Abstract
Global climate change has resulted in a gradual sea level rise. Sea level rise can cause saline water to migrate upstream in estuaries and rivers, thereby threatening freshwater habitat and drinking-water supplies. In the present study, a three-dimensional hydrodynamic model was established to simulate salinity distributions and transport time scales in the Wu River estuary of central Taiwan. The model was calibrated and verified using tidal amplitudes and phases, time-series water surface elevation and salinity distributions in 2011. The results show that the model simulation and measured data are in good agreement. The validated model was then applied to calculate the salinity distribution, flushing time and residence time in response to a sea level rise of 38.27 cm. We found that the flushing time for high flow under the present condition was lower compared to the sea level rise scenario and that the flushing time for low flow under the present condition was higher compared to the sea level rise scenario. The residence time for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario was between 10.51 and 34.23 h and between 17.11 and 38.92 h, respectively. The simulated results reveal that the residence time of the Wu River estuary will increase when the sea level rises. The distance of salinity intrusion in the Wu River estuary will increase and move further upstream when the sea level rises, resulting in the limited availability of water of suitable quality for municipal and industrial uses.
1. Introduction
Global warming is irrefutably causing sea level to rise. The global mean sea level raised by ~20 cm, along with a rise in the regional mean sea level, as the global air temperature increased by ~0.5–0.6 °C during the 20th century [1,2]. In Taiwan, the surface temperature has raised approximately 1.0–1.4 °C over the last 100 years [3]. Over the past 80 years, the annual precipitation has increased in northern Taiwan and declined in central and southern Taiwan [4]. The changing climate has also caused some impacts on river ecosystems in Taiwan; more-frequent habitat disturbances have caused both a shift in aquatic organism distributions and population decline [5].
Sea level rise can cause saline water to migrate upstream to points where freshwater previously existed [6]. Several studies indicated that sea level rise would increase the salinity in estuaries [7,8], which would result in changes in stratification and estuarine circulation [9]. Salinity migration could cause shifts in salt-sensitive habitats and could thus affect the distribution of flora and fauna.
Salinity intrusion may decrease the water quality in an estuary, so that its water becomes unsuitable for certain uses, such as agricultural, industrial and drinking purposes. Therefore, the determination of the salinity distribution along an estuary is a major interest for water managers in estuaries and coastal regions. The evaluation of transport time scales is highly related to the water quality and ecological health of different aquatic systems [10].
Several numerical modeling studies have shown that increases in sea level have impacts on estuarine salinity. Hull and Tortoriello [11] used a one-dimensional model to estimate the impacts of sea level rise and found that a sea level rise of 0.13 m would result in a salinity increase of 0.4 psu (practical salinity unit) in the upper portion of the Delaware Bay during low-flow periods. Grabemann et al. [12] simulated a 2-km upstream advance of the brackish water zone for a sea level rise of 0.55 m in the Weser Estuary, Germany. Hilton et al. [7] found an average salinity increase of approximately 0.5 with a 0.2 m sea level rise based on model simulations in Chesapeake Bay. Chua et al. [13] found that the intrusion of salt water into San Francisco Bay and the flushing rate both increase as the sea level rises. Bhuiyan and Dutta [8] applied a one-dimensional model to investigate the impact of sea level rise on river salinity in the Gorai River network and found that a sea level rise of 0.59 m increased salinity by 0.9 at a distance of 80 km upstream of the river mouth. Rice et al. [14] concluded that salinity in the James River would intrude about 10 km farther upstream for a sea level rise of 1.0 m using a three-dimensional hydrodynamic model.
Numerous studies have reported the influences of sea level rise on estuarine salinity, stratification, exchange flow, residence time, material transport processes and other relevant processes in estuaries [8,9,14]. However, the reports regarding the impacts of sea level rise on salinity intrusion and transport time scales have not yet been studied in Taiwan’s estuaries. The objective of the present study is to examine the salinity intrusion, flushing time and residence time in response to sea level rise in the Wu River estuary of central Taiwan using a three-dimensional hydrodynamic and salinity transport model. The model was validated with observed amplitudes and phases, water levels and salinity to ascertain the model’s accuracy and capability. The model was then applied to the Wu River estuary to calculate the salinity distributions and transport time scales based on sea level rise projections. The model results were used to investigate how sea level rise affects salinity intrusion, flushing time and residence time in Taiwan’s Wu River estuary.
2. Study Area
The Wu River system is the most important river in central Taiwan (Figure 1a). The mean tidal range at the mouth of the Wu River is 3.8 m above mean sea level. Tidal propagation is the dominant mechanism controlling the water surface elevation. The M2 (principal lunar semi-diurnal) tide is the primary tidal constituent at the mouth of the Wu River [15]. The main tributaries are the Fazi River, Dali River, Han River and Maoluo River. The downstream reaches of the main Wu River are affected by tides, whereas the tributaries are not subject to tidal effects and are therefore not affected by salt water intrusion. The drainage basin of the Wu River, which is the fourth-largest river basin in Taiwan, covers approximately 2026 km2. The total channel length is 117 km, and the mean channel slope is 1/92. The morphology of the Wu River displays different features in each segment, molded by natural forces, as well as anthropogenic activities exerted upon the paleo-riverbed built ages ago. The riverbed is composed of silt and sand in the estuary. The mean annual precipitation in this region is 2087 mm. The ample flow season is from May to September, accounting for 70% of the river discharge, and the dry season is from January to February. The daily flow data from 1969 to 2011 at the Dadu Bridge, collected by the Water Resources Bureau of Taiwan, are analyzed in this study. The data analysis indicates that the Q75 low flow is 41.2 m3/s. The definition of Q75 is the flow that is equaled or exceeded for 75% of the time. The river, which flows into the Taiwan Strait, is located in a temperate area characterized by intense agricultural and industrial activities. The Wu River catchment is also an important water supply source for central Taiwan. Figure 1b shows the topography of the Wu River estuary and its adjacent coastal sea. This figure indicates that the greatest depth in the study area is 70 m (below mean sea level) near the corner of the coastal sea.
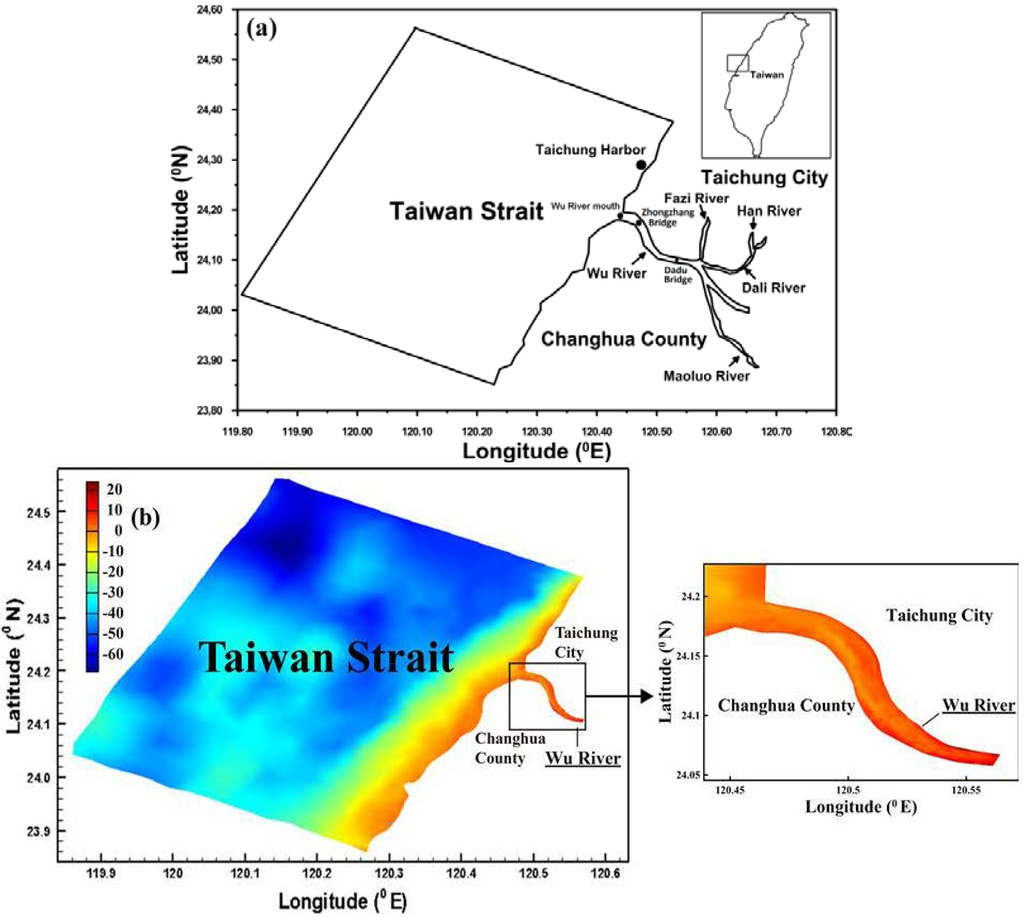
Figure 1.
(a) Map of the Wu River system and (b) bathymetry of the Wu River estuary and adjacent coastal sea.
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Sea Level Rise Projection
The existence of sea level rise is undeniable. Church and White [16] estimated the global mean sea level rise rates from tidal gauges and satellite altimetry as follows: 1.7 ± 0.2 mm year−1 for 1900–2009 and 1.9 ± 0.4 mm year−1 for 1961–2009, both of which are comparable to the ~1.8 mm year−1 rate obtained from GPS-derived crustal velocities and tidal gauges around North America [17]. Global tide gauge records, satellite data and modeling provide mean historical rates of ~1.7–1.8 mm year−1 for the 20th century and ~3.3 mm year−1 for the last few decades [18].
