Quantitative Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Water-Surface Area Variations from the 1990s to 2013 in Honghu Lake, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Region and Data Source
2.1. Study Region
2.2. Data Source

3. Methods
3.1. Extraction of Water-Surface Area
3.2. Influence Factors of Water-Surface Area Variations
3.2.1. Precipitation and Evaporation Estimate
3.2.2. Land Use Change
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Variation Characteristics of Honghu Lake

| Month | Area/Year | January | February | March | April | May | June | July | August | September | October | November | December |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Area | 293.75 | 298.53 | 298.90 | 280.99 | 295.97 | 283.37 | 294.89 | 282.47 | 303.26 | 294.23 | 295.12 | 296.06 |
| Year | 2004 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2003 | 2000 | 2003 | 2010 | 1996 | 2010 | 2003 | 1996 | |
| Minimum | Area | 258.65 | 218.89 | 230.04 | 140.20 | 153.49 | 232.43 | 243.04 | 237.27 | 208.69 | 198.02 | 236.25 | 242.07 |
| Year | 2013 | 1989 | 2006 | 2011 | 2011 | 2010 | 2012 | 2012 | 2001 | 2001 | 2001 | 2001 | |
| Max/Min ratio | 1.14 | 1.36 | 1.30 | 2.00 | 1.93 | 1.22 | 1.21 | 1.19 | 1.45 | 1.49 | 1.25 | 1.22 | |
| Year | Area/Year | 1990’s | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum | Area | 303.3 | 298.5 | 284.6 | 290.0 | 296.0 | 293.8 | 298.9 | 266.1 |
| Month | September | February | January | December | May | January | March | January | |
| Minimum | Area | 218.9 | 261.1 | 198.0 | 243.7 | 277.4 | 217.3 | 229.6 | 200.1 |
| Month | February | August | October | March | April | April | May | April | |
| Max/Min ratio | 1.39 | 1.14 | 1.44 | 1.19 | 1.07 | 1.35 | 1.30 | 1.33 | |
| Year | Area/Year | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 1990s-2013 |
| Maximum | Area | 267.7 | 277.6 | 284.7 | 294.2 | 270.4 | 278.8 | 278.2 | 303.3 |
| Month | January | November | March | October | January | March | December | ||
| Minimum | Area | 233.3 | 220.9 | 241.4 | 217.0 | 140.2 | 197.7 | 210.7 | 140.2 |
| Month | May | October | October | May | April | April | April | ||
| Max/Min ratio | 1.15 | 1.26 | 1.18 | 1.36 | 1.93 | 1.41 | 1.32 | 2.16 | |


4.2. Influence Factors
4.2.1. Climate Factors

4.2.2. Human Activities
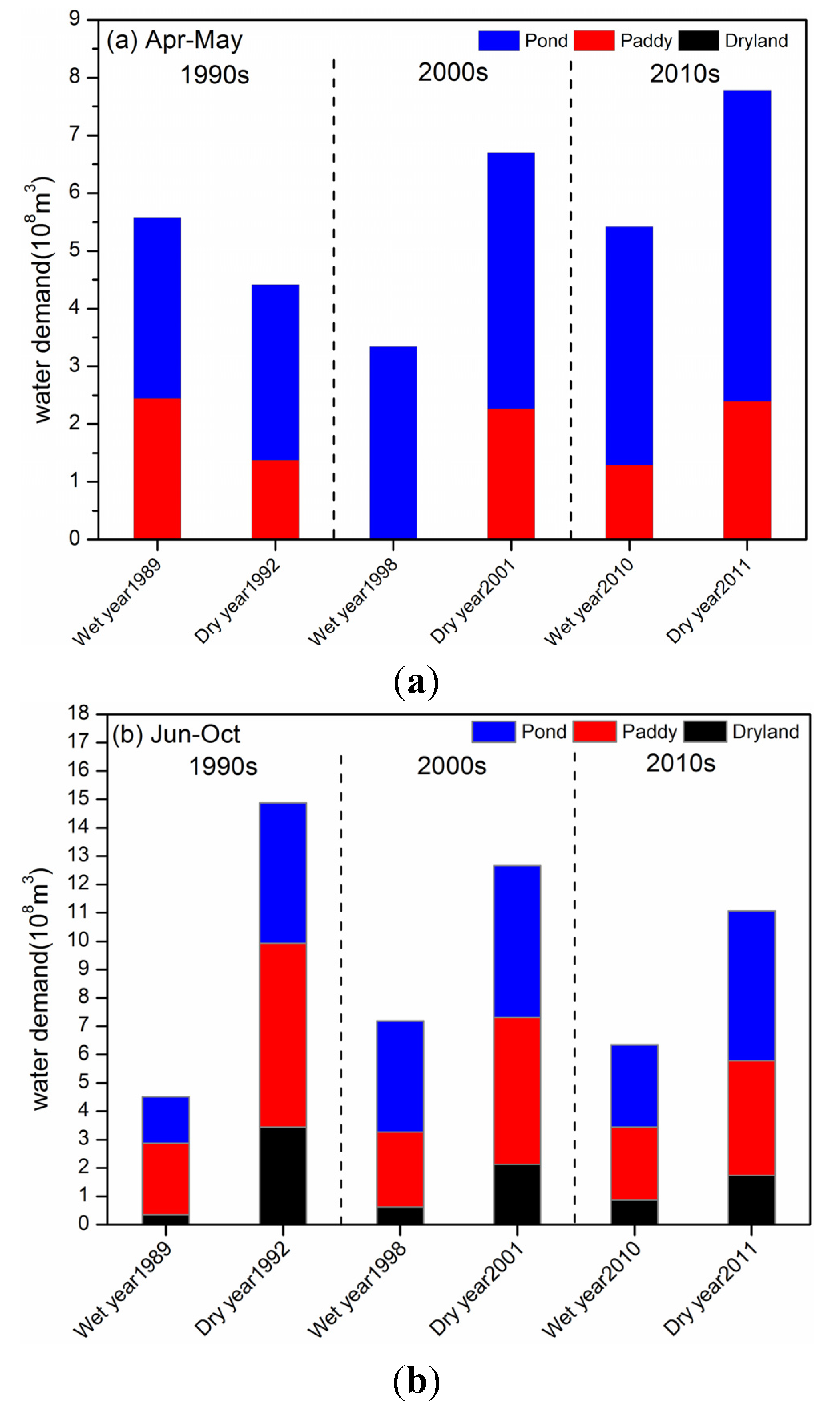
4.2.3. Comparison of the Effects of Climate Factor and Human Activities on Water-Surface Area
| Period | Multiple Linear Regression Model | R2 |
|---|---|---|
| April–May | 0.684 | |
| June | 0.643 | |
| July | 0.606 | |
| August | 0.518 | |
| September | 0.513 | |
