Estimating Aquifer Transmissivity Using the Recession-Curve-Displacement Method in Tanzania’s Kilombero Valley
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Kilombero Valley of Central Tanzania
2.2. Datasets Considered
2.2.1. Hydrograph Data
2.2.2. Borehole and Pumping Test Data
2.3. Estimation of Streamflow-Derived Aquifer Transmissivity
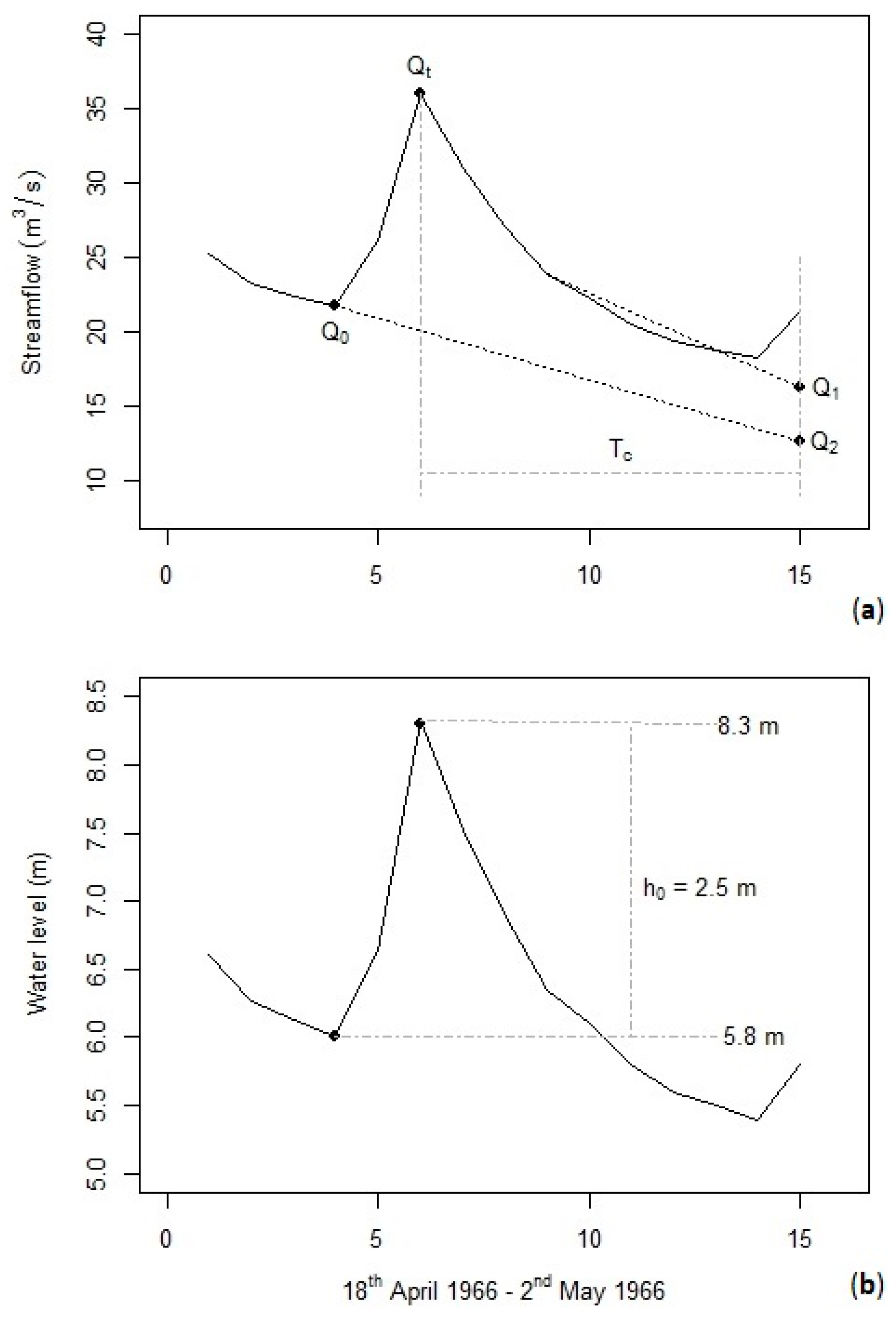
2.3.1. Theoretical Development of the Recession-Curve-Displacement Method
2.3.2. Estimation of K Using the RECESS Program
2.3.3. Estimation of Q0, Q1, Q2, and Qt Using RORA Program
