Assessment of the Impact of Subsurface Agricultural Drainage on Soil Water Storage and Flows of a Small Watershed
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
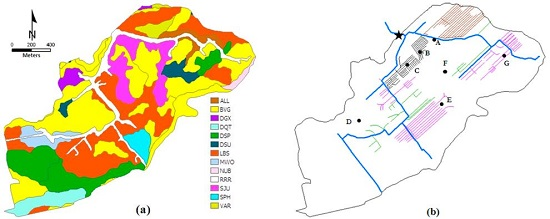
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data Source
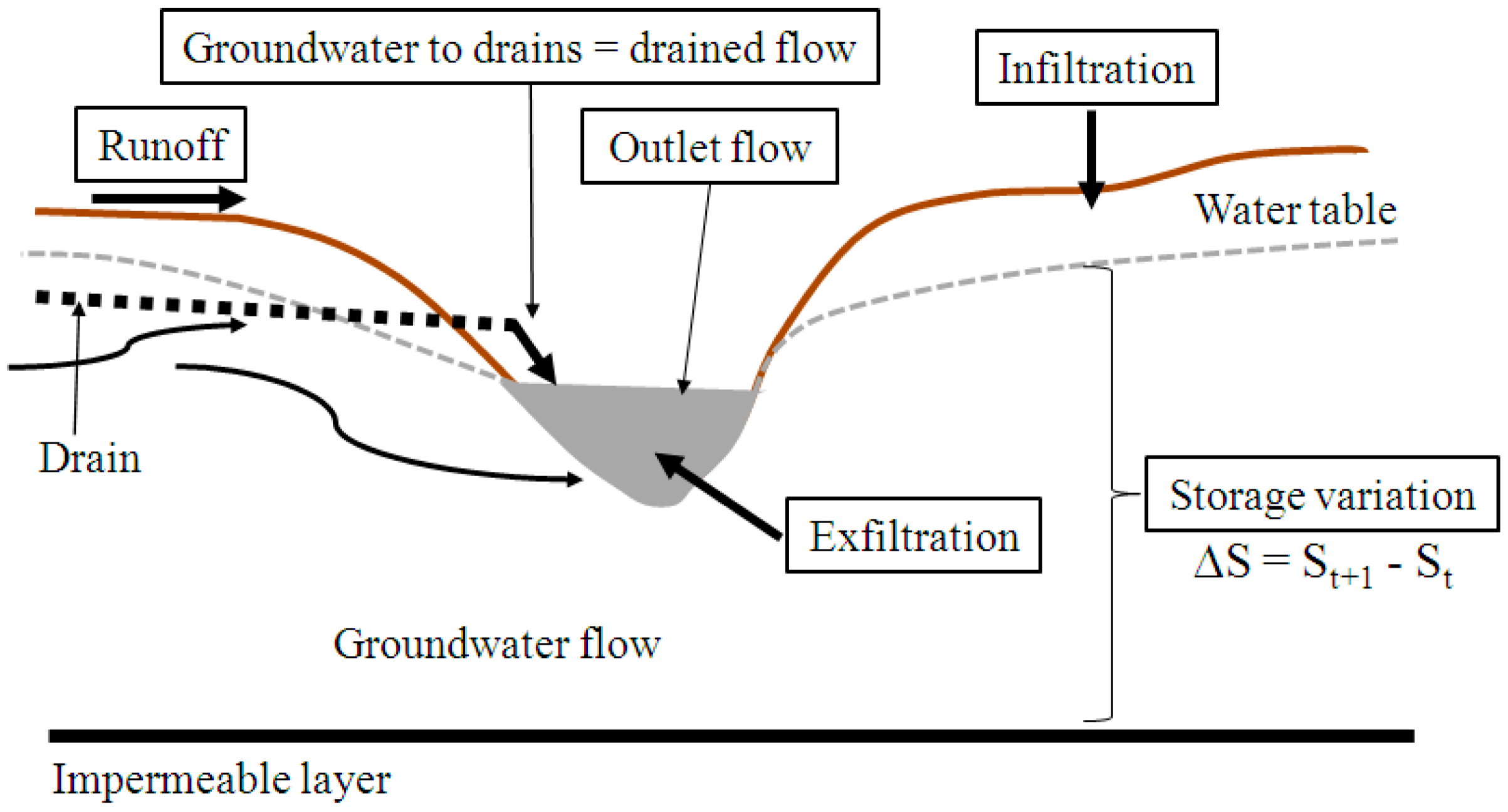
2.3. The CATHY Model
2.4. Setting up CATHY at the Watershed Scale
2.4.1. Discretization of the Porous Medium
2.4.2. Boundary Conditions and Initial Humidity Conditions in the Soil
2.4.3. Variables Analyzed
2.4.4. Evaluation of Model Performance
3. Results
3.1. Simulation of the Flow at the Micro-Watershed Outlet and Analysis of the Effect of Subsurface Drainage on the Storage Variation
3.1.1. Calibration and Validation of the Model: Micro-Watershed Outlet Flow
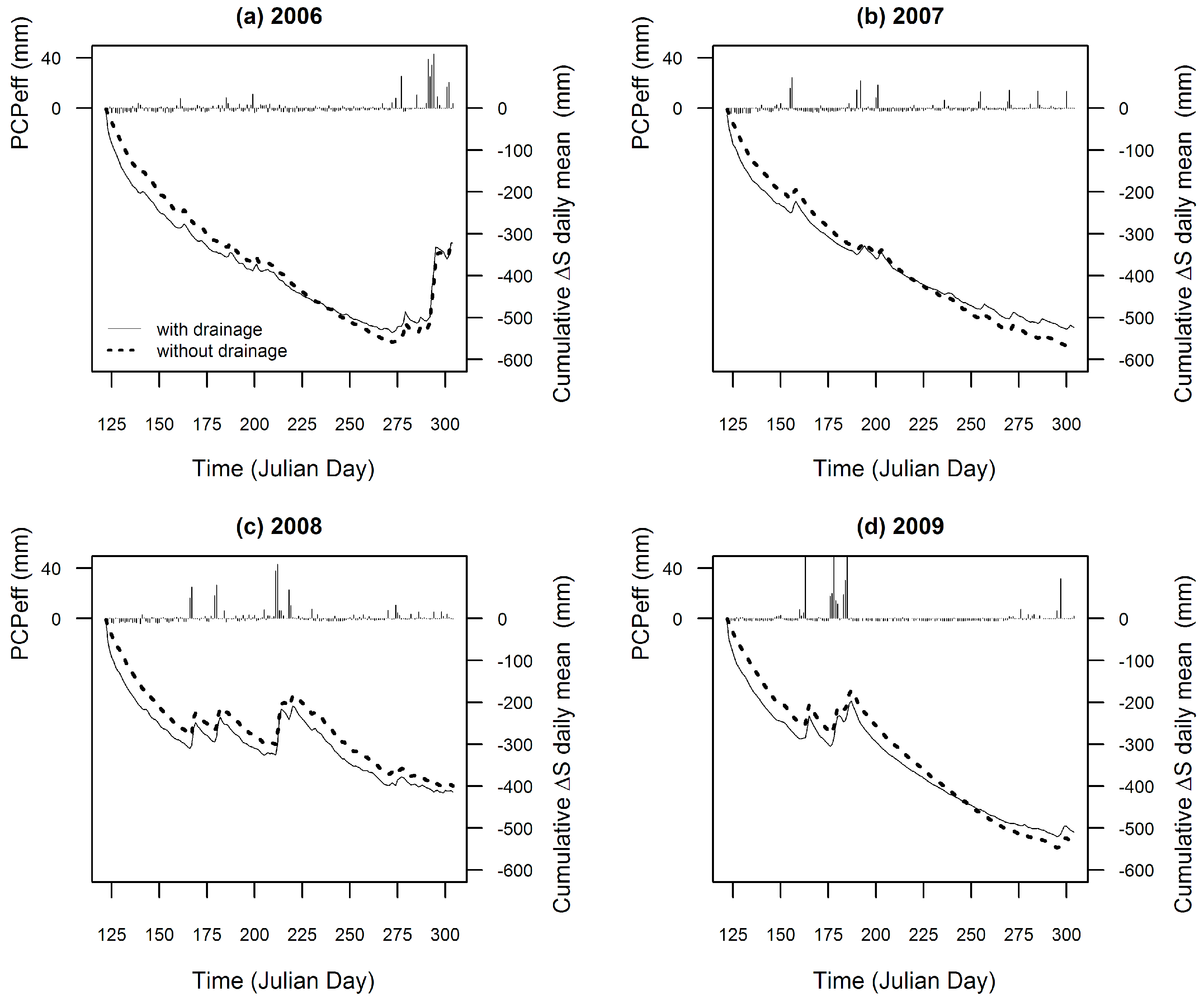
3.1.2. Effect of Subsurface Drainage on Storage Variation
3.2. Impact of Subsurface Drainage and Soil Hydraulic Conductivity on Micro-Watershed Outlet Flow