| October | 0.234 |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Verschuren, D.; Johnson, T.C.; Kling, H.J.; Edgington, D.N.; Leavitt, P.R.; Brown, E.T.; Talbot, M.R.; Hecky, R.E. History and timing of human impact on Lake Victoria, East Africa. Proc. R. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2002, 269, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFries, R.; Eshleman, N.K. Land-Use change and hydrologic processes: A major focus for the future. Hydrol. Process. 2004, 18, 2183–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.H.; Yang, G.S.; Duan, H.T.; Jiang, J.H.; Wang, S.M.; Feng, X.Z.; Li, A.N.; Kong, F.X.; Xue, B.; Wu, J.L.; et al. China’s lakes at present: Number, area and spatial distribution. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2011, 54, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.P.; Xie, M.P.; Wu, Y.H. Quantitative analysis of lake area variations and the influence factors from 1971 to 2004 in the Nam Co basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2010, 55, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Xie, H.J.; Kang, S.C.; Yi, D.H.; Ackley, S.F. Monitoring lake level changes on the Tibetan Plateau using icesat altimetry data (2003–2009). Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.Q.; Xie, H.J.; Yao, T.D.; Kang, S.C. Water balance estimates of ten greatest lakes in China using icesat and landsat data. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 3815–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Wang, W. The response of lake change to climate fluctuation in north Qinghai-Tibet Plateau in last 30 years. J. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Y.H.; Zhu, L.P. The response of lake-glacier variations to climate change in Nam Co catchment, central Tibetan Plateau, during 1970–2000. J. Geogr. Sci. 2008, 18, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.H.; Duan, H.T.; Hu, C.M.; Feng, X.Z.; Li, A.N.; Ju, W.M.; Jiang, J.H.; Yang, G.S. A half-century of changes in China’s lakes: Global warming or human influence? Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.Y.; Teng, Y.G.; Wang, J.S. A framework of characteristics identification and source apportionment of water pollution in a river: A case study in the Jinjiang River, China. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 2071–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, X.; Wu, Q.Z.; Pan, B.Z.; Du, Y.; Feng, Q. Application of composite water quality identification index on the water quality evaluation in spatial and temporal variations: A case study in Honghu Lake, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2014, 186, 4237–4247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Xue, H.P.; Wu, S.J.; Ling, F.; Xiao, F.; Wei, X.H. Lake area changes in the middle Yangtze region of China over the 20th century. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.T.; Wen, X.F.; Liu, K.Q.; Tan, D.B.; Cao, B. Dynamics change of water surface area and its driving force analysis for Honghu Lake in recent 40 years based on remote sensing technique. In Proceedings of the 2013 Fifth International Conference on Measuring Technology and Mechatronics Automation, Hongkong, China, 16–17 January 2013; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 500–506.