2.3.4. Applying the Recession-Curve-Displacement Method in an Automated Manner
3. Results
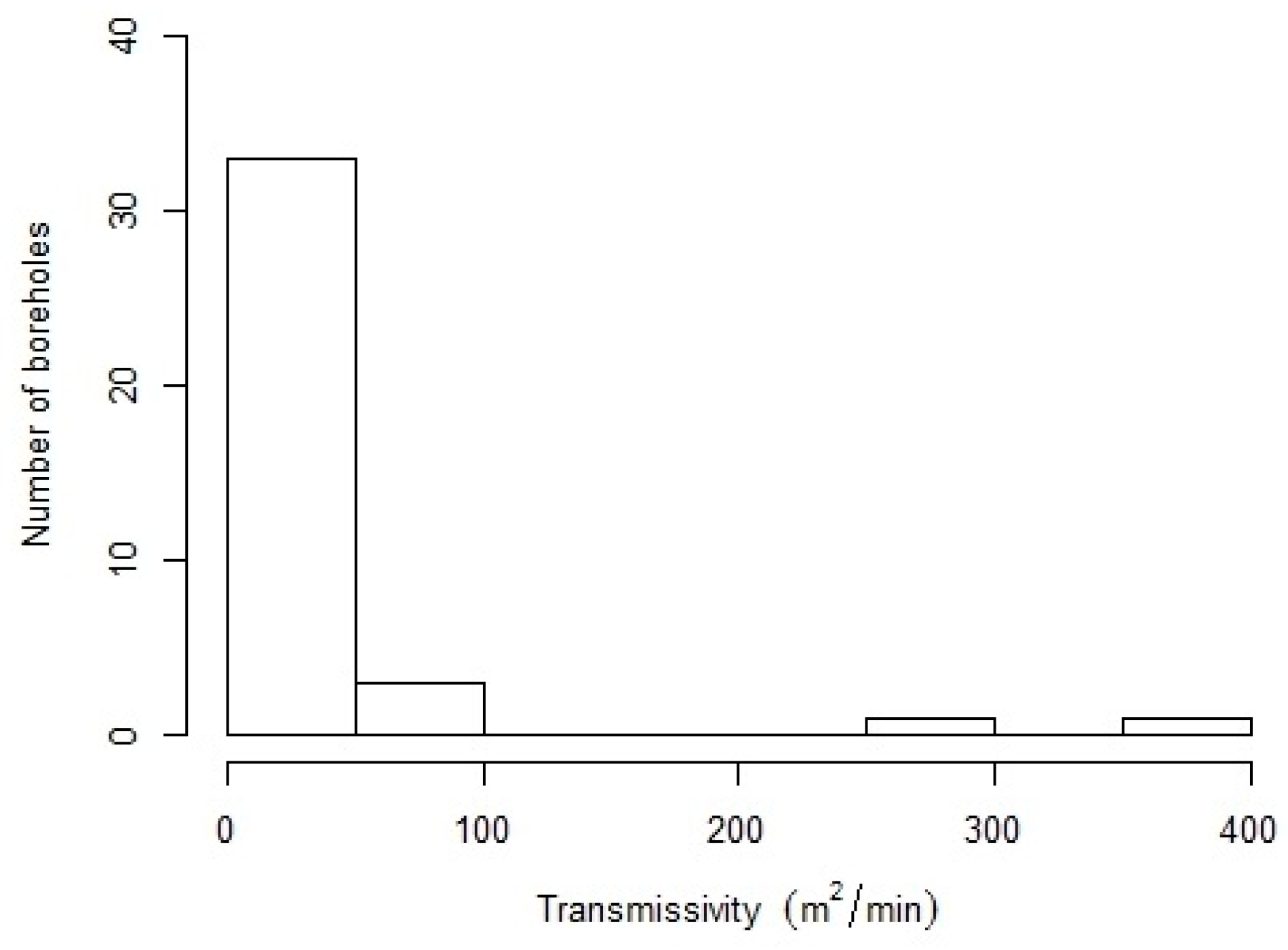
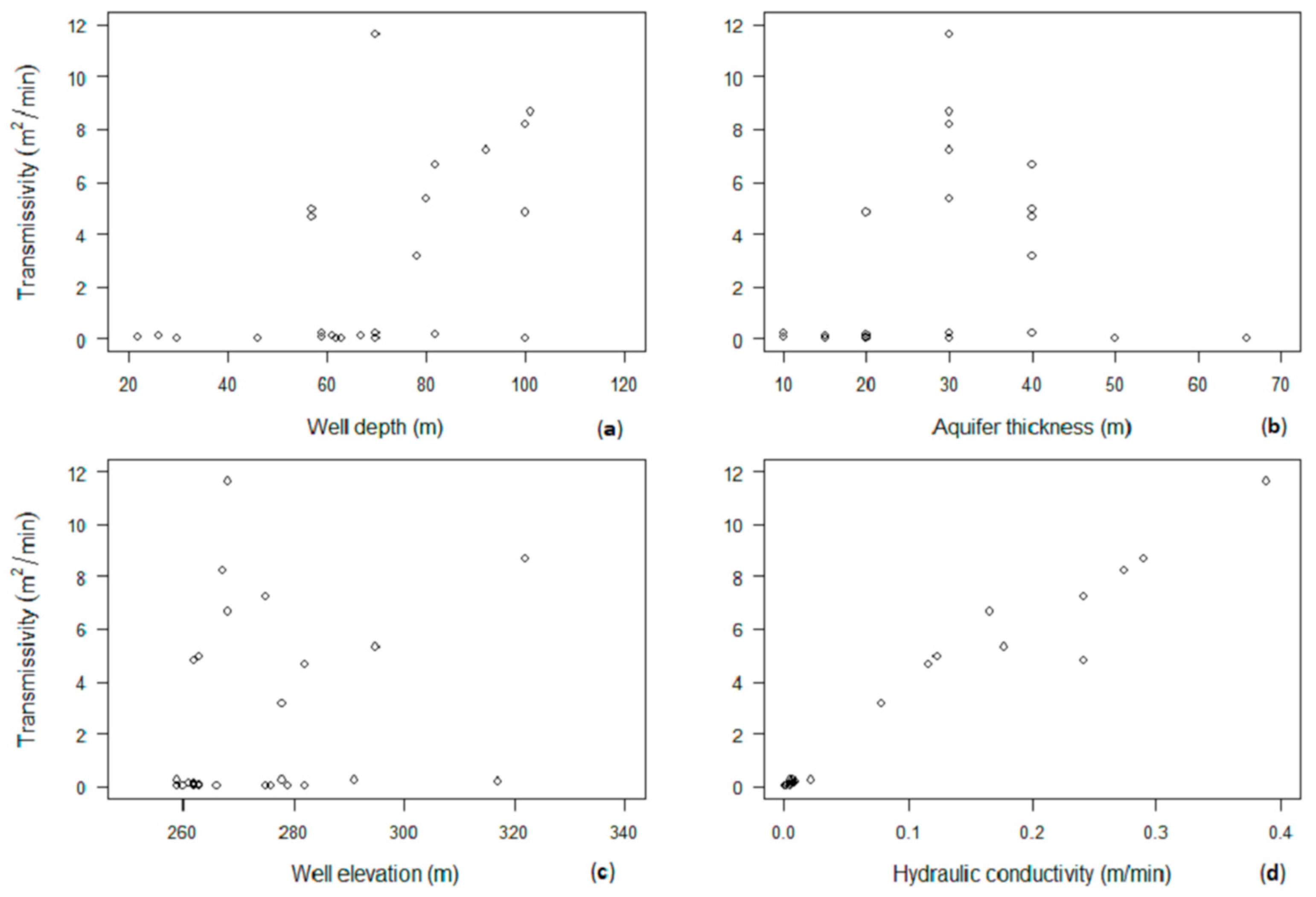
3.1. Local-Scale T Estimates from Pumping Tests
3.2. Regional-Scale T Estimates from Streamflow
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison of Pumping-Test and Recession-Curve-Displacement Assessments
4.2. On Limitations and Potential for Misrepresentation
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vorosmarty, C.; Green, P.; Salisbury, J.; Lammers, R. Global water resources: Vulnerability from climate change and population growth. Science 2000, 289, 284–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Singh, V. Review on regional water resources assessment models under stationary and changing climate. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 591–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alley, W.; Healy, R.; LaBaugh, J.; Reilly, T. Hydrology—Flow and storage in groundwater systems. Science 2002, 296, 1985–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, R.C. Basic Ground-Water Hydrology; Water Supply Paper; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1983; p. 86.
