Abstract
Drainage networks are essential compartments in an urban infrastructure system for the efficient collection and prompt drainage of flood water. In addition to the advances in numerical techniques on urban flood simulation, the topological characteristics of urban drainage networks and their impacts on flooding have not been investigated thoroughly despite their importance. This study evaluated the urban drainage networks in Seoul, South Korea, in terms of the network configuration and its implication for peak flows and flood mitigation. Gibbs’ model was used to analyze the network configuration of 31 urban catchments with various slope ranges. The results showed that urban drainage networks can be less efficient than river in nature in terms of the drainage time, which is counter-intuitive. On the other hand, the analysis showed that efficient networks have risks of flood concentration and, hence, increase potential flood risks. This study showed that efficient networks tend to have higher peak flows at the outlet and vice versa. Therefore, an alternative drainage network layout, which is less efficient and more sinuous, was introduced and it resulted in reduced peak flows and flooding. This result shows managing a proper drainage network layout can contribute to flood mitigation in urban catchments.
1. Introduction
In 2010 and 2011, the metropolitan city of Seoul, South Korea suffered from floods that the city had not experienced before. Seoul had a record flood in 1990, which was caused by flooding of the Han River that crosses the city. Since the flood in 1990, the city government has invested heavily to reinforce the levees and pumping stations primarily to prevent a similar flood. In contrast to their predecessors, the floods in 2010 and 2011 were both caused by local heavy rainstorm converged on very small areas rather than by flooding from the Han River. In particular, the flood damage in 2011 was caused by heavy rainfall; more than 200 mm fell over a six hour periods on 27 July in Gangnam areas, which have a high-density of assets and population in the southeastern part of Seoul. Seoul has a design criteria for drainage networks to deal with rainfall amount of a 30 year-return period. The heavy rainfall in 2011 at the Gangnam area was equivalent to the rainfall-amount of a 50 year-return period, which was slightly greater than the design standards, resulting in flooding of more than four square kilometers of the city’s heart near Gangnam subway station [1].
Flood disasters are the main cause of losses from natural hazards and are responsible for a large number of damaging events that threaten human safety [2]. With urbanization and climate change, many cities face increasing flooding risks playing a significant role in people’s lives and the economy. Although there have been advances in the study of urban flood [3,4,5,6,7,8], most efforts have been concentrated on improving the accuracy of flood modeling in urban areas with complex geometry using cutting edge numerical methods and observations. Drainage networks are essential compartments in an urban infrastructure system for the most efficient collection and prompt drainage of flood water. On the other hand, despite their importance, the geomorphological characteristics of urban drainage networks and their impacts on flooding have not been investigated thoroughly compared to precise numerical schemes.
The relationship between the drainage network topology and shape of hydrographs has been a long standing topic in hydrology [9,10]. The configuration of the drainage network layout depends strongly on the problem size, location of the outlet, and the topography of a catchment. In contrast, the small difference in the elevation in flat areas makes the problems totally different [11]. There is no guidance, such as topography, for a designer to delineate the layout of a drainage network. In general, drainage networks in urban catchments aim at the efficient collection and prompt drainage of water as much as possible. Seo and Schmidt [12,13] examined the drainage networks of the southwestern part of Chicago, where the catchments are located at flat areas. The results revealed a wide range of network configurations in urban drainage networks in the flat areas in southwestern Chicago.
Seo and Schmidt [12] utilized the one-parameter Gibbs’ model [14] to categorize the networks. As the parameter (β) tends to be zero, the resulting Gibbs’ model is close to the uniform model [15,16] whereas the Gibbs’ model is close to the Scheidegger model [17] as the parameter tends to infinity. The Gibbs’ model is based on Gibbs’ measure [18], which has maximum entropy and properties of a Markov random field [19]. As a stochastic network model, Gibbs’ model is useful for categorizing an existing network, and also useful for generating an alternative layout of the drainage network. Seo and Schmidt [13] reported that Gibbs’ model is efficient in terms of reproducing the original width function of a corresponding urban catchment. Seo and Schmidt [20,21] also, evaluated drainage networks under moving storms using Gibbs’ model.
As Haghighi [11] mentioned, in steep areas, drainage networks are typically cost-effective if they are designed based on the topography. In contrast, in flat areas like Chicago, there are not only efficient and optimized networks in terms of the drainage time, but also inefficient and highly sinuous networks as reported by Seo and Schmidt [12]. Combined with the effects of network topology on the resulting hydrographs of a catchment, the configuration of drainage network layout can be a crucial point in terms of mitigating the flood risks in urban catchments.
In this regard, this study examined urban drainage networks in Seoul in terms of the network configuration and its implication for peak flows and flood mitigation. Gibb’s model was used to analyze the network configuration, and the parameter, β, of Gibbs’ model was used to represent the configuration. Compared to previous studies on flat areas [12,14], the methodology was evaluated for a range of urban catchments, which are hilly and have suffered from inundation in recent years. A test catchment (Seocho4) was selected among 31 catchment to demonstrate the effect of drainage network layout on the peak flows of the resulting hydrographs by comparing the hydrographs from the original network and Gibbs’ model. Actual rainfall records in 2011 were used for this purpose to show how network layout affects the peak flows and floods.
2. Methods
2.1. Gibbs’ Model
Gibbs’ model sets the probability based on Gibbs’ measure, which originated from the Ising model [18]. Any positive measure with the property of a Markov random field can be regarded a Gibbs’ measure with an appropriate energy function [19]. The stochastic network model based on Gibbs’ measure [14] defined a Markov chain with the spanning trees S as the state space. A tree is a graph in which any two vertices are connected by precisely one simple path and a spanning tree is an acyclic tree connecting all points in the network without loops or cycles. Let s belongs to Ss and two trees, s1 and s2, be adjacent if one can be obtained from the other. To achieve this, a point must be selected randomly in s1 and a new direction defined from that point will be a new spanning tree, s2. The transition probability from s1 to s2, Rs1s2, can be defined as follows [14]:
where N(s1) is the set of trees adjacent to s1, and β is a parameter that represents the extent to which the sinuosity of the network is reflected in the generation of the new spanning tree, s2. For example, when β is equal to zero, the overall sinuosity of a network has no relationship with the transition probability and the transition probabilities are the same in all possible directions, which is identical to the uniform distribution. The maximum degree of the points in S, r, is defined as follows [14]:
The degree, r, refers to the maximum number of directions that can be selected, except for the existing direction. H(s) is a measure of the sinuosity of a given spanning tree, s:
where s is a spanning tree, d is a point of a finite and connected graph B, and D(B) is the set of the total points of B. ξs is the distance to an outlet along s from v, while ξB is the shortest distance to the outlet from d. During every generation of adjacent spanning trees, a check is made to determine if there is any loop inside the network.
