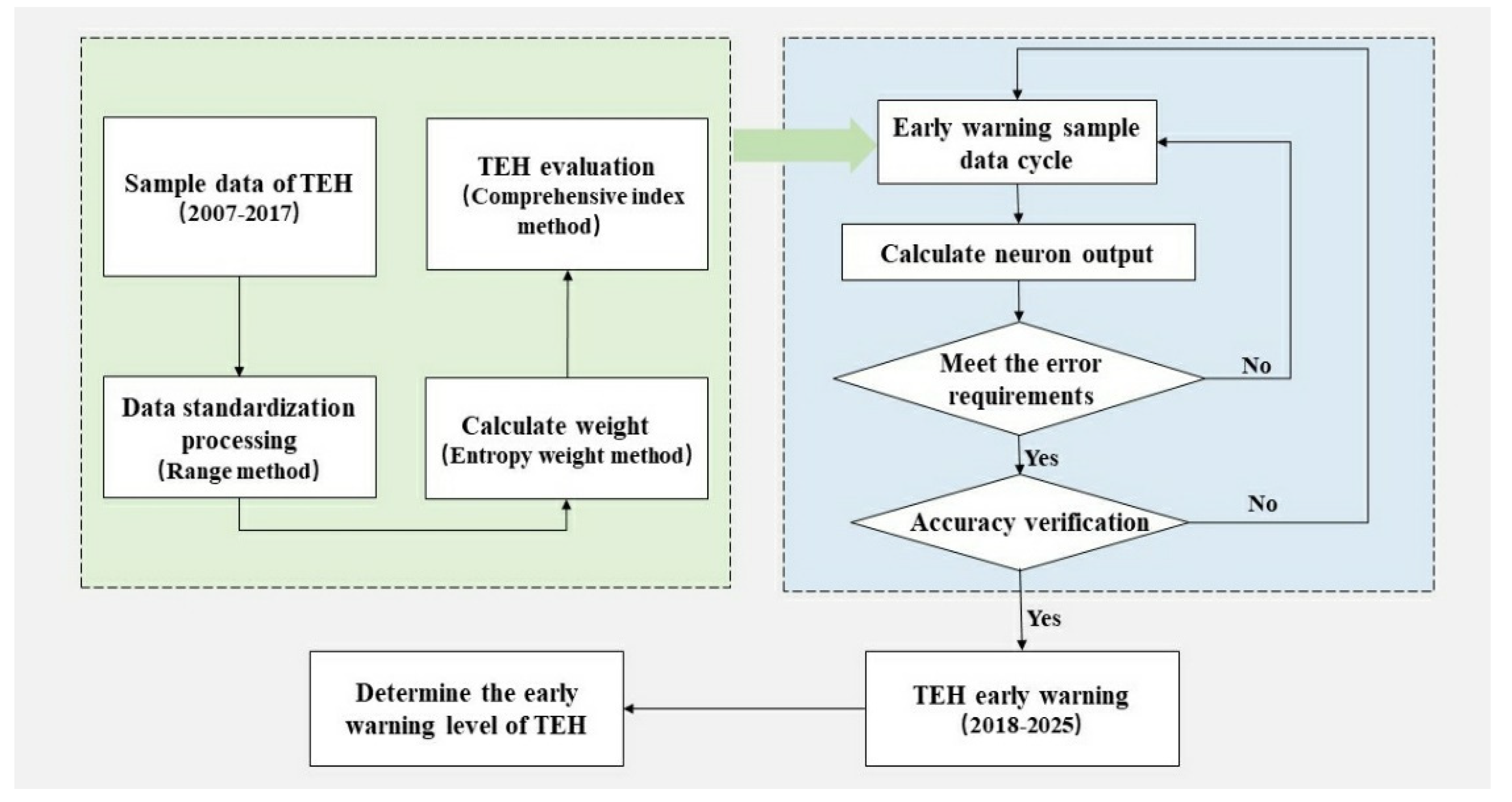
2.4.2. The Early Warning Process
2.4.3. Determining the Early-Warning Levels
3. Results
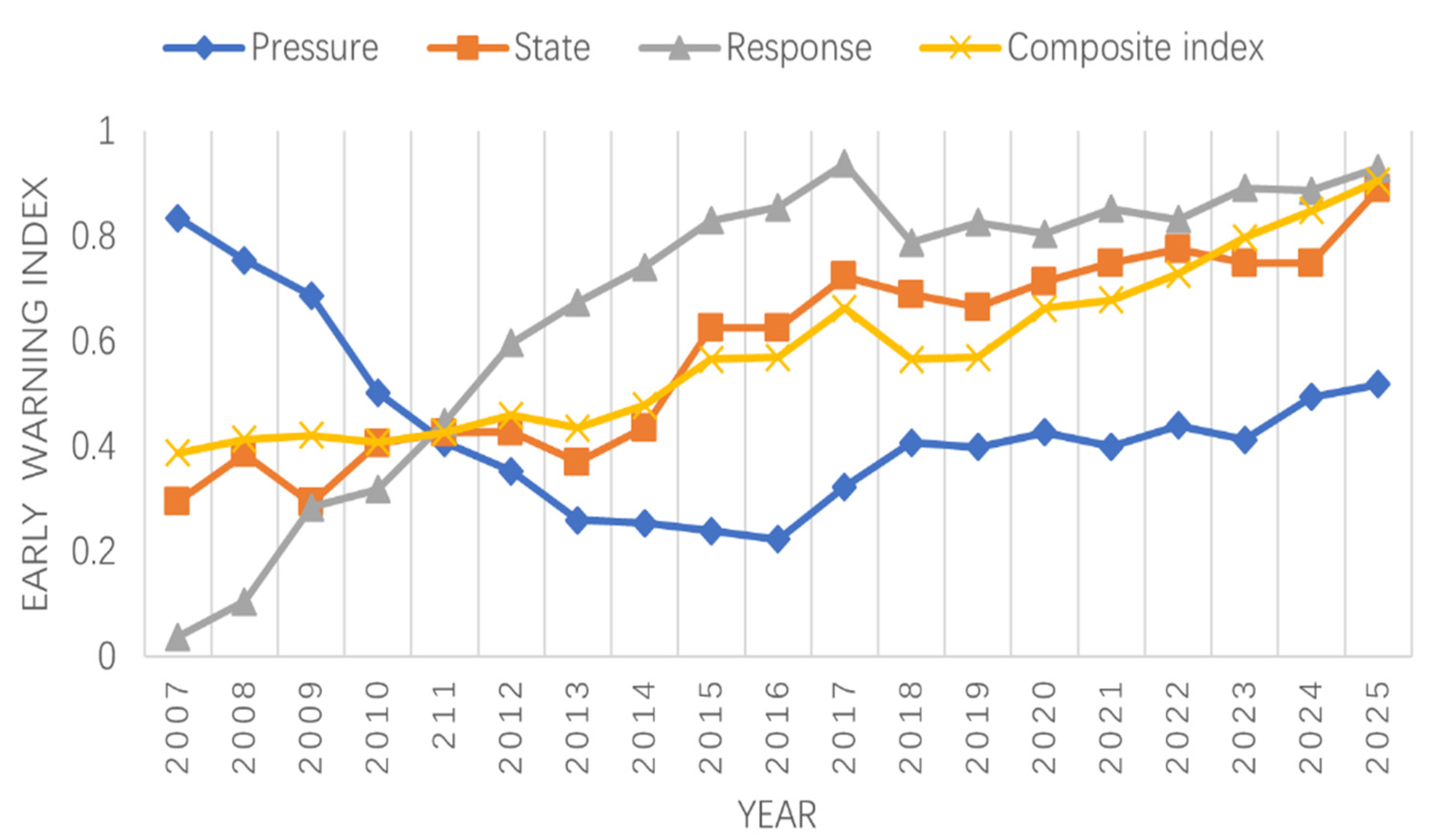
3.1. Evaluation of the Early Warnings of the TEH
3.2. Evaluation of the Early-Warning Index of the Pressure System
3.3. Evaluation of the Early-Warning Index of State System
3.4. Evaluation of the Early-Warning Index of the Response System
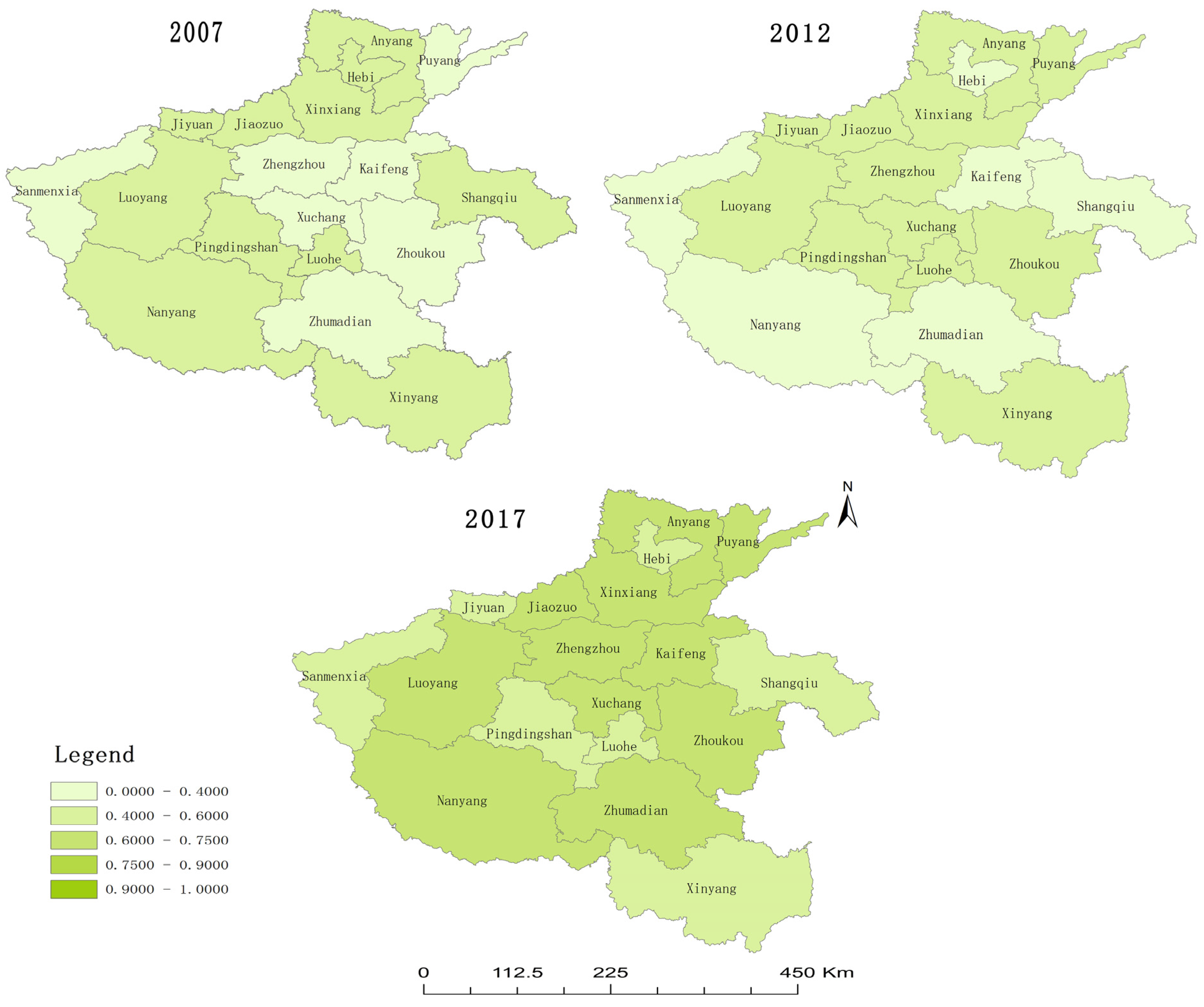
3.5. Spatial Distribution Pattern of TEH Warning Information in Henan Province
4. Discussion
4.1. Analysis of the TEH in Henan Province
4.2. Analysis of Factors Affecting TEH
4.3. Suggestions
4.4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Standardization of Indicator Data
Appendix A.2. Determination of Index Weight
Appendix A.3. Calculating Early-Warning Index
Appendix A.4. Learning Process of the RBF Neural Network
- (1)
- Using the range method to transfer the variables to the range that the network can handle;
- (2)
- Calculate the output value of the hidden layer: ;
- (3)
- Calculate the output value of the -th index of the output layer;
- (4)
- Calculate the error of the output layer:where represents the actual value of the -th neuron
- (5)
- Adjust the weight coefficient to make the error of neural network meet the requirements:where represents the adjusted weight, is the learning efficiency of neural net.