3.3. Impact of Subsurface Drainage and Soil Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity on Surface Runoff, Surface Water and Groundwater Coupling
3.4. Impact of Subsurface Drainage and Soil Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity on the Outlet Flow Hydrograph
4. Discussion
4.1. Simulation of the Flow at the Micro-Watershed Outlet and Analysis of the Effect of Subsurface Drainage on the Storage Variation
4.2. Impact of Subsurface Drainage and Soil Hydraulic Conductivity on the Micro-Watershed Outlet Flow
4.3. Impact of Subsurface Drainage and Soil Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity on Surface Runoff, Surface Water and Groundwater Coupling
4.4. Behavior of the Outlet Hydrograph Components
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Eggelsmann, R. Dränanleitung für den Landbau, Ingenieurbau und Landschaftsbau, 2nd ed.; Verlag Paul Parey: Hamburg, Germany, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Skaggs, R.W.; Brevé, M.A.; Gilliam, J.W. Hydrologic and water quality impacts of agricultural drainage. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1994, 24, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eidman, V. Minnesota farmland drainage: Profitability and concerns. Minn. Agric. Econ. 1997. No 688. Department of Applied Economics, University of Minnesota, St. Paul, MN, USA, 1997. Available online: http://ageconsearch.umn.edu/bitstream/13165/1/mae688a.pdf (accessed on 2 June 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Fausey, N.R. Drainage: Inadequacy and crop response. In Encyclopedia of Water Science; Stewart, B.A., Howell, T., Eds.; Taylor and Francis: Oxford, UK, 2003; pp. 132–134. [Google Scholar]
- Fausey, N.R. Drainage management for humid regions. Int. Agric. Eng. J. 2005, 14, 209–214. [Google Scholar]
- Basin Technical and Scientific Advisory Committee (BTSAC). Water Management Options for Subsurface Drainage: Briefing Paper 2. 2012. Available online: http://www.rrbdin.org/archives/4520 (accessed on 28 June 2014).
