ENSO Influence on Rainy Season Precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
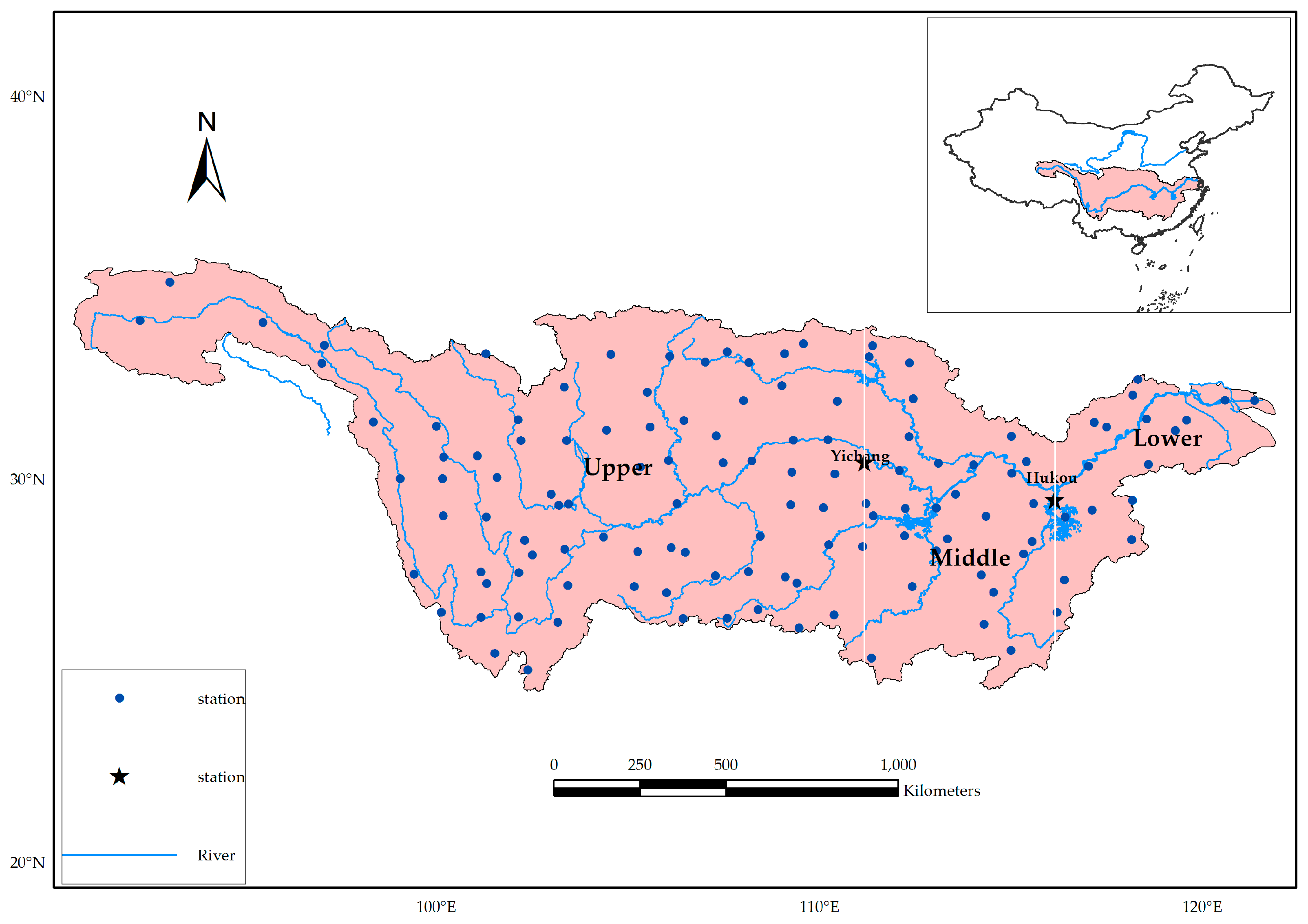
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
3. Methodology
3.1. Determination of the Rainy Season
3.2. Pettitt Test
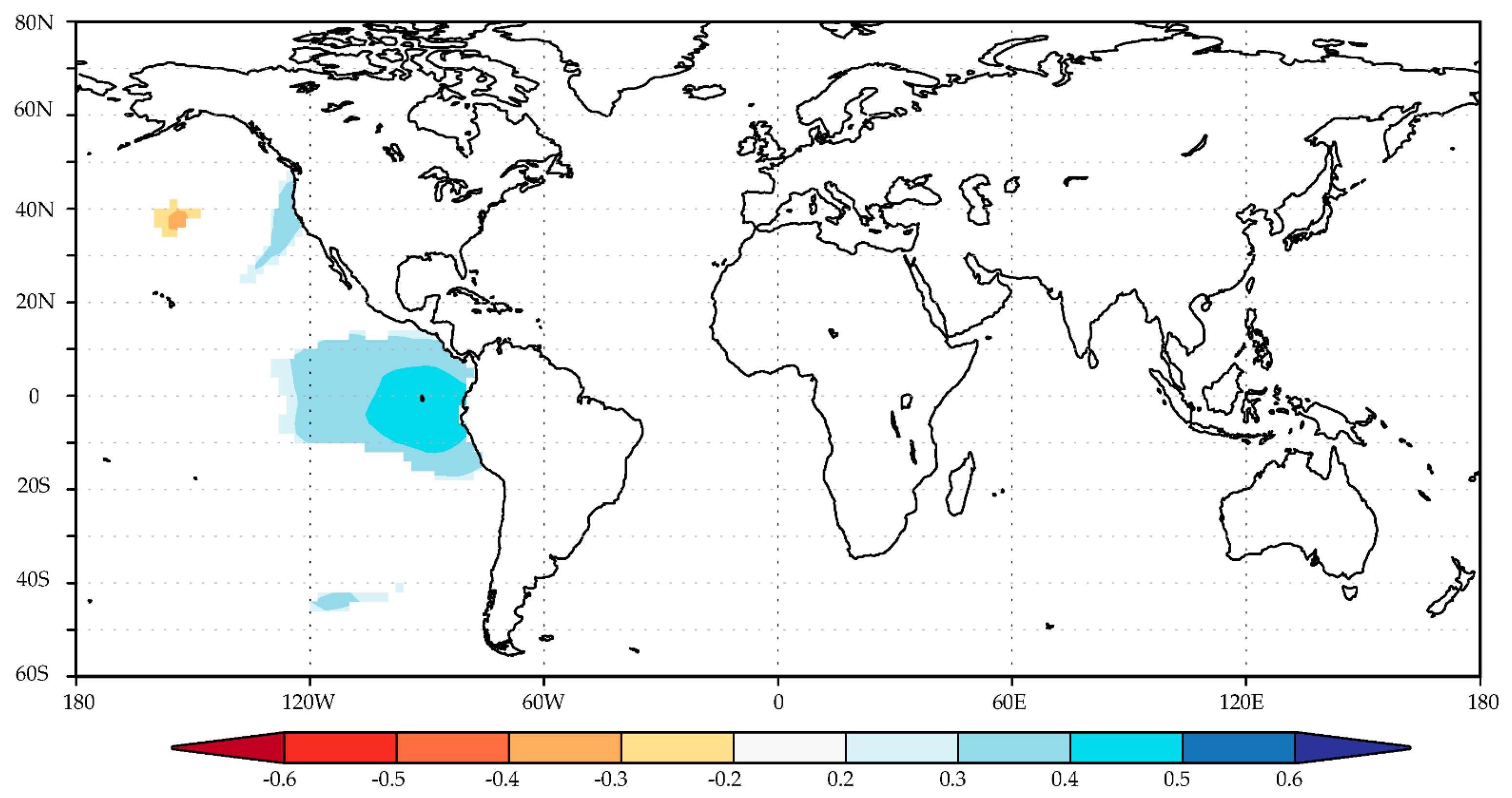
3.3. Correlation between Precipitation and SST
