Characterization and Sorptivity of the Plesiomonas shigelloides Strain and Its Potential Use to Remove Cd2+ from Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sediment Analysis and Cadmium-Resistant Bacteria Isolation
2.2. Identification and Characterization of the Cadmium-Resistant Bacteria
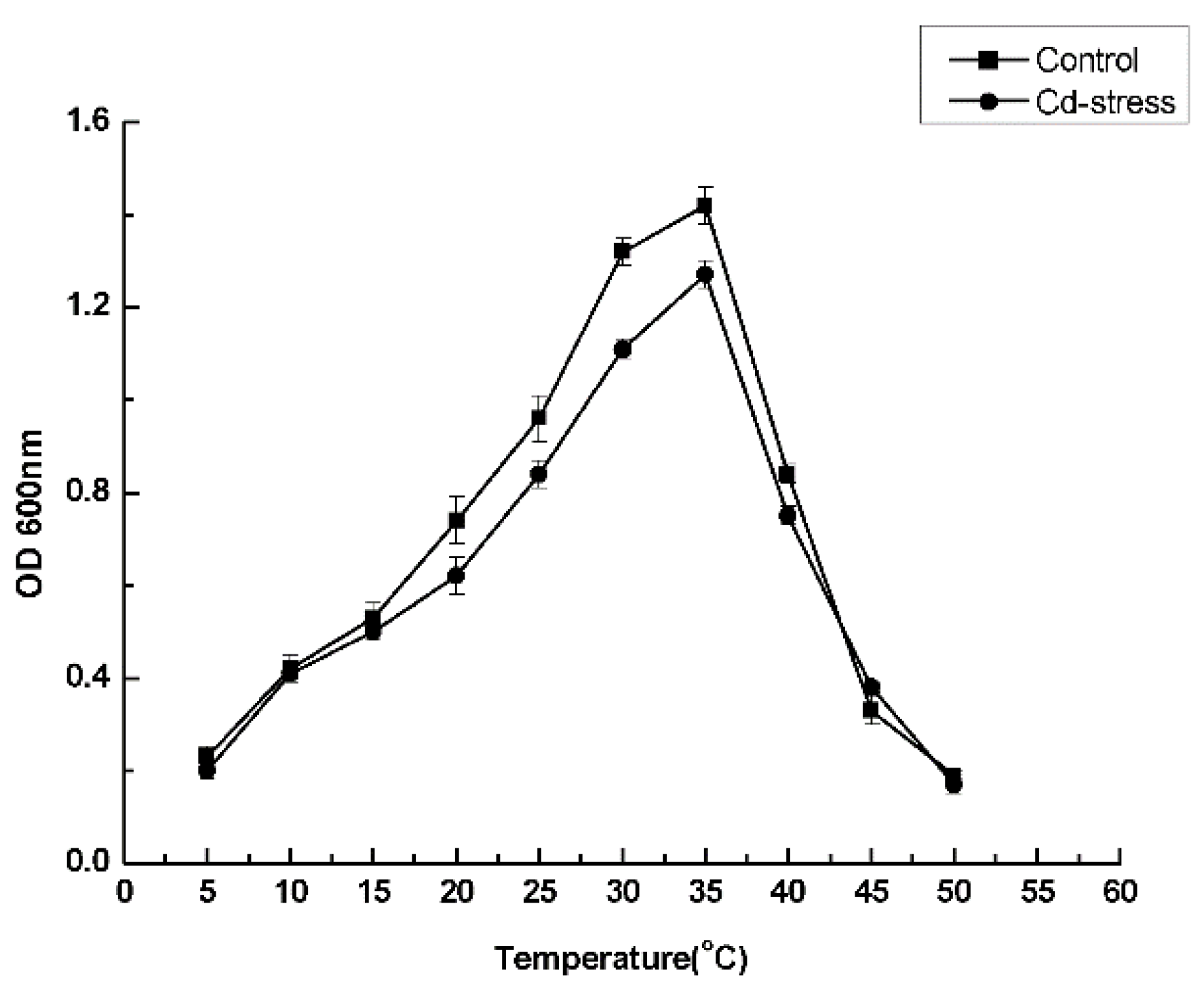
