Abstract
Uranium contamination of groundwater increasingly concerns rural residents depending on home wells for their drinking water in communities where uranium is a source of contamination. Established technologies to clean up contaminated aquifers are ineffective in large contaminated areas or are prohibitively expensive. Permeable reactive barriers (PRBs) are a low-cost alternative to these methods. In this paper, the applicability of clay ceramic pellets was investigated as permeable reactive barriers (PRBs) material for the treatment of uranium-contaminated groundwater. Flow-through columns were fabricated and used to mimic the flow path of a contaminant plume through the reactive media. Experiment results show that clay ceramic pellets effectively remove uranium from uranium-contaminated water and also can be a cost-efficient technique for remediating uranium contaminated groundwater by a clay pellet barrier. Using clay ceramic pellets is also a practical treatment method for uranium removal from drinking water and can supply potable water for households in the affected areas.
1. Introduction
Uranium contamination of groundwater increasingly concerns rural residents depending on home wells for their drinking water in communities with a legacy of mining [1] as well as those living in areas naturally occurring uranium is a source of contamination [2,3,4]. In the United States, naturally occurring elevated uranium in groundwater is widespread in the west and is scattered in Eastern states [2,5]. Also significant problems stemming from the legacy of uranium development still exist today in the Colorado Plateau area [6].
Uranium in ground water is most commonly found in its hexavalent oxidation state U(VI) as the uranyl ion (UO22+) [7]. The aqueous solubility of U(VI) makes it difficult to physically remove uranyl from water. Clean-up of contaminated aquifers is difficult due to the inaccessibility to the subsurface and the volume of soil and groundwater requiring treatment [8]. Established technologies such as pump-and-treat and soil excavation are ineffective in large contaminated areas or are prohibitively expensive [9]. Permeable reactive barriers (PRBs) are a low-cost alternative to these methods [10]. The PRB is an in situ permeable treatment zone designed to intercept and remediate a contaminant plume. Several mechanisms have been proposed for the treatment of uranium using elemental iron (zero-valent iron) as PRB material, including reductive precipitation [11,12], sorption onto hydrous ferric oxide [13], and co-precipitation with iron oxides [14].
The purpose of the present study is to investigate the applicability of low temperature sintering clay ceramics as PRB material for the treatment of uranium-contaminated groundwater. Natural clays are characterized with sorption ability of different chemical compositions [15,16,17,18,19,20] and thus are suitable materials for environmental technologies. Clay adsorption capacity is generally increased by granulation [21]. However, such materials have a weak point. Considering the colloidal character of clay minerals, after purification of polluted water such water contains another kind of pollution—colloidal particles of clay containing adsorbate. Low temperature sintered clay ceramics can help to resolve this disadvantage for water purification technologies [22]. The sintering treatment makes clay ceramics insoluble in water. Clay ceramics used in this study have negatively charged sites on their surfaces which adsorb and hold positively charged uranyl ions by electrostatic force. Clay ceramics are water-insoluble and easy to remove from water after treating contaminated water. Flow-through columns were built and used to mimic the flow path of a contaminant plume through the reactive media. A peristaltic pump slowly fed the contaminant medium. Uranyl nitrate was used as a source of Uranium(VI). We also tested the efficiency and practicability of clay ceramic pellets to facilitate abatement of uranium from drinking water. Underprivileged communities do not have access to expensive water purification systems and current methods for purifying water on a small scale are temporary solutions for a small volume of purified water and expensive. The clay ceramic pellets can be used to remove uranium in any environment where individuals are at risk of ingesting uranium contaminated water.
2. Materials and Methods
Two different clays from Arizona Cheto (smectite mineral) and New Mexico Gallup (illite mineral) were used for production of ceramic pellets. Both clays are 2:1 layer minerals where an octahedral sheet is bonded to two tetrahedral sheets. These clay minerals have significant permanent negative charges which contribute to the cation exchange capacity (CEC) of clays [23]. The permanent negative charge in the clay results from the substitution of divalent cations for trivalent cations in the octahedral sheet [24]. For example, the permanent negative charge in the smectite group results from substitution of divalent cations Mg2+ for trivalent cations Al3+ in the octahedral sheet. The CEC is a measure of the clay’s ability to hold positively charged ions. Uranium sorbs to clay through this unique characteristic.
