The Impact of Cropland Balance Policy on Ecosystem Service of Water Purification—A Case Study of Wuhan, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Sources
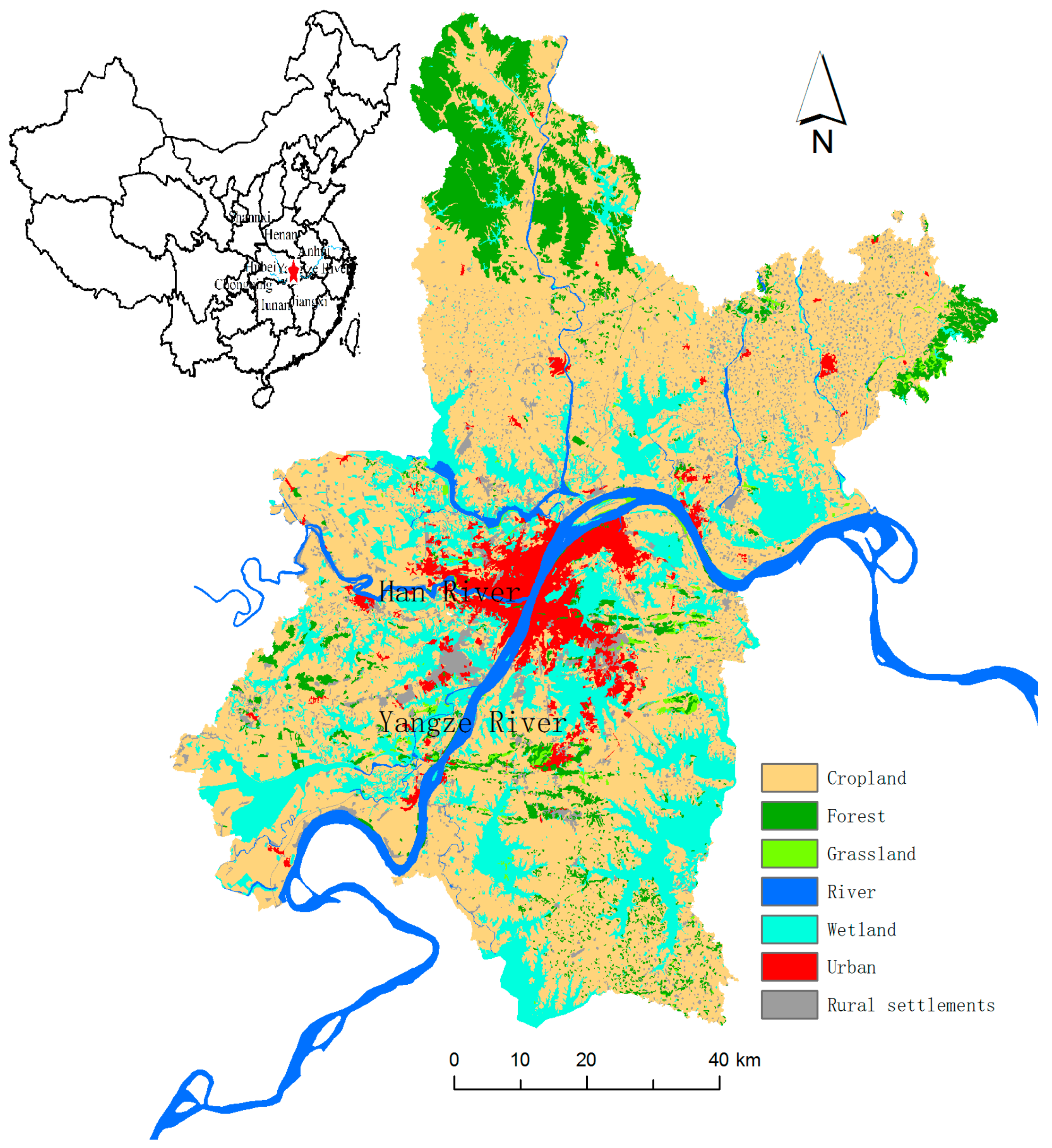
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Sources
3 Method
3.1. Scenarios of Land Use Strategies
3.2. Modeling Land Use Changes by LANDSCAPE Model
3.3. Assessing Nutrient Export by InVEST Model
4. Results
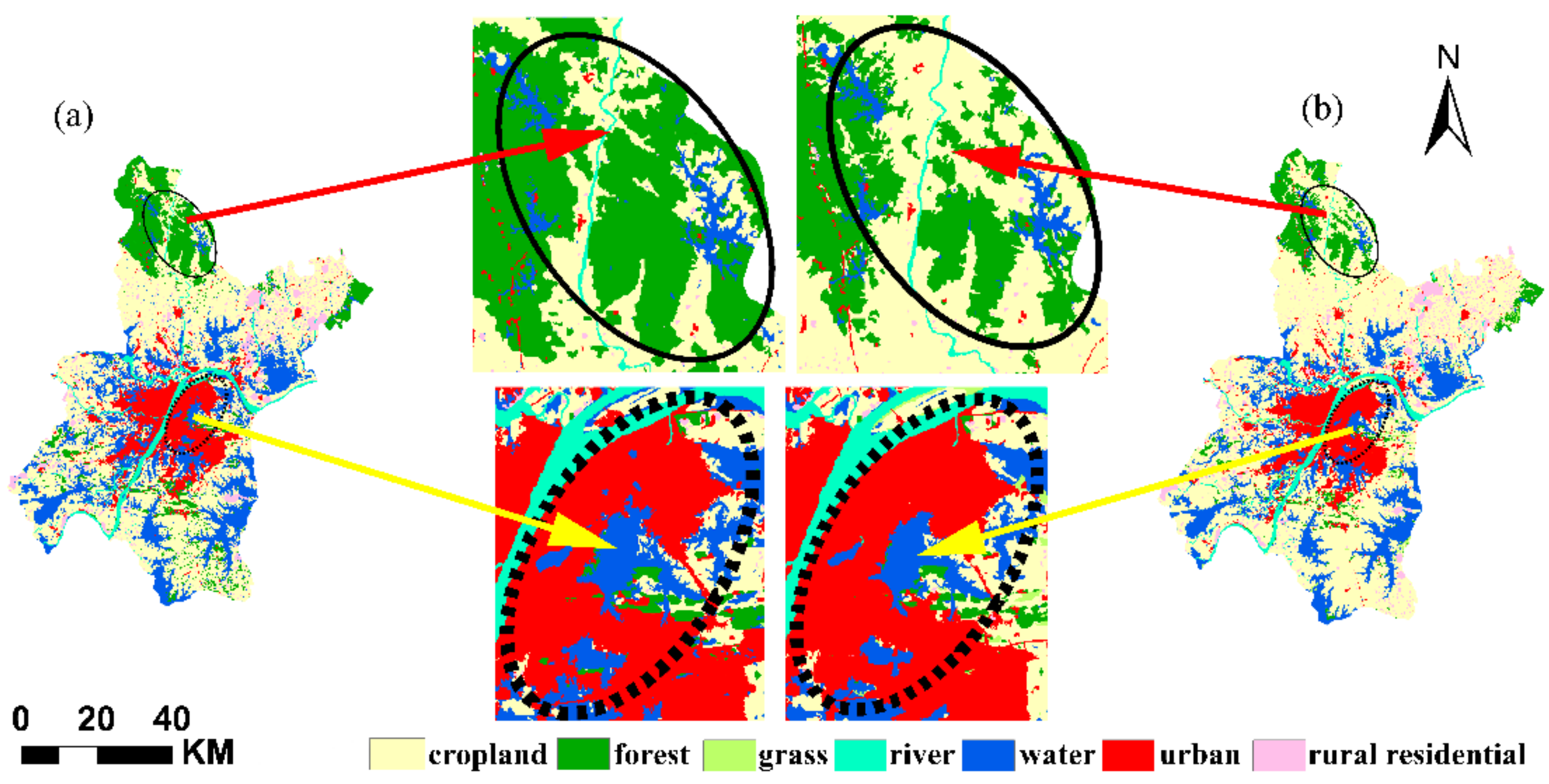
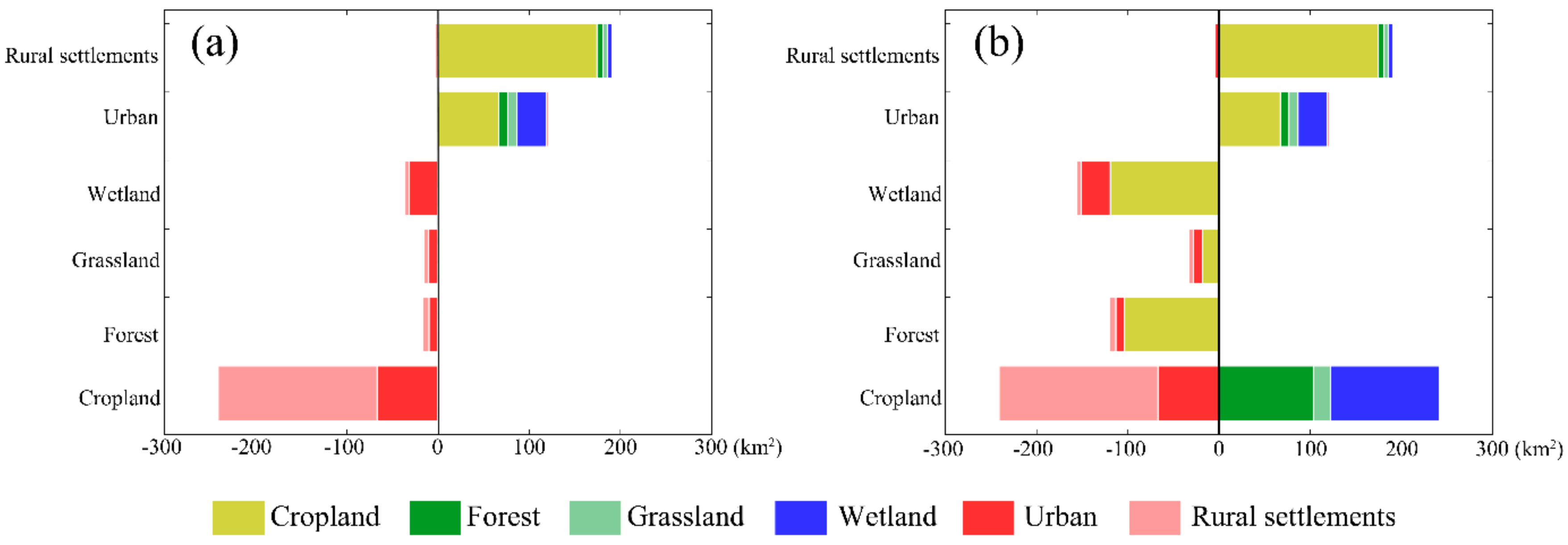
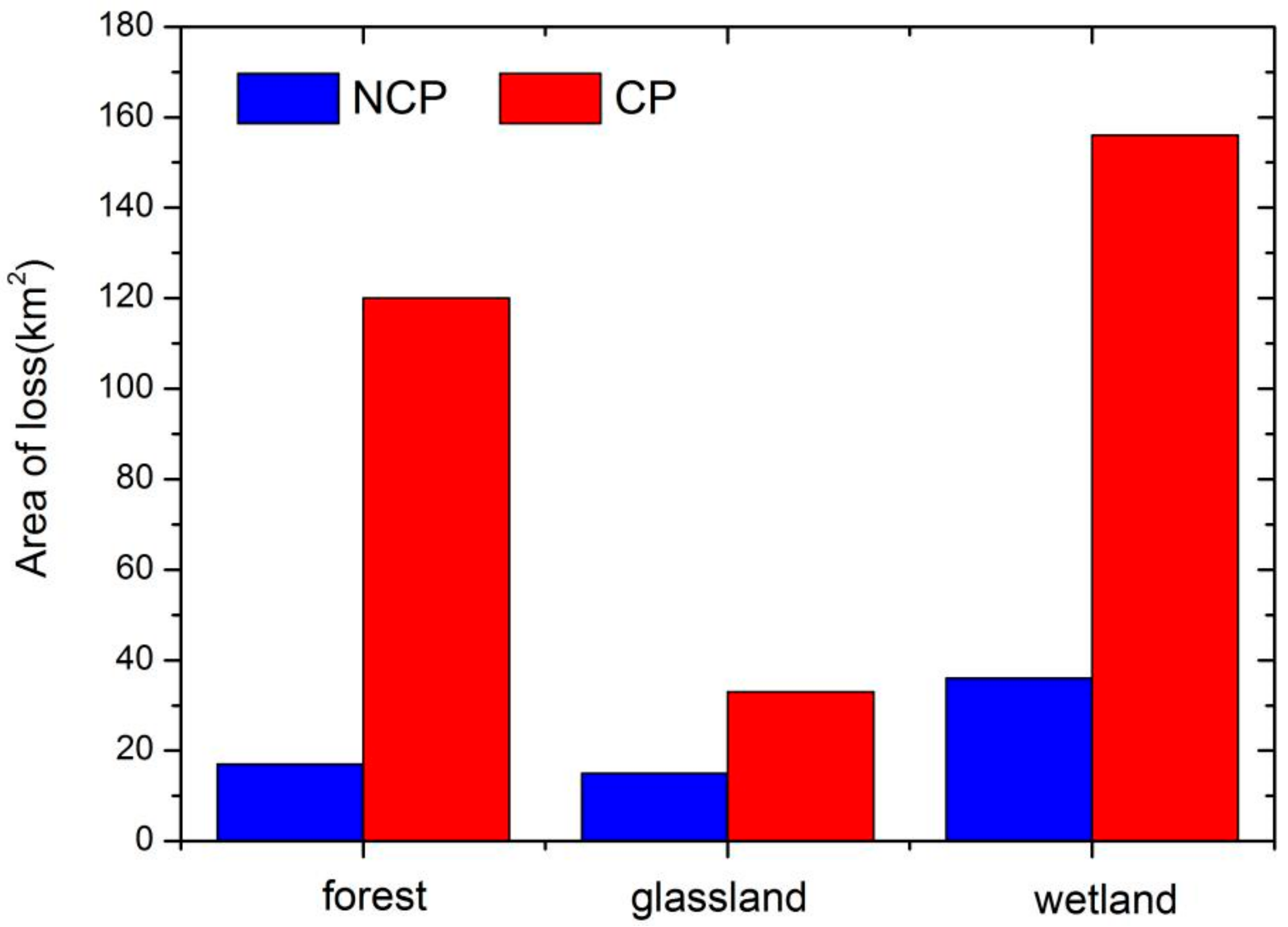
4.1. The Loss of Ecological Lands under the Two Scenarios
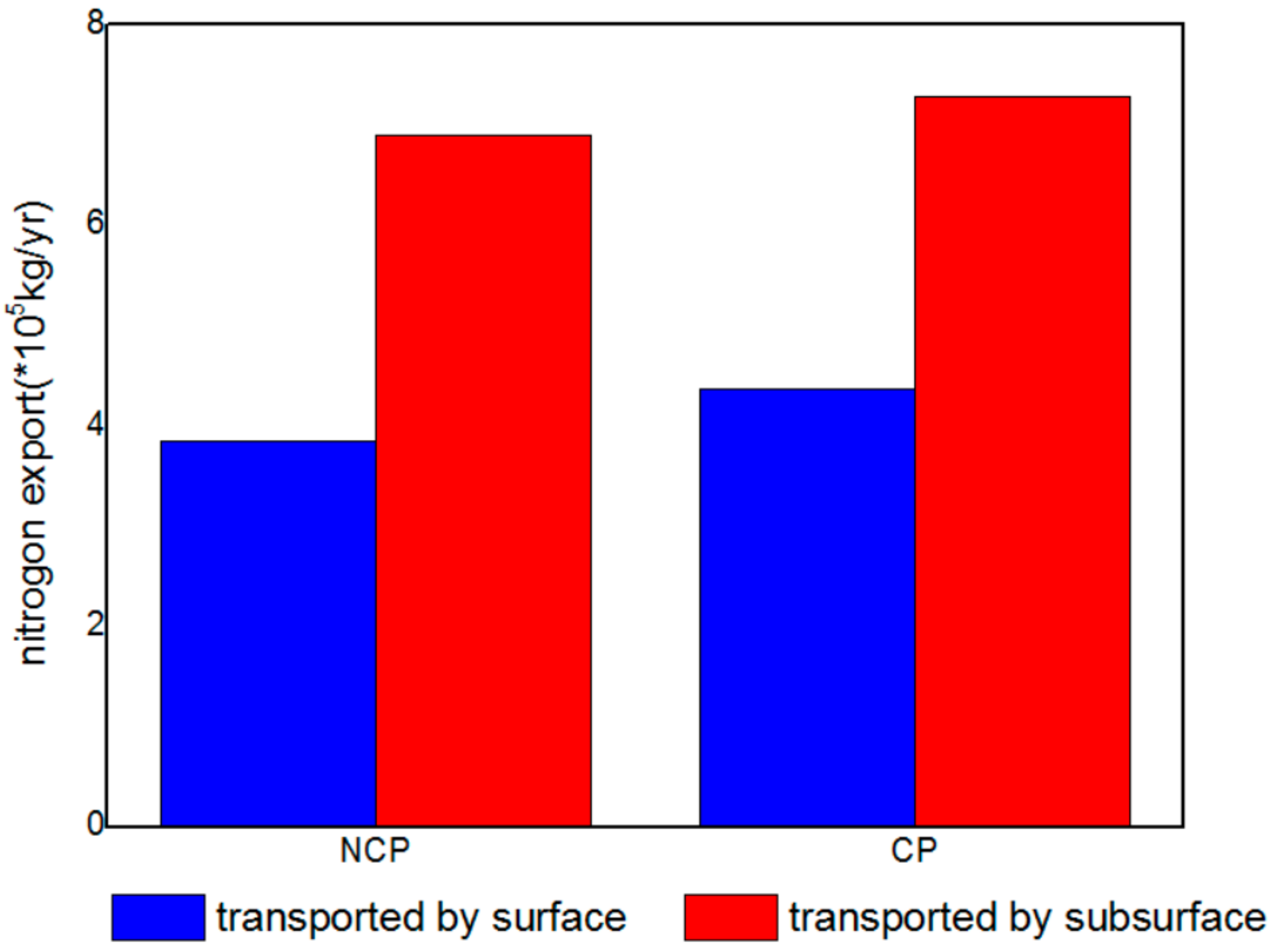
4.2. The Impact of Cropland Balance Policy on the Service of Water Purification
4.3. Mechanism of the Impacts of Cropland Protection Policy on Ecosystem Service of Water Purification
