Mapping Evapotranspiration Coefficients in a Temperate Maritime Climate Using the METRIC Model and Landsat TM
Abstract
:1. Introduction
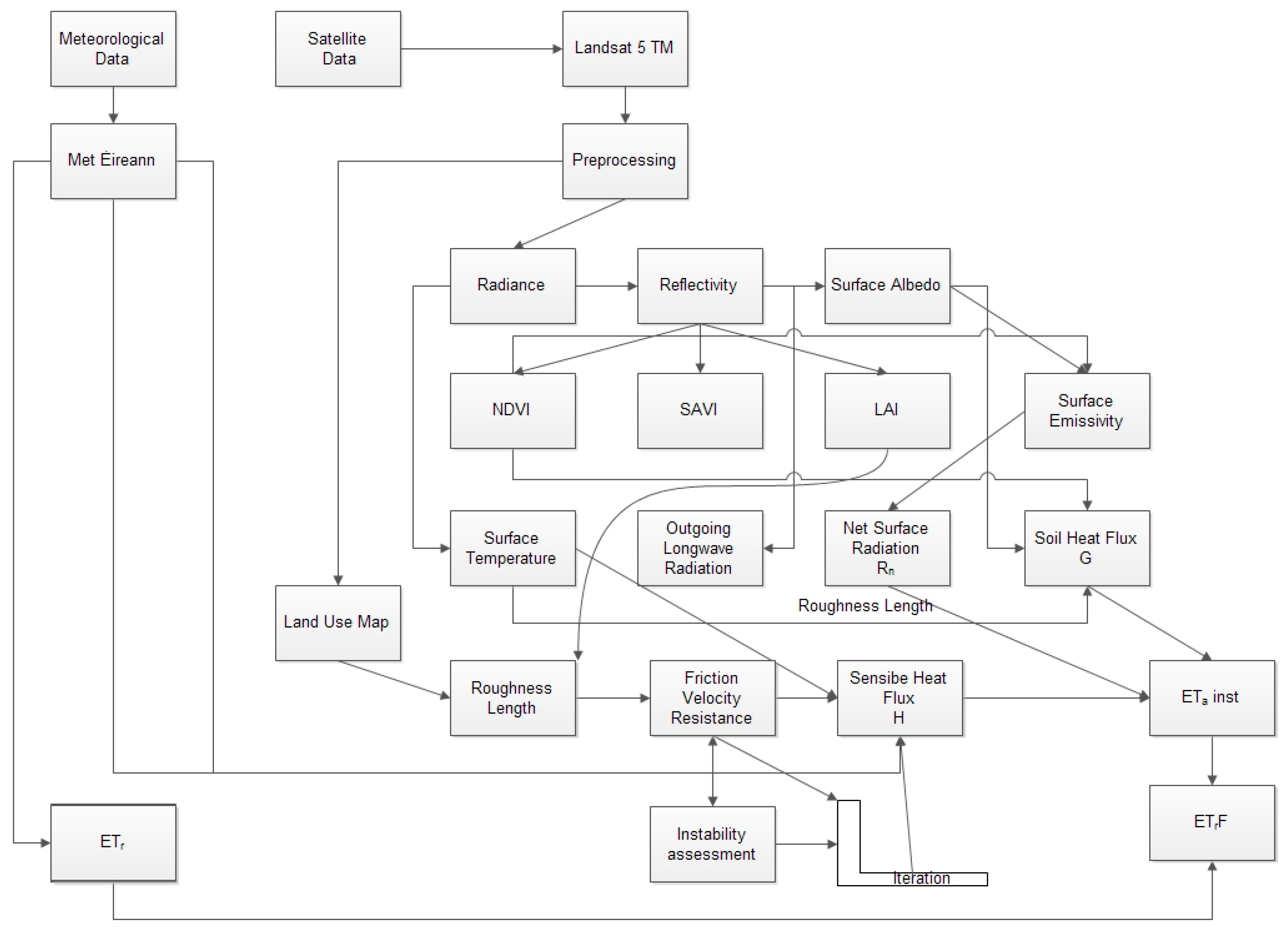
2. Methods
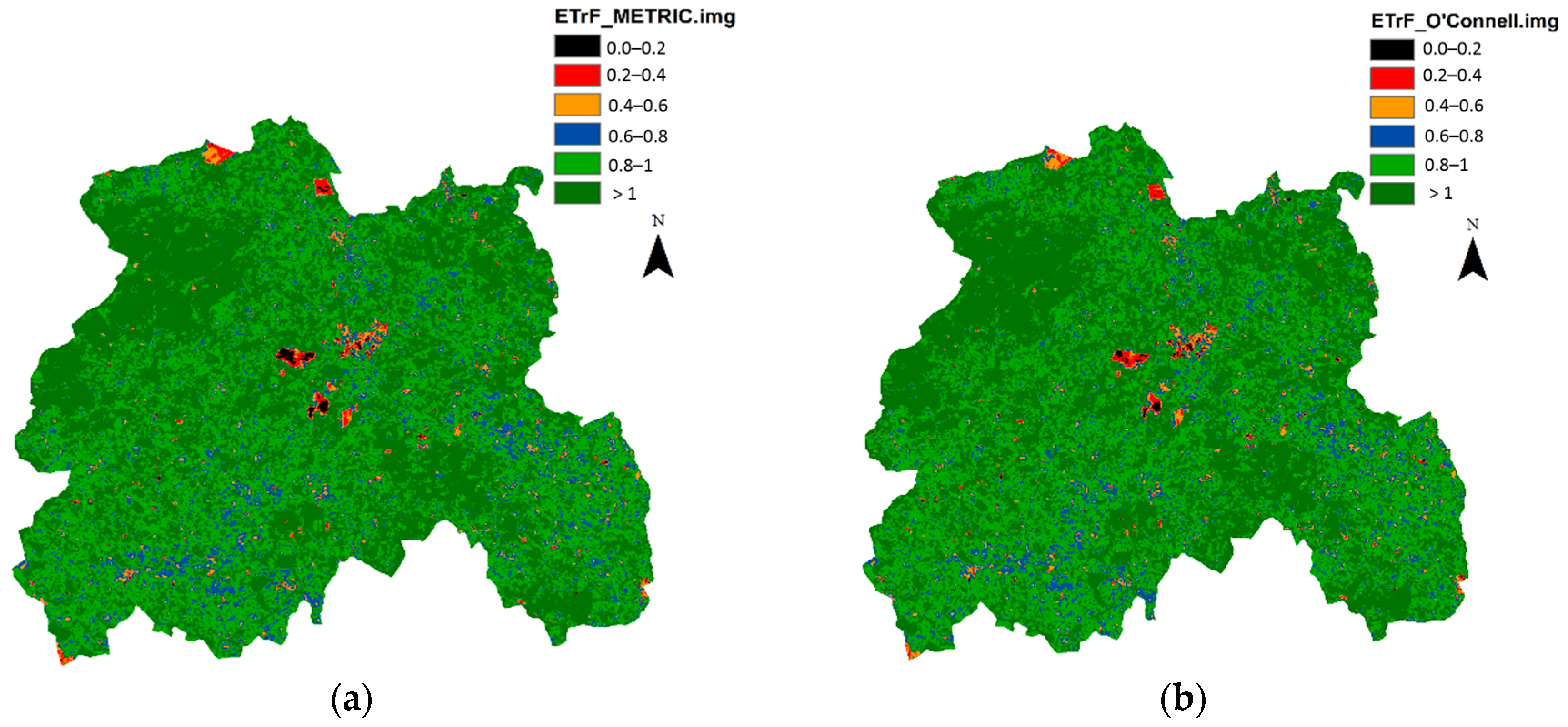
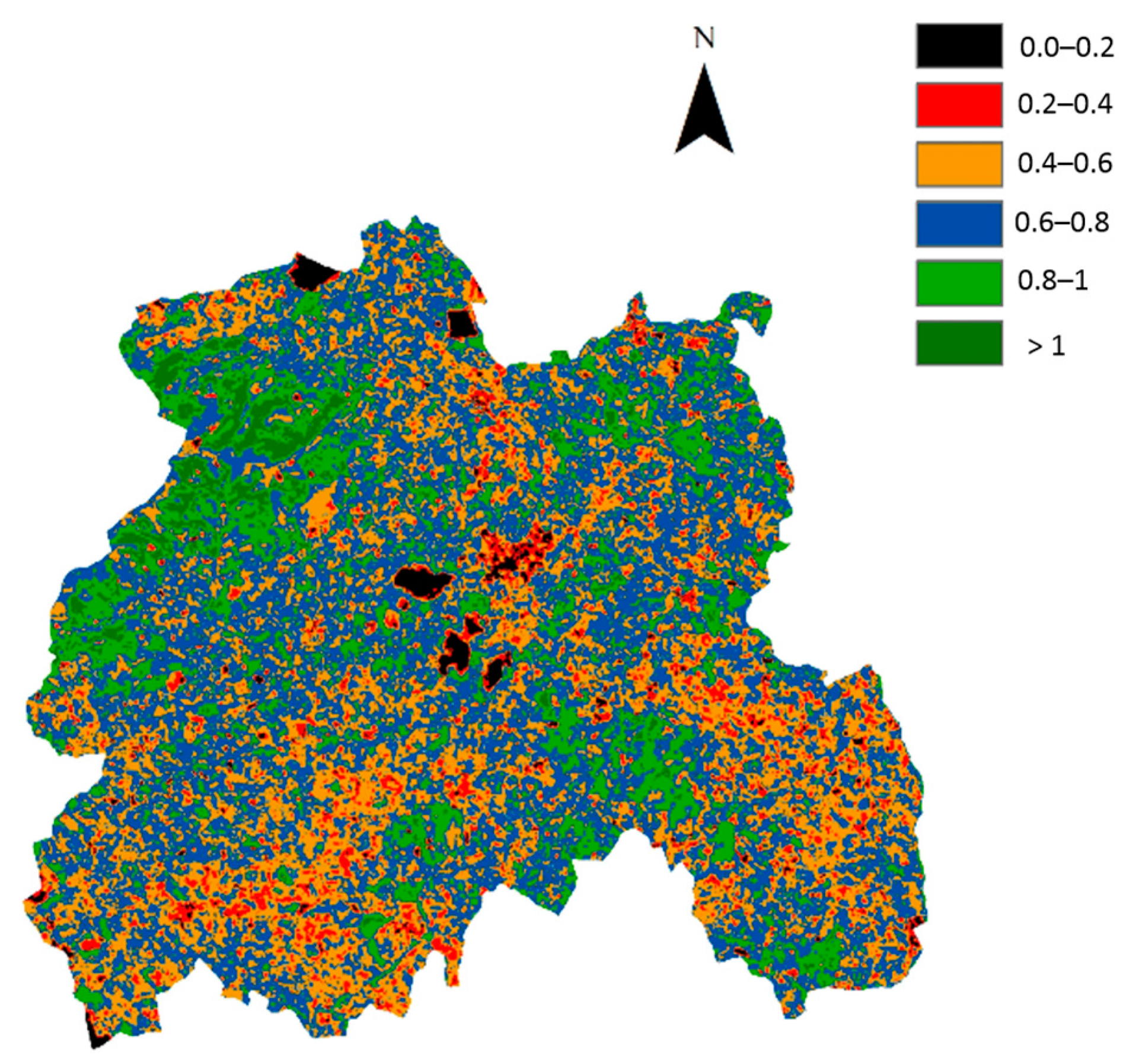
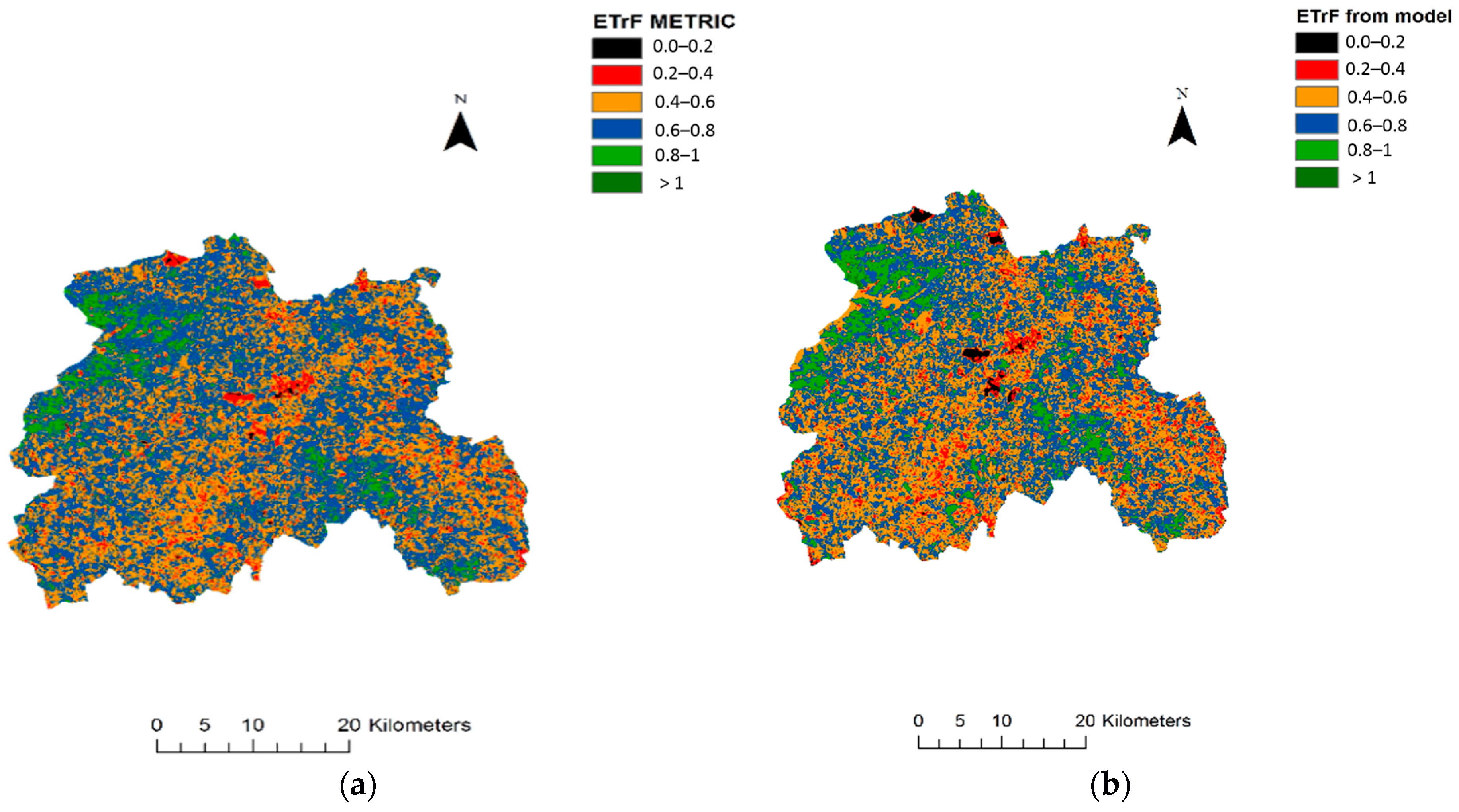
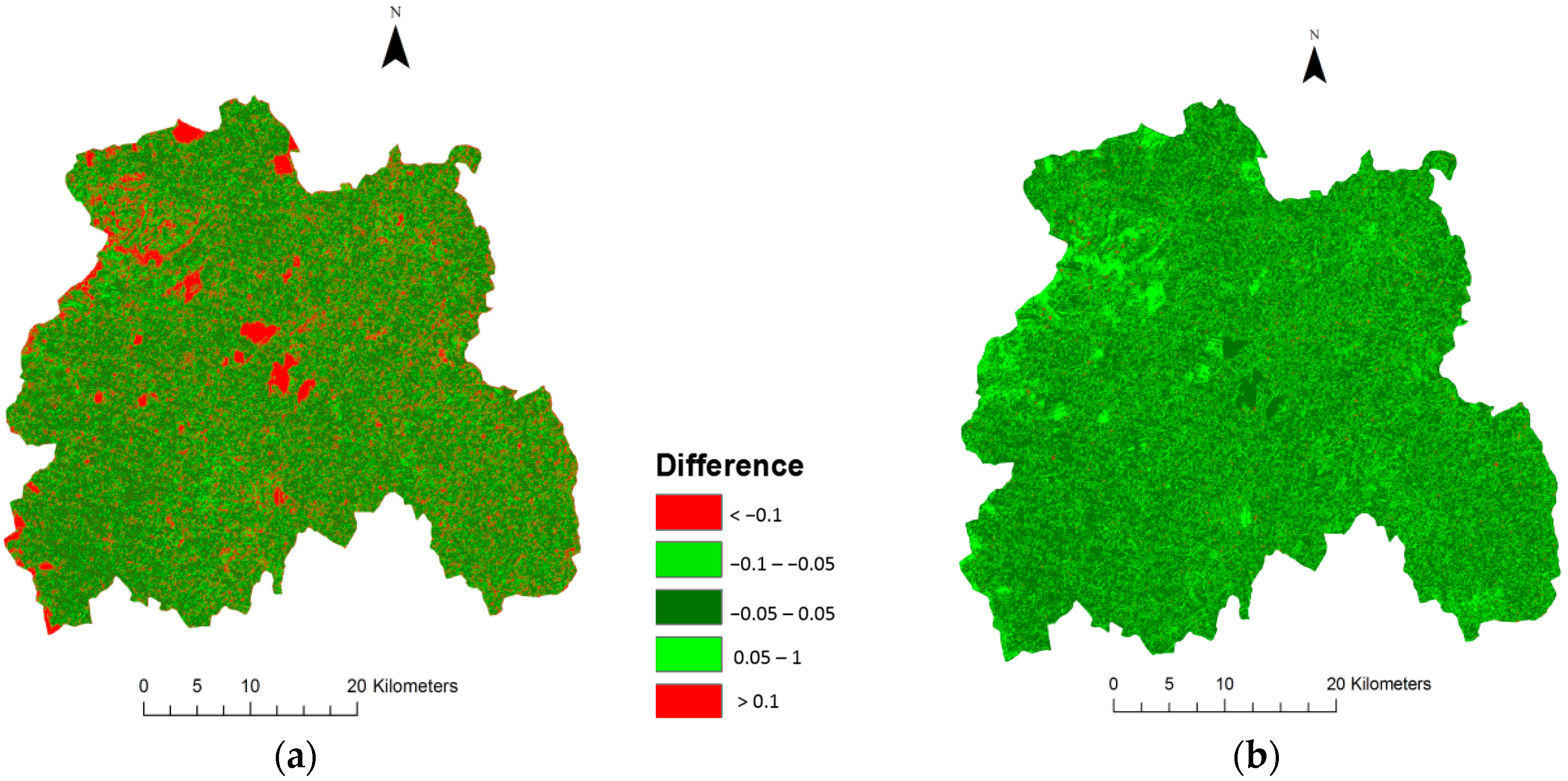
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wonsook, H.; Prasanna, H.G.; Terry, A.H. A review of downscaling methods for remote sensing-based irrigation management: Part I. Irrig Sci. 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penman, H.L. Vegetation and Hydrology; Tech. Comm. No. 53; Commonwealth Bureau of Soils: Harpenden, UK, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R.J. On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Weather Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liakatas, A.; Anadranistakis, M. Derived Meteorological Parameters: Evapotranspiration, Hydroscope: Creation of a National Databank for Hydrological and Meteorological Information; Contractor: Dep. of Water Resources, Hydraulic and Maritime Engineering—N.T.U.A, Report 5/4; Hellenic National Meteorological Service: Athens, Greece, 1992; p. 31. [Google Scholar]
- Shuttleworth, W.J. Evaporation. In Handbook of Hydrology; Maidment, D.R., Ed.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 4.1–4.53. [Google Scholar]
- Tsakiris, G. Water Resources: 1. In Technical Hydrology; Simmetria Publications: Athens, Greece, 1995. (In Greek) [Google Scholar]
- Olioso, A.; Chauki, H.; Courault, D.; Wigneron, J.P. Estimation of evapotranspiration and photosynthesis by assimilation of remote sensing data into SVAT models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1999, 68, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, A.; Kramber, W.J.; Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M. Use of the METRIC evapotranspiration model to compute water use by irrigated agriculture in Idaho. In Proceedings of the 2004 International Geophysical and Remote Sensing Symposium, Anchorage, AK, USA, 20–24 September 2004.
- Li, Z.L.; Tang, R.; Wan, Z.; Bi, Y.; Zhou, C.; Tang, B.; Yan, G.; Zhang, X. A review of current methodologies for regional evapotranspiration estimation from remotely sensed data. Sensors 2009, 9, 3801–3853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Menenti, M.; Feddes, R.A.; Holtslag, A.A.M. A remote sensing surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): 1. Formulation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 198–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Moreno, J.; Roerink, G.J.; van der Wal, T. The surface energy balance algorithm for land (SEBAL): Part 2 validation. J. Hydrol. 1998, 212–213, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—Model. ASCE J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Allen, R.G.; Smith, M.; Raes, D. Crop evapotranspiration estimation with FAO56: Past and future. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 147, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezza, R.; Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M. Estimation of actual evapotranspiration along the Middle Rio Grande of New Mexico using MODIS and Landsat imagery with the METRIC model. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5397–5423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M. SEBAL-based sensible and latent heat fluxes in the irrigated Gediz Basin, Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2000, 229, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexandridis, T.K.; Chemin, Y.; Cherif, I.; Tsakoumis, G.; Galanis, G.; Arampatzis, G.; Zalidis, G.C.; Silleos, N.G.; Stavrinos, E. Improving spatial resolution of agricultural water use estimation using ALOS AVNIR-2 imagery. In Proceedings of the ALOS Principal Investigators Symposium, Rhodes, Greece, 3–7 November 2008; p. 8.
