Spatio-Temporal Variation and Driving Forces of Land-Use Change from 1980 to 2020 in Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
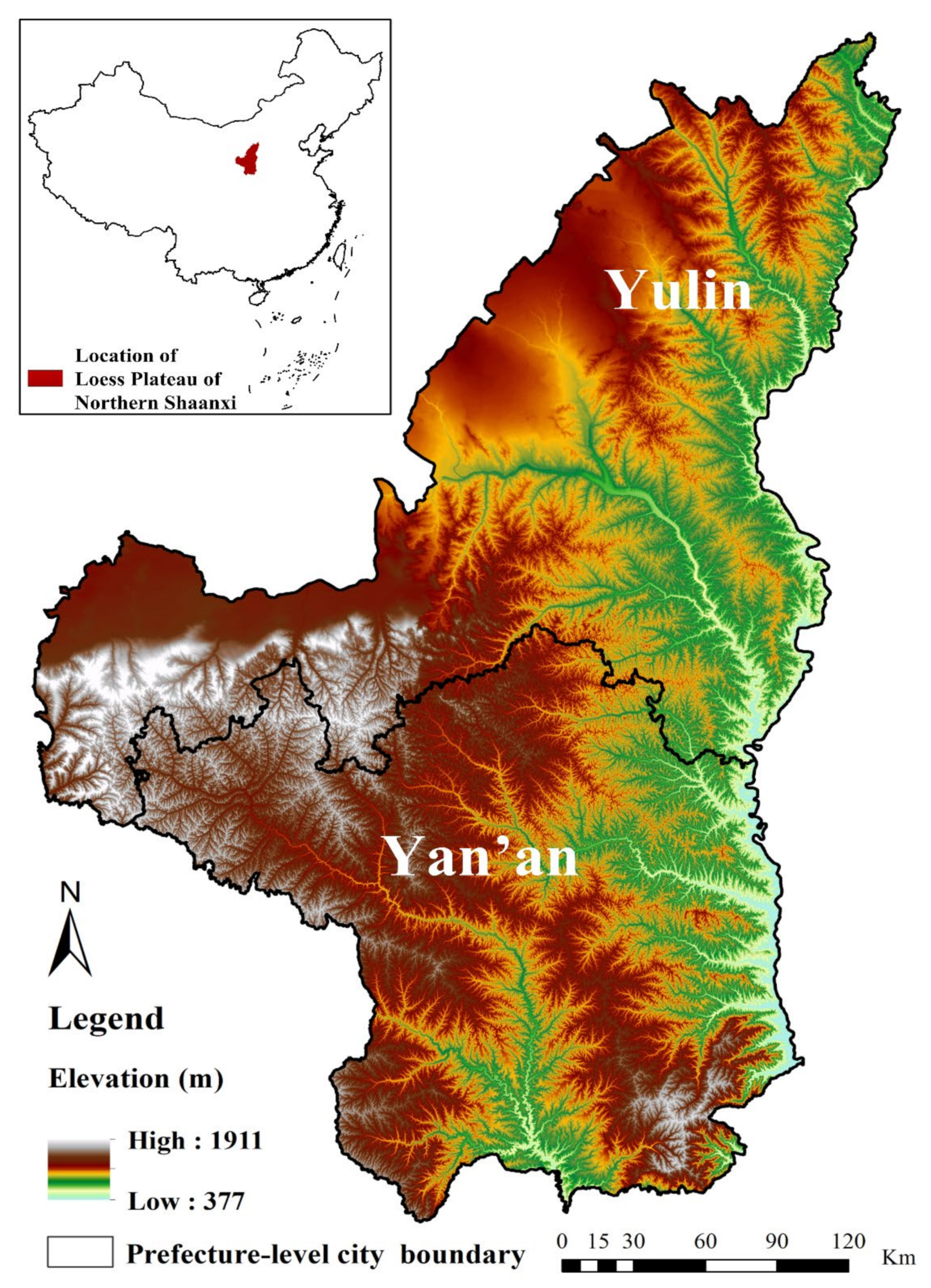
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source and Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Theoretical Framework
2.3.2. Land-Use Dynamic Degree
2.3.3. Land-Use Transfer Matrix
2.3.4. Landscape Pattern Metrics
2.3.5. Geographically and Temporally Weighted Regression
3. Results
3.1. Spatio-Temporal Pattern of Land-Use Change
3.1.1. Analysis of Land-Use Dynamic Degree
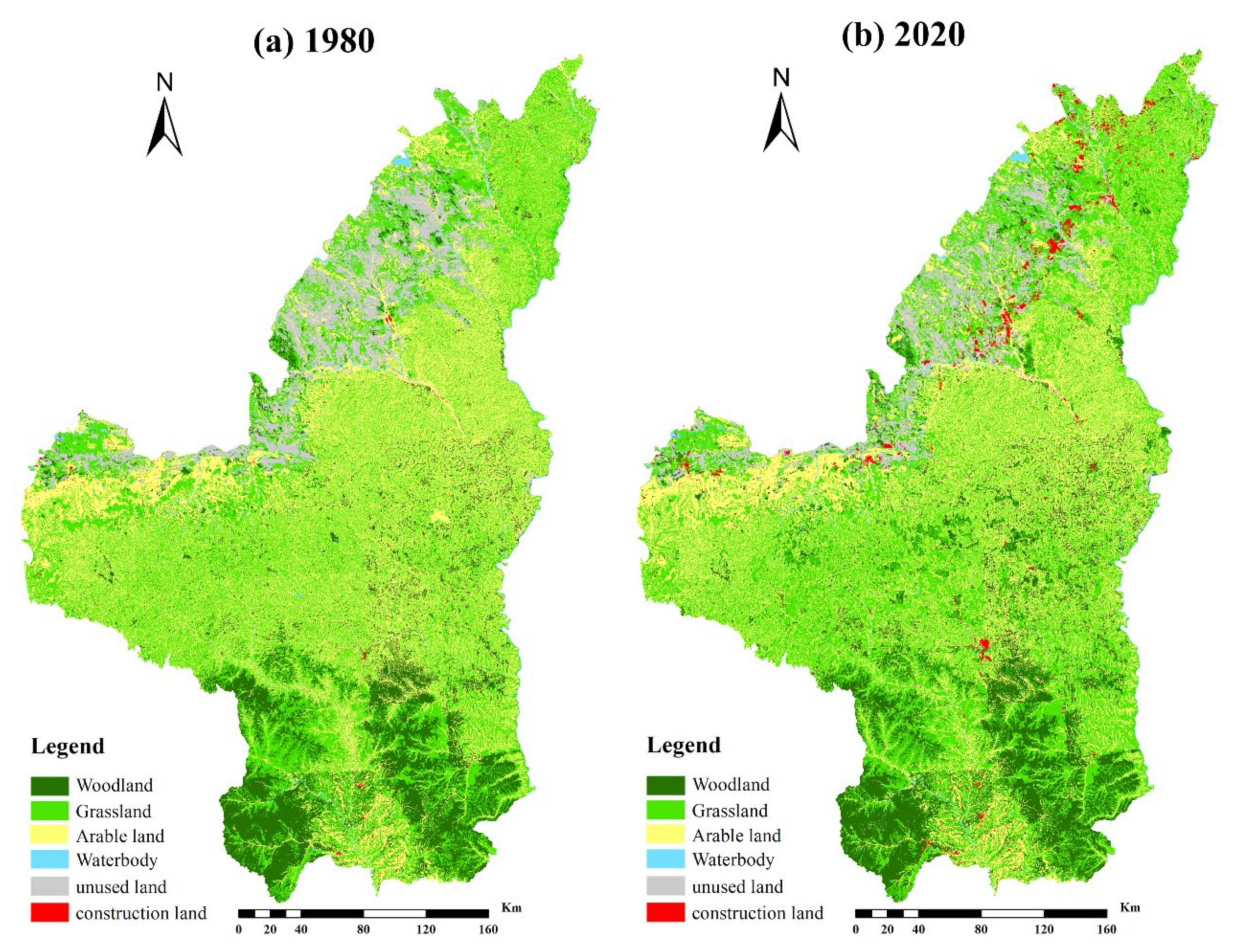
3.1.2. Analysis of the Land-Use Transfer Matrix
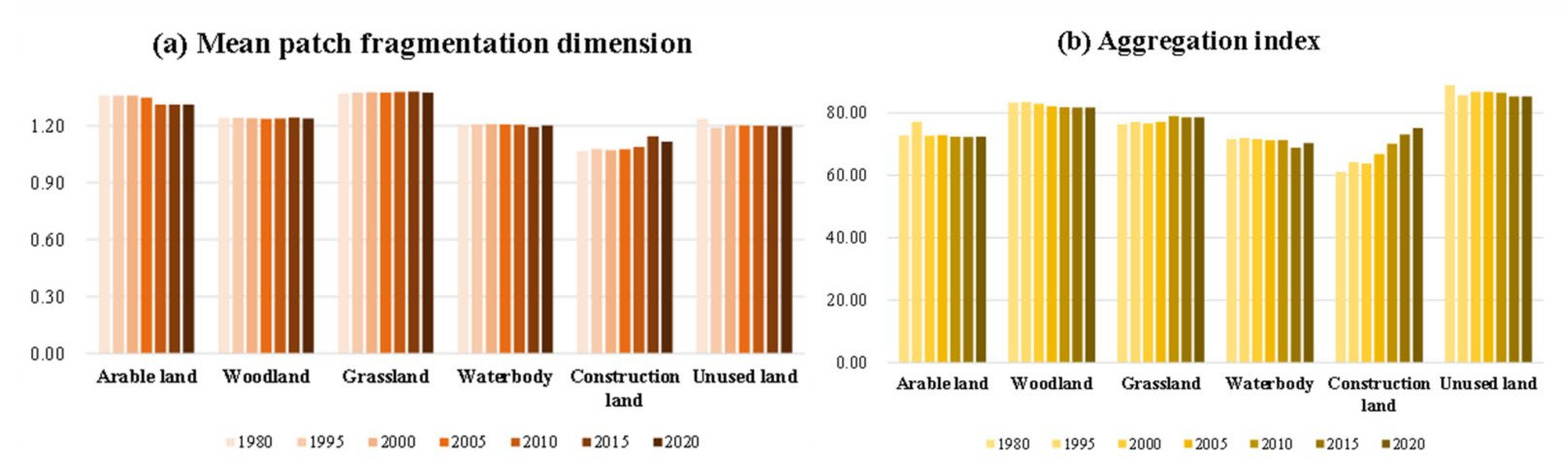
3.1.3. Analysis of Landscape Pattern Change
3.2. Driving Forces of Typical Land-Use Types
3.2.1. Model Comparison
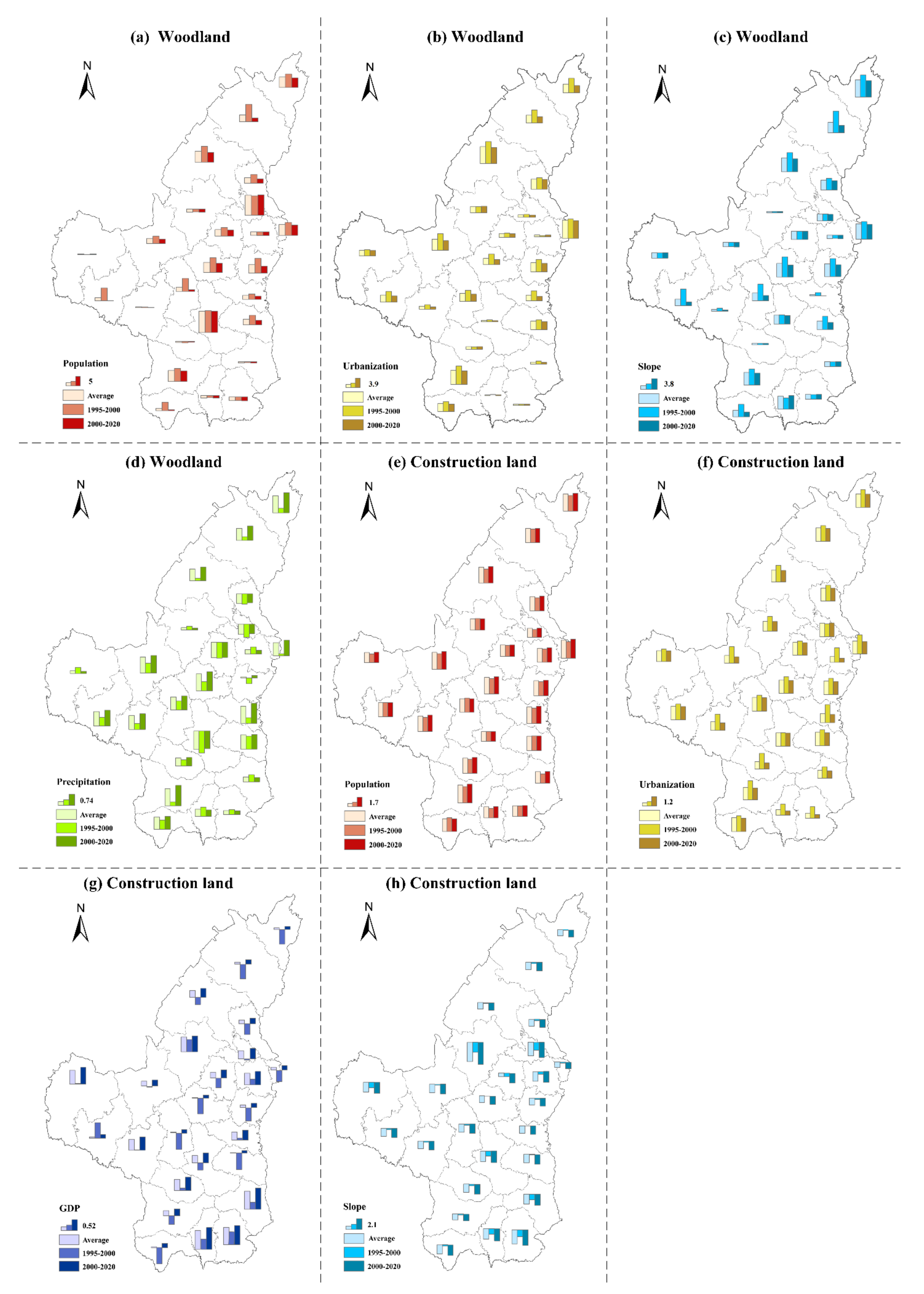
3.2.2. The Core Driving Forces of Diverse Land-Use Types
The Driving Forces of Arable Land
The Driving Forces of Grassland
The Driving Forces of Woodland
The Driving Forces of Construction Land
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Liu, M.; Zhuang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Deng, X. Study on spatial pattern of land-use change in China during 1995–2000. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2003, 46, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindesay, J.A.; Andreae, M.O.; Goldammer, J.G.; Harris, G.; Annegarn, H.J.; Garstang, M.; Scholes, R.J.; Van Wilgen, B.W. International geosphere-biosphere programme/international global atmospheric chemistry SAFARI-92 field experiment: Background and overview. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1996, 101, 23521–23530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhrqvist, O.; Linnér, B.-O. Narratives of the past for Future Earth: The historiography of global environmental change research. Anthr. Rev. 2015, 2, 159–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, E.; Ojima, D.S.; Buchmann, B.; Canadell, J.G.; Coomes, O.; Graumlich, L.; Jackson, R.; Jaramillo, V.; Lavorel, S.; Leadley, P. Global Land Project: Science Plan and Implementation Strategy, 1st ed.; IGBP Secretariat: Stockholm, Sweden, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Surya, B.; Ahmad, D.N.A.; Sakti, H.H.; Sahban, H. Land use change, spatial interaction, and sustainable development in the Metropolitan Urban Areas, South Sulawesi Province, Indonesia. Land 2020, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teklay, A.; Dile, Y.T.; Setegn, S.G.; Demissie, S.S.; Asfaw, D.H. Evaluation of static and dynamic land use data for watershed hydrologic process simulation: A case study in Gummara watershed, Ethiopia. Catena 2019, 172, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Meyfroidt, P. Land use transitions: Socio-ecological feedback versus socio-economic change. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rimal, B.; Baral, H.; Stork, N.E.; Paudyal, K.; Rijal, S. Growing City and rapid land use transition: Assessing multiple hazards and risks in the Pokhara Valley, Nepal. Land 2015, 4, 957–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bičík, I.; Jeleček, L.; Štěpánek, V. Land-use changes and their social driving forces in Czechia in the 19th and 20th centuries. Land Use Policy 2001, 18, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Liang, W.; Miao, C. Hydrogeomorphic ecosystem responses to natural and anthropogenic changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2017, 45, 223–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verburg, P.H.; Overmars, K.P. Dynamic simulation of land-use change trajectories with the CLUE-s model. In Modelling Land-Use Change; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; Volume 90, pp. 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atonya, S.; OLANG, L.; Morara, L. Future Land-use Changes in the transboundary Sio-Malaba-Malakisi Basin of East Africa: Simulations using the CLUE-S model and Classified Satellite Land Cover Datasets. Authorea Prepr. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Geist, H.J.; Lepers, E. Dynamics of land-use and land-cover change in tropical regions. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2003, 28, 205–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cao, M.; Zhu, Y.; Quan, J.; Zhou, S.; Lü, G.; Chen, M.; Huang, M. Spatial sequential modeling and predication of global land use and land cover changes by integrating a global change assessment model and cellular automata. Earth’s Futur. 2019, 7, 1102–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, G.; Ye, P.; Ding, L.; Quinones, A.; Li, Y.; Jiang, N. Spatio-temporal patterns of land use and cover change from 1990 to 2010: A case study of Jiangsu province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qian, M.; Zeng, Z. Land Use Transition and Driving Forces in Chinese Loess Plateau: A Case Study from Pu County, Shanxi Province. Land 2021, 10, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xystrakis, F.; Psarras, T.; Koutsias, N. A process-based land use/land cover change assessment on a mountainous area of Greece during 1945–2009: Signs of socio-economic drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 587, 360–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López, E.; Bocco, G.; Mendoza, M.; Duhau, E. Predicting land-cover and land-use change in the urban fringe. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2001, 55, 271–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapola, D.M.; Martinelli, L.A.; Peres, C.A.; Ometto, J.P.H.B.; Ferreira, M.E.; Nobre, C.A.; Aguiar, A.P.D.; Bustamante, M.M.C.; Cardoso, M.F.; Costa, M.H.; et al. Pervasive transition of the Brazilian land-use system. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piorr, H.P. Environmental policy, agri-environmental indicators and landscape indicators. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 98, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.J.; Zhang, Q.J.; Chen, L.D.; Zhao, W.W.; Gulinck, H.; Liu, G.B.; Yang, Q.K.; Zhu, Y.G. Temporal change in land use and its relationship to slope degree and soil type in a small catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2006, 65, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.J.; Fu, B.J.; Chen, L.D.; Zhao, W.W.; Yang, Q.K.; Liu, B.G.; Gulinck, H. Dynamics and driving factors of agricultural landscape in the semiarid hilly area of the Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 103, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, J. Conversion from rural settlements and arable land under rapid urbanization in Beijing during 1985–2010. J. Rural Stud. 2017, 51, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nendel, C.B.; Hu, Y.; Lakes, T. Land-use change and land degradation on the Mongolian Plateau from 1975 to 2015—A case study from Xilingol, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1595–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Wang, J.; Fu, B.; Qiu, Y. Land-use change in a small catchment of northern Loess Plateau, China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2001, 86, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zhang, D. Evaluating the effect of ecological policies from the pattern change of persistent green patches—A case study of Yan’an in China’s loess plateau. Ecol. Inform. 2021, 63, 101305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Introduction to land use and rural sustainability in China. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Chen, L.; Ma, K.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J. The relationships between land use and soil conditions in the hilly area of the loess plateau in northern Shaanxi, China. Catena 2000, 39, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fang, F.; Li, Y. Key issues of land use in China and implications for policy making. Land Use Policy 2014, 40, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Qu, Y. Land use transitions and land management: A mutual feedback perspective. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.; Li, X.; Xie, H.; Lu, C. Urban land expansion and arable land loss in China—A case study of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. Land Use Policy 2005, 22, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Ma, Z.; Yang, Q.; Han, Y.; Mahmood, R.; Zheng, Z. Land use/land cover changes and regional climate over the Loess Plateau during 2001–2009. Part I: Observational evidence. Clim. Change 2015, 129, 427–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, W.; Lin, Y.; Glendinning, A.; Xu, Y. Land-use changes and land policies evolution in China’s urbanization processes. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 375–387. [Google Scholar]
