Lake Fluctuation Effectively Regulates Wetland Evapotranspiration: A Case Study of the Largest Freshwater Lake in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data Source
2.1. Study Area
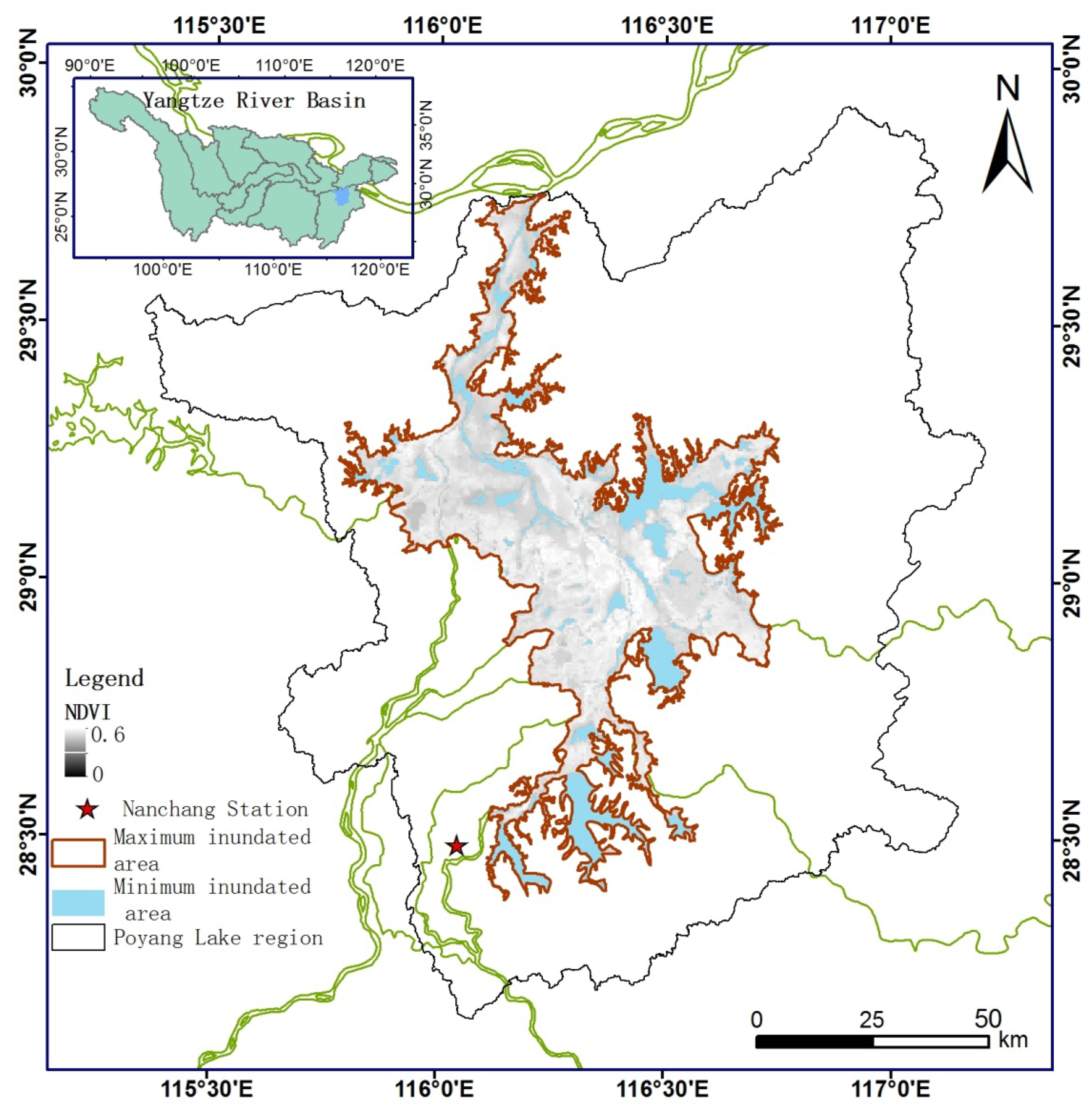
2.2. Remote Sensing Data
| MODIS products | Spatial resolution | Parameters contained |
|---|---|---|
| MOD03 | 1 km | Solar zenith and azimuth angles, satellite zenith and azimuth angles |
| MOD09GA | 500 m | Surface reflectance after atmospheric correction |
| MOD09GQ | 250 m | Reflectance of RED and near-infrared band |
| MOD07 | 5 km | Air temperature and dew point temperature |
| MOD11_L2 | 1 km | Surface emissivity and temperature |
| MOD43B3 | 1 km | Black- and white sky albedos |
2.3. Field Measurement Data
3. Methods
3.1. ET Estimation


 is the land surface temperature (K) in a pixel; and
is the land surface temperature (K) in a pixel; and  is the lowest temperature of full vegetation cover for each NDVI interval (NDVIi ), which forms the wet edge in the triangular space of
is the lowest temperature of full vegetation cover for each NDVI interval (NDVIi ), which forms the wet edge in the triangular space of  versus NDVIi .
versus NDVIi .  is the highest temperature for each NDVI interval (NDVIi ), which forms the dry edge.
is the highest temperature for each NDVI interval (NDVIi ), which forms the dry edge.