The purpose of this study is to identify the response of the Wu River estuary to potential future sea level rise based on the analyzed results of observed sea level. Tseng et al. [19] investigated the pattern and trends of sea level rise in the region seas around Taiwan through the analyses of long-term tide-gauge and satellite altimetry data. They found that consistent with the coastal tide-gauge records, satellite altimetry data showed similar increasing rates (+5.3 mm/year) around Taiwan. They did not include wave breaking around the river mouth and coastal seas, resulting in water level rise due to wave set-up. In this study, the wave set-up issue also did not take into account. The linear regression method was used to yield the sea level rise trend according to the monthly average water surface elevation collected from 1971 to 2011 at the Taichung Harbor station, which is shown in Figure 2. The equation of linear regression can be expressed as:
where X is the time (year) and Y is the sea water level (cm). We found that the rate of sea level rise was 4.3 mm/year at the Taichung Harbor station. Huang et al. [20] estimated the sea level rise at the Taichung Harbor station using the data of tidal gauge and satellite altimetry and found that the rate of sea level rise was 3.7 mm/year. Their results are similar to our estimation on the rate of sea level rise. The sea level rise in 2011 was set up zero to project the sea level rise in 2010. The future projected sea level rise of 38.27 cm in 2100 was used in the simulation scenario.
Y = 0.43X − 591.8
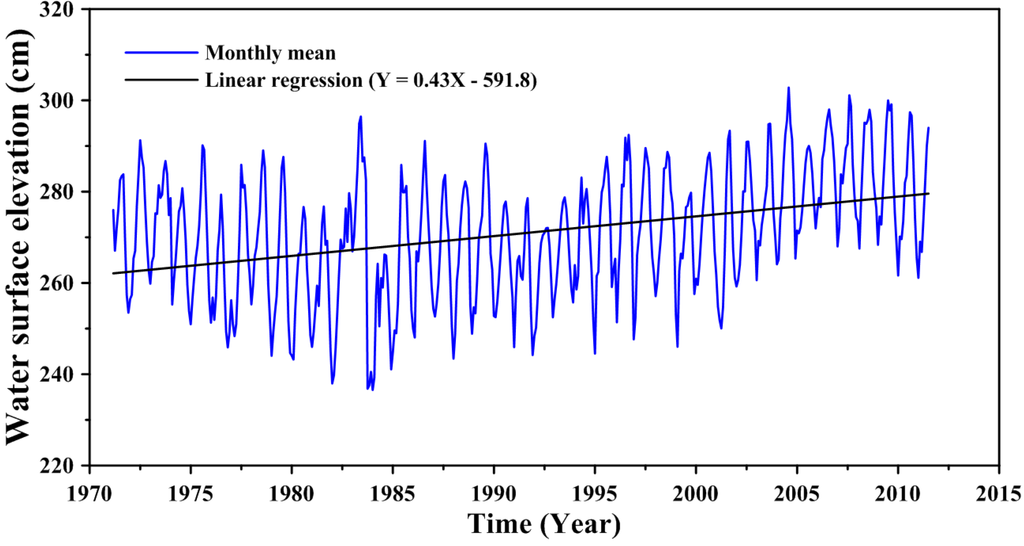
Figure 2.
Linear regression for the sea level rise trend at the Taichung Harbor station.
3.2. Three-Dimensional Hydrodynamic Model
A three-dimensional, semi-implicit Euler-Lagrange finite-element model (SELFE) [21] was implemented to simulate the hydrodynamics and salinity transport in the Wu River estuary and its adjacent coastal sea. SELFE solves the Reynolds-stress averaged Navier-Stokes equations, which consist of the conservation laws for mass and momentum and the use of the hydrostatic and Boussinesq approximations, yielding the following free-surface elevation and three-dimensional water velocity equations:
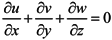
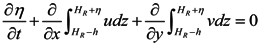
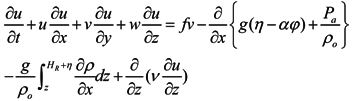
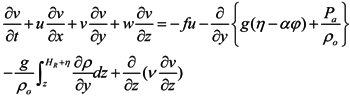
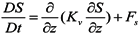 where (x,y) are the horizontal Cartesian coordinates; (ϕ,λ) are the latitude and longitude, respectively; z is the vertical coordinate, positive upward; t is time; HR is the z-coordinate at the reference level (mean sea level); η(x,y,t) is the free-surface elevation; h(x,y) is the bathymetric depth; u,v and w are the velocities in the x, y and z directions, respectively; f is the Coriolis force; g is the acceleration of gravity;φ(ϕ,λ) is the tidal potential; α is the effective earth elasticity factor (=0.69);
where (x,y) are the horizontal Cartesian coordinates; (ϕ,λ) are the latitude and longitude, respectively; z is the vertical coordinate, positive upward; t is time; HR is the z-coordinate at the reference level (mean sea level); η(x,y,t) is the free-surface elevation; h(x,y) is the bathymetric depth; u,v and w are the velocities in the x, y and z directions, respectively; f is the Coriolis force; g is the acceleration of gravity;φ(ϕ,λ) is the tidal potential; α is the effective earth elasticity factor (=0.69); 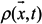 is the water density, of which the default reference value; ρo, is set to 1,025 kg/ m3; Pa(x,y,t) is the atmospheric pressure at the free surface; p is the pressure; v is the vertical eddy viscosity; S is the salinity; Kv is the vertical eddy diffusivity for salinity and Fs is the horizontal diffusion for the transport equation.
is the water density, of which the default reference value; ρo, is set to 1,025 kg/ m3; Pa(x,y,t) is the atmospheric pressure at the free surface; p is the pressure; v is the vertical eddy viscosity; S is the salinity; Kv is the vertical eddy diffusivity for salinity and Fs is the horizontal diffusion for the transport equation.
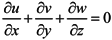
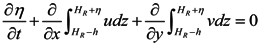
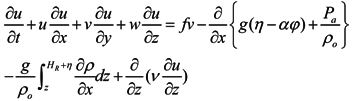
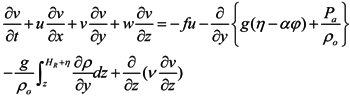
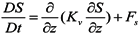
ρ = ρ0(p, S)
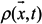 is the water density, of which the default reference value; ρo, is set to 1,025 kg/ m3; Pa(x,y,t) is the atmospheric pressure at the free surface; p is the pressure; v is the vertical eddy viscosity; S is the salinity; Kv is the vertical eddy diffusivity for salinity and Fs is the horizontal diffusion for the transport equation.
is the water density, of which the default reference value; ρo, is set to 1,025 kg/ m3; Pa(x,y,t) is the atmospheric pressure at the free surface; p is the pressure; v is the vertical eddy viscosity; S is the salinity; Kv is the vertical eddy diffusivity for salinity and Fs is the horizontal diffusion for the transport equation.The vertical boundary conditions for the momentum equation, especially the bottom boundary condition, play an important role in the SELFE numerical formulation, as it involves the unknown velocity. In fact, as a crucial step in solving the differential system, SELFE uses the bottom condition to decouple free-surface Equation (3) from momentum Equations (4) and (5). The vertical boundary conditions for the momentum equation are presented as below.
At the water surface, the balance between the internal Reynolds stress and the applied shear stress yields:
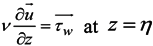 where the specific stress, τw, can be parameterized using the approach [22].
where the specific stress, τw, can be parameterized using the approach [22].
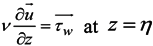
The boundary condition at the bottom plays an important role in the SELFE formulation, as it involves unknown velocity. Specifically, at the bottom, the no-slip condition (U =V =0) is usually replaced by a balance between the internal Reynolds stress and the bottom frictional stress, i.e.,
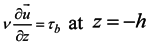 where the bottom stress is
where the bottom stress is 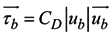 .
.
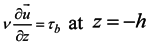
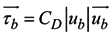 .
.The velocity profile inside the bottom boundary layers obeys the logarithmic law:
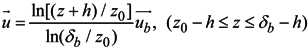 which is subject to be smoothly matched to the exterior flow. In Equation (10), δb is the thickness of the bottom computational cell; z0 is the bottom roughness, which is determined through model calibration and verification; and ub is the bottom velocity, measured at the top of the bottom computational cell. The Reynolds stress inside the boundary layer is derived from Equation (11) as:
which is subject to be smoothly matched to the exterior flow. In Equation (10), δb is the thickness of the bottom computational cell; z0 is the bottom roughness, which is determined through model calibration and verification; and ub is the bottom velocity, measured at the top of the bottom computational cell. The Reynolds stress inside the boundary layer is derived from Equation (11) as:
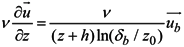
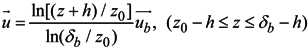
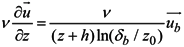
The SELFE model uses the Generic Length Scale (GLS) turbulence closure approach of Umlauf and Burchard [23], which has the advantage of incorporating most of the 2.5-equation closure model. The SELFE model treats advection in the momentum equation using a Euler–Lagrange methodology. A detailed description of the turbulence closure model, the vertical boundary conditions for the momentum equation and the numerical solution methods can be found in Zhang and Baptista [21].
