Taxonomy of Means and Ends in Aquaculture Production—Part 4: The Mapping of Technical Solutions onto Multiple Treatment Functions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Review
2.2. The Quality Function Deployment
3. The Taxonomy of Technical Solutions
3.1. Controlling Solids
3.2. Controlling pH, Alkalinity and Hardness
3.3. Controlling DO and CO2
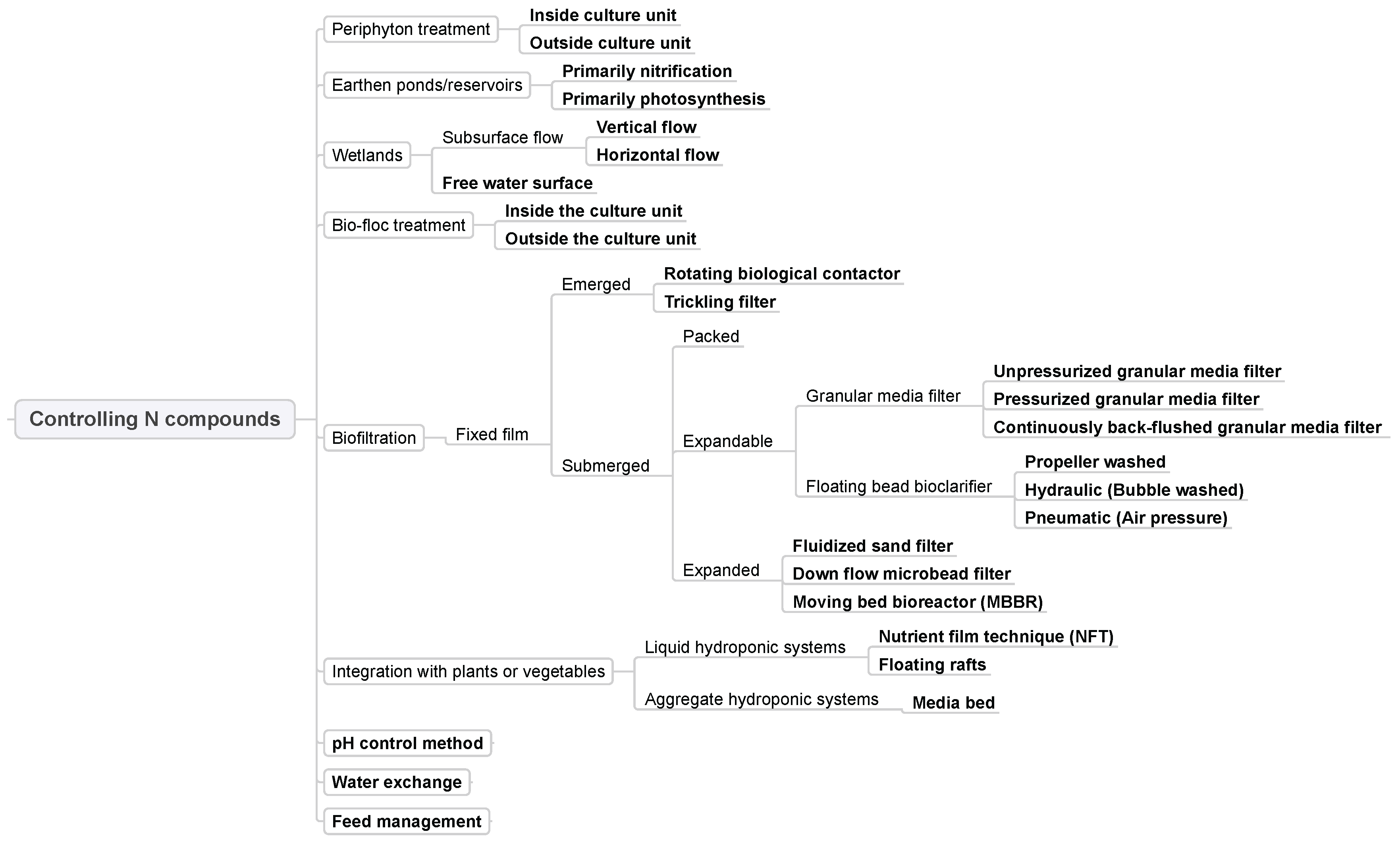
3.4. Controlling N Compounds
3.5. Controlling Organic Matter
3.6. Controlling P Compounds
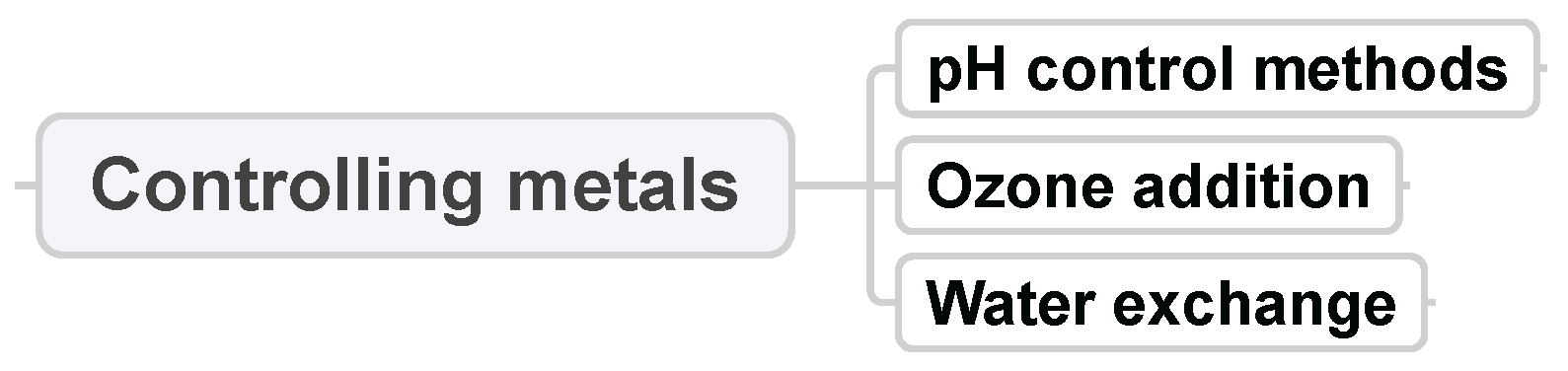
3.7. Controlling Metals
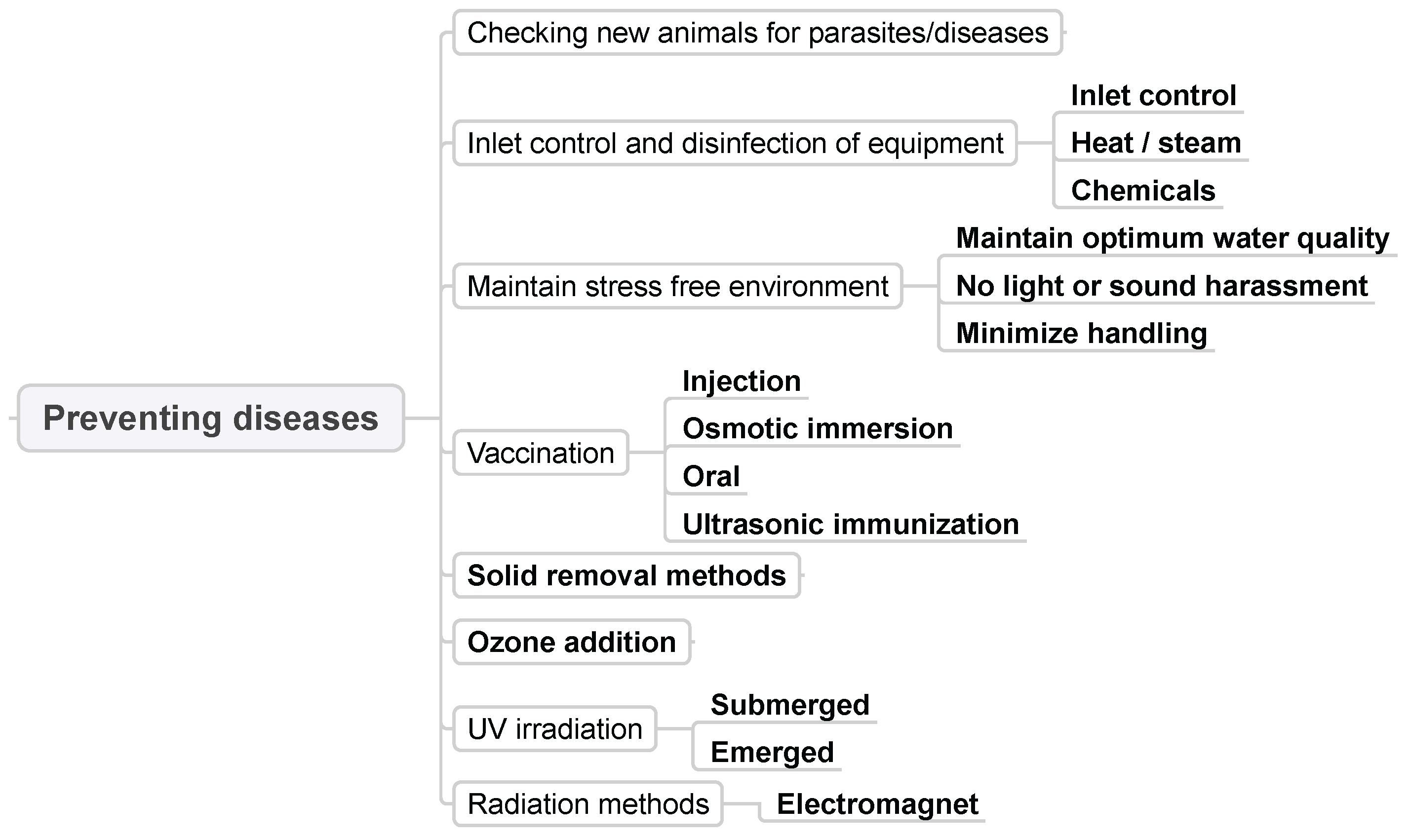
3.8. Preventing Diseases
3.9. Controlling Temperature
4. The Quality Function Deployment Matrix of Technical Solutions and Treatment Functions
Means vs. Treatment Functions
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martins, C.; Eding, E.; Verdegem, M.; Heinsbroek, L.; Schneider, O.; Blancheton, J.; D’Orbcastel, E.R.; Verreth, J. New developments in recirculating aquaculture systems in Europe: A perspective on environmental sustainability. Aquac. Eng. 2010, 43, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badiola, M.; Mendiola, D.; Bostock, J. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS) analysis: Main issues on management and future challenges. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 51, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björnsdóttir, R.; Oddsson, G.V.; Thorarinsdottir, R.; Unnthorsson, R. Taxonomy of means and ends in aquaculture production—Part 1: The functions. Water 2016, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilbergsson, B.; Oddsson, G.V.; Unnthorsson, R. Taxonomy of means and ends in aquaculture production—Part 2: The technical solutions of controlling solids, disolved gasses and pH. Water 2016, 8, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilbergsson, B.; Oddsson, G.V.; Unnthorsson, R. Taxonomy of means and ends in aquaculture production—Part 3: The technical solutions of controlling N compounds, organic matter, P compounds, metals, temperature and preventing disease. Water 2016, 8, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahill, A.T.; Chapman, W.L. A Tutorial on Quality Function Deployment. Eng. Manag. J. 1993, 5, 24–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liltved, H.; Cripps, S. Removal of particle-associated bacteria by prefiltration and ultraviolet irradiation. Aquac. Res. 1999, 30, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, R.C.; Penne, C.R. Solids removal in a recirculating aquaculture system where the majority of flow bypasses the microscreen filter. Aquac. Eng. 2005, 33, 214–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebeling, J.; Welsh, C.; Rishel, K. Performance evaluation of an inclined belt filter using coagulation/flocculation aids for the removal of suspended solids and phosphorus from microscreen. