Impact of Industrial Pollution of Cadmium on Traditional Crop Planting Areas and Land Management: A Case Study in Northwest China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
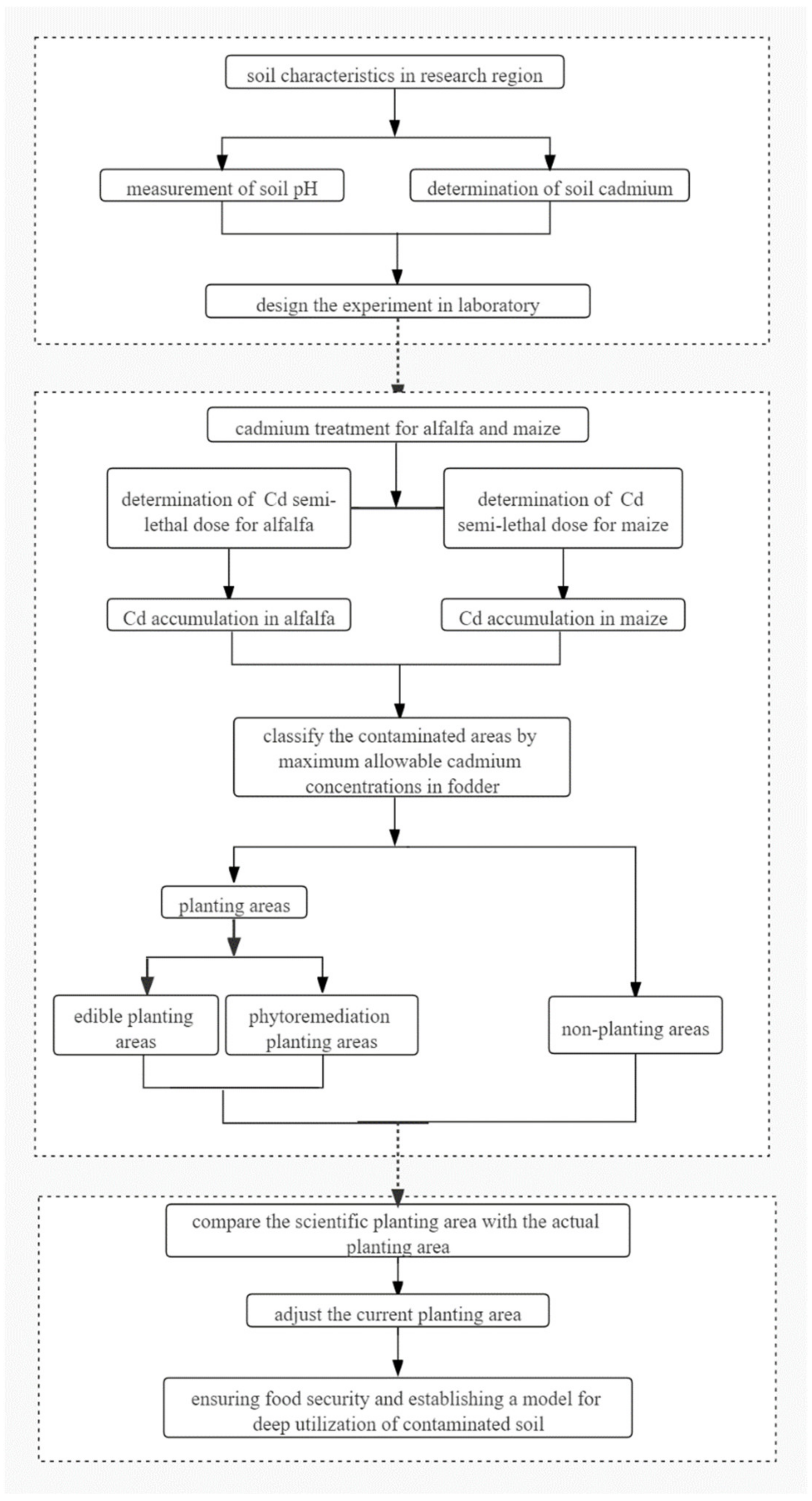
2. Materials and Methods
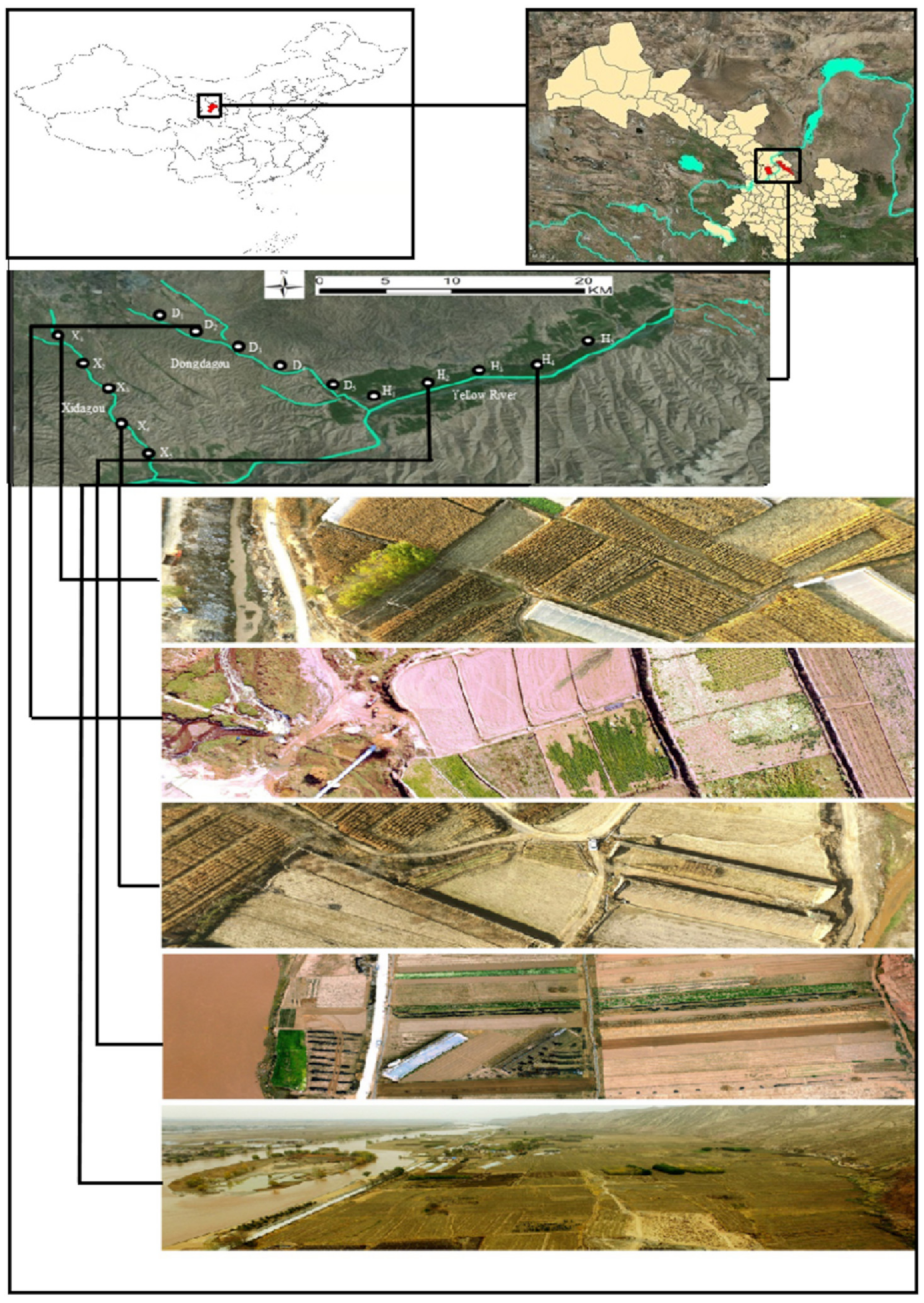
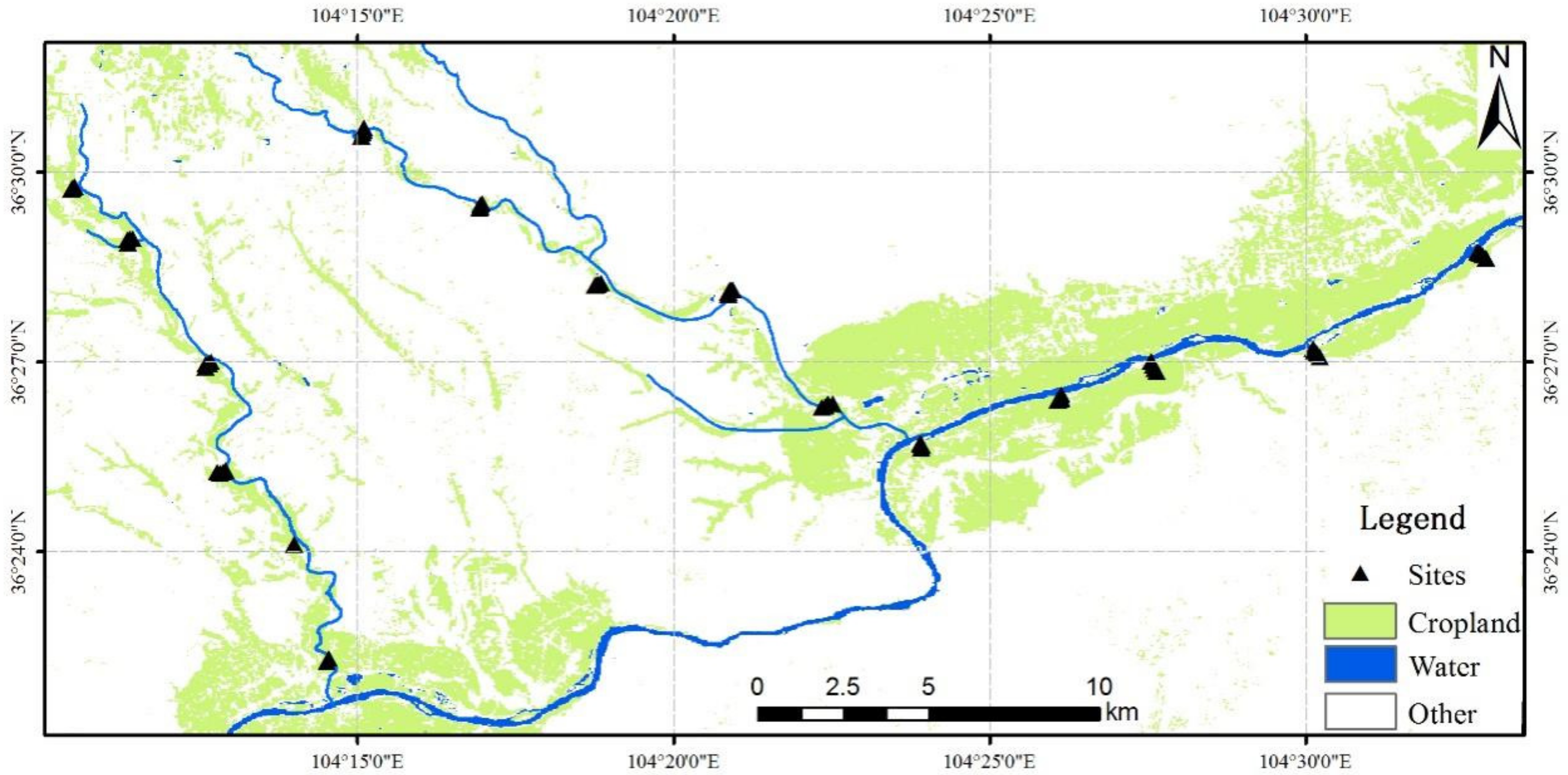
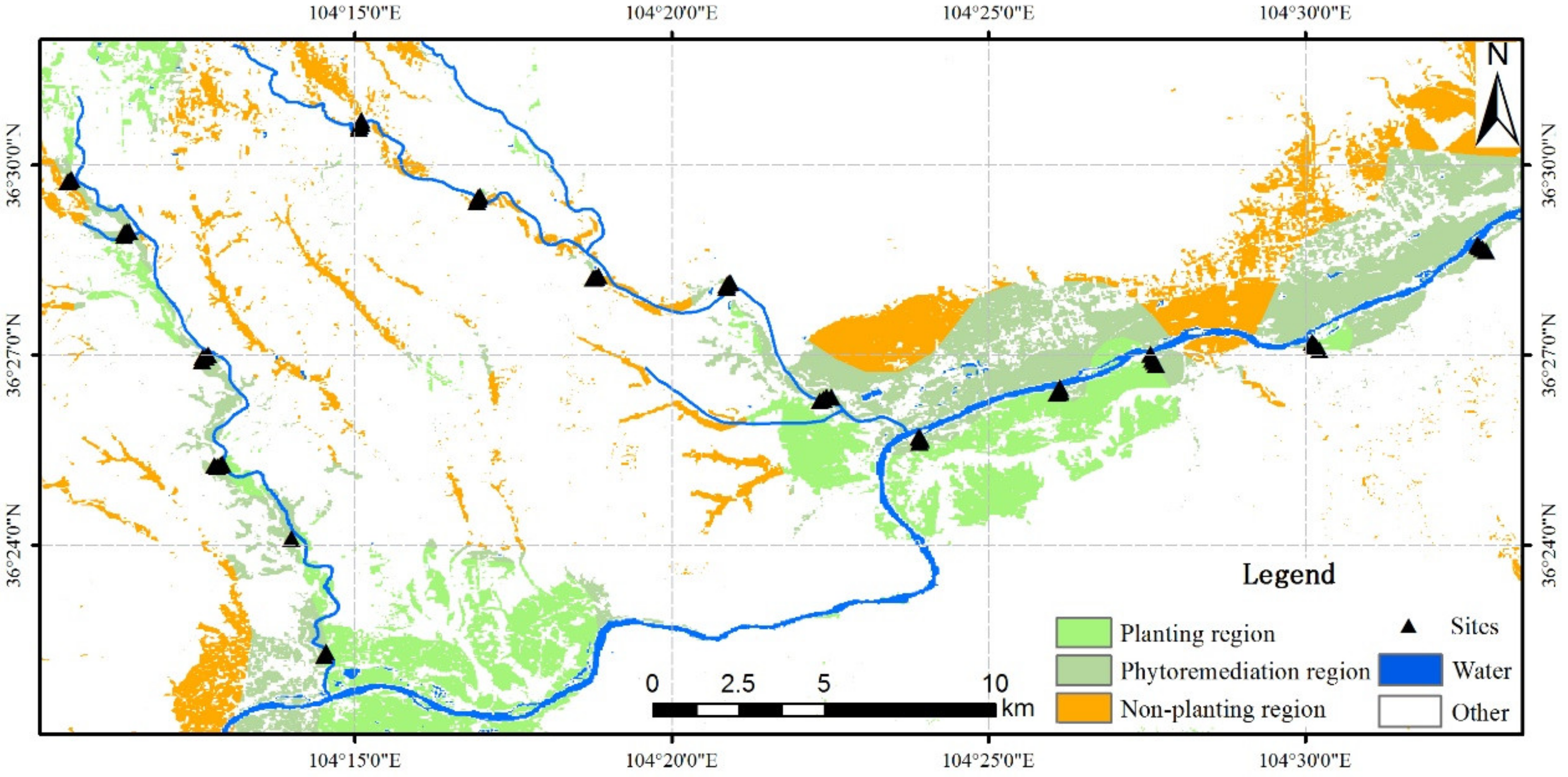
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection and Analysis
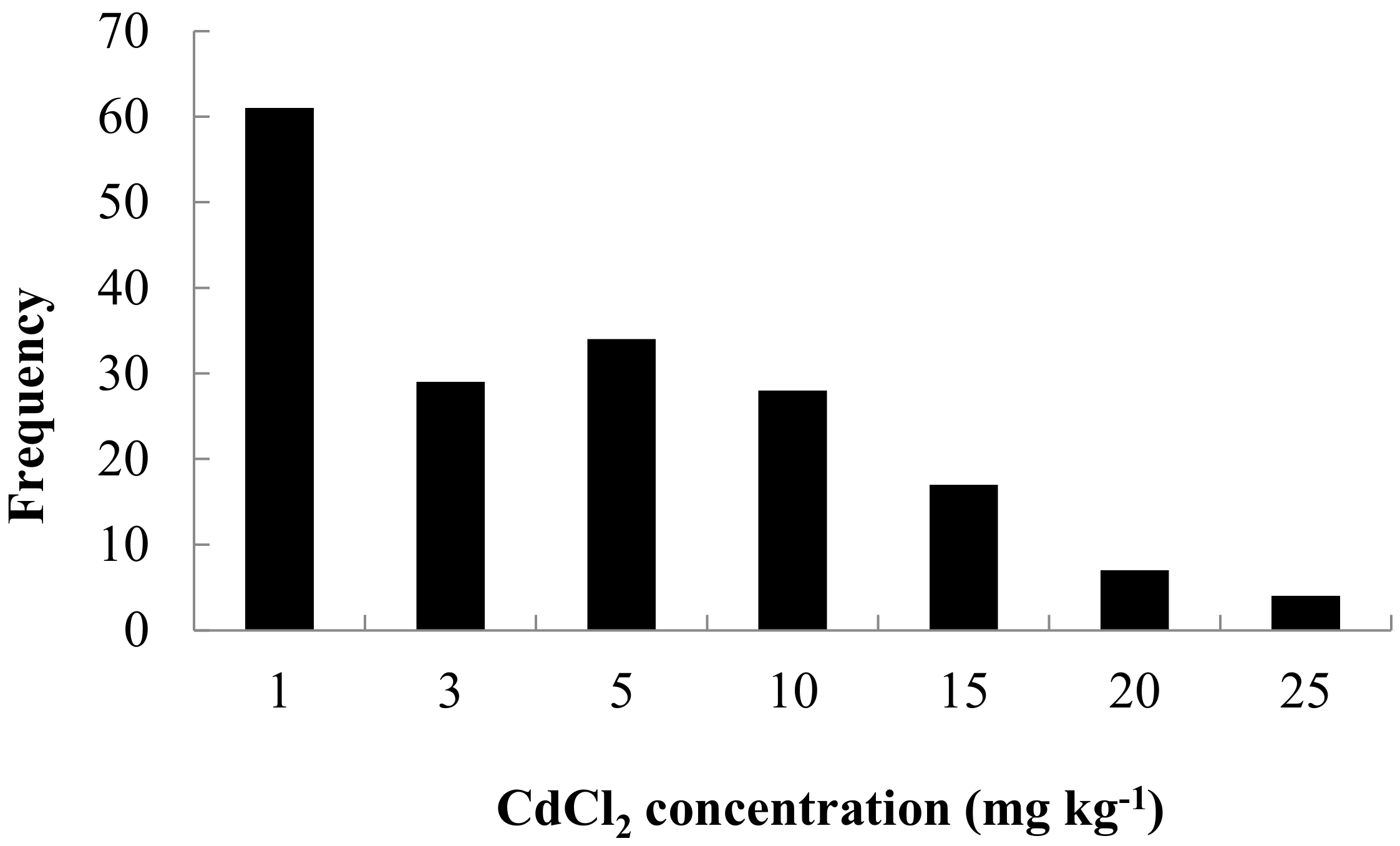
2.3. Plant Materials and Hydroponics Procedure
2.4. Cadmium Accumulation in Plant Materials
2.5. Scanning Electron Microscopy and Energy Dispersive X-rays Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis
2.7. GIS Spatial Analysis
3. Results
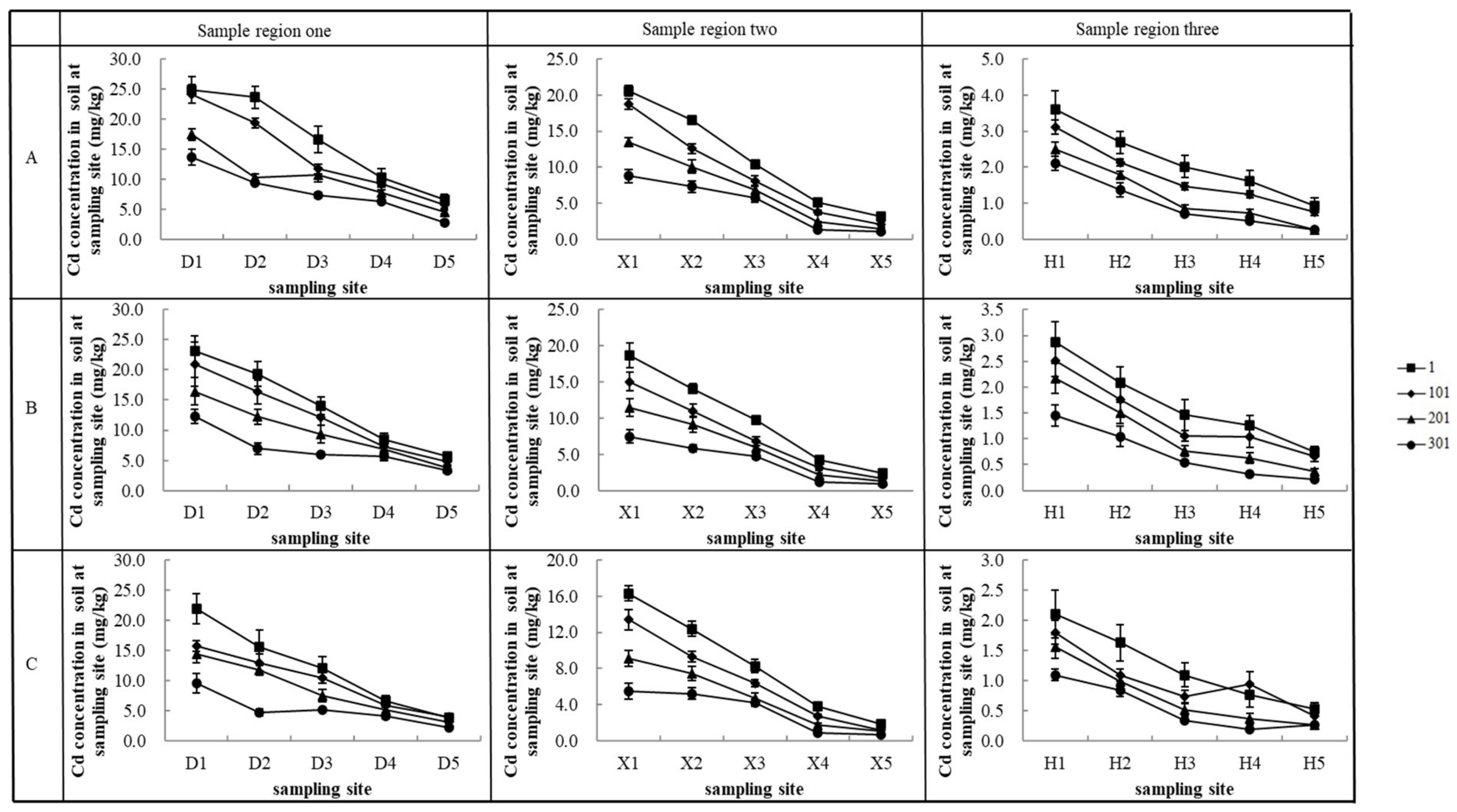
3.1. Spatial Distribution of Cadmium in the Sampling Areas
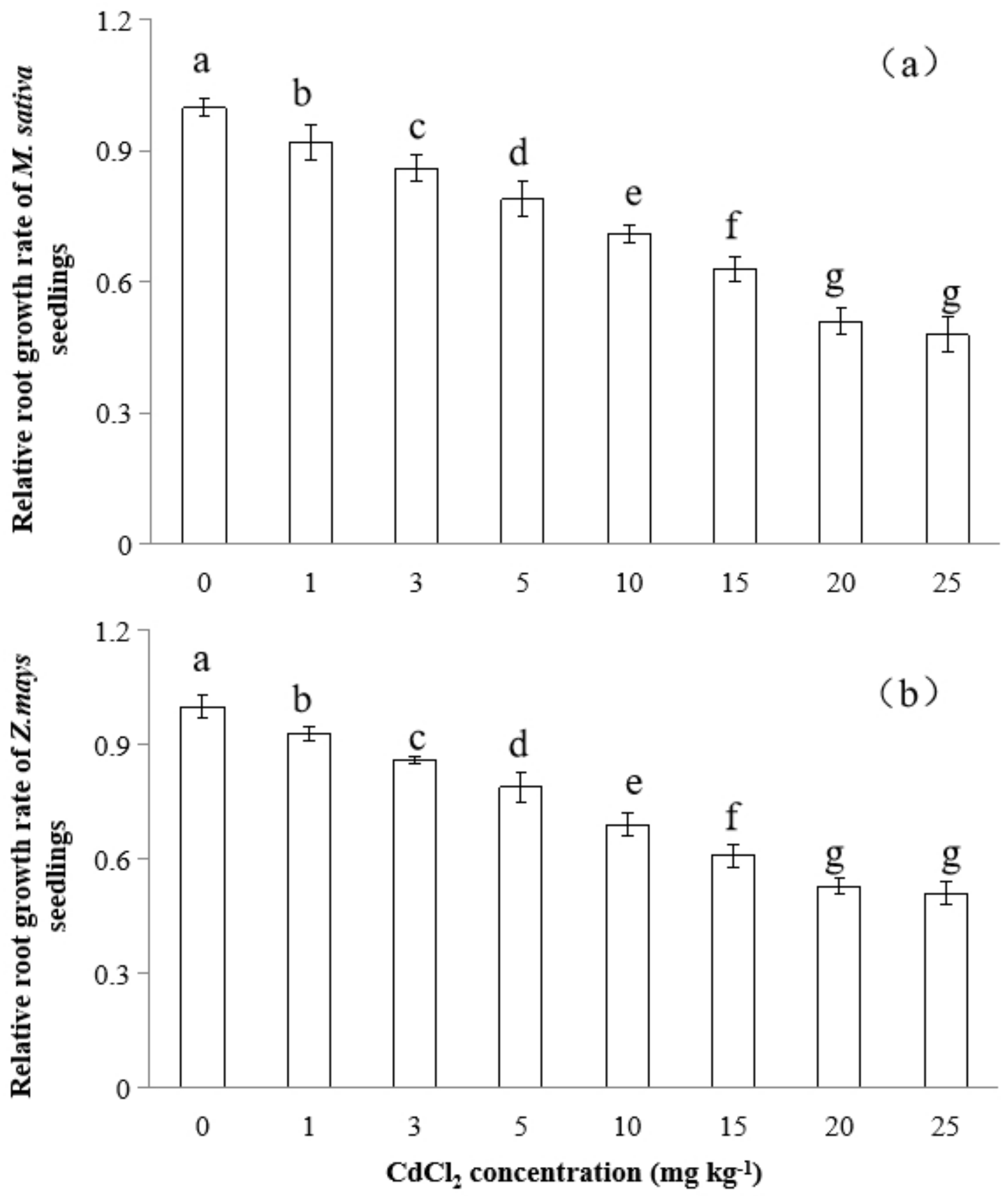
3.2. Cadmium Accumulation in M. sativa and Z. mays
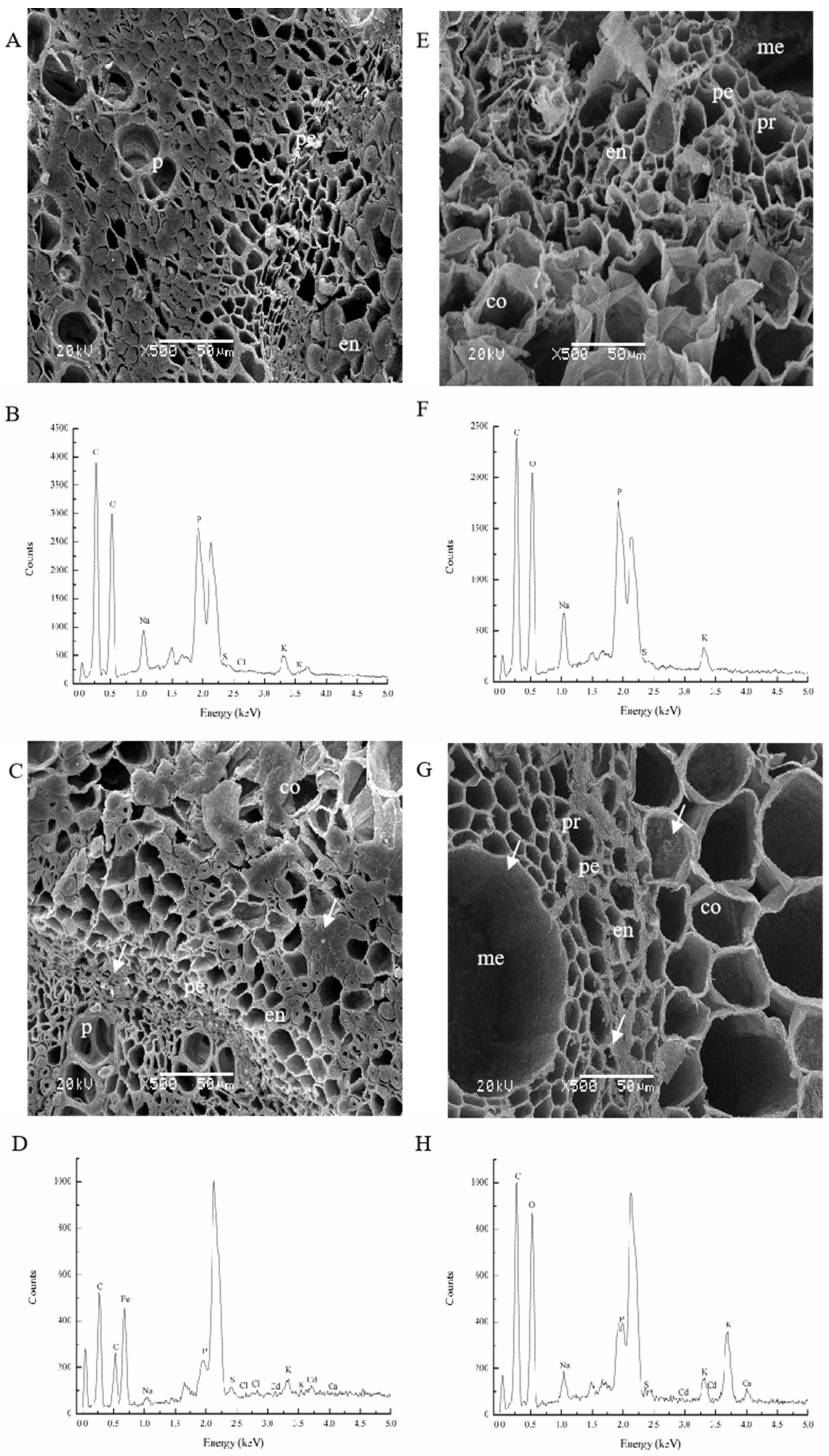
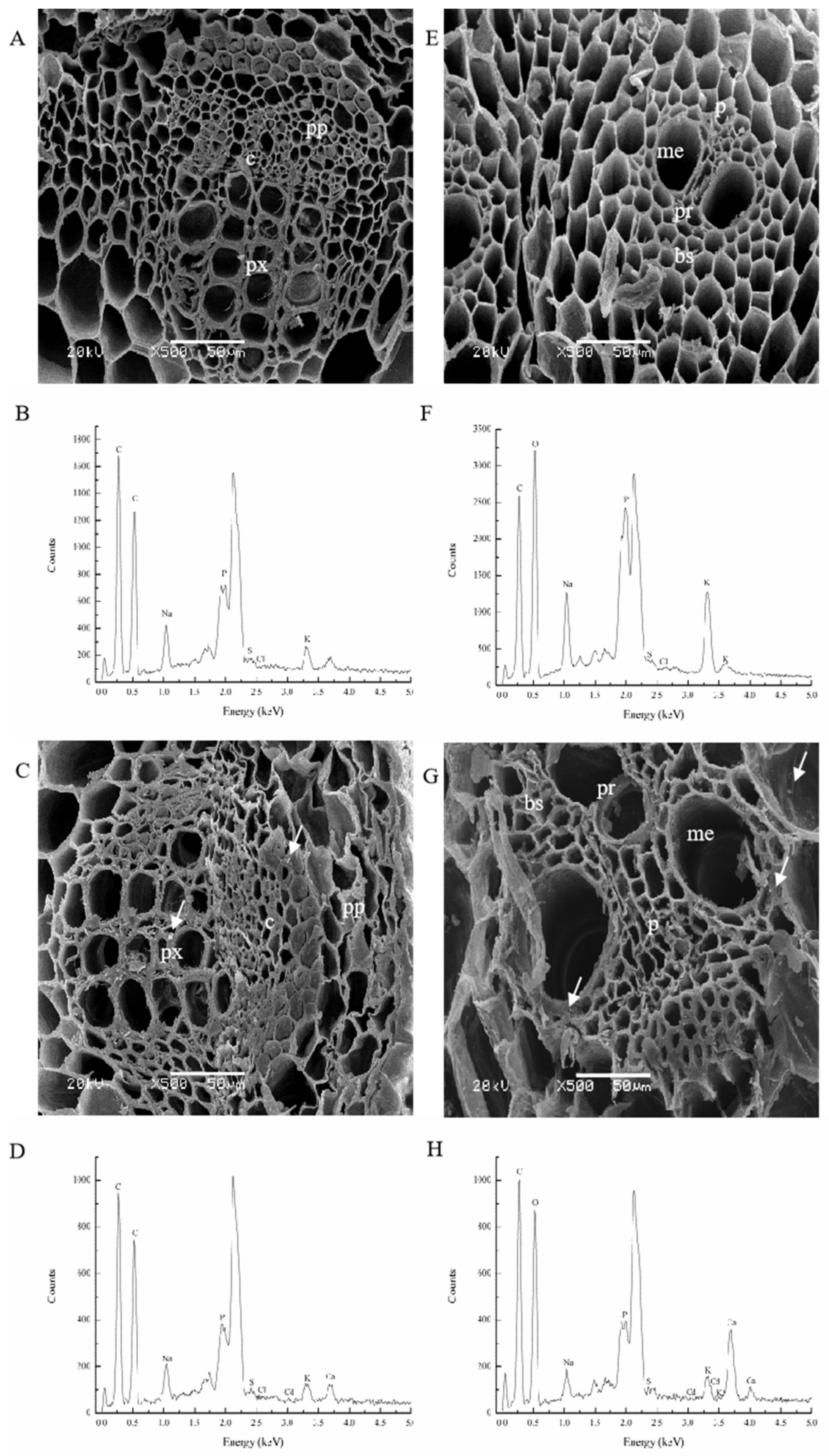
3.3. Cadmium Subcellular Determination in M. sativa and Z. mays
3.4. Situation of Soil Cadmium Pollution in the Study Area
4. Discussion
4.1. Deep Utilization Patterns of M. sativa and Z. mays
4.2. Classified Management Pattern of Contaminated Soil
4.3. Establishment of Deep Utilization Model of Contaminated Soil
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jie, C.; Xie, C.Y.; Hou, Z.R. Transport patterns and numerical simulation of heavy metal pollutants in soils of lead-zinc ore mines. J. Moutain Sci. 2021, 18, 2345–2356. [Google Scholar]
- Do Nascimento, A.R.V.J.; Cunha, G.K.G.; do Nascimento, C.W.A.; da Cunha, K.P.V. Assessing Soil Quality and Heavy Metal Contamination on Scheelite Mining Sites in a Tropical Semi-arid Setting. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebonye, N.M.; Eze, P.N.; John, K.; Agyeman, P.C.; Němeček, K.; Borůvka, L. An in-depth human health risk assessment of potentially toxic elements in highly polluted riverine soils, Příbram (Czech Republic). Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimek, B.; Sitarz, A.; Choczyński, M.; Niklińska, M. The Effects of Heavy Metals and Total Petroleum Hydrocarbons on Soil Bacterial Activity and Functional Diversity in the Upper Silesia Industrial Region (Poland). Water Air Soil Pollut. 