- Ostwald, M.; Chen, D. Land-use change: Impacts of climate variations and policies among small-scale farmers in the Loess Plateau, China. Land Use Policy 2006, 23, 361–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Chen, Z. Impacts of climatic warming on cropping system borders of China and potential adaptation strategies for regional agriculture development. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 755, 142415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Shi, X.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, Y. Quantitative assessment of the ecological effects of land use/cover change in the arid region of Northwest China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, J.; Dong, J.; Chen, J.; Xiao, X. Impacts of ecological restoration projects on agricultural productivity in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2013, 23, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Zhao, X.; Liang, S.; Zhao, J.; Xu, P.; Wu, D. Quantitatively assessing and attributing land use and land cover changes on China’s loess plateau. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yao, Z.; Wang, B.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.; Deng, R.; Yang, Q. Analysis of Land Use Changes and Driving Forces in the Yanhe River Basin from 1980 to 2015. J. Sensors 2021, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Zheng, X.Q.; Zang, X.B. Accuracy assessments of land use change simulation based on Markov-cellular automata model. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 13, 1238–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ge, Y.; Zhang, K.; Yang, X. A 110-year pollen record of land use and land cover changes in an anthropogenic watershed landscape, eastern China: Understanding past human-environment interactions. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 2906–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Asselen, S.; Verburg, P.H. Land cover change or land-use intensification: Simulating land system change with a global-scale land change model. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2013, 19, 3648–3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Chen, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, M.; Xia, X. Suitability evaluation of large-scale farmland transfer on the Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2019, 30, 1258–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Fan, P.; Sun, J.; Liu, Y. Land use and landscape change driven by gully land consolidation project: A case study of a typical watershed in the Loess Plateau. J. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 719–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, C. Land consolidation and rural revitalization in China: Mechanisms and paths. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Rural land system reforms in China: History, issues, measures and prospects. Land Use Policy 2020, 91, 104330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taillefumier, F.; Piégay, H. Contemporary land use changes in prealpine Mediterranean mountains: A multivariate gis-based approach applied to two municipalities in the Southern French Prealps. Catena 2003, 51, 267–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, V.H. The relationship between land-use change and climate change. Ecol. Appl. 1997, 7, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Deng, Y.; Liu, X. The contribution of forest and grassland change was greater than that of cropland in human-induced vegetation greening in China, especially in regions with high climate variability. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 792, 148408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.R.; Anapashsha, R.; Kumar, S.; Saha, S.K.; Dadhwal, V.K. Assessing potential of MODIS derived temperature/vegetation condition index (TVDI) to infer soil moisture status. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2009, 30, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F.; Turner, B.L.; Geist, H.J.; Agbola, S.B.; Angelsen, A.; Bruce, J.W.; Coomes, O.T.; Dirzo, R.; Fischer, G.; Folke, C. The causes of land-use and land-cover change: Moving beyond the myths. Glob. Environ. Chang. 2001, 11, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ningal, T.; Hartemink, A.E.; Bregt, A.K. Land use change and population growth in the Morobe Province of Papua New Guinea between 1975 and 2000. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 87, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhou, Y. Reflections on China’s food security and land use policy under rapid urbanization. Land Use Policy 2021, 109, 105699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Anna, H.; Zhang, L.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, J.; Ouyang, Z. Spatial and temporal changes of arable land driven by urbanization and ecological restoration in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 29, 809–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Sun, P.; Huang, A.; Zheng, W. Land use change and its driving forces toward mutual conversion in Zhangjiakou City, a farming-pastoral ecotone in Northern China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Land use change and driving factors in rural China during the period 1995–2015. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontius, R.G.; Huang, J.; Jiang, W.; Khallaghi, S.; Lin, Y.; Liu, J.; Quan, B.; Ye, S. Rules to write mathematics to clarify metrics such as the land use dynamic degrees. Landsc. Ecol. 2017, 32, 2249–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Gao, W.; Watari, K.; Fukahori, H. Land use change of Kitakyushu based on landscape ecology and Markov model. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 455–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lu, J. Simulation of Land Use Pattern Evolution from a Multi-Scenario Perspective: A Case Study of Suzhou City in Anhui Province, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zheng, X.; Zhang, C.; Chen, Y. Impact of land-use and land-cover change on meteorology in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei Region from 1990 to 2010. Sustainability 2018, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bachmair, S.; Weiler, M.; Nützmann, G. Controls of land use and soil structure on water movement: Lessons for pollutant transfer through the unsaturated zone. J. Hydrol. 2009, 369, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenerette, G.D.; Wu, J. Analysis and simulation of land-use change in the central Arizona–Phoenix region, USA. Landsc. Ecol. 2001, 16, 611–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadashpoor, H.; Azizi, P.; Moghadasi, M. Land use change, urbanization, and change in landscape pattern in a metropolitan area. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, A.; Pandey, M.; Mishra, V.N.; Kumar, R.; Rai, P.K.; Costache, R.; Punia, M.; Di, L. Comparative evaluation of geospatial scenario-based land change simulation models using landscape metrics. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 128, 107810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafouri, B.; Amiri, B.J.; Shabani, A.A.; Songer, M. Examining Relationships Between Socioeconomic Factors and Landscape Metrics in the Southern Basin of the Caspian Sea. Environ. Model. Assess. 2016, 21, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, R.V.; Krummel, J.R.; Gardner, R.H.; Sugihara, G.; Jackson, B.; DeAngelis, D.L.; Milne, B.T.; Turner, M.G.; Zygmunt, B.; Christensen, S.W.; et al. Indices of landscape pattern. Landsc. Ecol. 1988, 1, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, H.; Heilig, G.K.; Li, X.; Zhang, M. Socio-economic development and land-use change: Analysis of rural housing land transition in the Transect of the Yangtse River, China. Land Use Policy 2007, 24, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, L.; Genxu, W.; Guangsheng, L.; Yun, L.; Xiangyang, S. The ecological implications of land use change in the Source Regions of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2013, 13, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.; Wu, B.; Barry, M. Geographically and temporally weighted regression for modeling spatio-temporal variation in house prices. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2010, 24, 383–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Li, Z.; Wang, S. The varying driving forces of urban land expansion in China: Insights from a spatial-temporal analysis. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 766, 142591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadnazar, A.; Mahdinia, I.; Ahmad, N.; Khattak, A.J.; Liu, J. Understanding how relationships between crash frequency and correlates vary for multilane rural highways: Estimating geographically and temporally weighted regression models. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2021, 157, 106–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltani, A.; Pettit, C.J.; Heydari, M.; Aghaei, F. Housing price variations using spatio-temporal data mining techniques. J. Hous. Built Environ. 2021, 36, 1199–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msofe, N.K.; Sheng, L.; Lyimo, J. Land use change trends and their driving forces in the Kilombero Valley Floodplain, Southeastern Tanzania. Sustainability 2019, 11, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, P. Spatiotemporal Analysis of Environmental Factors on the Birdstrike Risk in High Plateau Airport with Multi-Scale Research. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. When and where did the Loess Plateau turn “green”? Analysis of the tendency and breakpoints of the normalized difference vegetation index. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 162–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, J.; Yang, Y. Strategic adjustment of land use policy under the economic transformation. Land Use Policy 2018, 74, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Reilly, M.K. A meta-analysis of global urban land expansion. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e23777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Shi, X.; Fu, Y.; Yuan, Y. Evaluation and simulation of the impact of land use change on ecosystem services trade-offs in ecological restoration areas, China. Land Use Policy 2020, 99, 105020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kroll, F.; Haase, D. Does demographic change affect land use patterns?: A case study from Germany. Land Use Policy 2010, 27, 726–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, R.; Zhang, B.; He, X.; Su, T.; Li, Y.; Long, B.; Wang, X.; Yang, W.; He, C. Historical Water Storage Changes Over China’s Loess Plateau. Water Resour. Res. 2021, 57, e2020WR028661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Labzovskii, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, T. Re-orienting ecological restoration in degraded drylands for a more sustainable soil–water relationship: Non-linear boundary of limited water resources in combating soil loss. J. Arid. Environ. 2019, 167, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, Z.P.; Zheng, S.X. Ecological properties of soil water and effects on forest vegetation in the Loess Plateau. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Ecol. 2006, 13, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Type | Factors | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Natural factors | Elevation | The average elevation in a county |
