Development of a Comprehensive Fouling Model for a Rotating Membrane Bioreactor System Treating Wastewater
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Modelling Approach
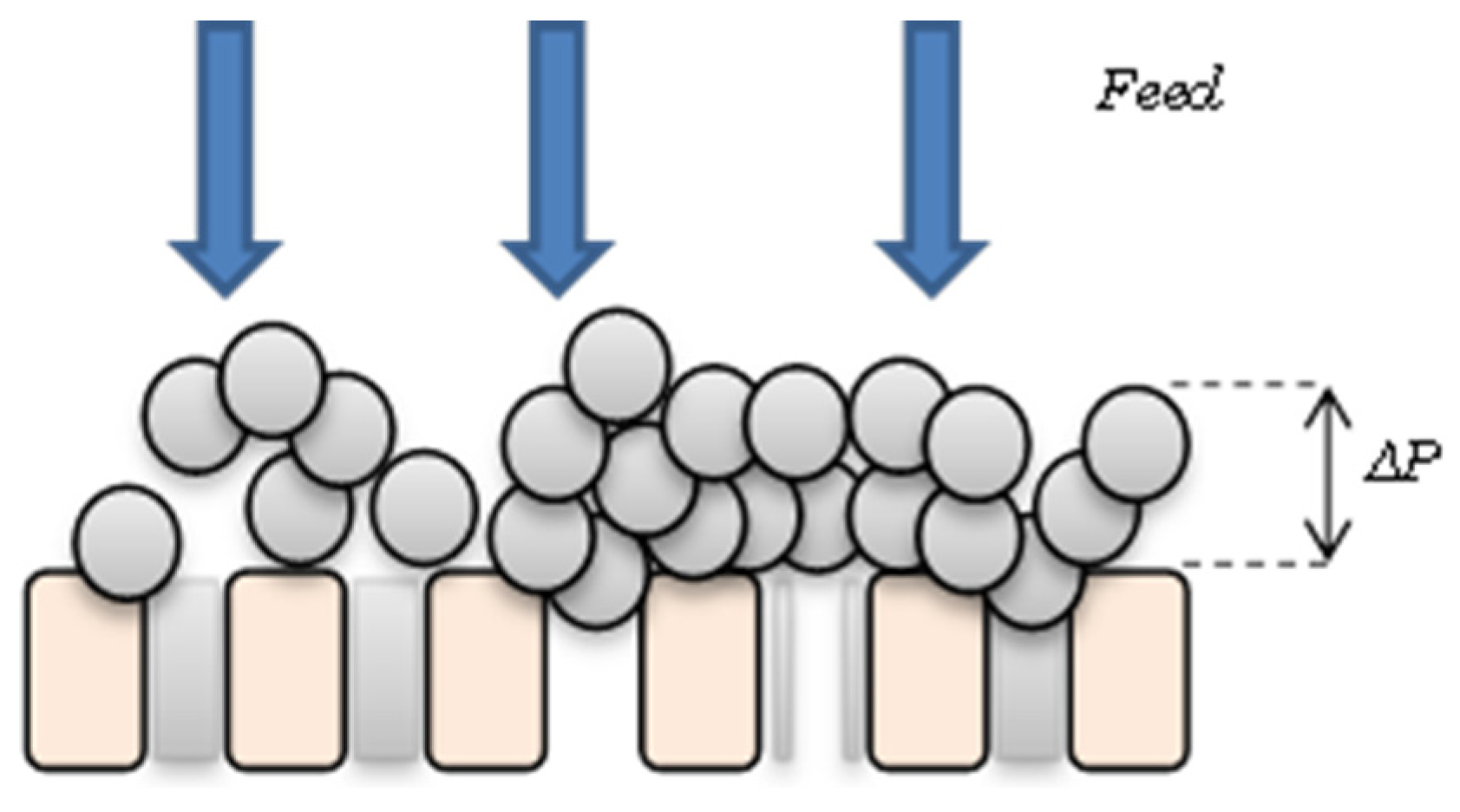
2.1. Hydrodynamic Regime
2.2. Soluble Microbial Products’ (SMP) Inclusion
2.3. Constant Flow/Varying Trans-Membrane Pressure (TMP) Mode
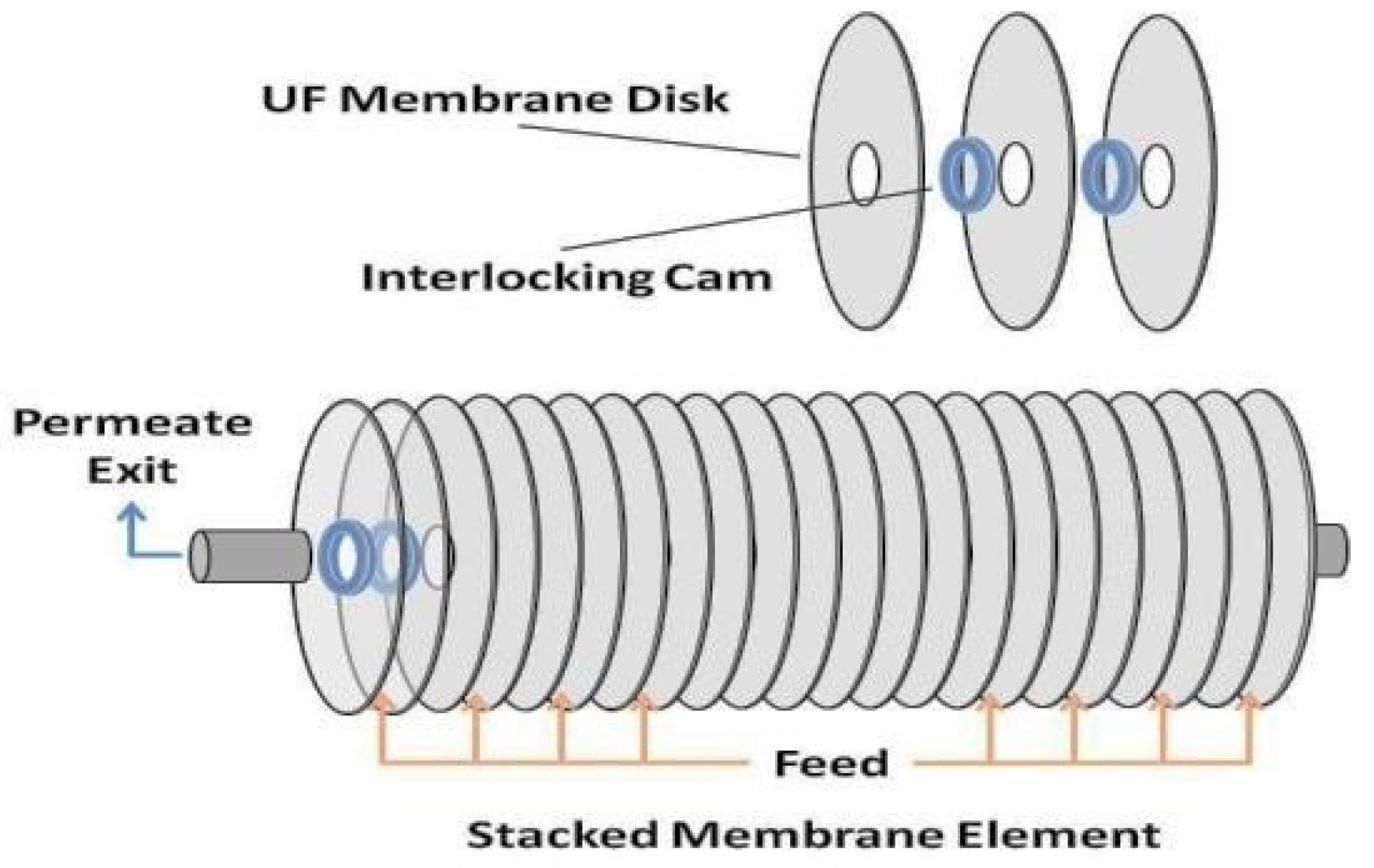
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials

| Description | Unit | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Membrane outer diameter | m | 0.177 |
| Membrane inner diameter | m | 0.055 |
| Membrane area | m2 | 1.6006 |
| Angular velocity | rad/s | 2.094 |
| Permeate flux | L.m2.H−1 | Up to 50 |
| TSS (Total suspended solids) | g L−1 | 8–30 |
| Transmembrane pressure | bar | ≤2 |
3.2. Filtration Experiments
3.2.1. Shear and Viscosity Experiments
3.2.2. Flux Steps Filtration Tests
3.2.3. SMP Inclusion Experiments
3.2.4. Constant Flow Rate Experiments
4. Results and Discussion
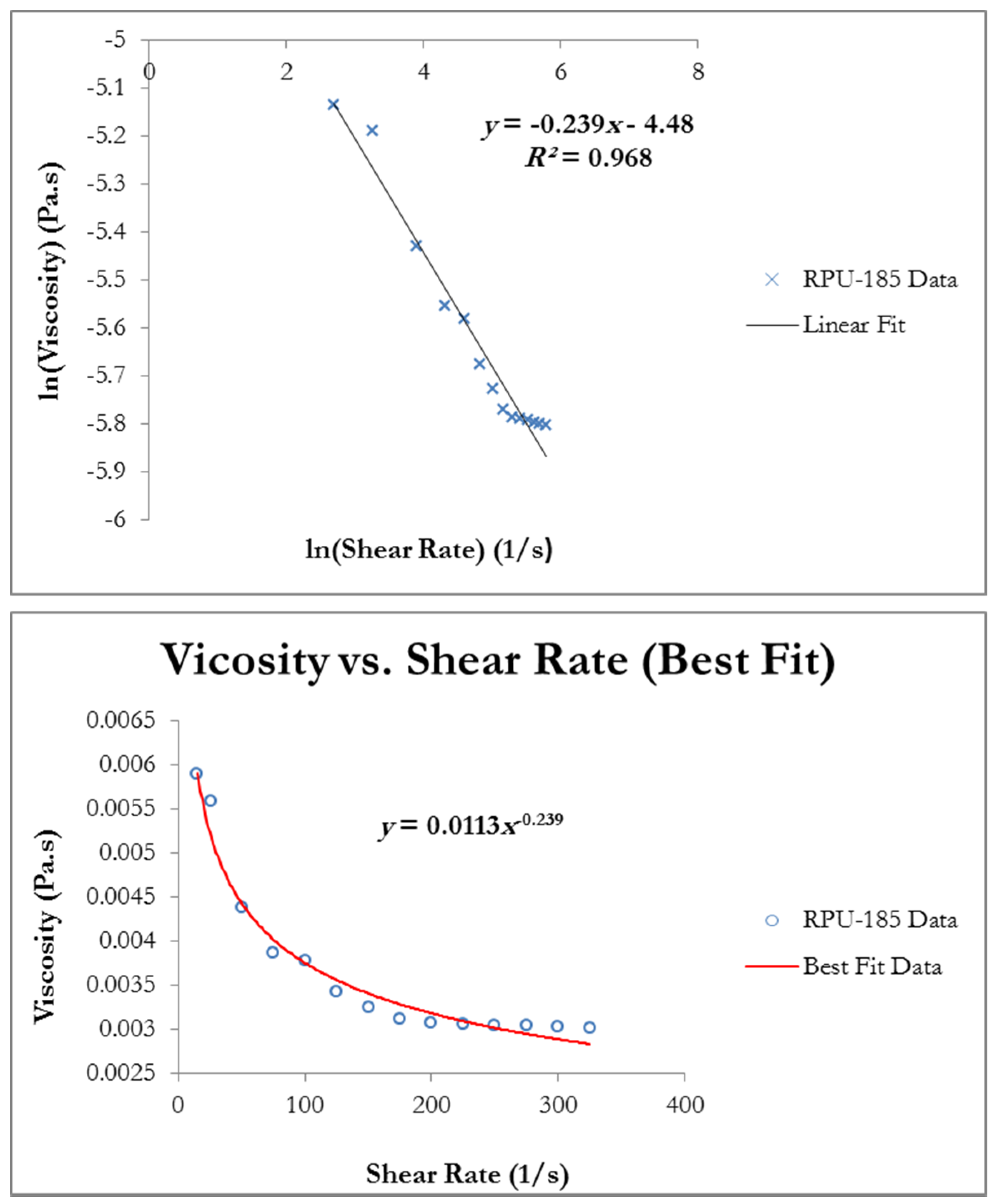
4.1. Shear and Viscosity Relationship
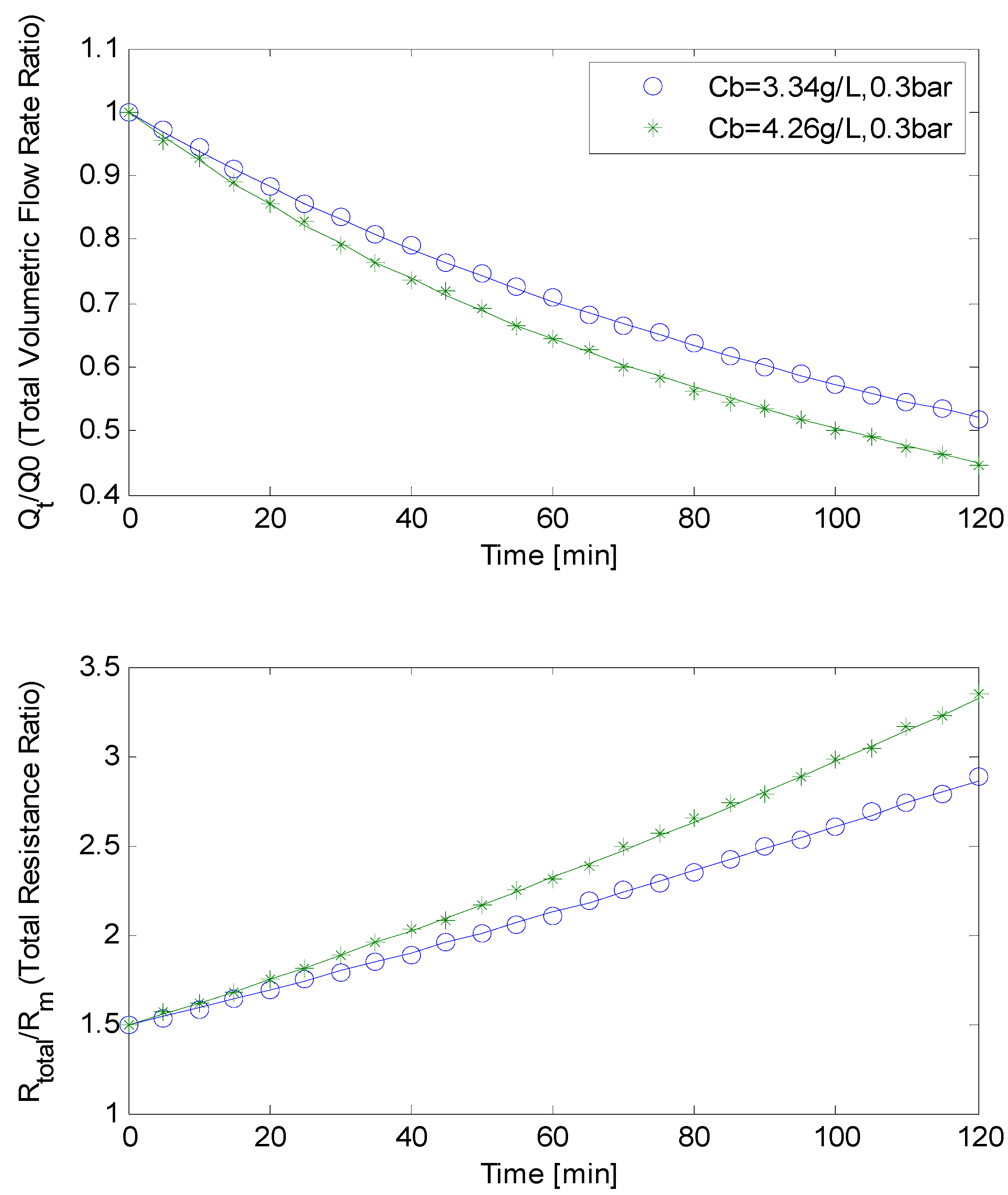
4.2. Model Validation-Hydrodynamic Regime
| Parameter | Unit | 15 kPa Flux Step | 30 kPa Flux Step | 45 kPa Flux Step | 58 kPa Flux Step |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Best Fit Simulation Values | |||||
| go | – | 21.792 | 3.178 | 70.628 | 35.6743 |
| kAb | – | 29.787 | 229.77 | 29.27 | 0.382 |
| Rbo/Rm | – | 0.174 | 0.867 | 0.239 | 0.390 |
| f’·R’ | m/kg | 489.04 × 109 | 435.88 × 109 | 490.67 × 109 | 65.72 × 109 |
