Spatial–Temporal Dynamics of Wetland Vegetation Related to Water Level Fluctuations in Poyang Lake, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
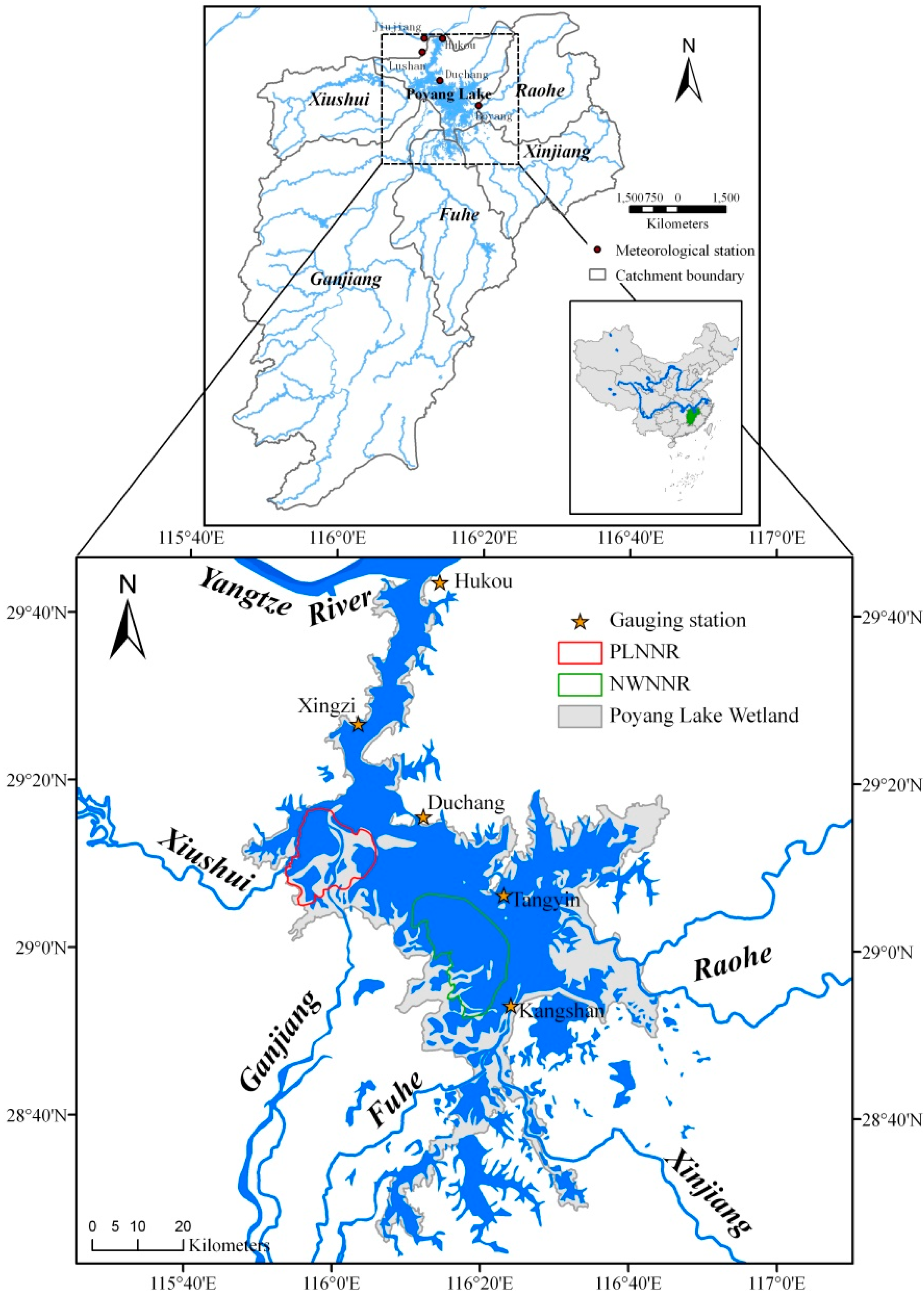
2.1. Study Area
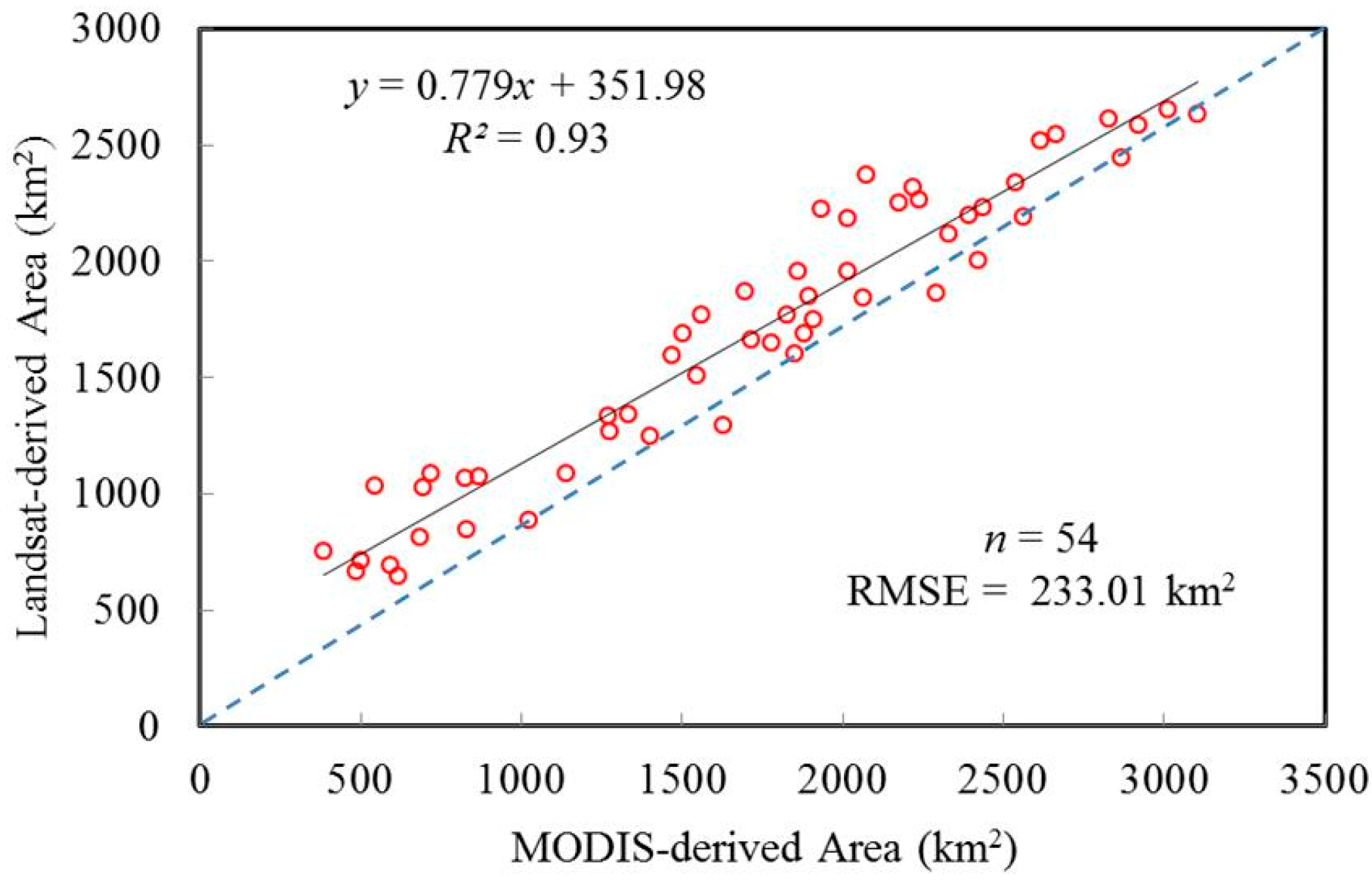
2.2. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS)
2.3. Water Level Information
2.4. Sen’s Slope Estimator and Mann–Kendall (MK) Test
2.5. Gaussian Regression Model
3. Results and Discussion
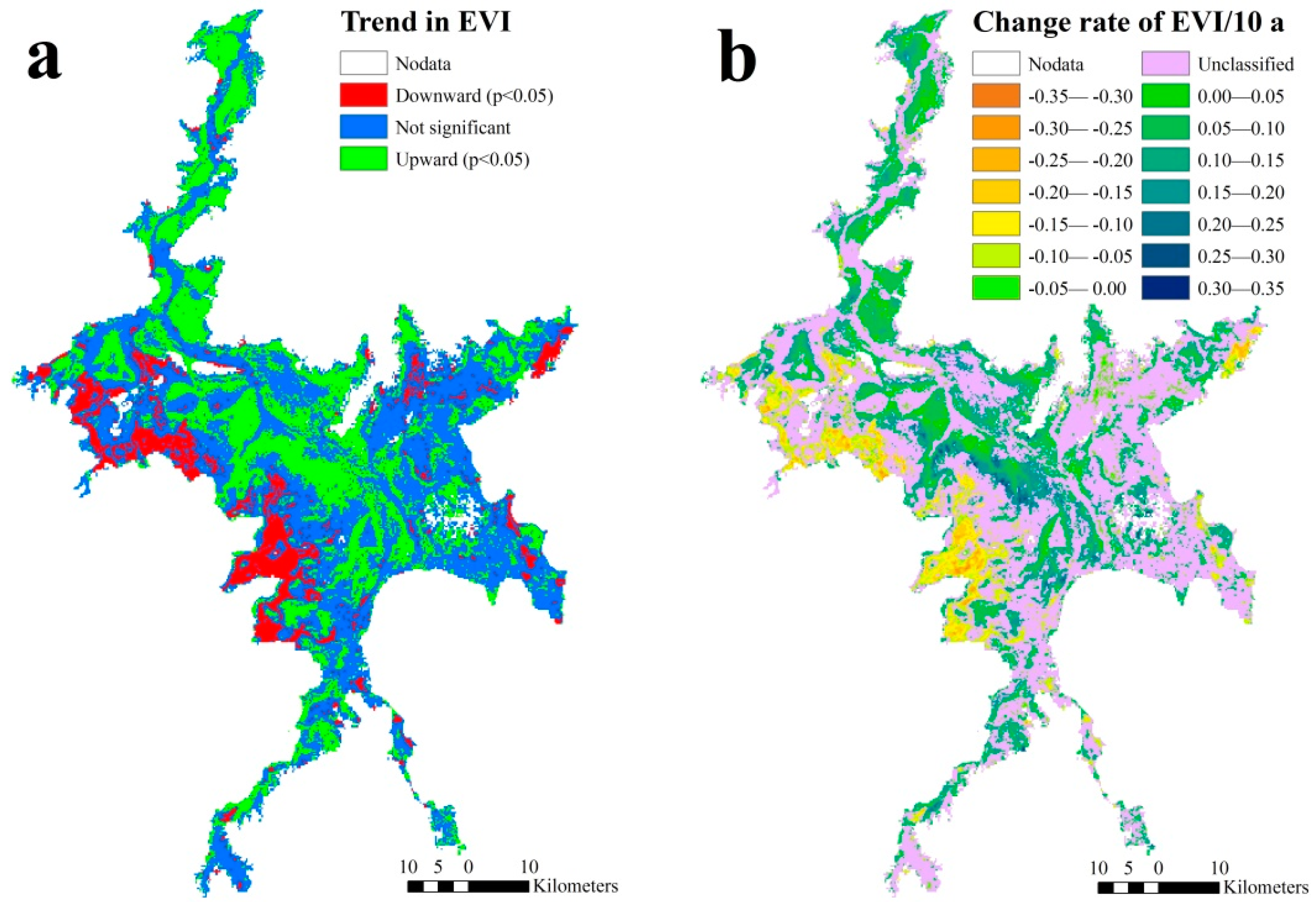
3.1. Spatial and Temporal Variability of EVI
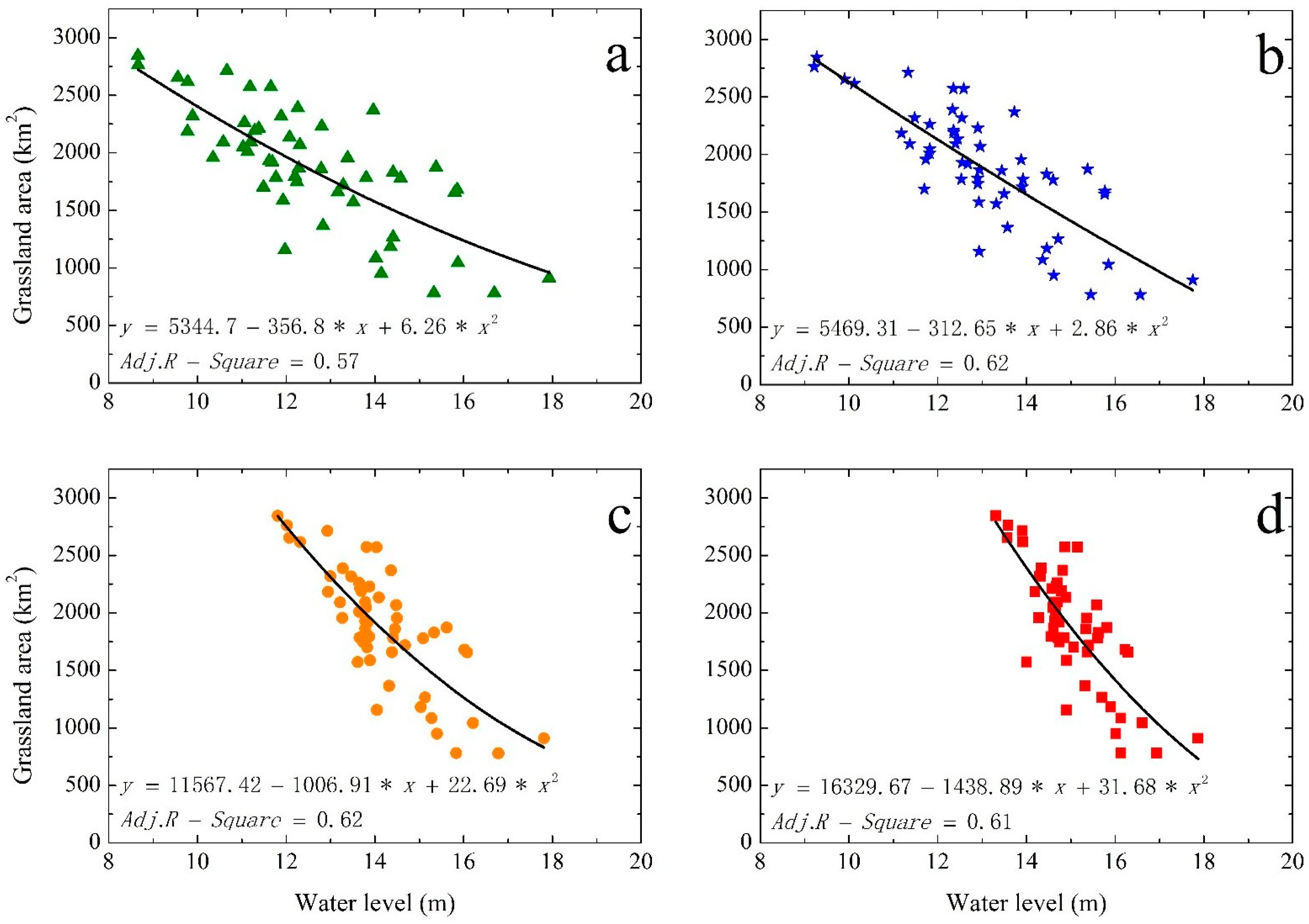
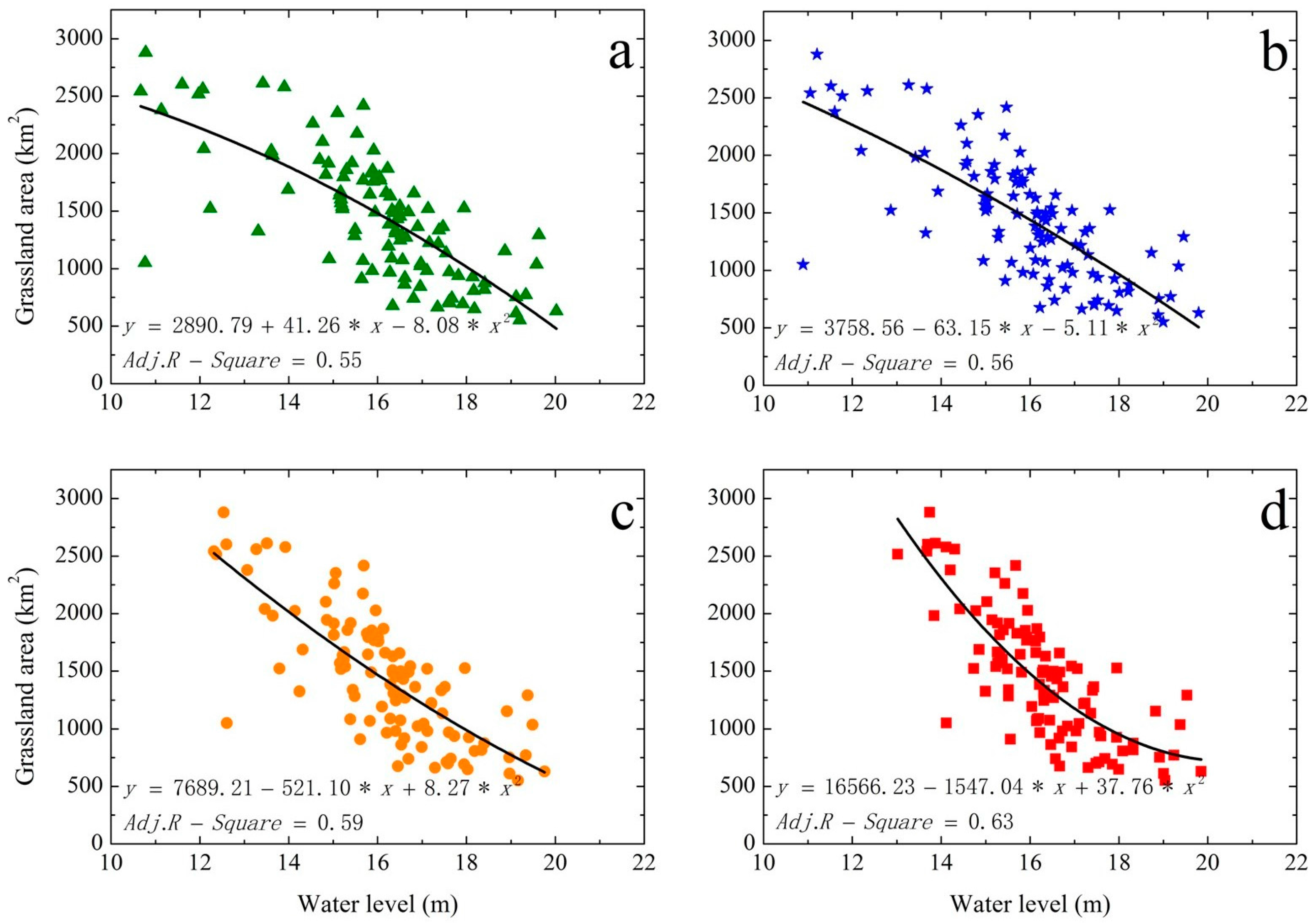
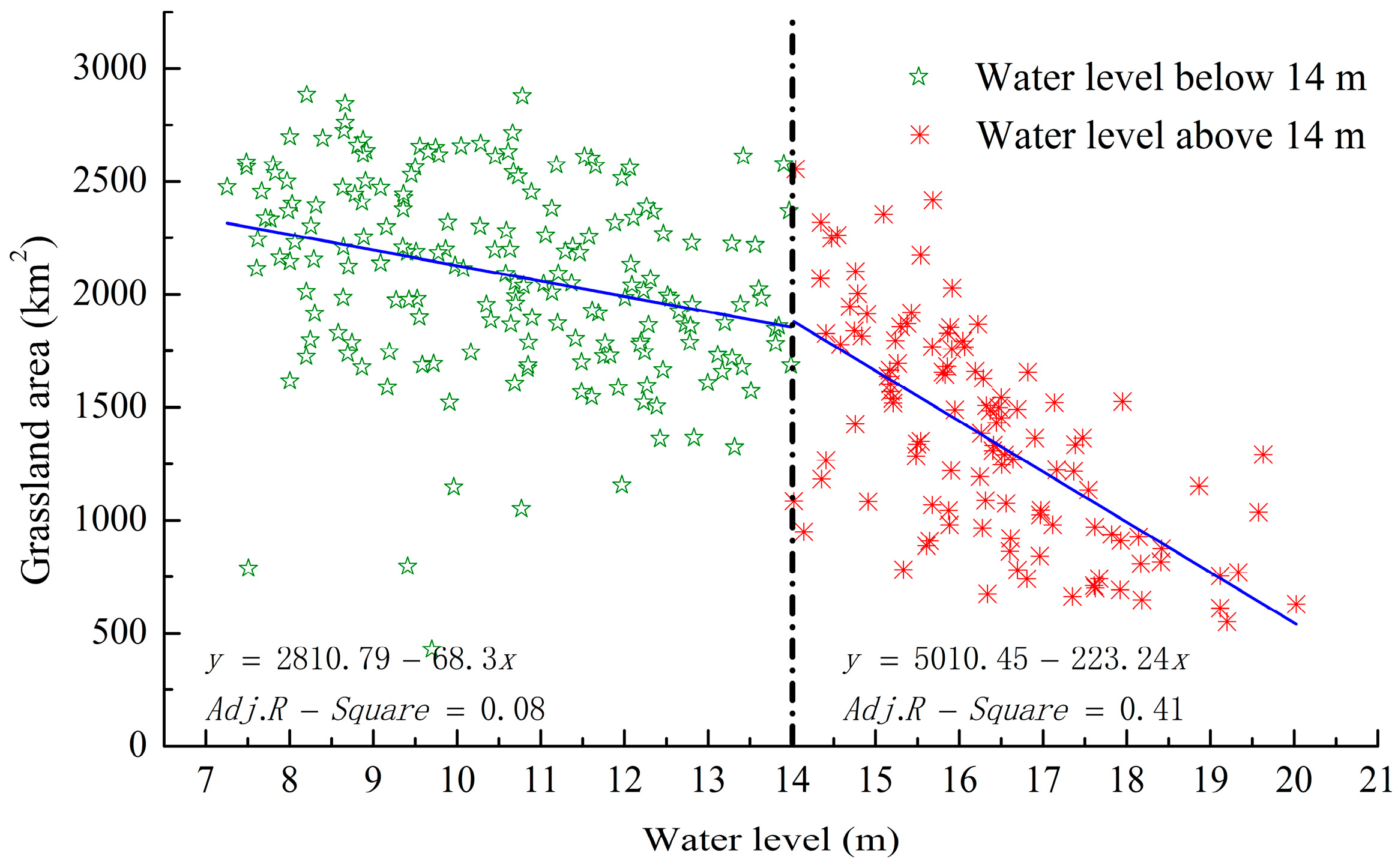
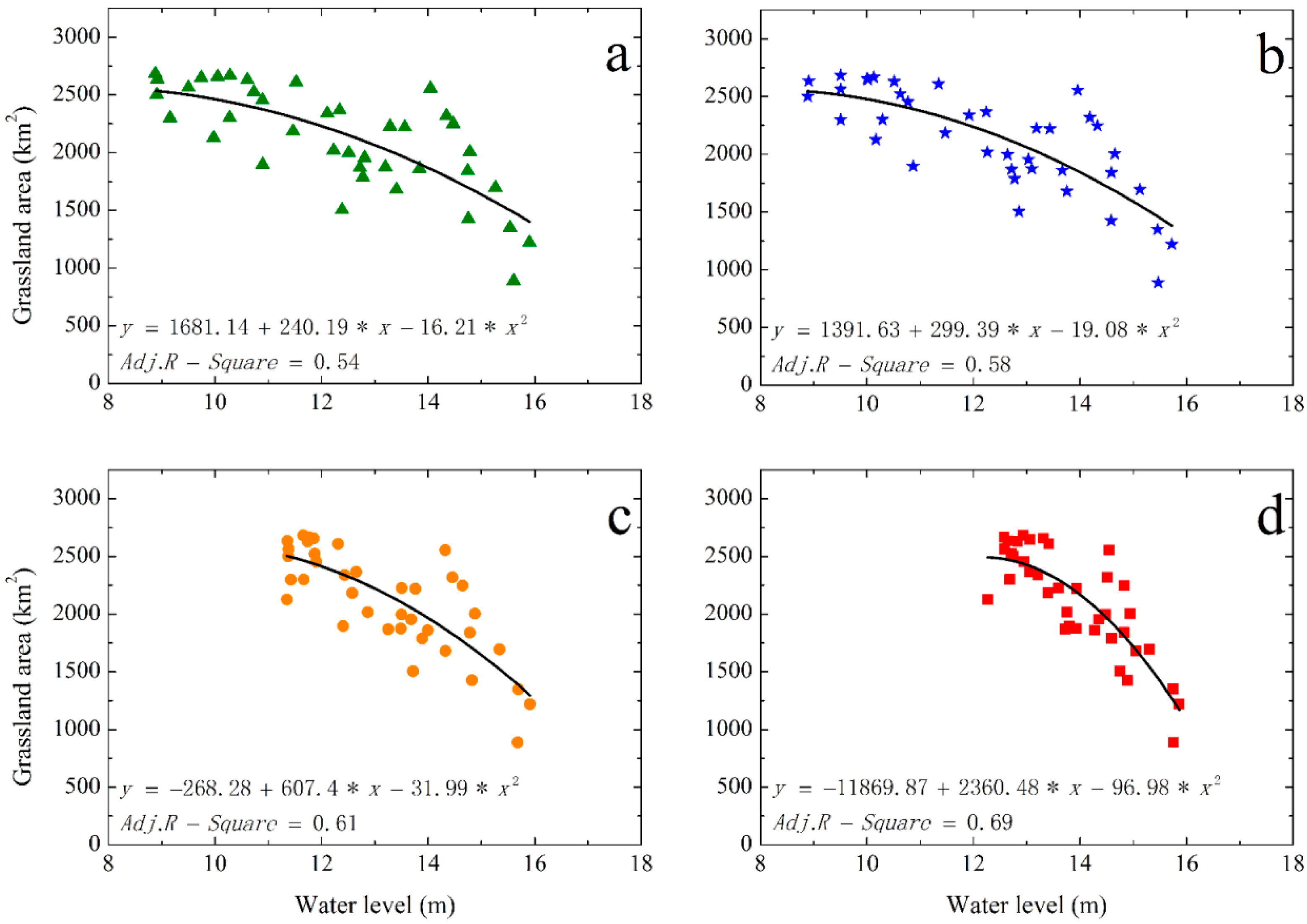
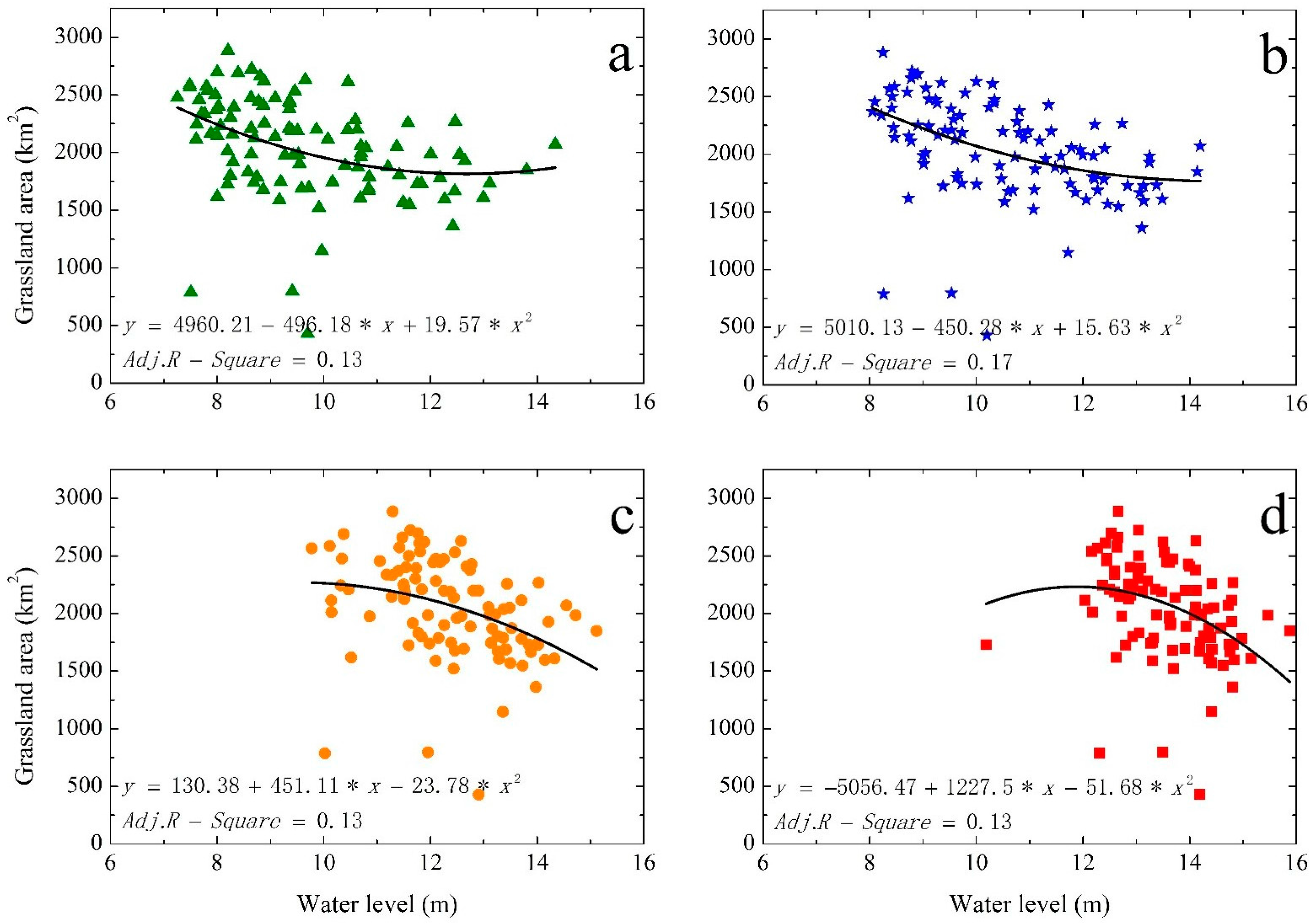
3.2. Relations between Grassland Area and Water Level
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joyce, C.B.; Wade, P.M. European Wet Grasslands: Biodiversity, Management and Restoration; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Mountford, J.; Roy, D.; Cooper, J.; Manchester, S.; Swetnam, R.; Warman, E.; Treweek, J. Methods for targeting the restoration of grazing marsh and wet grassland communities at a national, regional and local scale. J. Nat. Conserv. 2006, 14, 46–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toogood, S.E.; Joyce, C.B. Effects of raised water levels on wet grassland plant communities. Appl. Veg. Sci. 2009, 12, 283–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connell, J.H. The influence of interspecific competition and other factors on the distribution of the barnacle Chthamalus stellatus. Ecology 1961, 42, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtwright, J.; Findlay, S.E. Effects of microtopography on hydrology, physicochemistry, and vegetation in a tidal swamp of the Hudson River. Wetlands 2011, 31, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.L.; Han, J.Y.; Xu, L.G.; Wan, R.R.; Chen, Y.W. Soil Characteristics in Relation to Vegetation Communities in the Wetlands of Poyang Lake, China. Wetlands 2014, 34, 829–839. [Google Scholar]