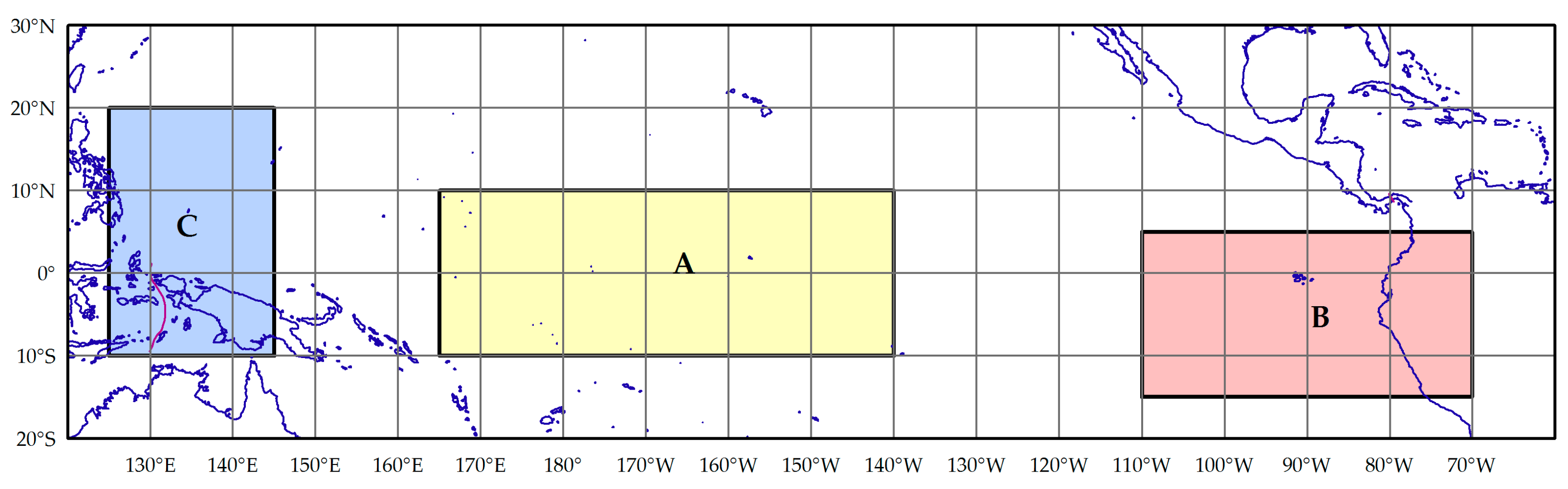
3.4. Classification of ENSO and ENSO Modoki Regimes
3.5. Precipitation Anomaly Index during the Rainy Season (PARS)
4. Results and Discussion
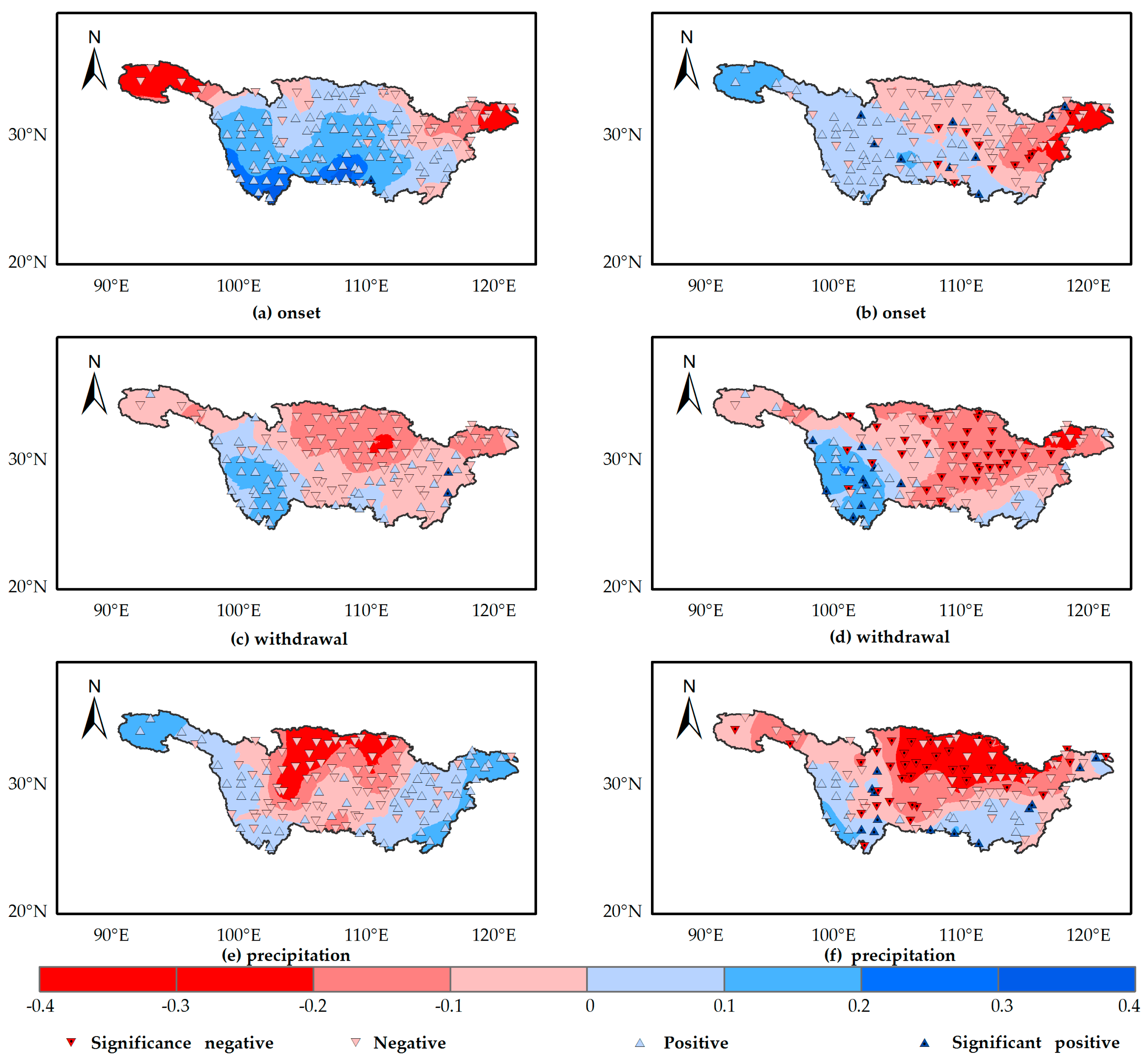
4.1. Spatial and Temporal Patterns of Rainy Season Features
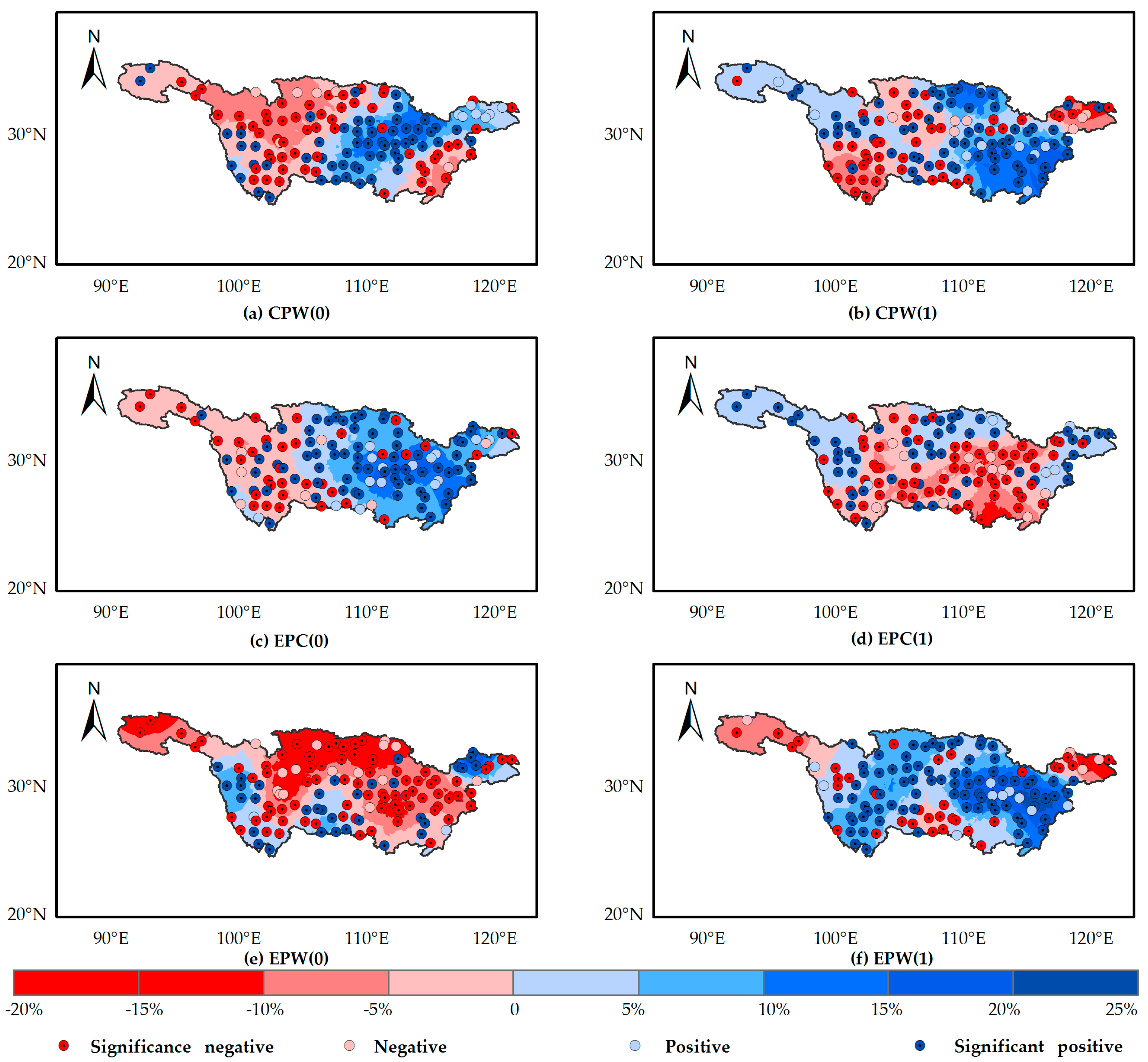