| α | m2/kg | 0.332 | 0.0579 | 4.929 | 0.670 |
| β | kg | 2.342 | 0.856 | 1.751 | 0.472 |
| Key Data Used During Simulations | |||||
| m | Pa sn | 0.0113 ± 0.01 | 0.0113 ± 0.01 | 0.0113 ± 0.01 | 0.0113 ± 0.01 |
| n | – | 0.761 ± 0.02 | 0.761 ± 0.02 | 0.761 ± 0.02 | 0.761 ± 0.02 |
| αv | – | 0.0292 | 0.0292 | 0.0292 | 0.0292 |
| δ | m−1 | 4.6 × 10−4 | 4.6 × 10−4 | 4.6 × 10−4 | 4.6 × 10−4 |
| kω | rad−1 | 2.446 × 10−5 | 4.484 × 10−5 | 5.503 × 10−5 | 6.725 × 10−5 |
| σa | kg m3 | 1.788 × 10−16 | 6.535 × 10−17 | 1.336 × 10−16 | 3.601 × 10−17 |

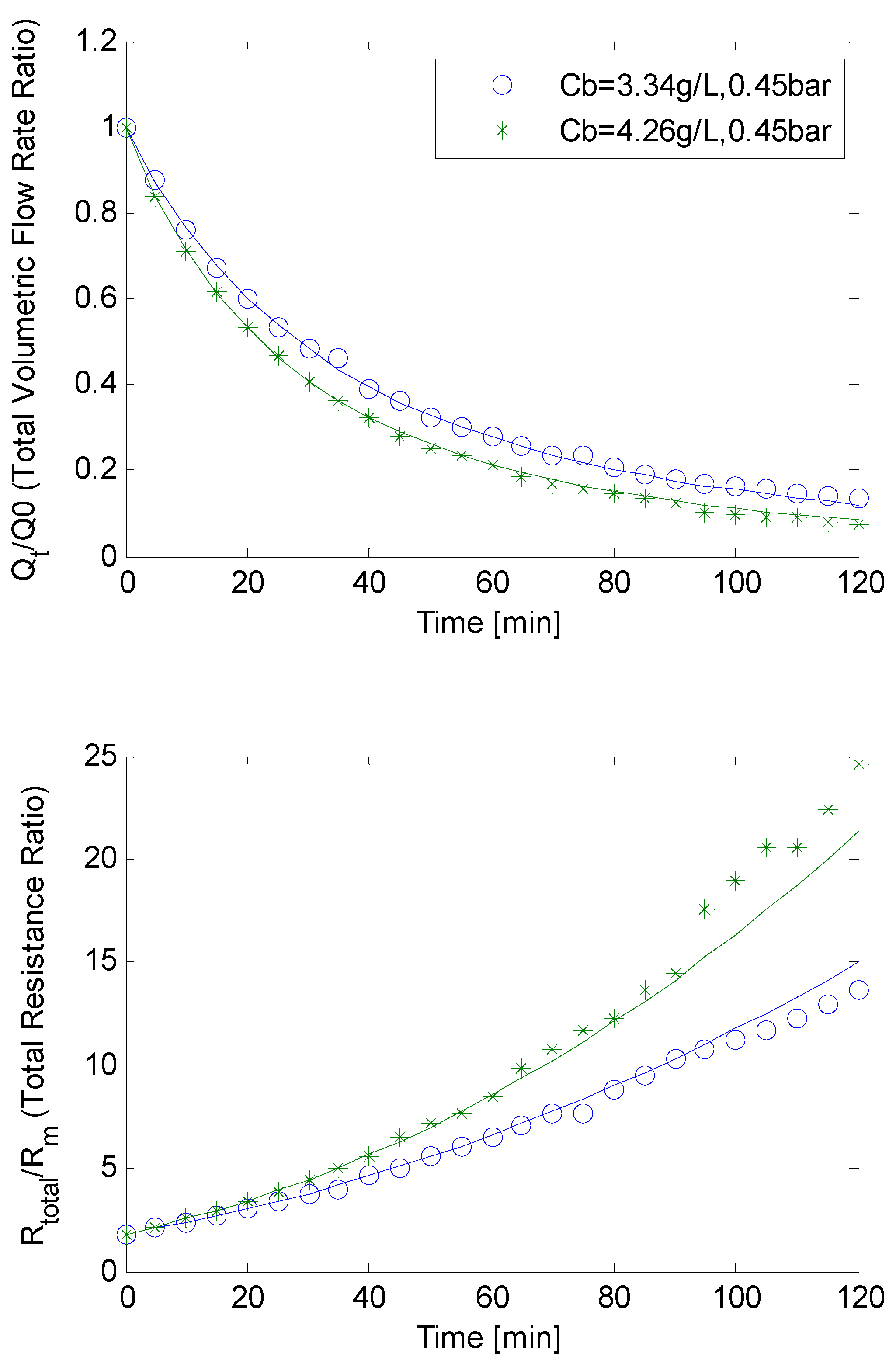
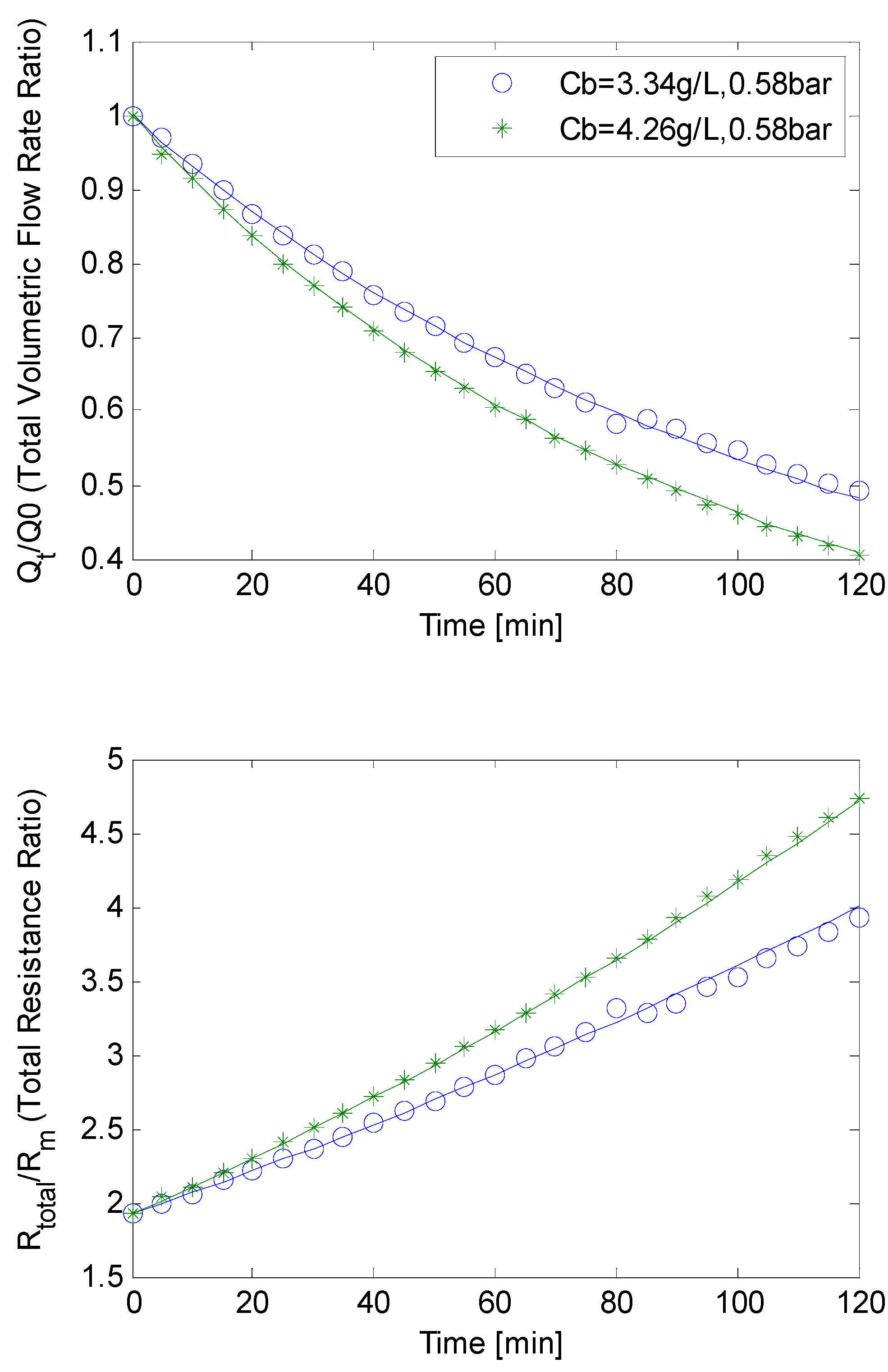
4.3. SMP Inclusion
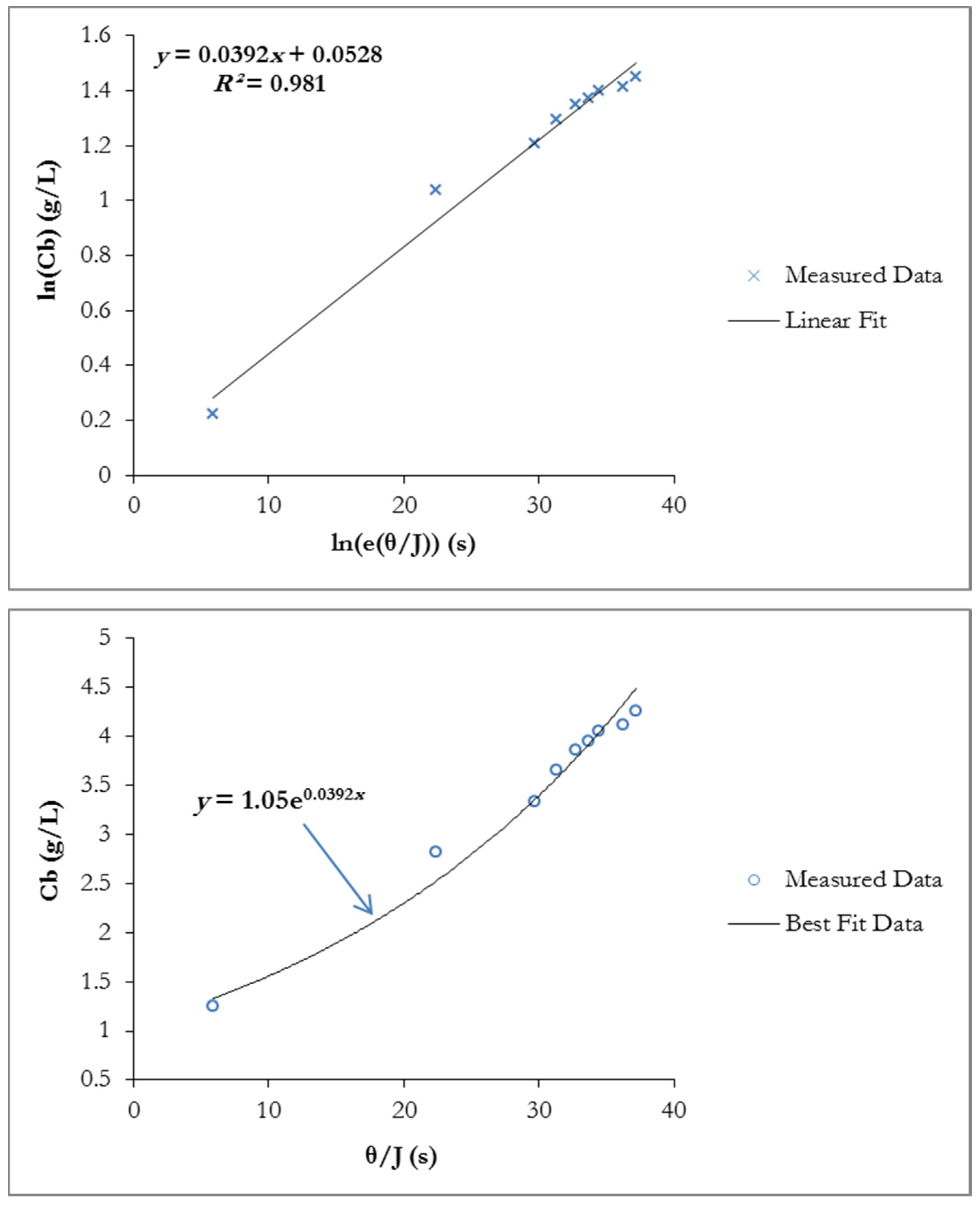
4.4. Constant Flow Rate/Varying TMP Mode
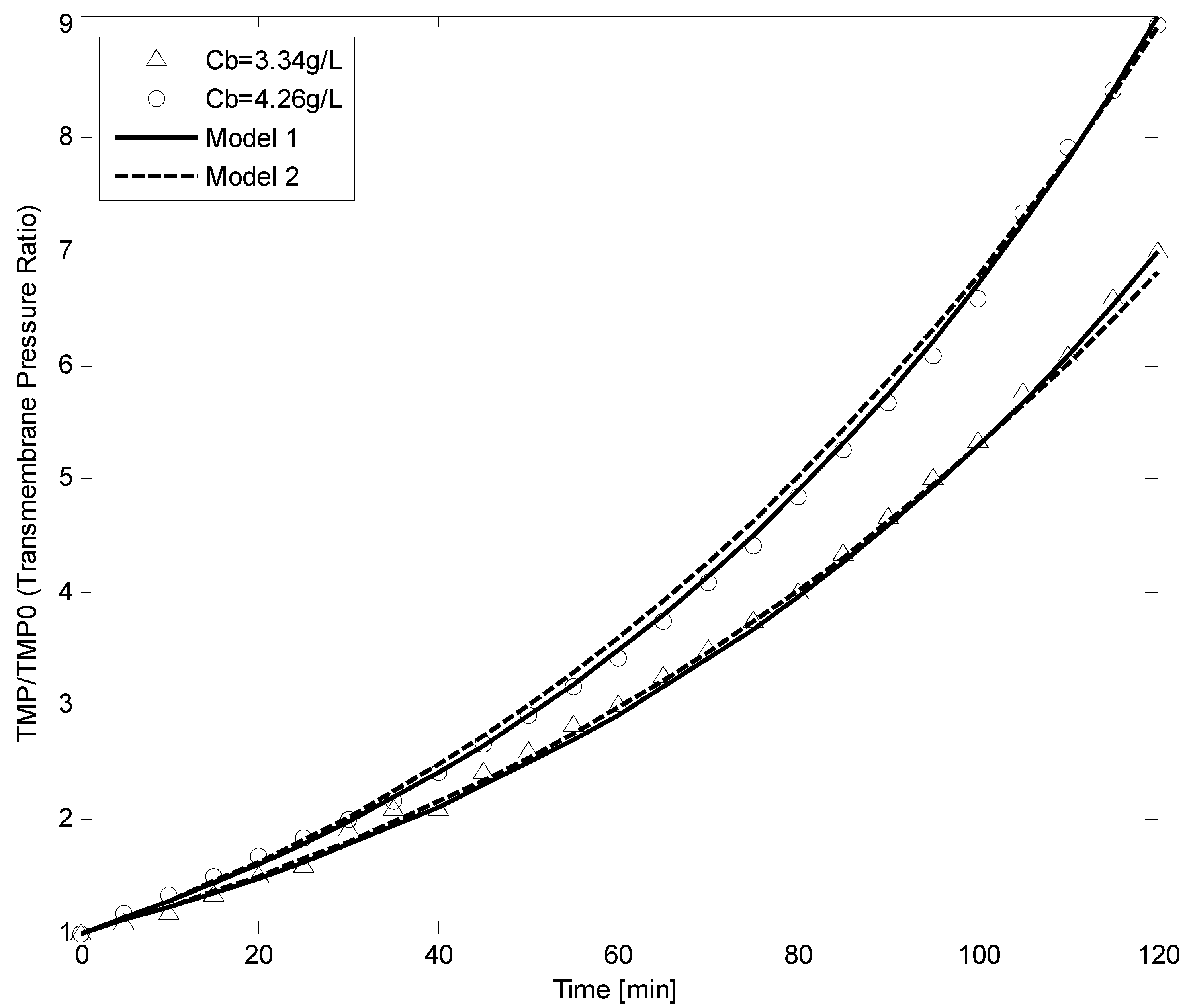
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Abbreviations
| A | remaining membrane area available for permeate (m2); |
| A0 | total membrane area (m2); |
| Au0 | initial unblocked area (m2); |
| Cb | liquid bulk concentration (g/L); |
| Cb’ | concentration of the clogging particles in the bulk liquid (g/L); |
| Cd | solid content in bulk (kgm−3); |
| CMLSS | mixed liquor suspended solids concentration (g/L); |
| dpi | mean diameter of floc particle forming the cake (m); |
| go | adjustable parameter or cake removal factor (−), |
| f’ | fractional amount of total foulants contributing to deposit growth (−); |
| J0 | initial filtrate flux of clean membrane (m s−1); |
| Jmo | initial total flux (m/s); |