- Wen, X.; Hu, D.; Cao, B.; Shen, S.; Tang, X. Dynamics change of Honghu Lake’s water surface area and its driving force analysis based on remote sensing technique and topmodel model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2014, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, M.H.; Wang, X.L.; Wu, H.J.; Cai, S.M.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, H.L. Ecosystem health assessment of Honghu Lake wetland of China using artificial neural network approach. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2009, 19, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. http://glovis.usgs.gov// (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- China Centre for Resources Satellite Data and Application. http://www.cresda.com/n16/index.html (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Wang, Q.A.; Wu, C.Q.; Li, Q.; Li, J.S. Chinese HJ-1A/B satellites and data characteristics. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2010, 53, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System. http://cdc.cma.gov.cn/home.do (accessed on 10 June 2015).
- Gao, Y.; Mas, J.F.; Maathuis, B.H.P.; Zhang, X.M.; van Dijk, P.M. Comparison of pixel-based and object-oriented image classification approaches––A case study in a coal fire area, Wuda, Inner Mongolia, China. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 4039–4055. [Google Scholar]
- Frohn, R.C.; Autrey, B.C.; Lane, C.R.; Reif, M. Segmentation and object-oriented classification of wetlands in a karst Florida landscape using multi-season Landsat-7 ETM+ imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 32, 1471–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.J.; Meng, Q.Y.; Gu, X.F.; Jancso, T.; Yu, T.; Wang, K.; Mavromatis, S. A hybrid method combining pixel-based and object-oriented methods and its application in Hungary using Chinese HJ-1 satellite images. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2013, 34, 4655–4668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullerova, J.; Pergl, J.; Pysek, P. Remote sensing as a tool for monitoring plant invasions: Testing the effects of data resolution and image classification approach on the detection of a model plant species Heracleum mantegazzianum (giant hogweed). Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2013, 25, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T.; Lang, S.; Lorup, E.; Strobl, J.; Zeil, P. Object-Oriented image processing in an integrated GIS/remote sensing environment and perspectives for environmental applications. Environ. Inf. Plan. Polit. Public 2000, 2, 555–570. [Google Scholar]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the normalized difference water index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.Q. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Wang, S.X.; Zhou, Y.; Han, X.D.; Yao, Y. The study of the index models used in extraction of water body based on HJ-1 CCD imagery. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Multimedia Technology (ICMT), Hangzhou, China, 26–28 July 2011; IEEE: New York, NY, USA; pp. 904–907.
