Changes in Phytoplankton and Water Quality during Sustainable Restoration of an Urban Lake Used for Recreation and Water Supply
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
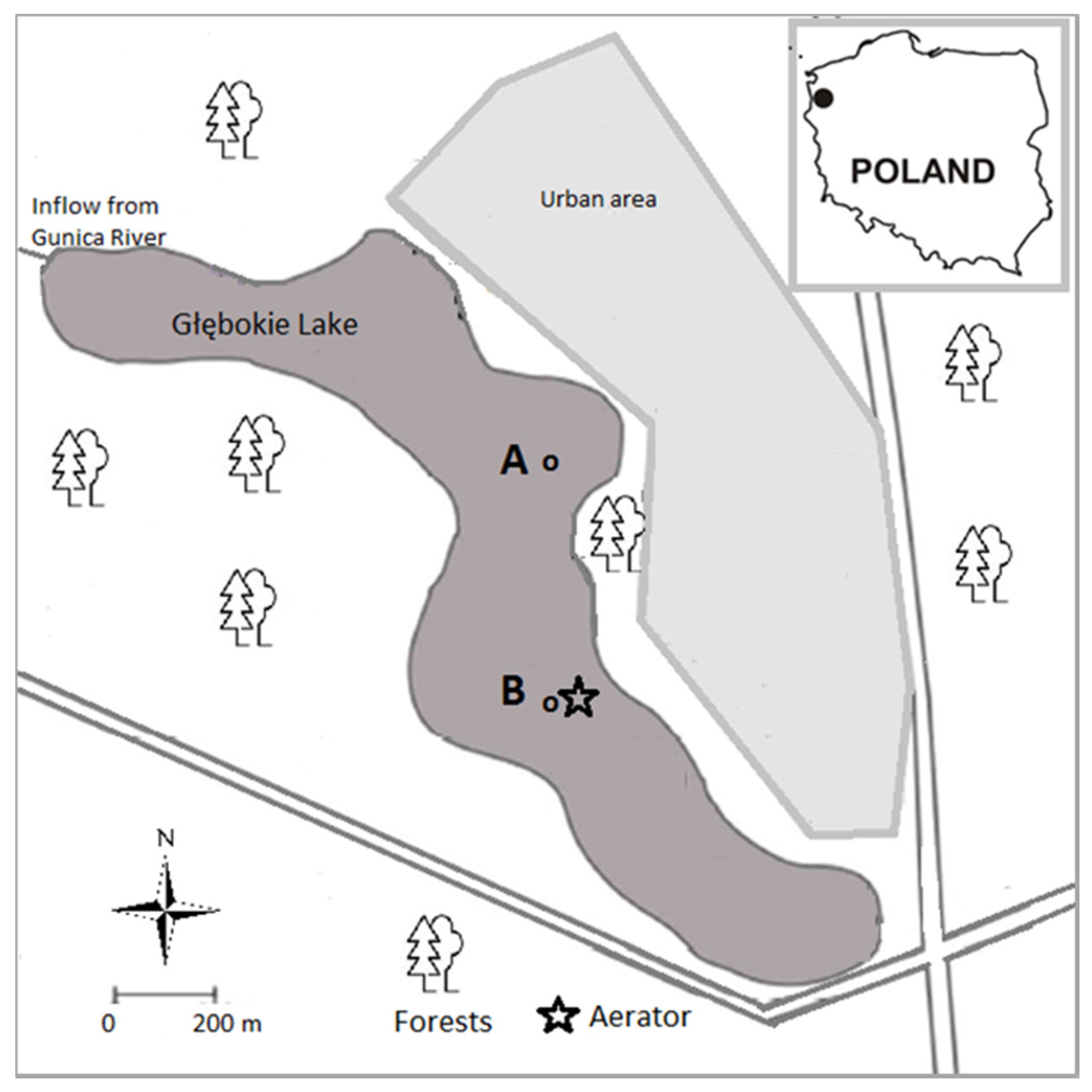
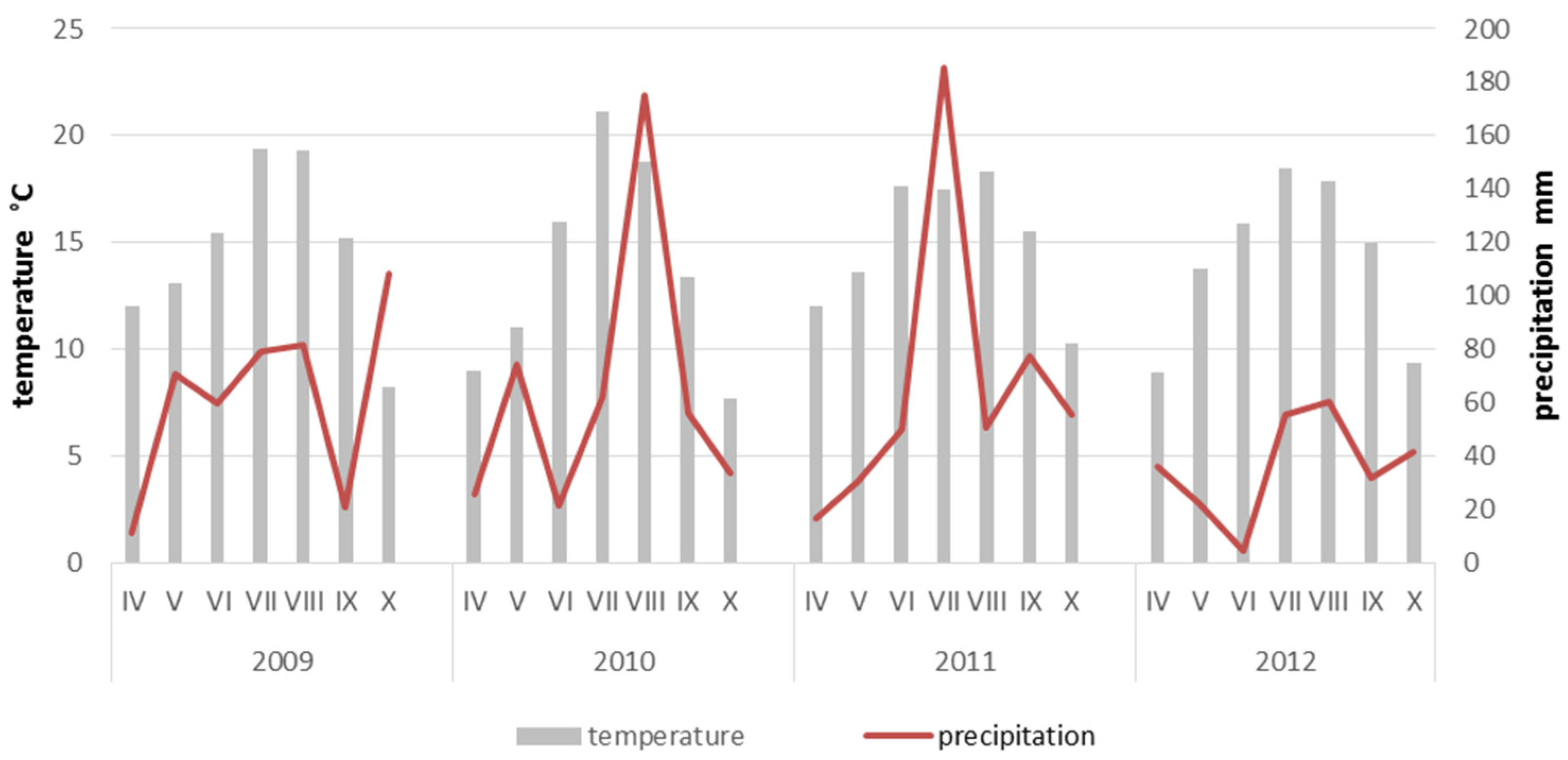
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Restoration Treatments
2.3. Sampling and Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analyses
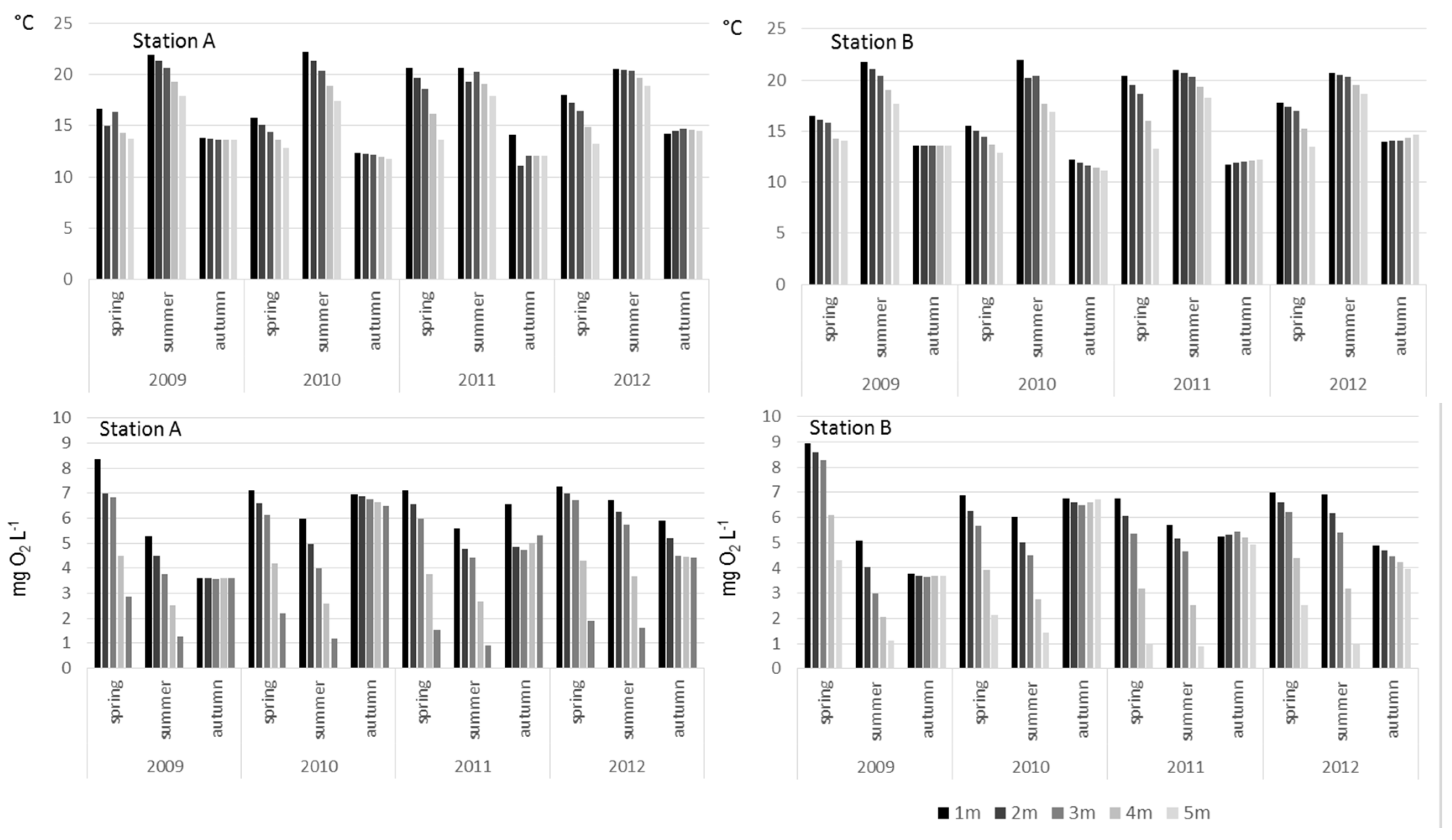
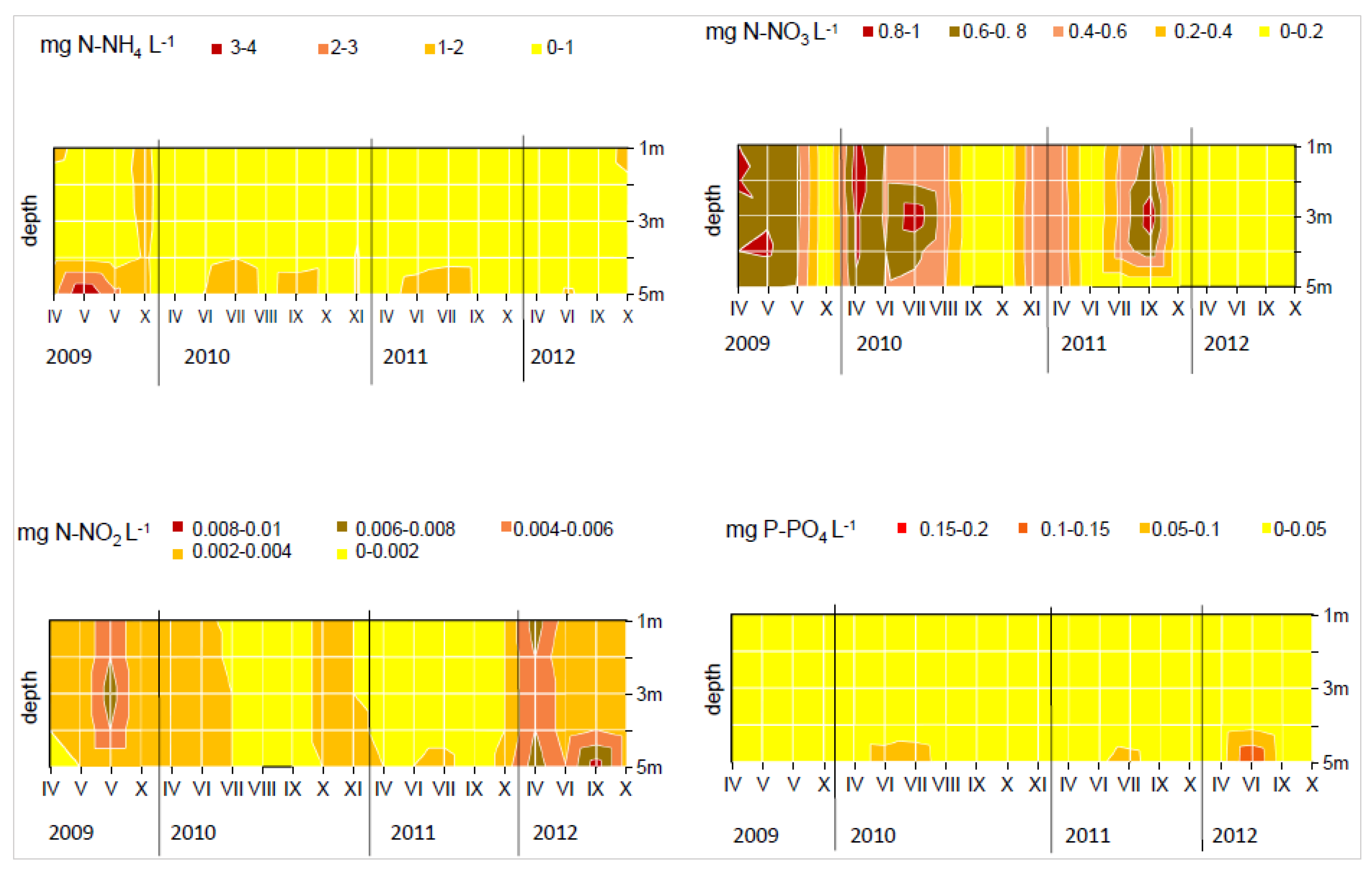
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lossow, K.; Gawrońska, H.; Jaszczułt, R. Attempts to use wind energy for artificial destratification of Lake Starodworskie. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 1998, 7, 221–227. [Google Scholar]
- Klapper, H. Technologies in lake restoration. J. Limnol. 2003, 62, 73–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, K.I. Hypolimnetic aeration of a naturally eutrophic lake: Physical and chemical effects. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 1983, 40, 1343–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutel, M.W.; Horne, A.J. A review of the effects of hypolimnetic oxygenation on lake and reservoir water quality. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1999, 15, 285–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, F.L. Case study: Blue-green algal control in australia by year-round automatic aeration. Lake Reserv. Manag. 1994, 10, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzozowska, R.; Gawrońska, H. The influence of a long-term artificial aeration on the nitrogen compounds between sediments and water in Lake Długie. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2009, 38, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrel, M.H.; Confer, J.C.; Kirschner, D.; Fast, A.W. Effects of hypolimnetic aeration on nitrogen and phosphorus in a eutrophic lake. Water Res. 1977, 13, 343–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowska, J.; Gawrońska, H. Restoration effectiveness of a degraded lake using multi-year artificial aeration. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2004, 13, 671–681. [Google Scholar]
- McQueen, D.J.; Lean, D.R.S. Hypolimnetic aeration: an overview. Water Qual. Res. J. Can. 1986, 21, 205–217. [Google Scholar]
- Gafsi, M.; Kettab, A.; Benmamar, S.; Benziada, S. Comparative studies of the different mechanical oxygenation systems used in the restoration of lakes and reservoirs. J. Food Agric. Environ. 2009, 7, 815–822. [Google Scholar]