| Ju | unblocked flux (m s−1); |
| kAb | area constant parameter for blocked pores (−); |
| ki | 1st order particle removal coefficient (1/s); |
| Kα | area distribution density (m−1); |
| kω | angular velocity factor (−); |
| m | flow consistency index (Pa sn); |
| n | flow behaviour index (−); |
| PT | trans-membrane pressure at membrane periphery (Pa); |
| Q | volumetric flow rate (m3 s−1); |
| Qb | blocked volumetric flow rate (m3 s−1) |
| Q0 | initial volumetric flow rate (m3 s−1); |
| Qu | unblocked volumetric flow rate (m3 s−1); |
| R’ | specific protein layer or cake layer resistance (m/kg); |
| Rb | resistance of solids deposit over a region of membrane (m−1); |
| Rbo | initial resistance of solids deposit (m−1); |
| Rc = R’c θc | total net cake’s resistance (m−1); |
| R’c | specific cake resistance (m−2); |
| ReNN | radial Reynolds number (−); |
| ri | membrane’s inner radius (m); |
| Rin,b | membrane’s resistance & resistance from pore constriction (m−1); |
| ro | membrane’s outer radius (m); |
| r’0 | distance radius from the spinning axis (m), thus (r’0 = ro − ri); |
| Rm | clean membrane’s resistance (m−1); |
| rp | radius of membrane pore (m); |
| Rt0 | initial total membrane’s resistance (m−1) at t = 0; |
| t, | filtration time (s); |
| tb | time at which a membrane region was first blocked (s); |
| TMP | trans-membrane pressure (Pa); |
| TMP0 | initial trans-membrane pressure (Pa); |
| α | pore blockage parameter (m2/kg); |
| αv | air scouring coefficient (−); |
| β | pore constriction parameter (kg); |
