Spatial and Temporal Variations in Environmental Variables in Relation to Phytoplankton Community Structure in a Eutrophic River-Type Reservoir
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Measurements
2.4. Species Distribution and Diversity
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
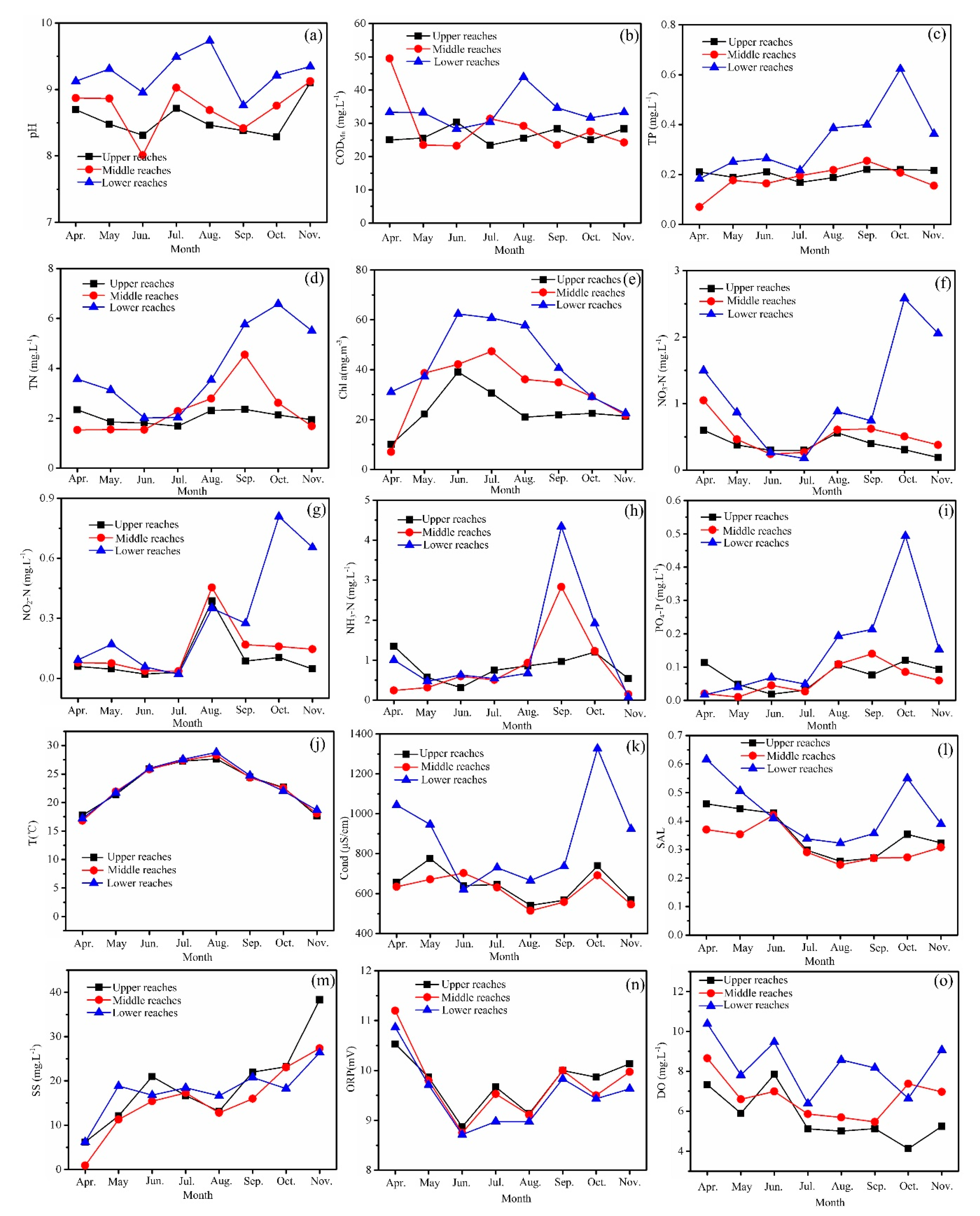
3.1. Environmental Factors
3.2. Phytoplankton Community Structure
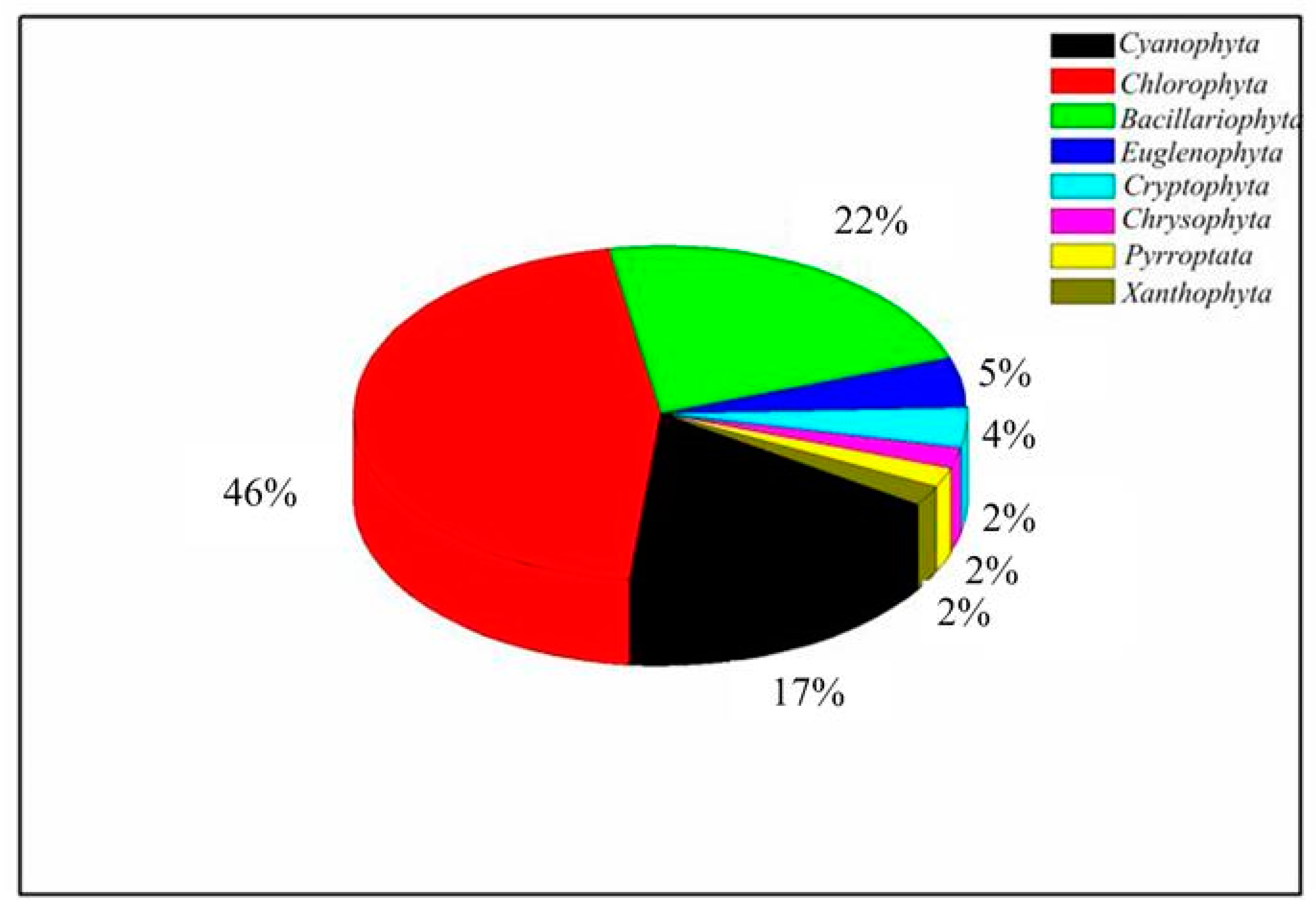
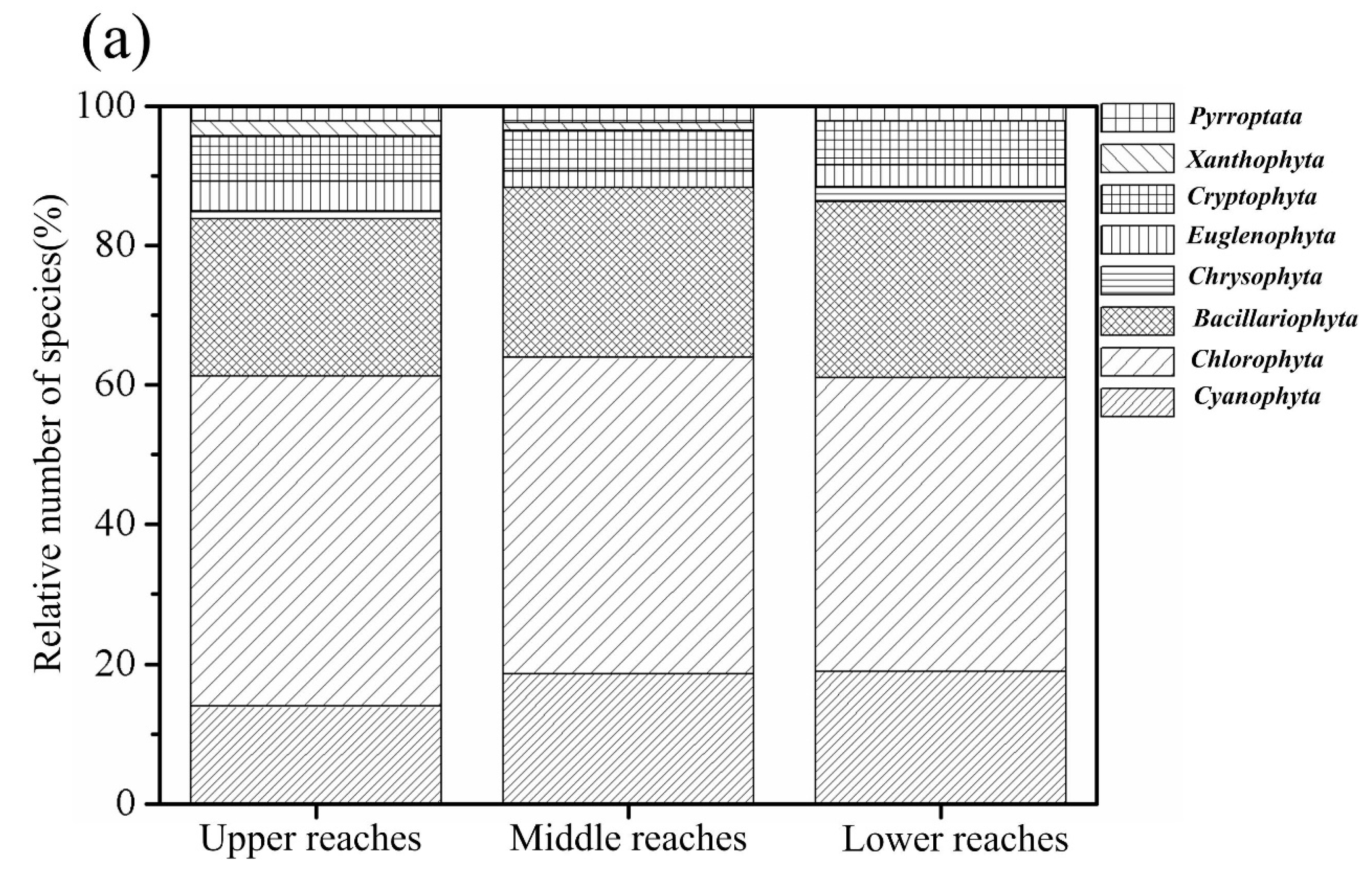
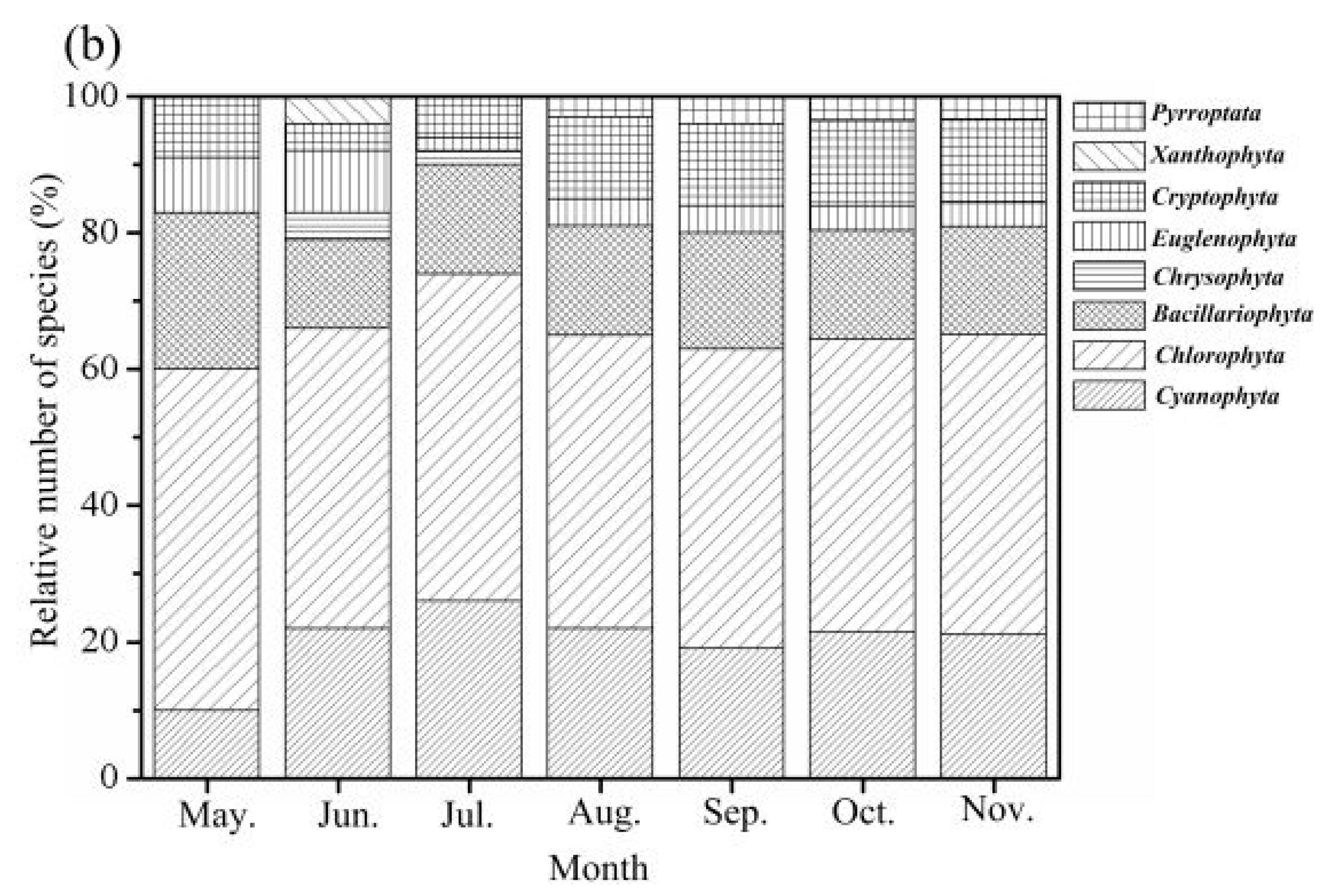
3.2.1. Phytoplankton Composition
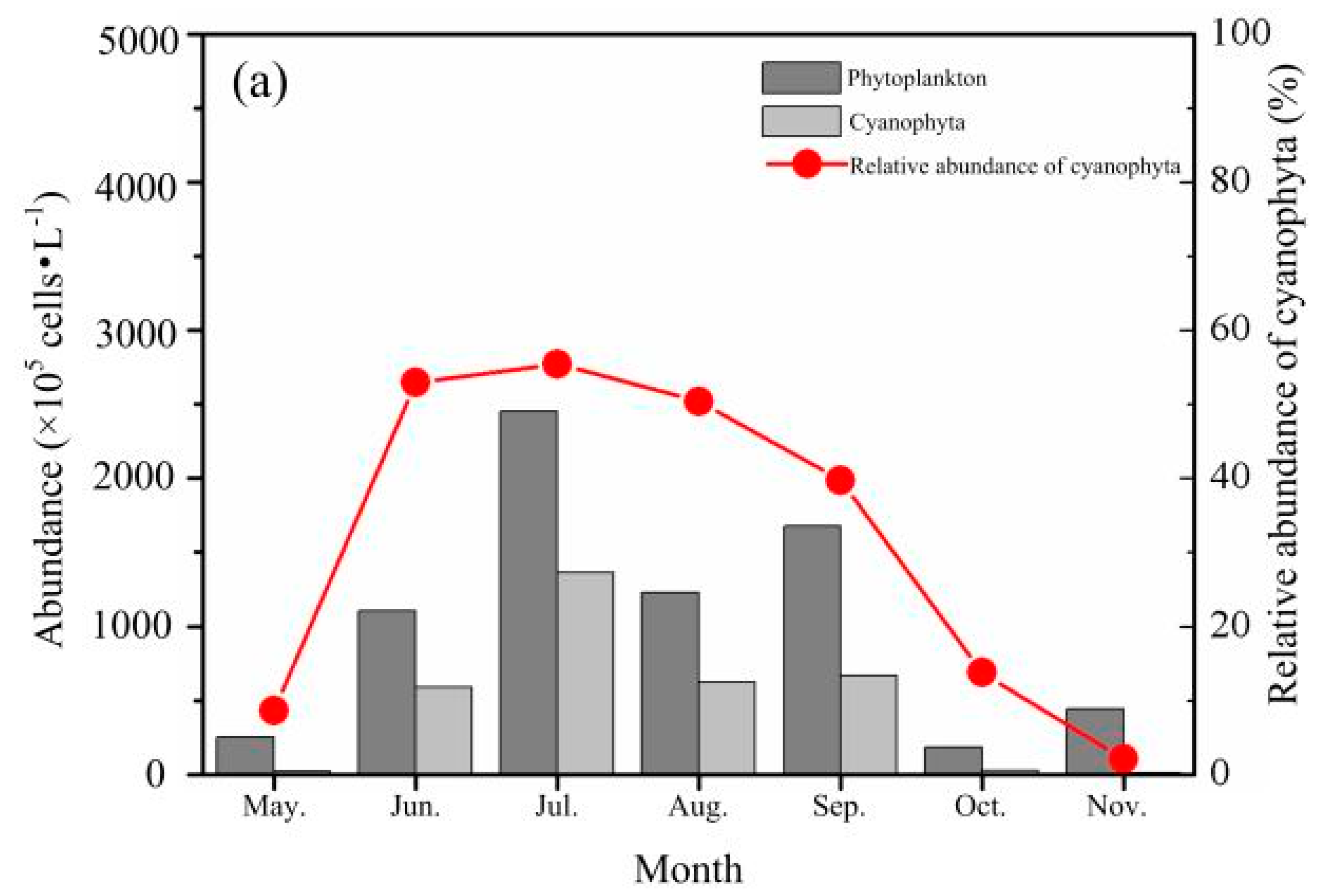
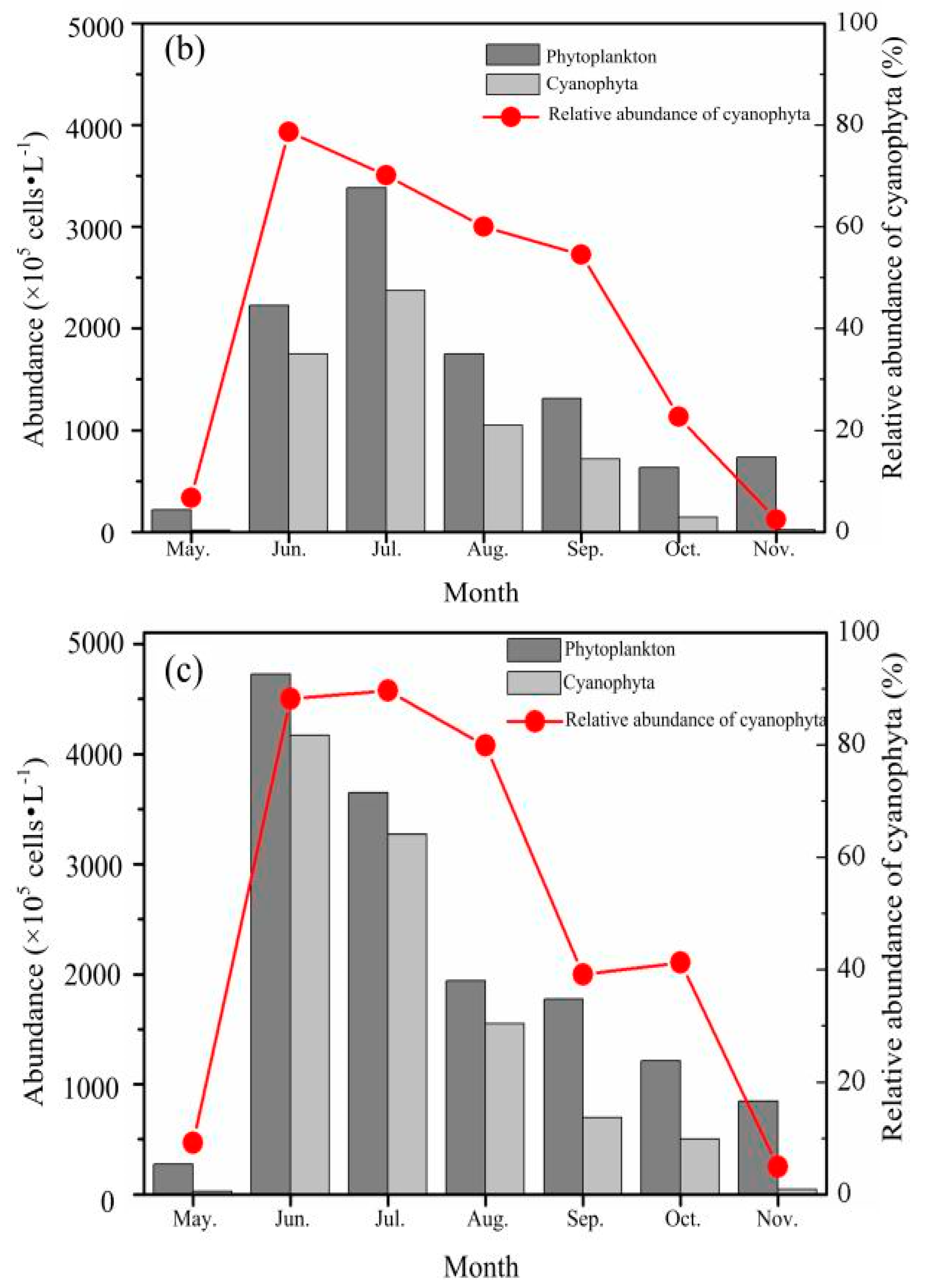
3.2.2. Phytoplankton Abundance
3.2.3. Dominant Species
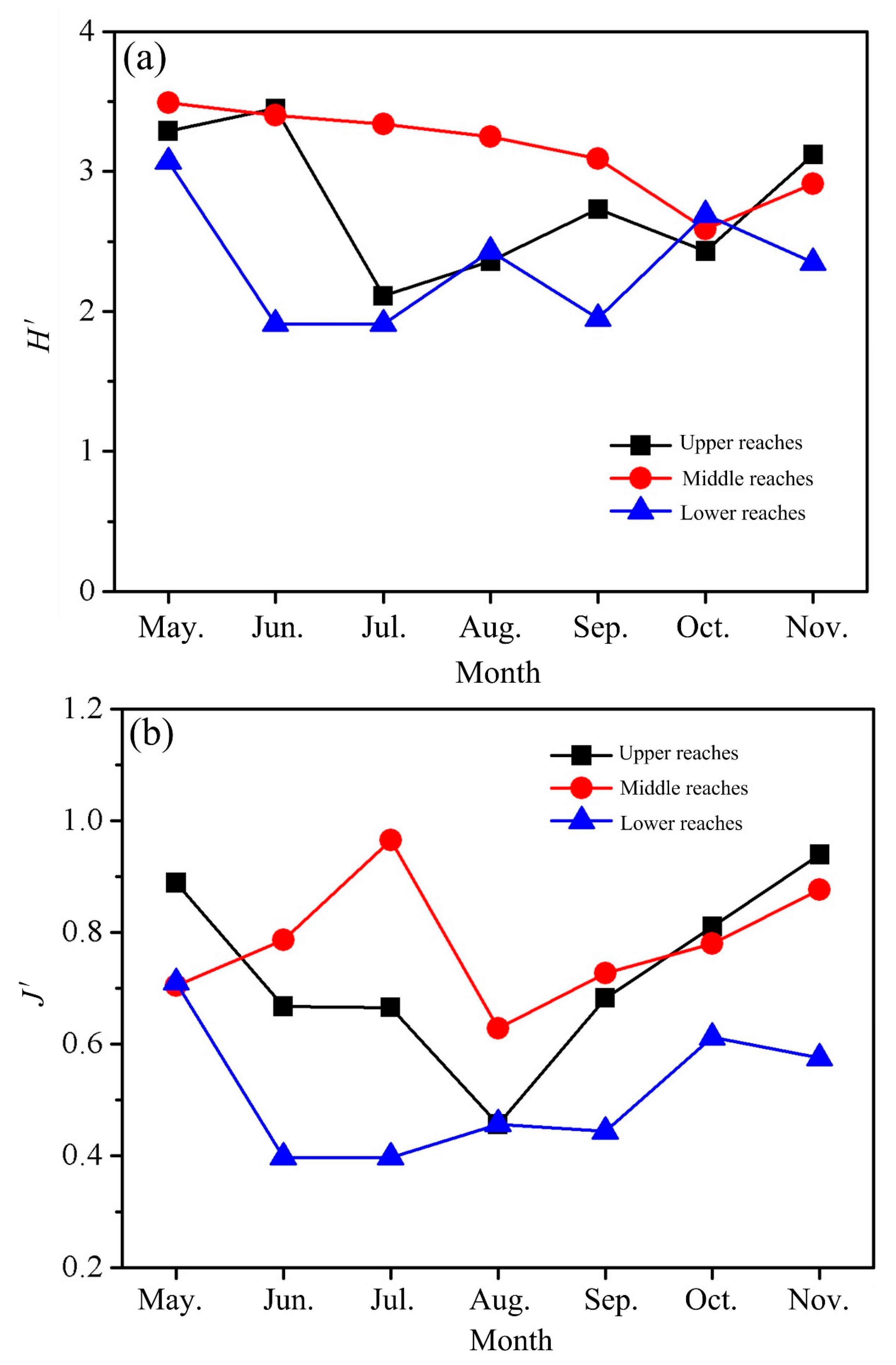
3.2.4. Species Diversity
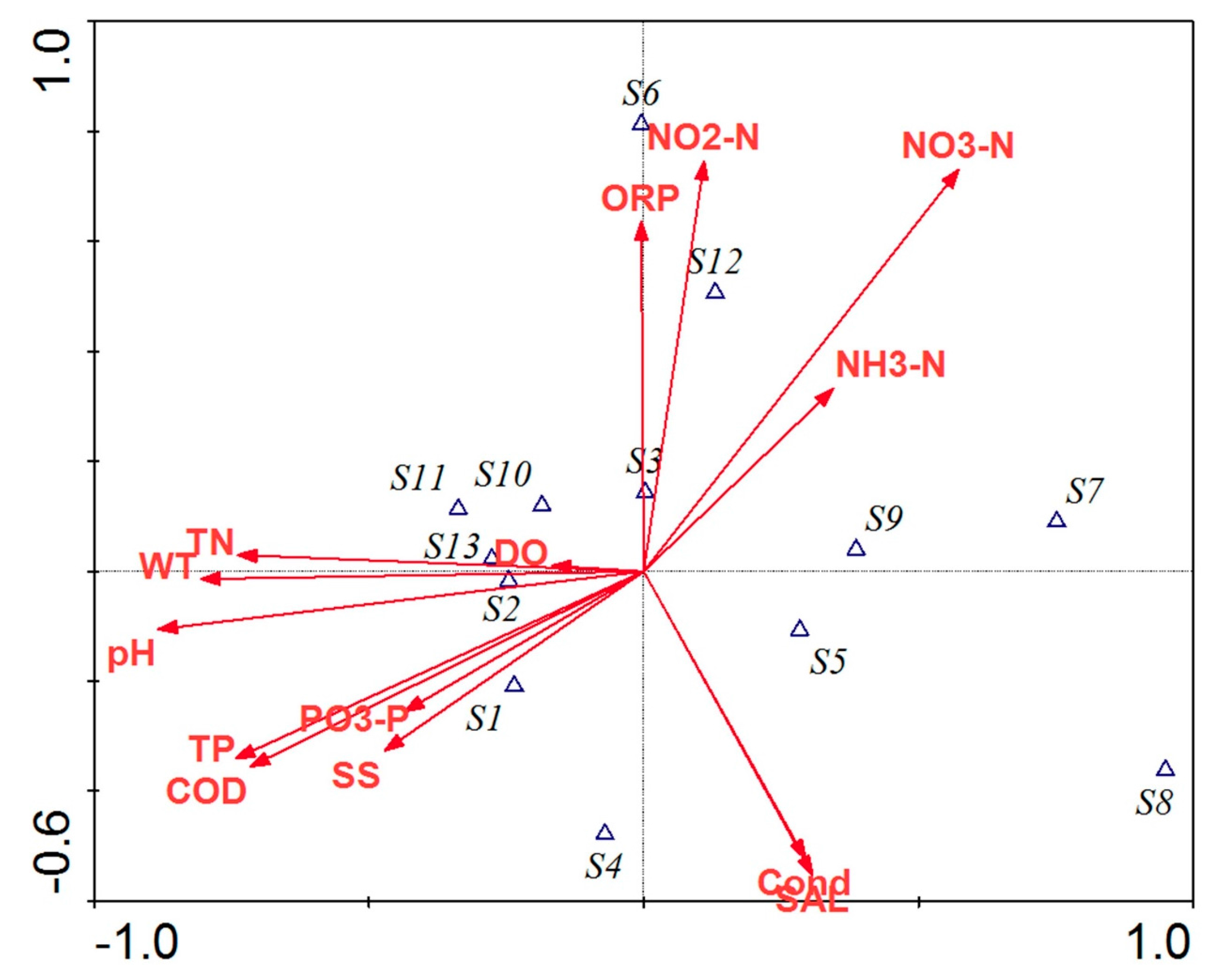
3.3. Relationships between Phytoplankton Community and Physicochemical Parameters
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, W.; Jin, X.; Liu, D.; Lang, C.; Shan, B. Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen and phosphorus and eutrophication assessment for a typical arid river—Fuyang River in northern China. J. Environ. Sci. 2017, 55, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minaudo, C.; Meybeck, M.; Moatar, F.; Gassama, N.; Curie, F. Eutrophication mitigation in rivers: 30 years of trends in spatial and seasonal patterns of biogeochemistry of the Loire River (1980–2012). Biogeosciences 2015, 12, 2549–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, V.H. Effects of eutrophication on maximum algal biomass in lake and river ecosystems. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima-Fernandes, E.; Fernandes, I.; Pereira, A.; Geraldes, P.; Cássio, F.; Pascoal, C. Eutrophication modulates plant-litter diversity effects on litter decomposition in streams. Freshw. Sci. 2014, 34, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Lee, C.W. Effects of eutrophication on diatom abundance, biovolume and diversity in tropical coastal waters. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skácelová, O.; Lepš, J. The relationship of diversity and biomass in phytoplankton communities weakens when accounting for species proportions. Hydrobiologia 2014, 724, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-J.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Qin, N.; Ouyang, H.-L.; Wang, Q.-M.; Kong, X.-Z.; He, Q.-S.; Yang, C.; Yang, B. The seasonal and spatial variations of phytoplankton community and their correlation with environmental factors in a large eutrophic Chinese lake (Lake Chaohu). Ecol. Indic. 2014, 40, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Jiang, Y.-J.; He, W.; Liu, W.-X.; Kong, X.-Z.; Jørgensen, S.E.; Xu, F.-L. The tempo-spatial variations of phytoplankton diversities and their correlation with trophic state levels in a large eutrophic Chinese lake. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 66, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellinger, E.G.; Sigee, D.C. Freshwater Algae: Identification and Use as Bioindicators; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.G.; Mao, J.Q.; Dai, H.C.; Liu, D.F. Impacts of water release operations on algal blooms in a tributary bay of Three Gorges Reservoir. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2011, 54, 1588–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ha, S.Y.; Park, H.K.; Han, M.S.; Shin, K.H. Identification of key factors influencing primary productivity in two river-type reservoirs by using principal component regression analysis. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.K.; Cho, K.H.; Won, D.H.; Lee, J.; Kong, D.S.; Jung, D.I. Ecosystem responses to climate change in a large on-river reservoir, Lake Paldang, Korea. Clim. Chang. 