2.1. Fabrication of Clay Pellet and Flow-Through Column
Dry clays from Arizona Cheto and New Mexico Gallup were mixed with water and spread into a silicon mold in the form of a pellet. These samples were sintered (thermal curing) in a laboratory furnace. A first densification took place below 150 °C from drying the residual water on clay surface [25]. The clay pellets were further heated until chemically bonded water with clay molecules escaped from the clay. The curing process is well described in Reference [22].
Flow-through columns were fabricated using acrylic tubes having an effective height of 25.4 cm and internal diameter of 2.5 cm. The columns have four lateral sampling ports capped with Mininert valves. The columns were equipped with check valves at the inlet and outlet, which allowed for draining liquids out of the columns. These columns were used for flow-through experiments for uranium removal from groundwater as well as water purification experiments for uranium removal from drinking waters as shown in Figure 1.
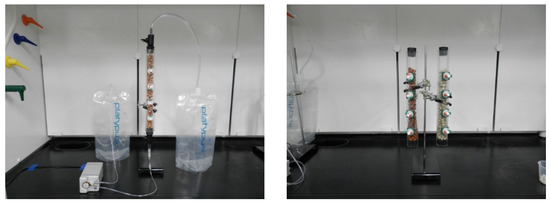
Figure 1.
Flow-through column apparatus and experimental setup for nonstationary flow-through experiments (left) and stationary water purification experiments (right).
2.2. Experimental Procedure and Sampling
The columns were packed with clay ceramic pellets. Uranium solution was prepared by dissolving 0.0015 g uranyl nitrate hexahydrate into 2 L of deionized water (about 400 ppb uranium solution). A peristaltic pump was used to feed the uranium medium at 5.75 mL/h to the column. Waste liquid was collected in a 2 L playtypus platy bottle. Samples were taken from the side ports to obtain concentration profile within a column as shown in Figure 2. A 20-gauge needle was injected through the Mininert port valve (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) to withdraw 5 mL of fluid with a disposable syringe. Samples were taken every 24 h and data were collected for five days. Samples were analyzed using Agilent 7500 Series ICP-MS (Santa Clara, CA, USA) equipped with a Agilent micromist nebulizer part No. (G3266-65003) (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) and Cetac (Omaha, NE, USA), ASX 520 Autosampler (Cetac, Omaha, NE, USA).
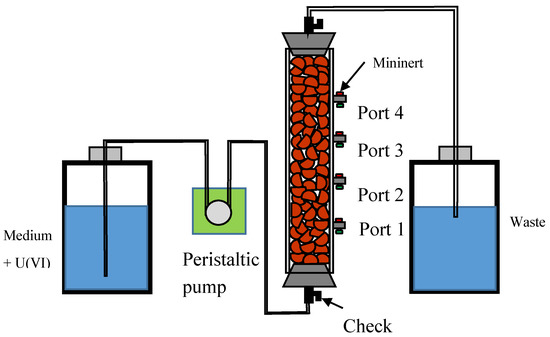
Figure 2.
Schematic of the flow-through experimental setup.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Clay Characterization
Ceramic pellets were made from Arizona Cheto clay and New Mexico Gallup clay as shown in Figure 3. These samples were imaged using the scanning electron microscopy (SEM) (Hitachi High Technologies, Dallas, TX, USA). Figure 4 shows SEM images of Cheto (Cheto, AZ, USA) and Gallup clay (Gallup, NM, USA) pellet samples. Both clays have open structures formed by laminar particles which keep edge-to-edge and edge-to-face contacts. Cheto clay particles appear as small and irregularly-shaped flakes, which is a distinctive morphology of smectite clay. It has been reported that clays in Northern New Mexico were formed by smectite and illite [26]. The SEM image of Gallup clay shows abundant pseudo-hexagonal illite platelets, which suggests that Gallup clay has a morphology closer to that of illite than that of smectite.

Figure 3.
Arizona Cheto clay pellet (0.7 cm in diameter, white) and New Mexico Gallup clay pellet (0.9 cm in diameter, red).