- St-Hilaire, A.; Duchesne, A.S.; Rousseau, A.N. Floods and water quality in Canada—A review of the interactions with urbanization, agriculture and forestry. Can. Water Resour. J. 2015, 41, 273–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, K.E.; Helmers, M. Effects of subsurface drainage tiles on streamflow in Iowa agricultural watersheds: Exploratory hydrograph analysis. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 4497–4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano, S.E.; Whiteley, H.R.; Irwin, R.W. Effects of agricultural drainage on streamflow in the Middle Thames River, Ontario, 1949–1980. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1985, 12, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magner, J.A.; Payne, G.A.; Steffen, L.J. Drainage effects on stream nitrate-n and hydrology in south-central Minnesota (USA). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2004, 91, 183–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomer, M.D.; Meek, D.W.; Kramer, L.A. Agricultural practices influence flow regimes of headwater streams in Western Iowa. J. Environ. Qual. 2005, 34, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, K.W.; Fausey, N.R.; Williams, M.R. Effect of subsurface drainage on streamflow in an agricultural headwater watershed. J. Hydrol. 2014, 519, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macrae, M.L.; English, M.C.; Schiff, S.L.; Stone, M. Intra-annual variability in the contribution of tile drains to basin discharge and phosphorus export in a first-order agricultural catchment. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 92, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culley, J.L.B.; Bolton, E.F. Suspended solids and phosphorus loads from a clay soil: II. Watershed study. J. Environ. Qual. 1983, 12, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; David, M.B.; Gentry, L.E.; Kovacic, D.A. Kinetics and modeling of dissolved phosphorus export from a tile-drained agricultural watershed. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 917–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.; Rycroft, D.W. The impact of drainage on stream flows. Agron. Monogr. 1999, 38, 767–800. [Google Scholar]
- Dolezal, F.; Kulhavy, Z.; Soukup, M.; Kodesova, R. Hydrology of tile drainage runoff. Phys. Chem. Earth B Hydrol. Ocean Atmos. 2001, 26, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M. Impact of Improved Land Drainage on River Flows; Institute of Hydrology Center for Ecology and Hydrology: Edinburgh, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Bengtson, R.L.; Carter, C.E.; Fouss, J.L.; Southwick, L.M.; Willis, G.H. Agricutural drainage and water quality in the Mississippi delta. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1995, 121, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucker, L.A.; Brown, L.C.E. (Eds.) Agricultural Drainage: Water Quality Impacts and Subsurface Drainage Studies in the Midwest; The Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 1998.
- Kleinman, P.J.A.; Smith, D.R.; Bolster, C.H.; Easton, Z.M. Phosphorus Fate, Management, and Modeling in Artificially Drained Systems. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 460–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiskow, E.; van der Ploeg, R.R. Calculation of drain spacings for optimal rainstorm flood control. J. Hydrol. 2003, 272, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, K.W.; Williams, M.R.; Faussey, N.R. Contributions of systematic tile drainage to watershed-scale phosphorus transport. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.R.; King, K.W.; Johnson, L.; Francesconi, W.; Richards, P.; Baker, D.; Sharpley, A.N. Surface runoff and tile drainage transport of phosphorus in the midwestern United States. J. Environ. Qual. 2015, 44, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schottler, S.P.; Ulrich, J.; Belmont, P.; Moore, R.; Lauer, W.J.; Engstrom, D.R.; Almendinger, J.E. Twentieth century agricultural drainage creates more erosive rivers. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1951–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, S.M.; Mackay, R. Modelling the hydrological impact of open ditch drainage. J. Hydrol. 1996, 179, 37–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; Chapman, P.J.; Labadz, J.C. Artificial drainage of peatlands: Hydrological andhydrochemical process and wetland restoration. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2004, 28, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidon, P.; Cuadra, P.E. Phosphorus dynamics in tile-drain flow during storms in the US Midwest. Agric. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, K.J.S.; Kladivko, E.J.; Gish, T.J.; Steenhuis, T.S.; Bubenzer, G.; Helling, C.S. Quantifying preferential flow by breakthrough of sequentially applied tracers: Silt loam soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1296–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bixio, A.C.; Orlandini, S.; Paniconi, C.; Putti, M. Modeling groundwater-surface water interactions including effects of morphogenetic depressions in the Chernobyl exclusion zone. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 162–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orlandini, S. On the spatial variation of resistance to flow in upland channel networks. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniconi, C.; Troch, P.A.; van Loon, E.E.; Hilberts, A.G.J. Hillslope-storage Boussinesq model for subsurface flow and variable source areas along complex hillslopes: 2. Intercomparison with a three-dimensional Richards equation model. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Haese, C.M.F.; Putti, M.; Paniconi, C.; Verhoest, N.E.C. Assessment of adaptive and heuristic time stepping for variably saturated flow. Int. J. Numer. Methods Fluids 2007, 53, 1173–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, M.J.; Camporese, M.; Rivard, C.; Paniconi, C.; Larocque, M. A modeling study of heterogeneity and surface water-groundwater interactions in the Thomas Brook catchment, Annapolis Valley (Nova Scotia, Canada). Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 1583–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, M.; Meyerhoff, S.B.; Paniconi, C.; Maxwell, R.M.; Putti, M.; Kollet, S.J. A comparison of two physics-based numerical models for simulating surface water-groundwater interactions. Adv. Water Resour. 2010, 33, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, M.; Paniconi, C.; Camporese, M. Impact of grid resolution on the integrated and distributed response of a coupled surface–subsurface hydrological model for the des Anglais catchment, Quebec. Hydrol. Process. 2011, 25, 1853–1865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, M.; Paniconi, C.; Rivard, C.; Harvey, R.; Chaumont, D. Assessment of climate change impacts at the catchment scale with a detailed hydrological model of surface-subsurface interactions and comparison with a land surface model. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W01513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broda, S.; Paniconi, C.; Larocque, M. Numerical investigation of leakage in sloping aquifers. J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanello, F.; Teatini, P.; Putti, M.; Gambolati, G. Long term peatland subsidence: Experimental study and modeling scenarios in the Venice coastland. J. Geophys. Res. Earth Surf. 2011, 116, F04002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagès, C.; Paniconi, C.; Sulis, M. Analysis of coupling errors in a physically-based integrated surface water-groundwater model. Adv. Water Resour. 2012, 49, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, C.; Nastev, M.; Paniconi, C.; Sulis, M. Comparison of two modeling approaches for groundwater–surface water interactions. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 2258–2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passadore, G.; Monego, M.; Altissimo, L.; Sottani, A.; Putti, M.; Rinaldo, A. Alternative conceptual models and the robustness of groundwater management scenarios in the multi-aquifer system of the Central Veneto Basin, Italy. Hydrogeol. J. 2012, 20, 419–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, G.-Y.; Paniconi, C.; Troch, P.A.; Scott, R.L.; Durcik, M.; Zeng, X.; Huxman, T.; Goodrich, D.C. An integrated modelling framework of catchment-scale ecohydrological processes: 1. Model description and tests over an energy-limited watershed. Ecohydrology 2013, 7, 427–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamontagne, L.; Martin, A.; Nolin, M.C. Étude Pédologique du Bassin Versant du Bras d'Henri (Québec); Laboratoires de Pédologie et D’agriculture de Précision, Centre de Recherche et de Développement sur les sols et les Grandes Cultures, Service National D’information sur les Terres et les eaux, Direction Générale de la Recherche, Agriculture et Agroalimentaire Canada: Sainte-Foy, QC, Canada, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Agriculture & Agri-Food Canada. Greencover Canada. Government of Canada. 2004a. Available online: http://www.agr.gc.ca/env/greencover-verdir/index_e.phtml (accessed on 20 May 2015).
- Agriculture & Agri-Food Canada. Watershed Evaluation of BMPs (WEBs). Government of Canada. 2004b. Available online: http://www.agr.gc.ca/env/greencover-verdir/webs_abstract_e.phtml (accessed on 20 May 2015).
- Agriculture & Agri-Food Canada. Watershed Evaluation of BMPs (WEBs). Government of Canada. 2004c. Available online: http://www.agr.gc.ca/AAFC-AAC/displa-afficher.do?id=1228497657135&lang=eng (accessed on 20 May 2015).