3.3. Computation of Flushing Time
The flushing time can be conveniently determined by the freshwater fraction approach [24,25,26,27], which can be determined from salinity distributions. This technique provides an estimation of the time scale over which contaminants and/or other material released in the estuary are removed from the system. Using the freshwater fraction method, the flushing time in an estuary can be expressed as:
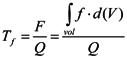 where F is the accumulated freshwater volume in the estuary, which can be calculated by integrating the freshwater volume; d(V), in all the sub-divided model grids over a period of time. In estuaries with unsteady river flow and tidal variations; F and Q are the approximate average freshwater volume and average freshwater input, respectively, over several tidal cycles for a period of time, such as a week or a month [20,21]. The term, f, is the freshwater content or the freshwater fraction, which is described by:
where F is the accumulated freshwater volume in the estuary, which can be calculated by integrating the freshwater volume; d(V), in all the sub-divided model grids over a period of time. In estuaries with unsteady river flow and tidal variations; F and Q are the approximate average freshwater volume and average freshwater input, respectively, over several tidal cycles for a period of time, such as a week or a month [20,21]. The term, f, is the freshwater content or the freshwater fraction, which is described by:
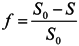 where S0 is the salinity in the ocean; and S is the salinity at the study location.
where S0 is the salinity in the ocean; and S is the salinity at the study location.
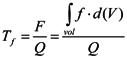
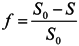
3.4. Computation of Residence Time
The time scales associated with the residence time of water parcels and their associated dissolved and suspended materials in a specific water body due to different transport mechanisms (i.e., advection and dispersion) are fundamental physical characteristics of that water body. Residence time is defined as the time required for a water parcel to leave the region of interest for the first time [28]. Several methodologies for the computation of residence time have been reported in the literature [29,30,31,32,33,34]. In the present study, the computational method follows the procedures outlined by Takeoka [30]. Consider that a region of interest contains a finite mass of tracer given by M(0) at the initial time t = t0. If we define the remaining mass of tracer at a certain time, t, within the system as M(t), the distribution function of the residence time can be defined as:
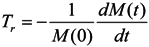 where Tr is the distribution function of residence time. The total mass of the tracer will completely leave the system at a given moment when limt→∞ M(t) is equal to zero. The average residence time of the tracer can be computed by:
where Tr is the distribution function of residence time. The total mass of the tracer will completely leave the system at a given moment when limt→∞ M(t) is equal to zero. The average residence time of the tracer can be computed by:
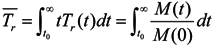
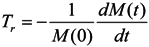
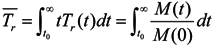
The r(t) = M(t)/ M(0) fraction of mass is known as the remnant function. Note that M(t), the mass of the tracer that remains in the region of interest at a certain time; t, can be computed numerically based on the tracer concentration by:
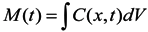 where C(x,t) is the tracer concentration in a differential volume ;dV, at a given time; t, and position, x, within the system. It is expected that a mass of tracers injected close to the boundaries of a given region has a lower residence time than does the residence time of tracers injected at the center of such a region.
where C(x,t) is the tracer concentration in a differential volume ;dV, at a given time; t, and position, x, within the system. It is expected that a mass of tracers injected close to the boundaries of a given region has a lower residence time than does the residence time of tracers injected at the center of such a region.
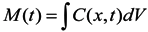
3.5. Model Schematization
An accurate representation of the bottom topography in the model grid is critical for successful estuarine, coastal and ocean modeling. In this study, the bottom topography data in the coastal seas and Wu River estuary were obtained from the databank of the National Science Council and the Water Resources Agency in Taiwan, respectively. The modeling domain in the horizontal plane covers an area of 60 km × 45 km at the coastal sea boundary. Because SELFE uses a combination of Eulerian–Lagrangian and implicit time stepping, it does not have to satisfy the usual Courant–Friedrich–Levy (CFL) constraint for numerical stability [21]. However, 120 s was chosen as the time step (Δt). Trial-and-error tests with other time steps demonstrated that the model results did not improve significantly with lower values. The model meshes for the Wu River estuary and the coastal sea consisted of 3541 polygons and 1974 grids, respectively (Figure 3). Because the model domain covers deep bathymetry in the coastal sea and shallow bathymetry near the coastline, ten levels, varying in thickness from 0.2 to 7 m, were adopted for vertical discretization in the SELFE model.
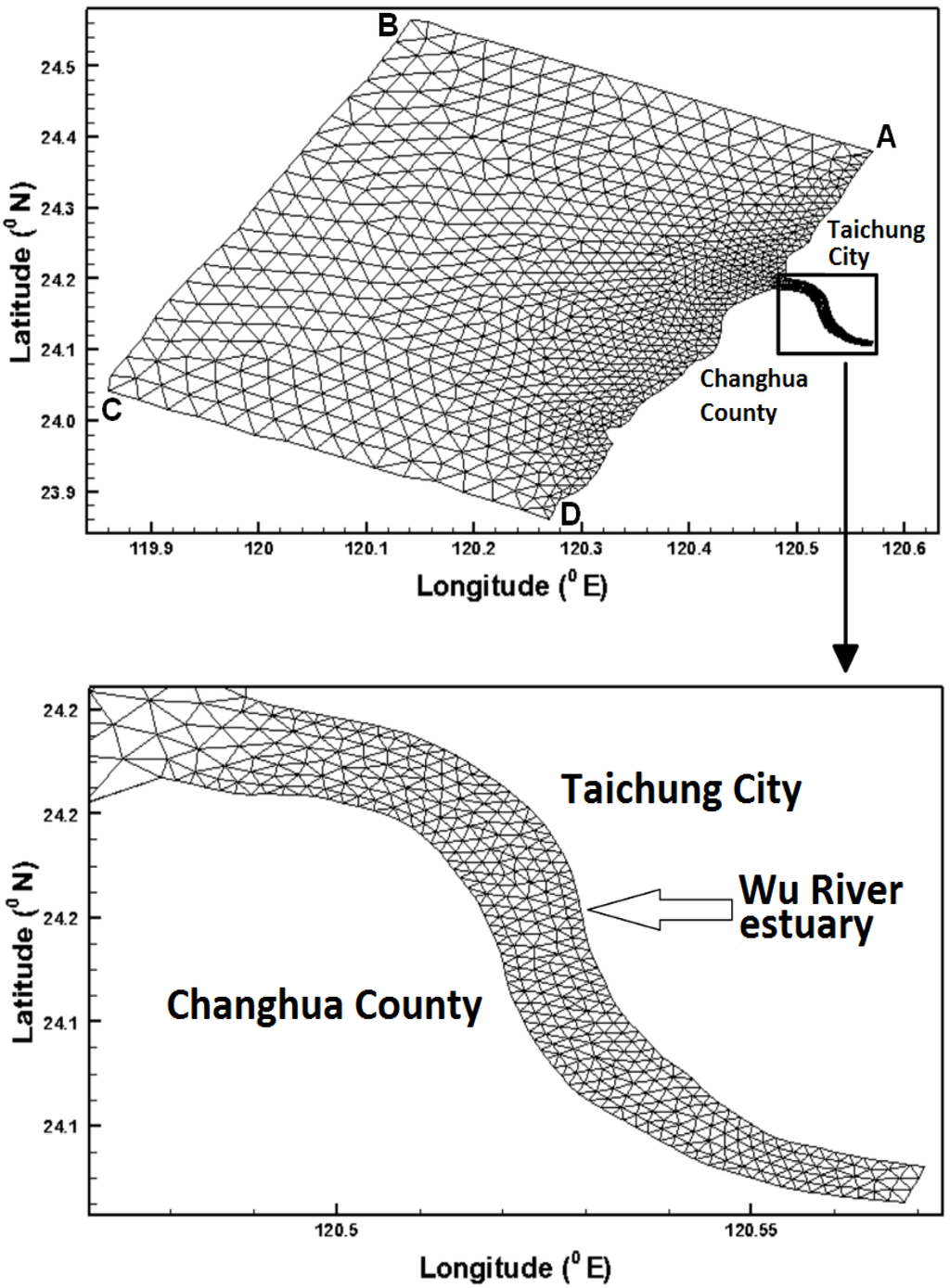
Figure 3.
Unstructured grids in the modeling domain.
4. Model Calibration and Verification
To ascertain the model accuracy for applications on the assessment of sea level rise on salinity intrusion and transport time scales, a set of observational data collected in 2011 were used to calibrate and verify the model and to validate its capability to predict amplitudes and phases, water surface elevation and salinity distribution.
4.1. Calibration with Amplitudes and Phases
The local bottom roughness height (zo) is similar to the Manning coefficient, affecting the water level calculations for the coastal sea and estuary. The values of local bottom roughness height were iteratively adjusted by trial and error until the simulated and observed tidal levels were satisfactory [35]. In this study, the bottom roughness was adjusted to calibrate the amplitudes and phases at Taichung Harbor. The model calibration of the amplitudes and phases was conducted using measured data on the daily freshwater discharge at the Dadu Bridge in 2011. A five-constituent tide (i.e., M2, S2, N2, K1 and O1) was adopted in the model simulation as a forcing function at the coastal sea boundaries (shown in Table 1). Because the amplitudes of fourth-diurnal, such as M4 (first overtide of M2 constituent) and MS4 (a compound tide of M2 and S2), comparing to diurnal and semi-diurnal tides, were relatively small, a five-constituent tide was used to force the open boundaries only. The amplitudes and phases of these five tidal constituents were used to generate time-series water surface elevations along the open boundaries. The freshwater discharge inputs from Dadu Bridge in 2011 are shown in Figure 4. The maximum freshwater discharge reached 690 m3/s during the typhoon event.
The model simulation was run for one year in 2011. Harmonic analysis was performed on the time series of the model simulated water surface elevation at Taichung Harbor. The bottom roughness height was adjusted carefully, and the results are presented in Figure 5. The results show the comparison of the amplitudes and phases of harmonic constants between computed and observed tides. The differences between the computed and observed tidal constituents for amplitude and phase are in the range of 0.01–0.02 m and 0.45°–4.21°, respectively. The differences in amplitude and phase are quite small.

Table 1.
