Abstract
Steel slag, which makes up a gigantic amount of metallurgical industrial solid waste, was in this experiment successfully synthesized an inexpensive adsorbent used to remove nitrate pollution from aqueous solution. This adsorbent was obtained by mixing steel slag, aluminium hydroxide and deionized water, and aging this at a mass ratio of 3:0.45:2, and then activating it at 800 °C. The physicochemical characteristics of the steel slag before and after modification were investigated to compare the effect of their surface properties on the adsorption behaviour of nitrate. The effects of adsorbent dosage, pH, and contact time on the adsorption process were investigated. The results showed that an increase in specific surface area and the formation of a positive surface of the modified steel slag (MSS) compared with the original steel slag (OSS) could effectively increase the number of the active adsorption sites and nitrate removal ability. The optimum parameters for nitrate removal were as follows: the concentration of nitrate was 20 mg/L, the dosage was 1 g/100 mL, the pH was four, and the reaction time was 180 min. The adsorption capacity of the MSS was approximately 1.9 times that of the OSS. The nitrate adsorption of the MSS was in accordance with the pseudo-second-order model and the Freundlich model, which indicated that the adsorption of nitrate on the MSS was mainly single layer chemical adsorption. The mechanism of nitrate removal mainly included ion exchange, hydrogen bonding, electrostatic interactions and intermolecular interactions. In addition, regeneration experiments indicated that the MSS after regeneration still had the capacity to remove nitrate.
1. Introduction
Nowadays, large areas of surface and groundwater are exposed to the risk of nitrate contamination in various countries and regions. This is mainly related to the continuous increase of industrial wastewater, chemical fertilizer, domestic sewage and waste manure, surface rainfall and other water pollution sources [1]. The high concentration of nitrate in water can affect human health and produce environmental risks, which may induce human cancer, eutrophication of surface water, and the destruction of biodiversity in the region [2,3,4,5,6,7]. Among the many methods of nitrate removal, adsorption methods have the advantage of simple operation, low energy consumption and a short treatment cycle. Therefore, it is very important to select the appropriate nitrate adsorption material [8,9]. Many materials, such as activated carbon, sepiolite, chitosan and ion exchange resin [8,10,11,12] can remove nitrate in water, but most of these compounds have high production costs, complex synthesis processes or are difficult to regenerate. Accordingly, they are not suitable for the treatment of large areas of nitrate-contaminated water.
In recent years, the use of cheap industrial and agricultural waste as an adsorbent for wastewater treatment has attracted more and more attention [13]. Steel slag is a solid waste produced in the metallurgical industry. It has a loose and porous structure, high density, settles fast in water, a short cycle of solid–liquid separation, and contains alkaline oxide and a large amount of iron and silicon. These features make steel slag a possibility for the adsorption of pollutants in wastewater [14]. A great deal of research has shown that steel slag is an inexpensive wastewater adsorbent that can effectively remove phosphate, ammonia, harmful metal and other pollutants in aqueous solution by chemical reaction and adsorption [15,16,17]. However, nitrates are almost completely soluble in water, compared with phosphate ions, ammonium ions and fluoride ions, etc., and it is difficult to form various insoluble substances attached to the surface of the adsorbent and there is some difficulty in removing them [18,19]. Compared with some industrial synthetic adsorbents, steel slag is a type of complex system of CaO-MgO-Al2O3-SiO2 whose surface combines with some minor elements in the process of crystallization or glass transition that can affect its adsorption function [20], so that the internal chemical composition cannot be effectively used. Therefore, the adsorption efficiency of steel slag to nitrate is relatively limited [7,21]. Compared with Fe3+ loaded chitosan (8.35 mg/g), nano alumina (4 mg/g) and activated carbon (1.22 mg/g) [22,23,24], the maximum adsorption capacity of steel slag on nitrate is 2.83 mg/g in aqueous solution based on previous research [7]. Therefore, it is necessary to improve the removal efficiency of nitrate with a modified method.
Researchers have applied different activation techniques to improve the adsorption capacity of steel slag to other pollutants [25,26,27], making steel slag an inexpensive wastewater adsorbent. According to previous studies, aluminium hydroxide (Al(OH)3) has been successfully used as a modifier for adsorbents in wastewater treatment to improve its adsorption efficiency [19,20,26,28]. Duan et al. [19] showed that the removal efficiency of nitrogen and phosphorus was significantly improved by using Al(OH)3 to modify steel slag, and the activated alumina (Al2O3) generated in the process of modification played an important role in the removal of pollutants. Activated alumina (Al2O3) has high specific surface area and amphoteric properties, which show good performance in removing nitrate from water [18,29,30]. However, the removal efficiency of nitrate in aqueous solution by MSS has not been studied.
Therefore, this study intended to modify the steel slag to prepare a new type of low-cost adsorbent to reduce the nitrate pollution in water. In this study, steel slag, Al(OH)3 and deionized water were mixed in a certain proportion, and activated at a high temperature to improve the nitrate removal efficiency of steel slag in aqueous solution. It has been found that this modification method could improve the nitrate removal efficiency by enlarging the porosity and surface properties, the amount of active substances and the positive charge on the surface of the steel slag to a large extent. In addition, regeneration experiments indicated that the MSS after regeneration still had the capacity to remove nitrate.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Materials
In this study, the steel slag (obtained from Iron & Steel Co., Ltd, Nanjing, China) was crushed, ground and sieved to pass through a 60-mesh sieve (0.25 mm). The samples were washed with deionized water and dried at 105 ± 0.5 °C for 4 h, and then cooled to room temperature in a desiccator. This steel slag was defined as the original steel slag (OSS).
Procedures for the preparation of the adsorbent (MSS) were as follows: the dry slag, deionized water and aluminium hydroxide (Fine Chemical Research Institute, Tianjin, China) were fully mixed at room temperature according to the following mass ratios for five groups (3:2:0.15, 3:2:0.30, 3:2:0.45, 3:2:0.60, 3:2:0.75). After aging at room temperature for 10 h and drying at a temperature of 105 ± 0.5 °C for 2 h, they were heated at 600, 700, 800and 900 °C for 2 h, respectively, and cooled to room temperature. Then, the 20 types of MSS (Table 1) were ground to pass through a 60-mesh sieve and stored in a desiccator. A total of 2 g of the above 20 adsorbents was placed in a series of 250 mL conical flasks, and potassium nitrate solution (100 mL) with a nitrate concentration of 300 mg/L was added to each conical flask and then shaken at 25 °C for 180 min.

Table 1.
All types of modification conditions and MSS.
All chemicals used are of analytical grade. A precise amount of potassium nitrate was dissolved in deionized water to prepare a stock solution of potassium nitrate, and other concentrations of the solution were prepared by diluting the stock solution. The pH of the solution was adjusted by 0.1 M HCl and 0.1 M NaOH solution. All the solutions in each group were freshly prepared.
2.2. Characterization, Test Methods and Equipment
The main chemical constituents of the samples were measured by X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF-1800, Shimadzu, Japan). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns of the samples were produced using an Ultima IV X-ray diffraction instrument (D8 ADVANCE, Bruker, German) operating with a Cu-Kα radiation source filtered with a graphic monochromator (λ = 1.5406) to reveal information about the crystallographic structure. The 2-Theta (2θ)angle was varied within a range of 10–90° with a 0.02° step size and a 1°/min scan speed. The surface morphology of the samples was measured by a scanning electron microscope (S-4800, HITACHI, Japan). The specific surface areas of the samples were calculated from the N2 sorption isotherms at 196 °C by the Brunauer, Emmett and Teller (BET) method, and the pore size distribution of samples was determined by the Bearrett-Joyner-Halenda (BJH) method with an ASAP 2020 device (Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA). The zeta potential of MSS at different pH conditions was determined with a Zeta Potentiometer (Zetasizer Nano Z, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, UK), and the chemical bonds in the slag were analysed by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) (Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) using KBr compression. The harmful metal elements such as Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd in the toxic leaching test were measured by inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectrometry (ICP-AES) (OPTIMA 7000DV, Perkin Elmer, Aachen, NRW, German). The concentration of nitrate was determined by Chinese industry standard-method ultraviolet spectrophotometry (HJ/T 346-2007) [31].
2.3. Toxicity Leaching Test
Research reports [32,33] have indicated that steel slag might release harmful metals such as Cu, Zn, Pb, and Cd. Therefore, to verify the feasibility of the modified steel slag as an adsorbent to rectify sewage, a leaching test was conducted to research the possibility of the release of harmful metal elements in the steel slag before and after modification. The toxic leaching concentration of this test was determined according to the National Environmental Protection Standard of the People’s Republic of China-Horizontal Oscillation Method for Leaching of Solid Waste Leaching (HJ 557-2010) [34].
First, 100 g of adsorbents (OSS and MSS), dried at 105 °C, and 1 L of deionized water were added to the 2 L extraction bottle, which was fixed in the hot vibrating screen vertically after tightening the cap. Then, the oscillation frequency was adjusted to 110 rpm and the amplitude was 40 mm. After shaking at room temperature for 8 h, the extraction flask was taken and held for 16 h. The filters were packed on a vacuum filter, the leachate was collected by filtration and the concentrations of copper, zinc, lead, chromium, vanadium and arsenic leached from steel slag before and after modification were measured. Each group of tests made three parallel samples, and the average of the parallel samples was recorded.
2.4. Batch Experiments
A series of 250 mL conical flasks with stopper received 100 mL of potassium nitrate solution with an initial pH value of four and nitrate concentration of 20 mg/L and 1.0 g of MSS and were shaken with a constant temperature shaker (25 °C) at 180 rpm. The supernatant was collected at 30, 60, 120, 180, 300 and 420 min after shaking and centrifuged for 10 min before it was filtered through a 0.45 μm microporous membrane. The concentration of nitrate in the filtrate was measured by UV spectrophotometer, and the adsorption of nitrate, qt (mg/g), at different times (t) was calculated by the formula Equation (1):
where C0 and Ct are the concentration of nitrate at baseline and after time t (mg/L), respectively, V is the volume of the solution (L), and m is the amount of adsorbent added (g).
The effect of the adsorbent dosage on nitrate removal was tested at a temperature of 25 °C. The adsorbent dosages were 0.2, 0.4, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0 and 2.0 g/100 mL, and the initial concentration of nitrate was 20 mg/L.
The initial pH of the solution (1.0 ± 0.1 to 10.0 ± 0.1) for nitrate removal was tested at a temperature of 25 °C, an adsorbent dosage of 1 g/100 mL and a nitrate initial concentration of 20 mg/L. The effect of pH on the zeta potential of the MSS particles was investigated by adding 1 g of the MSS to 100 mL of deionized water with the pH adjusted.
The conditions of the batch equilibrium experiments were as follows: a nitrate concentration range of 20–300 mg/L, an adsorbent dosage of 1 g/100 mL, a temperature of 25 °C and an oscillation time of 180 min. The equilibrium adsorption capacity, qe (mg/g), was calculated according to the following formula Equation (2):
where C0 and Ce are the concentrations of nitrate at baseline and equilibrium (mg/L), respectively. Each of the above experiments was repeated three times and the data were expressed as the average value with the standard deviation values.
2.5. Regeneration
The regeneration method for MSS after the adsorption of nitrate was calcined in a muffle furnace at 800 °C for 120 min and cooled to room temperature due to the MSS’s adsorption capacity for nitrate reaching saturation after a certain period of time.