2016, 227, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, J.; Franks, A.E.; Lu, Z.; Xu, J.; He, Y. Assembly and variation of root-associated microbiota of rice during their vegetative growth phase with and without lindane pollutant. Soil Ecol. Lett. 2021, 3, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Zhao, Z.; Xing, Z.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y. Comparison of Models for Spatial Distribution and Prediction of Cadmium in Subtropical Forest Soils, Guangdong, China. Land 2021, 10, 906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redondo-Gómez, S.; Mateos-Naranjo, E.; Andrades-Moreno, L. Accumulation and tolerance characteristics of cadmium in a halophytic Cd-hyperaccumulator, Arthrocnemum macrostachyum. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 184, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umer, S.; Hussain, M.; Arfan, M.; Rasul, F. Spatiotemporal variations of metals in urban roadside soils and ornamental plant species of Faisalabad Metropolitan, Pakistan. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Li, M.; Rizwan, M.; Dai, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Hossain, M.M.; Cao, M.; Xiong, S.; Tu, S. Synergistic effect of silicon and selenium on the alleviation of cadmium toxicity in rice plants. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 401, 123393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Gu, C.; Sun, Y.; Li, G.; Li, L.L.; Hao, L. Root defense in salicylic acid-altering Arabidopsis plants in responses to cadmium stress. J. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 40, 1764–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haider, F.U.; Liqun, C.; Coulter, J.A.; Cheema, S.A.; Wu, J.; Zhang, R.; Farooq, M. Cadmium toxicity in plants: Impacts and remediation strategies. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 211, 111887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Ma, X.; Ai, S.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Spatial distribution and source identification of heavy metals in soils under different land uses in a sewage irrigation region, northwest China. J. Soil Sediment. 