Comparative Study of Three Two-Stage Hybrid Ecological Wastewater Treatment Systems for Producing High Nutrient, Reclaimed Water for Irrigation Reuse in Developing Countries
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of the Wetland Systems
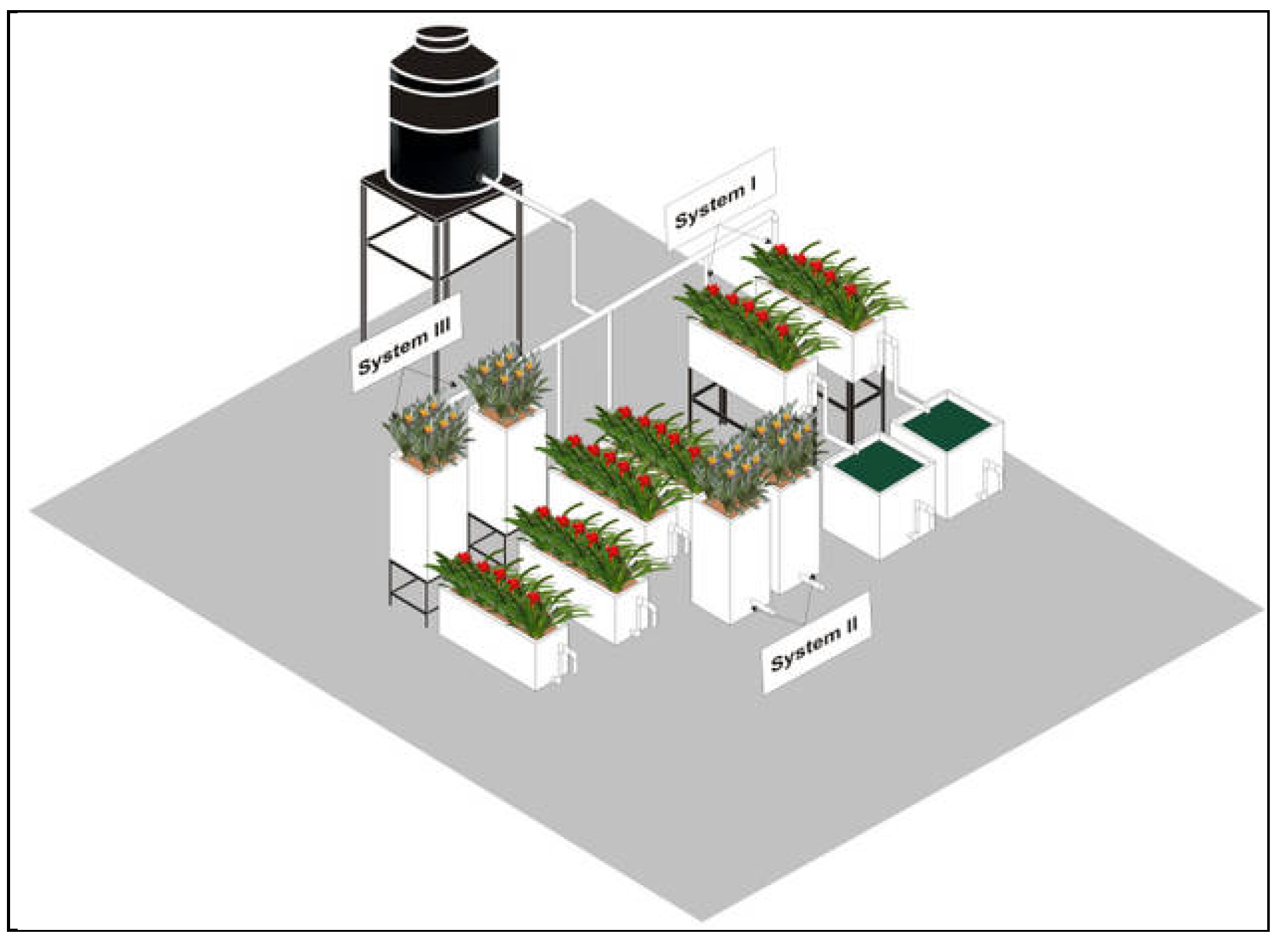
2.2. Water Quality Parameters
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Organic Nitrogen
| Parameter | Influent | System I: HF-SP | System II: HF-VF | System III: VF-HF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st stage HF-CW | 2nd stage SP | 1st stage HF-CW | 2nd stage VF-CW | 1st stage VF-CW | 2nd stage HF-CW | ||
| Org-N (mg/L) | 7.1 ± 1.2 | 3.2± 1.0 | 10.5± 1.0 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 1.6 ± 0.7 | 1.4 ± 0.8 | 1.2 ± 0.8 |
| Org-N Removal (%) | 54.9 | −228.1 (−47.9) | 60.6 | 42.9(77.5) | 80.3 | * (83.1) | |
| NH4+-N (mg/L) | 128.2 ± 11.4 | 103.1± 11.4 | 35.8 ± 12.2 | 103.4 ± 12.4 | 18.6 ± 5.6 | 25.1 ± 6.7 | 19.2 ± 6.2 |
| NH4+-N Removal (%) | 19.6 | 65.3 (72.0) | 19.3 | 82.0 (85.5) | 80.4 | * (85.0) | |
| NO3−-N (mg/L) | 4.2 ± 1.4 | 1.95± 0.3 | 14.1 ± 1.8 | 1.97 ± 0.6 | 91.4 ± 17.6 | 108 ± 16.3 | 82.5 ± 17.2 |
| NO3−-N Removal (%) | 53.6 | −623 (−236) | 53.1 | −4540 (−2076) | −2471 | 23.6 (−1864) | |
| TN (mg/L) | 139.5 ± 12.1 | 108.3±12.1 | 60.4 ± 9.9 | 108.2 ± 22.2 | 111.6 ± 13.2 | 134.5 ± 21.1 | 102.9 ± 13.1 |
| TN Removal (%) | 22.4 | 44.2 (56.7) | 22.4 | * (20) | * | 23.5 (26.2) | |
| TP (mg/L) | 12.4 ± 1.1 | 11.8± 1.0 | 11.4 ± 1.0 | 12.1 ± 1.1 | 12.2 ± 1.0 | 11.3 ± 1.1 | 12.4 ± 1.1 |
| TP removal (%) | * | * | * | * | * | * | |
3.2. Ammonium
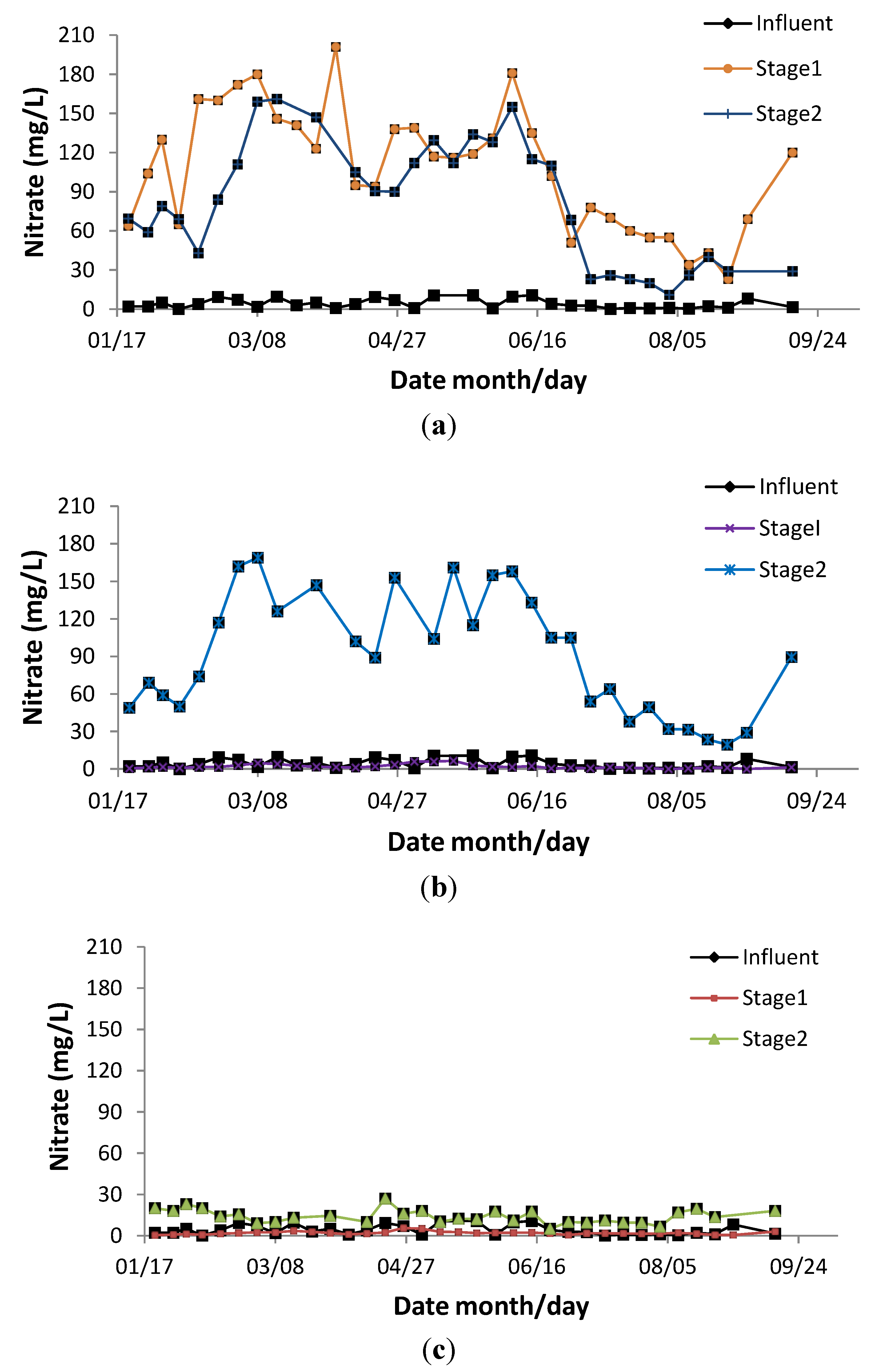
3.3. Nitrate
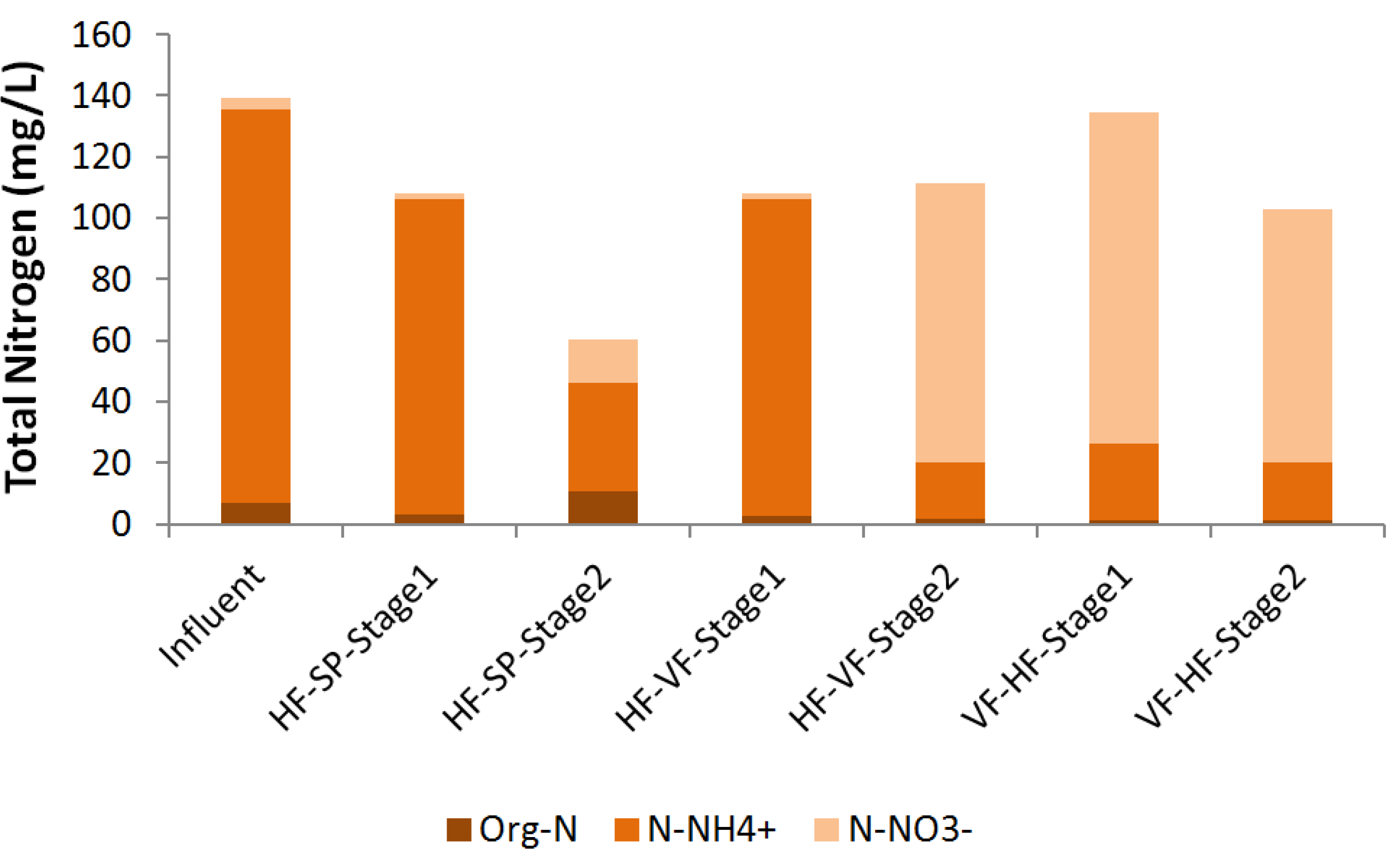
3.4. Total N
3.5. Total P
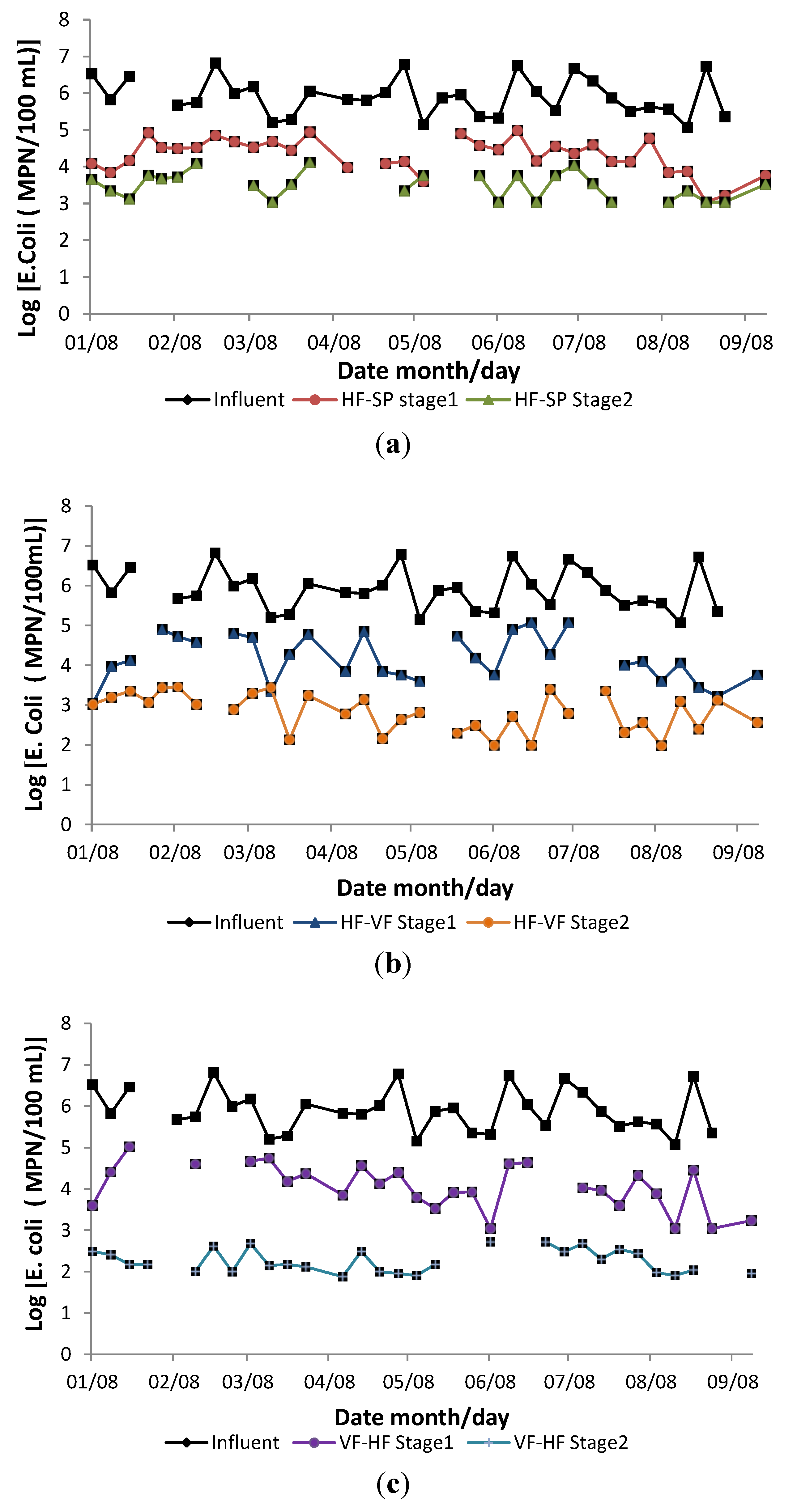
3.6. Disinfection Performance