1.0 g of regenerated MSS and 100 mL of potassium nitrate solution with an initial pH value of four and a nitrate concentration of 20 mg/L were added into the 250 mL conical flasks and shaken in a constant temperature shaker (25 °C) at 180 rpm. After filtration, the nitrate concentration in the filtrate was determined. The effect of regenerated MSS on nitrate removal and its variation was studied by repeating the above steps five times.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Adsorbents
After the analysis of the final nitrate content of each filtrate, the highest adsorption efficiency appeared in the MSS13, which mass ratio of steel slag, deionized water and Al(OH)3 was 3: 2: 0.45, and the calcination temperature was 800 °C. Therefore, the following experiments were all used in this method to modify the steel slag.
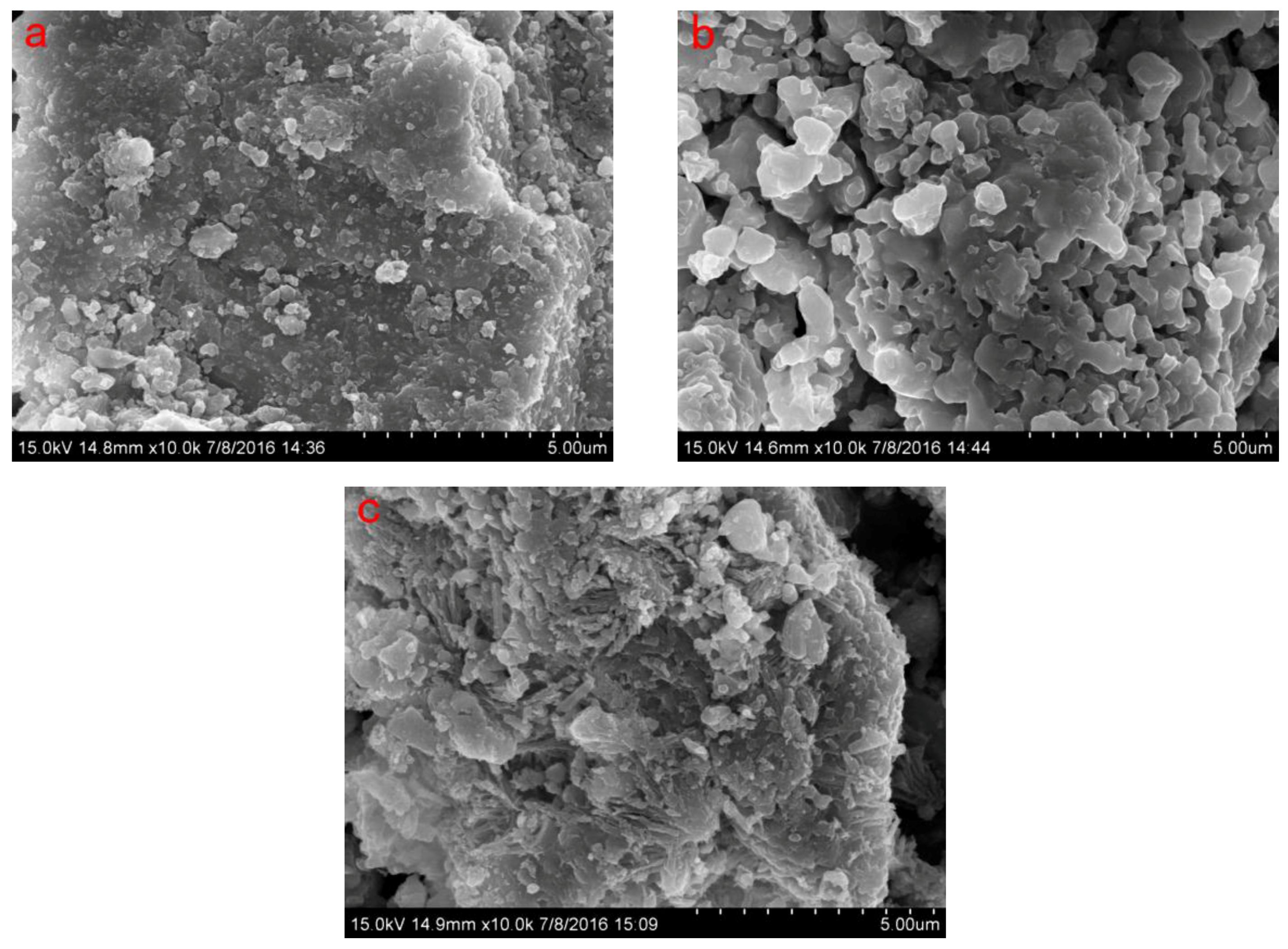
Significant differences between OSS and MSS were observed by scanning electron microscopy (Figure 1). The surface of the MSS appeared to have a rounded or indefinite shape, resulting in a large number of irregular protrusions and more pores. High temperature heating during modification can remove water molecules and some impurities in the steel slag, resulting in the opening of the channel inside and outside the steel slag, expansion of the pore size and formation of the high pore. These morphological changes led to a greater increase in the specific surface area (3.34 times higher than that of the OSS) and the volume of the total pore, mesopore and micropore (Table 2). Some studies have concluded that adsorption capacity can be enhanced by increasing the specific surface area and the adsorption sites on the surface of the adsorbent particles [27,28,35].
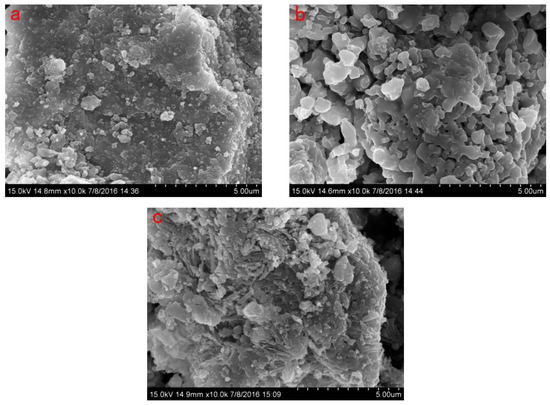
Figure 1.
Scanning electron microscope (SEM) of OSS, MSS and MSS after adsorption of nitrate (a): OSS; (b): MSS; (c): MSS after adsorption.

Table 2.
Physical properties of OSS and MSS.
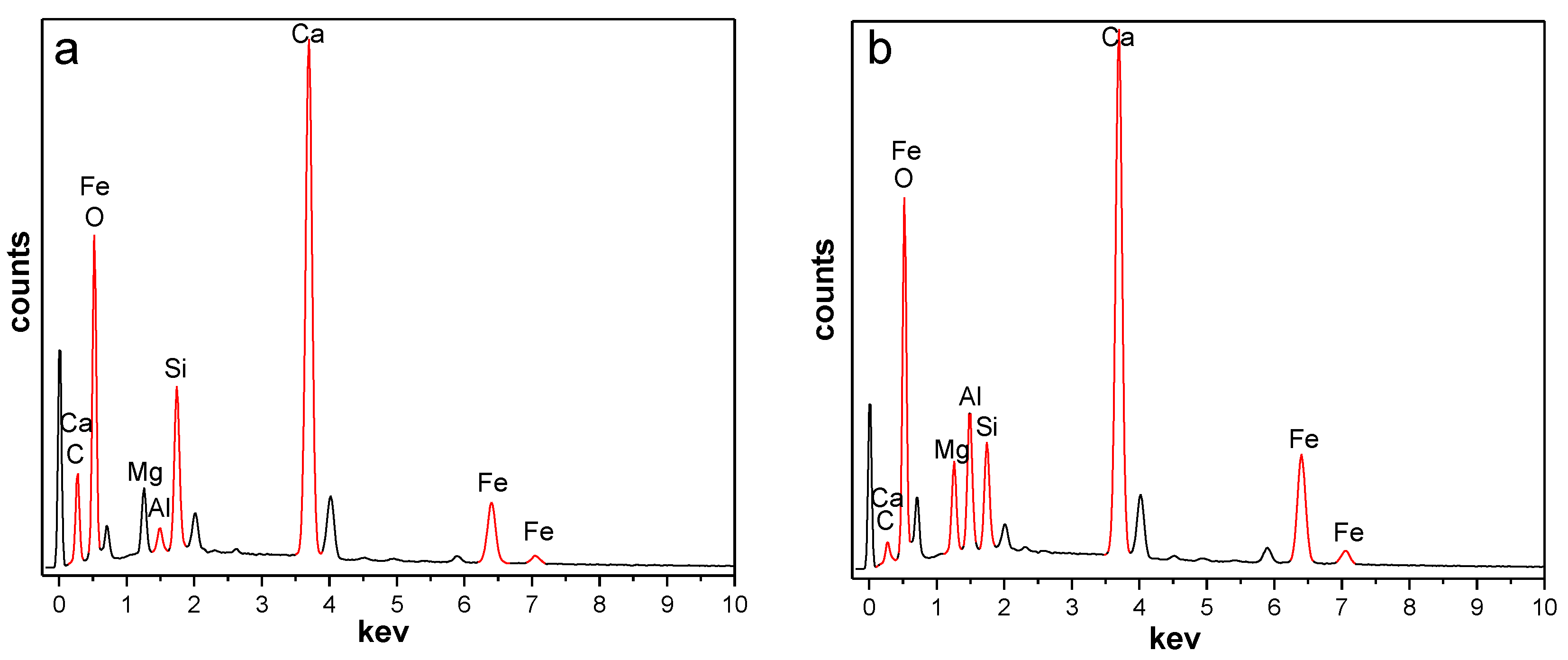
The OSS and MSS consisted mainly of CaO, Fe2O3, SiO2, MgO, P2O5, MnO, Al2O3, TiO2 and so on (more than 98% by mass), and the content of Al2O3 increased from 1.66% in OSS to 20.01% in MSS (Table 3). By comparing the energy dispersive spectrometer (EDS) pattern of the OSS and MSS (Figure 2), it was found that the aluminium content (wt) on the surface of the steel slag also increased after modification. Abbas N et al. [18] indicated that activated alumina has a good effect on nitrate removal. Due to the amphoteric properties of Al2O3, its surface is good for the adsorption of not only nitrate ions but also most of the oxy ions. In addition, the carbon content of MSS decreased after modification, which may be due to the high temperature decomposition of carbonates to increase cracks and holes on the surface of the steel slag. Therefore, the increase in alumina content and the number of pores can improve the number of active sites of adsorbents [19,26,28,30], which was beneficial to nitrate removal in aqueous solution.

Table 3.
Main chemical composition of original and modified steel slag (wt %).
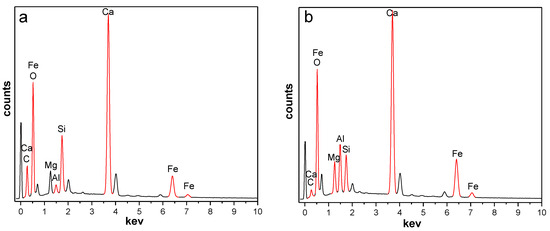
Figure 2.
EDS spectrum of OSS and MSS ((a): OSS; (b): MSS).
