Drought Mitigation Ability Index and Application Based on Balance between Water Supply and Demand
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area

2.2. Materials
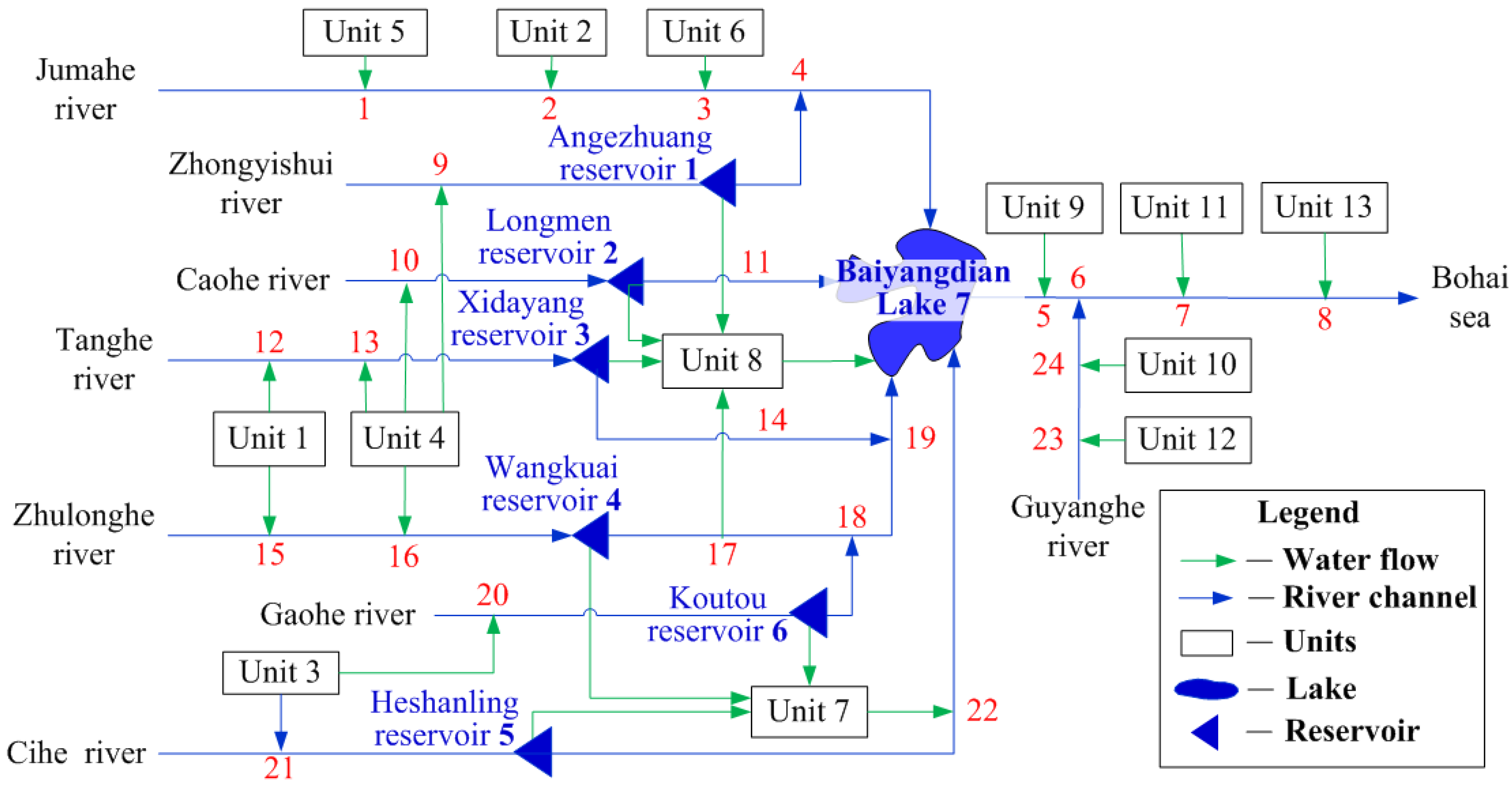
| Stations | Name | Number | Longitude/° | Latitude/° | Elevation/m | Period |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Beijing | 54511 | 116.5 | 39.8 | 31.3 | 1951–2010 |
| 2 | Wutaishan | 53588 | 113.5 | 39.0 | 2208.3 | 1951–2010 |
| 3 | Shijiazhuang | 53698 | 114.4 | 38.0 | 81.0 | 1955–2010 |
| 4 | Yuxian | 53593 | 114.6 | 39.8 | 909.5 | 1954–2010 |
| 5 | Bazhou | 54518 | 116.4 | 39.1 | 9.0 | 1957–2010 |
| 6 | Tianjin | 54527 | 117.1 | 39.1 | 2.5 | 1954–2010 |
| 7 | Baoding | 54602 | 115.5 | 38.9 | 17.2 | 1955–2010 |
| 8 | Raoyang | 54606 | 115.7 | 38.2 | 19.0 | 1957–2010 |
| 9 | Tanggu | 54623 | 117.7 | 39.1 | 4.8 | 1954–2010 |
| 10 | Huanghua | 54624 | 117.4 | 38.4 | 6.6 | 1960–2010 |
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Calculation of Water Demand
