Land–Lake Linkage and Remote Sensing Application in Water Quality Monitoring in Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
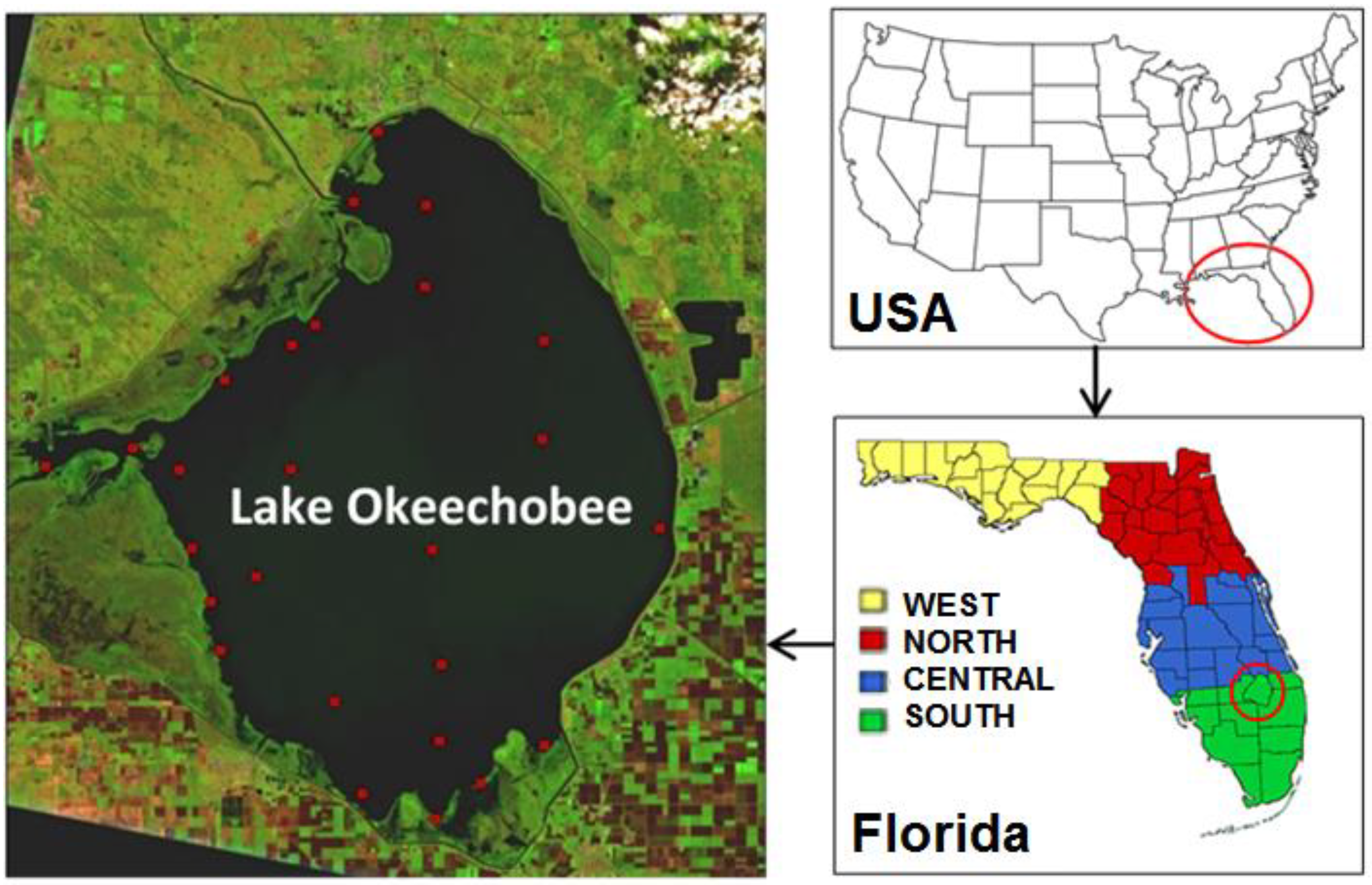
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Datasets
2.2.1. Limnological Data
2.2.2. Satellite Data
2.3. Methodology
2.3.1. Data Preprocessing: Landsat-5/TM
2.3.2. Data Preprocessing: Landsat-8/OLI
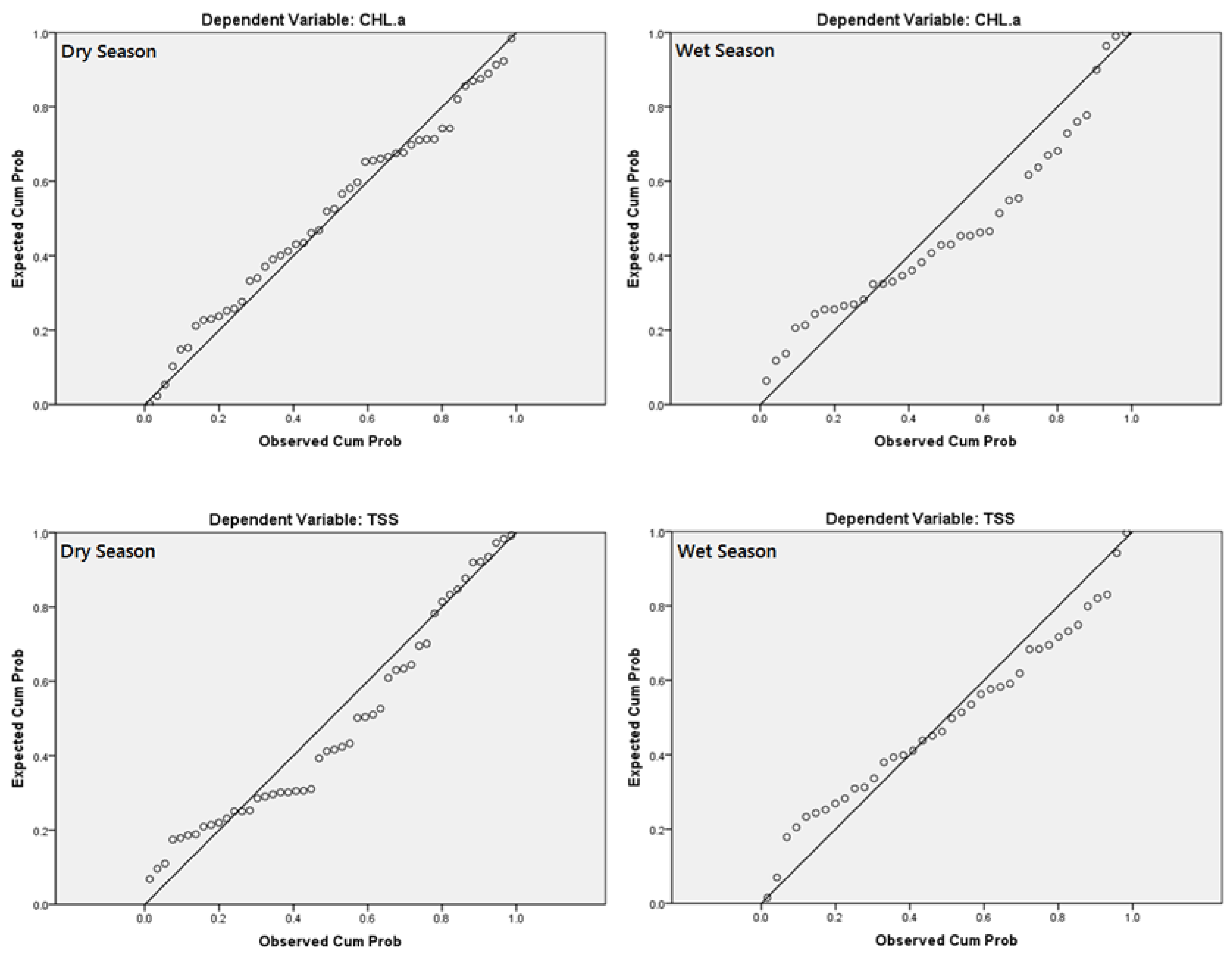
2.3.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
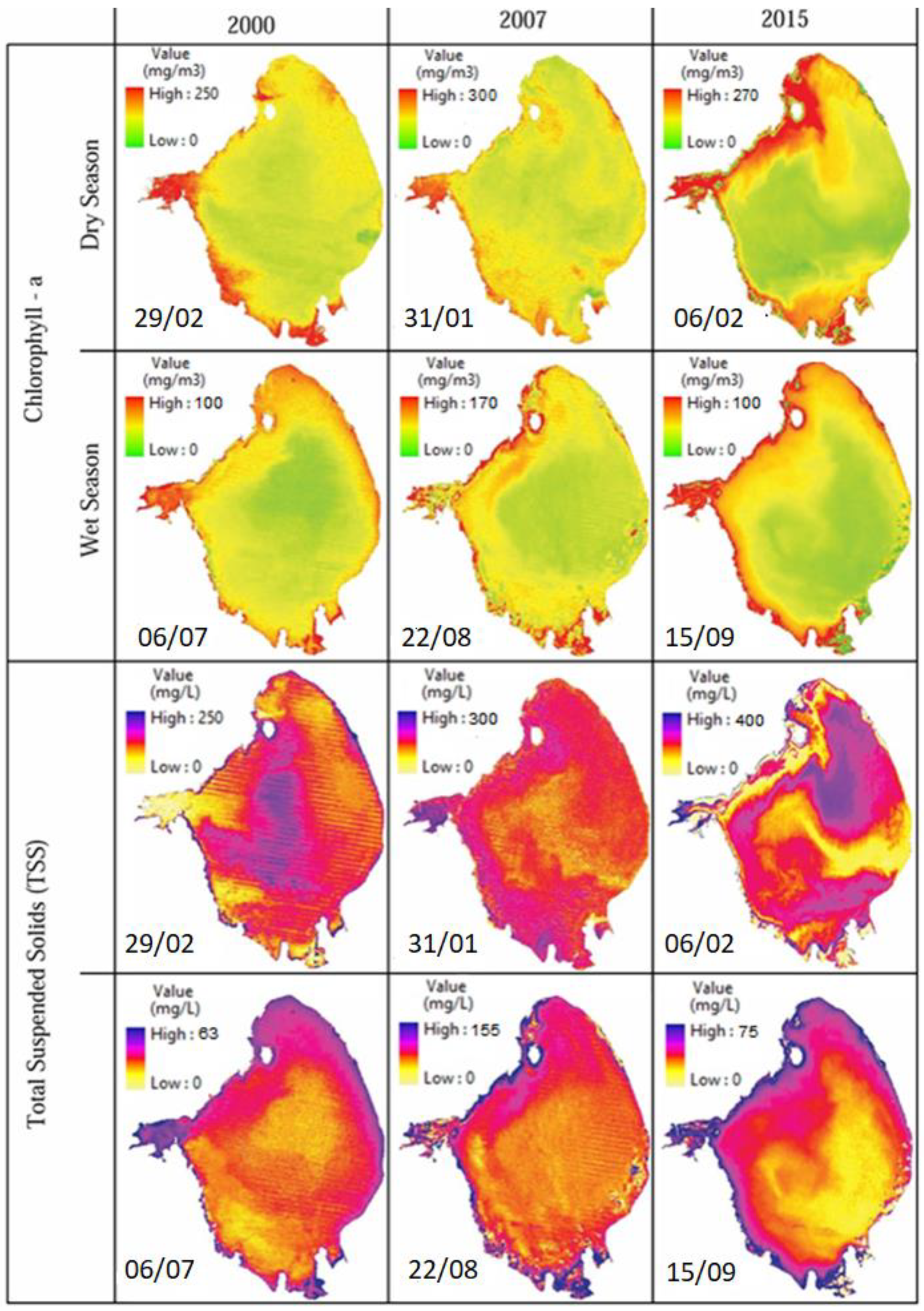
3.1. Chlorophyll-a and TSS
3.2. Nutrients
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alparslan, E.; Aydöner, C.; Tüfekçi, V.; Tüfekci, H. Water quality assessment at Ömerli Dam using remote sensing techniques. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2007, 135, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anding, D.; Kauth, R. Estimation of sea surface temperature from space. Remote. Sens. Environ. 1970, 1, 217–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brando, V.; Dekker, A. Satellite hyperspectral remote sensing for estimating estuarine and coastal water quality. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote. Sens. 2003, 41, 1378–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Din, M.S.; Gaber, A.; Koch, M.; Ahmed, R.S.; Bahgat, I. Remote Sensing Application for Water Quality As-sessment in Lake Timsah, Suez Canal, Egypt. J. Remote Sens. Technol. 2013, 1, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Bresciani, M.; Cazzaniga, I.; Schenk, K.; Rieger, P.; Braga, F.; Matta, E.; Brando, V.E. Evaluation of Multi-Resolution Satellite Sensors for Assessing Water Quality and Bottom Depth of Lake Garda. Sensors 2014, 14, 24116–24131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadjimitsis, D.; Clayton, C.R. Assessment of temporal variations of water quality in inland water bodies using atmospheric corrected satellite remotely sensed image data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2008, 159, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellweger, F.; Schlosser, P.; Lall, U.; Weissel, J. Use of satellite imagery for water quality studies in New York Harbor. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2004, 61, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondratyev, K.Y.; Pozdnyakov, D.V.; Pettersson, L.H. Water quality remote sensing in the visible spectrum. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 957–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koponen, S.; Pulliainen, J.; Kallio, K.; Hallikainen, M. Lake water quality classification with airborne hyper-spectral spectrometer and simulated MERIS data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maillard, P.; Santos, N.A.P. A spatial-statistical approach for modeling the effect of non-point source pollu-tion on different water quality parameters in the Velhas river watershed–Brazil. J. Environ. Manag. 