- Muma, M.; Gumiere, S.J.; Rousseau, A.N. Analyses de sensibilité globales du modèle CATHY aux propriétés hydrodynamiques du sol d’un micro-bassin agricole drainé. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2014, 59, 1606–1623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratte-Fortin, C. Développement d’une Méthode D’évaluation de L’impact de Pratiques de Gestion Bénéfiques sur les Flux de Contaminants Agricoles: Cas du Micro-Bassin Versant D’intervention du Bras d’Henri, Québec, Canada; Mémoire de Maîtrise, Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique—Centre Eau Terre Environnement (INRS-ETE): Ville de Québec, QC, Canada, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer, H.; Rice, R.C. A slug test for determining hydraulic conductivity of unconfined aquifers with completely or partially penetrating wells. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandit, N.S.; Miner, R.F. Interpretation of slug test data. Ground Water 1986, 24, 743–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camporese, M.; Paniconi, C.; Putti, M.; Orlandini, S. Surface-subsurface flow modeling with path-based runoff routing, boundary condition-based coupling, and assimilation of multisource observation data. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W02512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniconi, C.; Putti, M. A comparison of Picard and Newton iteration in the numerical solution of multidimensional variably saturated flow problems. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 3357–3374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministère de l’Agriculture, des Pêcheries et de l’Alimentation du Québec (MAPAQ). Profil de la région Chaudière-Appalaches (région 12)-Climat [en ligne]. Ministère de l’Agriculture, Pêcheries et Alimentation du Québec: Canada, 2007. Available online: http://www.mapaq.gouv.qc.ca/Fr/Regions/chaudiereappalache/vraiprofil/ (accessed on 26 June 2015). [Google Scholar]
- Allen, R.G.; Pereira, L.S.; Raes, D.; Smith, M. Crop Evapotranspiration: Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; Irrigation and Drainage, FAO: Roma, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Fortin, J.P.; Turcotte, R.; Massicotte, S.; Moussa, R.; Fitzback, J.; Villeneuve, J.P. A distributed watershed model compatible with remote sensing and GIS data. Part 1: Description of the model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2001, 6, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.P.; Turcotte, R.; Massicotte, S.; Moussa, R.; Fitzback, J.; Villeneuve, J.P. A distributed watershed model compatible with remote sensing and GIS data. Part 2: Application to the Chaudière Watershed. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2001, 6, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fortin, J.P.; Moussa, R.; Bocquillon, C.; Villeneuve, J.P. Hydrotel, un model hydrologique distribué pouvant bénéficier des données fournies par la télédétection et les systèmes d'information géographique. Rev. Sci. de l'Eau 1995, 8, 97–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, A.N.; Savary, S.; Hallema, D.W.; Gumiere, S.J.; Foulon, E. Modeling the effects of agricultural BMPs on sediments, nutrients and water quality of the Beaurivage River watershed (Quebec, Canada). Can. Water Resour. J. 2013, 38, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagacé, R. Infiltration et Drainage, Notes de Cours: Bilan Hydrique au Québec. Département des Sols et de Génie Agroalimentaire, Université Laval: Québec City, QC, Canada, 2012. Available online: http://www.grr.ulaval.ca/gaa_7003/Documents/Notes_cours_2012/CH_10_Bilan_QC.pdf (accessed on 12 January 2015).