| Units | Ecological Water Demand | Domestic Water Demand | Industry Water Demand | Agricultural Water Demand |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unit 1 | 34.12 | 622.72 | 358.28 | 4197.40 |
| Unit 2 | 29.76 | 543.05 | 312.44 | 9503.21 |
| Unit 3 | 238.28 | 4348.63 | 2501.95 | 32,117.37 |
| Unit 4 | 27.19 | 496.28 | 285.53 | 1596.28 |
| Unit 5 | 402.14 | 2380.93 | 1506.43 | 10,750.44 |
| Unit 6 | 778.66 | 4610.16 | 2916.88 | 22,614.60 |
| Unit 7 | 5119.20 | 30,308.91 | 19,176.68 | 160,680.06 |
| Unit 8 | 70.65 | 1289.32 | 741.80 | 8120.21 |
| Unit 9 | 775.44 | 3673.83 | 3247.97 | 15,162.34 |
| Unit 10 | 3259.42 | 15,442.15 | 13,652.15 | 64,608.18 |
| Unit 11 | 3422.81 | 16,216.27 | 14,336.53 | 67,564.54 |
| Unit 12 | 181.60 | 860.37 | 760.64 | 3369.58 |
| Unit 13 | 4560.73 | 21,607.38 | 19,102.72 | 57,188.71 |
2.3.2. Calculation of Water Supply
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Index Validation
3.1.1. Temporal Scale

3.1.2. Spatial Scale