2.3. Experiment on Optimal Culture Conditions
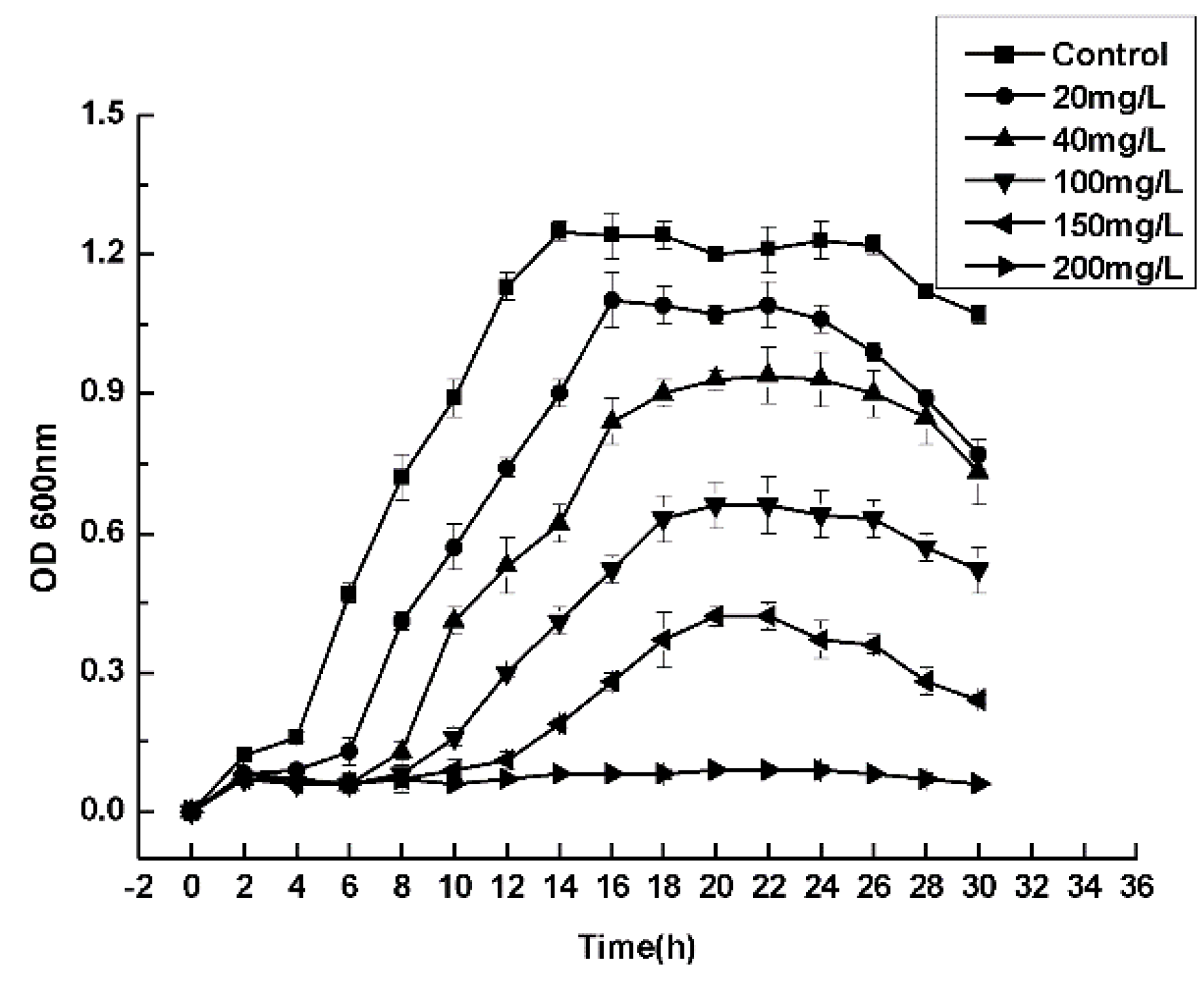
2.4. Experiment on Maximum Tolerance Concentrations
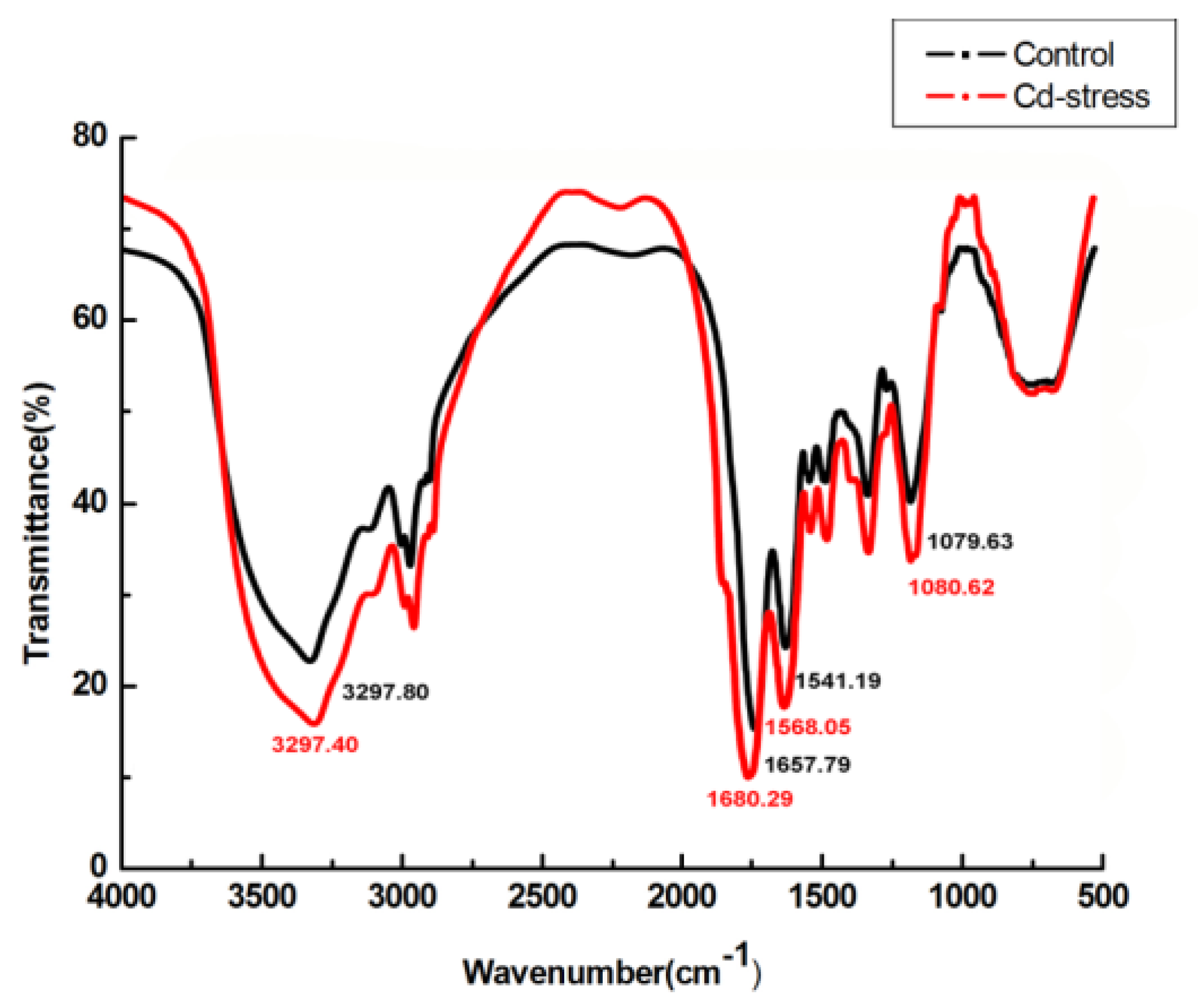
2.5. FTIR, SEM, EDX, and TEM Analysis
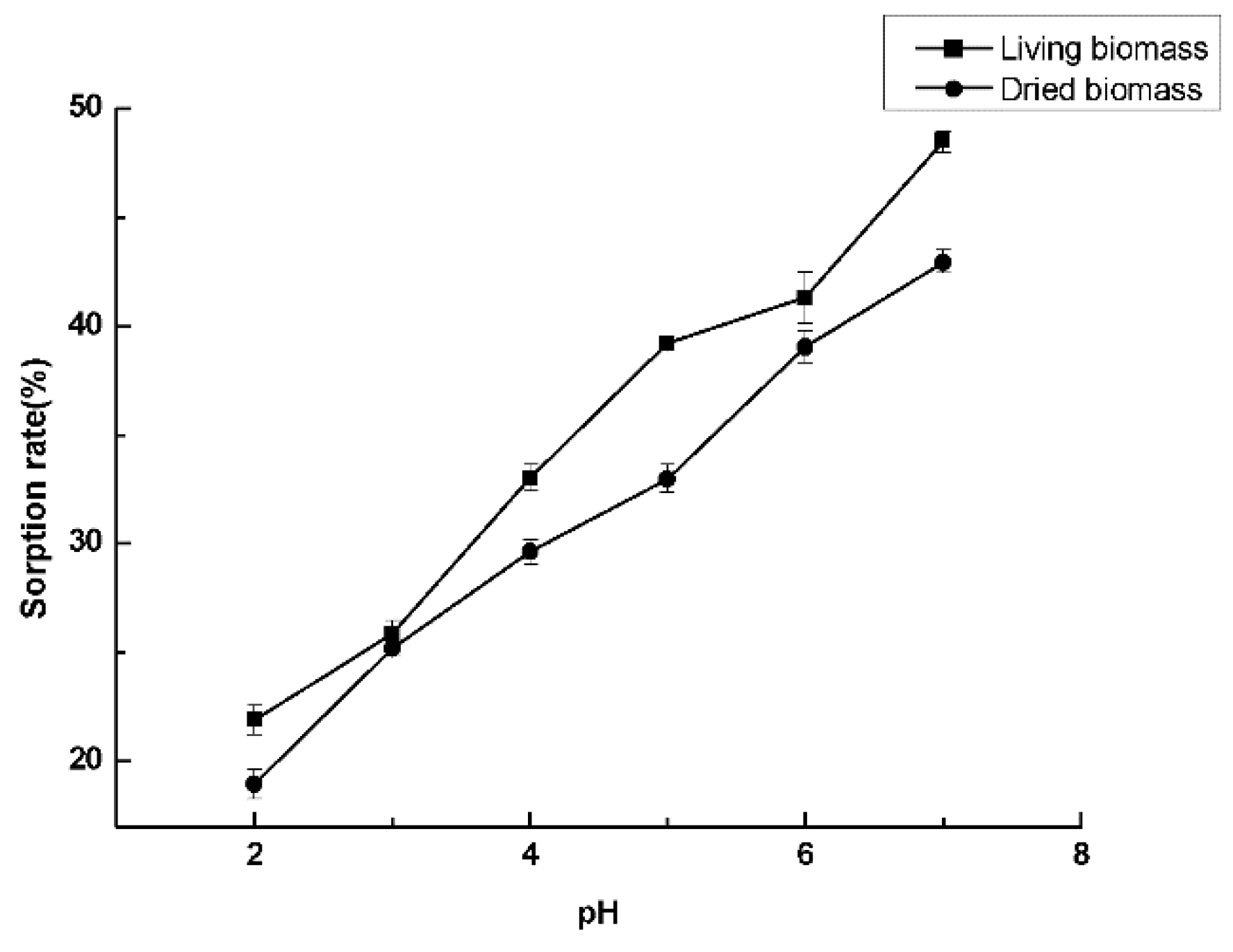
2.6. Cadmium Sorption Experiments
2.7. Adsorption Kinetic Models