3.2. Inundated Area Extraction

4. Results and Discussion
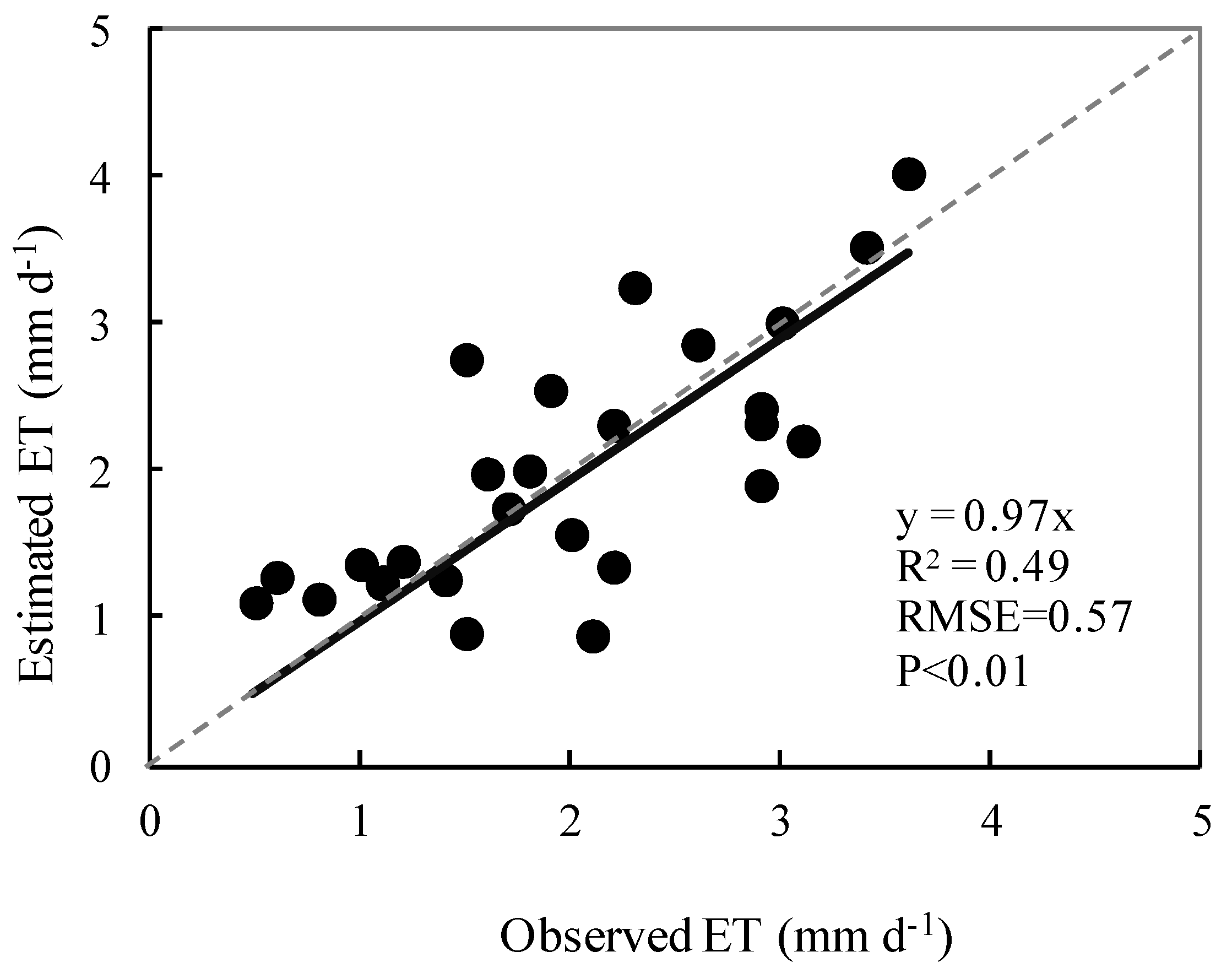
4.1. Validation of ET Retrievals
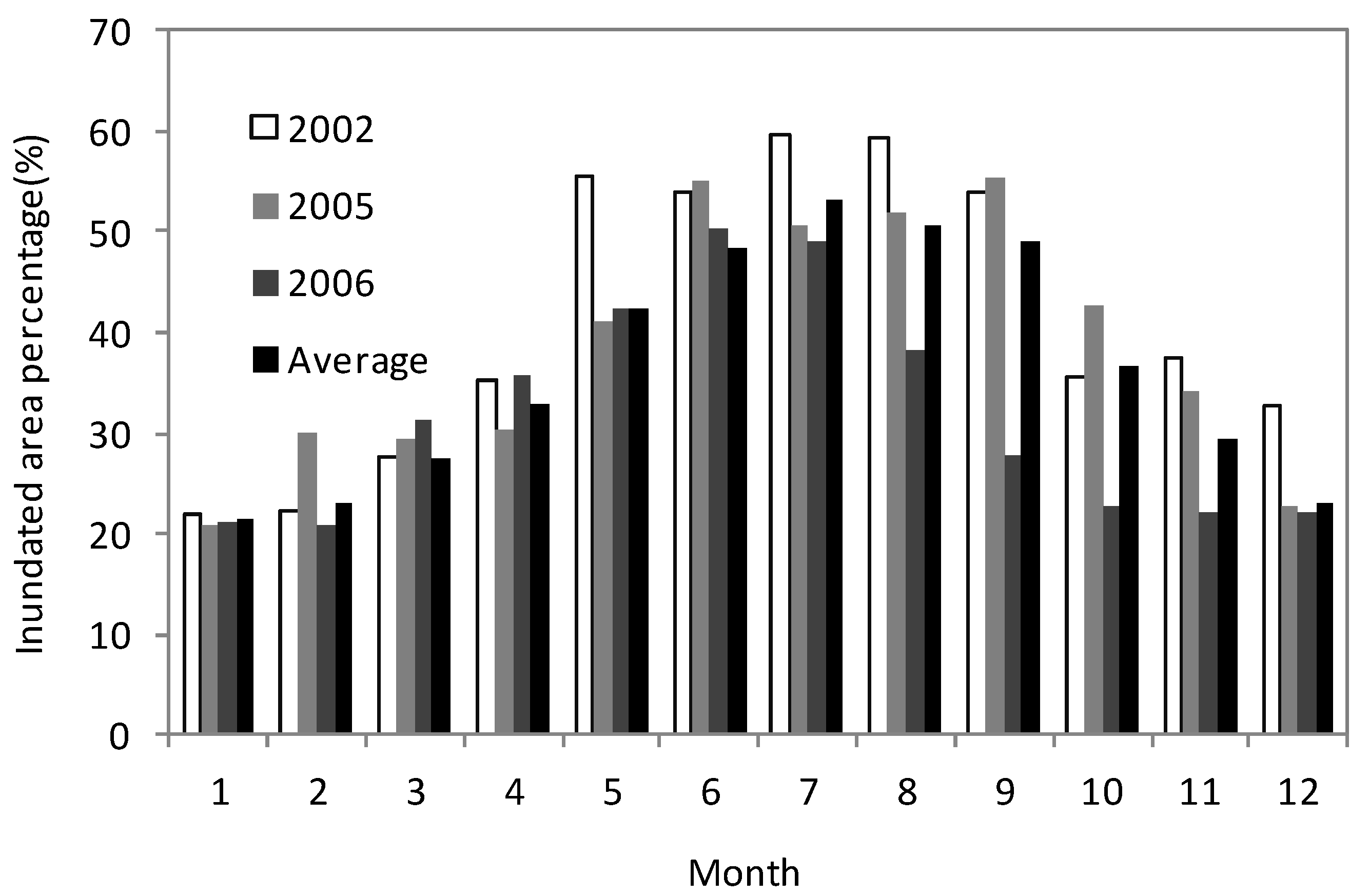
4.2. Lake Fluctuation in the Poyang Lake Wetland