- Theis, C.V. The relation between the lowering of the Piezometric surface and the rate and duration of discharge of a well using ground-water storage. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1935, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.H.; Jacob, C.E. A generalized graphical method for evaluating formation constants and summarizing well-field history. Eos Trans. Am. Geophys. Union 1946, 27, 526–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza, G.; Steenhuis, T.; Walter, M.; Parlange, J. Estimating basin-wide hydraulic parameters of a semi-arid mountainous watershed by recession-flow analysis. J. Hydrol. 2003, 279, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soupios, P.M.; Kouli, M.; Vallianatos, F.; Vafidis, A.; Stavroutakis, G. Estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters from surficial geophysical methods: A case study of Keritis Basin in Chania (Crete-Greece). J. Hydrol. 2007, 338, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zecharias, Y.; Brutsaert, W. The influence of basin morphology on groundwater outflow. Water Resour. Res. 1988, 24, 1645–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.; Hendricks Franssen, H.-J.; Kgotlhang, L.; Bauer-Gottwein, P.; Kinzelbach, W. How can remote sensing contribute in groundwater modeling? Hydrogeol. J. 2007, 15, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A. Groundwater resources management through the applications of simulation modeling: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 499, 414–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Camp, M.; Mjemah, I.C.; Al Farrah, N.; Walraevens, K. Modeling approaches and strategies for data-scarce aquifers: Example of the Dar es Salaam aquifer in Tanzania. Hydrogeol. J. 2013, 21, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevans, H.E. Estimating stream-aquifer interactions in coal areas of eastern Kansas using streamflow records. In U.S. Geological Survey Water-Supply Paper; U.S. Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 1986; pp. 51–64. [Google Scholar]
- Lyon, S.W.; Koutsouris, A.; Scheibler, F.; Jarsjo, J.; Mbanguka, R.; Tumbo, M.; Robert, K.K.; Sharma, A.N.; van der Velde, Y. Interpreting characteristic drainage timescale variability across Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 1912–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rorabaugh, M.I. Estimating changes in bank storage and ground-water contribution to streamflow. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Publ. 1964, 63, 432–441. [Google Scholar]
- Tallaksen, L.M. A review of baseflow recession analysis. J. Hydrol. 1995, 165, 349–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.-P.; Kung, W.-J.; Lee, C.-H. Estimating aquifer transmissivity in a basin based on stream hydrograph records using an analytical approach. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 63, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.-P.; Lee, C.-H. Estimating ground-water recharge from streamflow records. Environ. Geol. 2003, 44, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo, R.K.; Merkel, B.J. Investigation of the potential surface–groundwater relationship using automated base-flow separation techniques and recession curve analysis in Al Zerba region of Aleppo, Syria. Arab. J. Geosci. 2015, 8, 10543–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, A.T.; Daniel, C.C. Testing an automated method to estimate ground-water recharge from streamflow records. Ground Water 1994, 32, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rutledge, A.T. Computer Programs for Describing the Recession of Ground-Water Discharge and for Estimating Mean Ground-Water Recharge and Discharge from Streamflow Records-Update; Water-Resources Investigations Report; U.S. Dept. of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey; Information Services: Reston, VA, USA, 1998.