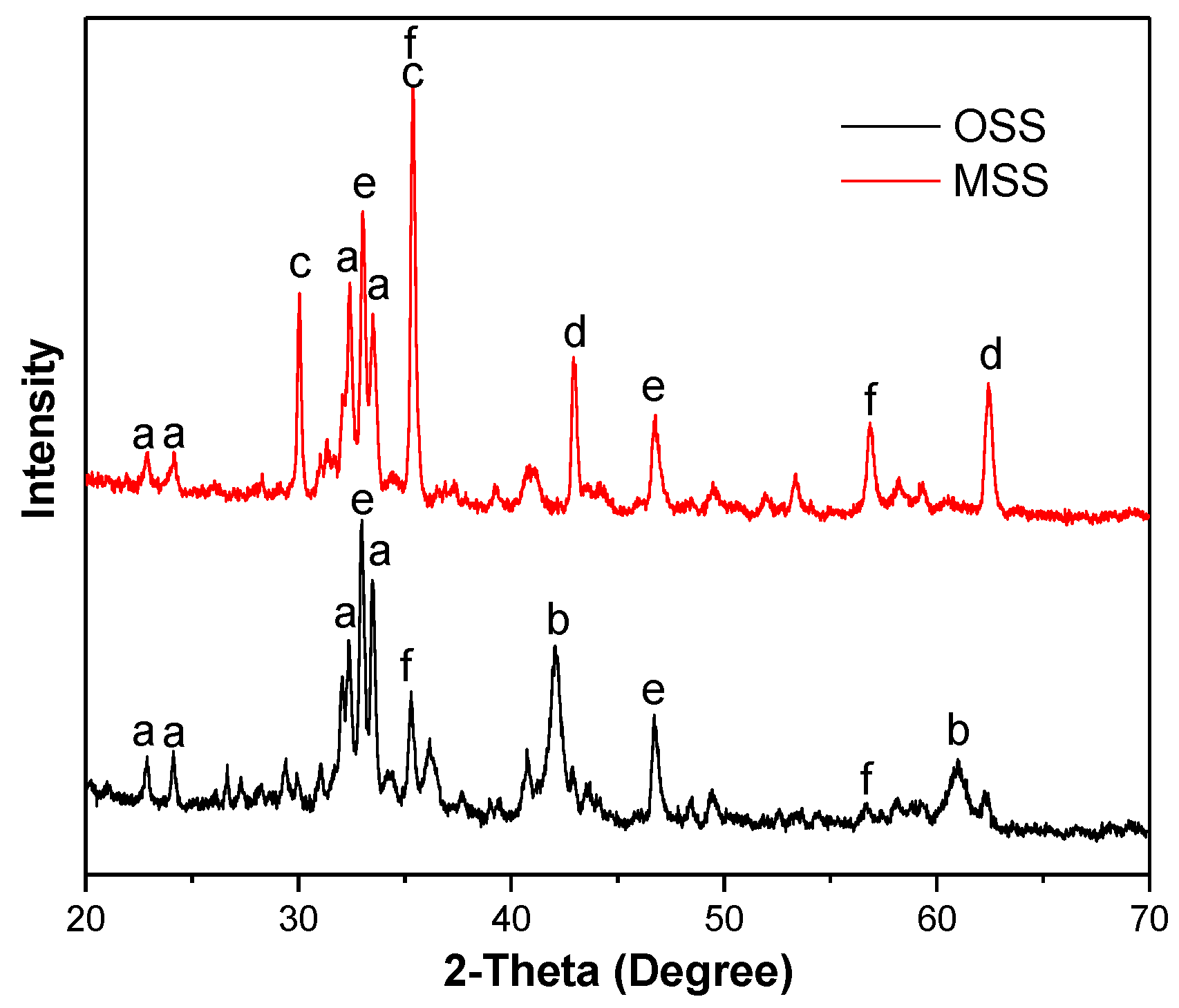
By comparing the XRD patterns of OSS and MSS, some diffraction peaks were significantly reduced and some new peaks were produced (Figure 3). Both the OSS and MSS contained the ferrite mineral phase (Ca2Fe2O5, JCPDS No.18-0286), calcium iron titanium oxide (Ca4Fe2Ti2O11, JCPDS No.40-0131) and titanomagnetite (Fe2.75Ti0.25O4, JCPDS No.75-1374). Compared with OSS, the new mineral phase of calcium aluminate (CaO·Al2O3, JCPDS No.34-0440) and magnesium oxide (MgO, JCPDS No.43-1022) appeared, and ferrous oxide (FeO, JCPDS No.01-1223) disappeared in the XRD pattern of MSS. The appearance of calcium aluminate may be due to the high temperature reaction of calcium hydroxide and aluminium hydroxide in the process of modification, see Equation (3). Numerous researchers have shown that activated alumina (Al2O3) has high specific surface area and amphoteric properties, which have good performance in nitrate removal from water [18,29,30]. Therefore, the increase in the amount of activated alumina on the surface of the MSS is favourable for nitrate removal. The disappearance of ferrous oxide may be due to the formation of dicalcium ferrite or other phases in high temperature environments.
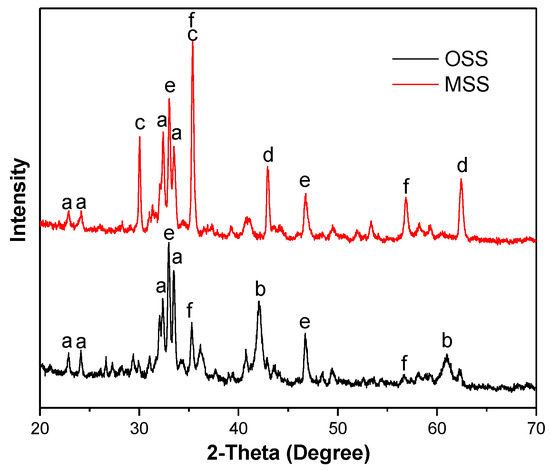
Figure 3.
X-ray diffraction (XRD) pattern of OSS and MSS (a: Ca2Fe2O5, b: FeO; c: CaO·Al2O3; d: MgO; e: Ca4Fe2Ti2O11; f: Fe2.75Ti0.25O4).
3.2. Toxicity Analysis
The concentration of toxic elements released into the solution before and after modification (Table 4) were below the detection limit of the ICP-AES, and were far less than the class III values of the environmental quality standards for surface water (GB 3838-2002) [36]. This result was consistent with Chamteut Oh’s study of the leaching characteristics of the elements in the steel slag through the Korean Standard Leaching Experiment (KSLT) [37]. It can be seen that these elements of the steel slag have very small leaching probability, and short-term use as a wastewater adsorbent does not produce toxic pollution.

Table 4.
Concentration of toxic elements in the leaching solution of OSS and MSS (mg/L).
3.3. Adsorption Characteristics of MSS
3.3.1. Effect of Adsorbent Dosage
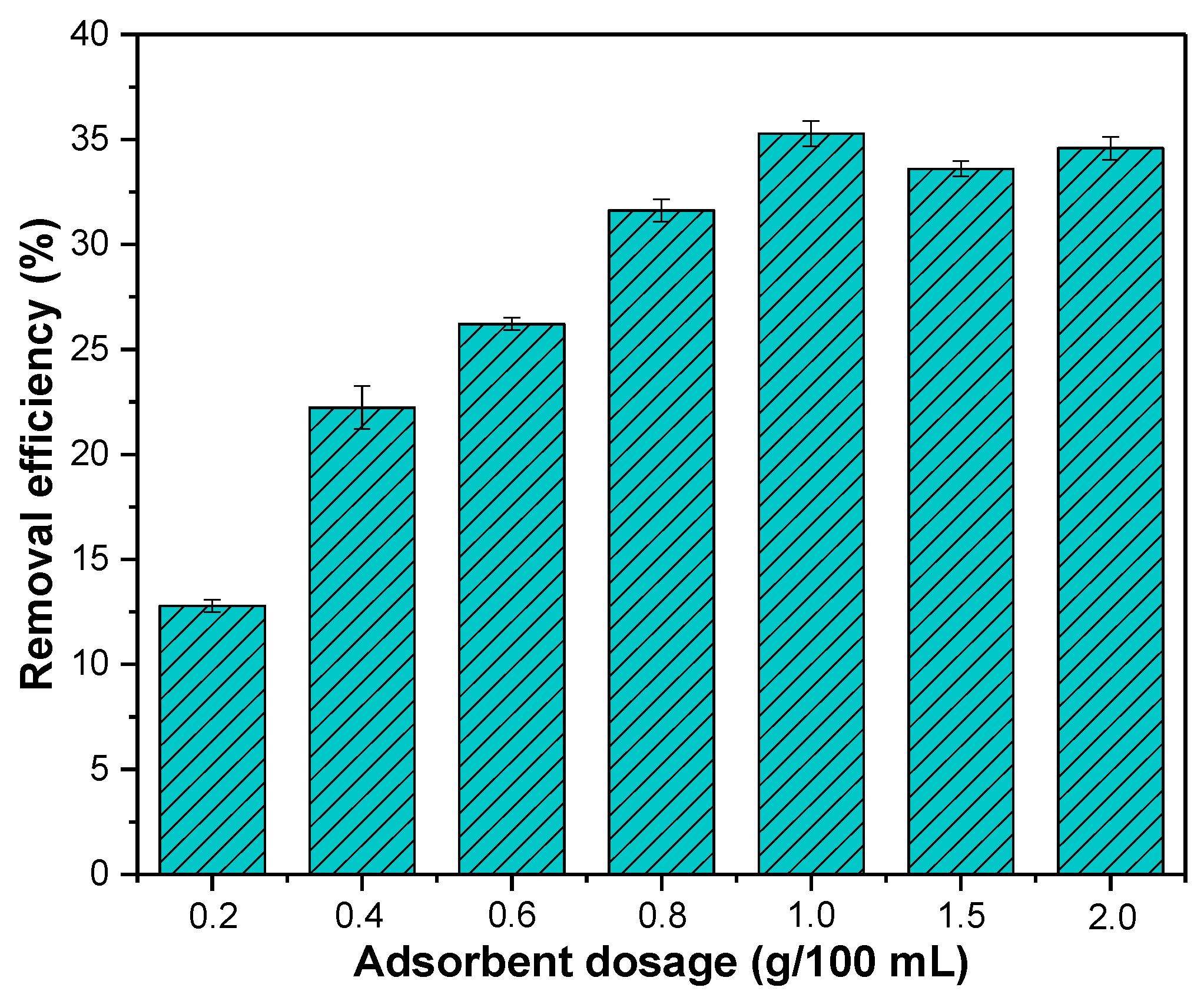
With the increasing dosage of adsorbent from 0.2 g/100 mL to 1 g/100 mL, the removal efficiency of nitrate increased from 12.78% to 35.27% (Figure 4). The increase in the dosage of adsorbent can provide a larger specific surface area and more adsorption sites for nitrate removal. However, as the adsorbent dosage increased from 1 g/100 mL to 2 g/100 mL, the removal efficiency of nitrate decreased slightly and became stable. This may be due to the aggregation of adsorbent particles with the increase in adsorbent dosage, leading the surface adsorption sites to fail to be fully utilized [38].