The amplitudes and phases used for the model simulation at the coastal sea boundaries.
| Constituent | Boundary at Point A | Boundary at Point B | Boundary at Point C | Boundary at Point D | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude (m) | Phase (°) | Amplitude (m) | Phase (°) | Amplitude (m) | Phase (°) | Amplitude (m) | Phase (°) | |
| M2 | 1.82 | 266.06 | 1.88 | 266.91 | 1.60 | 272.39 | 1.57 | 267.23 |
| S2 | 0.51 | 14.45 | 0.53 | 16.34 | 0.44 | 26.29 | 0.43 | 20.55 |
| N2 | 0.25 | 28.89 | 0.26 | 29.77 | 0.22 | 36.02 | 0.21 | 31.15 |
| K1 | 0.27 | 161.62 | 0.29 | 160.20 | 0.29 | 167.21 | 0.28 | 167.16 |
| O1 | 0.21 | 279.53 | 0.22 | 277.24 | 0.23 | 283.55 | 0.22 | 284.03 |
Notes: boundaries at Points A, B, C and D are shown in Figure 3; M2 is principal lunar semi-diurnal constituent; S2 is principal solar semi-diurnal constituent; N2 is larger lunar elliptic semi-diurnal constituent; K1 is luni-solar declinational diurnal constituent; and O1 is lunar declinational diurnal constituent.
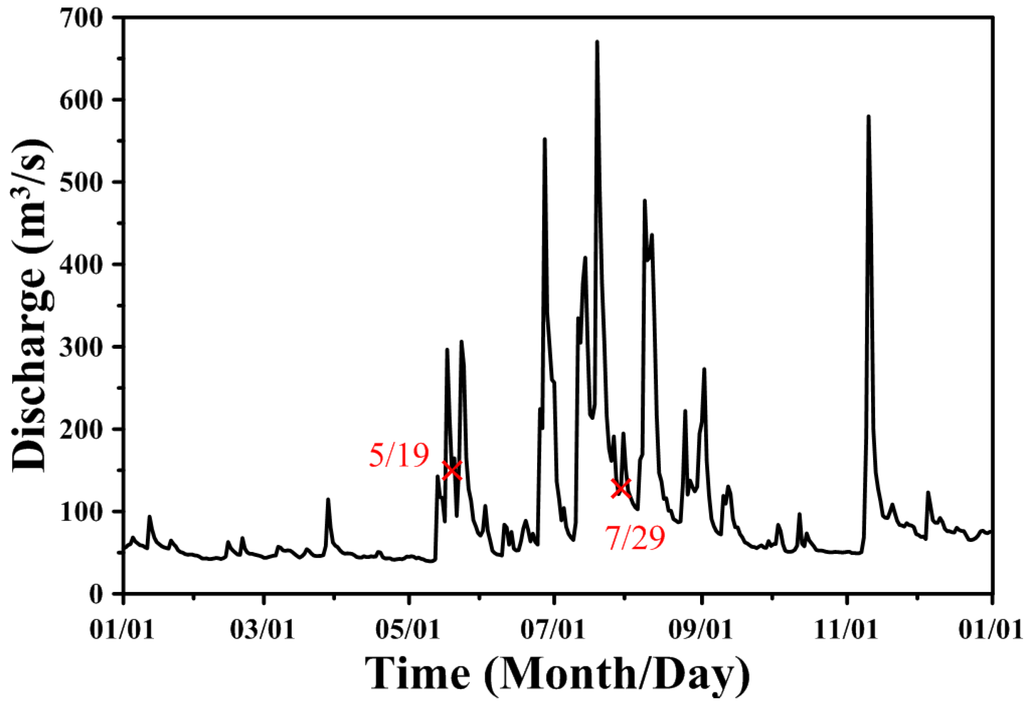
Figure 4.
Freshwater discharge inputs at the Dadu Bridge in 2011.
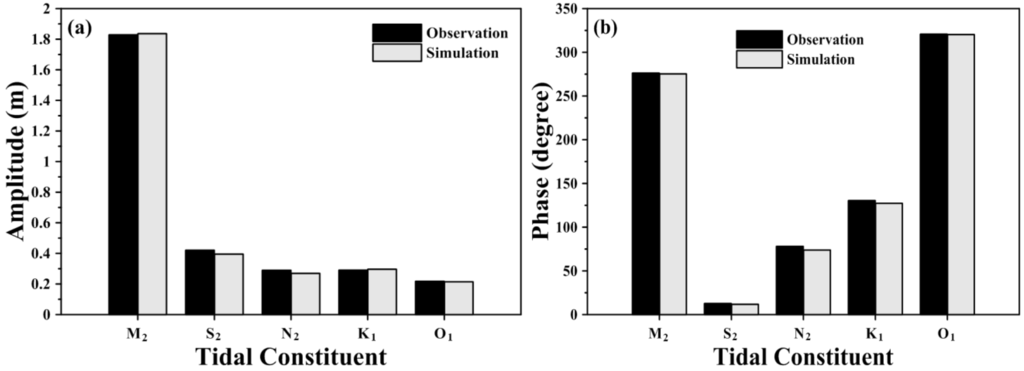
Figure 5.
Comparisons of amplitude and phase of five major tidal harmonics computed with a three-dimensional model and obtained from tide measurements (a) amplitude; (b) phase.
4.2. Verification of Water Surface Elevation
After calibrating the amplitudes and phases, the time-series data of observed water surface elevation were used to verify the model. Figure 6 presents the verified results for water surface elevations at Taichung Harbor station in May and July, 2011. The mean absolute errors of the differences between the measured hourly water levels and the computed water levels for 11–21 May and 22–31 July were 0.147 m and 0.157 m, respectively. The corresponding root-mean-square errors were 0.183 m and 0.193 m, respectively. These results demonstrate that the model can accurately predict the water surface elevation for varying river discharge input and tidal forcing at coastal sea boundaries. A constant bottom roughness height (zo = 0.01 cm) was adopted in the model for calibration and verification.
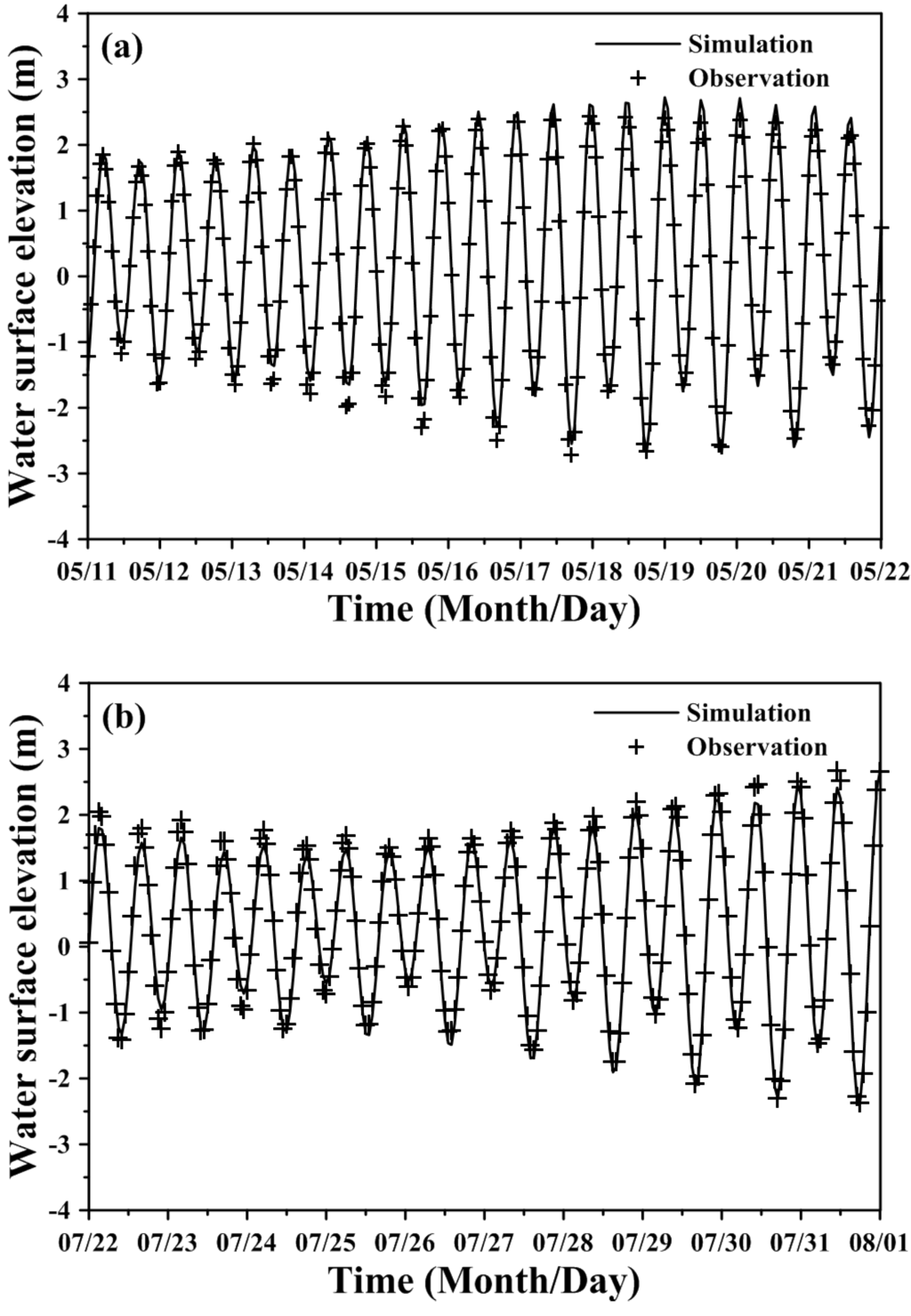
Figure 6.
Comparison of model results and observed water surface elevation during the periods of (a) 11–21May 2011 and (b) 22–31 July 2011 at the Taichung Harbor station.