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Metal Contents of Sediment and Screening of Cd2+-Resistant Bacteria
3.2. Characterization and Identification of Cd2+-Resistant Bacteria
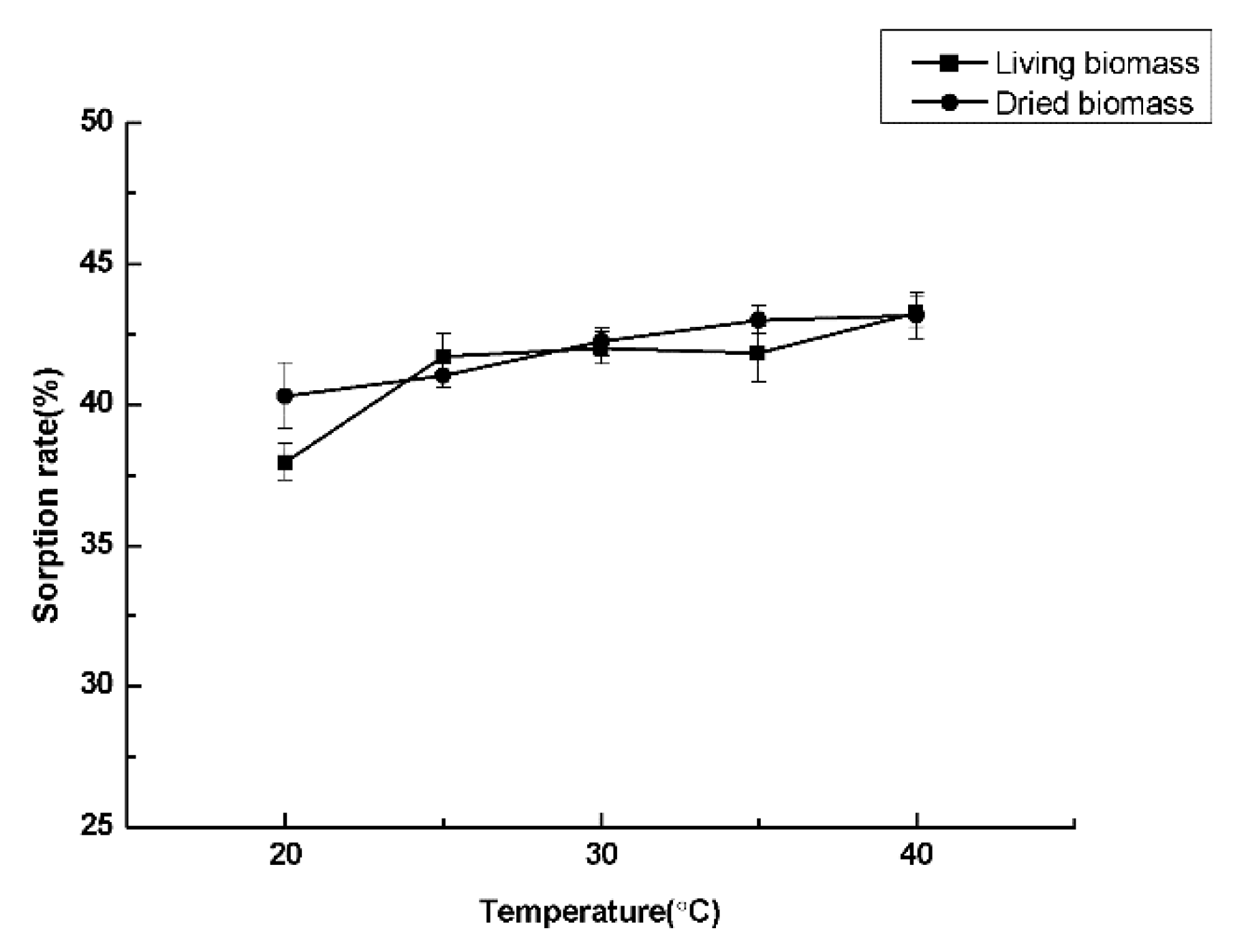
3.3. Optimal Culture Conditions
3.4. Maximum Tolerance Concentrations
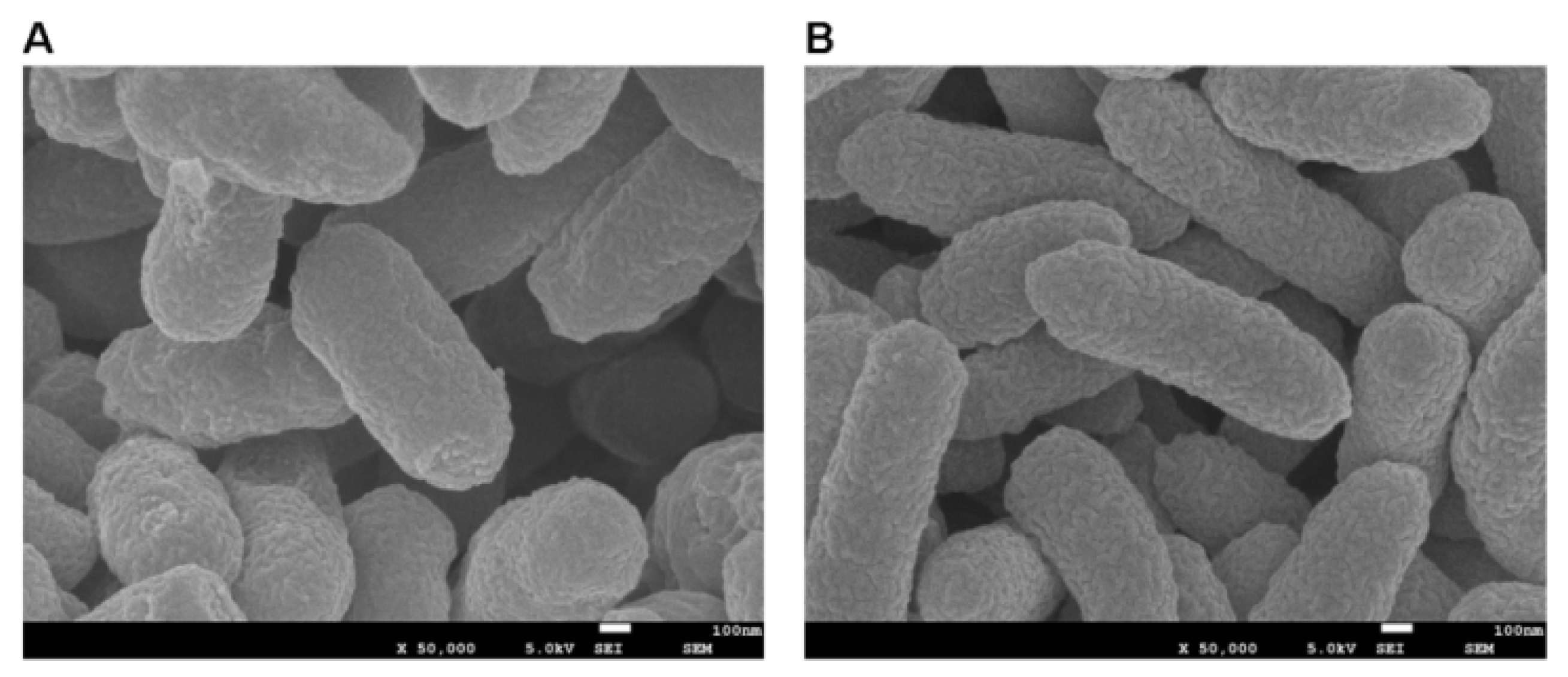