- Spiliotopoulos, M.; Loukas, A.; Michalopoulou, H. Contribution to the study of regional actual evapotranspiration with the use of surface energy balance and remote sensing for central Greece. In Advances in Meteorology, Climatology and Atmospheric Physics; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 309–315. [Google Scholar]
- Papadavid, G.; Perdikou, S.; Hadjimitsis, M.; Hadjimitsis, D. Remote sensing applications for planning irrigation management. The use of SEBAL methodology for estimating crop evapotranspiration in Cyprus. Environ. Clim. Technol. 2012, 9, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, Y.A.; Kar, S.K. Evapotranspiration estimation with remote sensing and various surface energy balance algorithms—A review. Energies 2014, 7, 2821–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morton, C.G.; Huntington, J.L.; Pohll, G.M.; Allen, R.G.; Mcgwire, K.C.; Bassett, S.D. Assessing calibration uncertainty and automation for estimating evapotranspiration from agricultural areas using METRIC. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2013, 49, 549–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.H.; Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Ahmad, M.D.; Bos, M.G. Reviewing SEBAL input parameters for assessing evapotranspiration and water productivity for the Low-Middle Sao Francisco River basin, Brazil Part A: Calibration and validation. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrillo-Rojas, G.; Silva, B.; Córdova, M.; Célleri, R.; Bendix, J. Dynamic mapping of evapotranspiration using an energy balance-based model over an andean páramo catchment of southern Ecuador. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Zayed, I.S.; Elagib, N.A.; Ribbe, L.; Heinrich, J. Satellite-based evapotranspiration over Gezira Irrigation Scheme, Sudan: A comparative study. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 177, 66–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, J.; Huang, M. Comparison of three remote sensing based models to estimate evapotranspiration in an oasis-desert region. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 165, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liaqat, U.W.; Choi, M. Surface energy fluxes in the Northeast Asia ecosystem: SEBS and METRIC models using Landsat satellite images. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2015, 214–215, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bala, A.; Rawat, K.S.; Misra, A.K.; Srivastava, A. Assessment and validation of evapotranspiration using SEBAL algorithm and Lysimeter data of IARI agricultural farm, India. Geocarto Int. 2016, 31, 739–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaber, H.S.; Mansor, S.; Pradhan, B.; Ahmad, N. Evaluation of SEBAL model for Evapotranspiration mapping in Iraq using remote sensing and GIS. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2016, 11, 3950–3955. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, S. Remote estimation of terrestrial evapotranspiration by Landsat 5 TM and the SEBAL model in cold and high-altitude regions: A case study of the upper reach of the Shule River Basin, China. Hydrol. Process. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CSO. Available online: http://www.cso.ie (accessed on 5 July 2016).
- Met Éireann. Available online: http://www.met.ie (accessed on 5 July 2016).
- Laois County Council (Laois County Development Plan, Appendix 6 Landscape Character Assessment, 2011–2017). Available online: http://www.laois.ie/media/Media,7818,en.pdf (accessed on 5 July 2016).
- Price, J.C. Calibration of satellite radiometers and the comparison of vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 1987, 21, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, J.R. Introductory Digital Image Processing: A Remote Sensing Perspective, 2nd ed.; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1996; p. 316. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B. Revised Landsat-5 TM radiometric calibration procedures and post-calibration dynamic ranges. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 2674–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riaño, D.; Chuvieco, E.; Salas, J.; Aguado, I. Assessment of different topographic corrections in Landsat-TM data for mapping vegetation types. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2003, 41, 1056–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landsat 7 Science Data Users Handbook. Project Science Office at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, MD, USA. Available online: http://landsat.gsfc.nasa.gov/wp-content/uploads/2016/08/Landsat7_Handbook.pdf (accessed on 29 December 2016).