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, C.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S.; Shao, Z. On electricity consumption and economic growth in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 76, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyfroidt, P.; Lambin, E.F. Global Forest Transition: Prospects for an End to Deforestation. Annu. Rev. Environ. Resour. 2011, 36, 343–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Hui, C.; Choguill, C.; Jia, S. The new urbanization policy in China: Which way forward? Habitat Int. 2015, 47, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Liu, Z.; Tian, J.; Ma, Q. Urban expansion dynamics and natural habitat loss in China: A multiscale landscape perspective. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, S.; Pijanowski, B.C. The effects of China’s cultivated land balance program on potential land productivity at a national scale. Appl. Geogr. 2014, 46, 158–170. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberg, E.; Ding, C. Assessing Farmland Protection Policy in China. Land Use Policy 2008, 25, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Scott, S.; Wang, K. The effects of basic arable land protection planning in Fuyang County, Zhejiang Province, China. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 422–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vliet, J.V.; Bregt, A.K.; Brown, D.G.; Delden, H.V.; Heckbert, S. A review of current calibration and validation practices in land-change modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 82, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global forecasts of urban expansion to 2030 and direct impacts on biodiversity and carbon pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nhapi, I.; Hoko, Z.; Siebel, A.; Gijzen, H.J. Assessment of the MajorWater Andnutrient Flows in the Chivero Catchment Area, Zimbabwe. Phys. Chem. Earth 2002, 27, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyanga, Y.; Nkedi Kizza, P.; Wu, Q.T.; Shinde, D.; Huang, C.H. Assessment of Seasonal Variations in Surface Water Quality. Water Res. 2006, 40, 3800–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekholm, P.; Kallio, K.; Salo, S.; Pietilainen, O.P.; Rekolainen, S. Relationship between Catchment Characteristics and Nutrient Concentrations in an Agricultural River System. Water Res. 2000, 34, 3709–3716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, R.E.; Rabalais, N.N. Linking Landscape and Water Quality in the Mississippi River Basin for 200 Years. Bioscience 2003, 53, 563–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Qi, L.; Zeng, C. A partitioned and asynchronous cellular automata model for urban growth simulation. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2015, 30, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Meng, F.; Ke, X. Analysis on Urban Lake Change during Rapid Urbanization Using a Synergistic Approach: A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Phys. Chem. Earth 2015, 80–90, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, P.A.M.; Garlick, J.D.; Smith, R.G. Near-global validation of the SRTM DEM using satellite radar altimetry. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 49, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Government of Hubei Province. Land Use Planning for Hubei Province (2016–2020). 2009. Available online: http://www.hubei.gov.cn/zwgk/zdlyxxgk/zdhfwzs/tdlygh/201208/t20120821_392757_1.shtml (accessed on 17 August 2017).