2016, 16, 1547–1556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.; Yang, B.; Xue, Z.; Wang, Z. Assessing Heavy Metal Contamination Risk in Soil and Water in the Core Water Source Area of the Middle Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, China. Land 2021, 10, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Contaminated land by wildfire effect on ultramafic soil and associated human health and ecological risk. Land 2020, 9, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrikova, A.G.; Apostolova, E.L.; Hanć, A.; Yotsova, E.; Borisova, P.; Sperdouli, I.; Moustakas, M. Cadmium toxicity in Salvia sclarea L.: An integrative response of element uptake, oxidative stress markers, leaf structure and photosynthesis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 209, 111851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Zee, L.; Remigio, A.C.; Casey, L.W.; Purwadi, I.; Yamjabok, J.; van der Ent, A.; Kootstra, G.; Aarts, M.G.M. Quantification of spatial metal accumulation patterns in Noccaea caerulescens by X-ray fluorescence image processing for genetic studies. Plant Methods 2021, 17, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhter, M.F.; Omelon, C.R.; Gordon, R.A.; Moser, D.; Macfie, S.M. Localization and chemical speciation of cadmium in the roots of barley and lettuce. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2014, 100, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavker, N.; Yadav, V.K.; Yadav, K.K.; Cabral-Pinto, M.; Alam, J.; Shukla, A.K.; Alhoshan, M. Removal of cadmium and chromium by mixture of silver nanoparticles and nano-fibrillated cellulose isolated from waste peels of citrus sinensis. Polymers 2021, 13, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koptsik, G.N.; Koptsik, S.V.; Smirnova, I.E.; Sinichkina, M.A. Effect of Soil Degradation and Remediation in Technogenic Barrens on the Uptake of Nutrients and Heavy Metals by Plants in the Kola Subarctic. Eurasian Soil Sci. 2021, 54, 1252–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Wu, F.B.; Zhang, G.P. Influence of cadmium on antioxidant capacity and four microelement concentrations in tomato seedlings (Lycopersicon esculentum). Chemosphere 2006, 64, 1659–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batwa-Ismail, M.Z.; Moodley, R.; Mutanga, O. Elemental analysis of soils along the South African National Road (N3)—a combined approach including statistics, pollution indicators, and geographic information system (GIS). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2021, 19, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Facchinelli, A.; Sacchi, E.; Mallen, L. Multivariate statistical and GIS-based approach to identify heavy metal sources in soils. Environ. Pollut. 