4.3. Calibration and Verification of Salinity Distribution
Salinity distributions reflect the combined results of all processes, including density circulation and mixing processes [36]. In the present study, the salinity distributions were measured in situ using conductivity-temperature-depth equipment at six locations in the Wu River estuary during the flood tide surveys. The salinities at four vertical layers of each station in the water column were measured and were then used for model calibration and verification. The salinities of open boundaries in the coastal sea were set to a constant value (i.e., 35 psu). The upstream boundary at the Dadu Bridge was also specified with daily freshwater discharges, and the salinity was set to 0 psu. Figure 7 and Figure 8 present the comparisons of measured and simulated salinity distributions on 19 May and 29 July, 2011, for model calibration and verification purposes, respectively. The freshwater discharges on 19 May and 29 July 2011, were 149.3 m3/s and 127.47 m3/s, respectively (shown in Figure 4). The results show that the model-computed salinity distributions agree well with the field observations. The root-mean-square errors for 19 May and 29 July, 2011, were 0.75 psu and 0.53 psu, respectively.
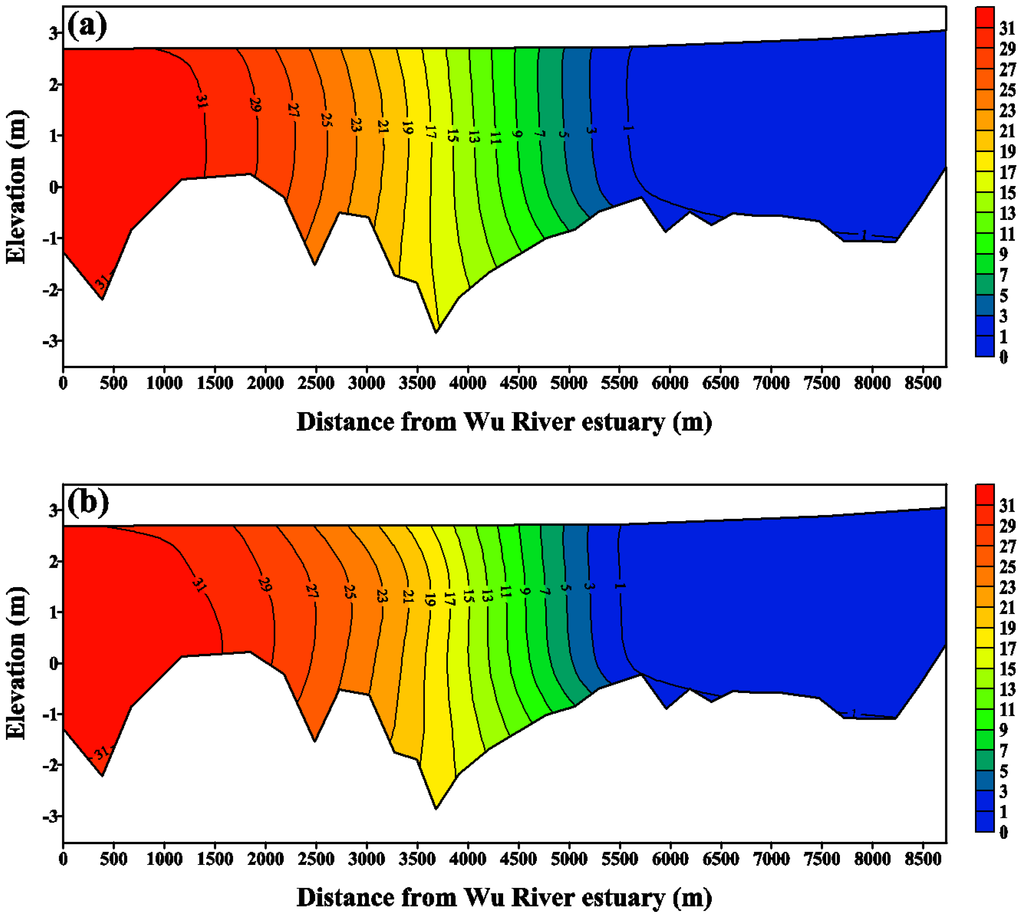
Figure 7.
Comparison of salinity distribution along the Wu River estuary. (a) measurements and (b) model simulation on 19 May 2011, for model calibration.
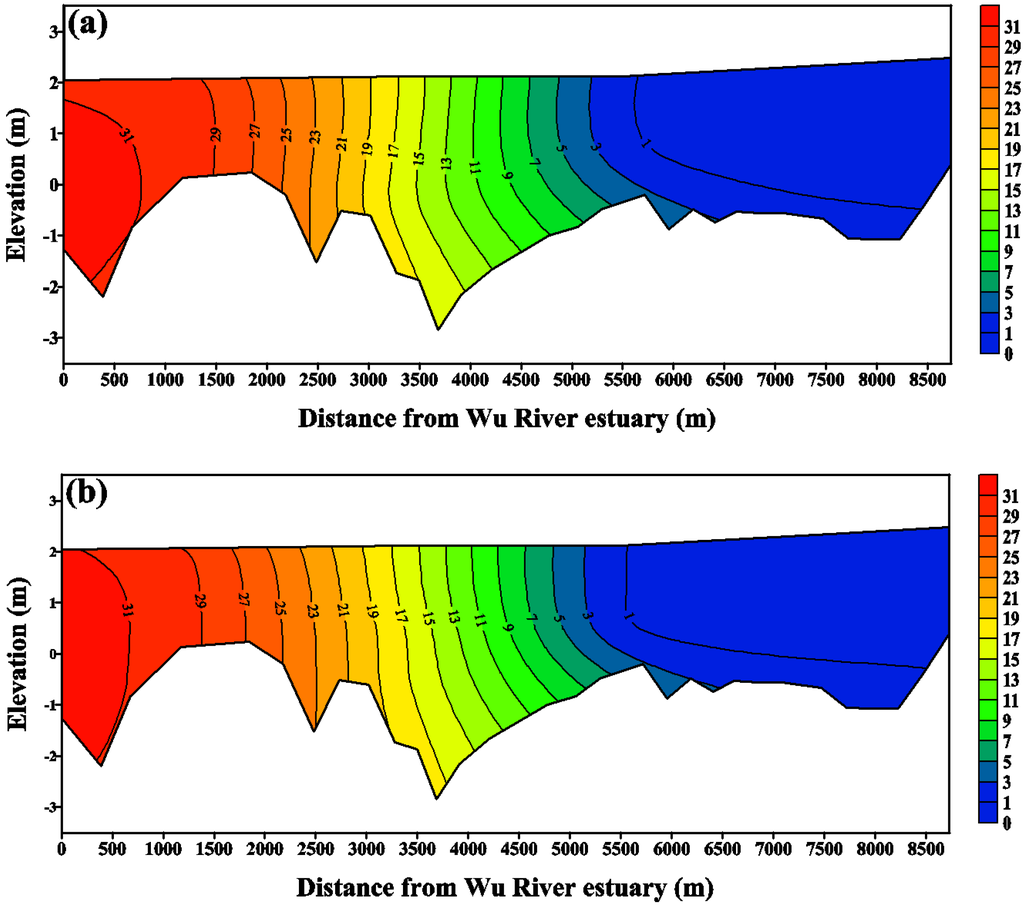
Figure 8.
Comparison of salinity distribution along the Wu River estuary. (a) measurements and (b) model simulation on 29 July 2011 for model verification.
5. Results and Discussion
The validated three-dimensional hydrodynamic model was used to calculate the salinity distribution and transport time scale response to different discharges with sea level rise scenarios and without sea level rise (i.e., the present condition) in the Wu River estuary. Figure 9 presents flow duration curves at the Dadu Bridge. The daily flow data from 1969 to 2011, collected by the Central Water Resources Bureau of Taiwan, were analyzed. The freshwater discharges with Q10 (the flow that is equaled or exceeded 10% of time) to Q90 flow conditions are listed in Table 2. For the cases of Q10 and Q90 flows, the discharges at the Dadu Bridge are 229.0 and 26.0 m3/s, respectively. Five tidal constituents (M2, S2, N2, K1 and O1) were specified to generate a time-series of water surface elevation as the open boundary conditions at the coastal sea for model simulation. A constant salinity of 35 psu at the open boundaries was used for model simulation. A future sea level rise of 38.27 cm in 2100 was used for the model simulation scenario.
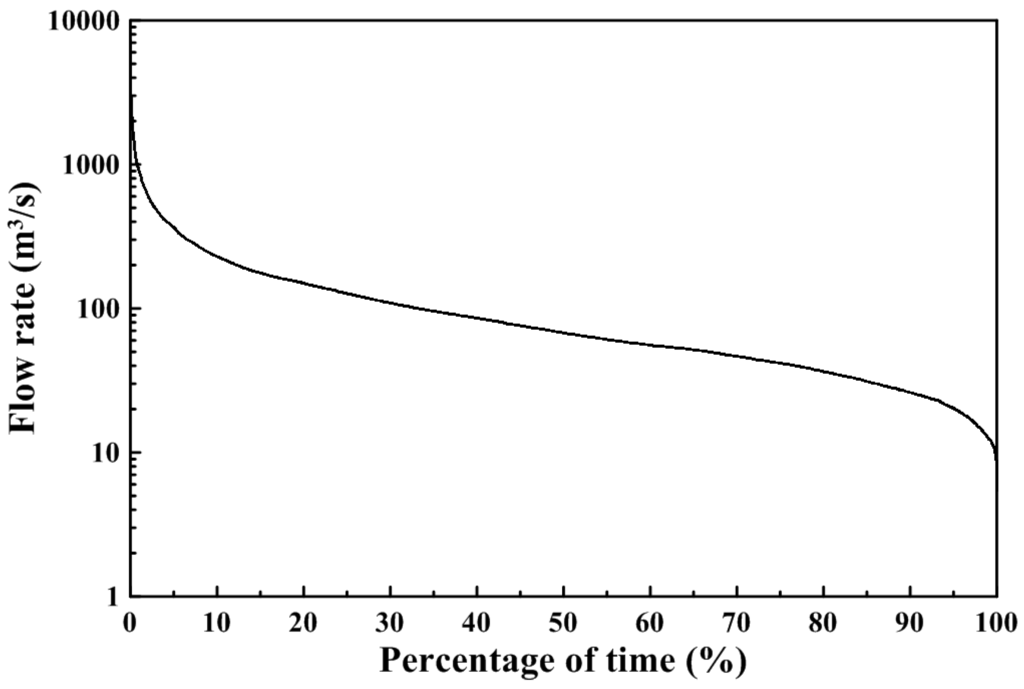
Figure 9.
