The Impact of Impervious Surface on Water Quality and Its Threshold in Korea
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
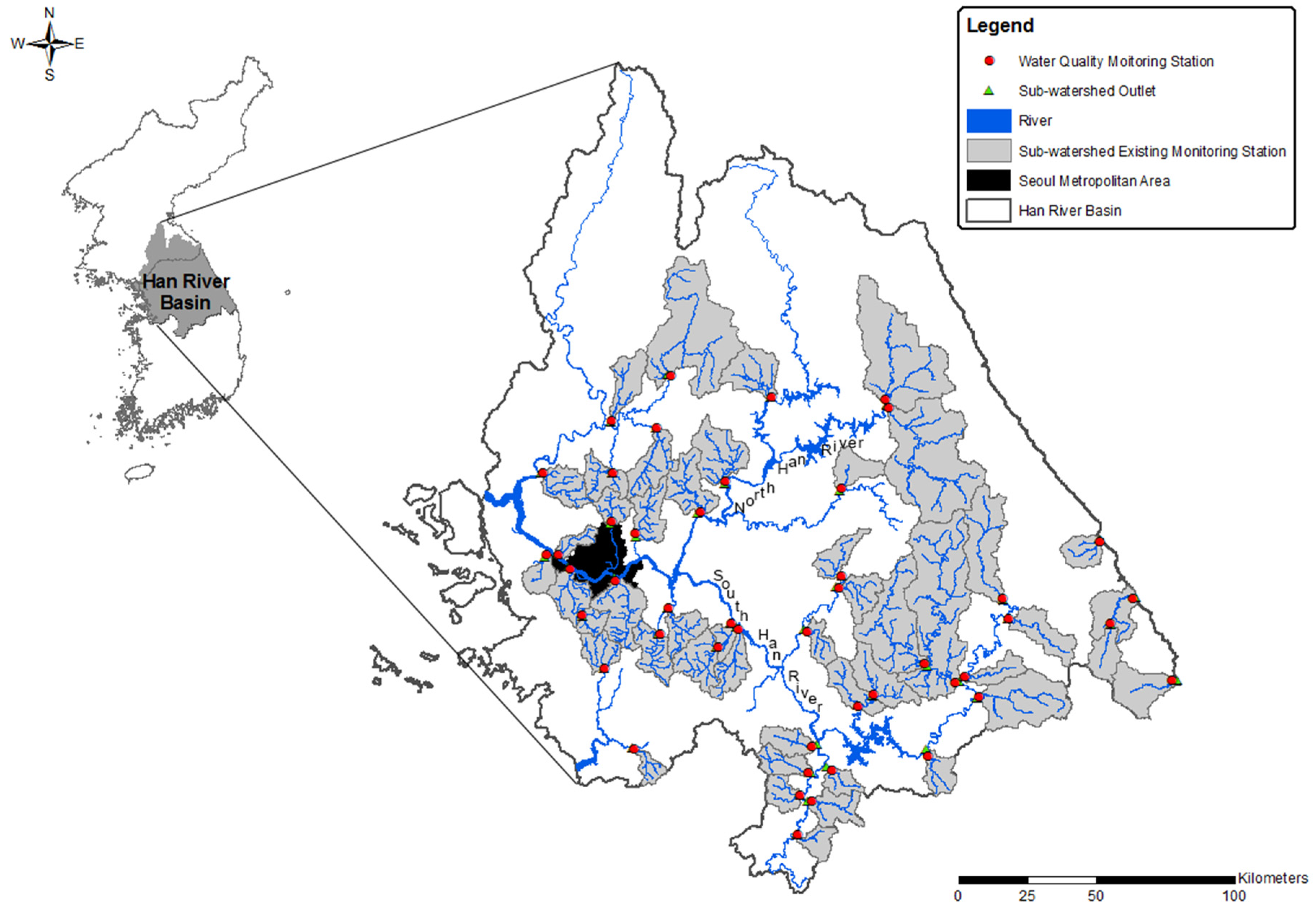
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Selection of Sub-Watershed
2.3. Impervious Surface Analysis
2.4. Water Quality Data
2.5. Relationship between PISA and Water Quality
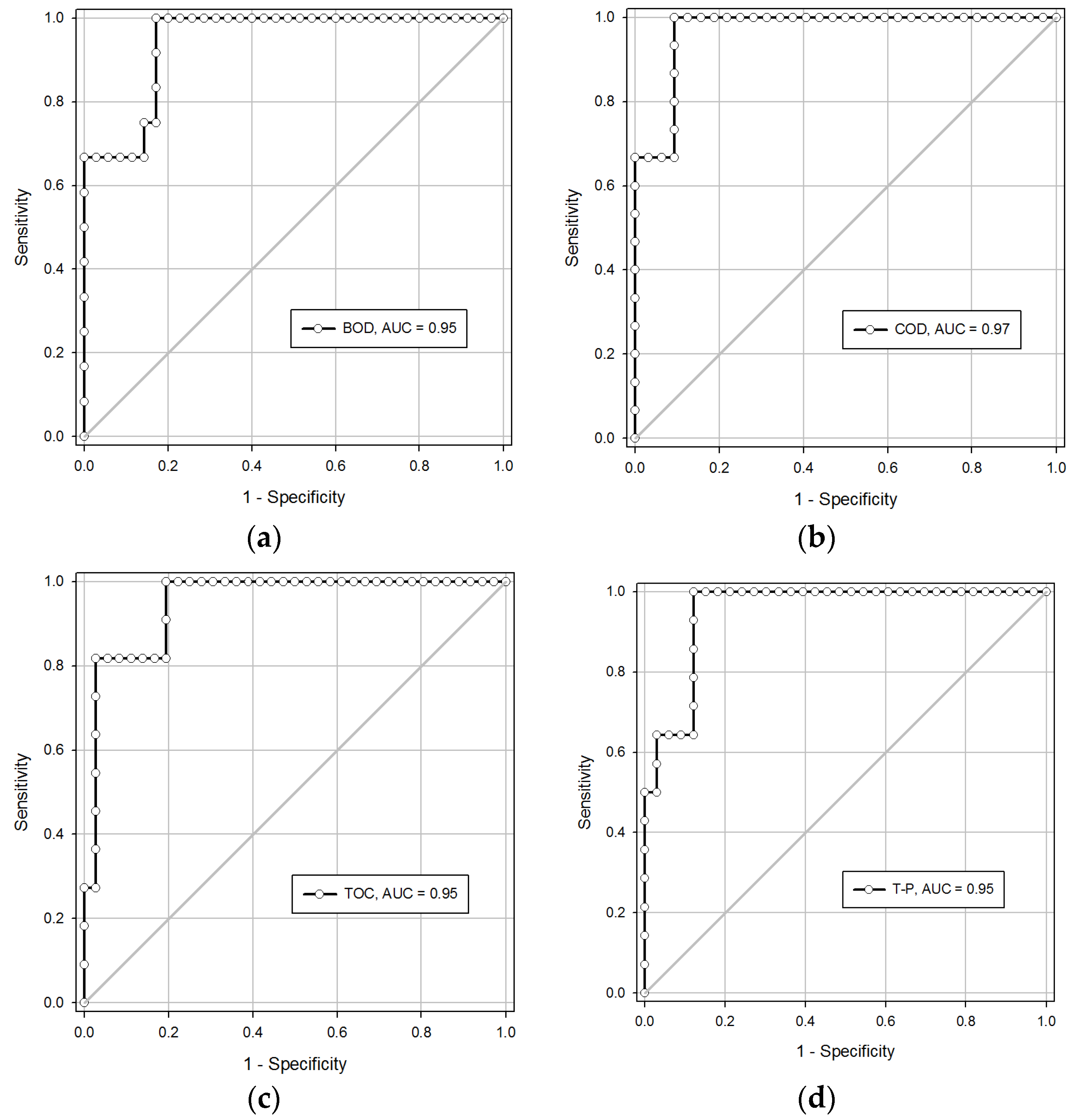
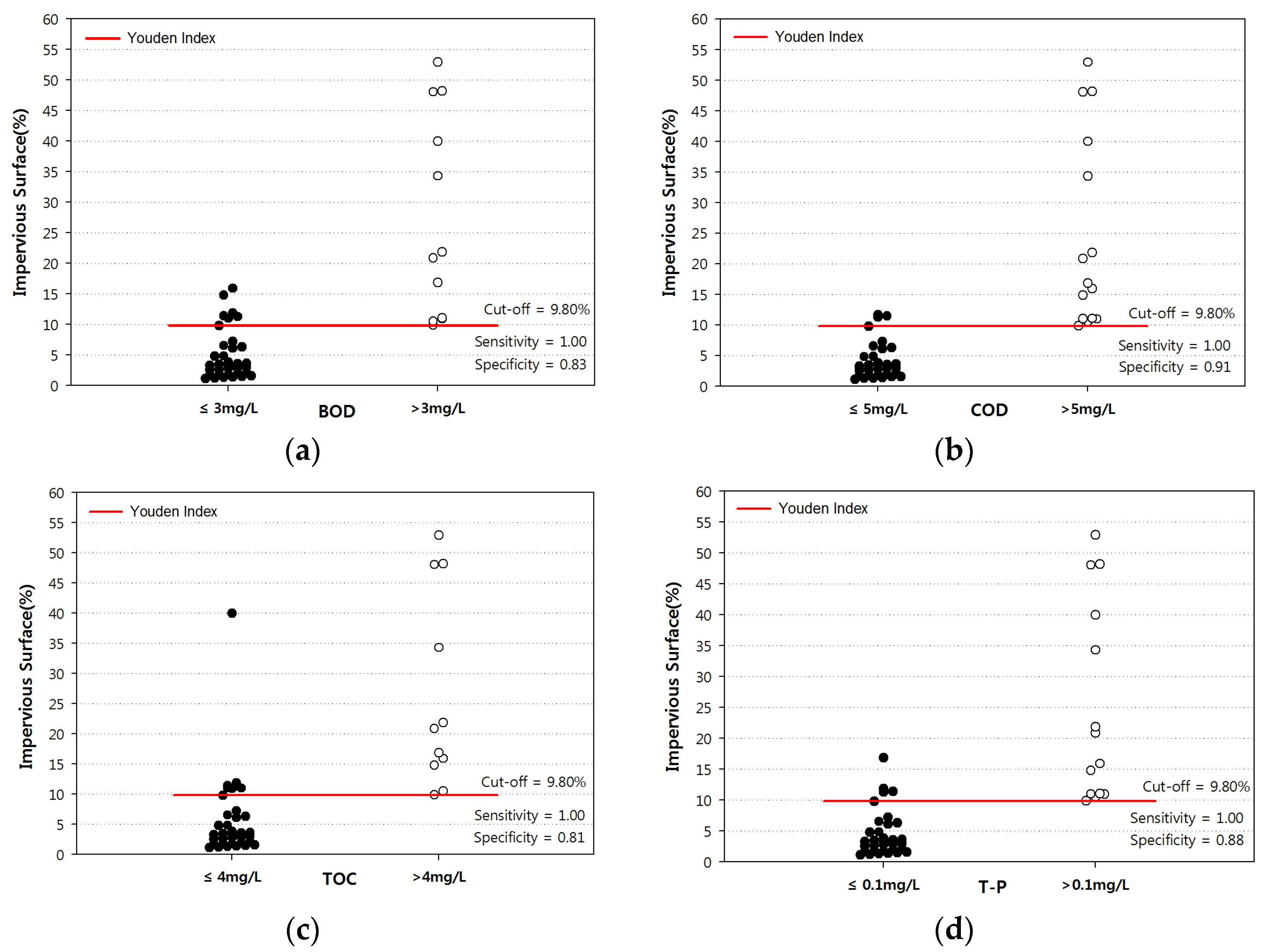
2.6. Threshold of PISA
3. Results and Discussion
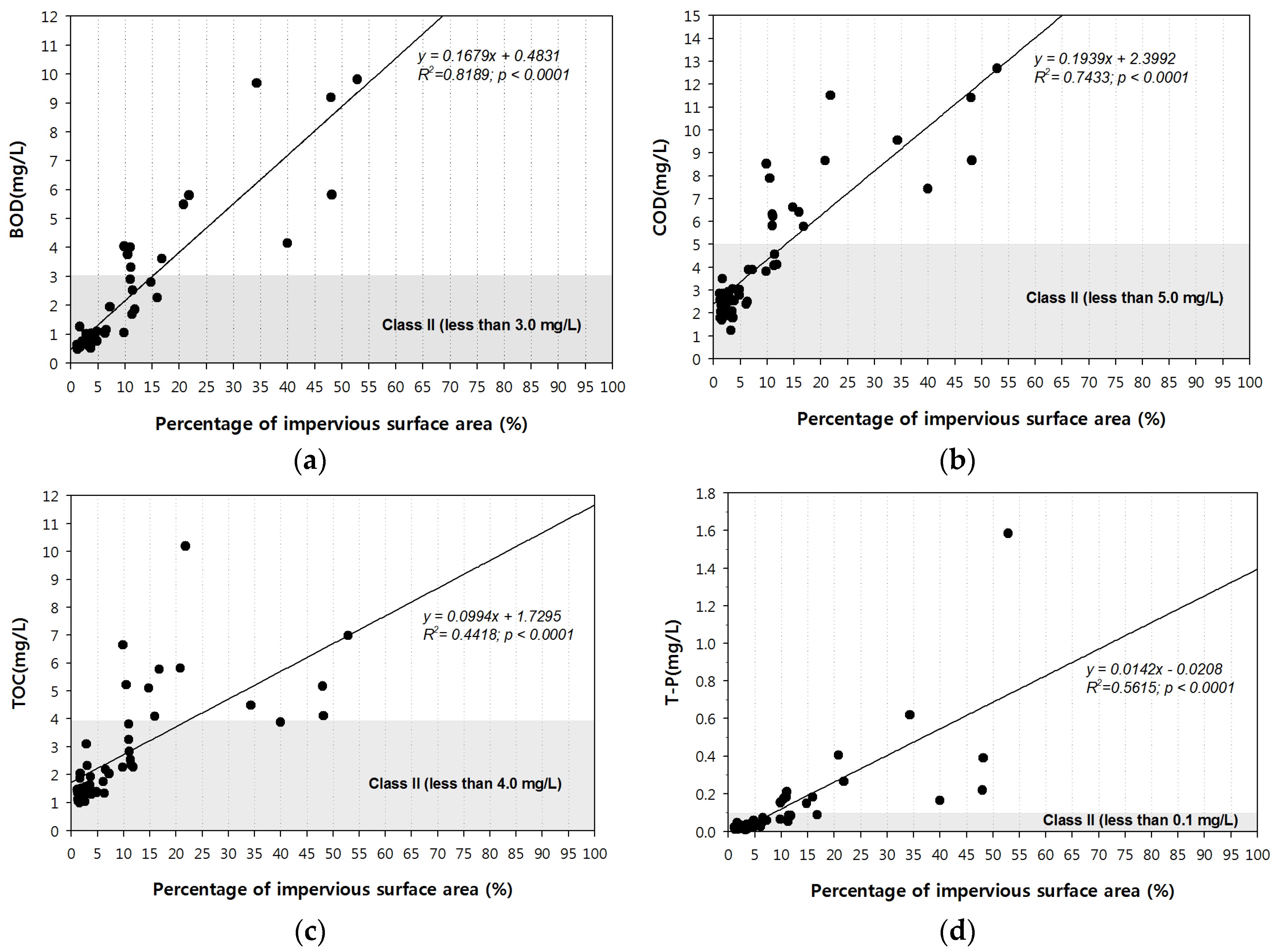
3.1. Relationship between PISA and Water Quality
3.2. PISA Threshold
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brabec, E.; Schulte, S.; Richards, P.L. Impervious surface and water quality: A review of current literature and its implications for watershed planning. J. Plann. Lit. 2002, 16, 499–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, C.L.; Gibbons, C.J. Impervious surface coverage: The emergence of a key environmental indicator. J. Am. Plan. Assoc. 