Appendix A.5. Precision Check of Forecast Model
Appendix B
| City | Pressure Index | State Index | Response Index | Composite Index | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2007 | 2012 | 2017 | 2007 | 2012 | 2017 | 2007 | 2012 | 2017 | 2007 | 2012 | 2017 | |
| Zhengzhou | 0.6609 | 0.356 | 0.3562 | 0.4475 | 0.4488 | 0.6177 | 0.0199 | 0.4294 | 0.9693 | 0.3742 | 0.4115 | 0.6494 |
| Kaifeng | 0.6601 | 0.3466 | 0.3414 | 0.2254 | 0.4693 | 0.7753 | 0.172 | 0.3368 | 0.8483 | 0.3519 | 0.3841 | 0.6557 |
| Luoyang | 0.8077 | 0.3254 | 0.2414 | 0.4306 | 0.5517 | 0.6653 | 0.143 | 0.5992 | 0.972 | 0.4715 | 0.4866 | 0.6139 |
| Pingdingshan | 0.858 | 0.3163 | 0.2025 | 0.376 | 0.5761 | 0.6911 | 0.2447 | 0.5354 | 0.8396 | 0.4913 | 0.4763 | 0.5794 |
| Anyang | 0.8199 | 0.4524 | 0.2714 | 0.3312 | 0.5327 | 0.6859 | 0.1295 | 0.6609 | 0.8656 | 0.4257 | 0.5491 | 0.6087 |
| Hebi | 0.7638 | 0.3026 | 0.1488 | 0.4452 | 0.3887 | 0.6477 | 0.1241 | 0.4137 | 0.9324 | 0.4426 | 0.3686 | 0.5783 |
| Xinxiang | 0.8414 | 0.2729 | 0.2545 | 0.3295 | 0.431 | 0.6782 | 0.1662 | 0.5967 | 0.9744 | 0.4452 | 0.4338 | 0.6364 |
| Jiaozuo | 0.6972 | 0.4123 | 0.3656 | 0.3751 | 0.4574 | 0.6253 | 0.1763 | 0.5174 | 0.8656 | 0.4149 | 0.4627 | 0.6201 |
| Puyang | 0.7425 | 0.3118 | 0.2328 | 0.3257 | 0.418 | 0.807 | 0.0698 | 0.6712 | 0.9008 | 0.3782 | 0.4677 | 0.6478 |
| Xuchang | 0.6889 | 0.4133 | 0.4368 | 0.3516 | 0.4742 | 0.696 | 0.0717 | 0.6918 | 0.9236 | 0.3699 | 0.5269 | 0.6862 |
| Luohe | 0.7589 | 0.3624 | 0.2385 | 0.3748 | 0.5059 | 0.615 | 0.2051 | 0.5947 | 0.9266 | 0.4454 | 0.4881 | 0.5947 |
| Sanmenxia | 0.6747 | 0.2269 | 0.341 | 0.229 | 0.4878 | 0.734 | 0.1966 | 0.4305 | 0.6492 | 0.3659 | 0.382 | 0.5752 |
| Nanyang | 0.6685 | 0.2417 | 0.3143 | 0.3711 | 0.3562 | 0.832 | 0.2333 | 0.3074 | 0.851 | 0.4232 | 0.3018 | 0.6668 |
| Shangqiu | 0.8121 | 0.3607 | 0.1845 | 0.2949 | 0.4801 | 0.6655 | 0.1994 | 0.3049 | 0.8646 | 0.4341 | 0.3815 | 0.5732 |
| Xinyang | 0.8456 | 0.2618 | 0.0917 | 0.3304 | 0.5153 | 0.6647 | 0.2464 | 0.5048 | 0.9588 | 0.4732 | 0.4276 | 0.5732 |
| Zhoukou | 0.7294 | 0.4294 | 0.2298 | 0.3349 | 0.5588 | 0.6368 | 0.1105 | 0.5385 | 0.9286 | 0.3901 | 0.5091 | 0.6001 |
| Zhumadian | 0.7065 | 0.3685 | 0.1393 | 0.2642 | 0.3537 | 0.8236 | 0.1491 | 0.4175 | 0.9027 | 0.3719 | 0.3801 | 0.6236 |
| Jiyuan | 0.6514 | 0.4828 | 0.2579 | 0.5513 | 0.3144 | 0.6503 | 0.0146 | 0.642 | 0.8763 | 0.4046 | 0.4802 | 0.5957 |
References
- Mukul, S.A.; Sohel, M.S.I.; Herbohn, J.; Inostroza, L.; König, H. Integrating Ecosystem Services Supply Potential from Future Land-Use Scenarios in Protected Area Management: A Bangladesh Case Study. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Wang, J.; Jia, M.; Zhang, B.; Xu, S. Evaluation of China’s Land Use System Health Based on System Dynamics. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2020, 29, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, S.; Shi, P.; Yang, W.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Yang, S. Health Evaluation and Obstacle Factor Diagnosis of Land Use System Based on PSR Model: A case study of Yanchang County. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 26, 283–289. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, F.; Yan, M.; Liu, Y.; Xiao, M.; Qin, W. Spatial pattern of land use intensity in China in 2000. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2016, 71, 1130–1143. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, R. Analysis of agricultural non-point sources pollution-taking Henan Province as an example. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2016, 37, 67–71. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Yang, D.; Sun, J.; Tang, H.; Wang, P.; Lu, S. Analysis on agricultural non-point source pollution loadings and its characteristics in China. Water Resour. Prot. 2021, 32, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, Y.; Tian, J.; Chen, J. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Core Region Grain Production Capacity in Henan Province. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2018, 46, 193–197. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S. Study on ecological reconstruction of grain core production area in Henan Province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2017, 38, 171–176. [Google Scholar]
- Sanaullah, M.; Usman, M.; Wakeel, A.; Cheema, S.A.; Ashraf, I.; Farooq, M. Terrestrial Ecosystem Functioning Affected by Agricultural Management Systems: A Review. Soil Tillage Res. 2020, 196, 104464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, T.; Wang, J.; Fang, Y.; Qin, Y.; Huang, L.; Chen, Y. Assessing Ecological Risks Caused by Human Activities in Rapid Urbanization Coastal Areas: Towards an Integrated Approach to Determining Key Areas of Terrestrial-Oceanic Ecosystems Preservation and Restoration. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 135153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shou-guang, Y.; Hui, L.; Hai-dong, L.; Yin-long, Z. Ecosystem health assessment method of eco-redline based on land use and landscape pattern in Nanjing. J. Nat. Resour. 2020, 35, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Cao, J.; Zhao, Y.; Han, L.; Liu, Z. Health evaluation of land ecosystem in Shaanxi Province, Northwest China based on PSR Model. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2021, 11, 1563–1572. [Google Scholar]