- Lu, S.L.; Wu, B.F.; Yan, N.N.; Wang, H. Water body mapping method with HJ-1A/B satellite imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2011, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troin, M.; Vallet-Coulomb, C.; Sylvestre, F.; Piovano, E. Hydrological modelling of a closed lake (Laguna Mar Chiquita, Argentina) in the context of 20th century climatic changes. J. Hydrol. 2010, 393, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical approaches for incorporating elevation into the spatial interpolation of rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 113–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valiantzas, J.D. Simplified versions for the penman evaporation equation using routine weather data. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 690–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.J. Environmental problems and ecological countermeasures for the Honghu Lake in Hubei province. J. Cent. China Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2001, 35, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Strahler, A.H. Change-Vector analysis in multitemporal space––A tool to detect and categorize land-cover change processes using high temporal-resolution satellite data. Remote Sens. Environ. 1994, 48, 231–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.D.; Kasischke, E.S. Change vector analysis: A technique for the multispectral monitoring of land cover and condition. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1998, 19, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, G.C.; Liu, K.K.; Chiang, K.P.; Hsiung, T.M.; Chang, J.; Chen, C.C.; Hung, C.C.; Chou, W.C.; Chung, C.C.; Chen, H.Y. Yangtze River floods enhance coastal ocean phytoplankton biomass and potential fish production. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.M.; Chen, X.L.; Cai, X.B.; Tian, L.Q.; Gan, W.X. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using modis observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.Z.; Zhang, S.X.; Yang, H.W.; Wang, K.; Feng, G.L. Analysis of characteristics of a sharp turn from drought to flood in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River in spring and summer in 2011. Acta Phys. Sin. 2012, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, R.; Cao, C.; Peng, L.; Ma, G.; Bao, D.; Guo, J.; Yomwan, P. The use of HJ-1A/B satellite data to detect changes in the size of wetlands in response in to a sudden turn from drought to flood in the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River system in China. Geomat. Nat. Hazards Risk 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avnimelech, Y.; Ritvo, G. Shrimp and fish pond soils: Processes and management. Aquaculture 2003, 220, 549–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.F.; Liu, Z.D.; Chen, Y.M. Study on the water requirement and water requirement regulation of maize in China. J. Maize Sci. 2008, 4, 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.W.; Su, R.R.; Geng, Y.F.; Zhu, J.Q.; An, K.Z.; Cai, W. Drought and flood grades classification considering water demand at each growth stage of cotton in Jingzhou. Chin. J. Agrometeorol. 2014, 3, 317–322. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.H.; Yu, W.Y.; Wang, F. Analysis of rice water requirement test on Chuzhou. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2008, 36, 10810–10812. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, K.Q.; Liang, Y.T.; Zhou, J.L.; Liu, M. Impact analysis of human activities and climate change on Honghu Lake’s spring drought. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2014, 34, 1302–1310. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.B.H.; Huang, S.S.; Fan, H.P.; Dai, Y.H. Analysis of the economic benefits on the snail control project through environmental modification supported by world bank loan project for schistosomiasis control in Hubei province. J. Trop. Med. 2006, 6, 696–699. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, J.; Li, R.D.; Xu, X.J.; Yu, C.H.; Xia, X.; Hong, X.C.; Chang, B.R.; Yi, F.J.; Shi, Y.Y. Identifying determinants of oncomelania hupensis habitats and assessing the effects of environmental control strategies in the plain regions with the waterway network of China at the microscale. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 6571–6585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, B.; Li, R.; Zhu, C.; Liu, K. Quantitative Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Water-Surface Area Variations from the 1990s to 2013 in Honghu Lake, China. Water 2015, 7, 2881-2899. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062881
Chang B, Li R, Zhu C, Liu K. Quantitative Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Water-Surface Area Variations from the 1990s to 2013 in Honghu Lake, China. Water. 2015; 7(6):2881-2899. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062881
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Bianrong, Rendong Li, Chuandong Zhu, and Kequn Liu. 2015. "Quantitative Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Water-Surface Area Variations from the 1990s to 2013 in Honghu Lake, China" Water 7, no. 6: 2881-2899. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062881
APA StyleChang, B., Li, R., Zhu, C., & Liu, K. (2015). Quantitative Impacts of Climate Change and Human Activities on Water-Surface Area Variations from the 1990s to 2013 in Honghu Lake, China. Water, 7(6), 2881-2899. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7062881