4.2. Precipitation Anomalies during the Rainy Season (PARS) Influenced by CPW, EPC, and EPW Regimes
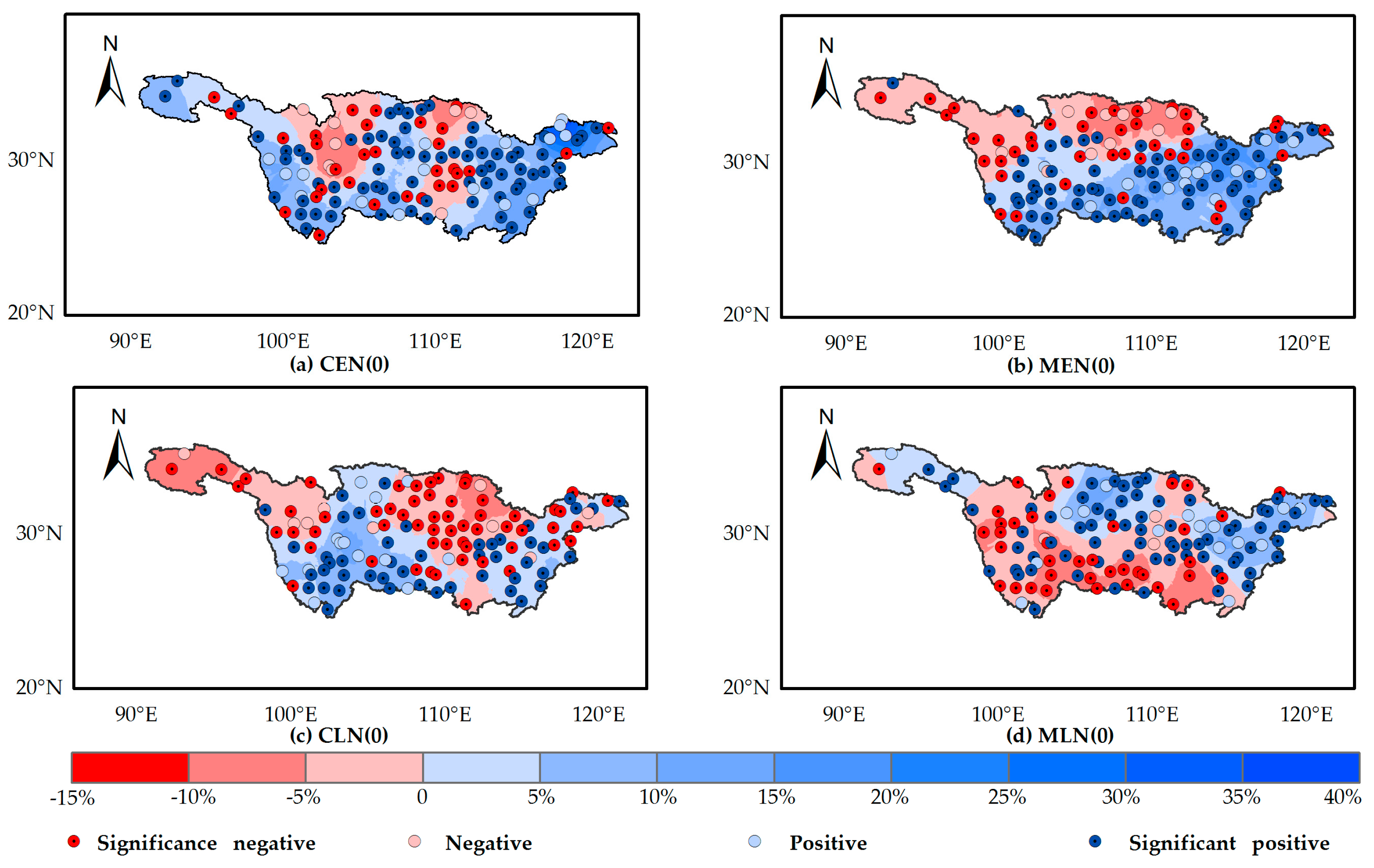
4.3. Precipitation Anomaly during the Rainy Season (PARS) Impacted by ENSO and ENSO Modoki Regimes
5. Conclusions
- (1)
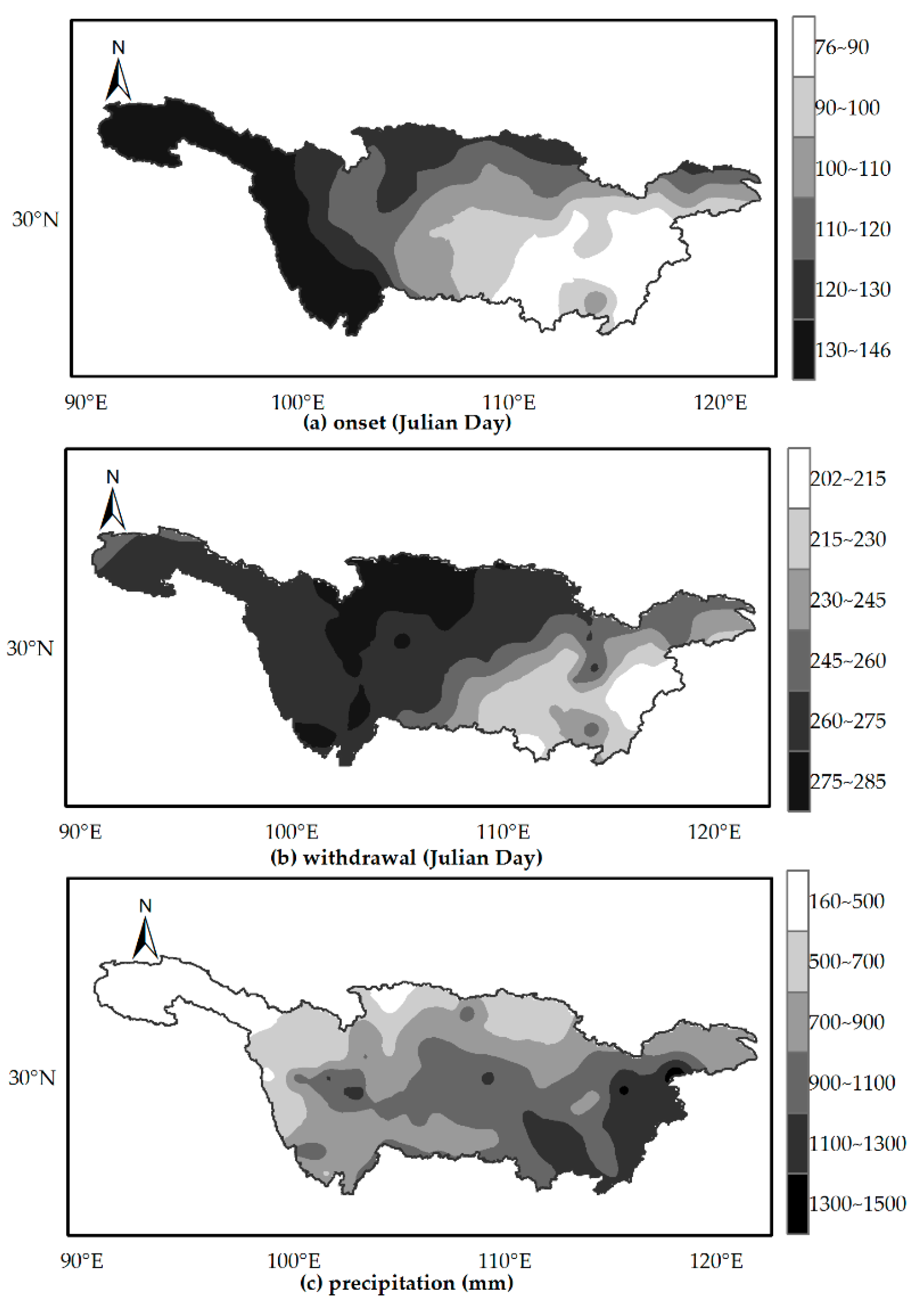
- The rainy season over the YRB starts in early March in southeastern parts of the basin and progresses north-and westwards, with latest onset occurring in late May in western parts of the upper reach. The temporal distribution of withdrawal is similar to onset, with rainy season ending at the earliest in mid-July in the southeastern region and at the latest in mid-October in the northern parts of the upper reach of the YRB. In contrast to the spatial pattern of onset and withdrawal, rainy season precipitation increases from the northwest (160–500 mm) to southeast (1300–1500 mm). Withdrawal and rainy season precipitation generally display a stable temporal distribution at the interannual scale, but onset has a tendency to become more and more delayed.
- (2)
- CPW and EPW in their decaying phases are indicating wetter signals as compared to the corresponding the developing phases. The decaying EPC and developing EPW are important since they signal dry spells in most areas of the YRB.