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Noordman, E.J.M.; Pelgrum, H.; Davids, G.; Thoreson, B.P.; Allen, R.G. SEBAL Model with Remotely Sensed Data to Improve Water Resources Management under Actual Field Conditions. ASCE J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2005, 131, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.G.; Tasumi, M.; Morse, A.; Trezza, R.; Wright, J.L.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Kramber, W.; Lorite, I.; Robinson, C.W. Satellite-based energy balance for mapping evapotranspiration with internalized calibration (METRIC)—Applications. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2007, 133, 395–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J. The atmospheric effect on remote sensing and its correction. In Theory and Applications of Optical Remote Sensing; Asrar, G., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Trezza, R.; Waters, R.; Bastiaanssen, W. Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land (SEBAL)–Advanced Training and Users Manual; Idaho Department of Water Resources, University of Idaho: Moscow, ID, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kübert, C.; Conrad, C.; Falk, U.; Hendrickx, J. Assessing the impact of atmospheric corrections on modeling surface energy balance fluxes with SEBAL. In Global Change and Water Resources in West Africa the German-African GLOWA Projects, Proceedings of the International Conference, Ouagadougou, Burkina Faso, 25–28 August 2008; Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF): Bonn, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Brutsaert, W. Evaporation into the Atmosphere, Theory, History, and Applications; D. Reidel: Boston, MA, USA, 1982; p. 299. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, R.; Friedl, M.A. Determination of roughness lengths for heat and momentum over boreal forests. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 2003, 107, 581–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, G.; Gowda, P.H.; Vara Prasad, P.V.; Howell, T.A.; Aiken, R.M.; Neale, C.M.U. Investigating the influence of roughness length for heat transport (zoh) on the performance of SEBAL in semi-arid irrigated and dry land agricultural systems. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 231–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). CORINE Land Cover 2000 Update (Ireland) Final Report 2013; EPA: Johnstown Castle, Ireland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Monin, A.S.; Obukhov, A.M. Basic laws of turbulent mixing in the surface layer of the atmosphere. Tr. Akad. Nauk SSSR Geofiz. Inst. 1954, 24, 163–187. [Google Scholar]
- Pôças, I.; Paço, T.A.; Cunha, M.; Andrade, J.A.; Silvestre, J.; Sousa, A.; Santos, F.L.; Pereira, L.S.; Allen, R.G. Satellite-based evapotranspiration of a super-intensive olive orchard: Application of METRIC algorithms. Biosyst. Eng. 2014, 128, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paço, T.A.; Pôças, I.; Cunha, M.; Silvestre, J.C.; Santos, F.L.; Paredes, P.; Pereira, L.S. Evapotranspiration and crop coefficients for a super intensive olive orchard. An application of SIMDualKc and METRIC models using ground and satellite observations. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 2067–2080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T. Development of a two-band enhanced vegetation index without a blue band. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 3833–3845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha, A.; Shaver, G. Advantages of a two band EVI calculated from solar and photosynthetically active radiation fluxes. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1560–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.; Connolly, J.; Holden, N.M. A monitoring protocol for vegetation change on Irish peatland and heath. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 31, 130–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connell, J.; Connolly, J.; Vermote, E.F.; Holden, N.M. Radiometric normalization for change detection in peatlands: a modified temporal invariant cluster approach. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 2905–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palle, E.; Butler, C. Sunshine records from Ireland: cloud factors and possible links to solar activity and cosmic rays. Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 709–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wukelic, G.E.; Gibbons, D.E.; Martucci, L.M.; Foote, H.P. Radiometric calibration of Landsat Thematic Mapper thermal band. Remote Sens. Environ. 1989, 28, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cob, A. Use of thermal units to estimate corn crop coefficients under semiarid climatic conditions. Irrig. Sci. 2008, 26, 335–345. [Google Scholar]
- Bautista-Capetillo, C.; Zavala, M.; Martínez-Cob, A. Using thermal units for crop coefficient estimation and irrigation scheduling improves yield and water productivity of corn (Zea mays L.). J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 2013, 139, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhungel, R.; Allen, R.G.; Trezza, R.; Robison, C.W. Comparison of latent heat flux using aerodynamic methods and using the penman–monteith method with satellite-based surface energy balance. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 8844–8877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.; Sharma, B.R.; Matin, M.A.; Sharma, D.; Gunasinghe, S. An Assessment of Crop Water Productivity in the Indus and Ganges River Basins: Current Status and Scope for Improvement; International Water Management Institute (IWMI): Colombo, Sri Lanka, 2010; p. 22. [Google Scholar]
- Nikam, B.R.; Ibragimov, F.; Chouksey, A.; Aggarwal, S.P. Retrieval of land surface temperature from Landsat 8 TIRS for the command area of Mula irrigation project. Environ. Earth Sci. 2016, 16, 1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, Z.; Wang, Q.; Batkhishig, O.; Ouyang, Z. Relationship between evapotranspiration and land surface temperature under energy- and water-limited conditions in dry and cold climates. Adv. Meteorol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, A.; Del Prado, A. Implications of climate change for grasslands in Europe, impacts, adaptations and mitigation options: a review. Grass Forage Sci. 2007, 62, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilliland, T.J.; Farrell, A.D.; Grogan, D. Differential responses to climatic conditions in Ireland by five grass species. In Grassland Farming and Land Management Systems in Mountainous Regions, Proceedings of the 16th Symposium of the European Grassland Federation, Gumpenstein, Austria, 29–31 August 2011; Potch, E.M., Krautzer, B., Hopkins, A., Eds.; Agricultural Research and Education Center (AREC) Raumberg-Gumpenstein: Irdning, Austria, 2011; Volume 16, pp. 217–219. [Google Scholar]
- Congalton, R.G.; Green, K. Assessing the Accuracy of Remotely Sensed Data: Principles and Practices; Lewis Publishers: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; p. 137. [Google Scholar]
- Foody, G.M. What is the difference between two maps? A remote sensor’s view. J. Geogr. Syst. 2006, 8, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myint, S.W.; Yuan, M.; Cerveny, R.S.; Giri, C.P. Comparison of remote sensing image processing techniques to identify tornado damage areas from Landsat TM data. Sensors 2008, 8, 1128–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, D.J.; Sader, S.A. Comparison of change-detection techniques for monitoring tropical forest clearing and vegetation regrowth in a time series. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2001, 67, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar]
- Scavone, G.; Sánchez, J.M.; Telesca, V.; Caselles, V.; Copertino, V.A.; Pastore, V.; Valor, E. Pixel-oriented land use classification in energy balance modelling. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, N.W.T.; Epshtein, O. Seasonally-managed wetland footprint delineation using landsat ETM+ satellite imagery. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 54, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Morton, C.; Kamble, B.; Kilic, A.; Huntington, J.; Thau, D.; Gorelick, N.; Erickson, T.; Moore, R.; Trezza, R.; et al. EEFlux: A Landsat-based Evapotranspiration mapping tool on the Google Earth Engine. In Proceedings of the Joint ASABE/IA Irrigation Symposium 2015: Emerging Technologies for Sustainable Irrigation, Long Beach, CA, USA, 10–12 November 2015; pp. 424–433.