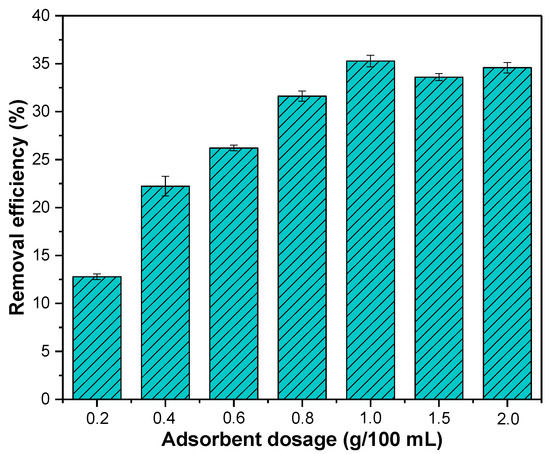
Figure 4.
Effect of dosage on nitrate removal efficiency. Initial concentration of nitrate: 20 mg/L; initial pH: 4; reaction time: 180 min; temperature: 25 °C.
3.3.2. Effect of pH
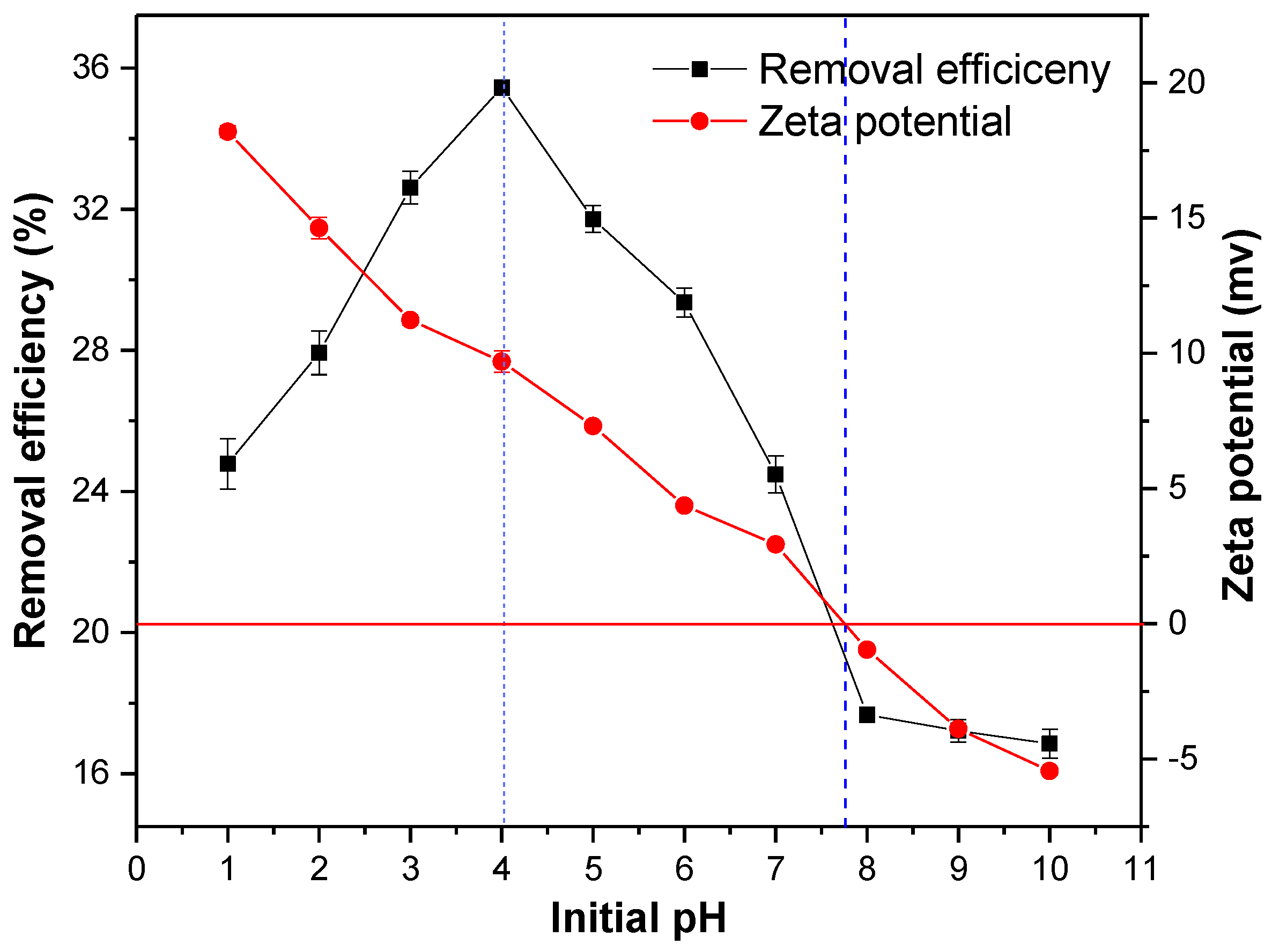
The pH of the solution is one of the important parameters that affects the adsorption performance of the adsorbent. When the pH increased from one to four, the adsorption efficiency of the MSS increased, whereas it decreased from four to 10 (Figure 5), and the highest removal efficiency of nitrate (35.45%) occurred at a pH four. After measuring the zeta potential of the MSS particles, it was found that the surface charge of the modified steel slag decreased from +18.19 to −5.45 when the pH of the solution was between zero and 10, where the pHzpc (isoelectric point) was 7.8.
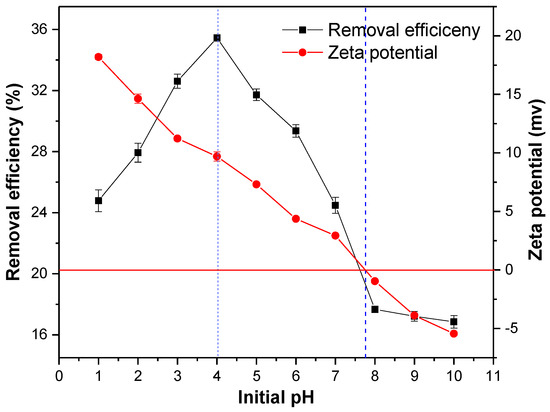
Figure 5.
Effect of initial pH on nitrate removal efficiency and zeta potential. Initial concentration of nitrate: 20 mg/L; adsorbent dosage: 1 g/100 mL; reaction time: 180 min; temperature: 25 °C.
The pH of the solution determined the protonated variable charge of the surface of the MSS [20,27], which affected the electrical properties of the adsorbent and thus had a great influence on the adsorption of nitrate. In the acidic medium, the hydration surface of the MSS underwent a protonation reaction, see Equation (4), and the dissolved metal cation was embedded in the surface of the MSS to obtain a positive charge [26,39]. With the increase of the initial pH, the OH− concentration in the solution increased and the deprotonation reaction occurred on the hydrated surface of the MSS to obtain a negative charge, see Equation (5). When the pH was less than 7.8, the nitrate in the presence of anions can be adsorbed by electrostatic attraction owing to the positively charged surface. Therefore, the reduction of pH is favourable for nitrate adsorption. However, when the pH was less than four, the active sites on the surface of the MSS were dissociated in the strong acid environment [27], and the hydrochloric acid added for the initial pH adjustment contained interfering ions of chloride ions, which inhibited the adsorption of nitrate [29,40]. The adsorption capacity could not reach a maximum when the pH was very low. The concentration of hydroxyl ions in the solution increased when the pH was between four and 7.8, resulting in a deprotonation reaction Equation (5) and a reduction in the number of surface positive charge sites and nitrate removal efficiency. Therefore, it was found that the best removal efficiency of nitrate was at a pH 4. When the pH was 7.8, the surface potential of the MSS was neutral, and the high density surface hydroxyl groups formed strong hydrogen bonds between the hydroxyl groups on the surface [41], which obstructed the adsorption of nitrate. When the pH was greater than 7.8, the nitrate adsorption capacity decreased due to the negatively charged surface of the MSS, which could produce electrostatic repulsion.
where Sur and Sur-OH represent the surface of the slag and the surface of the hydroxyl group, respectively.
Sur—OH + H+ → Sur—OH2+
Sur—OH + OH− → Sur—O− + H2O
3.4. Mechanisms of Nitrate Removal
3.4.1. Adsorption Kinetic Model
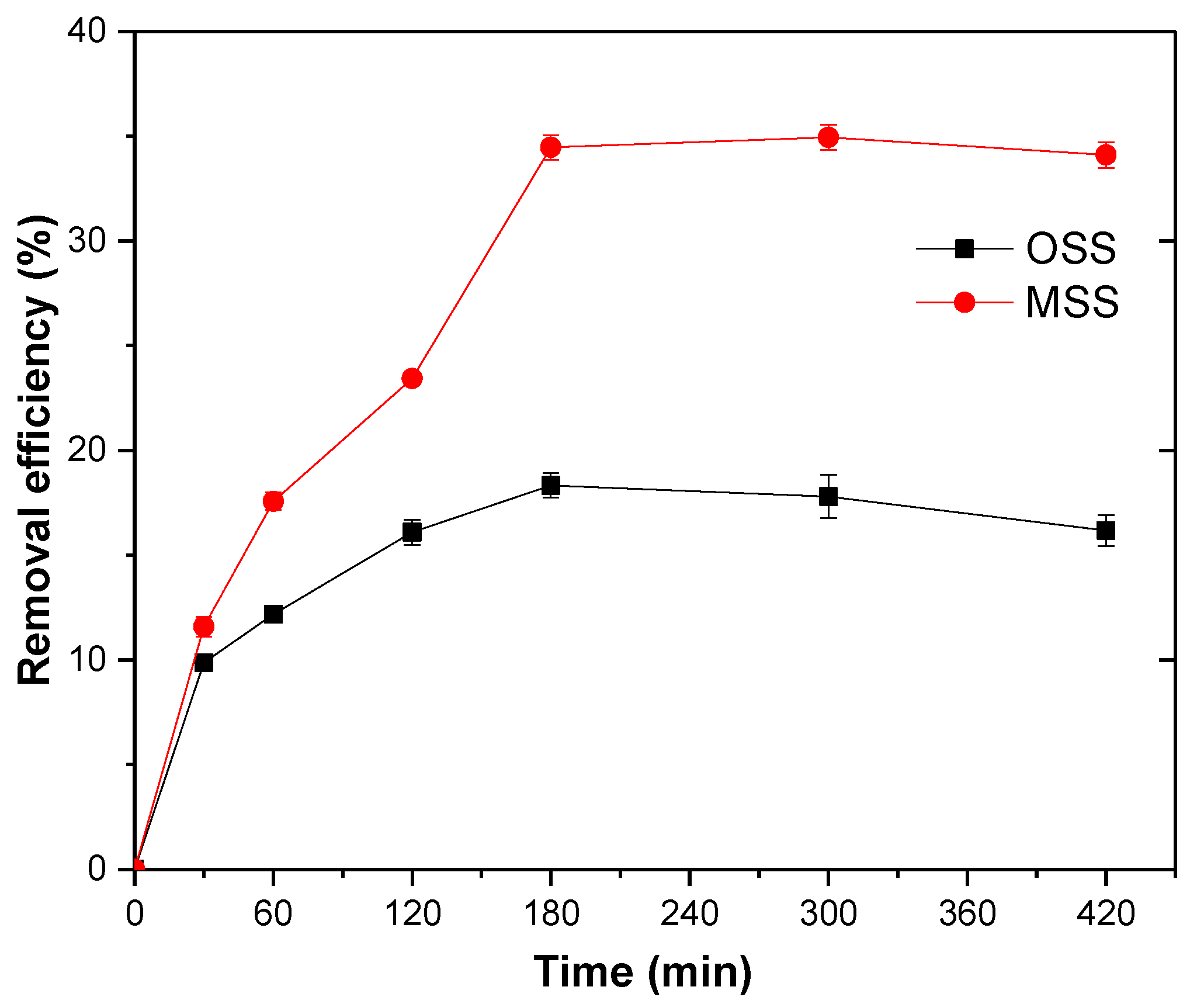
It was evident that the nitrate removal efficiency of the two adsorbents increased with time and reached a maximum at 180 min. The nitrate removal efficiency of the MSS was 1.9 times higher than that of the OSS (Figure 6).
