Application of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in Greece
Abstract
:1. Drought and Indicators
2. Drought and SPI application
3. Applied Methodology
3.1. Case Study Area and Data Processing
| Station | Altitude (m) | Time Series | X | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alexandroupolis | 3 | 1947–2004 | 662,821.24 | 4,523,618.93 |
| Herakleion | 39 | 1947–2004 | 607,395.45 | 3,910,363.07 |
| Pyrgos | 12 | 1948–2004 | 273,464.99 | 4,171,636.48 |
| Hellenicon | 15 | 1948–2004 | 476,989.70 | 4,193,354.66 |
| Araxos | 12 | 1949–2004 | 279,911.59 | 4,225,147.38 |
| Kerkyra | 4 | 1949–2004 | 147,783.91 | 4,391,112.67 |
| Larissa | 74 | 1949–2004 | 366,008.76 | 4,389,788.05 |
| Ioannina | 484 | 1950–2004 | 227,392.02 | 4,398,141.29 |
| Melos | 165 | 1950–2004 | 538,541.95 | 4,065,090.13 |
| Trikala | 110 | 1952–2004 | 308,723.25 | 4,380,419.84 |
| Kozane | 626 | 1955–2004 | 311,408.64 | 4,461,260.03 |
| Lesvos | 5 | 1955–2004 | 725,179.25 | 4,325,645.06 |
| Naxos | 10 | 1955–2004 | 622879.70 | 4,106,184.40 |