Flow duration curve at Dadu Bridge.
The influence of wind on estuarine circulation has been recognized for many years [37]. In a shallow estuary, the residence time can vary in response to variations in wind-induced flushing [38]. However, in the present study, the wind forcing was excluded in the model simulation for calculating transport time scales with sea level rise scenarios and without sea level rise (i.e., the present condition).

Table 2.
Freshwater discharge at upstream boundaries for the model simulation.
| Freshwater discharge | Flow rate at Dadu Bridge (m3/s) |
|---|---|
| Q10 | 229.0 |
| Q20 | 149.0 |
| Q30 | 108.7 |
| Q40 | 85.6 |
| Q50 | 67.5 |
| Q60 | 55.5 |
| Q70 | 46.5 |
| Q80 | 36.5 |
| Q90 | 26.0 |
5.1. Sea Level Rise Effects on Salinity Distribution
To quantify the spatial and vertical variations in salinity, the vertical salinity profile along the Wu River estuary shows the detailed changes in the salinity structure with sea level rise. Figure 10 and Figure 11 present the distributions of tidal-averaged salinity along the Wu River estuary under the Q10 and Q90 flows to represent the high and low flow conditions, respectively, for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario. It is clear that the salinity changes throughout the entire estuary. The limit of salt intrusion is represented by a 1 psu isohaline. The limits of salt intrusion are 3000 m and 6500 m for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario under Q10 flow conditions (Figure 10), while they are 5500 m and 8250 m for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario under Q90 flow conditions (Figure 11). These two figures indicate that sea level rise pushes the limit of salt intrusion farther upstream in the Wu River estuary. The intensified stratification results in stronger gravitation circulation, which raises the salt content by transporting more saline water into the estuary. However, the sea level rise did not change the tidal amplitude, but the water surface elevation increased in the sea level rise scenario. Moreover, the sea level rise extends to the tidal excursion farther upstream, 500 m and 900 m, respectively, under the Q10 and Q90 flow conditions (not shown in the figure).
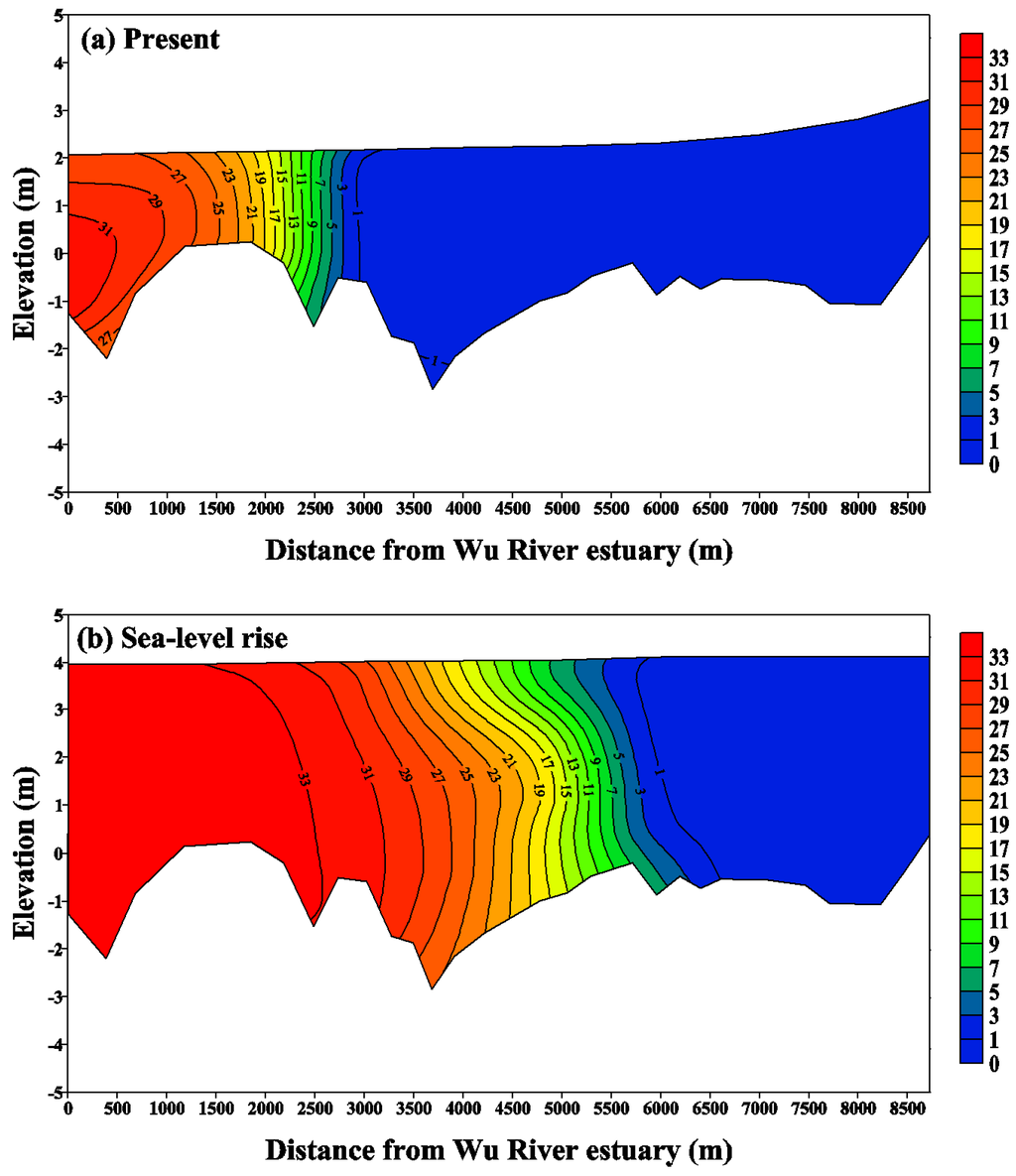
Figure 10.
Distribution of the tidal-averaged salinity along the Wu River estuary under the Q10 flow condition for (a) the present condition and (b) the sea level rise scenario. Note that the unit of salinity is psu (practical salinity unit).
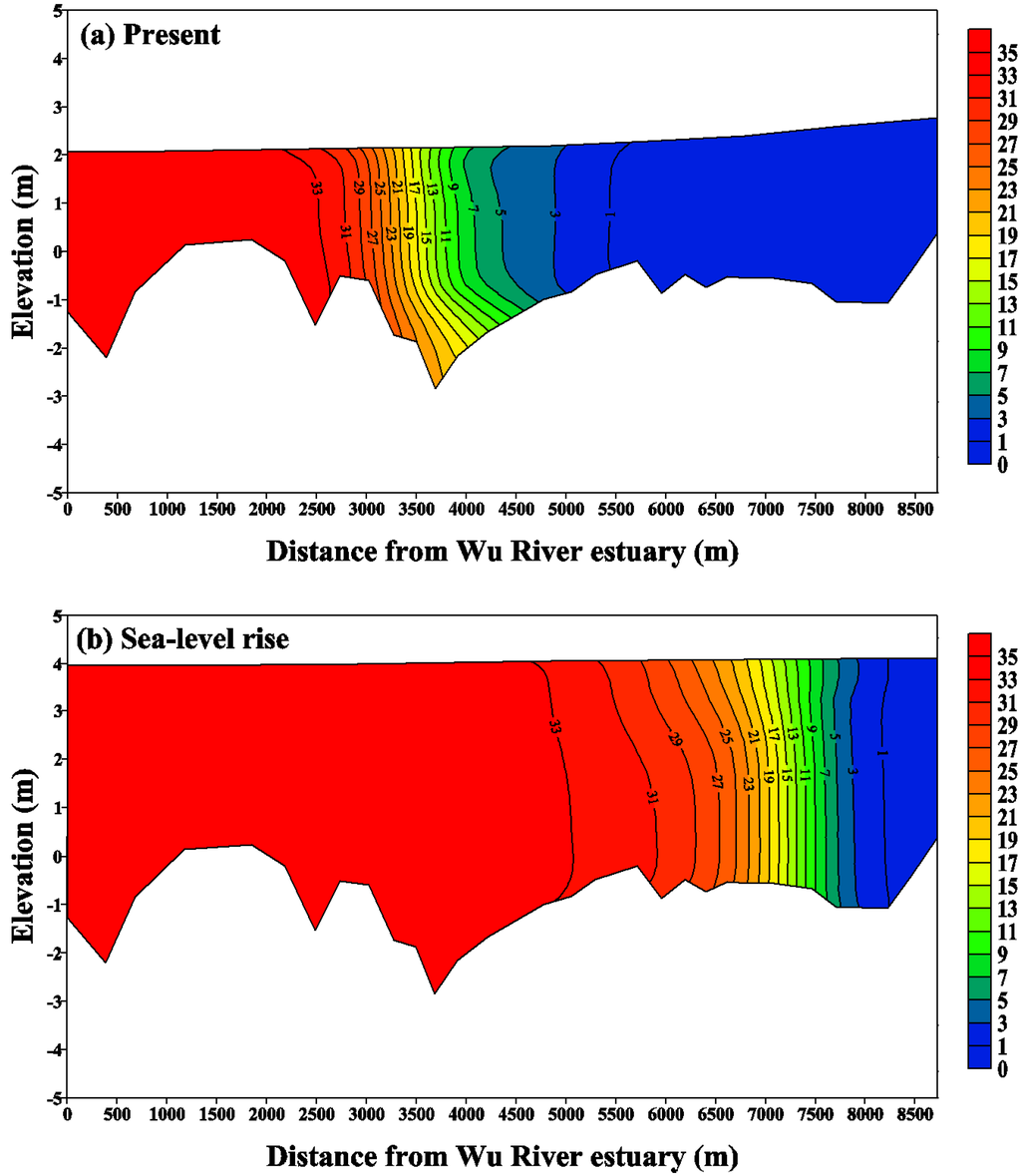
Figure 11.