2013, 120, 477–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.H.; Zhu, K.X.; Hu, Z.Y.; Lin, Z.; Yu, B.S.; Qin, Z. The effects of the Three Gorges Dam’s (TGD’s) experimental impoundment on the phytoplankton community in the Xiangxi River, China. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2010, 67, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; He, D.; Wang, H. Environmental consequences of damming the mainstream Lancang-Mekong River: A review. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2015, 146, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Hong-Juan, W.U.; Jing-An, M.A. Causes and characteristics of the eutrophication in large reservoirs in the Yangtze Basin. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Valley 2004, 13, 477–481. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.S.; Li, H.-F.; Pan, M.M.; Luo, Y.; Zhang, Z.G. Study on Phytoplankton Community during the Cyanobacteria Bloom in Haihe River. Yellow River 2013, 35, 63–65. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Zheng, H.; Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Ouyang, Z. Relationships between river water quality and landscape factors in Haihe River Basin, China: Implications for environmental management. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Lei, T.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X. Long-term heavy metals pollution and health risk assessment in the Haihe River, China. Feb-Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2016, 25, 3837–3846. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, S.; Wang, A.; Wang, X.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Z. The long-term variations of water quality in the Haihe River, China. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 873–880. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Huang, S.; Stanley, C.D.; Osborne, T.Z. Phosphorus Fractionation in Core Sediments from Haihe River Mainstream, China. Soil Sediment Contam. Int. J. 2011, 20, 30–53. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Tang, W.; Zhang, H.; Bi, J.; Jin, X.; Li, J.; Shan, B. Characterization of biogenic phosphorus in sediments from the multi-polluted Haihe River, China, using phosphorus fractionation and 31 P-NMR. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 71, 520–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese State Environmental Protection Administration. Water and Wastewater Monitoring Analysis Method; Chinese Environmental Science Publishers: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Kiteresi, L.; Ochieng, E.; Mwangi, S.; Mary, M. Potentially Harmful Algae along the Kenyan Coast: A Norm or Threat. J. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Armbrecht, L.H.; Thompson, P.A.; Wright, S.W.; Schaeffer, A.; Roughan, M.; Henderiks, J.; Armand, L.K. Comparison of the cross-shelf phytoplankton distribution of two oceanographically distinct regions off Australia. J. Mar. Syst. 2015, 148, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lampitt, R.S.; Wishner, K.F.; Turley, C.M.; Angel, M.V. Marine snow studies in the Northeast Atlantic Ocean: Distribution, composition and role as a food source for migrating plankton. Mar. Biol. 1993, 116, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E.; Weaver, W. The Mathematical Theory of Communication; University of Illinois Press: Champaign, IL, USA, 1949; pp. 379–423. [Google Scholar]
- Pielou, E.C. Species-diversity and pattern-diversity in the study of ecological succession. J. Theor. Biol. 1966, 10, 370–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Braak, C.J.F. Canonical Correspondence Analysis: A New Eigenvector Technique for Multivariate Direct Gradient Analysis. Ecology 1986, 67, 1167–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.B.; Gupta, S.; Das, T. Phytoplankton community of Lake Baskandi anua, Cachar District, Assam, North East India—An ecological study. Knowl. Manag. Aquat. Ecosyst. 