As shown in Figure 1, Gibbs’ model was simulated for one of the test catchments, Seocho4, for each value of the parameter, β. The thickness of the network represents the maximum width function at that location. The width function can be converted easily to a unit hydrograh. Therefore, the thickness can be interpreted as the maximum peak flow at each point. In this regard, the magnitude of the peak flow at the outlet itself is higher on Gibbs’ model with a greater value of β (e.g., when β = 100 in Figure 1) compared to the model with a smaller value of β (For example, when β = 10−4). Figure 1 shows that the maximum peak flows are observed not only at the outlet but also in other parts of the mainstream on Gibbs’ model with a smaller value of β. In contrast, although the magnitude of the peak flow is higher with larger β values, the maximum peak flow is observed near the outlet as β increases. A comparison of the flow distribution of Gibbs’ model indicates a close relationship between the spatial distribution of the peak flows and the drainage network, which is related directly to the risk of the corresponding drainage system.
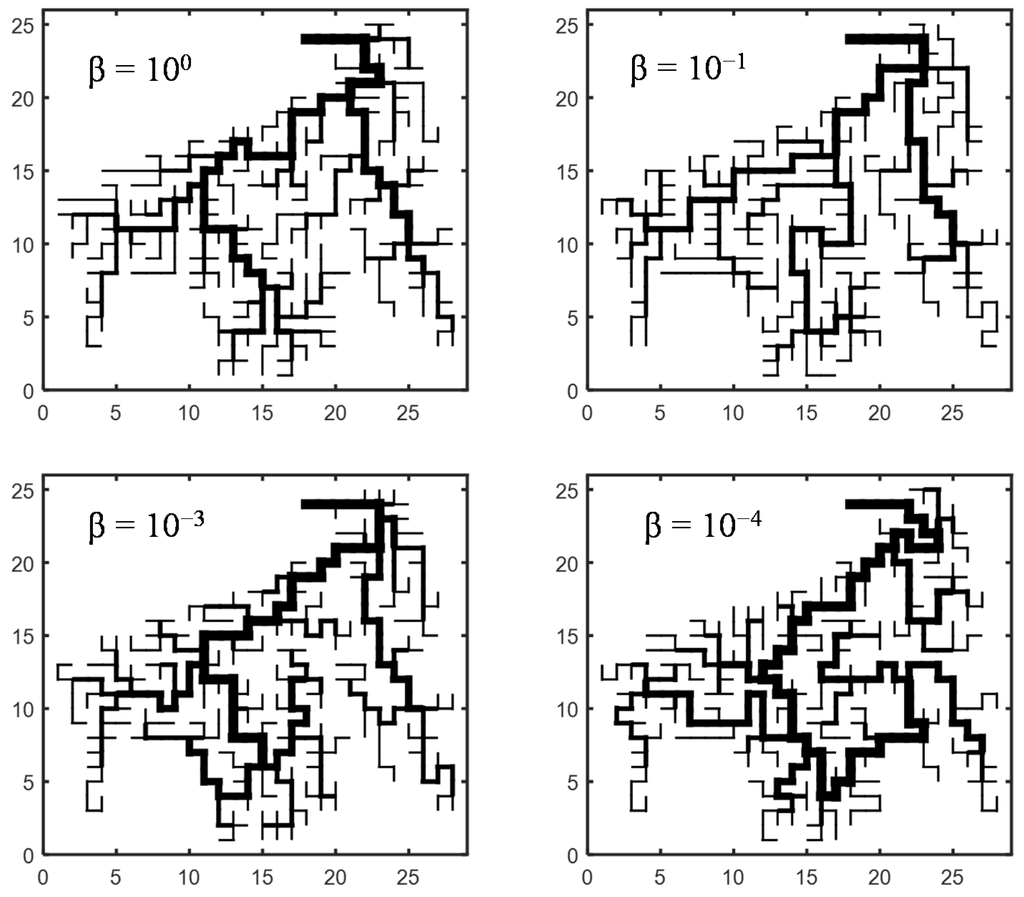
Figure 1.
Gibbs’ model generated for a test catchment, Seocho4 for each β with a grid size of 50 m. The horizontal and vertical axis denote distance by number of grids.
Figure 2 shows the width function of Gibbs’ model (Figure 1) at the outlet of the test catchment, Seocho4. As shown in Figure 2a, the total distance from the outlet becomes shorter as β increases whereas the peak becomes larger. Figure 2b shows the maximum value of Gibbs’ model averaged after one hundred simulations. Owing to the nature of stochastic network model, the averaged maximum value with β equal to 100 is smaller than that with β equal to 10−1, but the trend shows that the maximum value of the width function at the outlet tends to increase with β. This is important because, as mentioned earlier, the width function is related directly to the hydrologic response of a drainage network. Figure 2 shows that the peak flows of a drainage network are highly dependent on the configuration of the layout.
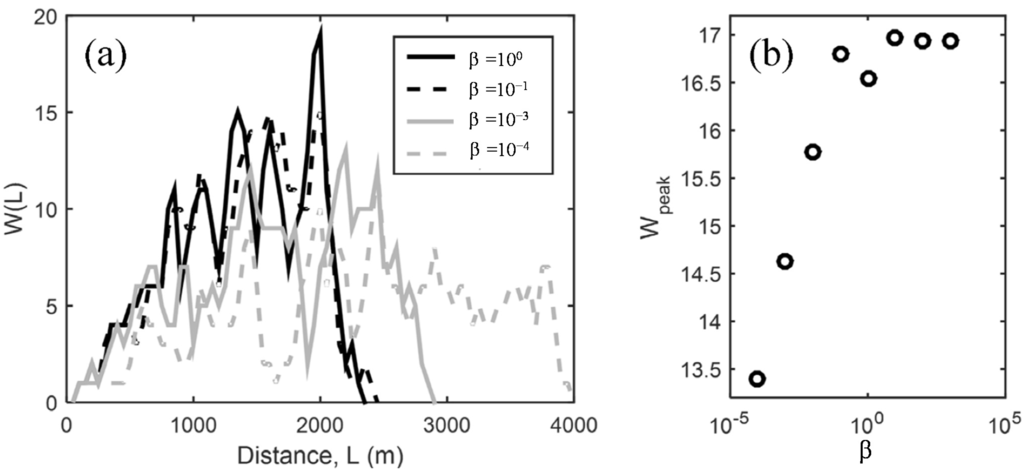
Figure 2.
(a) The width function at the outlet of Gibbs’ model depending on β and (b) the maximum value of the width functions averaged over 100 simulation for each β for a test catchment, Seocho4.