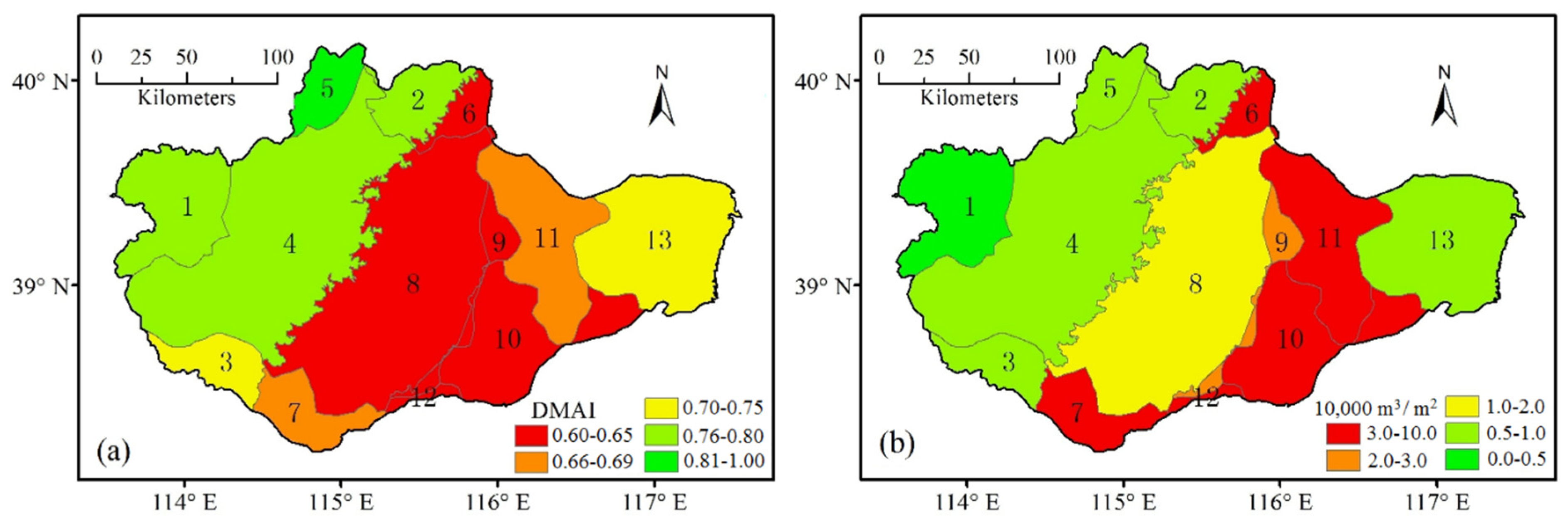
3.2. Evolution of the Drought Mitigation Ability Index (DMAI) Characteristics in the Daqinghe Watershed
3.2.1. Annual Evolution Characteristic of the Drought Mitigation Ability Index (DMAI)
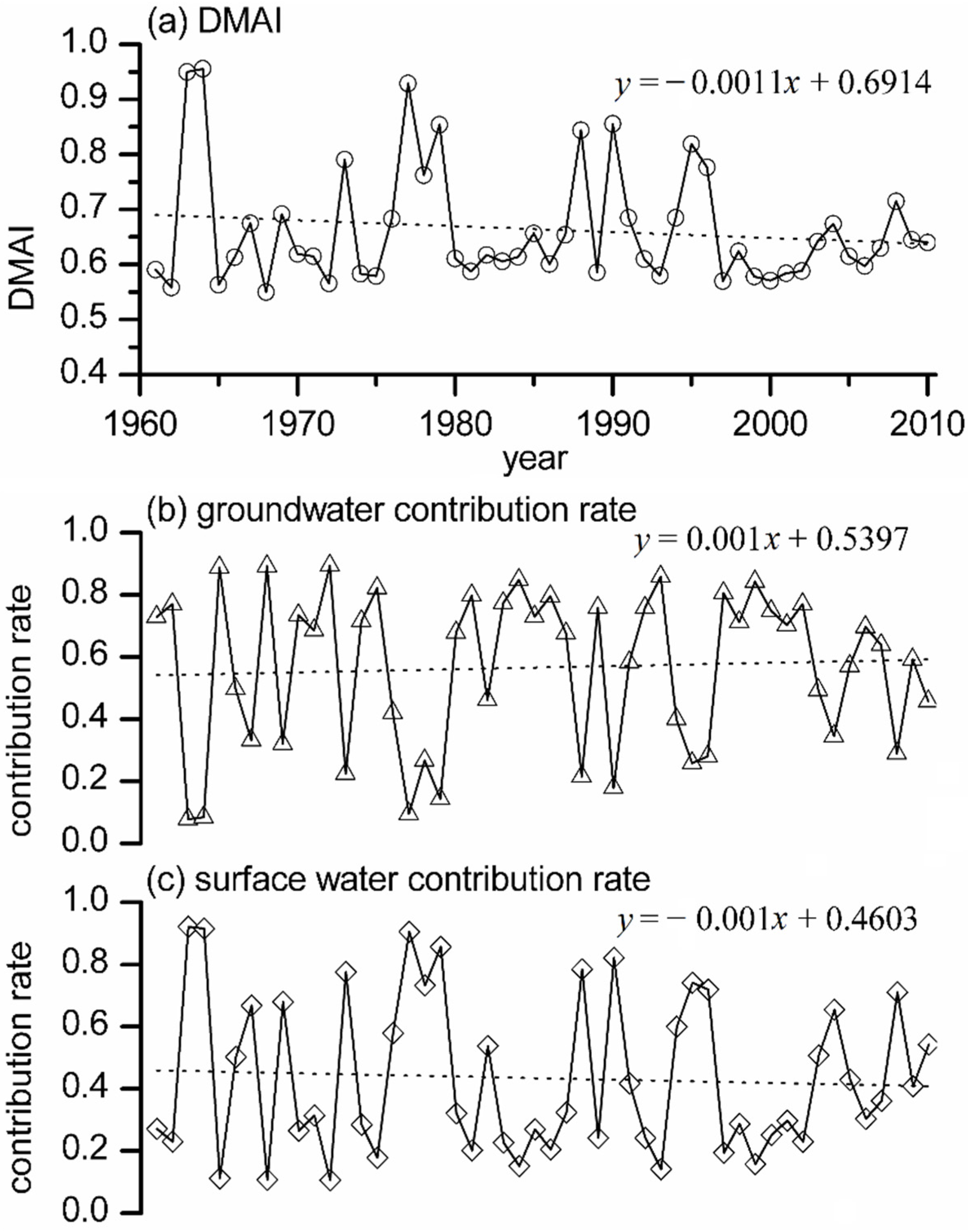
3.2.2. Evolution Characteristics of the Drought Mitigation Ability Index (DMAI) in Typical Drought Years

3.2.3. Inner-Annual Evolution Characteristics of the Drought Mitigation Ability Index (DMAI)

3.3. Drought Mitigation Ability Index (DMAI) Changes in the 2020
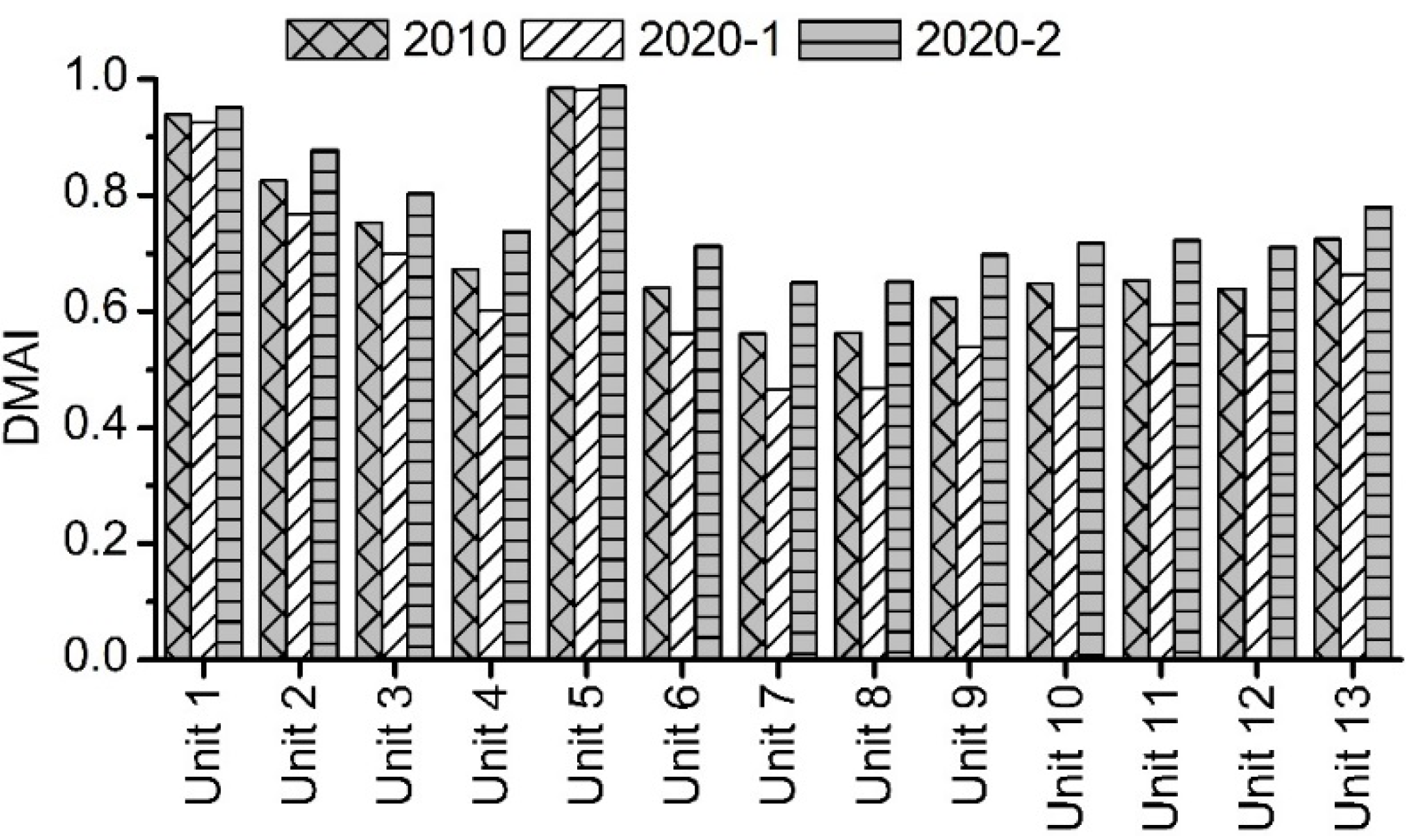
3.3.1. Water Resources Decrease Impact on Drought Mitigation Ability Index (DMAI)
3.3.2. Interbasin Water Transfer Project Impact on the Drought Mitigation Ability Index (DMAI)
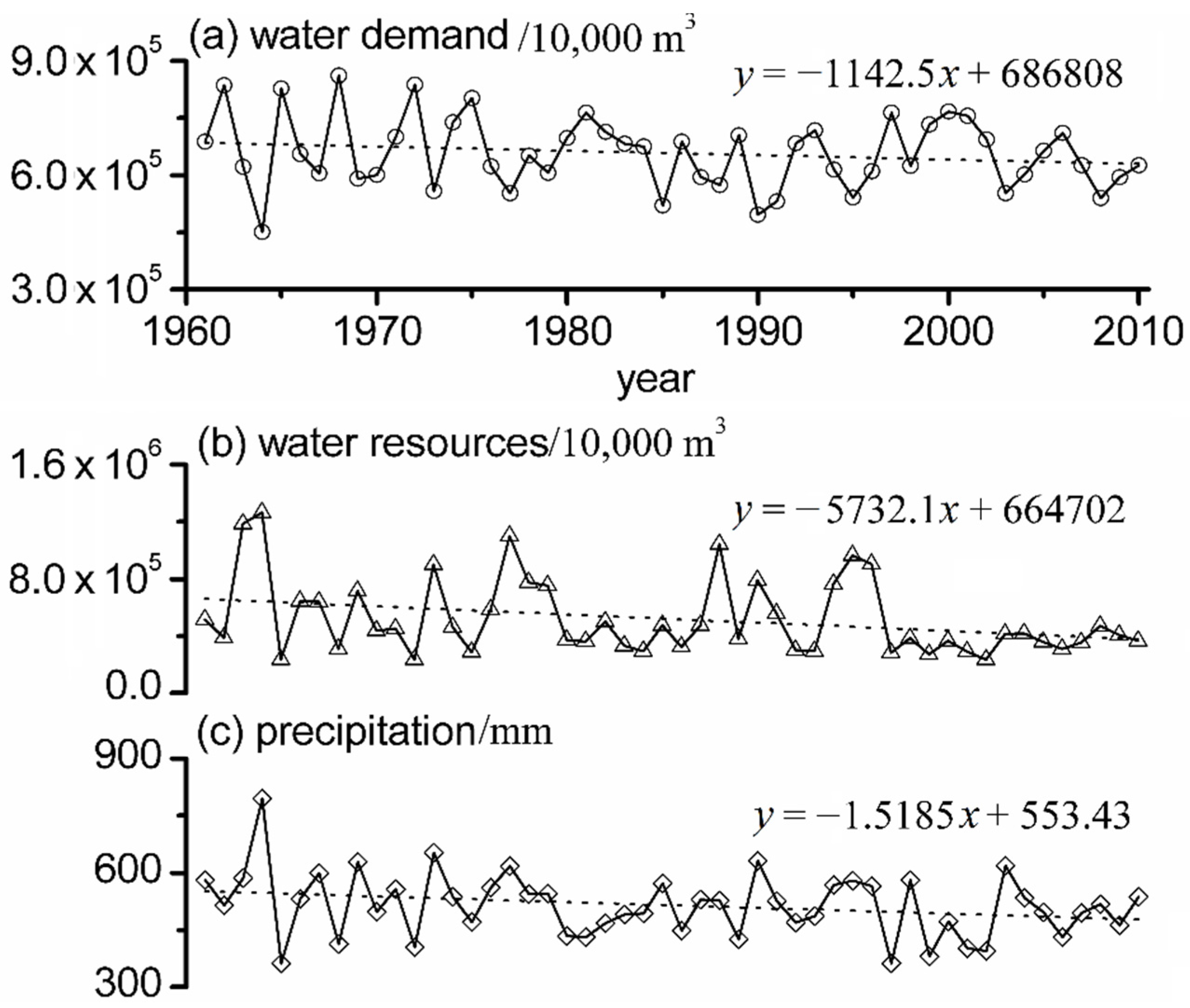
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heim, R.R., Jr. A review of twentieth-century drought indices used in the United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2002, 83, 1149–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. Drought modelling—A review. J. Hydrol. 