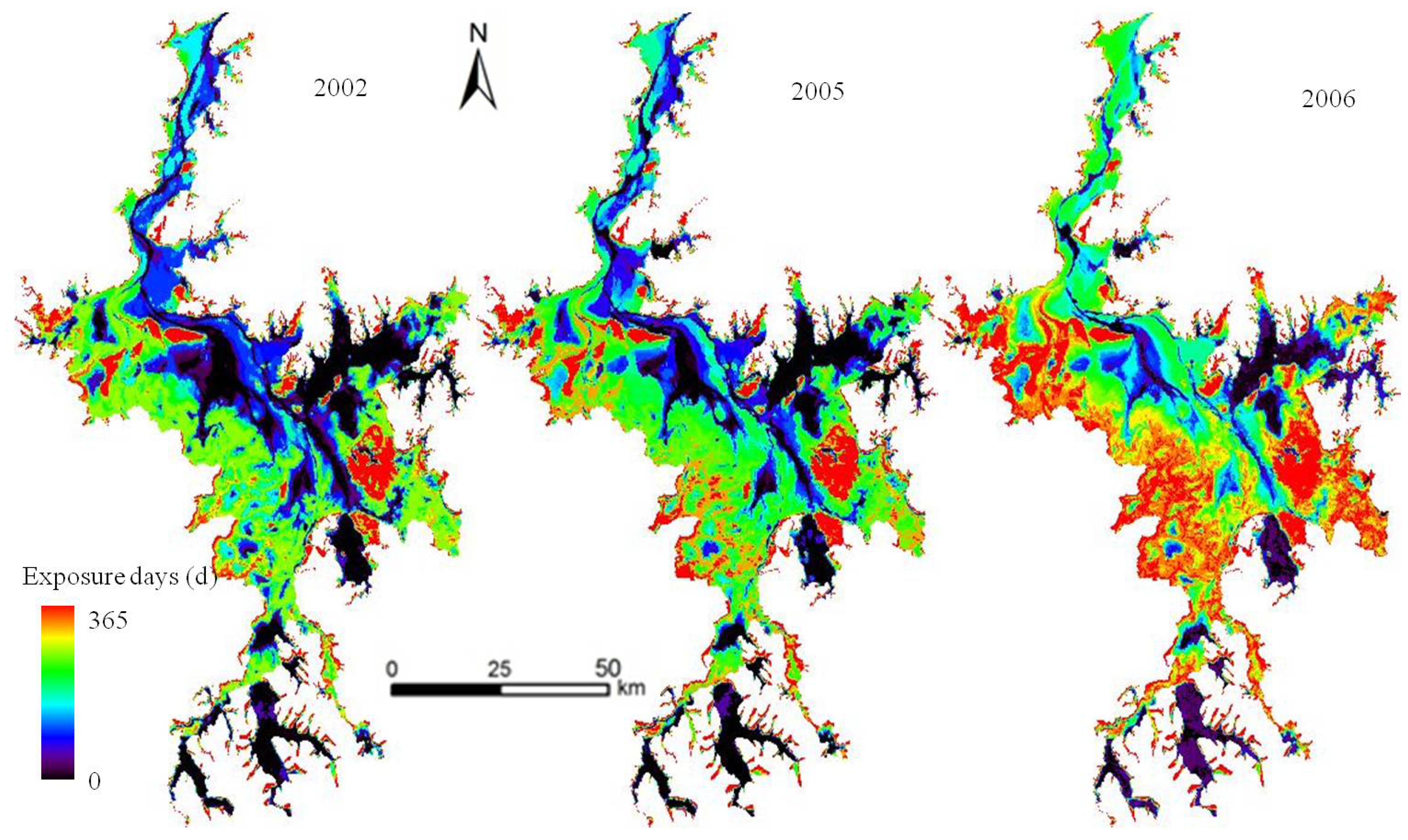
4.3. Spatial and Temporal Variation of ET in the Poyang Lake Wetland
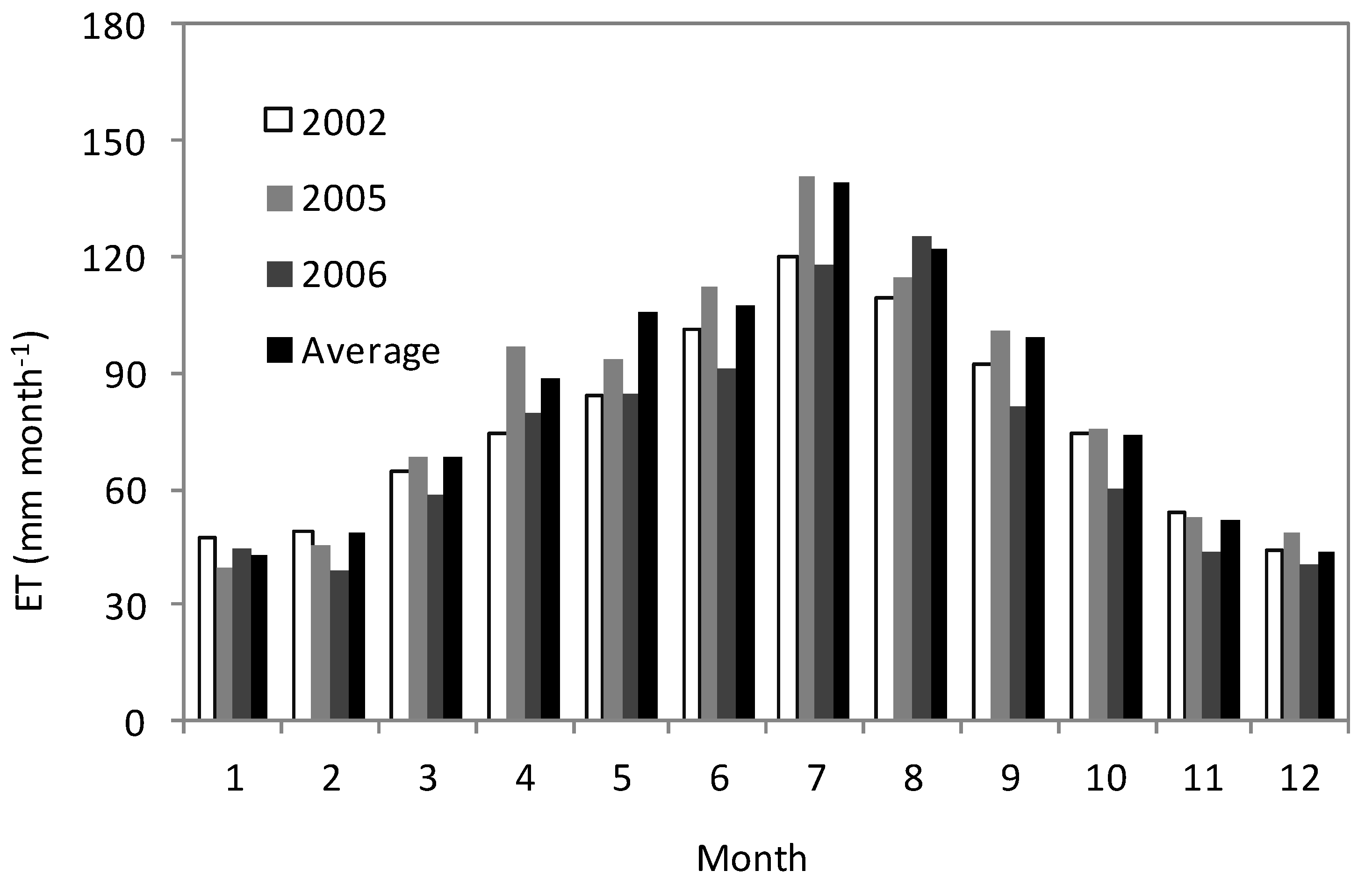
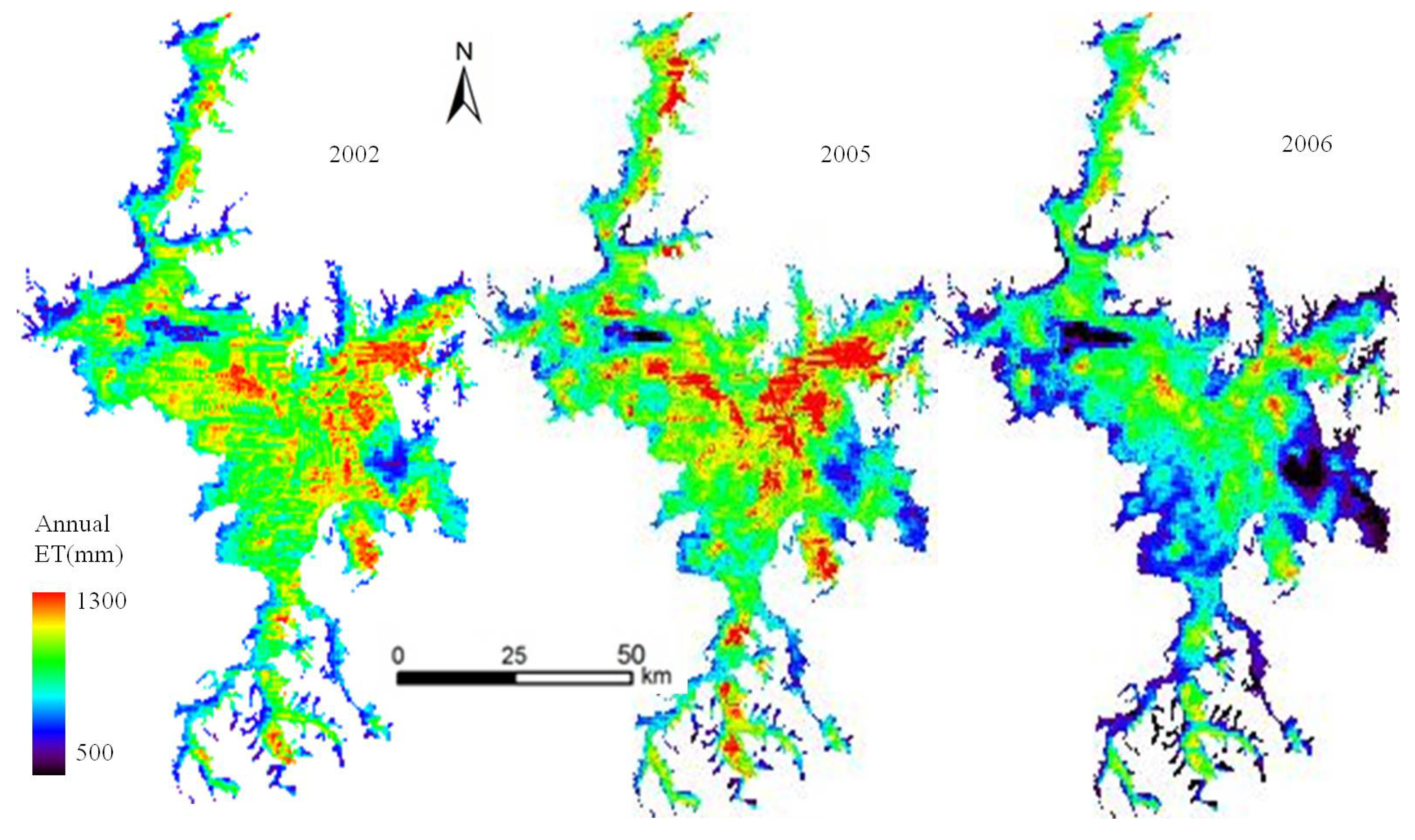
4.4. Combined Influences of Variables on ET in the Poyang Lake Wetland

 is the terrestrial evapotranspiration rate on the ith day (mm d−1) for land and
is the terrestrial evapotranspiration rate on the ith day (mm d−1) for land and  is the water evaporation rate on the ith day (mm d−1) for water.