- Piao, S.L.; Fang, J.Y.; Ji, W.; Guo, Q.H.; Ke, J.H.; Tao, S.; Woods, K. Variation in a satellite-based vegetation index in relation to climate in China. J. Veg. Sci. 2004, 15, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Euliss, N.H.; Smith, L.M.; Wilcox, D.A.; Browne, B.A. Linking ecosystem processes with wetland management goals: Charting a course for a sustainable future. Wetlands 2008, 28, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapin, D.M.; Paige, D.K. Response of Delta Vegetation to Water Level Changes in a Regulated Mountain Lake, Washington, WA, USA. Wetlands 2013, 33, 431–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, C.C.; Zhou, D.M. Modeling the spatial distribution of Carex pseudocuraica in a freshwater marsh, northeast China. Wetlands 2014, 34, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvertown, J.; Dodd, M.E.; Gowing, D.J.; Mountford, J.O. Hydrologically defined niches reveal a basis for species richness in plant communities. Nature 1999, 400, 61–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deegan, B.M.; White, S.D.; Ganf, G.G. The influence of water level fluctuations on the growth of four emergent macrophyte species. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 86, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Yang, G.S.; Wan, R.R.; Wang, X.L. Impact of water level change on wetland vegetation of rivers and lakes. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 813–821. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy, M.P.; Milne, J.M.; Murphy, K.J. Experimental growth responses to groundwater level variation and competition in five British wetland plant species. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 11, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keough, J.R.; Thompson, T.A.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Wilcox, D.A. Hydrogeomorphic factors and ecosystem responses in coastal wetlands of the Great Lakes. Wetlands 1999, 19, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.A.; Nichols, S.J. The effects of water-level fluctuations on vegetation in a Lake Huron wetland. Wetlands 2008, 28, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankman, D.; Liang, Q. Landscape changes and increasing flood frequency in China’s Poyang Lake region. Prof. Geogr. 