- Frontalini, F.; Coccioni, R. Benthic Foraminifera as Bioindicators of Pollution: A Review of Italian Research over the Last Three Decades. Revue de Micropaléontologie 2011, 54, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Microbial Indicators as a Diagnostic Tool for Assessing Water Quality and Climate Stress in Coral Reef Ecosystems. SpringerLink. Available online: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00227-017-3097-x (accessed on 18 September 2021).
- Cape, J.N. Surface Ozone Concentrations and Ecosystem Health: Past Trends and a Guide to Future Projections. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 400, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- An, K.-G.; Choi, J.-W.; Lee, Y.-J. Modifications of Ecological Trophic Structures on Chemical Gradients in Lotic Ecosystems and Their Relations to Stream Ecosystem Health. Anim. Cells Syst. 2013, 17, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Moura, E.G.; Gehring, C.; Braun, H.; Ferraz Junior, A.D.S.L.; Reis, F.D.O.; Aguiar, A.D.C.F. Improving Farming Practices for Sustainable Soil Use in the Humid Tropics and Rainforest Ecosystem Health. Sustainability 2016, 8, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kesgin Atak, B.; Ersoy Tonyaloğlu, E. Monitoring the Spatiotemporal Changes in Regional Ecosystem Health: A Case Study in Izmir, Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2020, 192, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nolan, C.; Overpeck, J.T.; Allen, J.R.M.; Anderson, P.M.; Betancourt, J.L.; Binney, H.A.; Brewer, S.; Bush, M.B.; Chase, B.M.; Cheddadi, R.; et al. Past and Future Global Transformation of Terrestrial Ecosystems under Climate Change. Science 2018, 361, 920–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Tang, L.; Qiu, Q.; Chen, H.; Wu, T.; Shao, G. Assessment of Regional Ecosystem Health-A Case Study of the Golden Triangle of Southern Fujian Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, R.; Yao, P.; Wang, W.; Yue, B.; Liu, G. Assessment of Wetland Ecosystem Health in the Yangtze and Amazon River Basins. ISPRS Int. J. Geo-Inf. 2017, 6, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Sun, R.; Kong, P. Land Use Changes and Socio-Economic Development Strongly Deteriorate River Ecosystem Health in One of the Largest Basins in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Qie, R.; Wang, D.; Liu, H. Health diagnosis on land use system based on grey correlation model: A case study of Jilin Province. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2016, 36, 9–17. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Feng, Z.; Liu, G.; Shi, Y.; Wang, J.; Lin, F.; Ma, X. Evaluation of land eco-security in Fenhe river Basin based on matter-element model. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 2061–2069. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Wu, R.; Ma, Q.; Chen, Y. Ecological Vulnerability Assessment Based on Multi-Sources Data and SD Model in Yinma River Basin, China. Ecol. Model. 2017, 349, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, R.; de Jonge, V.N.; Neto, J.M.; Domingos, T.; Marques, J.C.; Patrício, J. Towards a DPSIR Driven Integration of Ecological Value, Water Uses and Ecosystem Services for Estuarine Systems. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2013, 72, 64–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Das, A.; Mandal, A. Research Note: Ecosystem Health (EH) Assessment of a Rapidly Urbanizing Metropolitan City Region of Eastern India – A Study on Kolkata Metropolitan Area. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 204, 103938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Hou, P.; Jiang, J.; Xiao, R.; Zhai, J.; Fu, Z.; Hou, J. Ecosystem Health Assessment of Shennongjia National Park, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Song, G.; Lu, S. Assessment of Land Ecosystem Health with Monte Carlo Simulation: A Case Study in Qiqihaer, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 250, 119522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Wei, Z.; Ren, J.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, H. Early-Warning Measures for Ecological Security in the Qinghai Alpine Agricultural Area. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 9292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Ecological Security Early-Warning in Central Yunnan Province, China, Based on the Gray Model. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 111, 106000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibakhshi, S.; Groen, T.A.; Rautiainen, M.; Naimi, B. Remotely-Sensed Early Warning Signals of a Critical Transition in a Wetland Ecosystem. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ishtiaque, A.; Myint, S.W.; Wang, C. Examining the Ecosystem Health and Sustainability of the World’s Largest Mangrove Forest Using Multi-Temporal MODIS Products. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 569–570, 1241–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Q.; Zhessakov, A. Study on Ecological Evaluation of Urban Land Based on GIS and RS Technology. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahraminejad, M.; Rayegani, B.; Jahani, A.; Nezami, B. Proposing an Early-Warning System for Optimal Management of Protected Areas (Case Study: Darmiyan Protected Area, Eastern Iran). J. Nat. Conserv. 2018, 46, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekumah, B.; Armah, F.A.; Afrifa, E.K.A.; Aheto, D.W.; Odoi, J.O.; Afitiri, A.-R. Geospatial Assessment of Ecosystem Health of Coastal Urban Wetlands in Ghana. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2020, 193, 105226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okumura, K.; Ogoshi, T.; Asada, T.; Arimura, M.; Arreeras, T. Development of Downscaling Method Using the RBF Network Assessing the Hourly Population Inflow: A Case Study of the Sapporo Urban Area. Asian Transp. Stud. 2020, 6, 100019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitrakis, M.; Stogiannos, M.; Sarimveis, H.; Alexandridis, A. Multi-Ship Control and Collision Avoidance Using MPC and RBF-Based Trajectory Predictions. Sensors 2021, 21, 6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Teng, J.; Shen, L.; Yu, G.; Li, R.; Xu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liao, B.-Q.; Lin, H. Novel Insights into Membrane Fouling Caused by Gel Layer in a Membrane Bioreactor: Effects of Hydrogen Bonding. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 276, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alexandridis, A.; Chondrodima, E.; Sarimveis, H. Radial Basis Function Network Training Using a Nonsymmetric Partition of the Input Space and Particle Swarm Optimization. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2013, 24, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, G. Tunable and Transferable RBF Model for Short-Term Traffic Forecasting. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2019, 20, 4134–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Martín, J.D. Application of RBFN Network and GM (1, 1) for Groundwater Level Simulation. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 3345–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koo, K.-M.; Han, K.-H.; Jun, K.-S.; Lee, G.; Kim, J.-S.; Yum, K.-T. Performance Assessment for Short-Term Water Demand Forecasting Models on Distinctive Water Uses in Korea. Sustainability 2021, 13, 6056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Computational Ecology: Artificial Neural Networks and Their Applications; World Scientific: Singapore, 2010; ISBN 978-981-4282-62-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, S.; Yin, D.; Gao, X. Effect of Soil and Water Conservation on Ecosystem Service Value in Small Watersheds. Bull. Soi Water Conserv. 2012, 32, 286–291. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, N. Ecological Security Warning for Resource-Based Cities Based on RBF Neural Network Model: Taking Yulin City as an Example. Ecol. Econ. 2019, 35, 111–118. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wen, F.; Yang, Y.; Chen, L.; Zong, M. An Evaluation of Urban Land Use Performance Based on the Improved TOPSIS Method and Diagnosis of Its Obstacle Indicators: A Case Study of Chongqing. Resour. Sci. 2011, 33, 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, L.; Zhang, B.; Dan, J.; Ma, X. Dynamic evaluation and influencing factors of land ecological security in Jiayuguan City. Arid. Land Geogr. 2021, 44, 289–298. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, L.; Wu, F.; Lu, W. Co-evolution Relationship Between the Quality of Urbanization and the Health of Land Use System in Karst Regions. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 768–778. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xing, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Ding, D.; Wu, Y.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Hao, J. Progress of Air Pollution Control in China and Its Challenges and Opportunities in the Ecological Civilization Era. Engineering 2020, 6, 1423–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S. Evaluation on Urban Land Ecological Security Based on the PSR Model and Matter-Element Analysis: A Case Study of Zhuhai, Guangdong, China. J. Landsc. Res. 2019, 11, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Henan Provincial Bureau of Statistics. Available online: http://tjj.henan.gov.cn/tjfw/tjcbw/tjnj/ (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- China City Statistical Yearbook. Available online: https://data.cnki.net/trade/Yearbook/Single/N2013040146?z=Z006 (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Statistics of National Economic and Social Development of Henan Province. Available online: http://www.ha.stats.gov.cn/tjfw/tjgb/ (accessed on 21 December 2021).