is the water evaporation rate on the ith day (mm d−1) for water.  is the average daily ET rate (mm d−1) at the annual scale for land;
is the average daily ET rate (mm d−1) at the annual scale for land;  is the average daily evaporation rate (mm d−1) at the annual scale for water; and
is the average daily evaporation rate (mm d−1) at the annual scale for water; and  is the sum of evaporation (mm a−1) throughout the year for water.
is the sum of evaporation (mm a−1) throughout the year for water.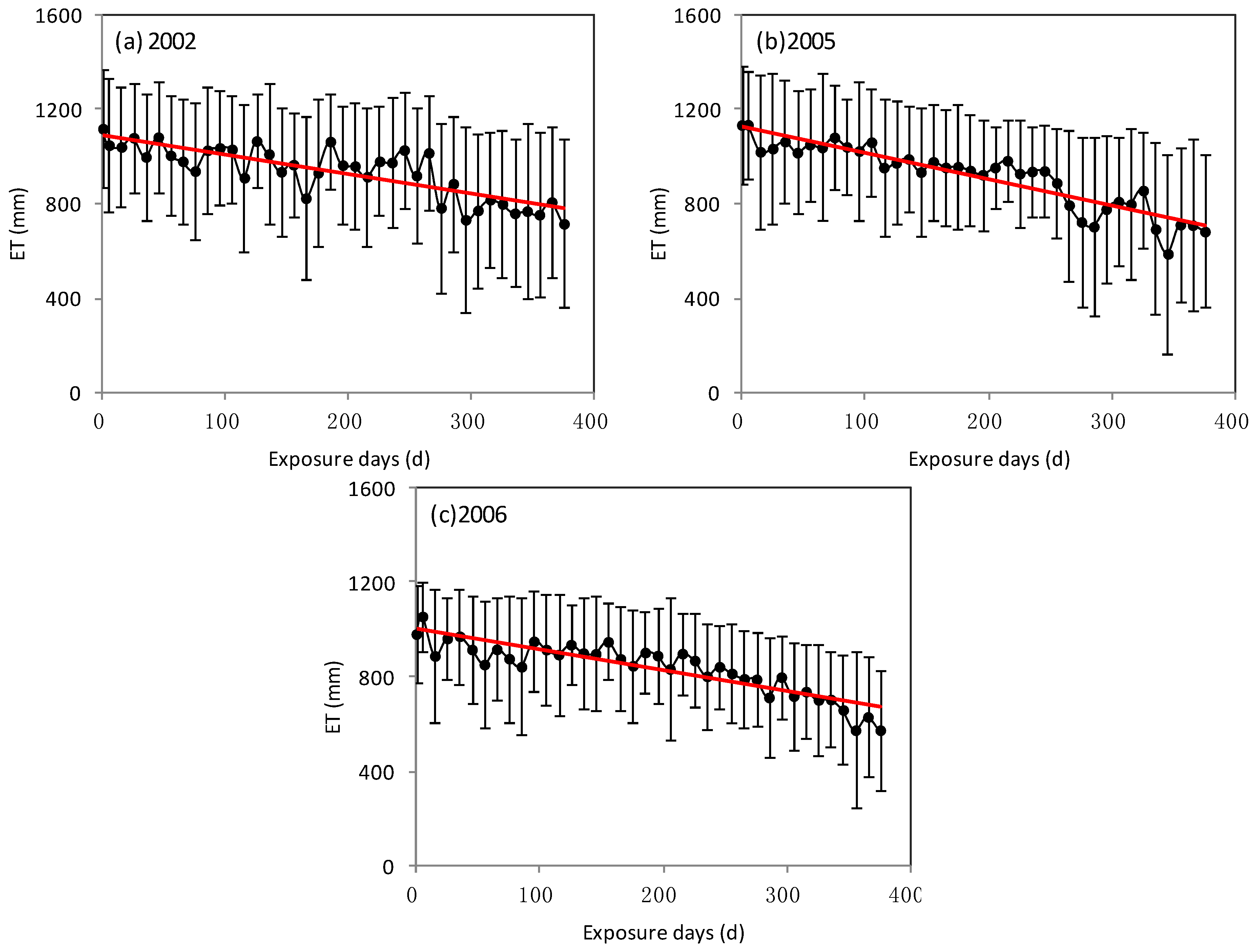

5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cowardin, L.M.; Carter, V.; Golet, F.C.; LaRoe, E.T. Classification of Wetlands and Deepwater Habitats of the United States; Fish and Wildlife Service, US Department of the Interior: Washington, DC, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, D.W. The cumulative effects of climate warming and other human stresses on Canadian freshwaters in the new millennium. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2001, 58, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolcox, D.A.; Meeker, J.E. Implications for faunal habitat related to altered macrophyte structure in regulated lakes in northern Minnesota. Wetlands 1992, 12, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poff, N.L.R.; Allan, J.D.; Bain, M.B.; Karr, J.R.; Prestegaard, K.L.; Richter, B.D.; Sparks, R.E.; Stromberg, J.C. The natural flow regime. BioScience 1997, 47, 769–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowlin, W.H.; Davies, J.-M.; Nordin, R.N.; Mazumder, A. Effects of water level fluctuation and short-term climate variation on thermal and stratification regimes of a British Columbia reservoir and lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2004, 20, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casanova, M.T.; Brock, M.A. How do depth, duration and frequency of flooding influence the establishment of wetland plant communities? Plant Ecol. 2000, 147, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonan, G.B. Forests and climate change: Forcings, feedbacks, and the climate benefits of forests. Science 2008, 320, 1444–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, M.; Reichstein, M.; Ciais, P.; Seneviratne, S.I.; Sheffield, J.; Goulden, M.L.; Bonan, G.; Cescatti, A.; Chen, J.; de Jeu, R. Recent decline in the global land evapotranspiration trend due to limited moisture supply. Nature 2010, 467, 951–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, L.; Sun, G.; Ford, C.; Vose, J. Modeling potential evapotranspiration of two forested watersheds in the southern Appalachians. Trans. ASABE 2011, 54, 2067–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.A.; Reichstein, M.; Buchmann, N.; Baldocchi, D.; Beer, C.; Schwalm, C.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Hasler, N.; Bernhofer, C.; Foken, T. Climate and vegetation controls on the surface water balance: Synthesis of evapotranspiration measured across a global network of flux towers. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinukollu, R.K.; Wood, E.F.; Ferguson, C.R.; Fisher, J.B. Global estimates of evapotranspiration for climate studies using multi-sensor remote sensing data: Evaluation of three process-based approaches. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 801–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Kanae, S. Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 2006, 313, 1068–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brutsaert, W. Evaporation into the atmosphere: Theory, history, and applications; D. Reidel Publishing Company: Dordrecht, Holland, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Alstad, K.; Chen, J.; Chen, S.; Ford, C.R.; Lin, G.; Liu, C.; Lu, N.; McNulty, S.G.; Miao, H. A general predictive model for estimating monthly ecosystem evapotranspiration. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Carrillo, S.; Angeler, D.G.; Sánchez-Andrés, R.; Alvarez-Cobelas, M.; Garatuza-Payán, J. Evapotranspiration in semi-arid wetlands: Relationships between inundation and the macrophyte-cover: Open-water ratio. Adv. Water Resour. 