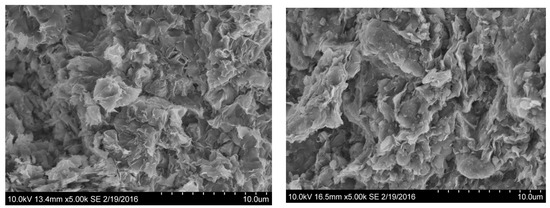
Figure 4.
SEM images of the samples of Cheto clay (left) and Gallup clay (right).
3.2. Flow-Through Experiments for Uranium Removal from Groundwater
Uranium concentration profiles were determined along the length of the column after 24 h of operation, when the hydraulic retention time was 12 h. Figure 5 depicts the concentration profiles along the length of the column for uranium abatement with Gallup and Cheto clay pellets. In this experiment, uranium levels were reduced from 370 ppb to 107 ppb with Gallup clay pellets and 370 ppb to 17 ppb with Cheto clay pellets. Cheto clay pellets have a faster reaction rate than Gallup clay pellets because of the high cation exchange capacity (CEC). Arizona Cheto clay belongs to the smectite clay group and has a high CEC value (about 120 cmolc/kg) [27,28]. Gallup clays are expected to have lower CEC values since illite has generally low CEC values (about 40 cmolc/kg) [26]. That is, 1 kg of Cheto and Gallup clay could take 120 centimols and 40 centimols of uranyl ion, respectively. This data indicates that slow reaction kinetics may require a treatment system with a longer hydraulic retention time.
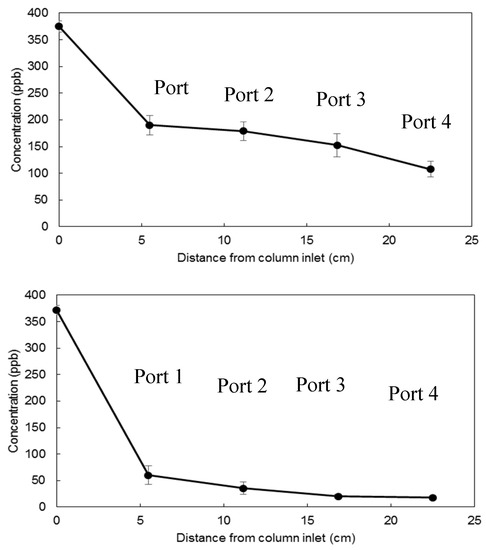
Figure 5.
Concentration profiles for Uranium abatement in the flow-through column with Gallup clay pellets (top) and Cheto clay pellets (bottom) after 24 h.
Figure 5 shows the rate of uranium removal in each solution. Hydraulic retention time in this experiment was 12 h. The sample medium retrieved from Port 1 was exposed to pellets about 2–3 h whereas the sample medium in Port 4 was exposed to pellets about 9–10 h. Uranium removal was fastest during the initial 2–3 h of the test, followed by a more gradual decline as the solution flew from Port 1 to Port 4 in the column. In order to make a judgment that the observed uranium abatement between Port 1 and Port 4 is statistically meaningful, the two-sample t-test [29] was conducted using Minitab Statistical Software [30]. Analysis results in Table 1 showed a statistically significant difference (p ≤ 0.05) between Port 1 and Port 4. The results indicate a significant difference between the two means at the 95 percent confidence level.

Table 1.
Statistical analysis of uranium concentration data for Port 1 and Port 4
3.3. Water Purification Experiments for Uranium Removal from Drinking Water
The US Environment Protection Agency (EPA) established the drinking water standard of 30 ppb for uranium in public drinking water supplies. Feasibility of uranium abatement in contaminated drinking water was tested using clay ceramic pellets. The uranium concentration was recorded until the concentration was decreased to 30 ppb. Uranyl nitrate solution was used in the experiments as a contaminated water source. The flow-through column was packed with clay pellets and uranium medium and sealed by rubber plugs. Samples were taken from Port 1 of the column and analyzed using ICP-MS to measure uranium concentration. The uranium removal rates were faster than those of flow-through experiments. A total 68% of uranium was removed during the initial two hours for Gallup clay pellets and 89% was removed in the first hour with Arizona clay pellets.
