Degradation of Acetaminophen and Its Transformation Products in Aqueous Solutions by Using an Electrochemical Oxidation Cell with Stainless Steel Electrodes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
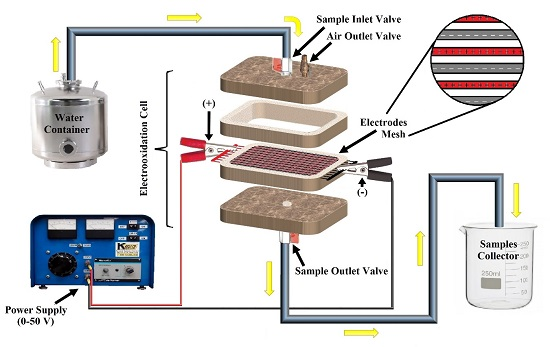
2.2. Experimental Device
2.3. Experimental Procedures
3. Results and Discussion
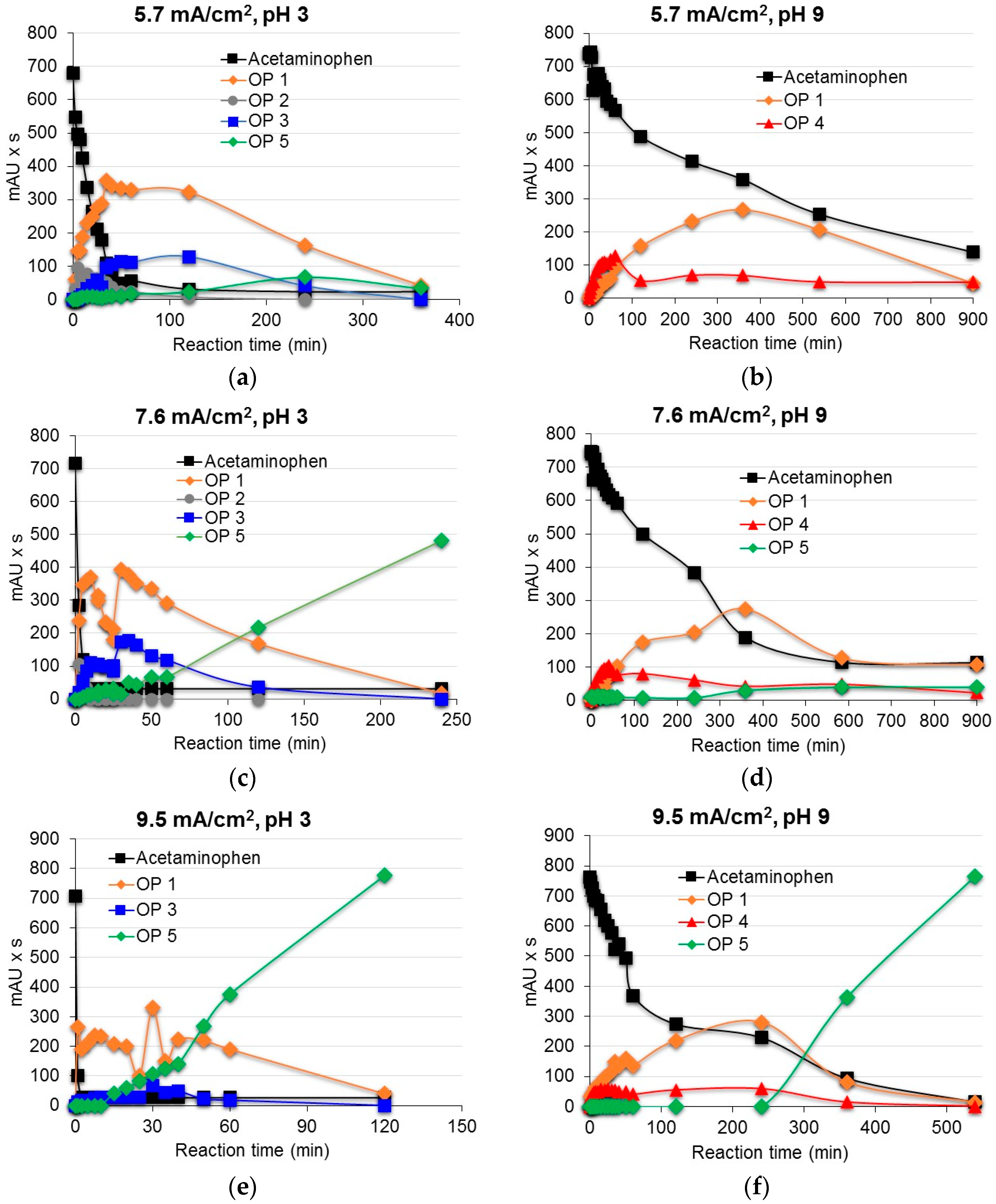
3.1. Degradation of Acetaminophen in the Innovative Electrochemical Oxidation Cell
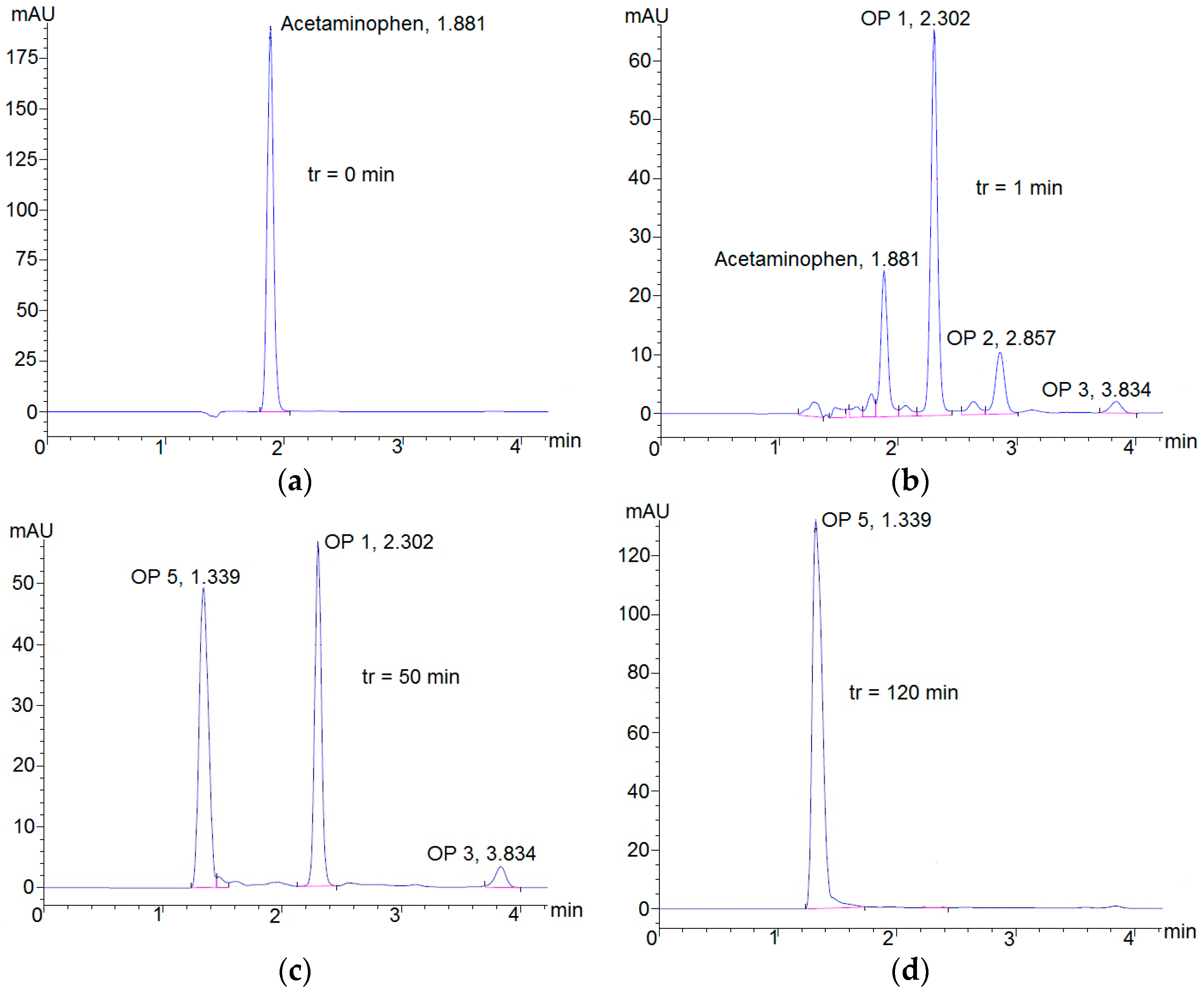
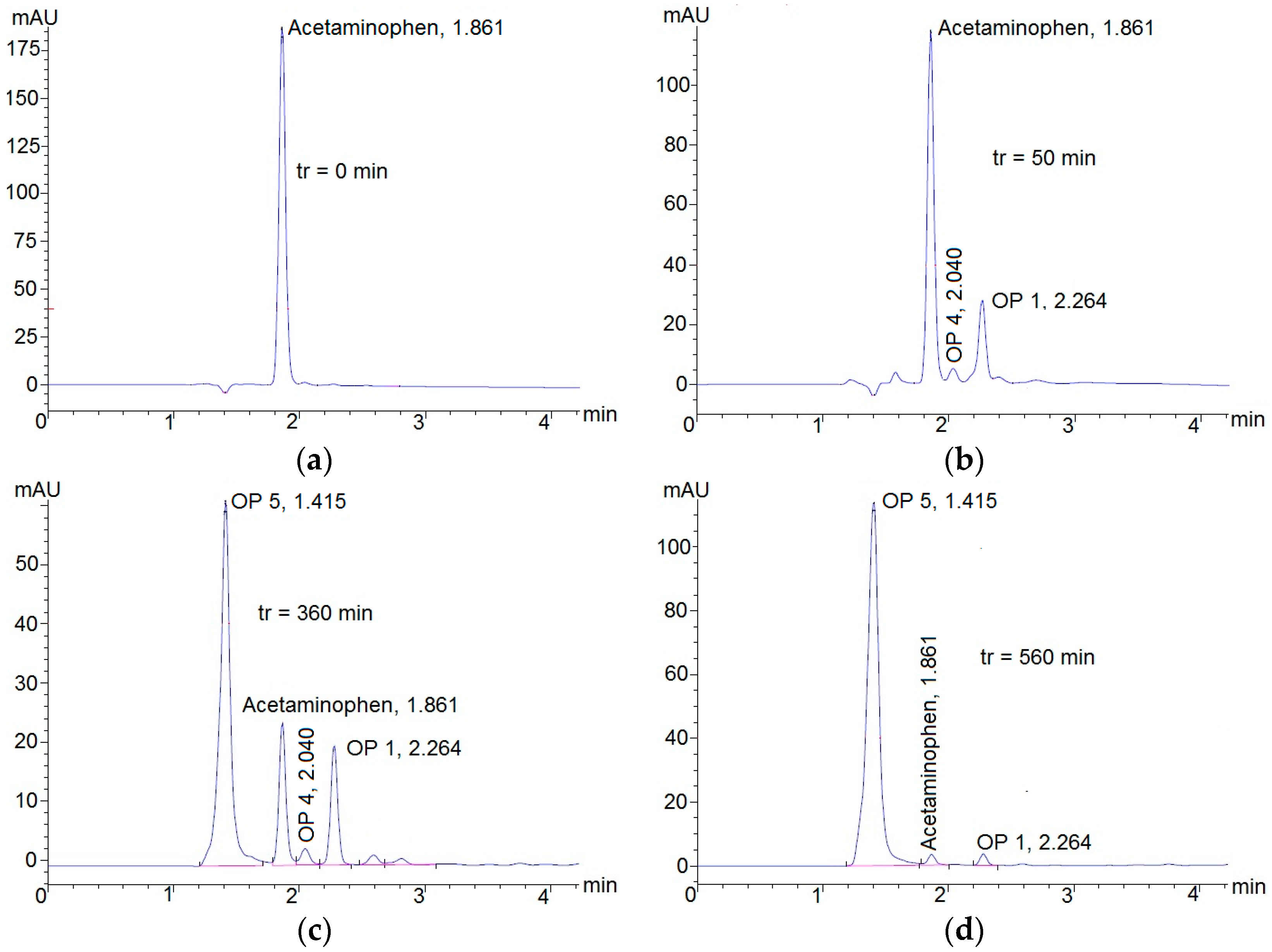
3.2. Degradation of Acetaminophen Intermediates/Oxidation Products in the Innovative Electrochemical Oxidation Cell
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Antunes, S.C.; Freitas, R.; Figueira, E.; Gonçalves, F.; Nunes, B. Biochemical effects of acetaminophen in aquatic species: Edible clams Venerupis decussata and Venerupis philippinarum. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2013, 20, 6658–6666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bedner, M.; MacCrehan, W.A. Transformation of acetaminophen by chlorination produces the toxicants 1,4-Benzoquinone and N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 516–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessems, J.G.; Vermeulen, N.P. Paracetamol (acetaminophen)-induced toxicity: Molecular and biochemical mechanisms, analogues and protective approaches. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2001, 31, 55–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, L.; Chen, J. Paracetamol in the environment and its degradation by microorganisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2012, 