- Gołdyn, R.; Podsiadłowski, S.; Dondajewska, R.; Kozak, A. The sustainable restoration of lakes—Towards the challenges of the WFD. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2014, 14, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łopata, M.; Gawrońska, H. Phosphorus immobilization in Lake Głęboczek following treatment with polyaluminum chloride. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2008, 37, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryding, S.O.; Rast, W. The Control of Eutrophication of Lakes and Reservoirs; Man and the Biosphere Series; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1989; Volume 1, pp. 1–314. [Google Scholar]
- Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Johansson, L.S.; Jeppesen, E. Repeated Fish Removal to Restore Lakes: Case Study of Lake Væng, Denmark—Two Biomanipulations during 30 Years of Monitoring. Water 2017, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, K.; Jeppesen, E.; Davidson, T.A.; Bjerring, R.; Johansson, L.S.; Søndergaard, M.; Lauridsen, T.L.; Svenning, J.-C. Long-term trends and temporal synchrony in plankton richness, diversity and biomass driven by re-oligotrophication and climate across 17 Danish Lakes. Water 2016, 8, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anttila, S.; Ketola, M.; Kuoppmaki, K.; Kairesalo, T. Identification of a biomanipulation-driven regime shift in Lake Vesijärvi: Implications for lake management Source of the Document. Freshw. Biol. 2013, 58, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, R.D.; Pires, L.M.D.; Van Donk, E. Lake restoration studies: Failures, bottlenecks and prospects of new ecotechnological measures. Limnologica 2008, 38, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofir, E.; Heymans, J.J.; Shapiro, J.; Goren, M.; Spanier, E.; Gal, G. Predicting the impact of Lake Biomanipulation based on food-webmodeling—Lake Kinneret as a case study. Ecol. Model. 2017, 348, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Dondajewska, R. Phytoplankton composition and abundance in restored Maltański reservoir under the influence of physico-chemical variables and zooplankton grazing pressure. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urrutia-Cordero, P.; Ekvall, M.K.; Hansson, L.A. Controlling harmful cyanobacteria: Taxa-Specific responses of cyanobacteria to grazing by large-bodied daphnia in a biomanipulation scenario. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Padisák, J.; Hajnal, E.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Dokulil, M.T.; Nõges, P.; Zohary, T. Convergence and divergence in organization of phytoplankton communities under various regimes of physical and biological control. Hydrobiologia 2010, 639, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borics, G.; Nagy, L.; Miron, S.; Grigorszky, I.; László-Nagy, Z.; Lukács, B.A.; Tóth, L.G.; Várbíró, G. Which factors affect phytoplankton biomass in shallow eutrophic lakes? Hydrobiologia 2013, 714, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsiapi, M.; Moustaka-Gouni, M.; Vardaka, E.; Kormas, K.A.R. Different phytoplankton descriptors show asynchronous changes in a shallow urban lake (L. Kastoria, Greece) after sewage diversion. Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2013, 182, 219–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, A.; Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R.; Holona, T. Water quality and phytoplankton in selected lakes and reservoirs under restoration measures in Western Poland. Pol. J. Natur. Sc. 2013, 28, 217–226. [Google Scholar]
- Søndergaard, M.; Liboriussen, L.; Pedersen, A.R.; Jeppesen, E. Lake Restoration by Fish Removal: Short- and Long-Term Effects in 36 Danish Lakes. Ecosystems 2008, 11, 1291–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schriver, P.; Bøgestrand, J.; Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M. Impact of submerged macrophytes on fish-zooplankton-phytoplankton interactions: Large-scale enclosure experiments in a shallow eutrophic lake. Freshw. Biol. 1995, 33, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.S.; Van Donk, E.; Immers, A.K. Lake restoration by in-lake iron addition: A synopsis of iron impact on aquatic organisms and shallow lake ecosystems. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A.A.; Garner, K.; Miller, R.J.; Lenihan, H.S. Toxicity of nano-zero valent iron to freshwater and marine organisms. PLoS ONE 2017, 7, e43983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zębek, E.; Napiórkowska-Krzebietke, A. Response of phytoplankton to protective-restoration treatments enhancing water quality in a shallow urban lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jańczak, J. Atlas of Polish Lakes; Bogucki Wydawnictwo Naukowe: Poznań, Poland, 1996; pp. 98–99. [Google Scholar]