2016, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Li, D. A niche model to predict Microcystis bloom decline in Chaohu Lake, China. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2012, 30, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, C.; Lu, X.; Pei, H.; Hu, W.; Xie, J. Seasonal dynamics of phytoplankton and its relationship with the environmental factors in Dongping Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 2627–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Archilla, A.I.; Moreira, D.; López-García, P.; Guerrero, C. Phytoplankton diversity and cyanobacterial dominance in a hypereutrophic shallow lake with biologically produced alkaline pH. Extremophiles 2004, 8, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; He, S.; Sun, Z.; Wang, J.; Chen, W. Removal efficiency of MIEX® pretreatment on typical proteins and amino acids derived from Microcystis aeruginosa. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60869–60876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Wate; GB3838-2002; China Environmental Press: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Dodds, W.K.; Jones, J.R.; Welch, E.B. Suggested classification of stream trophic state: Distributions of temperate stream types by chlorophyll, total nitrogen, and phosphorus. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1455–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Xu, Z. Prediction of algal blooming using EFDC model: Case study in the Daoxiang Lake. Ecol. Model. 2011, 222, 1245–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.-X.; Huang, Y.-L.; Song, L.-X.; Liu, D.-F.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, B. Prediction of chlorophyll a concentration using HJ-1 satellite imagery for Xiangxi Bay in Three Gorges Reservoir. Water Sci. Eng. 2014, 7, 70–80. [Google Scholar]