Distribution of the tidal-averaged salinity along the Wu River estuary under the Q90 flow condition for (a) the present condition and (b) the sea level rise scenario. Note that the unit of salinity is psu.
Hong and Shen [9] demonstrated that the mean salinity at the mouth and the water depth within Chesapeake Bay would increase with sea level rise. Bhuiyan and Dutta [8] also described that the sea level rise impact on salinity intrusion would be highly significant. In this study, the limit of salt intrusion will increase 3000 m and 2750 m under high and low flow conditions, respectively, for a 38.27 cm sea level rise. The maximum increased salinity reached 14.2 psu under the Q90 low flow. The increased salinity could cause socio-economic problems; the saline water would be unsuitable for drinking and industrial purposes. Salinity intrusion due to sea level rise would constrain the supply of water resources in the river.
5.2. Flushing Time in Response to Sea Level Rise
To calculate the flushing time in the estuary, different freshwater discharges shown in Table 2 were used to serve as the upstream boundary condition for the present condition and for the sea level rise scenario. The model simulated flushing time is plotted against river flow in Figure 12. The increase in river discharge is accompanied by a more rapid exchange of freshwater with the sea. The volume of fresh water accumulated in the estuary increases to a lesser extent compared to the volume in the discharge. Thus, the flushing time decreases with increasing river discharge. Least squares regression fitting by the power law [39] was conducted to express the empirical function for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario:
where Q is the freshwater discharge. With a higher correlation value (R2), the power law statistically fits the data better, especially in the low and the high flow ends. The power law reasonably shows physical characteristics between the freshwater fraction and freshwater flow.
Tf = 1030.54·Q−0.821, R2 = 0.99 for the present condition
Tf = 384.02·Q−0.599, R2 = 0.98 for the sea level rise scenario
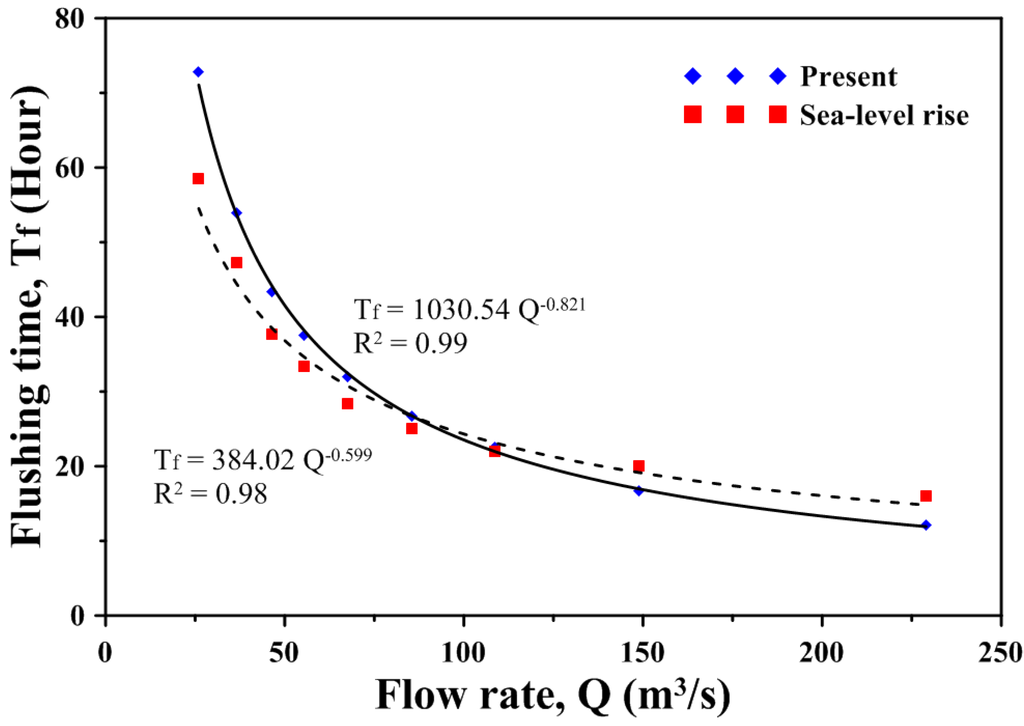
Figure 12.
Regression between flushing time and freshwater input for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario.
The flushing time is between 12.09 and 72.84 h under the present condition, while it is between 16.04 and 58.57 h under the sea level rise scenario. The results also indicate that the flushing time for high flow under the present condition is lower compared to the sea level rise scenario, while the flushing time for low flow under the present condition is higher compared to the sea level rise scenario. The freshwater volume thus increases under the sea level rise during high flow, and it decreases during low flow. Huang [39] applied a three-dimensional model to estimate the distributions of salinity and the freshwater fractions for flushing time estimation. He found that for the seven-day averaged flow ranging from 10 m3/s to 50 m3/s for a small estuary of North Bay, Florida, corresponding flushing time varies from 3.7 days to 1.8 days. The flushing time in the estuary of North Bay was similar to that in the Wu River estuary.
5.3. Residence Time in Response to Sea Level Rise
Passive tracers are used to simulate the material transport coming from the main river sources at the Dadu Bridge. Changing water levels and the propagation of tidal waves also result in changes in the residence time of water bodies and water constituents within the estuary and in changes in transport time through the estuary towards the sea.
The validated model was applied to explore the impact of sea level rise on residence time in the estuary. We calculated the residence time of the entire Wu River estuary under different freshwater discharge scenarios. After instantly releasing tracers throughout the entire Wu River estuary, the residence time corresponded to the time when the average tracer concentration reached its e-folding value (i.e., e−1 value). Model results reveal that the residence time decreases as the freshwater input increases for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario (shown in Figure 13). Finding a general regression relationship between the residence time and the freshwater input would be helpful in understanding the physical and hydrological processes in the estuary. Huang et al. [40] conducted regression analyses between estuarine residence time and freshwater input using a power-law function in Little Manatee River, Florida. The authors found that regression by the power law provided a better fit compared to an exponential function. A regression of the residence time (Tr) versus freshwater input (Q) was performed and indicated an excellent correlation (R2) through the power law function:
Tr = 207.18·Q−0.541, R2 = 0.99 for the present condition
Tr = 143.36·Q−0.385, R2 = 0.98 for the sea level rise scenario
The residence time is between 10.51 and 34.23 h under the present condition, while it is between 17.11 and 38.92 h under the sea level rise scenario. The residence time of the entire Wu River estuary increased 4.7 to 6.6 h based on different freshwater inputs due to sea level rise. The prolonged residence time will result in the deterioration of water quality and induce the limited application of water resources.
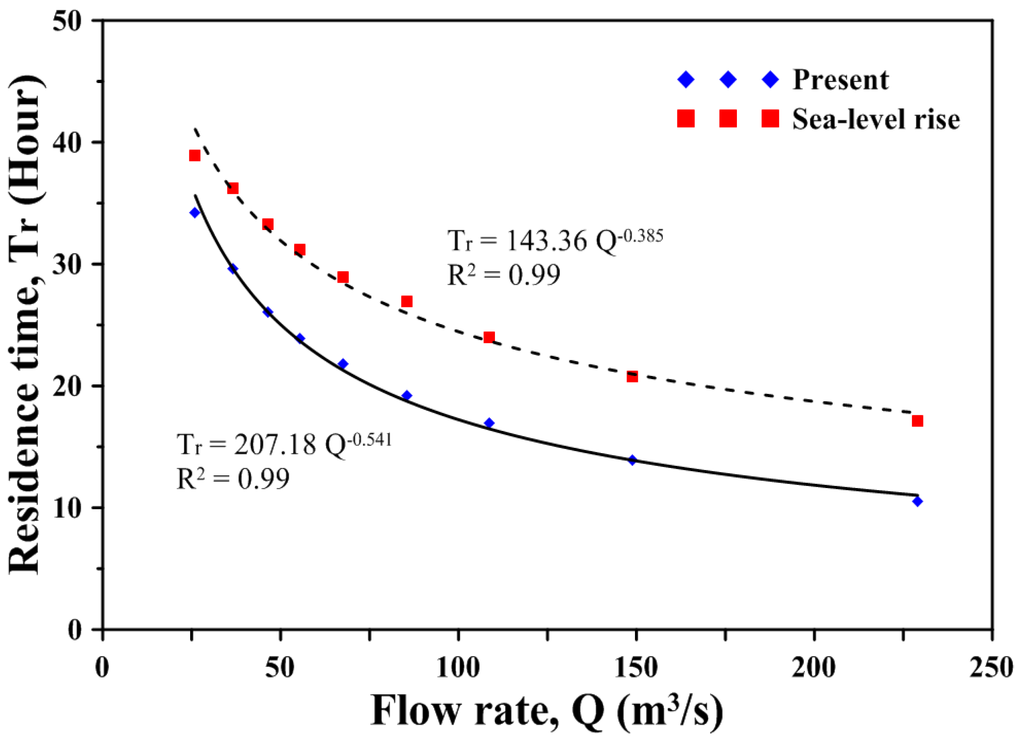
Figure 13.