- Daniel, J.F. Estimating groundwater evapotranspiration from streamflow records. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trainer, F.W.; Watkins, F.A.J. Use of base-runoff recession curves to determine areal transmissivities in the Upper Potomac River Basin. US Geol. Surv. J. Res. 1974, 2, 125–131. [Google Scholar]
- Rutledge, A.T. Computer Programs for Describing the Recession of Ground-Water Discharge and for Estimating Mean Ground-Water Recharge and Discharge from Streamflow Record; U.S. Geological Survey; U.S.G.S. Earth Science Information Center, Open-File Reports Section: Reston, VA, USA, 1993.
- Rutledge, A.T. Considerations for Use of the Rora Program to Estimate Ground-Water Recharge from Streamflow Records; U.S. Department of the Interior, U.S. Geological Survey; Branch of Information Services: Reston, VA, USA, 2000.
- Rutledge, A.T. Update on the use of the RORA program for recharge estimation. Ground Water 2007, 45, 374–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delin, G.N.; Healy, R.W.; Lorenz, D.L.; Nimmo, J.R. Comparison of local- to regional-scale estimates of ground-water recharge in Minnesota, USA. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mau, D.P.; Winter, T.C. Estimating ground-water recharge from streamflow hydrographs for a small mountain watershed in a temperate humid climate, New Hampshire, USA. Ground Water 1997, 35, 291–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonarius, H.; Zusammenarbeit, D.G.; Für, T. Physical Properties of Soils in the Kilombero Valley (Tanzania); German Agency for Technical Cooperation: Eschborn, Germany, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Beck, A.D. The Kilombero valley of south-central Tanganyika. East Afr. Geogr. Rev. 1964, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Koutsouris, A.J.; Chen, D.; Lyon, S.W. Comparing global precipitation data sets in eastern Africa: A case study of Kilombero Valley, Tanzania. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 2000–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashaigili, J.J. Assessment of Groundwater Availability and Its Current and Potential Use and Impacts in Tanzania; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- RBWO (Rufiji Basin Water Office). Water Resources Availability Assessment; RBWO: Iringa, Tanzania, 2010; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Rorabaugh, M.I.; Simons, W.D. Exploration of Methods of Relating Ground Water to Surface Water, Columbia River Basin-Second Phase; Open-File Report; U.S. Geological Survey (USGS): Reston, VA, USA, 1966.