96, 875–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postigo, C.; Richardson, S.D. Transformation of pharmaceuticals during oxidation/disinfection processes in drinking water treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 279, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moctezuma, E.; Leyva, E.; Aguilar, C.A.; Luna, R.A.; Montalvo, C. Photocatalytic degradation of paracetamol: Intermediates and total reaction mechanism. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 243, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiremath, D.C.; Hiremath, C.V.; Nandibewoor, S.T. Oxidation of paracetamol drug by a new oxidant diperiodatoargentate (III) in aqueous alkaline medium. E-J. Chem. 2006, 3, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogna, D.; Marotta, R.; Napolitano, A.; d’Ischia, M. Advanced oxidation chemistry of paracetamol. UV/H2O2-induced hydroxylation/degradation pathways and n-aided inventory of nitrogenous breakdown products. J. Org. Chem. 2002, 67, 6143–6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nematollahi, D.; Shayani-Jam, H.; Alimoradi, M.; Niroomand, S. Electrochemical oxidation of acetaminophen in aqueous solutions: Kinetic evaluation of hydrolysis, hydroxylation and dimerization processes. Electrochim. Acta 2009, 54, 7407–7415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waterston, K.; Wang, J.W.; Bejan, D.; Bunce, N.J. Electrochemical waste water treatment: Electro-oxidation of acetaminophen. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2006, 36, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brillas, E.; Sirés, I.; Arias, C.; Cabot, P.L.; Centellas, F.