2001, 114, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhaliwal, S.S.; Setia, R.K.; Bhatti, S.S.; Singh, J. Potential Ecological Impacts of Heavy Metals in Sediments of Industrially Contaminated Perennial Drain of India. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2021, 2021, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micó, C.; Recatalá, L.; Peris, M.; Sánchez, J. Assessing heavy metal sources in agricultural soils of an European Mediterranean area by multivariate analysis. Chemosphere 2006, 65, 863–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.P.; Wang, S.L.; Prete, D.; Xue, S.Y.; Nan, Z.R.; Zang, F.; Zhang, Q. Accumulation and interaction of fluoride and cadmium in the soil-wheat plants ystem from the waste water irrigated soil of an oasis region in northwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 595, 344–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Yang, F.; Xu, C.; Yang, H.; Liu, W. Status of metal accumulation in farmland soils across China: From distribution to risk assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 176, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, F.; Wang, S.; Nan, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y. Accumulation, spatio-temporal distribution, and risk assessment of heavy metals in the soil-corn system around a polymetallic mining area from the Loess Plateau, northwest China. Geoderma 2017, 305, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quispe-Jofré, A.; Philimon, P.P.; Alfaro-Lira, S. Socio-environmental conflict over abandoned mining waste in Copaquilla, Chile. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.A.H.; Parvez, L.; Islam, M.A.; Dampare, S.B.; Suzuki, S. Heavy metal pollution of coal mine-affected agricultural soils in the northern part of Bangladesh. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 173, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varol, M. Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 195, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.Q.; Yang, Z.F.; Yu, T.; Zhang, C.S.; Hou, Q.Y. Predicting spatial and temporal variation of Cd concentration in rice grains in the Lower Changjiang Plain during 2004–2014 based on soil geochemical survey data with GIS. J. Geochem. Explor. 