- Liu, X.; Li, X.; Liu, L.; He, J.; Ai, B. A bottom-up approach to discover transition 494 rules of cellular automata using ant intelligence. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2008, 22, 1247–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.; Brabyn, L. The extrapolation of social landscape values to a national level in New Zealand using landscape character classification. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 35, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.; Engelen, G. Cellular automata as the basis of integrated dynamic regional modelling. Environ. Plan. B Urban Anal. City Sci. 2008, 24, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y. A Generalized Model for Cellular Urban Dynamics. Geogr. Anal. 2010, 28, 350–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, X.; Zheng, W.; Zhou, T.; Liu, X. A CA-based land system change model: LANDSCAPE. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamel, P.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Sim, S.; Mueller, C. A new approach to modeling the sediment retention service (InVEST 3.0): Case study of the Cape Fear catchment, North Carolina, USA. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 524–525, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Q.; Zhao, Y. Assessing the potential impacts of urban expansion on regional carbon storage by linking the LUSD-urban and InVEST models. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 75, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Deng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Lei, X.; Chen, Z. Modelling the potential impacts of urban ecosystem changes on carbon storage under different scenarios by linking the CLUE-S and the InVEST models. Ecol. Model. 2017, 345, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endreny, T.A.; Wood, E.F. Watershed weighting of export coefficients to map critical phosphorous loading areas. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2003, 39, 165–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, P.M.; Reynolds, S.K.; Mccutchen, M.D.; Canfield, T.J. Meta-Analysis of Nitrogen Removal in Riparian Buffers. J. Environ. Qual. 2007, 36, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, M.; Dahlgren, R.A.; Eitzel, M. A review of vegetated buffers and a meta-analysis of their mitigation efficacy in reducing nonpoint source pollution. J. Environ. Qual. 2009, 39, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heathwaite, A.L.; Quinn, P.F.; Hewett, C.J.M. Modelling and managing critical source areas of diffuse pollution from agricultural land using flow connectivity simulation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Varis, O.; Yin, H. China’s water resources vulnerability: A spatio-temporal analysis during 2003–2013. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 142, 2901–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniwaki, R.J.; Cassiano, C.C.; Filoso, S.; Ferraz, S.F.B.; Camargo, P.B.; Martinelli, L.A. Impacts of converting low-intensity pastureland to high-intensity bioenergy cropland on the water quality of tropical streams in Brazil. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 15, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Different Scenarios | Cropland | Forest | Grassland | River | Wetland | Urban | Rural Settlements | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Amount (km2) (2000) | 5188 | 804 | 146 | 304 | 1458 | 378 | 228 |
| Amount (km2) (2010) | 4706 | 783 | 138 | 304 | 1531 | 789 | 255 | |
| NCP (2020) | Demand (km2) | - | - | - | - | - | 910 | 443 |
| Resistance (2010–2020) | 1.1 | 1.05 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.15 | |
| CP (2020) | Demand (km2) | 4706 | - | - | - | - | 910 | 443 |
| Resistance (2010–2020) | 1.1 | 1.05 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1.2 | 1.15 | |
| Scenarios | NCP | CP |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen export () | 10.75 | 11.65 |
| Load surface () | 5.43 | 5.56 |
| NDR surface | 0.16 | 0.17 |
| Load subsurface () | 3.57 | 3.76 |
| NDR subsurface | 0.22 | 0.22 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mei, Y.; Kong, X.; Ke, X.; Yang, B. The Impact of Cropland Balance Policy on Ecosystem Service of Water Purification—A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Water 2017, 9, 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080620
Mei Y, Kong X, Ke X, Yang B. The Impact of Cropland Balance Policy on Ecosystem Service of Water Purification—A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Water. 2017; 9(8):620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080620
Chicago/Turabian StyleMei, Yun, Xinghe Kong, Xinli Ke, and Bohan Yang. 2017. "The Impact of Cropland Balance Policy on Ecosystem Service of Water Purification—A Case Study of Wuhan, China" Water 9, no. 8: 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080620
APA StyleMei, Y., Kong, X., Ke, X., & Yang, B. (2017). The Impact of Cropland Balance Policy on Ecosystem Service of Water Purification—A Case Study of Wuhan, China. Water, 9(8), 620. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9080620