- Holona, T. Rekultywacja Jeziora Głębokie (Lake Głębokie restoration). In Rekultywacja i Rewitalizacja Terenów Zdegradowanych (Restoration and Revitalization of Demoted Areas); Malina, G., Ed.; PZITS, Oddział Wielkopolski: Poznań, Poland, 2010; pp. 91–102. [Google Scholar]
- Nędzarek, A.; Tórz, A.; Kubiak, J. Oxygen conditions and trophic state of Lake Głębokie (Szczecin, Poland) in the years 2008–2010. Limnol. Rev. 2010, 10, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WeatherOnline. Available online: https://www.weatheronline.pl (accessed on 29 January 2017).
- Osuch, E.; Podsiadłowski, S. Efficiency of pulverizing aeration on Lake Panieńskie. Limnol. Rev. 2012, 12, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podsiadłowski, S. Method of precise phosphorus inactivation in lake waters. Limnol. Rev. 2008, 8, 51–56. [Google Scholar]
- Holona, T.; Gołdyn, R. Rekultywacja Jeziora Głębokiego w Szczecinie w latach 2008–2011 [Restoration of Lake Głębokie in Szczecin in years 2008–2011]. Gaz Woda i Tech. Sanit. 2012, 2, 75–77. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Dojlido, J.R.; Hermanowicz, W. Physico-chemical analysis of water and sewage; Arkady Publ.: Warsaw, Poland, 1999; p. 555. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Wetzel, R.G.; Likens, G.E. Limnological Analyses; Springer-Verlag: New York, NY, USA, 1991; p. 391. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, Ø. PAST. Paleontological Statistics. Reference manual. Natural History Museum. University of Oslo. 1999–2016. 2016. Available online: http://folk.uio.no/ohammer/past/past3manual.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2017).
- ter Braak, C.J.F.; Šmilauer, P. CANOCO Reference Manual and CanoDraw for Windows User’s Guide: Software for Canonical Community Ordination (Version 4.5); TNO Institute of Applied Computer Science: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Gołdyn, R.; Dondajewska, R. Phosphorus release from the bottom sediments of Lake Rusałka (Poznań, Poland). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2010, 39, 135–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Role of sediment and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Jeppesen, E. Retention and internal loading of phosphorus in shallow, eutrophic lakes. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boström, B.; Andersen, J.M.; Fleischer, S.; Jansson, M. Exchange of phosphorus across the sediments-water interface. Hydrobiologia 1988, 170, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonschot, P.F.M.; Spears, B.M.; Feld, C.K.; Brucet, S.; Keizer-Vlek, H.; Borja, A.; Elliott, M.; Kernan, M.; Johnson, R.K. A comparative review of recovery processes in rivers, lakes, estuarine and coastal waters. Hydrobiologia 2013, 704, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzchowska, E. Wyniki Monitoringu Badawczego Wód Jeziora Głębokie z Roku 2008; The results of investigative monitoring of waters of Lake Głębokie from the year 2008; Regional Inspectorate for Environmental Protection in Szczecin: Szczecin, Poland, 2009; WIOŚ-WM-0712/04/2009. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Sobczyński, T.; Joniak, T.; Pronin, E. Assessment of the multi-directional experiment to restore Lake Góreckie (Western Poland) with particular focus on oxygen and light conditions: First results. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2012, 21, 1025–1031. [Google Scholar]
- Selmeczy, G.; Tapolczai, K.; Casper, P.; Krienitz, L.; Padisák, J. Spatial- and niche segregation of DCM-forming cyanobacteria in Lake Stechlin (Germany). Hydrobiologia 2015, 764, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunalska, J.A.; Staehr, P.A.; Jaworska, B.; Górniak, D.; Gomułka, P. Ecosystem metabolism in a lake restored by hypolimnetic withdrawal. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 73, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworska, B.; Gawrońska, H.; Łopata, M. Changes in the phytoplankton community of a lake restored with phosphorus inactivation (Lake Głęboczek, northern Poland). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2009, 38, 93–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, A. Seasonal changes occurring over four years in a reservoir’s phytoplankton composition. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2005, 14, 451–465. [Google Scholar]
- Kozak, A.; Gołdyn, R. Zooplankton versus phyto- and bacterioplankton in the Maltański Reservoir (Poland) during an extensive biomanipulation experiment. J. Plankton Res. 2004, 26, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triest, L.; Stiers, I.; van Onsem, S. Biomanipulation as a nature-based solution to reduce cyanobacterial blooms. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 461–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Backer, L.C. Cyanobacterial harmful algal blooms: Developing a public health response. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2002, 18, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H. The effect of cyanobacterial blooms in the Siemianówka Dam Reservoir on the phytoplankton structure in the Narew River. Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2011, 40, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Zhou, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, Q.; Zhang, X. Are fish fed with cyanobacteria safe, nutritious and delicious? A laboratory study. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zagajewski, P.; Gołdynm, R.; Fabiśm, M. Cyanobacterial volume and microcystins concentration in recreational lakes (Poznań–Western Poland). Oceanol. Hydrobiol. Stud. 2009, 38, 113–120. [Google Scholar]
- Jurczak, T.; Tarczynska, M.; Izydorczyk, K.; Mankiewicz, J.; Zalewski, M.; Meriluoto, J. Elimination of microcystins by water treatment processes—Examples from Sulejow Reservoir, Poland. Water Res. 2005, 39, 2394–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokociński, M.; Mankiewicz-Boczek, J.; Jurczak, T.; Spoof, L.; Meriluoto, J.; Rejmonczyk, E.; Hautala, H.; Vehniäinen, M.; Pawełczyk, J.; Soininen, J. Aphanizomenon gracile (Nostocales), a cylindrospermopsin-producing cyanobacterium in Polish lakes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 5243–5264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Padisák, J.; Sommer, U. Intermediate disturbance in the ecology of phytoplankton and the maintenance of species diversity: A synthesis. Hydrobiologia 1993, 249, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawecka, B.; Eloranta, P.V. Zarys Ekologii Glonów Wód Słodkich i Środowisk Lądowych (An Outline of Alga of Freshwater and Land Ecosystems); PWN: Warsaw, Poland, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Kuczyńska-Kippen, N.; Joniak, T. Zooplankton diversity and macrophyte biometry in shallow water bodies of various trophic state. Hydrobiologia 2016, 774, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakset, A.; Chankaew, W. Phytoplankton as a Bio-indicator of Water Quality in the Freshwater Fishing Area of Pak Phanang River Basin (Southern Thailand). Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2013, 40, 344–355. [Google Scholar]