2008, 86, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, A.; Prieur, L. Analysis of variations in ocean color1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozdnyakov, D.; Shuchman, R.; Korosov, A.; Hatt, C. Operational algorithm for the retrieval of water quality in the Great Lakes. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 352–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, M.M.; Melesse, A.M.; Scinto, L.J.; Rehage, J.S. Satellite Estimation of Chlorophyll-a Using Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Sensor in Shallow Coastal Water Bodies: Validation and Improvement. Water 2019, 11, 1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyhan, E.; Dekker, A. Application of remote sensing techniques for water quality monitoring. Aquat. Ecol. 1986, 20, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usali, N.; Ismail, M.H. Use of Remote Sensing and GIS in Monitoring Water Quality. J. Sustain. Dev. 2010, 3, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ma, T. Application of remote sensing techniques in monitoring and assessing the water quality of Taihu Lake. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2001, 67, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lillesand, T.; Kiefer, R.W.; Chipman, J. Remote Sensing and Image Interpretation; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Dekker, A.; Peters, S.W.M. The use of the Thematic Mapper for the analysis of eutrophic lakes: A case study in The Netherlands. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alparslan, E.; Coskun, H.G.; Alganci, U. Water quality determination of Küçükçekmece Lake, Turkey by using multispectral satellite data. Sci. World J. 2009, 9, 1215–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Choi, M. Assessment of water quality based on Landsat 8 operational land imager associated with hu-man activities in Korea. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Han, M. Mapping Chlorophyll-a Concentration in Laizhou Bay Using Landsat 8 OLI data. In Proceedings of the 36th IAHR World Congress (Hague), The Hague, The Netherlands, 28 June–3 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.-I.; Kim, H.-C.; Hyun, C.-U. High Resolution Ocean Color Products Estimation in Fjord of Svalbard, Arctic Sea using Landsat-8 OLI. Korean J. Remote Sens. 2014, 30, 809–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.; Walker, N. Quantification of surface suspended sediments along a river dominated coast with NO-AA AVHRR and SeaWiFS measurements: Louisiana, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 3229–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nechad, B.; Ruddick, K.G.; Park, Y. Calibration and validation of a generic multisensor algorithm for mapping of total suspended matter in turbid waters. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 854–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, P.; Hansom, J.; Plummer, S.; Pedley, M. Multispectral remote sensing of nearshore suspended sedi-ments: A pilot study. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1987, 8, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, E.; Hansom, J.; Curran, P. The effect of viewing geometry and wavelength on the relationship between reflectance and suspended sediment concentration. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1989, 10, 1357–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Song, Q. Influence of the Three Gorges Dam on total suspended matters in the Yangtze Estuary and its adjacent coastal waters: Observations from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxaran, D.; Froidefond, J.-M.; Lavender, S.; Castaing, P. Spectral signature of highly turbid waters: Applica-tion with SPOT data to quantify suspended particulate matter concentrations. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 81, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, J.C.; Zimba, P.V.; Everitt, J.H. Remote Sensing Techniques to Assess Water Quality. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2003, 69, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutser, T.; Arst, H.; Miller, T.; Käärmann, L.; Milius, A. Telespectrometrical estimation of water transparency, chlorophyll-a and total phosphorus concentration of Lake Peipsi. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 3069–3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xia, H.; Fu, J.; Sheng, G. Water quality change in reservoirs of Shenzhen, China: Detection using LANDSAT/TM data. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 328, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, J.; Qi, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H.; Lou, L.; Chen, Y. Empirical estimation of total phosphorus concentration in the mainstream of the Qiantang River in China using Landsat TM data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2309–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Wang, Z.; Blackwell, J.; Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Jiang, G. Water quality monitoring using Landsat Themate Mapper data with empirical algorithms in Chagan Lake, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2011, 5, 53506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, C.J.; Kryskalla, J.R. Methods of Analysis by the U.S. Geological Survey National Water Quality Laboratory: Evaluation of Alkaline Persulfate Digestion as an Alternative to Kjeldahl Digestion for Determination of Total and Dissolved Nitrogen and Phosphorus in Water; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, Virginia, 2003. [CrossRef]