2004, 27, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsawwaf, M.; Willems, P.; Pagano, A.; Berlamont, J. Evaporation estimates from Nasser Lake, Egypt, based on three floating station data and Bowen ratio energy budget. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2010, 100, 439–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.M.; Mergelsberg, S.L.; Lopera, A.F.; Myers, D.A. Evapotranspiration from a wet prairie wetland under drought conditions: Paynes Prairie Preserve, FL, USA. Wetlands 2002, 22, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winter, T.C.; Buso, D.C.; Rosenberry, D.O.; Likens, G.E.; Sturrock, A.M., Jr.; Mau, D.P. Evaporation determined by the energy-budget method for Mirror Lake, New Hampshire. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2003, 48, 995–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drexler, J.Z.; Anderson, F.E.; Snyder, R.L. Evapotranspiration rates and crop coefficients for a restored marsh in the Sacramento–San Joaquin Delta, California, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Cobelas, M.; Cirujano, S.; Sánchez-Carrillo, S. Hydrological and botanical man-made changes in the Spanish wetland of Las Tablas de Daimiel. Biol. Conserv. 2001, 97, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeBlanc, M.-C.; de Blois, S.; Lavoie, C. The invasion of a large lake by the Eurasian genotype of common reed: The influence of roads and residential construction. J. Great Lakes Res. 2010, 36, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kustas, W.; Norman, J. Use of remote sensing for evapotranspiration monitoring over land surfaces. Hydrol. Sci. J. 1996, 41, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, M.C.; Norman, J.M.; Mecikalski, J.R.; Otkin, J.A.; Kustas, W.P. A climatological study of evapotranspiration and moisture stress across the continental United States based on thermal remote sensing: 1. Model formulation. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, N.; Islam, S.; Venturini, V.; Bisht, G.; Jiang, L. Estimation and comparison of evapotranspiration from MODIS and AVHRR sensors for clear sky days over the Southern Great Plains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Improvements to a MODIS global terrestrial evapotranspiration algorithm. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 1781–1800. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Z.; Gong, P.; Cheng, X.; Guo, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Shen, S.; Wu, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Geographical characteristics of China’s wetlands derived from remotely sensed data. Sci. China Ser. D Earth Sci. 2009, 52, 723–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Downing, J.; Prairie, Y.; Cole, J.; Duarte, C.; Tranvik, L.; Striegl, R.; McDowell, W.; Kortelainen, P.; Caraco, N.; Melack, J. The global abundance and size distribution of lakes, ponds, and impoundments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 2388–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, B.; Döll, P. Development and validation of a global database of lakes, reservoirs and wetlands. J. Hydrol. 2004, 296, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, C.P.; Rover, J.A.; Stets, E.G.; Striegl, R.G. The regional abundance and size distribution of lakes and reservoirs in the United States and implications for estimates of global lake extent. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2012, 57, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B. Research of Poyang Lake; Shanghai Scientific & Technical Publishers: Shanghai, China, 1988; p. 572. [Google Scholar]
- Andreoli, R.; Yesou, Y.; Li, J.; Desnos, Y.; Shifeng, H.; de Fraipont, P. Poyang Hu (Jiangxi Province, PR of China) area variations between January 2004 and June 2006 using ENVISAT low and medium resolution time series. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 2007, 13, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Chen, X.; Wang, X,; Gan, W. Spatial difference of water stage and its impact upon wetland hydrological analysis in Poyang Lake. J. Huazhong Norm. Univ. Nat. Sci. 2011, 24, 139–144. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center Home Page. Available online: https://lpdaac.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 31 July 2011).