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Garrido, J.A. Mineralization of paracetamol in aqueous medium by anodic oxidation with a boron-doped diamond electrode. Chemosphere 2005, 58, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quesada-Peñate, I.; Julcour Lebigue, C.; Jáuregui Haza, U.J.; Wilhelm, A.M.; Delmas, H. Sonolysis of levodopa and paracetamol in aqueous solutions. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2009, 16, 610–616. [Google Scholar]
- Basavaraju, M.; Mahamood, S.; Vittal, H.; Shrihari, S. A novel catalytic route to degrade paracetamol by Fenton process. Int. J. Res. Chem. Environ. 2011, 1, 157–164. [Google Scholar]
- Trovó, A.G.; Pupo Nogueira, R.F.; Agüera, A.; Fernandez-Alba, A.R.; Malato, S. Paracetamol degradation intermediates and toxicity during photo-Fenton treatment using different iron species. Water Res. 2012, 46, 5374–5380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, A.; Monteagudo, J.M.; Carnicer, A.; Ruiz-Murillo, M. Photo-Fenton mineralization of synthetic municipal wastewater effluent containing acetaminophen in a pilot plant. Desalination 2011, 270, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trovó, A.G.; Melo, S.A.S.; Nogueira, R.F.P. Photodegradation of the pharmaceuticals amoxicillin, bezafibrate and paracetamol by the photo-Fenton process-application to sewage treatment plant effluent. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2008, 198, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirés, I.; Garrido, J.A.