- Koutsouris, A. Building a Coherent Hydro-Climatic Modelling Framework for the Data Limited Kilombero Valley of Tanzania. Ph.D. Thesis, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, A.M.; Bonsor, H.C.; Dochartaigh, B.É.Ó.; Taylor, R.G. Quantitative maps of groundwater resources in Africa. Environ. Res. Lett. 2012, 7, 24009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, K.; Destouni, G. Propagation of water pollution uncertainty and risk from the subsurface to the surface water system of a catchment. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 434–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, E.S.; Boll, J.; McDaniel, P.A. A hillslope-scale experiment to measure lateral saturated hydraulic conductivity. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beven, K.; Germann, P. Macropores and water flow in soils. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 1311–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.H.; Vertessy, R.A.; Silberstein, R.P. The sensitivity of a catchment model to soil hydraulic properties obtained by using different measurement techniques. Hydrol. Process. 1999, 13, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopmans, J.W.; Nielsen, D.R.; Bristow, K.L. How useful are small-scale soil hydraulic property measurements for large-scale vadose zone modeling? In Environmental Mechanics: Water, Mass and Energy Transfer in the Biosphere: The Philip Volume; Raats, P.A.C., Smiles, D., Warrick, A.W., Eds.; American Geophysical Union: Washington, DC, USA, 2002; pp. 247–258. ISBN 978-1-118-66865-8. [Google Scholar]
- Tumbo, M.; Hughes, D.A. Uncertain hydrological modelling: Application of the Pitman model in the Great Ruaha River basin, Tanzania. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2015, 60, 2047–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
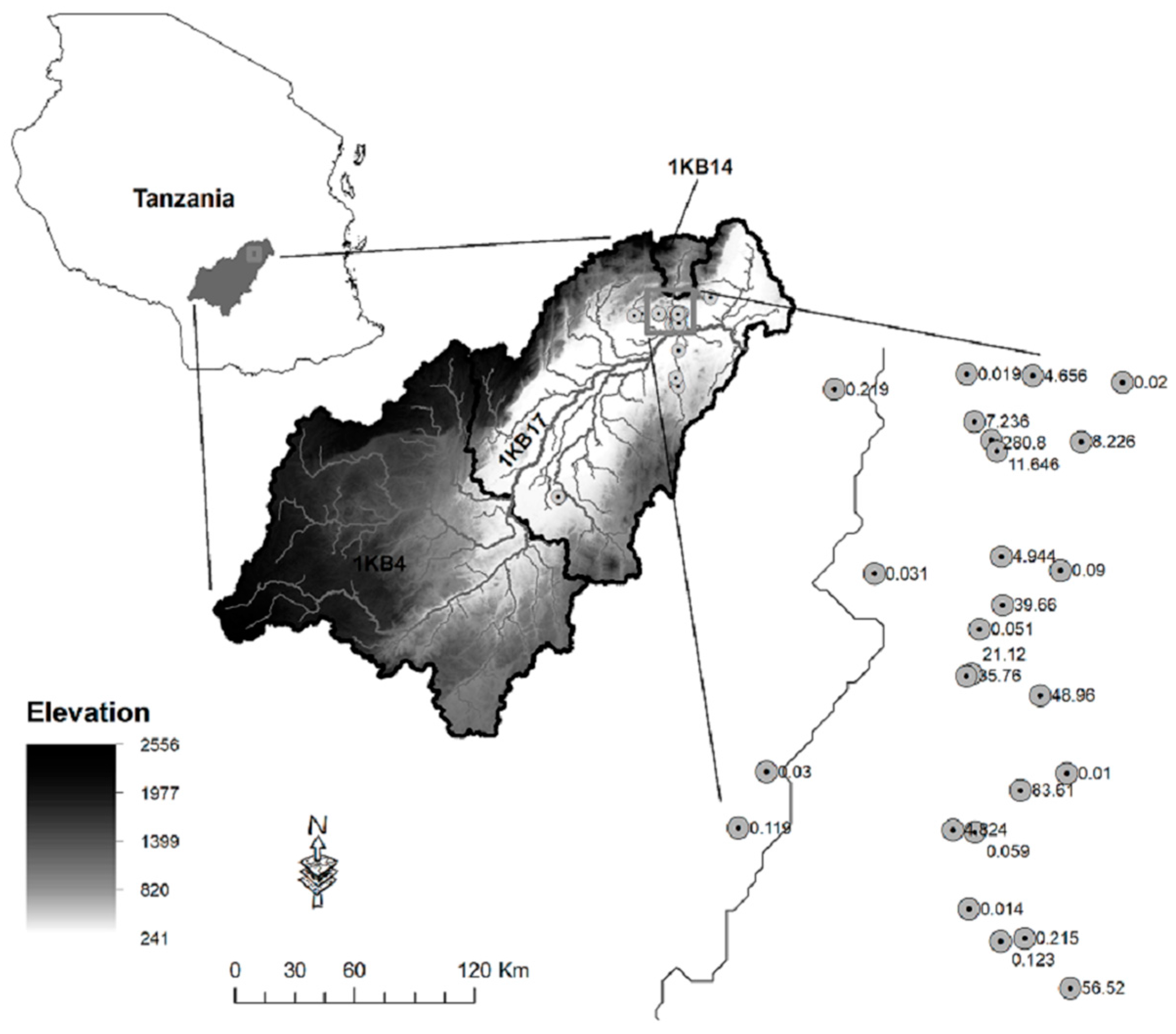
| Catchment ID | River | Catchment Area (km2) | Stream Length (km) | Average Flow (m3/s) | Min Flow (m3/s) | Max Flow (m3/s) | Specific Discharge (mm/d) | Period of Record | Missing Data (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KB17 | Kilombero | 34,230 | 5916 | 514.72 | 91.70 | 3310.90 | 1.30 | 1960–1982 | 1.8 |
| 1KB14 | Lumemo | 580 | 63 | 6.09 | 0.18 | 139.61 | 0.91 | 1960–1982 | 0.0 |
| 1KB4 | Kilombero | 18,048 | 2859 | 207.48 | 16.74 | 548.19 | 0.99 | 1960–1982 | 18.5 |
| Parameter | D (m) | h (m) | b (m) | kc (cm/s) | T (m2/min) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 22 | 252 | 10 | <0.01 | 0.01 |
| Median | 69 | 268 | 20 | 0.20 | 4.74 |
| Maximum | 101 | 322 | 66 | 31.24 | 370.80 |
| Average | 66 | 274 | 26 | 2.42 | 29.38 |