| Slope | The average slope in a county | |
| Precipitation | The average annual precipitation in a county | |
| Temperature | The average annual temperature in a county | |
| TVDI | Mean value of TVDI from May to October in a county | |
| Economic factors | GDP | The value added of GDP each year |
| Population | The total registered population each year | |
| Urbanization | the non-agricultural registered population divided by the total registered population each year |
| Land Use Types | Area (Unit: 104 ha) | LUDD | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1980–2000 | 2000–2020 | 1980–2020 | 1980–2000 | 2000–2020 | 1980–2020 | |
| Arable land | 2.69 | −34.80 | −32.11 | 0.05 | −0.61 | −0.28 |
| Woodland | 1.75 | 12.18 | 13.93 | 0.08 | 0.56 | 0.32 |
| Grassland | 7.82 | 16.99 | 24.82 | 0.11 | 0.24 | 0.18 |
| Waterbody | −0.13 | 0.21 | 0.07 | −0.10 | 0.15 | 0.03 |
| Construction land | 0.37 | 8.24 | 8.61 | 0.70 | 13.83 | 8.24 |
| Unused land | −12.49 | −2.82 | −15.31 | −1.06 | −0.30 | −0.65 |
| Land Use Types | Model Types | AICc | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Arable land | OLS | 237.81 | 0.51 |
| GTWR | 196.49 | 0.77 | |
| Woodland | OLS | 386.98 | 0.47 |
| GTWR | 316.49 | 0.84 | |
| Grassland | OLS | 322.22 | 0.23 |
| GTWR | 230.72 | 0.79 | |
| Construction land | OLS | 381.49 | 0.52 |
| GTWR | 393.24 | 0.65 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, X.; Zhou, Y. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Driving Forces of Land-Use Change from 1980 to 2020 in Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, China. Land 2021, 10, 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090982
Zhou X, Zhou Y. Spatio-Temporal Variation and Driving Forces of Land-Use Change from 1980 to 2020 in Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, China. Land. 2021; 10(9):982. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090982
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Xue, and Yang Zhou. 2021. "Spatio-Temporal Variation and Driving Forces of Land-Use Change from 1980 to 2020 in Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, China" Land 10, no. 9: 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090982
APA StyleZhou, X., & Zhou, Y. (2021). Spatio-Temporal Variation and Driving Forces of Land-Use Change from 1980 to 2020 in Loess Plateau of Northern Shaanxi, China. Land, 10(9), 982. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10090982