- Wang, P.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Chen, X.; Kong, X. Evaluation of health of land use system in ecological resettlement area based on PSR model-A case study of Hongsibu area. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 25, 270–276. [Google Scholar]
- Su, P. Study on the Health Evaluation of Land Use System Based on DPSIR-TOPSIS Model in Enshi. Master’s Thesis, Central China Normal University, Wuhan, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, W.; Xia, L.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Z. Diagnosis on ecological security of cultivated land based on entropy method and grey prediction model. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 36, 284–289. [Google Scholar]
- Moody, J.; Darken, C.J. Fast Learning in Networks of Locally-Tuned Processing Units. Neural Comput. 1989, 1, 281–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Zhu, X.; Liu, L. Early-warning of Land Ecological Security in Hunan Province Based on RBF. Acta Geogr. Sinisa 2012, 67, 1411–1422. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Fang, L.; Wang, B.; Ma, T. Prediction of urban built-up area based on RBF neural network-comparative analysis with BP neural network and linear regression. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2013, 22, 691–697. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.; Li, M. Spatiotemporal change of land ecological security in Hunan based on DPSIR. Chin. J. Ecol. 2020, 39, 2724–2736. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Zhou, Y. Cultivated land ecological security and spatial aggregation Pattern in Hebei Province. Trans. CSAE 2011, 27, 338–344. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Zhang, Q. Spatiotemporal pattern and obstacle factors of land eco-security early warning in Henan province. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 27, 238–246. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M.; Chen, W.; Xun, Y.; Ma, Y.; Guo, R. Evaluation on Farmland Ecological Security in Henan Province Based on Projection Pursuit Model. Res. Soil Water Conversat. 2018, 25, 257–269. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Pu, C.; Chen, Q.; Jiang, L.; Su, L.; Mu, F.; Liu, X. Health evaluation of land use system in Urumqi city based on entropy weight-set pair analysis method. Chin. J. Agric. Resour. Reg. Plan. 2018, 39, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Shu, B.; Liu, Y.; Xu, J.; He, B.; Wu, G. Early warning of ecological security based on BP-ANN: A case study of Suzhou. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2010, 19, 1080–1085. [Google Scholar]


| Target Layer | Criteria Layer | Index Layer | Assignment | Weight | Attribute |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Land ecosystem Health | Pressure (0.4451) | Population density (X1) | Total population/total land area | 0.1034 | − |
| Natural population growth rate (X2) | Natural population growth/total population | 0.0622 | − | ||
| Per capita cultivated land area (X3) | Total cultivated area/population | 0.0944 | + | ||
| Urbanization level (X4) | Nonagricultural population/total population | 0.0703 | − | ||
| The annual growth rate of GDP (X5) | GDP of the year/last year-1 | 0.0693 | − | ||
| The growth rate of fixed-asset investment (X6) | The current year/last year-1 | 0.0653 | − | ||
| Land reclamation rate (X7) | Cultivated land area/total land area | 0.1259 | − | ||
| Average fertilizer input (X8) | The total amount of fertilizer/total area of cultivated land | 0.1312 | − | ||
| Average pesticide input (X9) | The total amount of pesticide/total area of cultivated land | 0.1143 | − | ||
| Average input of agricultural film (X10) | The total amount of agricultural film/total area of cultivated land | 0.0977 | − | ||
| The proportion of construction land (X11) | Construction land area/total land area | 0.0659 | − | ||
| State (0.3321) | Per capita GDP (X12) | GDP/total population | 0.0857 | + | |
| Per capita grain yield (X13) | Total grain output/total cultivated land area | 0.1722 | + | ||
| The proportion of primary industry in GDP (X14) | The output value of the primary industry/GDP | 0.0698 | + | ||