2003, 55, 434–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.H.; Zhang, Q. Variation of floods characteristics and their responses to climate and human activities in Poyang Lake, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.W.; Han, D.; He, G.J.; Chen, M.H. Flood management selections for the Yangtze River midstream after the Three Gorges Project operation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 432–433, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Hu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Feng, S. Effects of the three gorges dam on Yangtze river flow and river interaction with Poyang Lake, China: 2003–2008. J. Hydrol. 2012, 416, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Tang, X.Y.; Tang, J.L.; Wang, C. Assessing water quality of three gorges reservoir, China, over a five-year period from 2006 to 2011. Water Resour. Manag. 2013, 27, 4545–4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, X.L.; Zhao, X. Dramatic inundation changes of China’s two largest freshwater lakes linked to the Three Gorges Dam. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 9628–9634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, X.J.; Liang, Q.H.; Jiang, J.H.; Huang, Q. Impoundment Effects of the Three-Gorges-Dam on Flow Regimes in Two China’s Largest Freshwater Lakes. Water Resour. Manag. 2014, 28, 5111–5124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toogood, S.E.; Joyce, C.B.; Waite, S. Response of floodplain grassland plant communities to altered water regimes. Plant. Ecol. 2008, 197, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Wang, L. Object-based analysis and change detection of major wetland cover types and their classification uncertainty during the low water period at Poyang Lake, China. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 3220–3236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; He, L.H.