- Savoie, V. Le Drainage de Surface; Formation OAQ, MAPAQ: Centre du Québec, QC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Bessière, H. Assimilation de Données Variationnelles Pour la Modélisation Hydrologique Distribuée des Crues à Cinétique Rapide. Thèse de Doctorat, Université de Toulouse, Institut National Polytechnique de Toulouse, Toulouse, France, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Larson, C.L.; Moore, I.D. Hydrologic impact of draining small depressional watersheds. J. Irrig. Drain. Div. 1980, 104, 345–363. [Google Scholar]
- Konyha, K.D.; Skaggs, R.W.; Gilliam, J.W. Effects of drainage and water management practices on hydrology. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1992, 118, 807–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.D.; Bree, T. Effect of improved land drainage on river flood flows. In Flood Studies Report-Five Years on; Thomas Talford: London, UK, 1981; pp. 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Rycrott, D.W.; Massey, W. The Effect of Field Drainage on the River Flood Flows; Field Drainage Experimental Unit, MAFF: London, UK, 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, A.R. The environmental impacts of agricultural land drainage. J. Environ. Manag. 1976, 4, 251–274. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, R.W.; Whitely, H.R. Effects of land drainage on stream flow. Can. Water Resour. J. 1983, 8, 88–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, D.L.; Perry, C.D.; Evans, R.O.; Izuno, F.T.; Stone, K.C.; Gilliam, J.W. Agricultural drainage effects on water quality in Southeastern U.S. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1995, 121, 277–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watelet, A.; Johnson, P.G. Hydrology and water quality of the Raisin River: Overview of impacts of recent land and channel changes in Eastern Ontario. Can. J. Water Qual. Res. 1999, 34, 361–390. [Google Scholar]
- Kasenow, M. Determination of Hydraulic Conductivity from Grain Size Analysis; Water Resources Publications, L.L.C.: Highlands, CO, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Winkler, R.D.; Moore, R.D.; Redding, T.E.; Spittlehouse, D.L.; Carlyle-Moses, D.E.; Smerdon, B.D. Hydrologic Processes and Watershed Response. In Compendium of Forest Hydrology and Geomorphology in British Columbia; Pike, R.G., Redding, T.E., Moore, R.D., Winkler, R.D., Bladon, K.D., Eds.; B.C. Min. For. Range, For. Sci. Prog., Victoria, B.C. and FORREX Forum for Research and Extension in Natural Resources, Kamloops, B.C. Land Manag. Handb; Government Publications Services: Victoria, BC, Canada, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Bennis, S. Hydraulique et Hydrologie, 2e Édition Revue et Augmentée; Presses de l’Université du Québec: Ville de Québec, QC, Canada, 2009. [Google Scholar]









| Soil Code | Soil Family | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BVG | Sandy | 67–97 | 2–28 | 1–13 |
| SJU | Fine sandy loam | 68–94 | 4–31 | 1–4 |
| VAR | Fine sandy loam | 73–97 | 2–21 | 1–6 |
| SPH | Silt loam | 55–76 | 22–41 | 2–5 |
| DGX | Coarse loamy | 29–59 | 34–60 | 5–13 |
| DSU | Coarse loamy | 45–62 | 33–43 | 5–12 |
| NUB | Loamy | 8–60 | 33–64 | 7–32 |
| LBS | Loamy | 9–30 | 58–73 | 12–23 |
| DQT | Coarse loamy | 64–84 | 7–19 | 9–20 |
| DSP | Coarse loamy | 52–58 | 33–42 | 6–10 |
| MWO | Coarse loamy | 57–84 | 10–27 | 6–17 |
| ALL | Loamy | 45–62 | 33–43 | 5–12 |
| RRR | Not classified | 7–30 | 58–73 | 12–23 |
| Soil Code | Soil Profile (cm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0–25 | 25–50 | 50–75 | 75–100 | 100–125 | |
| BVG00 | 5.44 × 10−5 | 1.91 × 10−5 | 2.94 × 10−4 | 1.78 × 10−4 | 1.78 × 10−4 |
| BVG49 | 2.78 × 10−5 | 9.03 × 10−5 | 1.39 × 10−4 | 1.39 × 10−4 | 1.39 × 10−4 |