2011, 403, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.T.; Hsiao, Y.Y. Water-deficit-based drought risk assessments in Taiwan. Nat. Hazards 2012, 64, 237–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, D.; Weng, B.; Wang, G.; Wang, H.; Yin, J.; Bao, S. Theoretical framework of generalized watershed drought risk evaluation and adaptive strategy based on water resources system. Nat. Hazards 2014, 73, 259–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, D.A.; Kingston, D.G.; Todd, M.C. Uncertainty in water resources availability in the Okavango River basin as a result of climate change. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alcamo, J.; Flörke, M.; Märker, M. Future long-term changes in global water resources driven by socio-economic and climatic changes. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2007, 52, 247–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P. A review of drought concepts. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flörke, M.; Kynast, E.; Bärlund, I.; Eisner, S.; Wimmer, F.; Alcamo, J. Domestic and industrial water uses of the past 60 years as a mirror of socio-economic development: A global simulation study. Glob. Environ. Change 2013, 23, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Savenije, H.H. Food consumption patterns and their effect on water requirement in China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2008, 12, 887–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, L.S.; Cordery, I.; Iacovides, I. Coping with Water Scarcity: Addressing the Challenges; Springer Science and Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Steduto, P.; Faurès, J.M.; Hoogeveen, J.; Winpenny, J.; Burke, J. Coping with Water Scarcity: An Action Framework for Agriculture and Food Security; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, F.J.; Wang, K.W. A systematical water allocation scheme for drought mitigation. J. Hydrol. 2013, 507, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D.; Hayes, M.J. Monitoring drought in the United States: Status and trends. In Monitoring and Predicting Agricultural Drought: A global Study; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 121–131. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Wood, E.F. Monitoring and predicting the 2007 US drought. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G.; Pangalou, D.; Vangelis, H. Regional drought assessment based on the Reconnaissance Drought Index (RDI). Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 821–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, B.S.; Yan, D.H.; Wang, H.; Qin, T.L.; Yin, J. Generalized drought assessment in Dongliao river basin based on water resources system. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2014, 2, 6703–6746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 Januray 1993.