| Parameter | Influent | System I: HF-SP | System II: HF-VF | System III: VF-HF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st stage HF CW | 2nd stage SP | 1st stage HF-CW | 2nd stage VF-CW | 1st stage VF-CW | 2nd stage HF-CW | ||
| Tot.Coliform (MPN/100mL) | 2.5 × 106 ± 9.9 × 105 | 2.0 × 105 ± 6.3 × 104 | 3.8 × 105 ± 1.4 × 105 | 2.1 × 105 ± 6.6 × 104 | 1.6 × 104 ± 5.7 × 103 | 1.1 × 105 ± 4.1 × 104 | 7.7 × 104 ± 2.5 × 104 |
| Tot.Coliform Removal (% ) | 92.0 | −90.0 (84.8) | 91.6 | 92.38 (99.36) | 95.6 | 30.00 (96.92) | |
| E. coli (MPN/100 mL) | 1.6 × 106 ± 6.8 × 105 | 3.1 × 104 ± 9.6 × 103 | 4210 ± 1457 | 3.1 × 104 ± 1.3 × 104 | 1060 ± 326 | 3.8 × 104 ± 6.2 × 103 | 213.1 ± 59.0 |
| E. coli Removal (%) | 98.06 | 86.42 (99.74) | 98.06 | 96.58 (99.93) | 97.63 | 99.44 (99.99) | |
3.7. BOD and COD
| Parameter | Influent | System I: HF-SP | System II: HF-VF | System: VF-HF | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st stage HF-CW | 2nd stage SP | 1st stage HF-CW | 2nd stage VF-CW | 1st stage VF-CW | 2nd stage HF-CW | ||
| BOD (mg/L) | 140.6 ± 28.2 | 27.3 ± 5.1 | 55.5 ± 9.6 | 24.3 ± 3.8 | 6.1 ± 0.9 | 6.7 ± 1.5 | 4.8 ± 0.72 |
| BOD Removal (%) | 80.6 | −103.3 (60.5) | 82.7 | 74.9 (95.7) | 95.2 | * (96.6) | |
| COD (mg/L) | 273.5 ± +50.0 | 96.9 ± 11.8 | 277.8 ± 43.5 | 95.4 ± 17.5 | 56.9 ± 7.4 | 66.7 ± 8.9 | 55.8 ± 8.2 |
| COD Removal (%) | 64.6 | −186.7 (0.0) | 65.1 | 40.4 (79.2) | 75.6 | * (79.6) | |
| TSS (mg/L) | 61.8 ± 11.7 | 12.3 ± 2.4 | 138.3 ± 31.0 | 8.3 ± 2.0 | 4.6 ± 1.0 | 10.6 ± 3.6 | 4.5 ± 1.0 |
| TSS Removal (%) | 80.1 | −1024.4 (−123.8) | 84.9 | 49.5 (92.4) | 82.8 | 57.4(92.7) | |
| Conductivity (µS/cm) | 1797 ± 359 | 1774 ± 119 | 1387 ± 119 | 1693 ± 375.5 | 1369 ± 291 | 1381 ± 285 | 1457 ± 409 |
| pH | 8.2 ± 0.08 | 8.0 ± 0.08 | 8.1 ± 0.08 | 8.2 ± 0.14 | 6.4 ± 0.13 | 6.7 ± 0.12 | 6.8 ± 0.12 |