1996, 62, 243–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, W.D.; Bonta, J.; Thurstron, H.; Warnemuende, E.; Smith, D.R. Impacts of impervious surface on watershed hydrology: A review. Urban Water J. 2005, 2, 263–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moring, J.B. Effects of Urbanization on the Chemical, Physical, and Biological Characteristics of Small Blackland Prairie Streams in and near the Dallas-Fort Worth Metropolitan Area, Texas; Geological Survey Scientific Investigations Report 2006-5101-C; U.S. Geological Survey: Austin, TX, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.; Sharkey, L.J.; Hunt, W.F.; Davis, A.P. Mitigation of impervious surface hydrology using bioretention in North Carolina and Maryland. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Driscoll, M.; Clinton, S.; Jefferson, A.; Manda, A.; McMillan, S. Urbanization effects on watershed hydrology and in-stream processes in the Southern United States. Water 2010, 2, 605–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Peng, J. Impervious surface impact on water quality in the process of rapid urbanization in Shenzhen, China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 2365–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, T.R.; Fraley-McNeal, L.; Cappiella, K. Is impervious cover still important? Review of recenty research. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2009, 14, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.D. Urbanization and stream quality impairment. Water Resour. Bull. 1979, 15, 948–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schueler, T.R. The importance of imperviousness. Watershed Prot. Tech. 1994, 1, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Holland, F.; Sanger, D.M.; Gawle, C.P.; Lerberg, S.B.; Santago, M.S.; Riekerk, G.H.M.; Zimmerman, L.E.; Scott, G.I. Linkages between tidal creek ecosystems and the landscape and demographic attributes of their watersheds. J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 2004, 298, 151–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environment (MOE) and Korea Environment Corporation (KECO). Estimation of impervious Surface Area in Korea; MOE: Sejong, Korea; KECO: Seoul, Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H. Spatial analysis of water quality trends in the Han River basin, South Korea. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3285–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greiner, M.; Pfeiffer, D.; Smith, R.D. Principles and practical application of the receiver-operating characteristic analysis for diagnostic tests. Prev. Vet. Med. 2000, 45, 23–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faucett, T. An introduction to ROC analysis. Pattern Recogn. Lett. 2006, 27, 861–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dos Santos, D.A.; Molineri, C.; Reynaga, M.C.; Basualdo, C. Which index is the best to assess stream health? Ecol. Indicat. 2008, 8, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storey, J.E.; Rowland, J.T.J.; Basic, D.; Conforti, A. A comparison of five clock scoring methods using ROC (receiver, operating characteristic) curve analysis. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2001, 16, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schisterman, E.F.; Perkins, N.J.; Liu, A.; Bondell, H. Optimal cut-point and its corresponding Youden index to discriminate individual using pooled blood samples. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, H.; Jeong, H.; Jeon, J.; Bae, S. The Impact of Impervious Surface on Water Quality and Its Threshold in Korea. Water 2016, 8, 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040111
Kim H, Jeong H, Jeon J, Bae S. The Impact of Impervious Surface on Water Quality and Its Threshold in Korea. Water. 2016; 8(4):111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040111
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Hakkwan, Hanseok Jeong, Jihye Jeon, and Seungjong Bae. 2016. "The Impact of Impervious Surface on Water Quality and Its Threshold in Korea" Water 8, no. 4: 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040111
APA StyleKim, H., Jeong, H., Jeon, J., & Bae, S. (2016). The Impact of Impervious Surface on Water Quality and Its Threshold in Korea. Water, 8(4), 111. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8040111