shear rate (s−1); | |
| δ | resistance distribution constant (m−1); |
| ∆P | cake’s trans-membrane pressure (Pa); |
| δm | membrane thickness (m); |
| εc | cake’s porosity (−); |
| ϵsmp | SMP concentration factor (−); |
| θc | cake’s depth or thickness (m); |
| µ | viscosity (Pa s); |
| υ | fluid kinematic viscosity (m2 s−1); |
| ρb | bulk cake density (kg m−3); |
| ρf | fluid’s density (kg m−3); |
| σa | adjustable parameter related to pore constriction (m3 kg); |
| τ | cake water content (−); |
| φ | adjustable parameter related to the total resistance (−); |
| ω | angular velocity (rad s−1). |
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhattacharjee, C.; Bhattacharya, P.K. Ultrafiltration of black liquor using rotating disk membrane module. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 49, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffrin, M.Y.; Ding, L.H.; Akoum, O.; Brou, A. A hydrodynamic comparison between rotating disk and vibratory dynamic filtration systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2004, 242, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Akoum, O.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Ding, L.H.; Paullier, P.; Vanhoutte, C. An hydrodynamic investigation of microfiltration and ultrafiltration in a vibrating membrane module. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 197, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzerar, R.; Paullier, P.; Jaffrin, M.Y. Concentration of mineral suspensions and industrial effluents using a rotating disk dynamic filtration module. Desalination 2003, 158, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frappart, M.; Jaffrin, M.Y.; Ding, L.H. Reverse osmosis of diluted skim milk: Comparison of results obtained from vibratory and rotating disk modules. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2008, 60, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Bhattacharjee, C. Modeling and analytical simulation of rotating disk ultra-filtration module. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 320, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Datta, D.; Sen, D.; Bhattacharjee, C. Simulation of continuous stirred rotating disk-membrane module: An approach based on surface renewal theory. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2011, 66, 2554–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torras, C.; Pallares, J.; Valls, R.G.; Jaffrin, M.Y. CFD simulation of a rotating disk flat membrane module. Desalination 2006, 200, 453–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bentzen, T.R.; Ratkovich, N.; Madsen, S.; Jensen, J.C.; Bak, S.N.; Rasmussen, M.R. Analytical and numerical modelling of Newtonian and non-Newtonian liquid in a rotational cross-flow MBR. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 66, 2318–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engler, J.; Mark, R.W. Particle fouling of a rotating membrane disk. Water Res. 2000, 34, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, M.K.; Malene, T.P.; Morten, L.C. Dependence