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Cabot, P.L.; Centellas, F.; Arias, C.; Brillas, E. Electrochemical degradation of paracetamol from water by catalytic action of Fe2+, Cu2+, and UVA light on electrogenerated hydrogen peroxide. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2006, 153, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skoumal, M.; Cabot, P.L.; Centellas, F.; Arias, C.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Garrido, J.A.; Brillas, E. Mineralization of paracetamol by ozonation catalyzed with Fe2+, Cu2+ and UVA light. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2006, 66, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radjenović, J.; Sirtori, C.; Petrović, M.; Barceló, D.; Malato, S. Solar photocatalytic degradation of persistent pharmaceuticals at pilot-scale: Kinetics and characterization of major intermediate products. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2009, 89, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, L.C.; Garcia-Segura, S.; Bocchi, N.; Brillas, E. Solar photoelectro-Fenton degradation of paracetamol using a flow plant with a Pt/air-diffusion cell coupled with a compound parabolic collector: Process optimization by response surface methodology. Appl. Catal. B-Environ. 2011, 103, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, R.; Caprio, V.; Marotta, R.; Vogna, D. Paracetamol oxidation from aqueous solutions by means of ozonation and H2O2/UV system. Water Res. 2003, 37, 993–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, L.E.; Ray, M.B. Photocatalytic oxidation of paracetamol: Dominant reactants, intermediates, and reaction mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalmázio, I.; Alves, T.M.A.; Augusti, R. An appraisal on