| Rodos | 12 | 1955–2004 | 866,517.69 | 4,035,914.60 |
| Agchialos | 15 | 1956–2004 | 396,082.70 | 4,342,228.76 |
| Lamia | 17 | 1956–2004 | 360,383.21 | 4,300,968.99 |
| Serres | 34.5 | 1957–2004 | 463,452.85 | 4,547,812.89 |
| Tympaki | 7 | 1959–2004 | 570,227.09 | 3,880,381.63 |
| Chania | 152 | 1959–2004 | 512,901.68 | 3,932,269.85 |
| Monastirakion | 390.2 | 1960–2004 | 327,850.86 | 4,328,853.22 |
| Tanagra | 140 | 1960–2004 | 461,951.48 | 4,243,016.32 |
| A.Fragista | 725.3 | 1960–2004 | 292,569.43 | 4,314,776.76 |
| Ardanovo | 357 | 1960–2004 | 278,052.56 | 4,336,273.11 |
| Thessalonike | 5 | 1960–2004 | 412,412.02 | 4,485,367.97 |
| Plastera | 801.2 | 1961–2004 | 307,017.61 | 4,353,851.56 |
| Thera | 34 | 1961–2004 | 632,478.91 | 4,029,392.55 |
| Tauropos | 793.8 | 1963–2004 | 335,686.29 | 4,356,201.41 |
| Kastrakion | 74.8 | 1964–2004 | 273,283.51 | 4,293,922.69 |
| Kremasta | 801.2 | 1964–2004 | 289,229.69 | 4,304,259.11 |
| Pertouli | 801.8 | 1964–2004 | 286,307.18 | 4,376,127.18 |