2.2. Study Area and Estimation of Beta
The metropolitan city of Seoul is composed of 238 catchments (Figure 3). The Han River crosses the city. The shaded area also shows the flooded areas caused by flash storms in 2010 and 2011. The storms converged on the southern part of Seoul. In particular, the damages that occurred in 2010 and 2011 were focused primarily on the southeastern (Shinweol) and southwestern areas (Gangnam), which have a high density of assets and population. Among the 238 catchments, the black-lined catchments in Figure 3 with flood damages in 2010 and 2011 were selected to estimate the value of β. Table 1 lists the test catchments selected in Seoul in this study. The areas of the selected test catchments ranges from 0.32 to 5.43 km2 and the mean area is 1.90 km2. The catchment slopes are rather steep, ranging from 2.92% to 19.32% with an average of 8.57%. The conduit slopes range from 0.67% to 7% with an average of 4%.
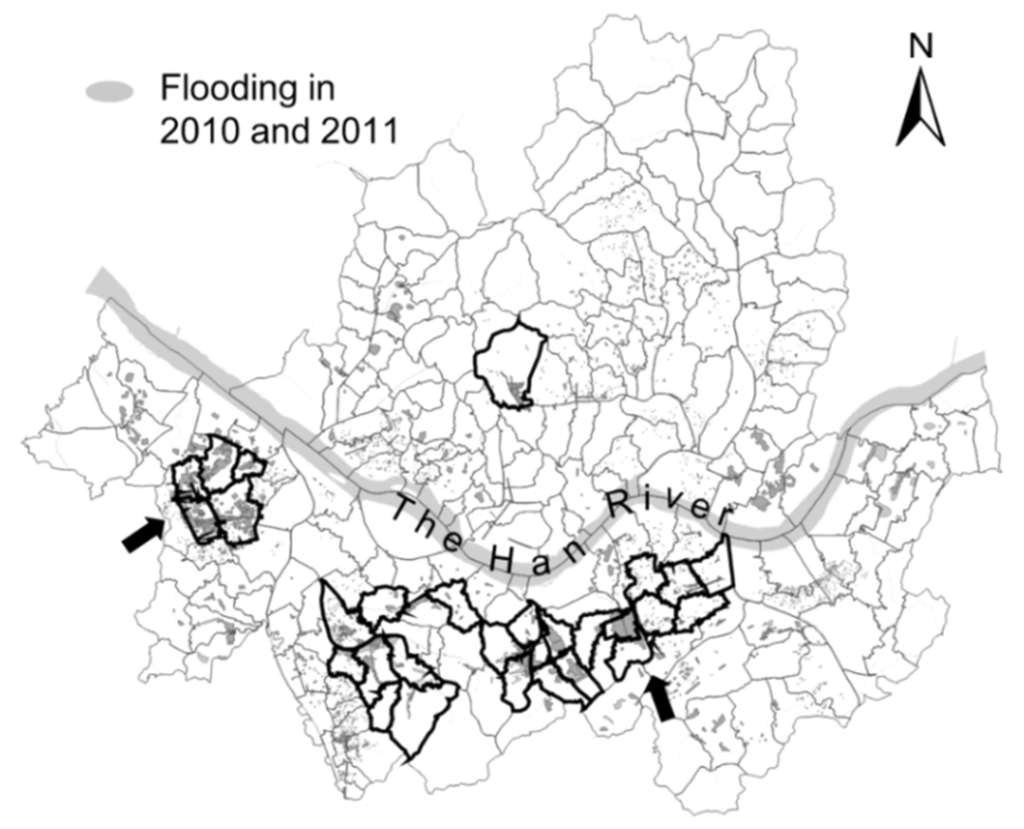
Figure 3.
Test catchments in Seoul: the black-lined catchments were selected to estimate the value of β; flood damages in 2010 and 2011 primarily occurred in the southwestern areas (Shinweol) and also southeastern areas (Gangnam).
This study used the width function to estimate β for each catchment. The width function is defined as the catchment area at a distance from the outlet [22]. The width function and the area function can be defined differently based on the channelization [23] but the width function basically represents the distance-area function [24]. In this study, the width function was defined as the number of grid points for a given distance from the outlet [12,20]. The value of β that best represents the network width function of a catchment was selected. The procedure is as follows: First, a drainage network was reconstructed on a lattice, from which the actual width was calculated. Using the previously simulated Gibbs’ models (one hundred simulation) for each beta, the width functions were then averaged with respect to distance from the outlet. The Nash-Sutcliffe model efficiency, E, was used to select the value of β that best respresented the original drainage network. Figure 4 presents the process of estimation for a catchment, BangBae3. The gray shaded areas are located between 25% and 75% quartiles. The dots are the averaged width function from Gibbs’ model. The model efficiency, E, increased to 0.96 for a value of β equal to 100 for BangBae3, which is one of the catchments, where flood occured in both 2010 and 2011.

Table 1.
Test catchments selected for study.