As shown in Figure 6, uranium concentration in the uranyl solution showed a rapid initial drop in the first hour of the experiment, followed by a more gradual decline during the remainder of the test. At constant ambient conditions, the uranium concentration decreased from 370 ppb to 30 ppb for Cheto pellets in 10 h and to 22.75 ppb for Gallup pallets in 34 h.
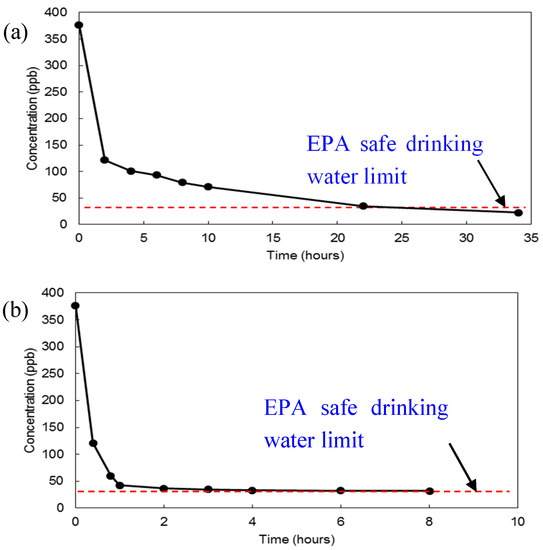
Figure 6.
Uranium abatement in time with Gallup clay pellet (34 h, a) and Cheto clay pellet (8 h, b).
4. Conclusions
Flow-through experiments suggest that clay pellet barriers can effectively intercept and remove uranium from contaminated groundwater. The removal efficiency was not decreased considerably in time and no noticeable permeability change was found in the column. Clay pellets are not susceptible to clogging or rapid passivation by reaction products unlike iron corrosion products. In the drinking water purification experiments, the uranium concentration was reduced to a concentration below the EPA’s safe drinking water limit of 30 ppb. The manageable end-product is easy to handle and dispose of. Results show that clay ceramic pellets effectively remove uranium from uranium-contaminated water and can be a cost-efficient technique for remediating uranium contaminated groundwater. This method is also a practical treatment method for uranium removal from drinking water and can supply potable water for households in the affected rural areas.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported in part by the U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) (Grant NO. 2014-38422-22078).
Author Contributions
Y.H.P. conceived the subject of the paper, performed the literature review, analyzed data, and wrote the paper. D.V.-R. performed the statistical analysis. A.L. and E.R. provided guidance in experimental design and fabricated clay ceramic pellets. C.F. fabricated the flow-through columns and carried out the experiments.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- DeLemos, J.L.; Burgge, D.; Cajero, M.; Downs, M.; Durant, J.L.; George, C.M.; Henio-Adeky, S.; Nez, T.; Manning, T.; Rock, T.; et al. Development of risk maps to minimize uranium exposures in the Native Churchrock Mining District. Environ. Health 2009, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arzuaga, X.; Rieth, S.H.; Bathija, A. Cooper, G.S. Renal effects of exposure to natural and depleted uranium: A review of the epidemiologic and experimental data. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health B Crit. Rev. 2010, 13, 527–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caldwell, R. Uranium and Other Radioactive Elements in Jefferson County Ground Water; U.S. Geological Survey: Helena, MT, USA, 2008.