- Yap, S.Y. Classifcation of a Malaysian river using biological indices: A preliminary attempt. Environmentalist 1997, 17, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejsmont-Karabin, J.; Kuczyńska-Kippen, N. Urban rotifers: Structure and densities of rotifer communities in water bodies of the Pozna´n agglomeration area (western Poland). Hydrobiologia 2001, 153, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C. The Ecology of Phytoplankton; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pajchrowska, M.; Szpakowska, B. Assessment of occurrence microphytes and trophic status of a small water body in the Wielkopolska Region (Western Poland). Pol. J. Natur. Sc. 2014, 29, 17–33. [Google Scholar]
- Padisák, J.; Reynolds, C.S. Selection of phytoplankton associations in Lake Balaton, Hungary, in response to eutrophication and restoration measures, with special reference to the cyanoprokaryotes. Hydrobiologia 1998, 384, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosińska, J.; Kozak, A.; Dondajewska, R.; Gołdyn, R. Cyanobacteria blooms before and during the restoration process of a shallow urban lake. J. Environ. Manag. 2017, 198, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokulil, M.T.; Treubner, K. Cyanobacterial doninance in lakes. Hydrobiologia 2000, 438, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, J. Current beliefs regarding dominance blue greens: The case for the importance of CO2 and pH. Verhandlungen des Internationalen Ver. Limnologie 1990, 24, 38–54. [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds, C.S. What factors influence the species composition of phytoplankton in lakes of different trophic status? Hydrobiologia 1998, 369, 11–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerasimova, T.N.; Pogozhev, P.I. The role of zooplankton in phytoplankton biomass decline and water transparency regulation in a water body subject to high organic and mineral load. Water Res. 2010, 37, 796–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peretyatko, A.; Teissier, S.; De Backer, S.; Triest, L. Biomanipulation of hypereutrophic ponds: When it works and why it fails. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 1517–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sikora, A.; Dawidowicz, P. Do the presence of filamentous cyanobacteria and an elevated temperature favor small-bodied Daphnia in interspecific competitive interactions? Fundam. Appl. Limnol. 2014, 185, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, C.; Koed, A. Habitat use of 0+ year pike in experimental ponds in relation to cannibalism, zooplankton, water transparency and habitat complexity. J. Fish Biol. 2004, 64, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skov, C.; Lousdal, O.P.; Johansen, H.; Berg, S. Piscivory of 0+ pike (Esox lucius L.) in a small eutrophic lake and its implication for biomanipulation. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