the degradation of paracetamol by TiO2/UV system in aqueous medium. Product identification by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS). J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2008, 19, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, L.E.; Ray, M.B. Degradation of paracetamol in aqueous solutions by TiO2 photocatalysis. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Wu, F.; Wu, X.; Chen, P.; Deng, N. Photodegradation of acetaminophen in TiO2 suspended solution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 157, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Obrero, M.; Mayén, G.; Mellado, J.M.R.; Rodríguez-Amaro, R. Electrocatalytic oxidation of acetaminophen on a PVC/TTF-TCNQ composite electrode modified by gold nanoparticles: Application as an amperometric sensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 2001–2011. [Google Scholar]
- He, F.Y.; Liu, A.L.; Xia, X.H. Poly(dimethylsiloxane) microchip capillary electrophoresis with electrochemical detection for rapid measurement of acetaminophen and its hydrolysate. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 379, 1062–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, P.; Hu, J. Degradation of acetaminophen by UVA/LED/TiO2 process. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 91, 89–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, P.; Hu, J. Decomposition of acetaminophen (Ace) using TiO2/UVA/LED system. Catal. Today 2016, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirés, I.; Brillas, E. Remediation of water pollution caused by pharmaceutical residues based on electrochemical separation and degradation technologies: A review. Environ. Int. 2012, 40, 212–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abidin, Z.Z.; Downes, L.; Markx, G.H. Novel electrode structures for large scale dielectrophoretic separations based on textile technology. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 130, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkharfy, K.M.; Frye, R.F. High-performance liquid chromatographic assay for acetaminophen glucuronide in human liver microsomes. J. Chromatogr. B. 2001, 753, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panizza, M.; Cerisola, G. Direct and mediated anodic oxidation of organic pollutants. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 6541–6569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marselli, B.; Garcia-Gomez, J.; Michaud, P.A.; Rodrigo, M.A.; Comninellis, C. Electrogeneration of hydroxyl radicals on boron-doped diamond electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2003, 150, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comninellis, C. Electrocatalysis in the electrochemical conversion/combustion of organic pollutants for waste water treatment. Electrochim. Acta 1994, 39, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxall, C.; Kelsall, G.H. Hypochlorite electrogeneration. II. Thermodynamics and kinetic model of the anode reaction layer. Inst. Chem. Eng. Symp. Ser. 1992, 127, 59–70. [Google Scholar]
- Boudreau, J.; Bejan, D.; Bunce, N.J. Competition between electrochemical advanced oxidation and electrochemical hypochlorination of acetaminophen at boron-doped diamond and ruthenium dioxide based anodes. Can. J. Chem. 2010, 88, 418–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