| SJU | 9.03 × 10−6 | 9.03 × 10−5 | 9.03 × 10−5 | 9.03 × 10−6 | 9.03 × 10−6 |
| VAR | 8.42 × 10−6 | 8.11 × 10−5 | 9.75 × 10−5 | 8.11 × 10−5 | 8.11 × 10−5 |
| SPH | 5.44 × 10−5 | 1.91 × 10−5 | 2.94 × 10−4 | 1.78 × 10−4 | 1.78 × 10−4 |
| DGX | 2.43 × 10−5 | 1.70 × 10−5 | 1.39 × 10−7 | 1.39 × 10−7 | 1.39 × 10−7 |
| DSU | 1.39 × 10−7 | 2.22 × 10−7 | 1.39 × 10−7 | 2.78 × 10−8 | 2.78 × 10−8 |
| NUB | 5.56 × 10−6 | 1.42 × 10−6 | 1.39 × 10−7 | 1.39 × 10−7 | 1.39 × 10−7 |
| LBS | 8.06 × 10−7 | 1.04 × 10−5 | 8.33 × 10−8 | 1.39 × 10−7 | 1.39 × 10−7 |
| DQT | 1.31 × 10−4 | 1.25 × 10−4 | 2.73 × 10−4 | 2.66 × 10−4 | 2.66 × 10−4 |
| DSP | 3.06 × 10−7 | 1.21 × 10−5 | 2.31 × 10−6 | 4.44 × 10−7 | 4.44 × 10−7 |
| MWO | 5.86 × 10−5 | 6.00 × 10−5 | 1.36 × 10−4 | 1.95 × 10−5 | 1.95 × 10−5 |
| ALL | 1.39 × 10−7 | 2.22 × 10−7 | 1.39 × 10−7 | 2.78 × 10−8 | 2.78 × 10−8 |
| RRR | 2.78 × 10−6 | 2.78 × 10−6 | 2.78 × 10−6 | 2.78 × 10−6 | 2.78 × 10−6 |
| Geometric mean of Ks | 6.04 × 10−6 | 1.16 × 10−5 | 7.07 × 10−6 | 3.51 × 10−6 | 3.51 × 10−6 |
| Layer Number | ΔZ (m) | Z (m) | KsXY (m/s) | KsZ (m/s) | Ss (m−1) | φ (-) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 6.06 × 10−5 | 6.06 × 10−6 | 3.75 × 10−3 | 0.52 |
| 02 | 0.15 | 0.25 | ||||
| 03 | 0.25 | 0.50 | 3.80 × 10−4 | 3.80 × 10−5 | 1.15 × 10−3 | 0.48 |
| 04 | 0.25 | 0.75 | 4.04 × 10−5 | 4.04 × 10−6 | 3.75 × 10−3 | 0.37 |
| 05 | 0.25 | 1.00 | 6.06 × 10−5 | 6.06 × 10−6 | 3.75 × 10−3 | 0.48 |
| 06 | 0.10 | 1.10 | ||||
| 07 | 0.10 | 1.20 | ||||
| 08 | 0.10 | 1.30 | ||||
| 09 | 0.30 | 1.60 | 4.20 × 10−4 | 4.20 × 10−5 | 1.15 × 10−3 | 0.50 |
| 10 | 0.45 | 2.05 | ||||
| 11 | 0.50 | 2.65 | ||||
| 12 | 0.60 | 3.26 | ||||
| 13 | 0.64 | 3.90 | ||||
| 14 | 0.70 | 4.60 | ||||
| 15 | 0.85 | 5.45 |
| Layers | Scenarios | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N° | ΔZ (m) | Z (m) | 1 (Reference) | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| 01 | 0.10 | 0.25 | ||||
| 02 | 0.15 | |||||
| 03 | 0.25 | 0.50 | ||||
| 04 | 0.25 | 0.75 | ||||
| 05 | 0.25 | 1.30 | ||||
| 06 | 0.10 | |||||
| 07 | 0.10 | |||||
| 08 | 0.10 | |||||
| 09 | 0.30 | 5.45 | ||||
| 10 | 0.45 | |||||
| 11 | 0.50 | |||||
| 12 | 0.60 | |||||
| 13 | 0.64 | |||||
| 14 | 0.70 | |||||
| 15 | 0.85 | |||||
| Criteria | Statistical Approach | Best Value | Goal and Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Error in peak flow rate | 0 |
| |
| Error in flow volume | |||
| Nash coefficient | 1 |
|
| Process | Year | EP | EV | NSE | NSEm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Calibration | 2006 | 0.16 | −0.04 | 0.71 | 0.89 |
| Validation | 2007 | 0.26 | −0.33 | 0.17 | 0.69 |
| 2008 | 0.36 | −0.05 | 0.72 | 0.91 | |
| 2009 | 0.42 | −0.74 | 0.67 | 0.81 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Muma, M.; Rousseau, A.N.; Gumiere, S.J. Assessment of the Impact of Subsurface Agricultural Drainage on Soil Water Storage and Flows of a Small Watershed. Water 2016, 8, 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080326
Muma M, Rousseau AN, Gumiere SJ. Assessment of the Impact of Subsurface Agricultural Drainage on Soil Water Storage and Flows of a Small Watershed. Water. 2016; 8(8):326. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080326
Chicago/Turabian StyleMuma, Mushombe, Alain N. Rousseau, and Silvio J. Gumiere. 2016. "Assessment of the Impact of Subsurface Agricultural Drainage on Soil Water Storage and Flows of a Small Watershed" Water 8, no. 8: 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080326
APA StyleMuma, M., Rousseau, A. N., & Gumiere, S. J. (2016). Assessment of the Impact of Subsurface Agricultural Drainage on Soil Water Storage and Flows of a Small Watershed. Water, 8(8), 326. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8080326