of shear and concentration on fouling in a membrane bioreactor with rotating membrane discs. AIChE J. 2014, 60, 706–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Judd, S. The MBR Book: Principles and Applications of Membrane Bioreactors, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, the Netherlands, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberger, S.; Laabs, C.; Lesjean, B.; Gnirss, R.; Amy, G.; Jekel, M.; Schrotter, J.C. Impact of colloidal and soluble organic material on membrane performance in membrane bioreactors for municipal wastewater treatment. Water Res. 2006, 40, 710–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, Y.T.; Choi, Y.K.; Jeong, H.S.; Shin, S.R. Modeling of extracellular polymeric substances and soluble microbial products production in a submerged MBR at various SRTs. Water Sci. Technol. 2006, 53, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermia, J. Constant pressure blocking filtration laws-application to power-law non-Newtonian fluids. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 1982, 60a, 183–187. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, F. Application of fractal permeation model to investigate membrane fouling in membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2005, 262, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Huang, X.; Sun, Y.F.; Qian, Y. Hydrodynamic effect on sludge accumulation over membrane surfaces in a submerged membrane bioreactor. Process Biochem. 2003, 39, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duclos-Orsello, C.; Li, W.; Hob, C.-C. A three mechanism model to describe fouling of microfiltration membranes. J. Membr. Sci. 2006, 280, 856–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, P. Development and testing of a fully adaptable membrane bioreactor fouling model for a sidestream configuration system. Membranes 2013, 3, 24–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffrin, M.Y. Dynamic shear-enhanced membrane filtration: A review of rotating disks, rotating membranes and vibrating systems. J. Membr. Sci. 2008, 324, 7–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, S.; Song, L.; Tao, G.; Kekre, K.A.; Seah, H. A modeling study of fouling development in membrane bioreactors for wastewater treatment. Water Environ. Res. 2006, 78, 857–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giraldo, E.; Le Chevallier, M. Dynamic mathematical modelling of membrane fouling in submerged membrane bioreactors. In Proceedings of the Water Environment Federation; Session 61 through Session 70. Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2006; Volume 19, pp. 4895–4913. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, F.; Bick, A.; Shandalov, S.; Brenner, A.; Oron, G. Yield stress and rheological characteristics of activated sludge in an airlift membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2009, 334, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratkovich, N.R.; Horn, W.; Helmus, F.; Rosenberger, S.; Naessens, W.; Nopens, I.; Bentzen, T.R. Activated