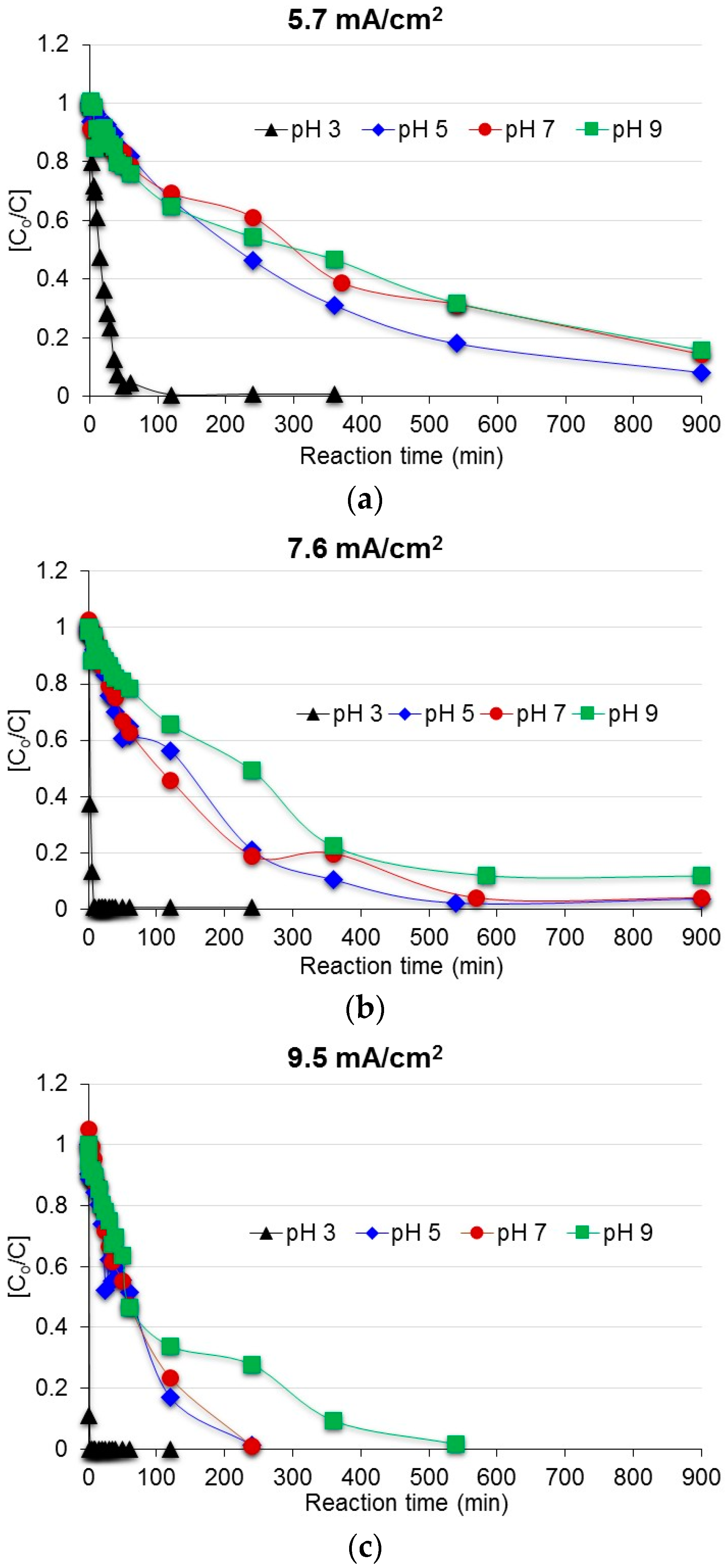
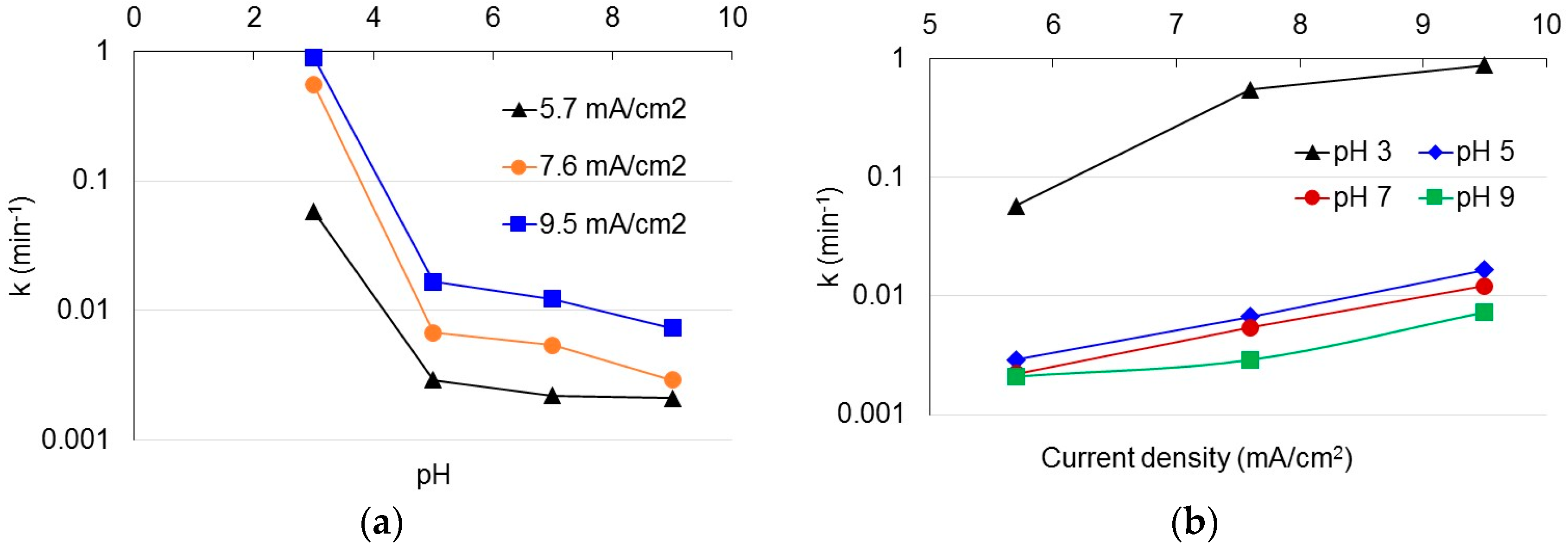
| Scenario | pH | Current Density (mA/cm2) | Scenario | pH | Current Density (mA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 3 | 5.7 | 7 | 7 | 5.7 |
| 2 | 7.6 | 8 | 7.6 | ||
| 3 | 9.5 | 9 | 9.5 | ||
| 4 | 5 | 5.7 | 10 | 9 | 5.7 |
| 5 | 7.6 | 11 | 7.6 | ||
| 6 | 9.5 | 12 | 9.5 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
López Zavala, M.Á.; Espinoza Estrada, E. Degradation of Acetaminophen and Its Transformation Products in Aqueous Solutions by Using an Electrochemical Oxidation Cell with Stainless Steel Electrodes. Water 2016, 8, 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090383
López Zavala MÁ, Espinoza Estrada E. Degradation of Acetaminophen and Its Transformation Products in Aqueous Solutions by Using an Electrochemical Oxidation Cell with Stainless Steel Electrodes. Water. 2016; 8(9):383. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090383
Chicago/Turabian StyleLópez Zavala, Miguel Ángel, and Eunice Espinoza Estrada. 2016. "Degradation of Acetaminophen and Its Transformation Products in Aqueous Solutions by Using an Electrochemical Oxidation Cell with Stainless Steel Electrodes" Water 8, no. 9: 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090383
APA StyleLópez Zavala, M. Á., & Espinoza Estrada, E. (2016). Degradation of Acetaminophen and Its Transformation Products in Aqueous Solutions by Using an Electrochemical Oxidation Cell with Stainless Steel Electrodes. Water, 8(9), 383. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8090383