3.5. FTIR, SEM, EDX, and TEM Analysis
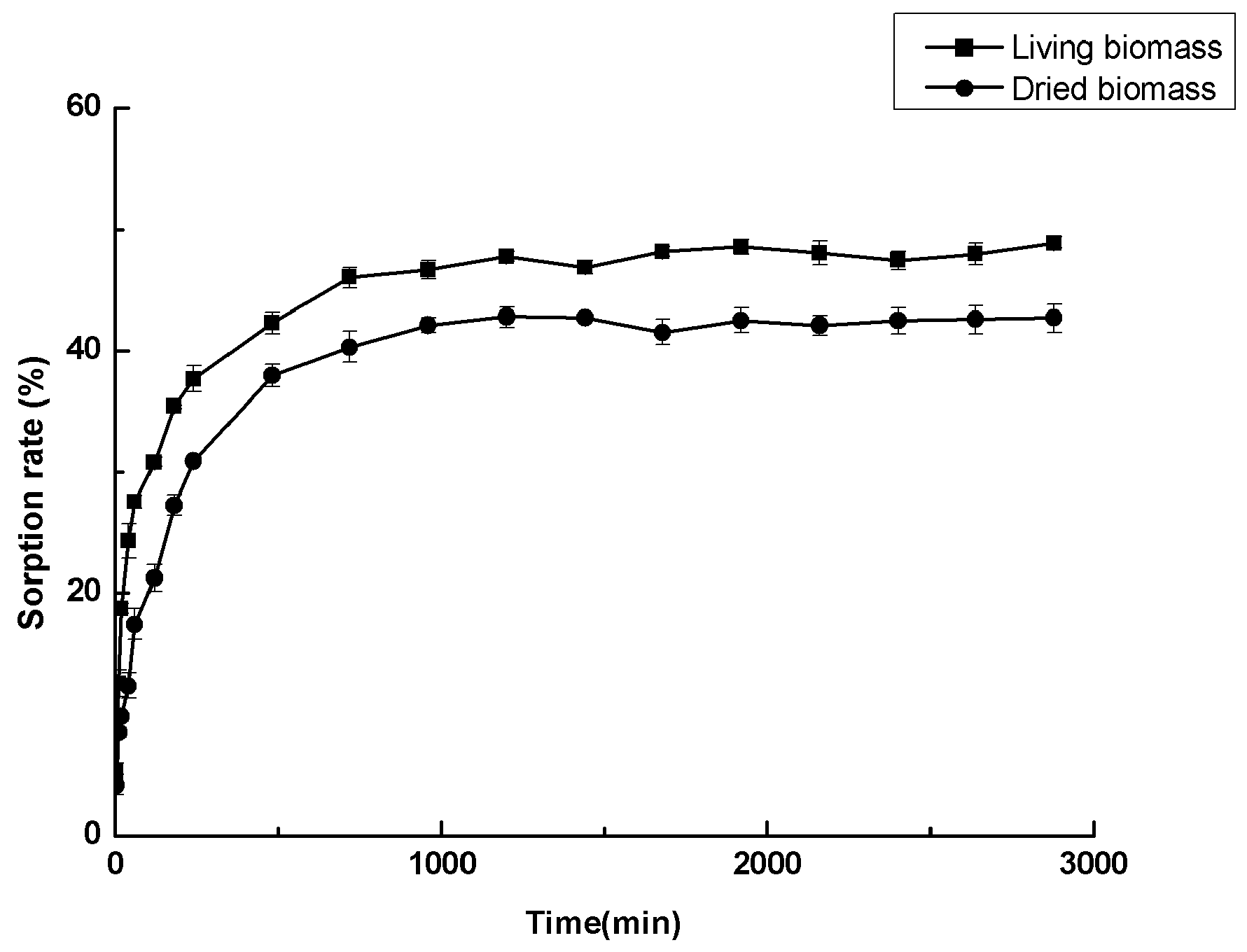
3.6. Cadmium Sorption Experiments
3.7. Adsorption Kinetic Models
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sanità di Toppi, L.; Gabbrielli, R. Response to cadmium in higher plants. Environ. Exp. Bot. 1999, 41, 105–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radotić, K.; Dučić, T.; Mutavdžić, D. Changes in peroxidase activity and isoenzymes in spruce needles after exposure to different concentrations of cadmium. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2000, 44, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; You, W.; Hu, H.; Hong, W.; Liao, X.; Xiao, S.; Wang, R.; Cai, J.; Fan, X.; Tan, Y. Spatial distribution of heavy metals (Cu, Pb, Zn, and Cd) in sediments of a coastal wetlands in eastern Fujian, China. J. For. Res. 2015, 26, 703–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AMAP Assessment 2011: Mercury in the Arctic; Arctic Monitoring and Assessment Programme: Oslo, Norway, 2011.