| DO (mg/L) | 1.5 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 0.6 | 8.8 ± 1.7 | 4.7 ± 0.7 | 4.3 ± 0.6 | 6.9 ± 0.5 | 5.2 ± 0.5 |
3.8. Total Suspended Solids
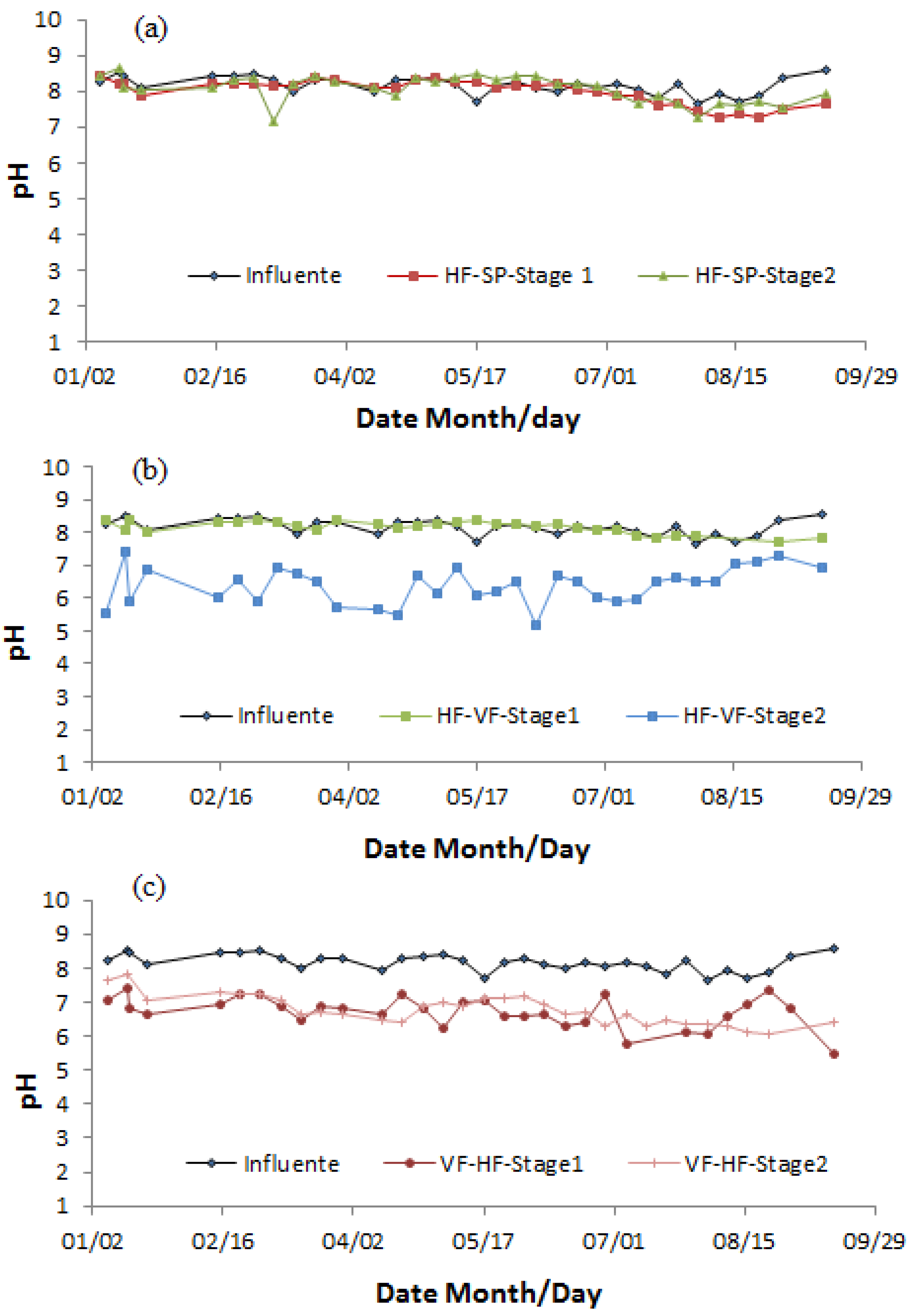
3.9. PH
3.10. Electrical Conductivity (EC)
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jiménez, B.; Drechsel, P.; Koné, D.; Bahri, A.; Raschid-Sally, L.; Qadir, M. Wastewater, sludge and excreta use in developing countries: An overview. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health. Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Drechsel, P., Scott, C.A., Raschid-Sally, L, Redwood, M., Bahri, A., Eds.; International Water Management Institute and International Development Research Centre (IDRC): London, UK, 2010; pp. 3–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, B. Irrigation in developing countries using wastewater. Int. Rev. Environ. Strateg. 2006, 2, 229–250. [Google Scholar]
- Bos, R.; Carr, R.; Keraita, B. Assessing and mitigating wastewater-related health risks in low-income countries: An introduction. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health. Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Drechsel, P., Scott, C.A., Raschid-Sally, L, Redwood, M., Bahri, A., Eds.; International Water Management Institute and International Development Research Centre (IDRC): London, UK, 2010; pp. 29–47. [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez, B.; Mara, D.; Carr, R.; Brissaud, F. Wastewater treatment for pathogen removal and nutrient conservation: Suitable systems for use in developing countries. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health. Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Drechsel, P., Scott, C.A., Raschid-Sally, L., Redwood, M., Bahri, A., Eds.; International Water Management Institute and International Development Research Centre (IDRC): London, UK, 2010; pp. 149–169. [Google Scholar]