Sludge Rheology: A critical review on data collection and modelling. Water Res. 2013, 47, 463–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Clech, P.; Jefferson, B.; Chang, I.S.; Judd, S.J. Critical flux determination by the flux-step method in a submerged membrane bioreactor. J. Membr. Sci. 2003, 227, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Kocic, A.; Andrew, L.Z. Analysis of humic acid fouling during microfiltration using a pore blockage–cake filtration mode. J. Membr. Sci. 2002, 198, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, P.; Anderson Jones, F. Development of a Comprehensive Fouling Model for a Rotating Membrane Bioreactor System Treating Wastewater. Water 2015, 7, 377-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7020377
Paul P, Anderson Jones F. Development of a Comprehensive Fouling Model for a Rotating Membrane Bioreactor System Treating Wastewater. Water. 2015; 7(2):377-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7020377
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Parneet, and Franck Anderson Jones. 2015. "Development of a Comprehensive Fouling Model for a Rotating Membrane Bioreactor System Treating Wastewater" Water 7, no. 2: 377-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7020377
APA StylePaul, P., & Anderson Jones, F. (2015). Development of a Comprehensive Fouling Model for a Rotating Membrane Bioreactor System Treating Wastewater. Water, 7(2), 377-397. https://doi.org/10.3390/w7020377