2019, 200, 276–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Subrahmanyam, G.; Mondal, R.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Shabnam, A.A.; Jigyasu, D.K.; Yu, Z.G. Bio-remediation approaches for alleviation of cadmium contamination in natural resources. Chemosphere 2021, 268, 128855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nan, Z.R.; Zhao, C.Y. Heavy metal concentrations in gray calcareous soils of Baiyin region, Gansu province, PR China. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2000, 118, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.T.; Ji, W.H.; Yang, F.; Lv, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. The function of constructed wetland in reducing the risk of heavy metals on human health. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 181, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, Y.-b.; Gou, X.; Su, Y.-B.; Wang, G. Risk assessment of heavy metals in soils and vegetables around non-ferrous metals mining and smelting sites, Baiyin, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 18, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.W.; Li, C.S. Competitive Adsorption on Exotic Heavy Metals Ions in Sediments of the Yellow River. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2003, 22, 693–696. [Google Scholar]
- Song, Y.; Jin, L.; Wang, X. Cadmium absorption and transportation pathways in plants. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2017, 19, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Song, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhuo, R.Y.; Jin, L. Screening of Cd tolerant genotypes and isolation of metallothionein genes in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 3627–3633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, M.I.N.; Guo, H.J.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, G.W.; Jun, Y.E.; Hou, Z.A. Irrigation water salinity and N fertilization: Effects on ammonia oxidizer abundance, enzyme activity and cotton growth in a drip irrigated cotton field. J. Integr. Agric. 