- (3)
- ENSO Modoki for years with the developing phase appear to present wetter or drier signals as compared to the corresponding conventional ENSO regimes. In contrast, conventional ENSO regimes in the decaying phase play a more significant role in flooding and drought monitoring as compared to ENSO Modoki, since it presents wetter or drier signals.
Acknowledgements
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McPhaden, M.J.; Zebiak, S.E.; Glantz, M.H. ENSO as an integrating concept in earth science. Science 2006, 314, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kayano, M.T.; Andreoli, R.V. Relationships between rainfall anomalies over northeastern Brazil and the El Niño–Southern Oscillation. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111, D13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, F.F.; Stuecker, M.F.; Wittenberg, A.T.; Timmermann, A.; Ren, H.L.; Kug, J.S.; Cai, W.; Cane, M. Unraveling El Niño’s impact on the East Asian Monsoon and Yangtze River summer flooding. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2016, 43, 11375–11382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Zhang, Q.; Singh, V.P. Influences of ENSO, NAO, IOD and PDO on seasonal precipitation regimes in the Yangtze River basin, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 3556–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Berndtsson, R.; Uvo, C.B.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, P. Summer precipitation prediction in the source region of the Yellow River using climate indices. Hydrol. Res. 2016, 47, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Yasuda, H.; Berndtsson, R.; Bertacchi Uvo, C.; Zhang, L.; Hao, Z.; Wang, X. Regional sea-surface temperatures explain spatial and temporal variation of summer precipitation in the source region of the Yellow River. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2016, 61, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, E.; Antweiler, R.C.; Neiman, P.J.; Ralph, F.M. Influence of ENSO on flood frequency along the California coast. J. Clim. 2004, 17, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-M.; Webster, P.J.; Curry, J.A. Impact of shifting patterns of Pacific Ocean warming on North Atlantic tropical cyclones. Science 2009, 325, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larkin, N.K.; Harrison, D. On the definition of El Niño and associated seasonal average US weather anomalies. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2005, 32, L13705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, F.; Luo, Z.; Ju, J. Differences between dynamics factors for interannual and decadal variations of rainfall over the Yangtze River valley during flood seasons. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 994–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, D.Y.; Ho, C.H. Shift in the summer rainfall over the Yangtze River valley in the late 1970s. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 101436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Kang, H.-S.; Lee, D.-K. Distribution of seasonal rainfall in the East Asian monsoon region. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2002, 73, 151–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemmer, M.; Jiang, T.; Su, B.; Kundzewicz, Z.W. Seasonal precipitation changes in the wet season and their influence on flood/drought hazards in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Quatern. Int. 2008, 186, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, D.; Zhou, W.; Li, C. Interdecadal modulation of the influence of La Niña events on mei-yu rainfall over the Yangtze River Valley. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omotosho, J.B.; Balogun, A.; Ogunjobi, K. Predicting monthly and seasonal rainfall, onset and cessation of the rainy season in West Africa using only surface data. Int. J. Climatol. 2000, 20, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, K.; Roncoli, M.; Kirshen, P. Opportunities and constraints for farmers of west Africa to use seasonal precipitation forecasts with Burkina Faso as a case study. Agric. Syst. 2002, 74, 331–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbier, B.; Yacouba, H.; Karambiri, H.; Zoromé, M.; Somé, B. Human vulnerability to climate variability in the Sahel: Farmers’ adaptation strategies in northern Burkina Faso. Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 790–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marteau, R.; Sultan, B.; Moron, V.; Alhassane, A.; Baron, C.; Traoré, S.B. The onset of the rainy season and farmers’ sowing strategy for pearl millet cultivation in Southwest Niger. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 1356–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, H.; Ashok, K.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Yamagata, T. Impacts of recent El Niño Modoki on dry/wet conditions in the Pacific rim during boreal summer. Clim. Dyn. 2007, 29, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, K.; Behera, S.K.; Rao, S.A.; Weng, H.; Yamagata, T. El Niño Modoki and its possible teleconnection. J. Geophys. Res. Oceans 2007, 112, C11007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kao, H.-Y.; Yu, J.-Y. Contrasting eastern-Pacific and central-Pacific types of ENSO. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 615–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taschetto, A.S.; England, M.H. El Niño Modoki impacts on Australian rainfall. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 3167–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedeschi, R.G.; Cavalcanti, I.F.A.; Grimm, A.M. Influences of two types of ENSO on South American precipitation. Int. J. Climatol. 2013, 33, 1382–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preethi, B.; Sabin, T.P.; Adedoyin, J.A.; Ashok, K. Impacts of the ENSO Modoki and other tropical Indo-Pacific climate-drivers on African rainfall. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.; Wang, L.; Chen, W.; Fong, S.K.; Leong, K.C. Different impacts of two types of Pacific Ocean warming on Southeast Asian rainfall during boreal winter. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D24122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Van Rensch, P.; Cowan, T.; Sullivan, A. Asymmetry in ENSO teleconnection with regional rainfall, its multidecadal variability, and impact. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 4944–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, E.; Slingo, J.; Sperber, K.R. An observational study of the relationship between excessively strong short rains in coastal East Africa and Indian Ocean SST. Mon. Weather Rev. 2003, 131, 74–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Harr, P.; Ju, J. Possible roles of Atlantic circulations on the weakening Indian monsoon rainfall—ENSO relationship. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 2376–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyutha, C.; Willems, P. Spatial and temporal variability of rainfall in the Nile Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2227–2246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, R.; Hu, Z.-Z.; Kirtman, B.P. Evolution of ENSO—Related rainfall anomalies in East Asia. J. Clim. 2003, 16, 3742–3758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Singh, V.P.; Gu, X.; Kong, D.; Xiao, M. Impacts of ENSO and ENSO Modoki+A regimes on seasonal precipitation variations and possible underlying causes in the Huai River basin, China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 533, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, J. Contrasting impacts of two types of ENSO on the boreal spring Hadley circulation. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 4773–4789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, F.-F.; Li, J.; Ren, H.-L. Contrasting impacts of two-type El Niño over the Western North Pacific during boreal autumn. J. Meteor. Soc. Jpn. 2011, 89, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Chan, J.C. ENSO and the South China Sea summer monsoon onset. Int. J. Climatol. 2007, 27, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Chen, W.; Tam, C.Y.; Zhou, W. Different impacts of El Niño and El Niño Modoki on China rainfall in the decaying phases. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 2091–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Jin, F.F.; Turner, A. Increasing autumn drought over southern China associated with ENSO regime shift. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2014, 41, 4020–4026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Klaus, F.; Zou, Y. A Scanning t test of multiscale abrupt changes and its coherence analysis. Chin. J. Geophys. 2001, 44, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Xiao, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Hou, B.; Lu, C. The Impact of Climate Change on the Duration and Division of Flood Season in the Fenhe River Basin, China. Water 2016, 8, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettitt, A.N. A non-parametric approach to the change-point problem. Appl. Stat. 1979, 28, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearson, K. Note on regression and inheritance in the case of two parents. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1895, 58, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Wang, Z. A study of rainy seasons in China. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2008, 100, 121–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, N.; Li, J. Interannual variability of autumn precipitation over South China and its relation to atmospheric circulation and SST anomalies. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 25, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Wu, R.; Lau, K. Interannual variability of the Asian summer monsoon: Contrasts between the Indian and the western North Pacific–East Asian monsoons. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 4073–4090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, S.; Li, J. The relationship between the summer precipitation in the Yangtze River valley and the boreal spring Southern Hemisphere annular mode. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2003, 30, 242266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Li, J.; He, J.; Jiang, Z. Large-scale atmospheric singularities and summer long-cycle droughts-floods abrupt alternation in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, F.; Tang, X.; Gao, S.; Luo, Z. A comparative study of the atmospheric circulations associated with rainy-season floods between the Yangtze and Huaihe River Basins. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1464–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| EPW | EPC | CPW |
|---|---|---|
| 1965, 1972, 1976, 1982, 1987, 1997, 2015 | 1964, 1970, 1973, 1975, 1988, 1998, 1999, 2007, 2010, 2011 | 1963, 1969, 1991, 1994, 2002, 2004, 2009 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, Q.; Hao, Z.; Yuan, F.; Su, Z.; Berndtsson, R. ENSO Influence on Rainy Season Precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin. Water 2017, 9, 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070469
Cao Q, Hao Z, Yuan F, Su Z, Berndtsson R. ENSO Influence on Rainy Season Precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin. Water. 2017; 9(7):469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070469
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Qing, Zhenchun Hao, Feifei Yuan, Zhenkuan Su, and Ronny Berndtsson. 2017. "ENSO Influence on Rainy Season Precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin" Water 9, no. 7: 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070469
APA StyleCao, Q., Hao, Z., Yuan, F., Su, Z., & Berndtsson, R. (2017). ENSO Influence on Rainy Season Precipitation over the Yangtze River Basin. Water, 9(7), 469. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9070469