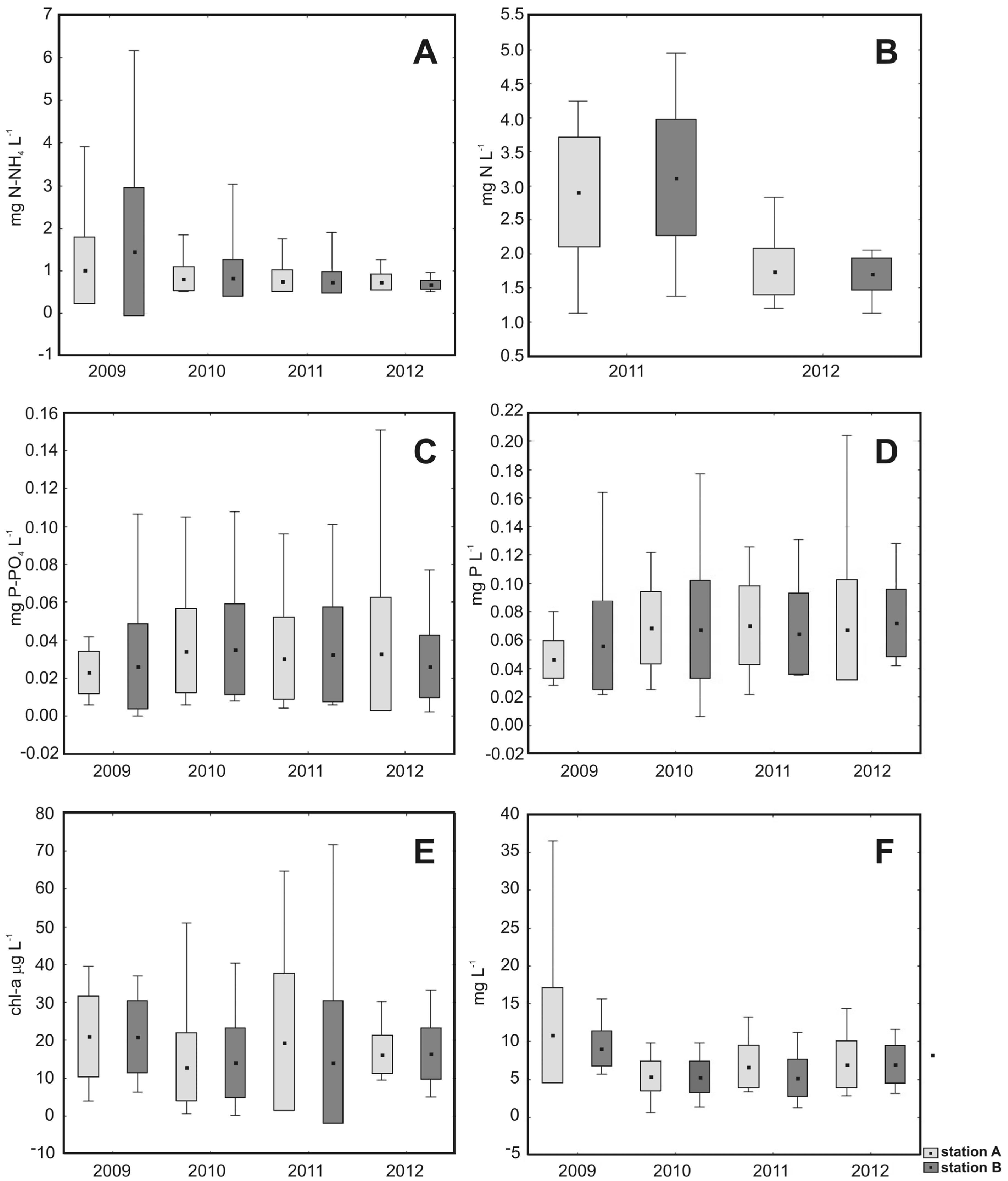
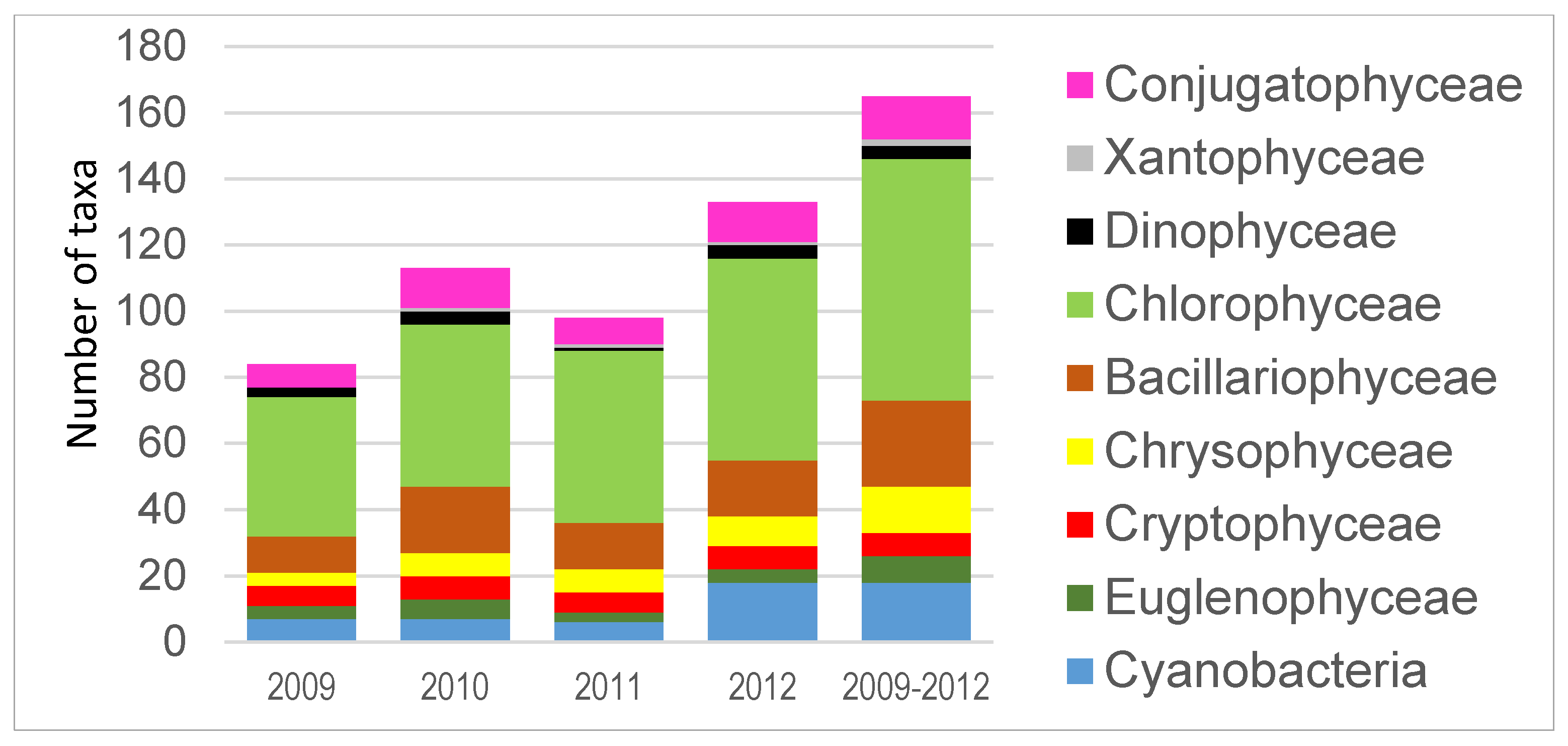

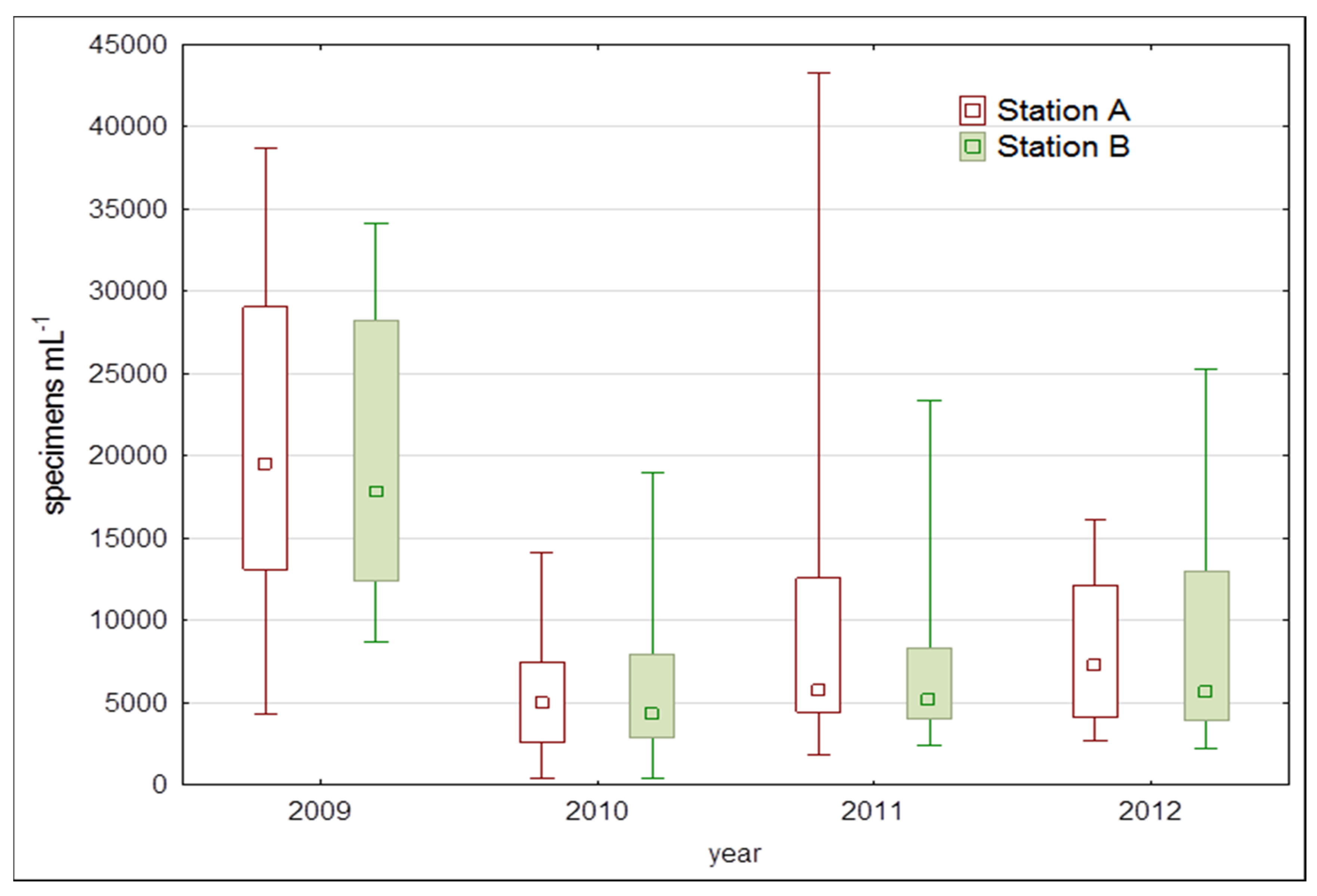
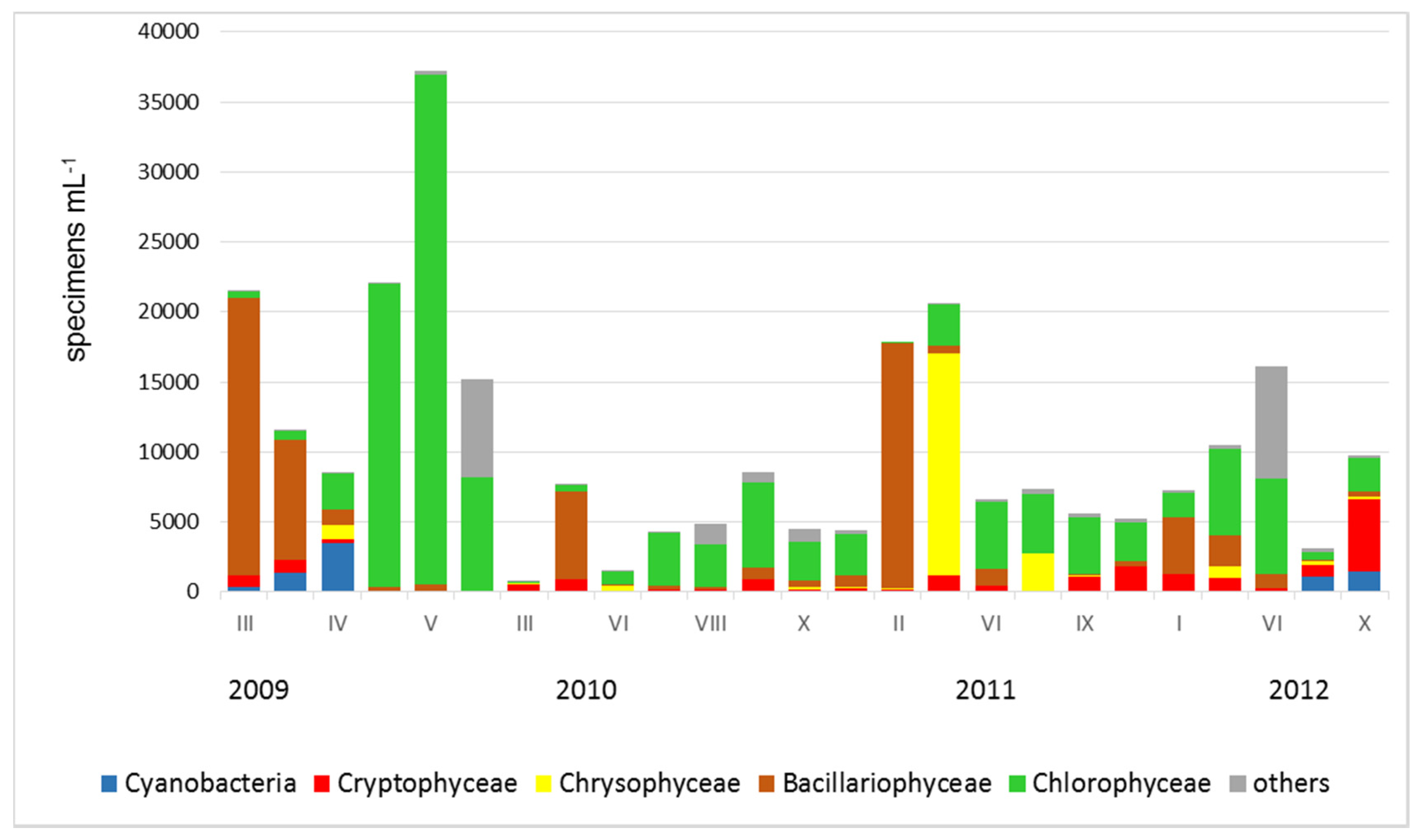
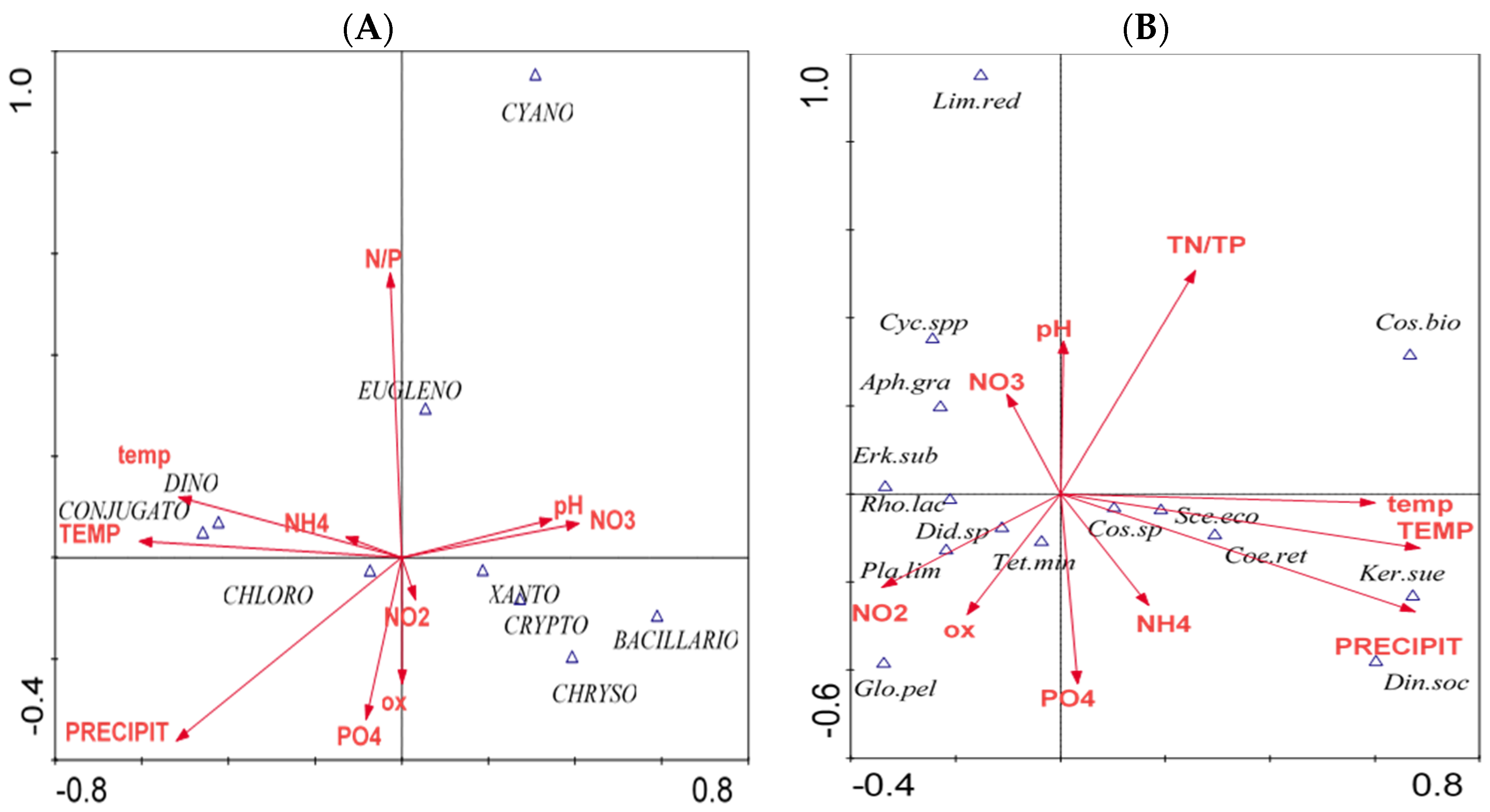
| Variable | Relationships between Environmental Variables and Abundance of Phytoplankton Groups | Relationships between Environmental Variables and Phytoplankton Dominating Taxa | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-value | F-ratio | p-value | F-ratio | |
| Precipitation | 0.002 | 13.42 | 0.002 | 3.43 |
| Air temperature | 0.002 | 9.09 | 0.002 | 3.97 |
| Water temperature | 0.004 | 5.27 | 0.030 | 2.05 |
| Dissolved oxygen | 0.004 | 4.97 | 0.396 | 1.06 |
| N:P (mineral forms) ratio | 0.002 | 9.58 | 0.006 | 3.09 |
| NH4-N | 0.230 | 1.34 | 0.004 | 2.72 |
| NO2-N | 0.004 | 4.38 | 0.196 | 1.42 |
| NO3-N | 0.002 | 16.01 | 0.002 | 2.97 |
| pH | 0.004 | 4.50 | 0.038 | 2.06 |
| PO4-P | 0.204 | 1.32 | 0.094 | 1.75 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kozak, A.; Gołdyn, R.; Dondajewska, R.; Kowalczewska-Madura, K.; Holona, T. Changes in Phytoplankton and Water Quality during Sustainable Restoration of an Urban Lake Used for Recreation and Water Supply. Water 2017, 9, 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090713
Kozak A, Gołdyn R, Dondajewska R, Kowalczewska-Madura K, Holona T. Changes in Phytoplankton and Water Quality during Sustainable Restoration of an Urban Lake Used for Recreation and Water Supply. Water. 2017; 9(9):713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090713
Chicago/Turabian StyleKozak, Anna, Ryszard Gołdyn, Renata Dondajewska, Katarzyna Kowalczewska-Madura, and Tomasz Holona. 2017. "Changes in Phytoplankton and Water Quality during Sustainable Restoration of an Urban Lake Used for Recreation and Water Supply" Water 9, no. 9: 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090713
APA StyleKozak, A., Gołdyn, R., Dondajewska, R., Kowalczewska-Madura, K., & Holona, T. (2017). Changes in Phytoplankton and Water Quality during Sustainable Restoration of an Urban Lake Used for Recreation and Water Supply. Water, 9(9), 713. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9090713