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, Y.W.; Wang, X.L. Effects of the Three Gorges Project on the typical wetland vegetations of Poyang Lake. Geogr. Res. 2011, 30, 134–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.D.; Liu, G.H.; Jin, J.F.; You, X.; Zhan, H.Y.; Jia, W.M.; Cao, R.; Gao, Y.Y.; Luo, H.; Gao, X. Structure Analysis of Beach Vegetation in Poyang Lake in Autumn. Jiangxi Sci. 2010, 28, 549–605. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Li, J. Scientists line up against dam that would alter protected wetlands. Science 2009, 326, 508–509. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.; Lai, G.Y.; Li, L. Predicting the Hydrological Impacts of the Poyang Lake Project Using an EFDC Model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 05015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.L.; Zhang, Q.; Tan, Z.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Wang, X.L. Effects of water-table depth and soil moisture on plant biomass, diversity, and distribution at a seasonally flooded wetland of Poyang Lake. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2015, 25, 739–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Xu, L.G.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, Y.W.; Xu, J. Change of Vegetation Community Structure and the Relationship between It and Soil Nutrients in Typical Beaches in Poyang Lake Area. Wetl. Sci. 2013, 11, 186–191. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.L.; Yin, J.X.; Jiang, Y.Z.; Wang, H. Relationship between the hydrological conditions and the distribution of vegetation communities within the Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve, China. Ecol. Inform. 2012, 11, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, H.L.; Xu, L.G.; Jiang, J.H.; Xu, J.X.; Deng, J.M.; Long, W.X. Responses of typical hygrophytes root growth characteristics to extreme water regimes in beach wetland of Poyang Lake, China. Chin. J. Ecol. 2013, 32, 3125–3130. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, M.; Ni, L.Y.; Jun, X.U.; Liang, H.E.; Hui, F.U.; Liu, Z.G. Annual Dynamics of the Wetland Plants Community in Poyang Lake in Response to Water-Level Variations. Res. J. Environ. Sci. 2013, 26, 1057–1063. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Dronova, I.; Gong, P.; Yang, W.B.; Li, Y.R.; Liu, Q. A new time series vegetation–water index of phenological–hydrological trait across species and functional types for Poyang Lake wetland ecosystem. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 125, 49–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ye, X.C.; Werner, A.D.; Li, Y.L.; Yao, J.; Li, X.H.; Xu, C.Y. An investigation of enhanced recessions in Poyang Lake: Comparison of Yangtze River and local catchment impacts. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.Q.; Zhang, Q.; Li, M.F.; Li, Y.L.; Xu, X.L.; Jiang, J.H. A study of the relationship between wetland vegetation communities and water regimes using a combined remote sensing and hydraulic modeling approach. Hydrol. Res. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.T.; Brock, M.A. How do depth, duration and frequency of flooding influence the establishment of wetland plant communities? Plant Ecol. 2000, 147, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zweig, C.L.; Kitchens, W.M. Effects of landscape gradients on wetland vegetation communities: Information for large-scale restoration. Wetlands 2008, 28, 1086–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.H.; Jia, J.; Kettner, A.J.; Xing, F.; Wang, Y.P.; Xu, X.N.; Yang, Y.; Zou, X.Q.; Gao, S.; Qi, S.; et al. Changes in water and sediment exchange between the Changjiang River and Poyang Lake under natural and anthropogenic conditions, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 481, 542–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B. Research of Poyang Lake; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1988. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sang, H.Y.; Zhang, J.X.; Lin, H.; Zhai, L. Multi-polarization ASAR backscattering from herbaceous wetlands in Poyang Lake region, China. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 4621–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessels, K.J.; De Fries, R.S.; Dempewolf, J.; Anderson, L.O.; Hansen, A.J.; Powell, S.L.; Moran, E.F. Mapping regional land cover with MODIS data for biological conservation: Examples from the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, USA and Para State, Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2004, 92, 67–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wardlow, B.D.; Egbert, S.L.; Kastens, J.H. Analysis of time-series MODIS 250 m vegetation index data for crop classification in the US Central Great Plains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 108, 290–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waring, R.; Coops, N.; Fan, W.; Nightingale, J. MODIS enhanced vegetation index predicts tree species richness across forested ecoregions in the contiguous USA. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huete, A.; Didan, K.; Miura, T.; Rodriguez, E.P.; Gao, X.; Ferreira, L.G. Overview of the radiometric and biophysical performance of the MODIS vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crist, E.P.; Cicone, R.C. A physically based transformation of Thematic Mapper data—The TM Tasseled Cap. IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 1984, 3, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.J.; Wiegand, C.L. Distinguishing vegetation from soil background information. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1977, 43, 1541–1552. [Google Scholar]
- Sen, P.K. Estimates of the regression coefficient based on Kendall’s tau. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 1968, 63, 1379–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, T.; Määttä, A.; Anttila, P.; Ruoho-Airola, T.; Amnell, T. Detecting Trends of Annual Values of Atmospheric Pollutants by the Mann-Kendall Test and Sen’s Slope Estimates—The Excel Template Application MAKESENS; Finnish Meteorological Institute: Helsinki, Finland, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Tabari, H.; Marofi, S.; Aeini, A.; Talaee, P.H.; Mohammadi, K. Trend analysis of reference evapotranspiration in the western half of Iran. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2011, 151, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Fraedrich, K.; Menz, C.; Zhai, J.Q. Trends in extreme temperature indices in the Poyang Lake Basin, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Wang, C.Y. Applicability of prewhitening to eliminate the influence of serial correlation on the Mann-Kendall test. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gause, G.F. The influence of ecological factors on the size of population. Am. Nat. 1931, 65, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.F.; Qi, S.H.; Liao, F.Q.; Zhang, Q.M. Analysis of distribution features of the emersed grassland in Poyang Lake based on remote sensing. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2011, 20, 1361–1367. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Fan, N.; Yu, X.B.; Xia, S.X.; Qi, S.H. Identification of wetland boundaries of Poyang Lake and analysis of seasonal change based on remote sensing and GIS technology. Resour. Sci. 2010, 32, 2239–2245. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.P.; Ge, G.; Liu, C.L.; Chen, F.S.; Li, S. Structure of Poyang Lake wetland plants ecosystem and influence of lake water level for the structure. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2010, 19, 597–605. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, G.P.; Liu, Y.B. Combining Multispectral Imagery with in situ Topographic Data Reveals Complex Water Level Variation in China’s Largest Freshwater Lake. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13466–13484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.L.; Tan, Y.J.; Lin, L.S.; Tao, H.; Tan, H. The wetland water level process and habitat of migratory birds in Lake Poyang. J. Lake Sci. 2011, 23, 129–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Barzen, J.; Engels, M.; Burnham, J.; Harris, J.; Wu, G. Potential Impacts of a Water Control Structure on the Abundance and Distribution of Wintering Waterbirds at Poyang Lake; International Crane Foundation: Baraboo, WI, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, S.H.; Liao, F.Q. A study on the scheme of water level regulation of the Poyang Lake hydraulic project. J. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2013, 68, 118–126. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, G.H.; Li, W.; Zhou, J.; Liu, W.Z.; Yang, D.; Davy, A.J. How does the propagule bank contribute to cyclic vegetation change in a lakeshore marsh with seasonal drawdown? Aquat. Bot. 2006, 84, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Statistical Index | Elevation (m) | |
|---|---|---|
| “Downward” Region | “Upward” Region | |
| Mean | 13.4 | 11.3 |
| Median | 13.6 | 11.3 |
| MIN | −6.0 | −9.8 |
| MAX | 20.2 | 20.2 |
| Var | 6.2 | 6.1 |
| Std | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Peak | 13.9 | 11.4 |
| FWHM | 2.8 | 3.0 |
| Range | 12.5–15.3 | 9.9–12.9 |
| Hydrological Period | Characteristics of Water Level | Month | Synchronous Data of EVI (DOY) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry | Maintain relatively stable low water level | Dec–Mar | 337, 353 and 1, 17, 33, 49, 65, 81 of the next year |
| Rising | Rapid rise of water level | Apr–May | 97, 113, 129 and 145 |
| Flood | Experience sustained high water level fluctuations | Jul–Sep | 161, 177, 193, 209, 225, 241 and 257 |
| Retreating | Steady decline of water level | Oct–Nov | 273, 289, 305 and 321 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, Z.; Jiang, J. Spatial–Temporal Dynamics of Wetland Vegetation Related to Water Level Fluctuations in Poyang Lake, China. Water 2016, 8, 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090397
Tan Z, Jiang J. Spatial–Temporal Dynamics of Wetland Vegetation Related to Water Level Fluctuations in Poyang Lake, China. Water. 2016; 8(9):397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090397
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Zhiqiang, and Jiahu Jiang. 2016. "Spatial–Temporal Dynamics of Wetland Vegetation Related to Water Level Fluctuations in Poyang Lake, China" Water 8, no. 9: 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090397
APA StyleTan, Z., & Jiang, J. (2016). Spatial–Temporal Dynamics of Wetland Vegetation Related to Water Level Fluctuations in Poyang Lake, China. Water, 8(9), 397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090397