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 35, 61–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holan, A.; Wold, P.A.; Leiknes, T. Intensive rearing of cod larvae (Gadus morhua) in recirculating aquaculture systems (RAS) implementing a membrane bioreactor (MBR) for enhanced colloidal particle and fine suspended solids removal. Aquac. Eng. 2014, 58, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cripps, S.J.; Bergheim, A. Solids management and removal for intensive land-based aquaculture production systems. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 22, 33–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tidwell, J. Aquaculture Production Systems; Wiley-Blackwell: Oxford, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Loyless, J.; Malone, R. A sodium bicarbonate dosing methodology for pH management in freshwater-recirculating aquaculture systems. Prog. Fish Cult. 1997, 59, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.; Tucker, C.; Viriyatum, R. Interpretation of pH, acidity, and alkalinity in aquaculture and fisheries. N. Am. J. Aquac. 2011, 73, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timmons, M.B.; Ebeling, J.M. Recirculating Aquaculture, 2nd ed.; Cayuga Aqua Ventures: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rosseland, B.O.; Skogheim, O.K. Neutralization of acidic brook-water using a shell-sand filter or sea-water: Effects on eggs, alevins and smolts of salmonids. Aquaculture 1986, 58, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekang, O. Aquaculture Engineering; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Teien, H.C.; Kroglund, F.; Atland, A.; Rosseland, B.O.; Salbu, B. Sodium silicate as alternative to liming-reduced aluminum toxicity for Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.) in unstable mixing zones. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 358, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furtado, P.S.; Gaona, C.A.P.; Poersch, L.H.; Wasielesky, W. Application of different doses of calcium hydroxide in the farming shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei with the biofloc technology (BFT). Aquac. Int. 2013, 22, 1009–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharrer, M.J.; Rishel, K.; Summerfelt, S. Evaluation of geotextile filtration applying coagulant and flocculant amendments for aquaculture biosolids dewatering and phosphorus removal. Aquac. Eng. 2009, 40, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, C.E.; Tucker, C.S.; Somridhivej, B. Alkalinity and Hardness: Critical but Elusive Concepts in Aquaculture. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2016, 47, 6–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whangchai, N.; Migo, V.P.; Alfafara, C.G.; Young, H.K.; Nomura, N.; Matsumura, M. Strategies for alkalinity and pH control for ozonated shrimp pond water. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 30, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, B.K.; Das, N. Impacts of quicklime (CaO) on the toxicity of copper (CuSO4, 5H2O) to fish and fish food organisms. Chemosphere 2005, 61, 186–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaviraj, A.; Dutta, T.K. Use of Quick Lime (CaO) as a Means to Reduce Cadmium Toxicity in Common Carp, Cyprinus carpio. J. Appl. Aquac. 2008, 10, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colt, J. Water quality requirements for reuse systems. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 143–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackney, G.E.; Colt, J.E. The performance and design of packed column aeration systems for aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 1982, 1, 275–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watten, B.J.; Sibrell, P.L.; Montgomery, G.A.; Tsukuda, S.M. Modification of pure oxygen absorption equipment for concurrent stripping of carbon dioxide. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 32, 183–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyless, J.; Malone, R.F. Evaluation of air-lift pump capabilities for water delivery, aeration, and degasification for application to recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 1998, 18, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrut, B.; Blancheton, J.P.; Champagne, J.Y.; Grasmick, A. Mass transfer efficiency of a vacuum airlift—Application to water recycling in aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 46, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seginer, I.; Mozes, N. A note on oxygen supply in RAS: The effect of water temperature. Aquac. Eng. 2012, 50, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.; Vinci, B.; Piedrahita, R. Oxygenation and carbon dioxide control in water reuse systems. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 22, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Losordo, T.; Masser, M.; Rakocy, J. Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems—A Review of Component Options; SRAC Publication: Stoneville, MS, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Timmons, M.B.; Holder, J.L.; Ebeling, J.M. Application of microbead biological filters. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazil, B.L. Performance and operation of a rotating biological contactor in a tilapia recirculating aquaculture system. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 261–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crab, R.; Avnimelech, Y.; Defoirdt, T.; Bossier, P.; Verstraete, W. Nitrogen removal techniques in aquaculture for a sustainable production. Aquaculture 2007, 270, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlin, H.; Michaels, J.; Beaulaton, C.; Graham, W.; Dutt, W.; Steinbach, P.; Losordo, T.; Schrader, K.; Main, K. Comparing denitrification rates and carbon sources in commercial scale upflow denitrification biological filters in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2008, 38, 79–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, J.; Good, C.; Welsh, C.; Summerfelt, S. The effects of ozone and water exchange rates on water quality and rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss performance in replicated water recirculating systems. Aquac. Eng. 2011, 44, 80–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T.; Sharrer, M.J. Design implication of carbon dioxide production within biofilters contained in recirculating salmonid culture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 32, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beveridge, M.; Beveridge, M.; Verdegem, M.; Van Dam, A.A.; Azim, M.E. The potential of fish production based on periphyton. Rev. Fish Biol. Fish. 2002, 12, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Azim, M.; Little, D. The biofloc technology (BFT) in indoor tanks: Water quality, biofloc composition, and growth and welfare of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquaculture 2008, 283, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, K. Nitrogen and phosphorus dynamics in the biofloc production of the pacific white shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2013, 44, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gál, D.; Pekár, F.; Kerepeczki, É.; Váradi, L. Experiments on the operation of a combined aquaculture-algae system. Aquac. Int. 2007, 15, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargreaves, J.A. Photosynthetic suspended-growth systems in aquaculture. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 344–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.F.; Jing, S.R.; Lee, D.Y. The potential use of constructed wetlands in a recirculating aquaculture system for shrimp culture. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 123, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadlec, R.; Wallace, S. Treatment Wetlands, 2nd ed.; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ayoub, G.M.; Saikaly, P. The combined effect of step-feed and recycling on RBC performance. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3009–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, S.; Teixeira, P.; Oliveira, R.; Mota, M. Rotating biological contactors: A review on main factors affecting performance. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2008, 7, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eding, E.; Kamstra, A.; Verreth, J.; Huisman, E.; Klapwijk, A. Design and operation of nitrifying trickling filters in recirculating aquaculture: A review. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 234–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, R.F.; Beecher, L.E. Use of floating bead filters to recondition recirculating waters in warmwater aquaculture production systems. Aquac. Eng. 2000, 22, 57–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukuda, S.; Christianson, L.; Kolb, A.; Saito, K.; Summerfelt, S. Heterotrophic denitrification of aquaculture effluent using fluidized sand biofilters. Aquac. Eng. 2015, 64, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusten, B.; Eikebrokk, B.; Ulgenes, Y.; Lygren, E. Design and operations of the Kaldnes moving bed biofilm reactors. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 322–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennard, W.A.; Leonard, B.V. A Comparison of Three Different Hydroponic Sub-systems (gravel bed, floating and nutrient film technique) in an Aquaponic Test System. Aquac. Int. 2006, 14, 539–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endut, A.; Jusoh, A.; Ali, N.; Wan Nik, W.B.; Hassan, A. A study on the optimal hydraulic loading rate and plant ratios in recirculation aquaponic system. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 1511–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrut, B.; Blancheton, J.P.; Callier, M.; Champagne, J.Y.; Grasmick, A. Foam fractionation efficiency of a vacuum airlift—Application to particulate matter removal in recirculating systems. Aquac. Eng. 2013, 54, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez-Wing, M.T.; Malone, R.F. Biological filters in aquaculture: Trends and research directions for freshwater and marine applications. Aquac. Eng. 2006, 34, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, S.S.; Ma, N.L.; Jusoh, A.; Ambak, M.A. Biological nutrient removal by recirculating aquaponic system: Optimization of the dimension ratio between the hydroponic & rearing tank components. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2015, 102, 107–115. [Google Scholar]
- Aitcheson, S.; Arnett, J.; Murray, K.; Zhang, J. Removal of aquaculture therapeutants by carbon adsorption. Aquaculture 2000, 183, 269–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, J.; Croot, P.; Von Dewitz, B.; Waller, U.; Hanel, R. Potential and limitations of ozone for the removal of ammonia, nitrite, and yellow substances in marine recirculating aquaculture systems. Aquac. Eng. 2011, 45, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T.; Sharrer, M.J.; Hollis, J.; Gleason, L.E.; Summerfelt, S.R. Dissolved ozone destruction using ultraviolet irradiation in a recirculating salmonid culture system. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 32, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- True, B.; Johnson, W.; Chen, S. Reducing phosphorus discharge from flow-through aquaculture I: Facility and effluent characterization. Aquac. Eng. 2004, 32, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masser, M.; Rakocy, J.; Losordo, T. Recirculating Aquaculture Tank Production Systems—Management of Recirculating Systems; SRAC Publication: Stoneville, MS, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Bullock, G.L.; Summerfelt, S.T.; Noble, A.C.; Weber, A.L.; Durant, M.D.; Hankins, J.A. Ozonation of a recirculating rainbow trout culture system I. Effects on bacterial gill disease and heterotrophic bacteria. Aquaculture 1997, 158, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamane, H.; Colorni, A.; Bar, I.; Ori, I.; Mozes, N. The use of an open channel, low pressure UV reactor for water treatment in low head recirculating aquaculture systems (LH-RAS). Aquac. Eng. 2010, 42, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerfelt, S.T.; Sharrer, M.J.; Tsukuda, S.M.; Gearheart, M. Process requirements for achieving full-flow disinfection of recirculating water using ozonation and UV irradiation. Aquac. Eng. 2009, 40, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nofouzi, K.; Sheikhzadeh, N.; Mohamad-Zadeh Jassur, D.; Ashrafi-Helan, J. Influence of extremely low frequency electromagnetic fields on growth performance, innate immune response, biochemical parameters and disease resistance in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Fish Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 41, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stickney, R.R. Aquaculture: An Introductory Text; CAB International: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]















© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vilbergsson, B.; Oddsson, G.V.; Unnthorsson, R. Taxonomy of Means and Ends in Aquaculture Production—Part 4: The Mapping of Technical Solutions onto Multiple Treatment Functions. Water 2016, 8, 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110487
Vilbergsson B, Oddsson GV, Unnthorsson R. Taxonomy of Means and Ends in Aquaculture Production—Part 4: The Mapping of Technical Solutions onto Multiple Treatment Functions. Water. 2016; 8(11):487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110487
Chicago/Turabian StyleVilbergsson, Bjorgvin, Gudmundur V. Oddsson, and Runar Unnthorsson. 2016. "Taxonomy of Means and Ends in Aquaculture Production—Part 4: The Mapping of Technical Solutions onto Multiple Treatment Functions" Water 8, no. 11: 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110487
APA StyleVilbergsson, B., Oddsson, G. V., & Unnthorsson, R. (2016). Taxonomy of Means and Ends in Aquaculture Production—Part 4: The Mapping of Technical Solutions onto Multiple Treatment Functions. Water, 8(11), 487. https://doi.org/10.3390/w8110487