- Spiliotopoulos, M.; Loukas, A.; Mylopoulos, N. A new remote sensing procedure for the estimation of crop water requirements. In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment, Paphos, Cyprus, 16–19 March 2015.
- Bierkens, M.F.P.; Finke, P.A.; Willigen, D.E. Upscaling and Downscaling Methods for Environmental Research; Wageningen University and Research Centre: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, H.; Hendrickx, J.; Borchers, B. Down-scaling of SEBAL derived evapotranspiration maps from MODIS (250) to Landsat (30 m) scales. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 32, 6457–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spiliotopoulos, M.; Adaktylou, N.; Loukas, A.; Michalopoulou, H.; Mylopoulos, N.; Toulios, L. A spatial downscaling procedure of MODIS derived actual evapotranspiration using Landsat images at central Greece. In First International Conference on Remote Sensing and Geoinformation of the Environment (RSCy2013); SPIE Conference Proceedings; The International Society for Optical Engineering (SPIE): Bellingham, WA, USA, 2013; Volume 8795. [Google Scholar]
- Bhattarai, N.; Quackenbush, L.J.; Dougherty, M.; Marzen, L.J. A simple Landsat–MODIS fusion approach for monitoring seasonal evapotranspiration at 30 m spatial resolution. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2015, 36, 115–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Im, J.; Park, S.; Gong, H. Downscaling of MODIS One kilometer evapotranspiration using Landsat-8 data and machine learning approaches. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickx, J.M.H.; Allen, R.G.; Brower, A.; Byrd, A.R.; Hong, S.H.; Ogden, F.L.; Pradhan, N.R.; Robison, C.W.; Toll, D.; Trezza, R.; et al. Benchmarking optical/thermal satellite imagery for estimating evapotranspiration and soil moisture in decision support tools. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2016, 52, 89–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Li, A.; Zhao, W.; Bian, J. Review of temporal scale expansion for evapotranspiration retrieved by remote sensing data. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 162–173. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro, A.; Rolim, J.; Miguel, I.; Catalão, J.; Silva, J.; Painho, M.; Vekerdy, Z. Crop monitoring based on SPOT-5 Take-5 and sentinel-1A data for the estimation of crop water requirements. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2017 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Spiliotopoulos, M.; Holden, N.M.; Loukas, A. Mapping Evapotranspiration Coefficients in a Temperate Maritime Climate Using the METRIC Model and Landsat TM. Water 2017, 9, 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010023
Spiliotopoulos M, Holden NM, Loukas A. Mapping Evapotranspiration Coefficients in a Temperate Maritime Climate Using the METRIC Model and Landsat TM. Water. 2017; 9(1):23. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010023
Chicago/Turabian StyleSpiliotopoulos, Marios, Nicholas M. Holden, and Athanasios Loukas. 2017. "Mapping Evapotranspiration Coefficients in a Temperate Maritime Climate Using the METRIC Model and Landsat TM" Water 9, no. 1: 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010023
APA StyleSpiliotopoulos, M., Holden, N. M., & Loukas, A. (2017). Mapping Evapotranspiration Coefficients in a Temperate Maritime Climate Using the METRIC Model and Landsat TM. Water, 9(1), 23. https://doi.org/10.3390/w9010023