- Zurita, F.; Roy, E.D.; White, J.R. Municipal wastewater treatment in Mexico: Current status and opportunities for employing ecological treatment systems. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharafi, K.; Fazlzadehdavil, M.; Pirsaheb, M.; Derayat, J.; Hazrati, S. The comparison of parasite eggs and protozoan cysts of urban raw wastewater and efficiency of various wastewater treatment systems to remove them. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García, J.A.; Paredes, D.; Cubillos, J.A. Effect of plants and the combination of wetland treatment type systems on pathogen removal in tropical climate conditions. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 58, 57–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, T.; Sun, G. Enhanced denitrification and organics removal in hybrid wetland columns: Comparative experiments. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marecos Do Monte, H.; Albuquerque, A. Analysis of constructed wetland performance for irrigation reuse. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 1699–1705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J. Horizontal sub-surface flow and hybrid constructed wetlands systems for wastewater treatment. Ecol. Eng. 2005, 25, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Melián, J.A.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.J.; Araña, J.; Gonzalez-Díaz, O.; González-Enríquez, J.J. Hybrid constructed wetlands for wastewater treatment and reuse in the Canary Islands. Ecol. Eng. 2010, 36, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita, F.; De Anda, J.; Belmont, M.A. Treatment of domestic wastewater and production of commercial flowers in vertical and horizontal subsurface-flow constructed wetlands. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association; American Water Works Association; Water Environment Federation. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005.
- Park, J.B.K.; Craggs, R.J.; Shilton, A.N. Wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds for biofuel production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayas, S.C.; Aktas, Ô.; Findik, N.; Akca, L.; Kinaci, C. Effect of recirculation on nitrogen removal in a hybrid constructed wetland system. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. Potential nitrification and denitrification rates in a phosphorus-impacted subtropical peatland. J. Environ. Qual. 2003, 32, 2436–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gikas, G.D.; Tsihrintzis, V.A. A small-size vertical flow constructed wetland for on-site treatment of household wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 44, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.; Salas, J.J.; Martín, I.; Aragón, C.; García, J. Integrated treatment of combined sewer wastewater and stormwater in a hybrid constructed wetland system in southern Spain and its further reuse. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 50, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.M.; White, J.R. Denitrification enzyme activity as a potential spatial indicator of nitrate loading in a Mississippi River diversion wetland soil. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- VanZomeren, C.; White, J.R.; DeLaune, R.D. Ammonification and denitrification rates in coastal louisiana bayou sediment and marsh soil: Implications for Mississippi River diversion management. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 54, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. The influence of nitrate and phosphorus loading on denitrifying enzyme activity in Everglades wetland soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1999, 63, 1945–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vymazal, J.; Kropfelová, L. A three-stage experimental constructed wetland for treatment of domestic sewage: First 2 years of operation. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, C.C.; Sukias, J.P.S.; Headley, T.R.; Yates, C.R.; Stott, R. Constructed wetlands and denitrifying bioreactors for on-site and decentralized wastewater treatment: Comparison of five alternative configurations. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masi, F.; Martinuzzi, N. Constructed wetlands for the Mediterranean countries: Hybrid systems for water reuse and sustainable sanitation. Desalination 2007, 215, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; DeLaune, R.D. Biogeochemistry of Wetlands: Science and Applications; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, P.C.C.; Lam, P.K.S. Major pathways for nitrogen removal in wastewater stabilization ponds. Water Air Soil Poll. 1997, 94, 125–136. [Google Scholar]
- Moustafa, M.Z.; White, J.R.; Coghlan, C.C.; Reddy, K.R. Influence of hydropattern and vegetation on P reduction in a constructed wetland under high and low mass loading rates. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 42, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bostic, E.M.; White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R.; Corstanje, R. Evidence of phosphorus distribution in wetland soil after the termination of nutrient loading. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 1808–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; White, J.R.; De Laune, R.D. Diverted Mississippi River sediment as a potential phosphorus source affecting louisiana water quality. J. Freshwater Ecol. 2012, 27, 575–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohla, C.; Kõiva, M.; Bavorb, H.J.; Chazarencc, F.; Mandera, U. Filter materials for phosphorus removal from wastewater in treatment wetlands—A review. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 70–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.; Xie, H.; Zhang, B. Nutrient removal in constructed microcosm wetlands for treating polluted river water in northern China. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.J.; Hui, Z.; Chao, X.; Nie, E.; Li, H.J.; He, J.; Zheng, Z. Efficiency of two-stage combinations of subsurface vertical down-flow and up-flow constructed wetland systems for treating variation in influent C/N ratios of domestic wastewater. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 1546–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmont, M.A.; White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. Phosphorus sorption characteristics of sediments in Lake Istokpoga and the upper chair of lakes. J. Environ. Quality 2009, 38, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, V.K.; Chopra, A.K.; Kazmi, A.A.; Kumar, A. Alternative microbial indicators of faecal pollution: Current perspective. Iran J. Environ. Health. Sci. Eng. 2006, 3, 205–216. [Google Scholar]
- Secretaría de Medio Ambiente y Recursos Naturales (SEMARNAT). Que Establece los Límites Máximos Permisibles de Contaminantes en las Descargas de Aguas Residuales en Aguas y Bienes Nacionales; Norma Oficial Mexicana NOM-001-SEMARNAT-1996; OfficialGazette of the Federation, Secretary of Government: Mexico City, Mexico, 1996.