- Mikkelsen, R. Ammonia emissions from agricultural operations: Fertilizer. Better Crop. 2009, 93, 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Gholizadeh, M.H.; Melesse, A.M.; Reddi, L. Water quality assessment and apportionment of pollution sources using APCS-MLR and PMF receptor modeling techniques in three major rivers of South Florida. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 566, 1552–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hood, R.R.; Subramaniam, A.; May, L.R.; Carpenter, E.J.; Capone, D.G. Remote estimation of nitrogen fixa-tion by Trichodesmium. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2001, 49, 123–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, C.E.; Waite, A.M.; Thompson, P.A.; Pattiaratchi, C.B. Phytoplankton community structure and ni-trogen nutrition in Leeuwin Current and coastal waters off the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2007, 54, 902–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, V.; Icely, J.; Newton, A.; Webster, R. The yield of chlorophyll from nitrogen: A comparison between the shallow Ria Formosa lagoon and the deep oceanic conditions at Sagres along the southern coast of Portugal. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2005, 62, 391–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.; Huang, J.-Z.; Li, Y.-M.; Lu, W.-N.; Wang, H.-J.; Wang, G.-X. Preliminary exploring of hyperspectral remote sensing experiment for nitrogen and phosphorus in water. Guang Pu Xue Yu Guang Pu Fen Xi Guang Pu 2008, 28, 839–842. [Google Scholar]
- Karakaya, N.; Evrendilek, F. Monitoring and validating spatio-temporal dynamics of biogeochemical proper-ties in Mersin Bay (Turkey) using Landsat ETM+. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 181, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busse, L.B.; Simpson, J.C.; Cooper, S.D. Relationships among nutrients, algae, and land use in urbanized southern California streams. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2006, 63, 2621–2638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, R.E. A trophic state index for lakes1. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1977, 22, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uusitalo, R.; Yli-Halla, M.; Turtola, E. Suspended soil as a source of potentially bioavailable phosphorus in surface runoff waters from clay soils. Water Res. 2000, 34, 2477–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyer, M.V.; Frazer, T.K.; Notestein, S.K.; Canfield, J.; Daniel, E. Nutrient, chlorophyll, and water clarity rela-tionships in Florida’s nearshore coastal waters with comparisons to freshwater lakes. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 59, 1024–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordon, H.R. Calibration requirements and methodology for remote sensors viewing the ocean in the visible. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 22, 103–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teillet, P.; Horler, D.; O’Neill, N. Calibration, validation, and quality assurance in remote sensing: A new par-adigm. Can. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 23, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maul, G.A. Introduction to Satellite Oceanography; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1985; Volume 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.; Jackson, R.D.; Slater, P.N.; Teillet, P.M. Evaluation of simplified procedures for retrieval of land surface reflectance factors from satellite sensor output. Remote Sens. Environ. 1992, 41, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, P.S. Image-based atmospheric corrections-revisited and improved. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1996, 62, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; E Bauer, M. Application of Landsat imagery to regional-scale assessments of lake clarity. Water Res. 2002, 36, 4330–4340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloiber, S.M.; Brezonik, P.L.; Olmanson, L.G.; Bauer, M.E. A procedure for regional lake water clarity as-sessment using Landsat multispectral data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lathrop, R.G. Use of Thematic Mapper data to assess water quality in Green Bay and central Lake Michigan. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1986, 52, 671–680. [Google Scholar]
- Mancino, G.; Nolè, A.; Urbano, V.; Amato, M.; Ferrara, A. Assessing water quality by remote sensing in small lakes: The case study of Monticchio lakes in southern Italy. Iforest Biogeosci. For. 2009, 2, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, M.; Gitelson, A.; Yacobi, Y.Z.; Ben-Avraham, Z. Chlorophyll distribution in Lake Kinneret determined from Landsat Thematic Mapper data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavery, P.; Pattiaratchi, C.; Wyllie, A.; Hick, P. Water quality monitoring in estuarine waters using the landsat thematic mapper. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 46, 268–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, R.M.; Forsythe, R.; Vaughan, G. Assessing water quality in Catawba River reservoirs using Landsat thematic mapper satellite data. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1998, 14, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giardino, C.; Pepe, M.; Brivio, P.A.; Ghezzi, P.; Zilioli, E. Detecting chlorophyll, Secchi disk depth and surface temperature in a sub-alpine lake using Landsat imagery. Sci. Total. Environ. 