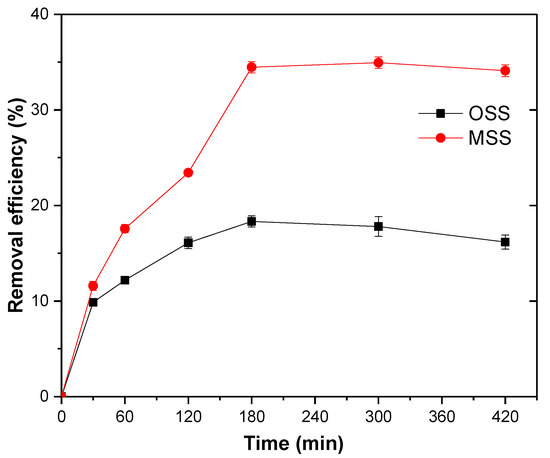
Figure 6.
Effect of reaction time on nitrate adsorption. Initial concentration of nitrate: 20 mg/L; steel slag dosage: 1 g/100 mL; initial pH: 4; temperature: 25 °C.
The kinetic model can be used to estimate the adsorption efficiency and derive an appropriate rate expression for the possible reaction mechanism. According to the time gradient, the adsorption kinetics data for OSS and MSS across 180 min (Figure 6) were analysed by two typical kinetic models, including the Lagergren pseudo-first-order kinetics model, see Equation (6) [42], and the pseudo-second-order kinetics model, see Equation (7) [43]. The pseudo-first-order kinetics model, based on the amount of solid adsorption, was applied to the liquid phase adsorption, and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model was based on the assumption that the adsorption rate was controlled by the chemical adsorption mechanism. The equations of the two kinetic models were as follows:
where qe (mg/g) is the equilibrium adsorption capacity, qt is the adsorption capacity at time t, and K1 (h−1) and K2 (g·mg−1·h−1) are the rate constant of the pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order, respectively.
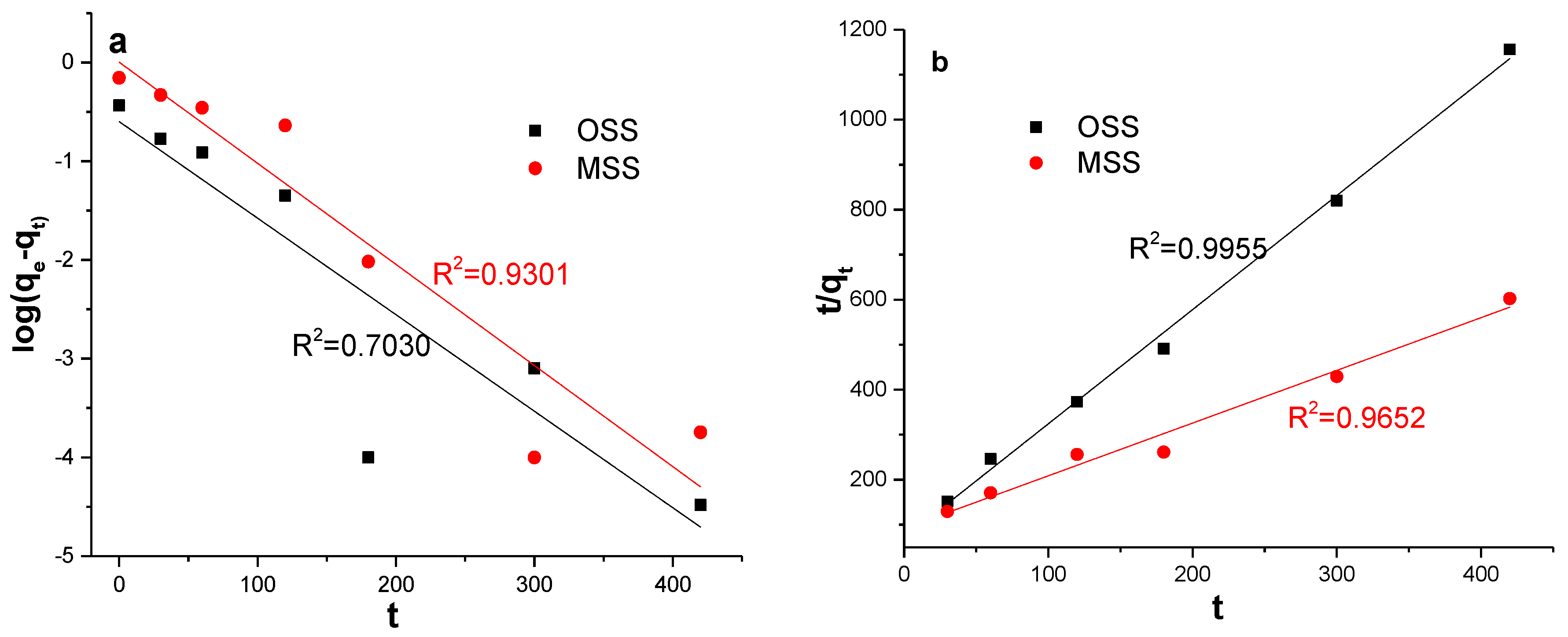
To obtain the rate parameters, fit graphs of the log (qe − qt) vs. t and t/qt vs. t were applied to pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetics models (Figure 7). The kinetic parameters for the adsorption of nitrate (Table 5) were calculated using these fit graphs. It can be seen that the pseudo-second-order kinetic model was more suitable for simulating the actual adsorption process of nitrate because the model had a high correlation coefficient (R2), and the theoretical qe,cal of the MSS were closer to experimental qe,exp. This finding indicated that the chemical adsorption process was a restriction factor for nitrate adsorption. The chemical adsorption involved the electron sharing or electron transfer between the adsorbent and the adsorbate [44], and the adsorption capacity was proportional to the number of active sites on the surface of the adsorbent particles [38]. Therefore, based on the high correlation coefficient and theoretical qe,cal, the adsorption process of MSS was more consistent with the secondary model.
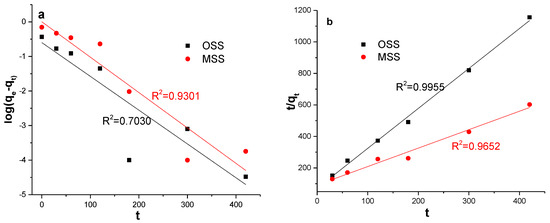
Figure 7.
Fit curves of two kinetic models for adsorption of nitrate by OSS and MSS (a): pseudo-first-order; (b): pseudo-second-order.

Table 5.
Kinetic parameters for adsorption of nitrate on OSS and MSS.
3.4.2. Isothermal Adsorption Model
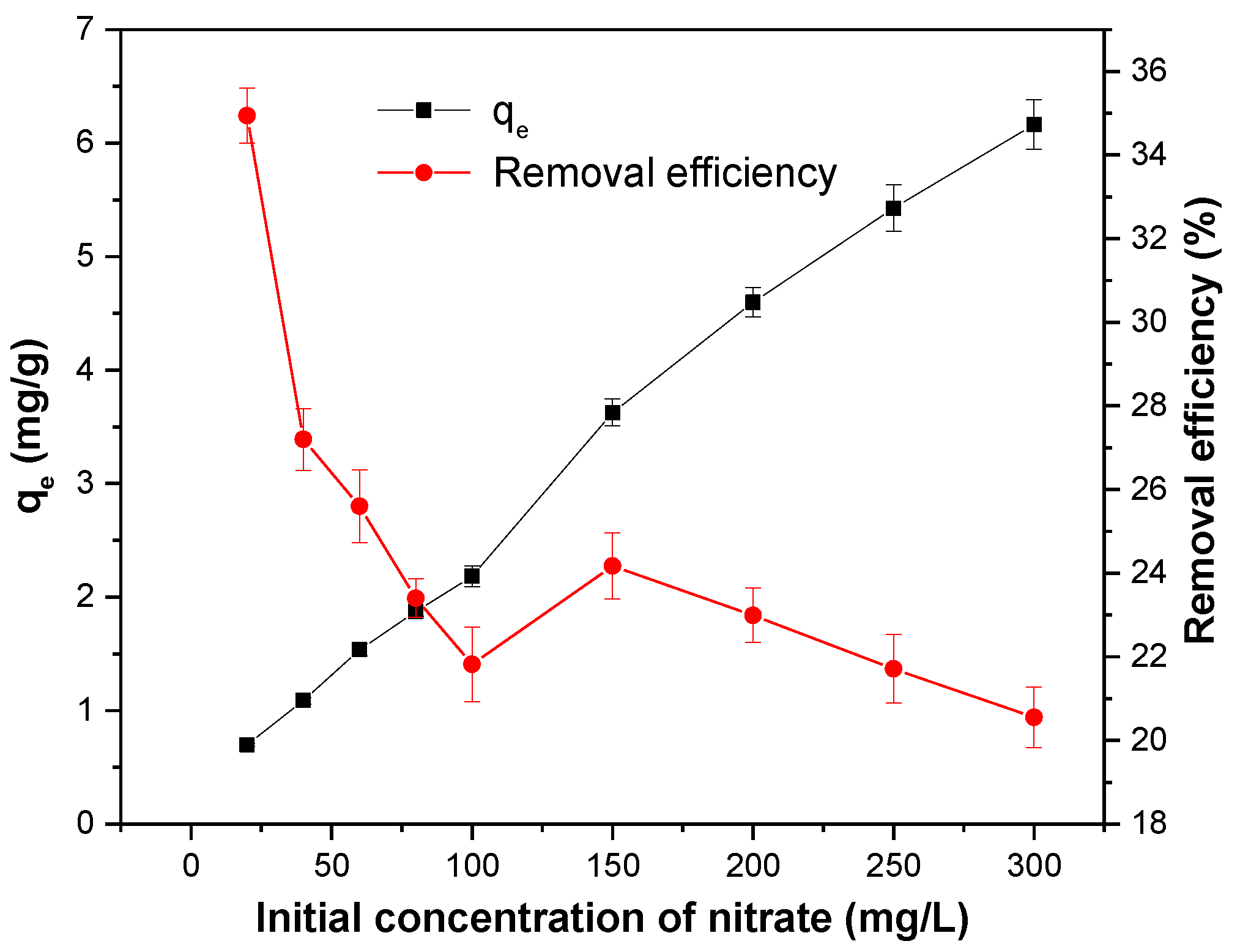
At the initial concentration of 20 to 300 mg/L, the amount of nitrate adsorbed did not reach the maximum, and the adsorption efficiency was lower in the high concentration range (Figure 8). It indicated that the MSS could adsorb the nitrate in the larger concentration range, which was similar to the results from Yang et al. [7]. The experimental data were analysed by the isotherm models of Langmuir Equation (8) [45] and Freundlich Equation (9) [46], which were expressed as follows:
where qe and qm are the equilibrium and maximum adsorption capacity, respectively; ce is the equilibrium concentration of the solution; KL is the equilibrium constant associated with the adsorption heat; and KF and n are the equilibrium constants associated with the adsorption capacity and intensity, respectively.