2016, 15, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Tu, C.; Ma, L.Q. Effects of arsenic concentrations and forms on arsenic uptake by the hyperaccumulator ladder brake. J. Environ. Qual. 2002, 31, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Cáceres, M.L.; Hattab, S.; Hattab, S.; Boussetta, H.; Banni, M.; Hernández, L.E. Specific mechanisms of tolerance to copper and cadmium are compromised by a limited concentration of glutathione in alfalfa plants. Plant. Sci. 2015, 233, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Retamal-Salgado, J.; Matus, I.; Walter, I.; Hirzel, J. Absorption and distribution of cadmium of three maize hybrids in three environments. J. Soil Sci. Plant Nutr. 2017, 17, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shakeel, A.A.; Mohsin, T.; Saddam, H.; Mingchen, B.; Wang, L.C.; Imran, K.; Ehsan, U.; Shahbaz, A.T.; Rana, A.S.; Babar, S. Cadmium toxicity in Maize (Zea mays L.): Consequences on antioxidative systems, reactive oxygen species and cadmium accumulation. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17022–17030. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO. Joint FAO/WHO Food Standard Programme, Codex Committee on Food Additives and Contaminants; 38th Session; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- FAO/WHO. Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives; Technical Report Series, 631; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Probst, A.; Liao, B. Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicholson, F.A.; Smith, S.R.; Alloway, B.J.; Carlton-Smith, C.; Chambers, B.J. An Inventory of Heavy Metals Inputs to Agricultural Soils in England and Wales. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mishra, R.K.; Sarma, K. Mapping spatial distribution of traffic induced criteria pollutants and associated health risks using kriging interpolation tool in Delhi. J. Transp. Health 2020, 18, 100879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, K.; Kumar, P.; Mann, G.S.; Khare, M. Mapping spatial distribution of particulate matter using Kriging and Inverse Distance Weighting at supersites of megacity Delhi. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 54, 101997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.C.; Noguchi, R.; Ahamed, T. Integrating an Expert System, GIS, and Satellite Remote Sensing to Evaluate Land Suitability for Sustainable Tea Production in Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 4136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selmy, S.A.; Al-Aziz, S.H.A.; Jiménez-Ballesta, R.; García-Navarro, F.J.; Fadl, M.E. Soil Quality Assessment