- Mara, D.; Bos, R. Risk analysis and epidemiology: The 2006 WHO guidelines for the safe use of wastewater in agriculture. In Wastewater Irrigation and Health. Assessing and Mitigating Risk in Low-Income Countries; Drechsel, P., Scott, C.A., Raschid-Sally, L, Redwood, M., Bahri, A., Eds.; International Water Management Institute and International Development Research Centre (IDRC): London, UK, 2010; pp. 51–62. [Google Scholar]
- Shilton, N.; Walmsley, A. Solids and Organics in Pond Treatment Technology; Shilton, A., Ed.; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, G.; Potter, R.B.; Nortcliff, S. Water reuse for irrigation in Jordan: Perceptions of water quality among farmers. Agr. Water Manag. 2011, 98, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghehsareh, A.M.; Samadi, N. Effect of soil acidification on growth indices and microelements uptake by greenhouse cucumber. Afr. J. Agr. Res. 2012, 7, 1659–1665. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz, F.J.; O’Geen, A.T.; Dahlgren, R.A. Agricultural pollutant removal by constructed wetlands: Implications for water management and design. Agr. Water Manag. 2012, 104, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyambadde, J.; Kansiime, F.; Dalhammar, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus removal in substrate-free pilot constructed wetlands with horizontal surface flow in Uganda. Water Air Soil Poll. 2005, 165, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zurita, F.; Del Toro-Sánchez, C.L.; Gutierrez-Lomelí, M.; Rodríguez-Sahagún, A.; Castellanos-Hernández, O.A; Ramírez-Martínez, G.; White, J.R. Preliminary study on the potential of arsenic removal by subsurface flow constructed mesocosms. Ecol. Eng. 2012, 47, 101–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrero, F.; Alarcón, J.J. Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on lemon. Desalination 2009, 246, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, A.; Martínez-Hernández, V.; Leal, M.; González-Naranjo, V.; de Bustamante, I.; Lillo, J.; Salas, J.J.; Palacios-Díaz, M.P. Short-term effects of reclaimed water irrigation: Jatropha curcas L. cultivation. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 50, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zurita, F.; White, J.R. Comparative Study of Three Two-Stage Hybrid Ecological Wastewater Treatment Systems for Producing High Nutrient, Reclaimed Water for Irrigation Reuse in Developing Countries. Water 2014, 6, 213-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6020213
Zurita F, White JR. Comparative Study of Three Two-Stage Hybrid Ecological Wastewater Treatment Systems for Producing High Nutrient, Reclaimed Water for Irrigation Reuse in Developing Countries. Water. 2014; 6(2):213-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6020213
Chicago/Turabian StyleZurita, Florentina, and John R. White. 2014. "Comparative Study of Three Two-Stage Hybrid Ecological Wastewater Treatment Systems for Producing High Nutrient, Reclaimed Water for Irrigation Reuse in Developing Countries" Water 6, no. 2: 213-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6020213
APA StyleZurita, F., & White, J. R. (2014). Comparative Study of Three Two-Stage Hybrid Ecological Wastewater Treatment Systems for Producing High Nutrient, Reclaimed Water for Irrigation Reuse in Developing Countries. Water, 6(2), 213-228. https://doi.org/10.3390/w6020213