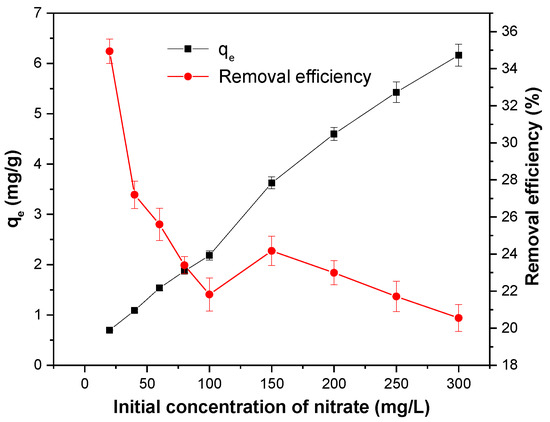
Figure 8.
Effect of the initial concentration of nitrate on the adsorption capacity of MSS. Initial concentration of nitrate: 20–300 mg/L; slag dosage: 1 g/100 mL, initial pH: 4; contact time: 180 min; temperature: 25 °C.
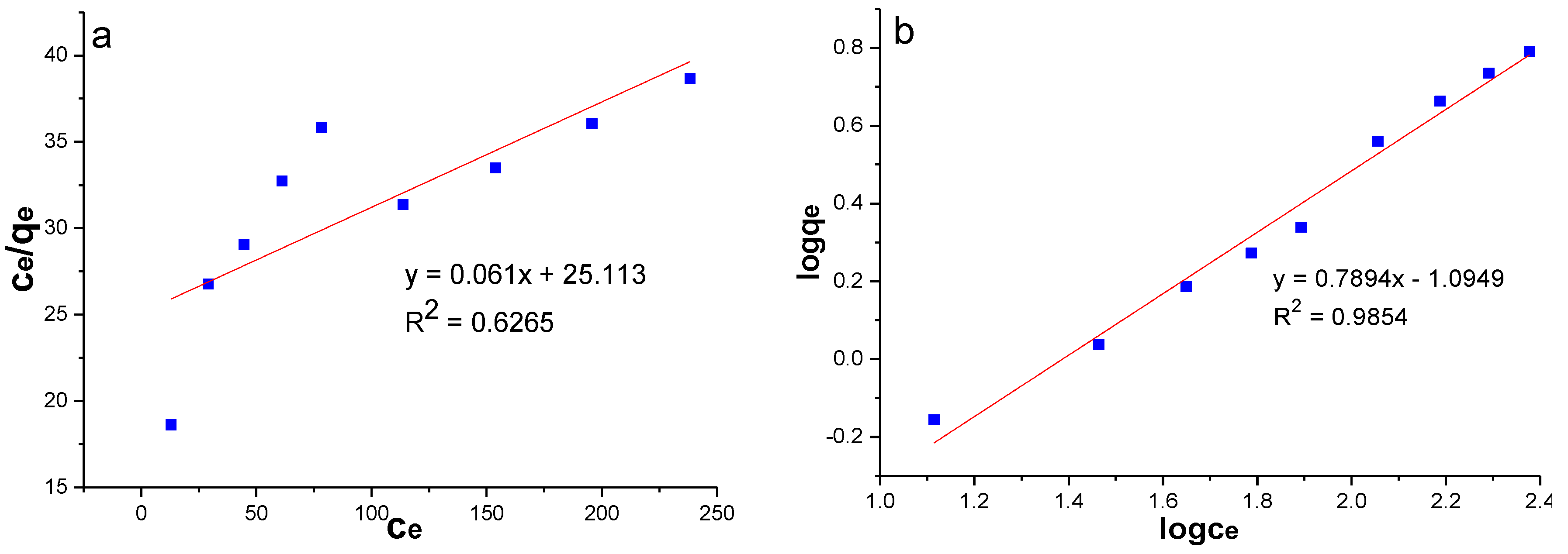
Comparing the correlation coefficients of the two models, the Freundlich model (R2 > 0.98) was more suitable for the experimental data of this paper (Table 6, Figure 9). It is generally believed that adsorption is more likely to occur when 1/n is between 0.1 and 1.0, whereas adsorption is more difficult when 1/n is greater than two [47,48]. In this experiment, MSS was favourable for the adsorption of nitrate (1/n = 0.7894). The Freundlich model assumes that adsorption takes place on uneven surfaces of adsorbent by monolayer adsorption with interaction among adsorbed ions. Therefore, it can be seen that the adsorption of nitrate by MSS is the chemical adsorption of a monomolecular layer by means of the adsorption kinetic model and Freundlich model.

Table 6.
Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm parameters for nitrate adsorption on MSS.
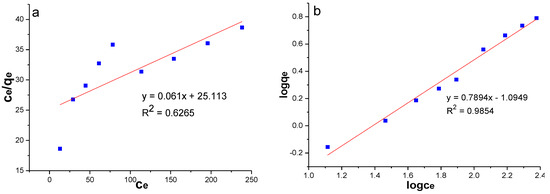
Figure 9.
Adsorption isotherms of nitrate: (a) Langmuir model; (b) Freundlich model.
3.4.3. Removal Mechanism
Compared with the OSS, the adsorption capacity of MSS increased, and was 1.9 times that of OSS. When the initial concentration of nitrate was 300 mg/L, the adsorption capacity of MSS was 6.165 mg/g, which reached a higher level compared with other adsorbent materials such as halloysite, nano-alumina and activated carbon and so on (Table 7) [22,23,24,49,50]. Therefore, the cheap steel slag after modification could be used as nitrate-contaminated water adsorbents.

Table 7.
Comparative evaluation of adsorption capacity and other experimental conditions of different sorbents for nitrate removal.
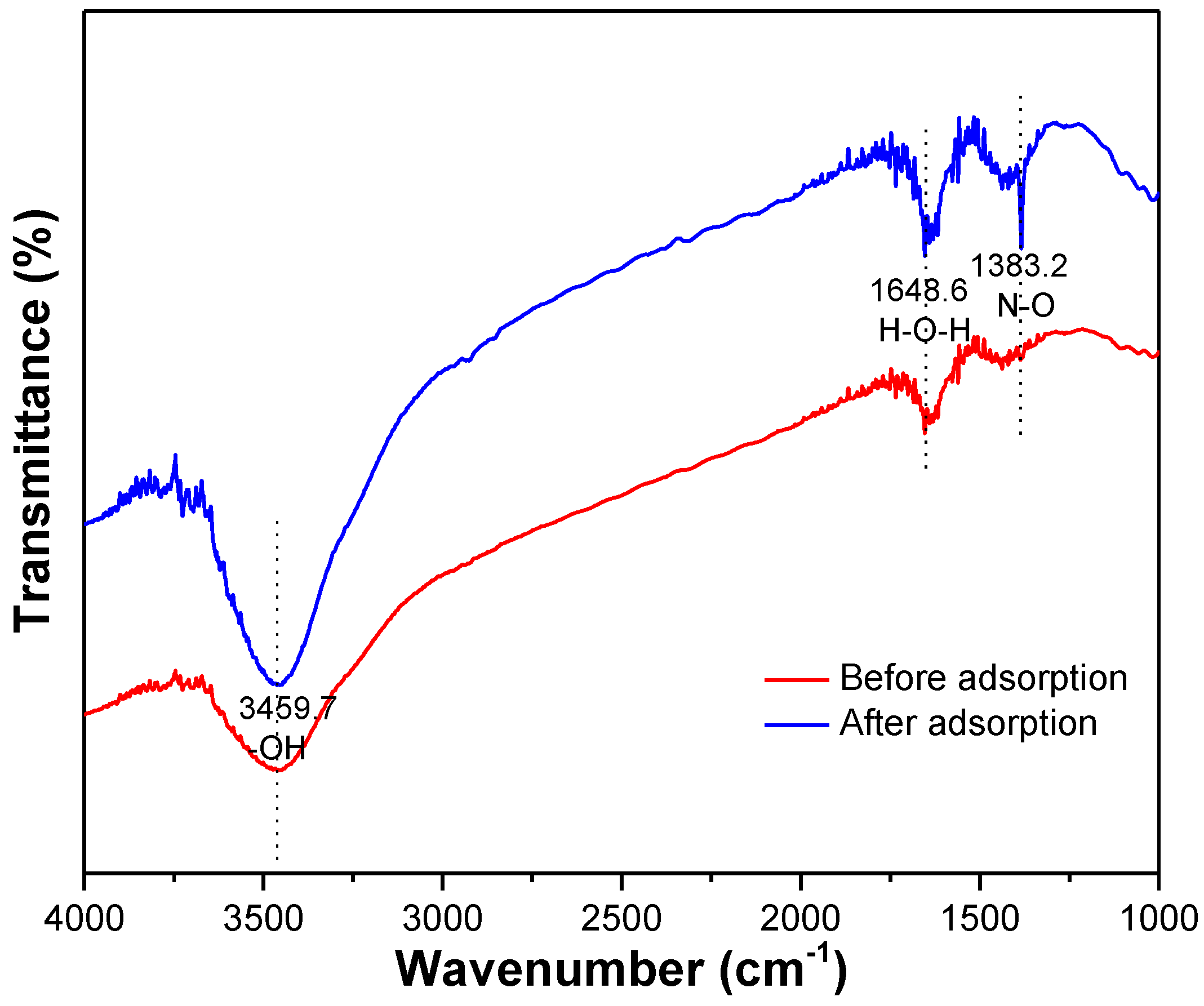
The surface morphology of the MSS after adsorption appeared with a series of different widths and depths of the pleats and flocculent structures and surface void reduction (Figure 1). The infrared spectra of the MSS before and after the adsorption of nitrate (Figure 10) show that the broad absorption peak near 3459.7 cm−1 belonged to the stretching vibration of hydrogen bonds on the hydroxyl groups, and its absorption intensity determined the shape of the absorption peak. The intermolecular association of the hydroxyl groups led to a wider peak before adsorption. After adsorption, the peak intensity increases and the shape is more sharpened at a peak of 3459.7 cm−1, which may be due to the formation of free hydroxyl groups without association. The bending vibration of H-O-H occurred at 1648.8 cm−1, and the peak intensity increased after adsorption, which indicates that the water content in the pores of the MSS increased. A strong absorption peak at 1383.2 cm−1 belonged to the N-O stretching vibration, indicating the presence of nitrate on MSS after adsorption experiments.
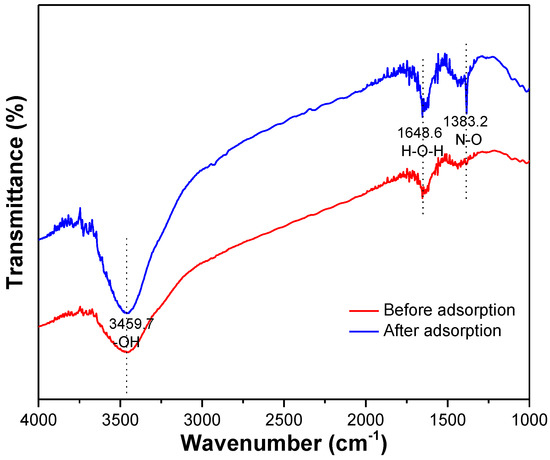
Figure 10.