Using Multivariate Approaches: A Case Study of the Dakhla Oasis Arid Lands. Land 2021, 10, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römkens, P.F.A.M.; Salomons, W. Cd, Cu, and Zn solubility in arable and forest soils: Consequences of land use changes for metal mobility and risk assessment. Soil Sci. 2000, 163, 859–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexakis, D.E. Multielement contamination of land in the margin of highways. Land 2021, 10, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Variety | Soil | Fodder | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH < 6.5 | 6.5 < pH < 7.5 | pH > 7.5 | Compound Feed | |
| Cd concentration (mg kg−1) | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| Soil Cadmium Concentration (mg kg−1) | Cadmium Concentration in Medicago sativa (mg kg−1) | Cadmium Concentration in Zea mays (mg kg−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Root | Stem | Leaf | Root | Stem | Leaf | |
| 0.15 | 0.31 ± 0.03a | 0.13 ± 0.01a | 0.09 ± 0.01a | 0.30 ± 0.03a | 0.14 ± 0.01a | 0.07 ± 0.01a |
| 1 | 359.14 ± 19.87b | 37.79 ± 13.64b | 25.71 ± 12.38b | 204.88 ± 11.87b | 63.81 ± 5.64b | 28.59 ± 3.38b |
| 3 | 616.04 ± 31.75c | 56.31 ± 20.18cd | 36.59 ± 18.98b | 580.73 ± 62.75c | 153.49 ± 17.18c | 79.41 ± 9.98c |
| 5 | 1337.51 ± 124.21bc | 47.41 ± 13.83bc | 35.35 ± 18.04b | 854.46 ± 89.21d | 324.61 ± 37.83d | 118.69 ± 13.04d |
| 10 | 1280.38 ± 108.21d | 71.70 ± 31.66d | 67.33 ± 41.21c | 1289.45 ± 138.21e | 798.96 ± 82.66e | 393.37 ± 42.21e |
| 15 | 1456.33 ± 142.30de | 129.71 ± 52.27e | 105.52 ± 53.25d | 1159.67 ± 122.30e | 518.65 ± 64.27ed | 281.97 ± 31.25e |
| 20 | 1576.14 ± 153.22ef | 148.78 ± 47.60f | 122.58 ± 63.53e | 1177.62 ± 123.22e | 697.23 ± 72.60ef | 358.14 ± 38.53e |
| 25 | 1662.63 ± 175.33f | 157.47 ± 61.26f | 139.43 ± 70.52f | 1528.70 ± 165.33f | 811.42 ± 86.26f | 465.46 ± 53.52f |
| Cd Concentration (mg kg−1) | M. sativa | Z. mays | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TF | BCF | TF | BCF | |
| 1 | 0.10 ± 0.0c | 36.6 ± 0.1d | 0.23 ± 0.1a | 46.3 ± 0.6c |
| 3 | 0.08 ± 0.1ab | 15.4 ± 0.1c | 0.20 ± 0.1a | 38.8 ± 0.8b |
| 5 | 0.03 ± 0.1a | 8.31 ± 0.2b | 0.26 ± 0.0ab | 44.4 ± 1.3c |
| 10 | 0.05 ± 0.1a | 6.94 ± 0.3a | 0.33 ± 0.0b | 39.1 ± 2.3b |
| 15 | 0.08 ± 0.1b | 7.83 ± 0.3ab | 0.36 ± 0.0b | 24.7 ± 4.2a |
| 20 | 0.09 ± 0.1b | 6.76 ± 0.3a | 0.42 ± 0.1c | 23.7 ± 5.1a |