Regression between residence time and freshwater input for the present condition and the sea level rise scenario.
Hong and Shen [9] estimated that the residence time could increase five to 20 days in response to different sea level rise scenarios in Chesapeake Bay. The increase of residence time response to sea level rise in the Wu River estuary is smaller than that in Chesapeake Bay, because the entire estuarine system in Chesapeake Bay is much larger than the Wu River estuary.
If the sea level rise rate is changed, the salinity intrusion and transport time scales would be changed. The increase in the sea level rise rate may extend the limit of salt intrusion farther upstream and increase the residence time in the estuary. In a future study, the wind forcing and seasonal freshwater discharge input from the Dadu Bridge can be considered in the model simulations to comprehend how the salinity intrusion and transport time scales respond to these factors.
6. Conclusions
A three-dimensional hydrodynamic and salt transport model, SELFE, was established to simulate the hydrodynamics and salinity distributions in the Wu River estuary and adjacent coastal sea in northern Taiwan. The model was calibrated and verified using observational amplitudes and phases, water surface elevations and salinity distributions in 2011. The model simulation results agree well with the field observations.
The validated model was used to perform a series of numerical experiments to identify the potential impacts of future sea level rise on salinity intrusion and transport time scales, including flushing time and residence time, in the Wu River estuary of central Taiwan. The model results indicate that salinity intrusion moves farther upstream by 2750 m and 3500 m under Q90 and Q10 flow conditions, respectively, due to sea level rise. The flushing time is between 12.09 and 72.84 h for the present condition, and it is between 16.04 and 58.57 h for the sea level rise scenario. We found that the flushing time for high flow under the present condition is lower compared to the sea level rise scenario, while the flushing time for low flow under the present condition is higher compared to the sea level rise scenario. The residence time of the entire Wu River estuary increased by 23.7 h and 21.8 h for high and low flows, respectively, during the sea level rise scenario. We found that the climate change (i.e., sea level rise) scenario implies not only a change in salt intrusion, but also an increase in the residence time. Sea level rise would alter the location of the river estuary, thereby causing a greater change in fish habitat and breeding ground location. Fishes breed in estuarine systems and develop in brackish waters, which is where fresh water and salt water mix. Sea level rise would move this interface backward, changing the habitat of fishing communities in the estuarine system. The increases in transport time scales (i.e., residence time) due to sea level rise would prolong the transport of dissolved substances in the estuary, resulting in the deterioration of water quality.
Acknowledgments
The project under which this study was conducted is supported by the National Science Council, Taiwan, under grant no. NSC 101-2625-M-239-001. The authors would like to express their thanks to the Taiwan Water Resources Agency for providing the observational data. Appreciation and thanks are also given to the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments and suggestions to improve this paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Yu, Y.F.; Yu, Y.X.; Zuo, J.C.; Wan, Z.W.; Chen, Z.Y. Effect of sea level variation on tidal characteristic values for the East China Sea. China Ocean Eng. 2003, 17, 369–382. [Google Scholar]
- IPCC. Climate Change 2007: The Physical Science Basis. In Contribution of Working Group 1 to the Fourth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Solomon, S., Qin, S., Manning, M., Chen, Z., Marquis, M., Averyt, K.B., Tignor, M., Miller, H.L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.H.; Chen, C.T. Observed and projected climate change in Taiwan. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2002, 79, 87–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.S.; Yang, T.C.; Kuo, C.C. Evaluating long-term trends in annual and seasonal precipitation in Taiwan. Water Resour. Manag. 2006, 20, 1007–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, M.C. Relationship of Stream Insects with Flooding and Dippers in Wuling Area. Master Thesis, National Chung Hsing University, Taichung, Taiwan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Poff, N.L.; Brinson, M.M.; Day, J.W., Jr. Aquatic Ecosystems and Global Climate Change; Pew Center on Global Change: Arlington, VA, USA, 2002; p. 45. [Google Scholar]
- Hilton, T.W.; Najjar, R.G.; Zhong, L.; Li, M. Is there a signal of sea level rise in Chesapeake Bay salinity? J. Geophys. Res. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhuiyan, M.J.A.N.; Dutta, D. Assessing impacts of sea level rise on river salinity in the Gorai river network, Bangladesh. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 96, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Shen, J. Responses of estuarine salinity and transport processes to potential future sea level rise in the Chesapeake Bay. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 104–105, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas, L.V. Implications of Estuarine Transport for Water Quality. In Contemporary Issues in Estuarine Physics; Valle-Levinson, A., Ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010; pp. 273–306. [Google Scholar]
- Hull, C.H.J.; Tortoriello, R. Sea Level Trend and Salinity in the Delaware Estuary; Staff Report; Delaware Basin Commission: West Trenton, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Grabemann, H.; Grabemann, I.; Herbers, D.; Muller, A. Effects of a specific climate scenario on the hydrograph and transport of conservative substances in the Weser estuary, Germany: A case study. Clim.Res. 2001, 18, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chua, V.P.; Fringer, O.B.; Monismith, S.G. Influence of sea level rise on salinity in San Francisco Bay. 2011; unpublished work. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, K.C.; Hong, B.; Shen, J. Assessment of salinity intrusion in the James and Chickahominy Rivers as a result of simulated sea level rise in Chesapeake Bay, East Coast, USA. J. Environ. Manag. 2012, 111, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.B.; Liu, W.C.; Wu, C.Y. Coupling of a one-dimensional river routing model and a three-dimensional ocean model to predict overbank flows in a complex river-ocean system. Appl. Math. Model. 2013, 37, 6163–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, J.A.; White, N.J. Sea level rise from the late 19th to the early 21st century. Surv. Geophys. 2011, 32, 585–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snay, R.; Cline, M.; Dillinger, W.; Foote, R.; Hilla, S.; Kass, W.; Ray, J.; Rohde, J.; Sella, G.; Soler, T. Using global positions system-derived crustal velocities to estimate rates of absolute sea level change from North American tidal gauge records. J. Geophys. Res. 2007, 112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholls, R.J.; Cazenave, A. Sea level rise and its impact on coastal zone. Science 2010, 328, 1517–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.H.; Breaker, L.C.; Cheng, T.Y. Sea level variations in the regional seas around Taiwan. J. Oceanogr. 2010, 66, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Hsu, T.W.; Wu, L.C. Application of Tide-Gauge and Satellite AltimetryData to Estimate Sea Level Rise; Report to Water Resources Agency: Taipei, Taiwan, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.L.; Baptista, A.M. SELFE: A semi-implicit Eulerian-Lagrangian finite-element model for cross-scale ocean circulation. Ocean Model. 2008, 21, 71–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhao, M.; Dickinson, R.E. Intercomparison of bulk aerodynamic algorithms for the computation of sea surface fluxes using TOGA COARE and TAO data. J. Clim. 1998, 11, 2628–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umlauf, L.; Buchard, H. A. generic length-scale equation for geophysical turbulence models. J. Mar. Res. 2003, 61, 235–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauff, G.E. Lyered Sediments of Tidal Flats, Beaches, and Shelf Bottoms of the North Sea. In American Association for the Advancement of Science Publication No. 83; American Association for the Advancement of Science: Washington, DC, USA, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Dyer, K.R. Estuaries: A Physical Introduction, 2nd ed.; John Wiley: London, UK, 1977; p. 195. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.C.; Hsu, M.H.; Kuo, A.Y.; Kuo, J.T. The influence of river discharge on salinity intrusion in the Tanshui Estuary, Taiwan. J. Coast. Res. 2001, 17, 544–552. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, W.; Spaulding, M. Modelling residence-time response to freshwater input in Apalachicola Bay, Florida, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2002, 16, 3051–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brye, B.; de Brauwere, A.; Gourge, O.; Delhez, E.J.M.; Deleersnijder, E. Water renewal timescales in the Scheldt Estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2012, 94, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, J.T.F. Mixing and flushing of tidal embayment in the western Dutch Wadden Sea. Part I: Description of salinity and calculation of mixing time scales. Neth. J. Sea Res. 1976, 10, 149–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeoka, H. Fundamental concepts of exchange and transport time scales in a coastal sea. Cont. Shelf Res. 1984, 3, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.C.; Chen, W.B.; Kuo, J.T.; Wu, C. Numerical determination of residual time and age in a partially mixed estuary using three-dimensional hydrodynamic model. Cont. Shelf Res. 2008, 28, 1068–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.G.; Wilkin, J.L.; Schofield, O.M.E. Simulation of water age and residence time in the New York Bight. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2010, 40, 965–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Brauwere, A.; de Brye, B.; Blaise, S.; Deleersnijder, E. Residence time, exposure time and connectivity in the Scheldt Estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2011, 84, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenov, I.A.; Garcia, A.C.; Neves, R. Residence time of water in the Mondego estuary (Portugal). Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2012, 106, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, G.; Wang, P. Anthropogenic influences on the tidal prism and water exchange in Jiaozhou Bay, Qingdao, China. J. Coast. Res. 2011, 27, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, M.H.; Kuo, A.Y.; Kuo, J.T.; Liu, W.C. Procedure to calibrate and verify numerical models of estuarine hydrodynamics. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 1999, 125, 166–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Officer, C.B. Physical Oceanography of Estuaries (and Associated Coastal Waters); Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, W.R. Influence of wind on dynamics and flushing of shallow estuaries. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 1997, 44, 713–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W. Hydrodynamic modeling of flushing time in small estuary of North Bay, Florida, USA. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2007, 74, 722–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Flannery, M.S. Critical flow for water management in a shallow tidal river based on estuarine residence time. Water Resour. Manag. 2011, 25, 2367–2385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).