| No | ID | Catchment | Area (Aw) | Perimeter (Bp) | Drainage Density (D) | Conduit Slope (Sp) | Catchment Slope (Sc) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | km | m/m2 | % | % | |||
| 1 | NH | Nonhyeon | 1.80 | 8.24 | 0.028 | 5.633 | 6.959 |
| 2 | DR | Daelim | 1.25 | 5.92 | 0.024 | 3.565 | 3.721 |
| 3 | DO | Daebang | 2.02 | 8.09 | 0.026 | 3.430 | 4.733 |
| 4 | DG | Dogok | 1.82 | 7.33 | 0.022 | 3.377 | 4.330 |
| 5 | DLO | Dorim1 | 2.71 | 9.10 | 0.037 | 0.668 | 2.921 |
| 6 | DCW | Deungchon2 | 0.87 | 4.57 | 0.022 | 5.638 | 8.461 |
| 7 | BBW | Bangbae2 | 1.37 | 7.62 | 0.026 | 4.107 | 9.395 |
| 8 | BBT | Bangbae3 | 1.66 | 7.31 | 0.011 | 6.270 | 17.273 |
| 9 | BBF | Bangbae4 | 1.56 | 7.05 | 0.010 | 5.382 | 17.392 |
| 10 | SD | Sadang | 1.83 | 6.81 | 0.021 | 4.448 | 11.364 |
| 11 | SSO | Samsung1 | 1.91 | 7.98 | 0.026 | 3.784 | 4.850 |
| 12 | SSW | Samdung2 | 2.10 | 6.88 | 0.021 | 3.076 | 5.822 |
| 13 | SDW | Sangdo2 | 1.94 | 7.76 | 0.028 | 3.321 | 9.451 |
| 14 | SCO | Seocho1 | 1.89 | 8.59 | 0.019 | 4.801 | 7.846 |
| 15 | SCT | Seocho3 | 1.79 | 8.69 | 0.017 | 3.437 | 6.959 |
| 16 | SCF | Seocho4 | 1.06 | 6.06 | 0.024 | 3.126 | 3.112 |
| 17 | SH | Shiheunggoji | 1.60 | 8.61 | 0.022 | 4.604 | 10.007 |
| 18 | SLA | Sillim1 | 1.98 | 8.84 | 0.033 | 4.489 | 9.503 |
| 19 | SLW | Sillim2 | 4.35 | 10.56 | 0.012 | 5.670 | 18.232 |
| 20 | SLM | Sillim3 | 1.36 | 5.82 | 0.019 | 6.996 | 19.319 |
| 21 | SLF | Sillim4_1 | 0.32 | 2.71 | 0.033 | 1.408 | 3.221 |
| 22 | SLF | Sillim4_2 | 2.23 | 9.08 | 0.025 | 3.342 | 9.953 |
| 23 | SWO | Sinwol1 | 1.52 | 7.46 | 0.025 | 2.663 | 5.205 |
| 24 | SWT | Sinwol3_1 | 1.20 | 5.77 | 0.035 | 2.345 | 3.014 |
| 25 | SWT | Sinwol3_2 | 0.52 | 3.48 | 0.027 | 2.540 | 3.539 |
| 26 | YS | Yeoksam | 1.93 | 7.40 | 0.030 | 3.637 | 4.996 |
| 27 | LM | Yimok | 2.09 | 8.37 | 0.023 | 5.372 | 11.820 |
| 28 | IS | Yisu | 1.37 | 5.62 | 0.024 | 4.211 | 10.168 |
| 29 | HGO | Hwagok1 | 2.28 | 7.22 | 0.025 | 4.404 | 9.820 |
| 30 | HKW | Hwagok2 | 3.26 | 10.07 | 0.029 | 3.969 | 6.243 |
| 31 | HY | Hyoja | 5.43 | 10.97 | 0.016 | 4.263 | 16.030 |
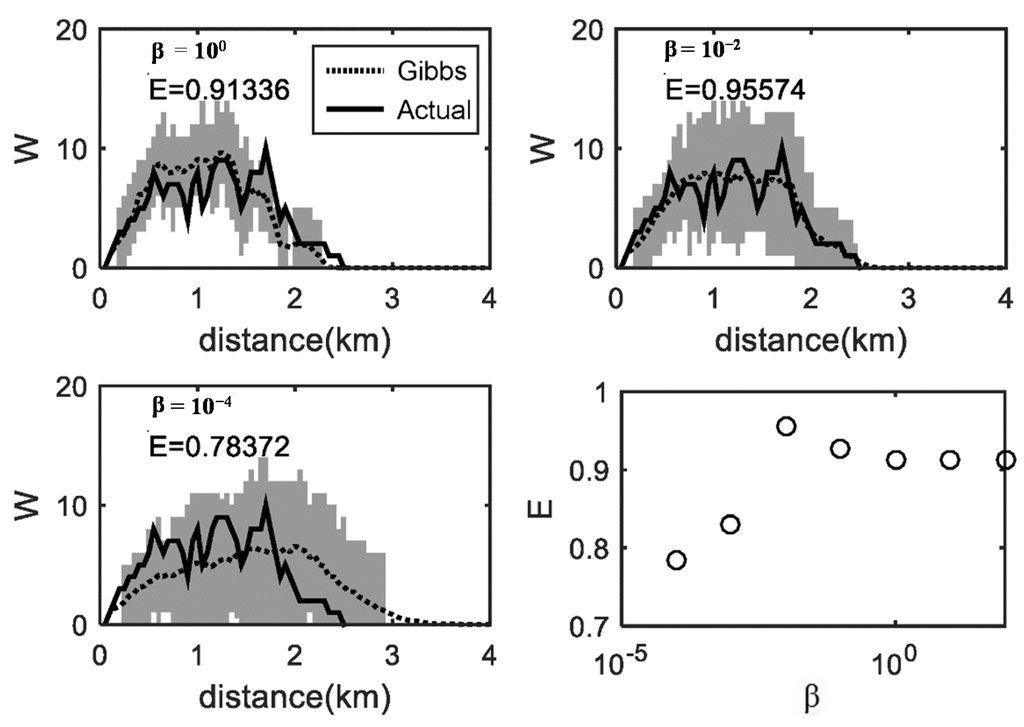
Figure 4.
Comparison of the width functions from the actual and simulated drainage networks; the resulting E is plotted as a function of β for a test catchment, BangBae3; the shaded area represents interval between the 25% and 75% quartiles.
2.3. Flood in 2010 and 2011 in a Test Catchment, Seocho4
Recent rainfall events were likely to have occurred under the influence of climate change. The climate variability and change have direct consequences on global flood hazards [25]. The increased frequency of the occurrence of flood events in the world is partially attributed to the climate change-driven increase in extreme precipitation [26]. Climate change is making weather less predictable, rains more uncertain and heavy storm rainfalls more likely [27]. The quantitative estimation of the impact of climate change on small-scale and extreme rainfall events is a developing research area, and there is a large degree of uncertainty with the current estimates [26].
As mentioned previously, the floods in 2010 and 2011 were caused mainly by the insufficient conveyance capacity of drainage networks. Previous floods in Seoul were due to inundation of the Han River or rising water surface elevation of the Han River accompanied by the insufficient pumping capacity. Therefore, the city government has invested in the reinforcement of levees and pumping stations primarily to prevent flooding from the Han River. In contrast to historical floods in Seoul, the floods both in 2010 and 2011 were caused by local heavy rainfall converging on very small areas of Seoul rather than by the Han River. In particular, the flood damage in 2011 was caused by heavy rainfall, more than 200 mm, during 6 h on July 27 in Gangnam areas, which have a high-density of assets and population in the southeastern part of Seoul. Seoul has the design criteria for drainage networks to deal with the rainfall amount of a 30 year-return period. The heavy rainfall in 2011 at the Gangnam area was equivalent to the rainfall-amount of a 50 year-return period, which is slightly greater than the design standards resulting in flooding over more than four square kilometers of the city’s heart near the Gangnam subway station [8]. Figure 5a presents Seocho4, which is one of the catchments around the Gangnam subway station that was flooded in both 2010 and 2011. The flood in 2010 was greater than that in 2011. Figure 5b shows the drainage network and topography of Seocho4. The arrow in Figure 5b indicates the flooded location where the conveyance capacity of the conduit was insufficient. The analysis shows that the overflowed water flows along the street and contributed to the flooding of the Gangnam subway station consequently [1].