| 25 | 0.09 ± 0.1bc | 5.93 ± 0.4a | 0.39 ± 0.1bc | 26.9 ± 5.6a |
| Cadmium Concentration (mg kg−1) | Aboveground Biomass (g) | Underground Biomass (g) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| M. sativa | Z. mays | M. sativa | Z. mays | |
| 0 | 0.041 ± 0.011a | 0.235 ± 0.047a | 0.0096 ± 0.011a | 0.053 ± 0.012a |
| 1 | 0.042 ± 0.009a | 0.242 ± 0.029a | 0.0094 ± 0.009a | 0.052 ± 0.013a |
| 3 | 0.039 ± 0.008b | 0.239 ± 0.026b | 0.0091 ± 0.008b | 0.052 ± 0.011a |
| 5 | 0.038 ± 0.009bc | 0.238 ± 0.023bc | 0.0086 ± 0.006c | 0.048 ± 0.009b |
| 10 | 0.037 ± 0.006c | 0.233 ± 0.031c | 0.0072 ± 0.004d | 0.039 ± 0.006c |
| 15 | 0.035 ± 0.004d | 0.219 ± 0.026cd | 0.0055 ± 0.004e | 0.033 ± 0.003d |
| 20 | 0.031 ± 0.004de | 0.208 ± 0.019d | 0.0051 ± 0.003f | 0.027 ± 0.001e |
| 25 | 0.021 ± 0.002f | 0.097 ± 0.005e | 0.0046 ± 0.002g | 0.022 ± 0.002f |
| Type | M. sativa | Z. mays | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | Area (km2) | Ratio (%) | |
| Non-planting region | 7.44 | 35.64 | 7.44 | 35.65 |
| Planting region | 5.924 | 28.374 | 5.884 | 28.184 |
| Phytoremediation region | 7.514 | 35.994 | 7.55 | 36.17 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, Y.; Li, W.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, C. Impact of Industrial Pollution of Cadmium on Traditional Crop Planting Areas and Land Management: A Case Study in Northwest China. Land 2021, 10, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10121364
Song Y, Li W, Xue Y, Zhou H, Wang W, Liu C. Impact of Industrial Pollution of Cadmium on Traditional Crop Planting Areas and Land Management: A Case Study in Northwest China. Land. 2021; 10(12):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10121364
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Yu, Wenlong Li, Yating Xue, Huakun Zhou, Wenying Wang, and Chenli Liu. 2021. "Impact of Industrial Pollution of Cadmium on Traditional Crop Planting Areas and Land Management: A Case Study in Northwest China" Land 10, no. 12: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10121364
APA StyleSong, Y., Li, W., Xue, Y., Zhou, H., Wang, W., & Liu, C. (2021). Impact of Industrial Pollution of Cadmium on Traditional Crop Planting Areas and Land Management: A Case Study in Northwest China. Land, 10(12), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/land10121364