- Sedwick, P.N.; Blain, S.; Quéguiner, B.; Griffiths, F.B.; Fiala, M.; Bucciarelli, E.; Denis, M. Resource limitation of phytoplankton growth in the Crozet Basin, Subantarctic Southern Ocean. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 2002, 49, 3327–3349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, N.; Schmalz, B.; Fohrer, N. Study Progress in Riverine Phytoplankton and its Use as Bio-Indicator a Review. Austin J. Hydrol. 2014, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.; Wang, F.; Sun, H.Y.; Chu, L.M.; Wang, J.L. Characteristics of Phytoplankton Community Structure and Evaluation of Trophic State of Water Body in Bosten Lake. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 864–867, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, G.E. The Paradox of the Plankton. Am. Nat. 1961, 95, 137–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalar, G. The use of phytoplankton patterns of diversity for algal bloom management. Limnol. Ecol. Manag. Inland Waters 2009, 39, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Song, J. Phytoplankton distributions and their relationship with the environment in the Changjiang Estuary, China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2005, 50, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; He, B.; Huang, Q. Canonical correspondence analysis of summer phytoplankton community and its environmental factors in Hanfeng Lake. Huan Jing Ke Xue 2015, 36, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Braak, C.J.F.; Smilauer, P. CANOCO, version 4.5; Software for Canonical Community Ordination, Biometris; Wageningen University and Research Centre: Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Pillsbury, F.C.; Miller, J.R. Habitat and landscape characteristics underlying anuran community structure along an urban–rural gradient. Ecol. Appl. 2008, 18, 1107–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johannes, F.I.; Hans, G.S.; Gaber, S.H.; Trüper, H.G. The Wadi Natrun: Chemical composition and microbial mass developments in alkaline brines of Eutrophic Desert Lakes. Geomicrobiology 1979, 1, 219–234. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, J.; Qin, B.; Paerl, H.W.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, P.; Ma, J.; Chen, Y. Effects of nutrients, temperature and their interactions on spring phytoplankton community succession in Lake Taihu, China. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reader, H.E.; Lindh, M.V.; Conley, D.J.; Kritzberg, E.S. Effects of wastewater treatment plant effluent inputs on planktonic metabolic rates and microbial community composition in the Baltic Sea. Biogeosciences 2016, 13, 4751–4765. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.C.; Liu, S.K.; Zhang, Z.S.; Tu, Q.Y.; Xu, N.N. China Lake Environment; Ocean Press: Beijing, China, 1995. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]

| Latin Name | May | August | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upper Reaches | Middle Reaches | Lower Reaches | Upper Reaches | Middle Reaches | Lower Reaches | |
| Cyanophyta | ||||||
| Chroococcus minutus | 0.025 | |||||
| Chroococcus turgidus | 0.079 | |||||
| Microcystis marginata | 0.042 | 0.102 | ||||
| Microcystis flos-aquae | 0.084 | 0.078 | ||||
| Oscillatoria sp. | 0.071 | 0.125 | 0.108 | |||
| Spirulina sp. | 0.028 | |||||
| Merismopedia sp. | 0.072 | 0.051 | ||||
| Chlorophyta | ||||||
| Scenedesmus quadricauda | 0.136 | 0.186 | 0.046 | |||
| Scenedesmus acuminatus | 0.043 | |||||
| Chlorogonium elongatum | 0.093 | 0.096 | 0.057 | |||
| Coccomyxa sp. | 0.027 | 0.024 | ||||
| Tetrastrum glabrum | 0.043 | |||||
| Gonatozygon sp. | 0.061 | 0.091 | ||||
| Pediastrum simplex | 0.132 | 0.062 | ||||
| Pediastrum simplex var. | 0.037 | |||||
| Bacillariophyta | ||||||