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. Drought monitoring with multiple time scales. In Ninth Conference on Applied Climatology; American Meteorological Society: Boston, MA, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; US Department of Commerce, Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Shafer, B.A.; Dezman, L.E. Development of a surface water supply index (SWSI) to assess the severity of drought conditions in snowpack runoff areas. In Proceedings of the Western Snow Conference, Reno, NV, USA, 19–23 April 1982.
- Hollinger, S.E.; Isard, S.A.; Welford, M.R. A new soil moisture drought index for predicting crop yields. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993.
- Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D.; Hayes, M.J. Understanding the complex impacts of drought: A key to enhancing drought mitigation and preparedness. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yevjevich, V.; Hall, J.D.; Salas, W. Drought Research Needs; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.C.; Chou, C.C. Drought early warning system in reservoir operation: Theory and practice. Water Resour. Res. 2005, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sechi, G.M.; Sulis, A. Drought mitigation using operative indicators in complex water systems. Phys. Chem. Earth 2010, 35, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, G.; Castiglione, L.; Bonaccorso, B. Guidelines for planning and implementing drought mitigation measures. In Methods and Tools for Drought Analysis and Management; Springer Netherlands: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 325–347. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Beguería, S.; Gimeno, L.; Eklundh, L.; Giuliani, G.; Weston, D.; Pegram, G.G. Challenges for drought mitigation in Africa: The potential use of geospatial data and drought information systems. Appl. Geogr. 2012, 34, 471–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogt, J.V.; Somma, F. Drought and Drought Mitigation in Europe; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Norwell, MA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shih, J.S.; ReVelle, C. Water-supply operations during drought: Continuous hedging rule. J. Water Resour. Plan. Manag. 1994, 120, 613–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilhite, D.A. Drought and Water Crises: Science, Technology, and Management Issues; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorolgical Data Sharing System. Available online: http://cdc.nmic.cn/home.do (accessed on 7 April 2015).
- Smith, M. CROPWAT: A Computer Program for Irrigation Planning and Management; Food and Agriculture Organization of the U.N. Rome: Rome, Italy, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Döll, P.; Siebert, S. Global modelling of irrigation water requirements. Water Resour. Res. 2002, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Yang, D.; Lei, H.; Xu, K.; Xu, X. Comparative analysis of drought based on precipitation and soil moisture indices in Haihe basin of North China during the period of 1960–2010. J. Hydrol. 2014, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.K.; Chen, J.; Jin, J.; Li, J.Q.; Xu, J.J.; Fei, Z.Y. Calculation method of agricultural drought loss risk curve under the actual drought resistance ability condition in Southern China. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2014, 7, 809–815. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, A.K.; Singh, V.P.; Desai, V.R. Drought characterization: A probabilistic approach. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2009, 23, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Luo, Y.Z.; Zhang, M.H.; Xia, J. Quantitative evaluation of sustainable development and eco-environmental carrying capacity in water-deficient regions: A case study in the Haihe River Basin, China. J. Integr. Agric. 2014, 13, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Cong, Z. Trends of precipitation intensity and frequency in hydrological regions of China from 1956 to 2005. Glob. Planet. Change 2014, 117, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Yan, D.; Wang, J.; Weng, B.; Wang, G.; Yang, M. Drought Mitigation Ability Index and Application Based on Balance between Water Supply and Demand. Water 2015, 7, 1792-1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051792
Liu S, Yan D, Wang J, Weng B, Wang G, Yang M. Drought Mitigation Ability Index and Application Based on Balance between Water Supply and Demand. Water. 2015; 7(5):1792-1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051792
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shaohua, Denghua Yan, Jianhua Wang, Baisha Weng, Gang Wang, and Meijian Yang. 2015. "Drought Mitigation Ability Index and Application Based on Balance between Water Supply and Demand" Water 7, no. 5: 1792-1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051792
APA StyleLiu, S., Yan, D., Wang, J., Weng, B., Wang, G., & Yang, M. (2015). Drought Mitigation Ability Index and Application Based on Balance between Water Supply and Demand. Water, 7(5), 1792-1807. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7051792