- Filipič, M.; Fatur, T.; Vudrag, M. Molecular mechanisms of cadmium induced mutagenicity. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2006, 25, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benavides, M.P.; Gallego, S.M.; Tomaro, M.L. Cadmium toxicity in plants. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2005, 17, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flora, S.J.S.; Megha, M.; Ashish, M. Heavy metal induced oxidative stress & its possible reversal by chelation therapy. Indian J. Med. Res. 2008, 128, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bai, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, G.; Li, B. Bioremediation of cadmium by growing rhodobacter sphaeroides: Kinetic characteristic and mechanism studies. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 7716–7722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halttunen, T.; Salminen, S.; Tahvonen, R. Rapid removal of lead and cadmium from water by specific lactic acid bacteria. Int. J. Food Microb. 2007, 114, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roane, T.M.; Pepper, I.L. Microbial responses to environmentally toxic cadmium. Microb. Ecol. 1999, 38, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbas, S.Z.; Rafatullah, M.; Ismail, N.; Lalung, J. Isolation, identification, characterization, and evaluation of cadmium removal capacity of enterobacter species. J. Basic Microb. 2014, 54, 1279–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neethu, C.S.; Mujeeb Rahiman, K.M.; Saramma, A.V.; Mohamed Hatha, A.A. Heavy-metal resistance in Gram-negative bacteria isolated from Kongsfjord, Arctic. Can. J. Microb. 2015, 61, 429–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Rama, M.; Torres, E.; Suárez, C.; Herrero, C.; Abalde, J. Sorption isotherm studies of Cd(II) ions using living cells of the marine microalga Tetraselmis suecica (Kylin) Butch. J. Environ. Manag. 2010, 91, 2045–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, X. Characterization of biological iron sulfide composites and its application in the treatment of cadmium-contaminated wastewater. J. Environ. Biol. 2015, 36, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vullo, D.L.; Ceretti, H.M.; Daniel, M.A.; Ramírez, S.A.M.; Zalts, A. Cadmium, zinc and copper biosorption mediated by Pseudomonas veronii 2E. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5574–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kılıç, N.K.; Dönmez, G. Environmental conditions affecting exopolysaccharide production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Micrococcus sp., and Ochrobactrum sp. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 154, 1019–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, J.J.; Ceri, H.; Stremick, C.; Turner, R.J. Differences in biofilm and planktonic cell mediated reduction of metalloid oxyanions. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2004, 235, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coral, G.; Arιkan, B.; Coral, M.N.Ü. A preliminary study on tellurite resistance in Pseudomonas spp. isolated from hospital sewage. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2006, 15, 517–520. [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst, F.E.; Chien, C.C.; Paster, B.J.; Ericson, R.L.; Orcutt, R.P.; Schauer, D.B.; Fox, J.G. Phylogeny of the defined murine microbiota: Altered schaedler flora. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1999, 65, 3287–3292. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.H.; Jin, F.; Wang, H.P.; Liu, J.S. Heavy metal resistance by two bacteria strains isolated from a copper mine tailing in China. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2010, 9, 4056–4066. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, L.; Chang, Q.; Wang, H.; Yang, K. Biosorption of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions by a newly isolated Bosea sp. strain Zer-1 from soil samples of a refuse processing plant. Can. J. Microbiol. 2015, 61, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Sun, M.; Liu, P.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, X. Enterococcus faecalis strain LZ-11 isolated from Lanzhou reach of the Yellow River is able to resist and absorb Cadmium. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 116, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, Z.; Nisar, M.A.; Hussain, S.Z.; Arshad, M.N.; Rehman, A. Cadmium resistance mechanism in Escherichia coli P4 and its potential use to bioremediate environmental cadmium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10745–10757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, S.; Le, T.P. A bacterial view of the periodic table: Genes and proteins for toxic inorganic ions. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2005, 32, 587–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nies, D.H. Efflux-mediated heavy metal resistance in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malin Mejare, L.B. Metal-binding proteins and peptides in bioremediation and phytoremediation of heavy metals. TRENDS Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piddock, L.J.V. Multidrug-resistance efflux pumps? Not just for resistance. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2006, 4, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuyama, R.; Kuninaga, N.; Morimoto, T.; Shibano, T.; Sudo, A.; Sudo, K.; Asano, M.; Suzuki, M.; Asai, T. Isolation and antimicrobial susceptibility of Plesiomonas shigelloides from great cormorants (Phalacrocorax carbo hanedae) in Gifu and Shiga Prefectures, Japan. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2015, 77, 1179–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoa-Farias, O.; Frati-Munari, A.C.; Peredo, M.A.; Flores-Juarez, S.; Novoa-Garcia, O.; Galicia-Tapia, J.; Romero-Carpio, C.E. Susceptibility of bacteria isolated from acute gastrointestinal infections to rifaximin and other antimicrobial agents in Mexico. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. 2015, 91, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuno, T.; Mejido, J.; Schmeisser, H.; Fey, S.; Morrow, A.; Nie, H.; Zhao, T.; Bekisz, J.; Goldman, N.; Zoon, K. Isolation and characterization of heavy-metal resistant microbes from roadside soil and phylloplane. Cotton Sci. 2012, 52, 53–65. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.Y.; Jin, M.R.; Chung, C.H.; Yun, Y.S.; Jahng, K.Y.; Yu, K.Y. Biosorption of cationic basic dye and cadmium by the novel biosorbent Bacillus catenulatus JB-022 strain(environmental biotechnology). J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 119, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Latitude | 45°75’47” N |
| Longitude | 126°57’57” E |
| sampling spots number | 6 |
| Water temperature (°C) | 4 |
| Water pH | 8.62 ± 0.16 |
| Cd | 2.51 ± 0.21 |
| Ni | 7.64 ± 0.14 |
| Cu | 6.14 ± 0.54 |
| Cr | 14.46 ± 0.32 |
| Pb | 18.32 ± 1.21 |
| Zn | 26.86 ± 1.84 |
| THB level (CFU/g) | 5.6–6.4 × 105 |
| Strain | H5 |
|---|---|
| Morphology | |
| Colony color | Yellowish |
| Gram nature | − |
| Cell morphology | Straight rod |
| Motility | + |
| Colony shape | Round |
| Elevation | Raised |
| Surface | Smooth |
| Optical | Opaque |
| Biochemical tests | |
| Lysine decarboxylase | + |
| Urease | − |
| Arginine dihydrolase | + |
| Indol production | + |
| O-nitrophenyl d-galactoside | + |
| H2S production | − |
| Gelatin hydrolysis | − |
| Citrate | − |
| Inositol | + |
| Glucose | + |
| Sucrose | − |
| Mannitol | − |
| Sorbitol | − |
| Rhamnose | − |
| Melibiose | − |
| Amy-gdalin | − |
| Arabinose | − |
| Tryptophan | − |
| Voges–Proskauer | − |
| Cytochrome oxidase | + |
| Living Biomass | Sorption Rate (%) | Sorption Amounts (mg/g) |
|---|---|---|
| P. shigelloides H5 | 48.91 ± 0.46 | 122.275 ± 1.15 |
| E. coli DH5α | 11.42 ± 0.16 | 28.55 ± 0.41 |
| Models | K1 or K2 | Qm | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lagergren pseudo-first-order | 0.0017 | 0.1392 | 0.7577 |
| Lagergren pseudo-second-order | 0.0003 | 109.891 | 0.9992 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xue, C.; Qi, P.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Characterization and Sorptivity of the Plesiomonas shigelloides Strain and Its Potential Use to Remove Cd2+ from Wastewater. Water 2016, 8, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060241
Xue C, Qi P, Li M, Liu Y. Characterization and Sorptivity of the Plesiomonas shigelloides Strain and Its Potential Use to Remove Cd2+ from Wastewater. Water. 2016; 8(6):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060241
Chicago/Turabian StyleXue, Chao, Peishi Qi, Mengsha Li, and Yunzhi Liu. 2016. "Characterization and Sorptivity of the Plesiomonas shigelloides Strain and Its Potential Use to Remove Cd2+ from Wastewater" Water 8, no. 6: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060241
APA StyleXue, C., Qi, P., Li, M., & Liu, Y. (2016). Characterization and Sorptivity of the Plesiomonas shigelloides Strain and Its Potential Use to Remove Cd2+ from Wastewater. Water, 8(6), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8060241