| Melosira italica | 0.293 | 0.121 | 0.079 | |||
| Diatoma vulgare | 0.080 | 0.158 | 0.236 | |||
| Cyclotella bodanica | 0.027 | 0.126 | 0.107 | |||
| Melosira granulata | 0.038 | |||||
| Codes | Phytoplankton |
|---|---|
| S1 | Microcystis marglnata |
| S2 | Microcystis flos-aquae |
| S3 | Oscillatoria sp. |
| S4 | Anabeana sp. |
| S5 | Merismopedia sp. |
| S6 | Spirulina sp. |
| S7 | Pediastrum simplex |
| S8 | Pediastrum simplex var. |
| S9 | Scenedesmus quadricauda |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, W.; Li, Y.; Jiao, Y.; Zhou, B.; Vogt, R.D.; Liu, H.; Ji, M.; Ma, Z.; Li, A.; Zhou, B.; et al. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Environmental Variables in Relation to Phytoplankton Community Structure in a Eutrophic River-Type Reservoir. Water 2017, 9, 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100754
Zhao W, Li Y, Jiao Y, Zhou B, Vogt RD, Liu H, Ji M, Ma Z, Li A, Zhou B, et al. Spatial and Temporal Variations in Environmental Variables in Relation to Phytoplankton Community Structure in a Eutrophic River-Type Reservoir. Water. 2017; 9(10):754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100754
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Wenxi, Yanying Li, Yongjie Jiao, Bin Zhou, Rolf D. Vogt, Honglei Liu, Min Ji, Zhe Ma, Anding Li, Beihai Zhou, and et al. 2017. "Spatial and Temporal Variations in Environmental Variables in Relation to Phytoplankton Community Structure in a Eutrophic River-Type Reservoir" Water 9, no. 10: 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100754
APA StyleZhao, W., Li, Y., Jiao, Y., Zhou, B., Vogt, R. D., Liu, H., Ji, M., Ma, Z., Li, A., Zhou, B., & Xu, Y. (2017). Spatial and Temporal Variations in Environmental Variables in Relation to Phytoplankton Community Structure in a Eutrophic River-Type Reservoir. Water, 9(10), 754. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9100754