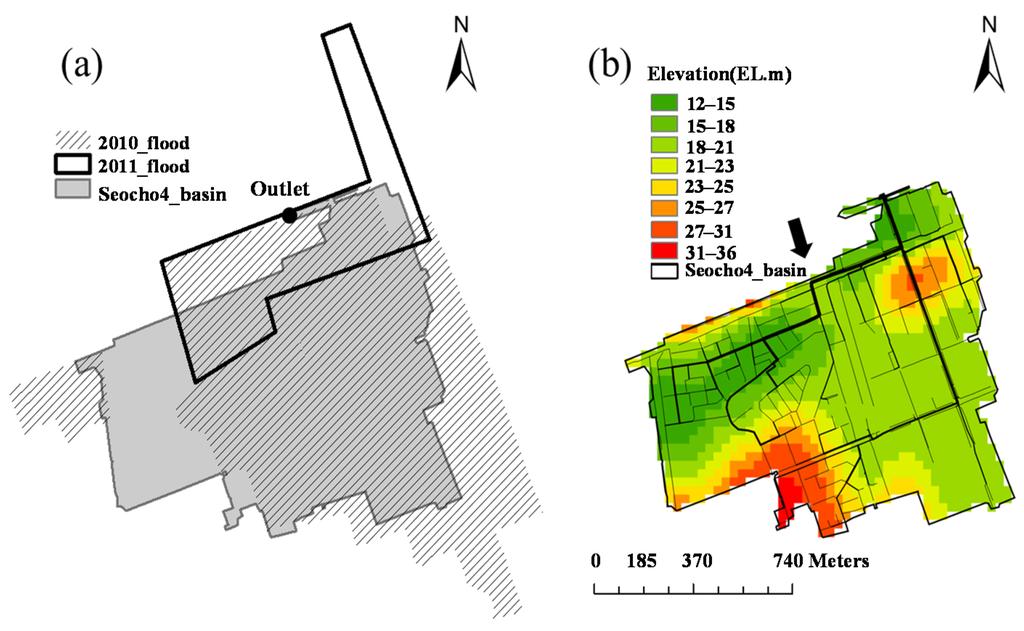
Figure 5.
(a) Test catchment, Seocho4 with flooded areas reported; (b) drainage network and topography.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Network Configuration of Urban Catchments in Seoul
Using the methodology described in the previous section, the network configuration of 31 drainage networks in Seoul was estimated. A constant grid size of 50 m was used to reconstruct the original network and also simulate Gibbs’ model to estimate the value of β. As mentioned earlier, the catchment slopes are rather steep from 2.92% to 19.32% with an average of 8.57%. The conduit slope ranges from 0.67% to 7% with an average of 4%. Seo and Schmidt [12] examined the value of β of Chicago area and found that β ranges form 10−2 to 102, where the catchment slope ranges from 0.51% to 1.05% with an average catchment slope of 0.8%. Although the catchments of Chicago and Seoul have similar average catchment areas, 2.81 and 1.90 square kilometers, they have significant difference in catchment slope; the average slope (8.57%) of Seoul’s catchments is more than 10 times steeper than that (0.80%) of Chicago areas.
Table 2 lists the values of β estimated for the 31 catchments in Seoul. The columns, n and m are the number of rows and columns used to reconstruct drainage networks. The goodness of fit is the Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency to determine the value of β, as shown in Figure 4. The Nash-Sutcliffe model efficiency ranges from 0.52 to 0.99 and the average is 0.83, which shows that Gibbs’ model successfully simulates the original drainage network. The result shows that the value of β ranges from 10−4 to 103, which is even wider than that of Chicago (10−2–102) reported by Seo and Schmidt [12]. Troutman and Karlinger [14] examined the value of beta in mountainous areas in Montana and found that rivers have the mean value of beta equal to 100. Seo et al. [28] showed that rivers in nature are close to the Scheidegger model, which is equivalent to Gibbs’ model with β of infinity. These previous studies show that rivers have evolved and transformed themselves to very efficient states in terms of drainage time. In contrast, the analysis using Gibbs’ model shows that urban drainage network can be less efficient compared to rivers.
As Haghighi [11] mentioned, in steep areas, the drainage networks are typically cost-effective if they were designed based on the topography. In contrast, in flat areas such as Chicago, there are not only efficient and optimized networks in terms of the drainage time or construction cost, but also inefficient and highly sinuous networks [12,13]. On the other hand, the analysis of catchments in Seoul, where the catchment slope is 10 times steeper than that of the Chicago catchments, still showed that the drainage network can be highly ineffective in terms of the drainage time.
Figure 6a shows the distribution of β for the 31 test catchments in Seoul, which shows a wide range of network configurations. As shown in Figure 2b, once β > 100, Gibbs’ model revealed little difference in the increased peak of the width function. Seo and Schmidt [13] also reported that Gibbs’ model does not demonstrate a difference in terms of the flow distance with β > 100. Therefore, a network with β ≥ 100 can be referred to as effective in terms of the drainage time. In this regard, among the 31 drainage networks analyzed in this study, 13 catchments (shaded bar in Figure 6a), which have values of β ≥ 100, are efficient in terms of the drainage time. The 31 test catchments analyzed in this study were selected among the catchments that suffered floods in 2010 and 2011. Therefore, these results suggest that an efficient network in terms of drainage time does not necessarily help protect the corresponding catchment from a flood. Obviously, there are many factors affecting the flooding condition of a catchment. The next section shows how the network configuration affects the resulting flood in the next section using the test catchment Seocho4 and historical storm simulations in 2010 and 2011 by applying different configurations of a drainage network.

Table 2.
Network configuration of drainage networks in Seoul.