- Kurttio, P.; Auvinen, A.; Salonen, L.; Saha, H.; Pekkanen, J.; Makelainen, I.; Vaisanen, S.B.; Penttila, I.M.; Komulainen, H. Renal Effects of Uranium in Drinking Water. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orloff, K.G.; Mistry, K.; Charp, P.; Metcalf, S.; Marino, R.; Shelly, T.; Melaro, E.; Donohoe, A.M.; Jones, R.L. Human exposure to uranium in groundwater. Environ. Res. 2004, 94, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore-Nall, A. The legacy of uranium development on or near Indian reservations and health implications rekindling public awareness. Geosciences 2015, 5, 15–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, J.; Bostick, W.D.; Jarabek, R.J.; Fiedor, J.N. Uranium Removal from Ground Water Using Zero Valent Iron Media. Groundwater 1999, 37, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darnault, C.J.G. Overexploitation and Contamination of Shared Groundwater Resources; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Freethey, G.F.; Naftz, D.L.; Rowland, R.C.; Davis, J.A. Deep Aquifer Remediation Tools: Theory, Design, and Performance Modeling. In Handbook of Groundwater Remediation Using Permeable Reactive Barriers; Naftz, D.L., Morrison, S.J., Davis, J.A., Fuller, C.C., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Naidu, R.; Birke, V. Permeable Reactive Barrier: Sustainable Groundwater Remediation; Chemical Rubber Company CRC Press: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, B.; Liang, L.; Dickey, M.J.; Yin, X.; Dai, S. Reductive Precipitation of Uranium (VI) by Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 3366–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, S.J.; Metzler, D.R.; Carpenter, C.E. Uranium Precipitation in a Permeable Reactive Barrier by Progressive Irreversible Dissolution of Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiedor, J.N.; Bostick, W.D.; Jarabek, R.J.; Farrell, J. Understanding the Mechanism of Uranium Removal from Groundwater by Zero-Valent Iron Using X Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1998, 32, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noubactep, C.; Meinrath, G.; Merkel, B.J. Investigating the Mechanism of Uranium Removal by Zero-Valent Iron. Environ. Chem. 2005, 2, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Suhas, L. Application of low-cost adsorbents for dye removal—A review. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2313–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiuhui, Q.U. Research progress of novel adsorption processes in water purification: A review. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Gupta, V.K.; Carrott, P.J.M.; Carrott, M.M.L.; Suhas, L. Low-cost adsorbents: Growing approach to wastewater treatment—A review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 783–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwaha, S.; Soni, H.; Ageethe, V.; Padmaja, P. An insight into the production, characterization and mechanisms of action of low-cost adsorbents for removal of organics from aqueous solution. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 43, 443–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svinka, R.; Svinka, V.; Petersone, E. The sorption properties of Latvian clays and use for the water purification. Latvian J. Chem. 1994, 3, 280–285. [Google Scholar]
- Luukkonen, T.; Veznikova, K.; Tolonen, E.T.; Runtti, H.; Yliniemi, J.; Hu, T.; Kemppainen, K.; Lassi, U. Removal of ammonium from municipal wastewater with powdered and gradulated metakaolin geopolymer. Environ. Technol. 2017, 16, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakevics, V.; Ruplis, A. Sorption properties of Latvian clays and research of clays innovative application. Sci. J. Riga Tech. Univ. Mater. Sci. Appl. Chem. 2011, 24, 20–25. [Google Scholar]
- Svinka, R.; Svinka, V.; Pudze, I.; Damberga, M. Clay ceramic pellets for water treatment. Mater. Sci. Appl. Chem. 2015, 32, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Sposito, G. The Surface Chemistry of Soils; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, J.A.; Kent, D.B. Surface Complexation Modeling in Aqueous Geochemistry; Hochella, M.F., White, A.F., Eds.; Mineral-Water Interface Geochemistry, Mineralogical Society of America: Chantilly, VA, USA, 1990; Volume 3, pp. 177–260. [Google Scholar]
- Kam, S.; Zerbo, L.; Bathiebo, J.; Soro, J.; Naba, S.; Wenmenga, U.; Traore, K.; Gomina, M.; Blanchart, P. Permeability to water of sintered clay ceramics. Appl. Clay Sci. 2009, 6, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caylor, E.; Rasmussen, C.; Dhakal, P. Lithologic Control on Secondary Clay Mineral Formation in the Valles Caldera, New Mexico. In Proceedings of the Abstract EP31B-1000 Presented at 2015 Fall Meeting, American Geophysical Union (AGU), San Francisco, CA, USA, 14–18 December 2015; Available online: http://adsabs.harvard.edu//abs/2015AGUFMEP31B1000C (accessed on 1 October 2017).
- Auebach, S.M.; Carrado, K.A.; Dutta, P.K. Handbook of Layered Materials; Marcel Dekker, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Bukka, K.; Miller, J.D. FTIR study of deuterated montmorillonites: Structural features relevant to pillared clay stability. Clays Clay Miner. 1992, 40, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montgomery, D.C.; Runger, G.C. Applied Statistics and Probability for Engineers, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Minitab 17 Documentation. 2006. Available online: https://www.minitab.com/uploadedFiles/Documents/getting-started/Minitab17_GettingStarted-en.pdf (accessed on 30 September 2017).
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).