2001, 268, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dekker, A.; Vos, R.J.; Peters, S.W.M. Analytical algorithms for lake water TSM estimation for retrospective analyses of TM and SPOT sensor data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2002, 23, 15–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, T.A.; Hassan, Q.K.; Achari, G. A remote sensing based framework for predicting water quality of dif-ferent source waters. Int. Arch. Photogramm. Remote Sens. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 38, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Brezonik, P.; Menken, K.D.; Bauer, M. Landsat-based remote Sensing of Lake Water Quality characteris-tics, Including Chlorophyll and Colored Dissolved Organic Matter (CDOM). Lake Reserv. Manag. 2005, 21, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Chl-a (mg/m3) | TSS (mg/L) | TP (mg/L) | TKN (mg/L) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry Season | 29/02/2000 | Min | 3.30 | 8.0 | 0.107 | 1.03 |
| Max | 67.7 | 53.0 | 0.192 | 1.96 | ||
| Mean | 17.8 | 29.5 | 0.156 | 1.31 | ||
| STD | 14.8 | 13.0 | 0.021 | 0.21 | ||
| 31/01/2007 | Min | 1.0 | 8.0 | 0.085 | 0.88 | |
| Max | 27.5 | 162.0 | 0.299 | 2.04 | ||
| Mean | 12.9 | 41.2 | 0.158 | 1.22 | ||
| STD | 7.1 | 36.0 | 0.050 | 0.30 | ||
| 06/02/2015 | Min | 1.86 | 5.0 | 0.0821 | 0.821 | |
| Max | 43.2 | 92.0 | 0.203 | 1.85 | ||
| Mean | 14.08 | 31.04 | 0.143 | 1.09 | ||
| STD | 8.38 | 21.54 | 0.033 | 0.22 | ||
| Wet Season | 06/07/2000 | Min | 6.20 | 3.0 | 0.036 | 0.95 |
| Max | 106.5 | 70.0 | 0.238 | 2.89 | ||
| Mean | 27.7 | 20.6 | 0.101 | 1.38 | ||
| STD | 23.4 | 15.3 | 0.044 | 0.48 | ||
| 22/08/2007 | Min | 3.50 | 4.0 | 0.016 | 0.87 | |
| Max | 76.5 | 22.0 | 0.280 | 2.61 | ||
| Mean | 16.1 | 11.3 | 0.092 | 1.35 | ||
| STD | 16.0 | 7.0 | 0.064 | 0.37 | ||
| 15/09/2015 | Min | 4.80 | 3.0 | 0.023 | 0.77 | |
| Max | 76.0 | 39.0 | 0.295 | 2.93 | ||
| Mean | 18.4 | 13.7 | 0.084 | 1.57 | ||
| STD | 16.8 | 9.3 | 0.047 | 0.34 | ||
| Bands/Band Ratios | Dry Season | Wet Season | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl-a (mg/m3) | TSS (mg/L) | Chl-a (mg/m3) | TSS (mg/L) | |
| Blue (B) | −0.70 ** | −0.29 | −0.45 ** | −0.55 ** |
| Green (G) | −0.60 ** | −0.27 | −0.31 ** | −0.35 ** |
| Red (R) | −0.80 ** | −0.07 | −0.42 ** | −0.41 ** |
| Near Infrared (NIR) | −0.63 ** | 0.20 | −0.24 | −0.32 ** |
| B/G | 0.26 | −0.27 | −0.23 | −0.15 |
| B/R | 0.78 ** | −0.36 ** | 0.20 | 0.05 |
| B/NIR | 0.60 | −0.47 ** | −0.30 ** | −0.36 ** |
| G/B | −0.25 | 0.25 | 0.14 | 0.06 |
| G/R | 0.82 ** | −0.22 | 0.76 ** | 0.64 ** |
| G/NIR | 0.54 | −0.46 ** | −0.12 | 0.49 ** |
| R/B | −0.76 ** | 0.32 | −0.28 | −0.29 |