IR spectra of MSS before and after adsorption of nitrate.
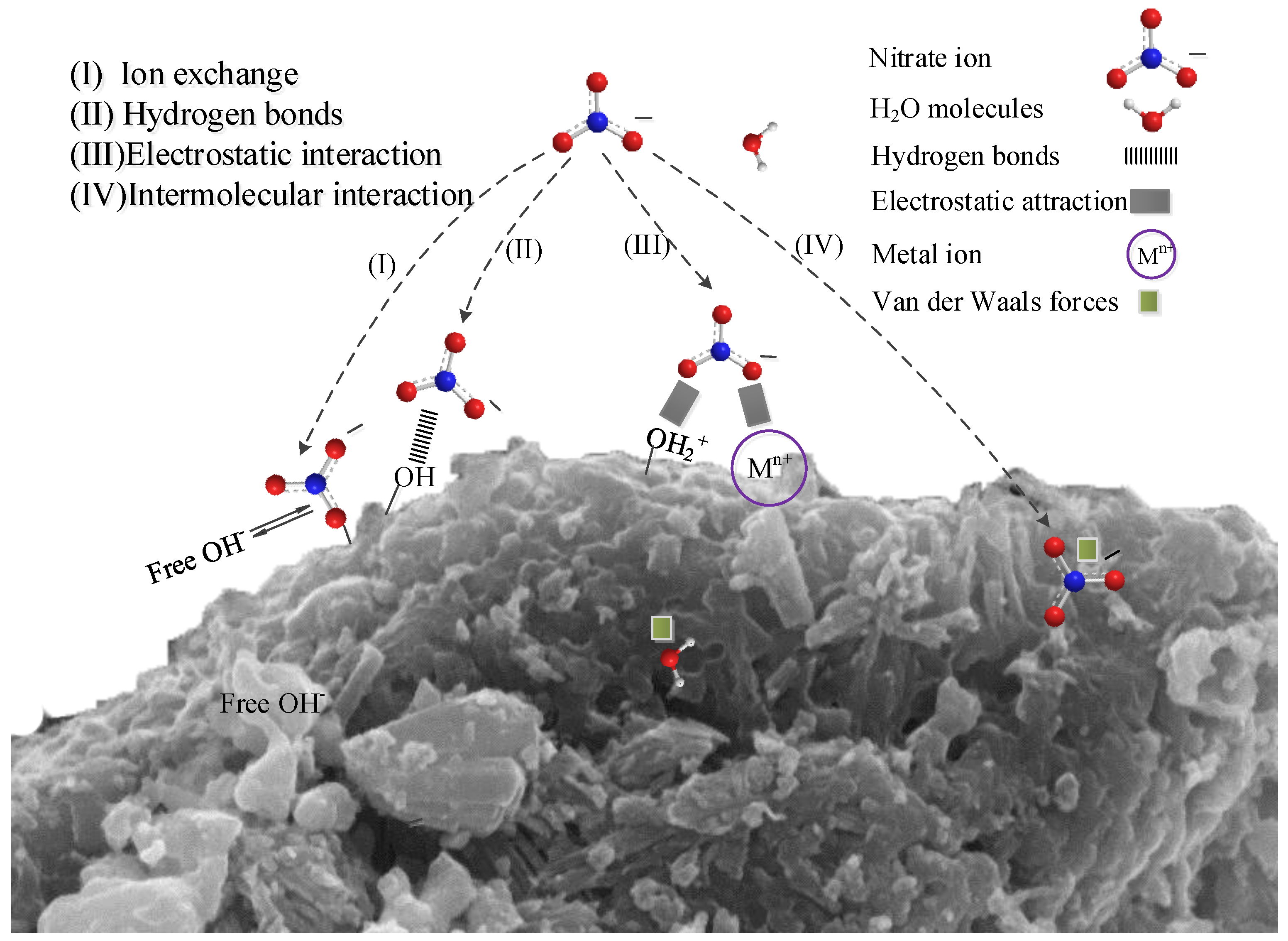
According to the above model and related characterization analysis, chemical adsorption plays a major role in the removal of nitrate from modified steel slag. According to the surface complexation theory, the aluminium ions on the surface of activated alumina are complexed with water molecules to form Al-OH groups [19,29]. In addition, metal ions such as calcium, iron and their metal oxides are hydrated on the surface of MSS to form hydroxides and hydrated metal oxides so that there are a large number of hydroxyl groups in a mutually associative or separate form present at the interface of the adsorbent, which has been confirmed in the infrared spectrum (Figure 10). Thus, the nitrate may be adsorbed by ion exchange (Equation (10), Figure 11I) [22,29,51,52] or through hydrogen bonding (Equation (11), Figure 11II) [38] with the hydroxyl group.
where M represents Al, Fe, and Ca.
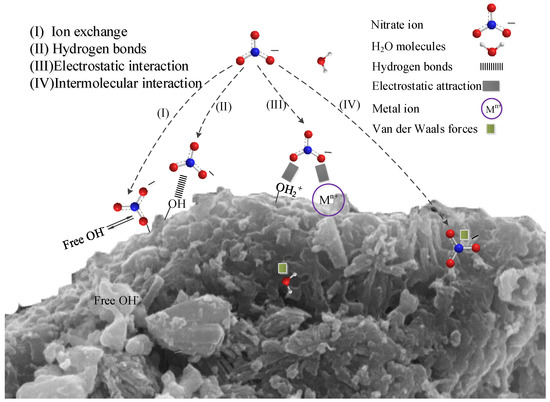
Figure 11.
Proposed adsorption mechanism between the adsorbent and nitrate.
When the pH of the solution was less than 7.8, the surface of the MSS was positively charged (Figure 5), which was mainly the result of protonation [20,27] or dissolved metal cations embedded on its surface, see Equation (4) [26,39]. This process favours the adsorption of the electrostatic attraction between the adsorbent and the nitrate, see (Equation (12), Figure 11III). Large-scale nitrate-contaminated water is generally neutral or acidic [53], so MSS can improve the removal efficiency of nitrate by electrostatic adsorption.
In addition, the Si-O-Si bond and the Al-O-Al bond on the surface of the MSS can generate dipolar–dipole bond adsorption (Van der Waals forces) with nitrates (Figure 11IV), and this adsorption is affected by the porosity and surface area of the steel slag. The modification process can improve the physical and chemical structure of steel slag, which is conducive to strengthening nitrate removal (Table 2, Figure 1), resulting in an increase in adsorption, effective use of internal chemical composition and improvement of surface energy.
3.5. Regeneration
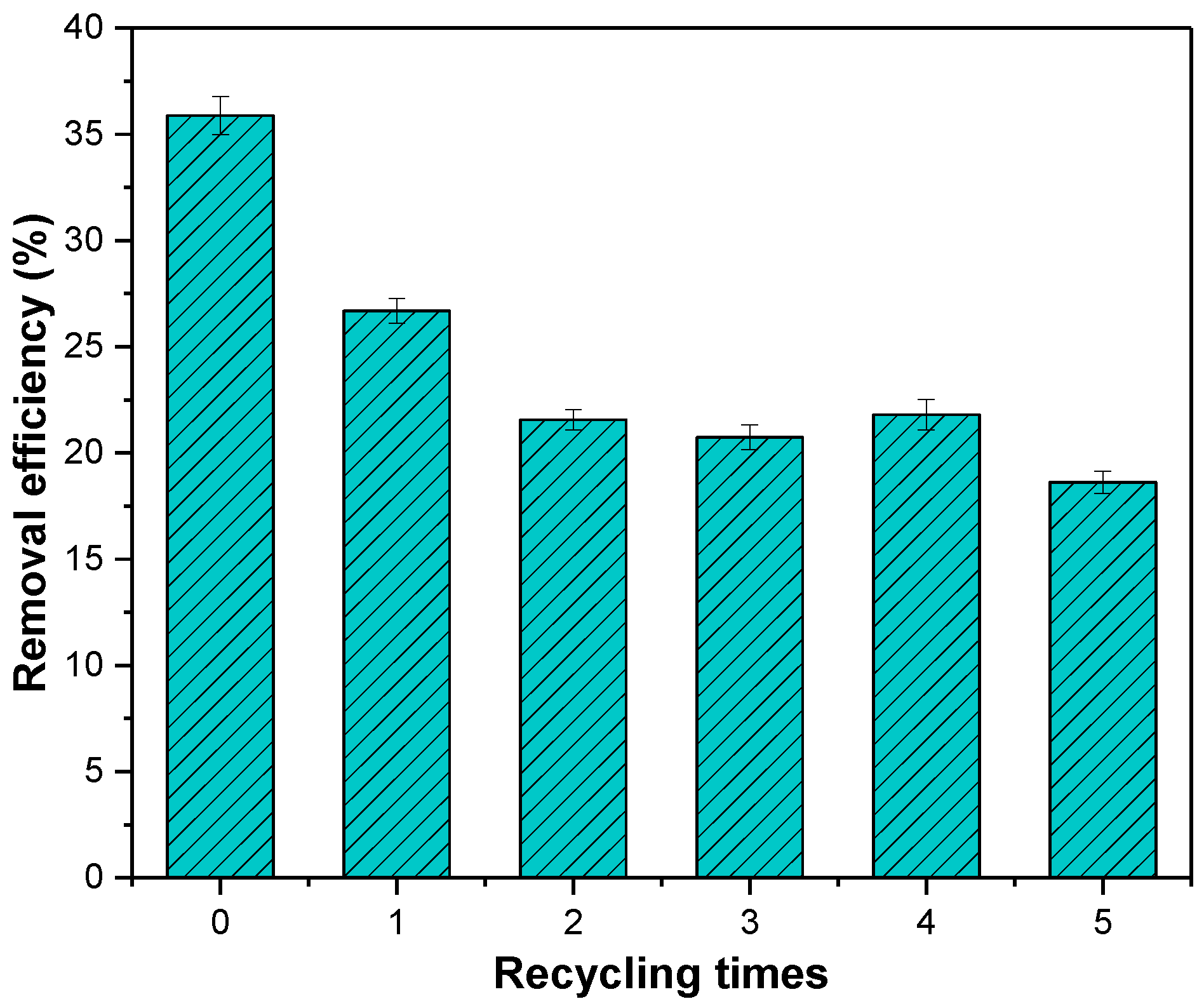
The adsorbed MSS was roasted in a muffle furnace at 800 °C for 120 min and cooled to continue the adsorption experiment for nitrate. The results (Figure 12) showed that the adsorption efficiency of the MSS reduced from 35.87% to 18.62% after reuse and regeneration five times. From the second reuse, the adsorption efficiency decreased less and stabilized at approximately 20% in the later period. The adsorption efficiency reduced to a lesser extent, and then stabilized at approximately 20%, indicating that after repeated regeneration the MSS still has the ability to remove nitrate.