- Schaaf, C.B.; Gao, F.; Strahler, A.H.; Lucht, W.; Li, X.; Tsang, T.; Strugnell, N.C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y.; Muller, J.-P. First operational BRDF, albedo nadir reflectance products from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 135–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, G.; Venturini, V.; Islam, S.; Jiang, L. Estimation of the net radiation using MODIS (Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer) data for clear sky days. Remote Sens. Environ. 2005, 97, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Zhai, J.; Gao, C.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y. A Comparison of Daily Actual Evapotranspiration Evaluation Models Based on Field Observational Data. Adv. Earth Sci. 2010, 9, 014. [Google Scholar]
- China Meteorological Data Sharing Service System Home Page. Available online: http://cdc.cma.gov.cn/ (accessed on 31 July 2011).
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S. A methodology for estimation of surface evapotranspiration over large areas using remote sensing observations. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1999, 26, 2773–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S. Estimation of surface evaporation map over southern Great Plains using remote sensing data. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Islam, S. An intercomparison of regional latent heat flux estimation using remote sensing data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2221–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priestley, C.H.B.; Taylor, R.J. On the assessment of surface heat flux and evaporation using large-scale parameters. Mon. Weath. Rev. 1972, 100, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Carlson, T. An overview of the “triangle method” for estimating surface evapotranspiration and soil moisture from satellite imagery. Sensors 2007, 7, 1612–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petropoulos, G.; Carlson, T.; Wooster, M.; Islam, S. A review of Ts/VI remote sensing based methods for the retrieval of land surface energy fluxes and soil surface moisture. Progr. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 224–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Loew, A. A direct algorithm for estimating daily regional Evapotranspiration from modis TOA radiances. In Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS), Munich, Germany, 22–27 July 2012; pp. 702–705.
- Tang, R.; Li, Z.L.; Tang, B. An application of the Ts-VI triangle method with enhanced edges determination for evapotranspiration estimation from MODIS data in arid and semi-arid regions: Implementation and validation. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 540–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stisen, S.; Sandholt, I.; Nørgaard, A.; Fensholt, R.; Jensen, K.H. Combining the triangle method with thermal inertia to estimate regional evapotranspiration—Applied to MSG-SEVIRI data in the Senegal River basin. Remote Sens. Environ. 2008, 112, 1242–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margulis, S.A.; Kim, J.; Hogue, T. A comparison of the triangle retrieval and variational data assimilation methods for surface turbulent flux estimation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2005, 6, 1063–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Moran, M.; Rahman, A.; Washburne, J.; Goodrich, D.; Weltz, M.; Kustas, W. Combining the Penman-Monteith equation with measurements of surface temperature and reflectance to estimate evaporation rates of semiarid grassland. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1996, 80, 87–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Loew, A. Estimation of evapotranspiration from MODIS TOA radiances in the Poyang Lake basin, China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1431–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, W.E.; Parlange, M.B.; Stricker, H. On the Concept of Equilibrium Evaporation and the Value of the Priestley-Taylor Coefficient. Water Resour. Res. 1996, 32, 161–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caparrini, F.; Castelli, F.; Entekhabi, D. Estimation of surface turbulent fluxes through assimilation of radiometric surface temperature sequences. J. Hydrometeorol. 2004, 5, 145–159. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Hiyama, T. Detectability of day-to-day variability in the evaporative flux ratio: A field examination in the Loess Plateau of China. Water Resour. Res. 2007, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, Y.; Wan, R. Satellite data application for the assessment of water balance in the Taihu watershed, China. J. Appl. Remote Sens. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farah, H.; Bastiaanssen, W.; Feddes, R. Evaluation of the temporal variability of the evaporative fraction in a tropical watershed. Int. J. Appl. Earth Observ. Geoinf. 2004, 5, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoedjes, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Jacob, F.; Ezzahar, J.; Boulet, G. Deriving daily evapotranspiration from remotely sensed instantaneous evaporative fraction over olive orchard in semi-arid Morocco. J. Hydrol. 2008, 354, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Xi, G.; Liu, S.; Huang, C.; Yan, Y.; Liu, G. Regional estimation of daily to annual regional evapotranspiration with MODIS data in the Yellow River Delta wetland. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 136, 1775–1787. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, J.; Borsche, M.; Liu, Y.; Loew, A. How representative are instantaneous evaporative fraction measurements of daytime fluxes? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 3913–3919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisht, G.; Bras, R.L. Estimation of net radiation from the MODIS data under all sky conditions: Southern Great Plains case study. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 1522–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, B.; Mallick, K.; Patel, N.; Parihar, J. Regional clear sky evapotranspiration over agricultural land using remote sensing data from Indian geostationary meteorological satellite. J. Hydrol. 2010, 387, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, Q.; Heinsch, F.A.; Zhao, M.; Running, S.W. Development of a global evapotranspiration algorithm based on MODIS and global meteorology data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 111, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davranche, A.; Lefebvre, G.; Poulin, B. Wetland monitoring using classification trees and SPOT-5 seasonal time series. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, A.; Kearney, M. Reducing signature variability in unmixing coastal marsh Thematic Mapper scenes using spectral indices. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 2317–2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.-C. NDWI—A normalized difference water index for remote sensing of vegetation liquid water from space. Remote Sens. Environ. 1996, 58, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.G. Application of AVHRR to monitoring a climatically sensitive playa. Case study: Chott el Djerid, southern Tunisia. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 1999, 24, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalma, J.D.; McVicar, T.R.; McCabe, M.F. Estimating land surface evaporation: A review of methods using remotely sensed surface temperature data. Surv. Geophys. 2008, 29, 421–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raupach, M. Combination theory and equilibrium evaporation. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2001, 127, 1149–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafleur, P.M.; Rouse, W.R. The influence of surface cover and climate on energy partitioning and evaporation in a subarctic wetland. Bound. Layer Meteorol. 1988, 44, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenters, J.D.; Kratz, T.K.; Bowser, C.J. Effects of climate variability on lake evaporation: Results from a long-term energy budget study of Sparkling Lake, northern Wisconsin (USA). J. Hydrol. 2005, 308, 168–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulden, M.L.; Litvak, M.; Miller, S.D. Factors that control Typha marsh evapotranspiration. Aquat. Bot. 2007, 86, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aires, L.M.; Pio, C.A.; Pereira, J.S. The effect of drought on energy and water vapour exchange above a Mediterranean C3/C4 grassland in Southern Portugal. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2008, 148, 565–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, E.G.; Loheide, S.P. Effects of evapotranspiration partitioning, plant water stress response and topsoil removal on the soil moisture regime of a floodplain wetland: Implications for restoration. Hydrol. Process. 2010, 24, 2934–2946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giambelluca, T.W.; Scholz, F.G.; Bucci, S.J.; Meinzer, F.; Goldstein, G.; Hoffmann, W.; Franco, A.; Buchert, M. Evapotranspiration and energy balance of Brazilian savannas with contrasting tree density. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2009, 149, 1365–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schedlbauer, J.L.; Oberbauer, S.F.; Starr, G.; Jimenez, K.L. Controls on sensible heat and latent energy fluxes from a short-hydroperiod Florida Everglades marsh. J. Hydrol. 2011, 411, 331–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenters, J.D.; Cutrell, G.J.; Istanbulluoglu, E.; Scott, D.T.; Herrman, K.S.; Irmak, A.; Eisenhauer, D. Seasonal energy and water balance of a Phragmites australis-dominated wetland in the Republican River basin of south-central Nebraska (USA). J. Hydrol. 2011, 408, 19–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San José, J.; Meirelles, M.; Bracho, R.; Nikonova, N. A comparative analysis of the flooding and fire effects on the energy exchange in a wetland community (Morichal) of the Orinoco Llanos. J. Hydrol. 2001, 242, 228–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, W.R. The energy and water balance of high-latitude wetlands: Controls and extrapolation. Glob. Change Biol. 2000, 6, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anda, A.; Boldizsár, A. Microclimate and transpiration of reedbeds on lakeshores with changing water levels. Acta Agron. Hungarica 2006, 54, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Trettin, C.C.; Li, H.; Sun, G. An integrated model of soil, hydrology, and vegetation for carbon dynamics in wetland ecosystems. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16, 9–1. [Google Scholar]
- Keough, J.R.; Thompson, T.A.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Wilcox, D.A. Hydrogeomorphic factors and ecosystem responses in coastal wetlands of the Great Lakes. Wetlands 1999, 19, 821–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldocchi, D.D.; Wilson, K.B. Modeling CO2 and water vapor exchange of a temperate broadleaved forest across hourly to decadal time scales. Ecol. Modell. 2001, 142, 155–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Churkina, G.; Schimel, D.; Braswell, B.H.; Xiao, X. Spatial analysis of growing season length control over net ecosystem exchange. Glob. Change Biol. 2005, 11, 1777–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angert, A.; Biraud, S.; Bonfils, C.; Henning, C.; Buermann, W.; Pinzon, J.; Tucker, C.; Fung, I. Drier summers cancel out the CO2 uptake enhancement induced by warmer springs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10823–10827. [Google Scholar]
- Moore, K.E.; Fitzjarrald, D.R.; Sakai, R.K.; Goulden, M.L.; Munger, J.W.; Wofsy, S.C. Seasonal variation in radiative and turbulent exchange at a deciduous forest in central Massachusetts. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1996, 35, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.B.; Baldocchi, D.D.; Hanson, P.J. Spatial and seasonal variability of photosynthetic parameters and their relationship to leaf nitrogen in a deciduous forest. Tree Physiol. 2000, 20, 565–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Hu, C.; Chen, X.; Cai, X.; Tian, L.; Gan, W. Assessment of inundation changes of Poyang Lake using MODIS observations between 2000 and 2010. Remote Sens. Environ. 2012, 121, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, C.; Zhao, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y. Vegetation biomass spatial-temporal variations and the influence of the water level in Poyang Lake National Nature Reserve. J. Lake Sci. 2013, 25, 707–714. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, X.; Liu, Y. Lake Fluctuation Effectively Regulates Wetland Evapotranspiration: A Case Study of the Largest Freshwater Lake in China. Water 2014, 6, 2482-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6082482
Zhao X, Liu Y. Lake Fluctuation Effectively Regulates Wetland Evapotranspiration: A Case Study of the Largest Freshwater Lake in China. Water. 2014; 6(8):2482-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6082482
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Xiaosong, and Yuanbo Liu. 2014. "Lake Fluctuation Effectively Regulates Wetland Evapotranspiration: A Case Study of the Largest Freshwater Lake in China" Water 6, no. 8: 2482-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6082482
APA StyleZhao, X., & Liu, Y. (2014). Lake Fluctuation Effectively Regulates Wetland Evapotranspiration: A Case Study of the Largest Freshwater Lake in China. Water, 6(8), 2482-2500. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6082482