| No | ID | Catchment | Basin Area (Aw) | Grid Size | n | m | Goodness of Fit (E) | O(β) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | m | |||||||
| 1 | NH | NonHyeon | 1.80 | 50 | 43 | 34 | 0.77 | 10−4 |
| 2 | DR | DaeLim | 1.25 | 50 | 24 | 27 | 0.91 | 10−2 |
| 3 | DO | DaeBang | 2.02 | 50 | 34 | 39 | 0.62 | 101 |
| 4 | DG | DoGok | 1.82 | 50 | 27 | 42 | 0.70 | 10−2 |
| 5 | DLO | DoRim1 | 2.71 | 50 | 48 | 36 | 0.52 | 10−4 |
| 6 | DCW | DeungChon2 | 0.87 | 50 | 22 | 21 | 0.99 | 10−1 |
| 7 | BBW | BangBae2 | 1.37 | 50 | 41 | 27 | 0.91 | 101 |
| 8 | BBT | BangBae3 | 1.66 | 50 | 21 | 31 | 0.96 | 10−2 |
| 9 | BBF | BangBae4 | 1.56 | 50 | 25 | 26 | 0.96 | 10−2 |
| 10 | SD | SaDang | 1.83 | 50 | 30 | 23 | 0.82 | 100 |
| 11 | SSO | SamSung1 | 1.91 | 50 | 36 | 38 | 0.87 | 103 |
| 12 | SSW | SamDung2 | 2.10 | 50 | 41 | 33 | 0.87 | 10−1 |
| 13 | SDW | SangDo2 | 1.94 | 50 | 33 | 38 | 0.93 | 101 |
| 14 | SCO | SeoCho1 | 1.89 | 50 | 47 | 36 | 0.73 | 10−1 |
| 15 | SCT | SeoCho3 | 1.79 | 50 | 28 | 40 | 0.79 | 101 |
| 16 | SCF | SeoCho4 | 1.06 | 50 | 25 | 28 | 0.96 | 100 |
| 17 | SH | ShiHeungGoJi | 1.60 | 50 | 49 | 36 | 0.88 | 102 |
| 18 | SLA | SilLim1 | 1.98 | 50 | 42 | 42 | 0.71 | 101 |
| 19 | SLW | SilLim2 | 4.35 | 50 | 34 | 44 | 0.89 | 101 |
| 20 | SLM | SilLim3 | 1.36 | 50 | 36 | 22 | 0.92 | 101 |
| 21 | SLF | SilLim4_1 | 0.32 | 50 | 12 | 13 | 0.99 | 10−1 |
| 22 | SLF | SilLim4_2 | 2.23 | 50 | 46 | 30 | 0.77 | 103 |
| 23 | SWO | Sinwol1 | 1.52 | 50 | 31 | 24 | 0.85 | 10−1 |
| 24 | SWT | Sinwol3_1 | 1.20 | 50 | 24 | 32 | 0.80 | 10−3 |
| 25 | SWT | Sinwol3_2 | 0.52 | 50 | 15 | 22 | 0.93 | 10−1 |
| 26 | YS | YeokSam | 1.93 | 50 | 33 | 35 | 0.78 | 10−4 |
| 27 | LM | YiMok | 2.09 | 50 | 39 | 42 | 0.80 | 102 |
| 28 | IS | YiSu | 1.37 | 50 | 37 | 24 | 0.73 | 10−4 |
| 29 | HGO | HwaGok1 | 2.28 | 50 | 38 | 30 | 0.88 | 101 |
| 30 | HKW | HwaGok2 | 3.26 | 50 | 43 | 40 | 0.76 | 10−4 |
| 31 | HY | HyoJa | 5.43 | 50 | 56 | 46 | 0.70 | 101 |
Figure 6b–f shows very weak relationships between β and the catchment properties, such as area, perimeter, drainage density, conduit slope, and catchment slope. In particular, Figure 6e,f shows that there is no correlation between the network configuration and conduit or catchment slopes. Therefore, the case study of urban catchments in Seoul shows that ineffective drainage network can exist in urban catchments regardless of the catchment slope. For example, the test catchment, YiSu, has a catchment slope of 10.17% but the value of β is 10−4. In contrast, SamSung1 has a catchment slope of 4.85 but the value of β is 103.
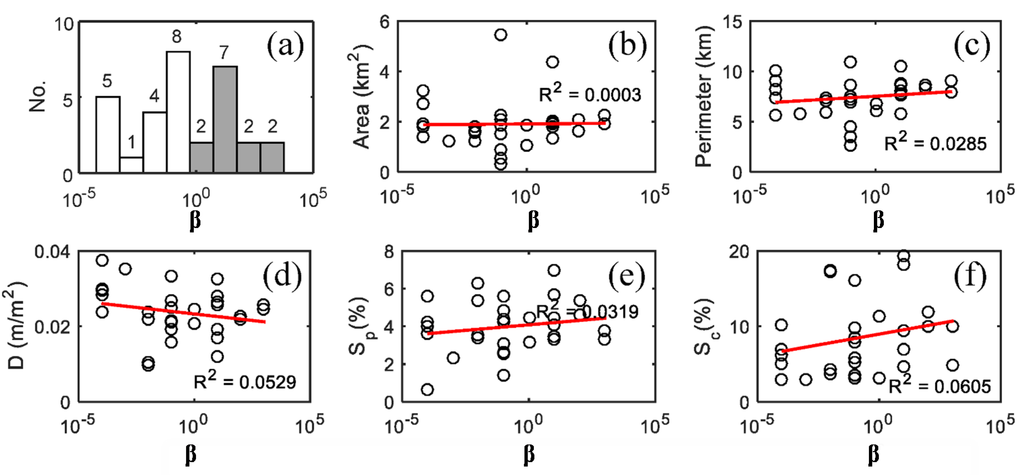
Figure 6.
(a) Distribution of β for 31 catchments in Seoul; (b) the value of β as a function of catchment area; (c) perimeter; (d) drainage density (D); (e) conduit slope (Sp) and (f) catchment slope (Sc).
3.2. The Effect of Drainage Network Layout
Note that the configuration of urban drainage network layout has no relationship with the catchment properties, such as catchment slope. This means that the configuration of the layout is not automatically or naturally determined by following topography. This also means that it is necessary to think of the configuration of drainage network layout intentionally because it has a relationship with flooding or peak flows of the drainage network runoff hydrographs [12]. To evaluate the effects of drainage network layout, a model was built using the US Environment Protection Agency (EPA) Stormwater Management Model (SWMM) of Seocho4 with the historical rainfall to reproduce the flooding condition in 2010 and 2011. A different layout was then provided by Gibbs’ model with β = 10−4 instead of the original layout, of which β = 100. Figure 7 depicts the SWMM model with the original and alternative drainage network for Seocho4. The diameters of the alternative drainage network were determined depending on the Strahler ordering. Table 3 lists the conduit information of the original network. The alternative layout (Figure 7b) was built to have the same diameter as the original network depending on the Strahler order. The impervious ratio of each grid was obtained using the land use map and the soil parameters for the Green-Ampt equation were based on the corresponding soil types [29]. Unfortunately, there is no flow record for the calibration of the SWMM model in Seocho4, but flood areas both in 2010 and 2011. The SWMM result of the original layout estimated total flooded volume of 41,328 m3 in 2010, which is close to the flooded area (Figure 5a) assuming a flooding depth of 0.25 m.
Figure 8a,b present the simulation results for storm events in 2010 and 2011, which show the cases with flooding whereas Figure 8c shows a case with no flooding with a storm event on 23 July 2014. The flooded volume in the urban surface area is shown as white bars under the hydrographs for the actual network and the grey bars denote the alternative (Gibbs’ model). The case with flooding (Figure 8a,b) showed no reduction in the peak flows. Instead, the flooded volume was reduced by 54% and 72%, respectively, compared to the actual (original) layout. In contrast, Figure 8c shows the simulation results for a rainfall event with no surcharging (flooding). The peak flow was reduced by 10.2% for the alternative layout obtained from one of Gibbs’ model with β = 10−4. The results with an alternative layout strongly highlight the importance of network configuration in terms of the reduction and mitigation of flood damages in urban environments.