| Per capita grain (X15) | Total food production/population | 0.0908 | + | ||
| GDP per capita (X16) | GDP/total land area | 0.0888 | + | ||
| Mechanization level of cultivated land (X17) | The weighted sum of the yield of tractor seeder | 0.0510 | + | ||
| Effective irrigation rate (X18) | Effective irrigation area/total cultivated land area | 0.0789 | + | ||
| Forest coverage rate (X19) | Forest area/total land area | 0.0797 | + | ||
| Ground average wastewater load (X20) | Wastewater discharge/total land area | 0.1213 | − | ||
| Natural disaster rate (X21) | Affected area/total cultivated area | 0.0750 | − | ||
| Water resources per capita (X22) | Total water resources/total population | 0.0869 | + | ||
| Response (0.3358) | Domestic sewage treatment rate (X23) | Treatment capacity/total production | 0.0954 | + | |
| Harmless treatment rate of domestic waste (X24) | Treatment capacity/total production | 0.1170 | + | ||
| Number of scientific and technological personnel per capita (X25) | Total scientific and technological personnel/total land area | 0.2657 | + | ||
| Per capita disposable income of farmers (X26) | Total consumer spending and savings | 0.2292 | + | ||
| The comprehensive utilization rate of industrial solid waste (X27) | Comprehensive utilization/total waste production | 0.0857 | + | ||
| The proportion of education investment in GDP (X28) | Education investment/GDP | 0.2069 | + |
| Warning Degree Extent | (0~0.4] | (0.4~0.6] | (0.6~0.75] | (0.75~0.9] | (0.9~1.0] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Warning degree | Extraordinary warning | Severe warning | Moderate warning | Light warning | No warning |
| Indicator light | Red light ● | Yellow light ★ | Orange light ▲ | Blue light ◆ | Green light ■ |
| Description | The ecological environment has been seriously damaged, ecological restoration and reconstruction are very difficult, and the current situation of the land ecological environment is very bad | The function of the ecosystem is greatly degraded, it is difficult to recover after external interference, and the ability of sustainable development is weak | The ecological service function has been degraded, but it can still maintain the current state, which is easy to deteriorate after being disturbed | The ecosystem is less damaged, the ecological restoration ability is strong, and there is no harm to human health | The ecosystem is not damaged, and the environmental quality is good |
| Year | Terrestrial Ecosystem Health Subsystem | TEH | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pressure System | State System | Response System | ||
| 2007 | ◆ | ● | ● | ★ |
| 2008 | ◆ | ★ | ● | ★ |
| 2009 | ▲ | ● | ● | ★ |
| 2010 | ★ | ★ | ● | ★ |
| 2011 | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ |
| 2012 | ★ | ★ | ★ | ★ |
| 2013 | ● | ★ | ▲ | ★ |
| 2014 | ● | ★ | ▲ | ★ |
| 2015 | ● | ▲ | ◆ | ★ |
| 2016 | ● | ▲ | ◆ | ★ |
| 2017 | ● | ▲ | ■ | ▲ |
| 2018 | ★ | 🔺 | 🔺 | ★ |
| 2019 | ● | ▲ | ◆ | ★ |
| 2020 | ★ | ▲ | ◆ | ▲ |
| 2021 | ● | ▲ | ◆ | ▲ |
| 2022 | ★ | ◆ | ◆ | ▲ |
| 2023 | ● | ▲ | ◆ | ◆ |
| 2024 | ★ | ▲ | ◆ | ◆ |
| 2025 | ▲ | ◆ | ■ | ■ |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Y.; Fan, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Du, R.; Li, M. Exploring Development Trends of Terrestrial Ecosystem Health—A Case Study from China. Land 2022, 11, 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11010032
Li Y, Fan Z, Li Z, Zhang X, Du R, Li M. Exploring Development Trends of Terrestrial Ecosystem Health—A Case Study from China. Land. 2022; 11(1):32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11010032
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Yingchao, Zhiyuan Fan, Zhenhao Li, Xuefang Zhang, Ruyu Du, and Minghui Li. 2022. "Exploring Development Trends of Terrestrial Ecosystem Health—A Case Study from China" Land 11, no. 1: 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11010032
APA StyleLi, Y., Fan, Z., Li, Z., Zhang, X., Du, R., & Li, M. (2022). Exploring Development Trends of Terrestrial Ecosystem Health—A Case Study from China. Land, 11(1), 32. https://doi.org/10.3390/land11010032