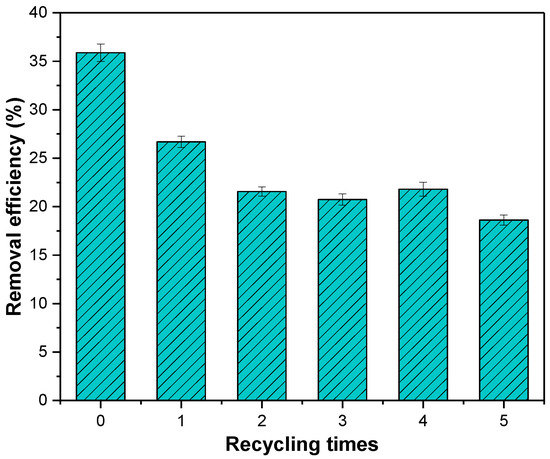
Figure 12.
Adsorption efficiency of MSS after repeated regeneration.
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The safety and ion release experiments showed that the MSS as a wastewater adsorbent did not produce toxic pollution, providing a certain degree of safety.
- (2)
- The surface area of MSS and its nitrate adsorption capacity were significantly enhanced to 3.34 times and 1.9 times higher than that of OSS, respectively. When the initial concentration of nitrate was 300 mg/L, the adsorption capacity of MSS was 6.165 mg/g, reaching a relatively higher level.
- (3)
- The adsorption of nitrate was in accordance with a pseudo-second-order kinetics model and a Freundlich isothermal model, which was mainly attributed to monolayer chemical adsorption. In addition, the increase in the specific surface area, the formation of active substances and the change in surface electrical properties can effectively improve the ability of MSS to remove nitrate.
- (4)
- The MSS still had some ability to remove nitrate after several reuses and removal efficiency was stable at 20% from the second regeneration experiments. Some other methods, such as combining steel slag with agricultural wastes or cationic surfactants for modification, could be used in the modified experiments to improve the adsorption capacity of steel slag. In addition, MSS for the treatment of actual wastewater needs to be further studied in the follow-up experiments.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for this study was provided by the Ten-Year Evaluation Project of the People’s Republic of China Ministry of Environmental Protection (STSN-06).
Author Contributions
L.Y. and M.Y. conceived and designed the experiments; M.Y. and P.X. performed the experiments; X.Z. analyzed the data; H.B. and H.L. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; L.Y. and M.Y. wrote the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Jin, Z.; Pan, Z.; Jin, M.; Li, F.; Wan, Y.; Gu, B. Determination of nitrate contamination sources using isotopic and chemical indicators in an agricultural region in China. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2012, 155, 78–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feleke, S. A bio-electrochemical reactor coupled with adsorber for the removal of nitrate and inhibitory pesticide. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3092–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajhamad, L.; Almasri, M.N. Assessment of nitrate contamination of groundwater using lumped-parameter models. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2009, 24, 1073–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keränen, A.; Leiviskä, T.; Hormi, O.; Tanskanen, J. Removal of nitrate by modified pine sawdust: Effects of temperature and co-existing anions. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 147, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandor, J.; Kiss, I.; Farkas, O.; Ember, I. Association between gastric cancer mortality and nitrate content of drinking water: Ecological study on small area inequalities. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2001, 17, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiesmann, U.; Choi, I.S.; Dombrowski, E.M. Fundamentals of Biological Wastewater Treatment. J. Egypt. Med. Assoc. 2007, 46, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.; Xu, P.; Yang, M.; Bai, H. The characteristics of steel slag and the effect of its application as a soil additive on the removal of nitrate from aqueous solution. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2017, 24, 4882–4893. [Google Scholar]
- Oztürk, N.; Bektaş, T.E. Nitrate removal from aqueous solution by adsorption onto various materials. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 112, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samatya, S.; Kabay, N.; Yüksel, Ü.; Arda, M.; Yüksel, M. Removal of nitrate from aqueous solution by nitrate selective ion exchange resins. React. Funct. Polym. 2006, 66, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Hu, W.; Liu, H. Kinetic and isotherm studies of nitrate adsorption on granular Fe-Zr-chitosan complex and electrochemical reduction of nitrate from the spent regenerant solution. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61944–61954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur, T.; Shim, W.G.; Loganathan, P.; Vigneswaran, S.; Kandasamy, J. Nitrate removal using Purolite A520E ion exchange resin: Batch and fixed-bed column adsorption modelling. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 12, 1311–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Song, X.L.; Huang, S.T.; Geng, B.Y.; Chang, C.H.; Sung, I. Adsorption of nitrate ions onto activated carbon prepared from rice husk by NaOH activation. Desalin. Water Treat. 2014, 52, 4935–4941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, S.J.T.; Fowler, G.D.; Sollars, C.J.; Perry, R. Low-cost adsorbents for waste and wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 116, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.S. The Comprehensive Application of Slag in Wastewater Treatment. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2010, 38, 18282–18283. [Google Scholar]
- Barca, C.; Gérente, C.; Meyer, D.; Chazarenc, F.; Andrès, Y. Phosphate removal from synthetic and real wastewater using steel slags produced in Europe. Water Res. 2012, 46, 2376–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claveau-Mallet, D.; Wallace, S.; Comeau, Y. Removal of phosphorus, fluoride and metals from a gypsum mining leachate using steel slag filters. Water Res. 2013, 47, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, V.K.; Kameshima, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Okada, K. Hazardous ions uptake behavior of thermally activated steel-making slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2004, 114, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, N.; Deeba, F.; Irfan, M.; Khan, R.A. Treatability Study of Arsenic, Fluoride and Nitrate from Drinking Water by Adsorption Process. J. Chem. Soc. Pak. 2014, 37. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, J.; Fang, H.; Lin, J.; Lin, J.; Huang, Z. Simultaneous removal of NH4+ and PO43− at low concentrations from aqueous solution by modified converter slag. Water Environ. Res. 2013, 85, 530–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Su, B. Removal characteristics of Cd(II) from acidic aqueous solution by modified steel-making slag. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 246, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.J. Studies on Removal Efficiency of Nitrogen and Phosphorus from Eutrophic Seawater with “Solidified Slag Concrete-Macroalgae” System. Master’s Thesis, Ocean University of China, Qingdao, China, May 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Kumar, E.; Sillanpää, M. Nitrate removal from water by nano-alumina: Characterization and sorption studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.; Chen, N.; Feng, C.; Hu, W.W. Nitrate adsorption from aqueous solution using granular chitosan-Fe3+ complex. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 347, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, P.C.; Patel, R.K. Use of agricultural waste for the removal of nitrate-nitrogen from aqueous medium. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teutli-Sequeira, A.; Solache-Ríos, M.; Balderas-Hernández, P. Modification Effects of Hematite with Aluminum Hydroxide on the Removal of Fluoride Ions from Water. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2012, 223, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.D.; Zhang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; He, M.H. Removal of aniline and phenol from water using raw and aluminum hydroxide-modified diatomite. Water Sci. Technol. J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2013, 67, 1620–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Wu, S.; Zhou, M. Adsorption characterization of Cu(II) from aqueous solution onto basic oxygen furnace slag. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 231, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jha, V.K.; Kameshima, Y.; Nakajima, A.; Okada, K. Utilization of steel-making slag for the uptake of ammonium and phosphate ions from aqueous solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 156, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B. Chemistry of alumina, reactions in aqueous solution and its application in water treatment. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 110, 19–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzouk, I.; Hannachi, C.; Dammak, L.; Hamrouni, B. Removal of chromium by adsorption on activated alumina. Desalin. Water Treat. 2011, 26, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Environmental Protection Agency. Water Quality-Determination of Nitrate-Nitrogen—Ultraviolet Spectrophotometry; HJ/T 346-2007; National Environmental Protection Agency: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- Mann, R.A.; Bavor, H.J. Phosphorus Removal in Constructed Wetlands Using Gravel and Industrial Waste Substrata. Water Sci. Technol. J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. Control. 1993, 27, 107–113. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Moreno, L.; Neretnieks, I. The long-term acid neutralizing capacity of steel slag. Waste Manag. 2000, 20, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Environmental Protection Agency. Solid Waste-Extraction Procedure for Leaching Toxicity-Acetic Aid Buffer Solution Method; HJ/T 300-2007; National Environmental Protection Agency: Beijing, China, 2007. (In Chinese)
- Malarvizhi, T.S.; Santhi, T. Adsorption of Zn(II) ions from aqueous solution on lignite-fired fly ash. Desalin. Water Treat. 2013, 51, 6777–6788. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Environmental Protection Agency. Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water; GB 3838-2002; National Environmental Protection Agency: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Oh, C.; Rhee, S.; Oh, M.; Park, J. Removal characteristics of As(III) and As(V) from acidic aqueous solution by steel making slag. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 213–214, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teimouri, A.; Nasab, S.G.; Vahdatpoor, N.; Habibollahi, S.; Salavati, H.; Chermahini, A.N. Chitosan /Zeolite Y/Nano ZrO2 nanocomposite as an adsorbent for the removal of nitrate from the aqueous solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 93, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, T.; Hirata, M.; Kimura, T. Hydrolysis of Al3+ from constrained molecular dynamics. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 74503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.J.; Lin, J.W.; Zhan, Y.H.; Wang, H. Adsorption Characteristics of Nitrate and Phosphate from Aqueous Solution on Zirconium-Hexadecyltrimethylammonium Chloride Modified Activated Carbon. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2015, 36, 2185–2194. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huo, L. Adsorption of nitrate on granular ferric hydroxide from simulated wastewater. Chin. J. Environ. Eng. 2012, 6, 3058–3062. [Google Scholar]
- Lagergren, S. Zur Theorie der Sogenannten Adsorption Gelöster Stoffe; Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens. Handlingar 1898, 24, 1–39. (In Germany) [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; Mckay, G. Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem. Eng. J. 1998, 70, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; Chiu, W.T.; Hsu, C.S.; Huang, C.T. Sorption of lead ions from aqueous solution using tree fern as a sorbent. Hydrometallurgy 2004, 73, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.; Heller, W. The Adsorption of cis- and trans-Azobenzene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1939, 61, 2228–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.C.; Kilduff, J.E.; Weber, W.J. Site energy distribution analysis of preloaded adsorbents. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 29, 1773–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derylo-Marczewska, A.; Jaroniec, M.; Gelbin, D.; Seidel, A. Heterogeneity effects in single-solute adsorption from dilute solutions on solids. Chem. Scr. 1984, 24, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, M.; Mishra, P.C.; Patel, R. Physicochemical characterization of hydroxyapatite and its application towards removal of nitrate from water. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, Y.; Mallavarapu, M.; Naidu, R. Adsorption of the herbicide 2,4-D on organo-palygorskite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2010, 49, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halajnia, A.; Oustan, S.; Najafi, N.; Khataee, A.R.; Lakzian, A. Adsorption-desorption characteristics of nitrate, phosphate and sulfate on Mg–Al layered double hydroxide. Appl. Clay Sci. 2013, 80, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milmile, S.N.; Pande, J.V.; Karmakar, S.; Chakrabarti, T.; Bansiwal, A.; Biniwale, R.B. Equilibrium isotherm and kinetic modeling of the adsorption of nitrates by anion exchange Indion NSSR resin. Desalination 2011, 276, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Chen, J.; Li, F. Investigation on the Key Factors and the Solution for pH Value Decrease in Carbon Filter in O3-BAC Process. Chin. J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 21, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).