| R/G | −0.81 ** | 0.22 | −0.76 ** | −0.68 ** |
| R/NIR | −0.06 | −0.49 ** | −0.43 ** | −0.62 ** |
| NIR/B | −0.56 | 0.43 ** | −0.01 | −0.06 |
| NIR/G | −0.51 | 0.46 ** | −0.01 | −0.01 |
| NIR/R | 0.08 | 0.50 ** | 0.29 | 0.08 |
| Season | Parameter | R2 | Standard Error | p Value | Durbin-Watson | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Chl-a | 0.84 | 8.84 | 0 | 1.797 | 48 |
| TSS | 0.67 | 6.07 | 0 | 2.249 | 48 | |
| Wet | Chl-a | 0.48 | 20.88 | 0.005 | 2.103 | 38 |
| TSS | 0.6 | 12.77 | 0.002 | 1.65 | 38 |
| Season | Water Quality Parameters | Regression Equations Derived |
|---|---|---|
| Dry | Chl-a (mg/m3) | = 881.1 × (B/R) − 1784.7 × (G/R) +5331.5 × (R/B) − 3096.2 × (R/G) × 1167 × (B) + 525.5 |
| TSS (mg/L) | = 517.91 × (R/NIR) − 8.86 × (G/NIR) − 799.23 × (NIR/B) + 127.76 × (NIR/G) + 1100.92 × (NIR/R) − 74.63 × (B/NIR) − 1037.79 | |
| Wet | Chl-a (mg/m3) | = −1067.77 × (G/R) − 2144.45 × (R/G) − 35.04 × (R/NIR) + 297.75 × (R) + 3095.6 |
| TSS (mg/L) | = 361.89 × (R) − 1018.25 × (G/R) − 1919.21 × (R/G) − 26.15 × (R/NIR) − 182.90 × (B) + 2855.76 |
| Bands | Season | Season | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | |
| TP (mg/L) | TKN (mg/L) | |||
| B | 0.34 ** | 0.59 ** | −0.36 ** | 0.01 |
| G | 0.35 ** | 0.55 ** | −0.12 | 0.03 |
| R | 0.50 ** | 0.59 ** | −0.31 ** | 0 |
| NIR | 0.31 ** | 0.61 ** | 0.03 | 0.08 |
| B/G | −0.21 | −0.17 | 0.19 | −0.05 |
| B/R | −0.52 ** | −0.40 ** | 0.19 | 0.05 |
| B/NIR | −0.28 | −0.54 ** | 0.07 | −0.29 ** |
| G/B | 0.21 | 0.2 | −0.19 | 0.07 |
| G/R | −0.53 ** | −0.58 ** | 0.03 | 0.29 ** |
| G/NIR | −0.21 | −0.62 ** | −0.1 | −0.32 ** |
| R/B | 0.52 ** | 0.47 ** | −0.17 | −0.08 |
| R/G | 0.52 ** | 0.60 ** | −0.04 | −0.29 ** |
| R/NIR | 0.19 | −0.52 ** | −0.15 | −0.49 ** |
| NIR/B | 0.27 | 0.62 ** | −0.06 | 0.21 |
| NIR/G | 0.21 | 0.66 ** | 0.07 | 0.25 |
| NIR/R | −0.2 | 0.59 ** | 0.14 | 0.42 ** |
| Chl-a (mg/m3) | −0.02 | 0.47 ** | 0.51 ** | 0.91 ** |
| TSS (mg/L) | 0.90 ** | 0.57 ** | 0.79 ** | 0.73 ** |
| Season | Parameter | R2 | Standard Error | Durbin-Watson | Observations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | TP | 0.92 | 0.015 | 1.974 | 50 |
| TKN | 0.94 | 0.097 | 2.027 | 50 | |
| Wet | TP | 0.89 | 0.025 | 2.488 | 38 |
| TKN | 0.93 | 0.166 | 1.627 | 48 |
| Season | Water Quality (mg/L) | Regression Equations Derived |
|---|---|---|
| Dry | TP | = 0.001(TSS) − 0.202(G/R) − 2.56(NIR) + 0.468 |
| TKN | = 0.008(TSS) + 0.009 (Chl-a) + 3.91(B) − 4.35(R) + 0.641 | |
| Wet | TP | = 0.002(TSS) + 0.154(B/R) + 1.66(NIR/G) − 1.23(NIR/R) − 0.232 |
| TKN | = 0.017(Chl-a) + 0.001(TSS) − 0.057(B/NIR) + 0.345(G/NIR) − 1.09(R/NIR) − 0.249(NIR/R) + 2.21 |
| Dry Season | Wet Season | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chl-a (mg/m3) | Year | 0–50 | 50–100 | 100–150 | 150–200 | >200 | 0–20 | 20–40 | 40–60 | 60–80 | 80–100 | >100 | |