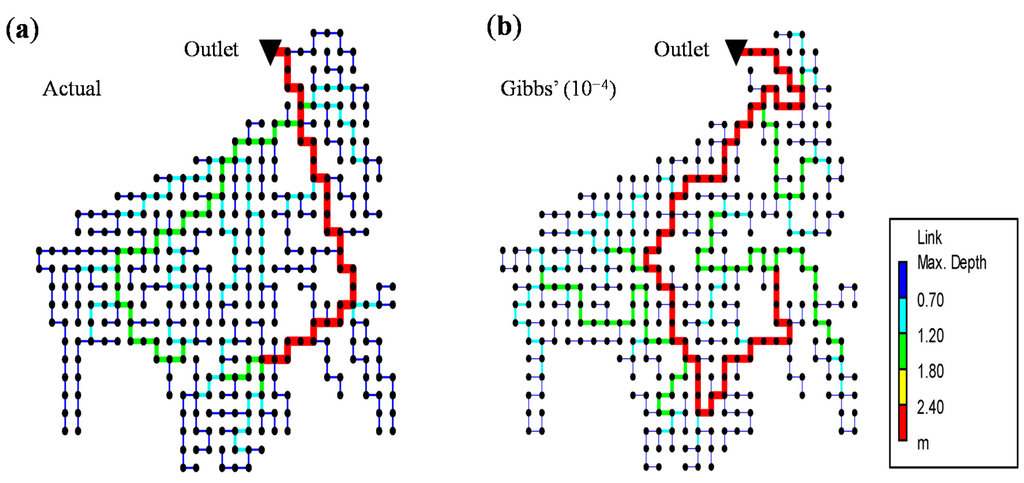
Figure 7.
(a) Actual drainage network; (b) alternative drainage network of Seocho4 built with SWMM.

Table 3.
Conduit information depending on Strahler ordering.
| Order | Diameter (m) | Sp (%) | Length (m, Averaged) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.58 | 2.72 | 37.88 |
| 2 | 0.80 | 0.19 | 31.37 |
| 3 | 1.05 | 2.97 | 30.03 |
| 4 | 2.11 | 1.02 | 40.09 |
| 5 | 2.95 | 0.35 | 31.18 |
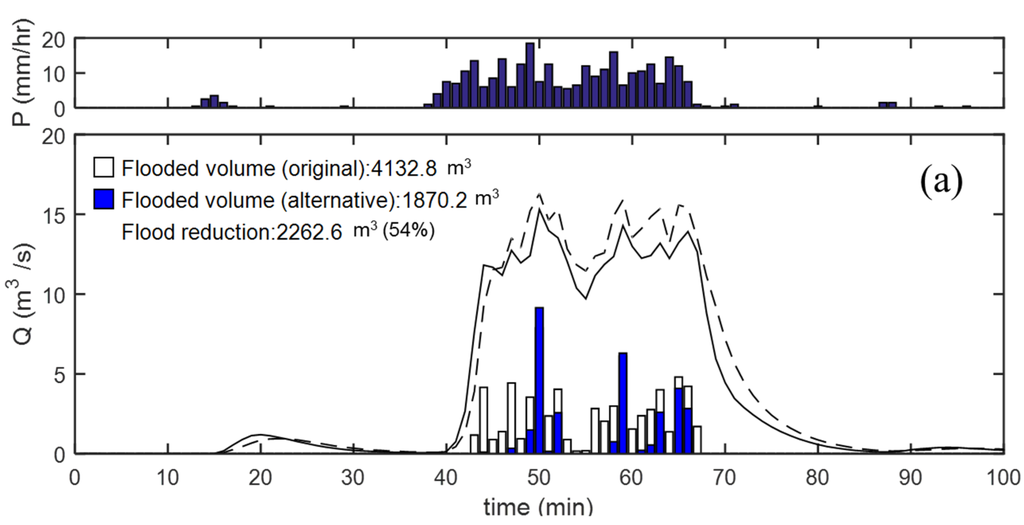
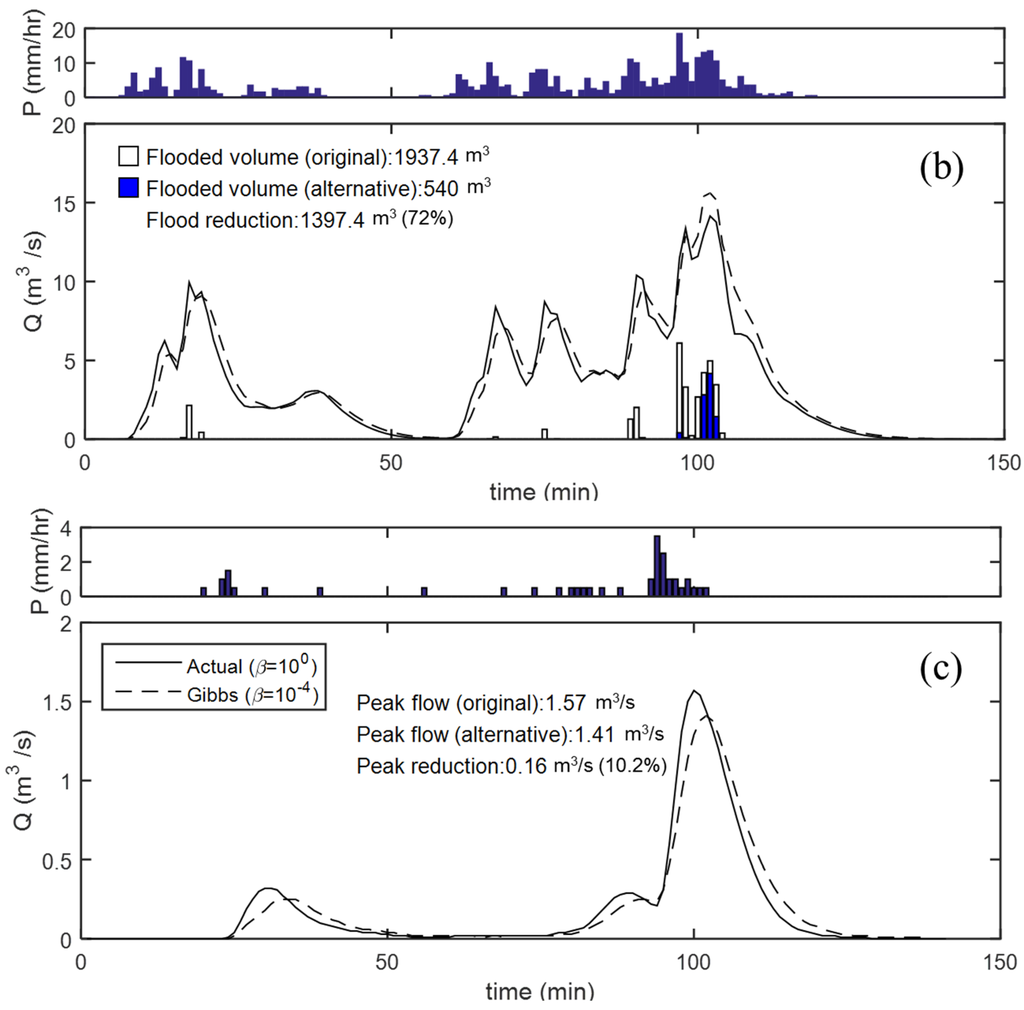
Figure 8.