| Standard Deviation | 23 | 17 | 13 | 6.14 | 74.63 |
| Parameter | All Wells | No Outliers |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Wells | 38 | 27 |
| Minimum (m2/min) | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| Median (m2/min) | 4.74 | 0.18 |
| Maximum (m2/min) | 370.80 | 11.65 |
| Average (m2/min) | 29.38 | 2.48 |
| Standard Deviation (m2/min) | 74.63 | 3.50 |
| Parameter | Catchment ID | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KB17 | 1KB14 | 1KB4 | ||||
| Season | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet |
| Total events | 8 | 6 | 8 | 7 | 8 | 5 |
| Minimum K (days) | 40 | 58 | 38 | 17 | 40 | 43 |
| Median K (days) | 63 | 80 | 79 | 44 | 193 | 89 |
| Maximum K (days) | 100 | 128 | 112 | 72 | 288 | 249 |
| Mean K (days) | 67 | 88 | 76 | 44 | 180 | 136 |
| Standard Deviation K (days) | 18 | 27 | 27 | 20 | 87 | 93 |
| Parameter | Catchment ID | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1KB17 | 1KB14 | 1KB4 | ||||
| Season | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet | Dry | Wet |
| Total events | 14 | 13 | 23 | 53 | 6 | 24 |
| Minimum T (m2/min) | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.01 | 0.01 | 0.24 | 0.01 |
| Median T (m2/min) | 0.66 | 0.14 | 0.51 | 0.05 | 0.70 | 0.16 |
| Maximum T (m2/min) | 10.60 | 7.93 | 9.59 | 0.97 | 1.46 | 1.91 |
| Average T (m2/min) | 2.40 | 1.18 | 1.16 | 0.12 | 0.73 | 0.31 |
| Standard Deviation T (m2/min) | 3.64 | 2.31 | 2.07 | 0.17 | 0.50 | 0.47 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Senkondo, W.; Tuwa, J.; Koutsouris, A.; Tumbo, M.; Lyon, S.W. Estimating Aquifer Transmissivity Using the Recession-Curve-Displacement Method in Tanzania’s Kilombero Valley. Water 2017, 9, 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120948
Senkondo W, Tuwa J, Koutsouris A, Tumbo M, Lyon SW. Estimating Aquifer Transmissivity Using the Recession-Curve-Displacement Method in Tanzania’s Kilombero Valley. Water. 2017; 9(12):948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120948
Chicago/Turabian StyleSenkondo, William, Jamila Tuwa, Alexander Koutsouris, Madaka Tumbo, and Steve W. Lyon. 2017. "Estimating Aquifer Transmissivity Using the Recession-Curve-Displacement Method in Tanzania’s Kilombero Valley" Water 9, no. 12: 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120948
APA StyleSenkondo, W., Tuwa, J., Koutsouris, A., Tumbo, M., & Lyon, S. W. (2017). Estimating Aquifer Transmissivity Using the Recession-Curve-Displacement Method in Tanzania’s Kilombero Valley. Water, 9(12), 948. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9120948