| 2000 | 51.6 | 287.3 | 722.9 | 175.2 | 93.1 | 514.7 | 842.9 | 50.5 | 7 | 0.1 | 0 | ||
| 2007 | 96.2 | 334.1 | 451 | 317.9 | 170.2 | 616.7 | 687.8 | 63.8 | 37.9 | 3.6 | 5.4 | ||
| 2015 | 117.4 | 226.6 | 767.3 | 247.9 | 8 | 913.5 | 346.2 | 80.6 | 66.1 | 8.8 | 0 | ||
| TSS (mg/L) | Year | 0–40 | 40–80 | 80–120 | 120–160 | >160 | 0–15 | 15–30 | 30–45 | 45–60 | 60–75 | >75 | |
| 2000 | 31.9 | 17.9 | 543.9 | 735.8 | 85.4 | 605.4 | 772.2 | 31.5 | 6 | 0.1 | 0 | ||
| 2007 | 46.9 | 74.2 | 389.9 | 845.2 | 58.5 | 555.8 | 739.8 | 67.1 | 42.4 | 3.5 | 6.3 | ||
| 2015 | 149.8 | 154.2 | 222.2 | 253.3 | 637 | 932.7 | 359.2 | 75.8 | 45.4 | 2.4 | 0 | ||
| Total Phosphate (mg/L) | Year | 0–0.07 | 0.07–0.15 | 0.15–0.20 | 0.20–0.25 | 0.25–0.30 | >0.30 | 0–0.07 | 0.07–0.15 | 0.15–0.20 | 0.20–0.25 | 0.25–0.30 | >0.30 |
| 2000 | 5.9 | 431.3 | 968 | 6.8 | 0.6 | 2 | 211.5 | 1166 | 22.3 | 5.9 | 3.5 | 6 | |
| 2007 | 57.4 | 530.5 | 627.4 | 178.1 | 18.5 | 3 | 209.8 | 997 | 45.9 | 23.3 | 20.7 | 117.8 | |
| 2015 | 71.7 | 15.8 | 885.3 | 442.5 | 0.01 | 0 | 104.5 | 1244 | 9.6 | 6.1 | 5.9 | 45.2 | |
| TKN (mg/L) | Year | 0–1.0 | 1–1.5 | 1.5–2.0 | 2.0–2.7 | 2.7–3.5 | >3.5 | 0–1.0 | 1–1.5 | 1.5–2.0 | 2.0–2.7 | 2.7–3.5 | >3.5 |
| 2000 | 6.7 | 1336 | 58.4 | 10.2 | 2.2 | 2 | 280.1 | 794 | 313 | 23.8 | 3.6 | 0 | |
| 2007 | 264.7 | 963.4 | 138.1 | 11.2 | 0.3 | 0 | 300.8 | 683 | 339 | 86.6 | 1.2 | 4.7 | |
| 2015 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 110.7 | 697.7 | 510.6 | 5 | 709.4 | 432 | 152 | 103 | 18.6 | 0 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hajigholizadeh, M.; Moncada, A.; Kent, S.; Melesse, A.M. Land–Lake Linkage and Remote Sensing Application in Water Quality Monitoring in Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA. Land 2021, 10, 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020147
Hajigholizadeh M, Moncada A, Kent S, Melesse AM. Land–Lake Linkage and Remote Sensing Application in Water Quality Monitoring in Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA. Land. 2021; 10(2):147. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020147
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajigholizadeh, Mohammad, Angelica Moncada, Samuel Kent, and Assefa M. Melesse. 2021. "Land–Lake Linkage and Remote Sensing Application in Water Quality Monitoring in Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA" Land 10, no. 2: 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020147
APA StyleHajigholizadeh, M., Moncada, A., Kent, S., & Melesse, A. M. (2021). Land–Lake Linkage and Remote Sensing Application in Water Quality Monitoring in Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA. Land, 10(2), 147. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10020147