Simulation results with actual and alternative layout from Gibbs’ model for storm events on (a) 21 September 2010; (b) 26 July 2011; (c) 23 July 2014.
4. Conclusions
This study analyzed the characteristics of urban drainage networks in Seoul using Gibbs’ model. The results showed that the drainage networks in Seoul have a wide range of network configurations. Combining the results from previous studies [12,14], this study showed that the network configuration has little relation with the catchment properties, such as the catchment slope. This is important because the configuration of the layout is not automatically or naturally determined by the topography. Therefore, it is necessary to consider the configuration of the drainage network layout with intent because it does have a relationship with flooding or the peak flows of the drainage network runoff hydrographs. The case study of Seoul highlights the need to seek an alternative drainage network layout. Typically, a drainage system is designed to drain water from developed areas as promptly as possible during floods. On the other hand, the case study in Seoul shows that efficient networks can have risks of flood concentration and increase potential flood risks. This study showed that efficient networks tend to have higher peak flows at the outlet in the case of no flooding. In contrast, an alternative drainage network layout of a test catchment, which is less efficient and more sinuous, resulted in reduced peak flows in the case of no flooding and also reduced flooded volume in the case of flooding. In this regard, managing a proper drainage network layout can be an alternative measure for efficient flood mitigation in urban environments.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant (14AWMP-B079364-01) from the Water Management Research Program funded by Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korean government.
Author Contributions
Seong Jin Noh proposed the basic idea, collected drainage networks, historical rainfall and flooding data in Seoul. Yongwon Seo designed the numerical experiment. Junshik Hwang conducted the simulation of network and SWMM models. The manuscript was written by Yongwon Seo with contribution from Junshik Hwang and Seong Jin Noh.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Choi, S.; Kang, S.; Han, S.; Lee, D.R. Urban flooding due to heavy rainstorm with focuses on gangnam areas in Seoul. Mag. Korea Water Resour. Assoc. 2011, 44, 25–29. [Google Scholar]
- Noh, S.J.; Tachikawa, Y.; Shiiba, M.; Kim, S. Ensemble Kalman filtering and particle filtering in a lag-time window for short-term streamflow forecasting with a distributed hydrologic model. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1684–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brodie, I.M. Rational Monte Carlo method for flood frequency analysis in urban catchments. J. Hydrol. 2013, 486, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Chen, P.A.; Lu, Y.R.; Huang, E.; Chang, K.Y. Real-time multi-step-ahead water level forecasting by recurrent neural networks for urban flood control. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.S.; Evans, B.; Djordjevic, S.; Savic, D.A. A coarse-grid approach to representing building blockage effects in 2D urban flood modelling. J. Hydrol. 2012, 426, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djordjević, S.; Prodanović, D.; Maksimović, Č. An approach to simulation of dual drainage. Water Sci. Technol. 1999, 39, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.B. A gis-based distributed parameter hydrologic model for urban areas. Hydrol. Process. 1993, 7, 45–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Wang, T.W.; Zhao, B.H. Calculation and visualization of flood inundation based on a topographic triangle network. J. Hydrol. 2014, 509, 406–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, I.; Valdes, J.B. Geomorphologic structure of hydrologic response. Water Resour. Res. 1979, 15, 1409–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saco, P.M.; Kumar, P. Kinematic dispersion in stream networks 1. Coupling hydraulic and network geometry. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghighi, A. Loop-by-loop cutting algorithm to generate layouts for urban drainage systems. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 2013, 139, 693–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Schmidt, A.R. The effect of rainstorm movement on urban drainage network runoff hydrographs. Hydrol. Process 2012, 26, 3830–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Schmidt, A.R. Application of Gibbs’ model to urban drainage networks: A case study in southwestern Chicago, USA. Hydrol. Process 2014, 28, 1148–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troutman, B.M.; Karlinger, M.R. Gibbs distribution on drainage networks. Water Resour. Res. 1992, 28, 563–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopold, L.B.; Langbein, W.B. The Concept of Entropy in Landscape Evolution; U.S. Government Printing: Washington, DC, USA, 1962. [Google Scholar]
- Karlinger, M.R.; Troutman, B.M. A random spatial network model based on elementary postulates. Water Resour. Res. 1989, 25, 793–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheidegger, A.E. A stochastic model for drainage patterns into an intramontane trench. Int. Assoc. Sci. Hydrol. Bull. 1967, 12, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ising, E. Beitrag zur theorie des ferromagnetismus. Z. für Phys. A Hadron. Nucl. 1925, 31, 253–258. (In German) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindermann, R.; Snell, J.L. Markov Random Fields and Their Applications; American Mathematical Society: Ann Arbor, MN, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, Y.; Schmidt, A.R. Network configuration and hydrograph sensitivity to storm kinematics. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1812–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Schmidt, A.R. Evaluation of drainage networks under moving storms utilizing the equivalent stationary storms. Nat. Hazard. 2014, 70, 803–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, R. What controls the width function shape, and can it be used for channel network comparison and regionalization? Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lashermes, B.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E. Area and width functions of river networks: New results on multifractal properties. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.T.; Delleur, J.W. A variable source area model of the rainfall-runoff process based on the watershed stream network. Water Resour. Res. 1976, 12, 1029–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milly, P.C.D.; Betancourt, J.; Falkenmark, M.; Hirsch, R.M.; Kundzewicz, Z.W.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Stouffer, R.J. Stationarity is dead: Whither water management? Science 2008, 319, 573–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachauri, R.K.; Reisinger, A. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change(IPCC): Geneva, Switzerland, 2007; p. 104. [Google Scholar]
- Huong, H.T.L.; Pathirana, A. Urbanization and climate change impacts on future urban flooding in Can Tho city, Vietnam. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 379–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, Y.; Schmidt, A.R.; Kang, B. Multifractal properties of the peak flow distribution on stochastic drainage networks. Stoch. Env. Res. Risk A 2014, 28, 1157–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mays, L.W. Water Resources Engineering; John Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).