| Ierapetra | 10 | 1964–2004 | 658,162.62 | 3,875,193.64 |
| Kythira | 321 | 1964–2004 | 411,309.62 | 4,014,666.13 |
| Andravida | 10 | 1967–2004 | 261,465.38 | 4,199,167.76 |
| Methone | 34 | 1967–2004 | 295,151.20 | 4,077,583.50 |
| Tripolis | 652 | 1967–2004 | 358,423.25 | 4,154,541.74 |
| Lymnos | 5 | 1968–2004 | 605,166.73 | 4,419,248.05 |
| Skyros | 28 | 1970–2004 | 541,787.38 | 4,312,174.03 |
| kalamata | 11 | 1971–2004 | 324,360.97 | 4,102,811.24 |
| Aktion | 4 | 1973–2004 | 219,283.86 | 4,312,709.01 |
| Chios | 4 | 1974–2004 | 687,028.85 | 4,245,693.86 |
| Arta | 10.5 | 1976–2004 | 240,224.50 | 4,338,878.73 |
| Samos | 7 | 1978–2004 | 756,986.43 | 4,175,249.62 |
| Argos | 11 | 1981–2004 | 388,373.27 | 4,164,292.45 |
| Kastoria | 604 | 1981–2004 | 269,220.67 | 4,480,918.49 |
| Kos | 129 | 1982–2004 | 775,821.87 | 4,076,770.28 |
| Chrysoupolis | 5 | 1985–2004 | 552,539.07 | 4,530,084.08 |

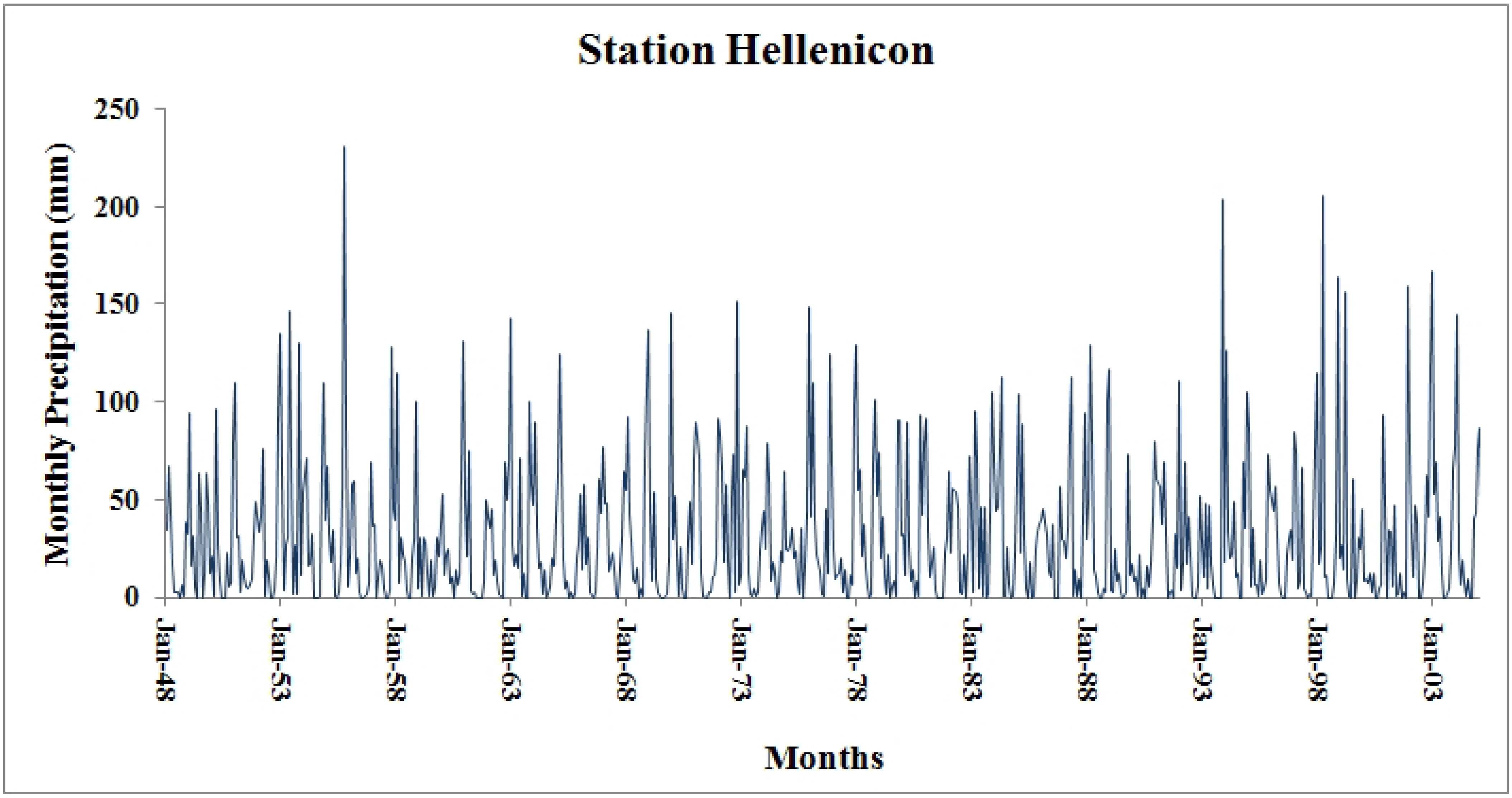
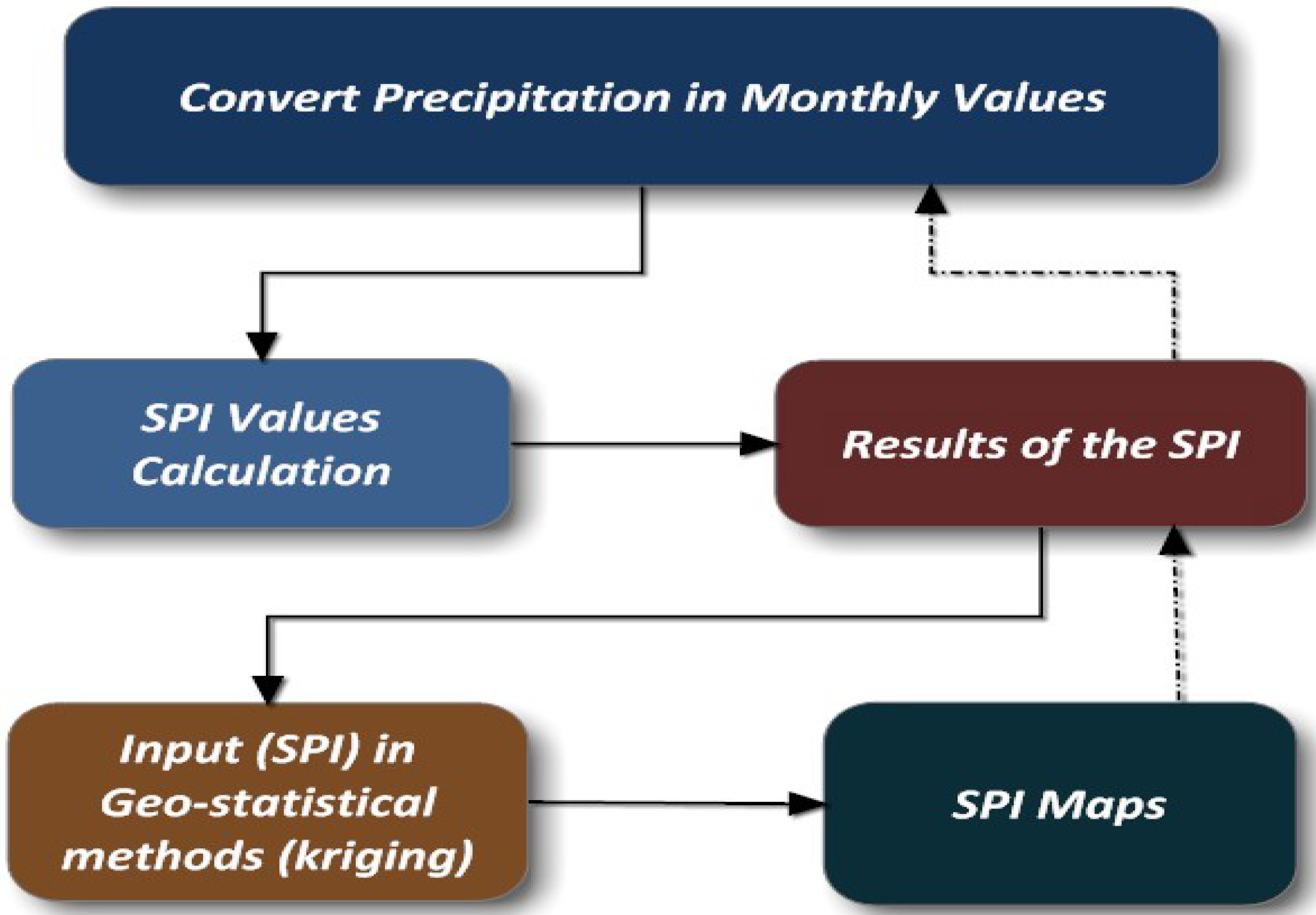
3.2. SPI Algorithm Application


4. Results and Discussion
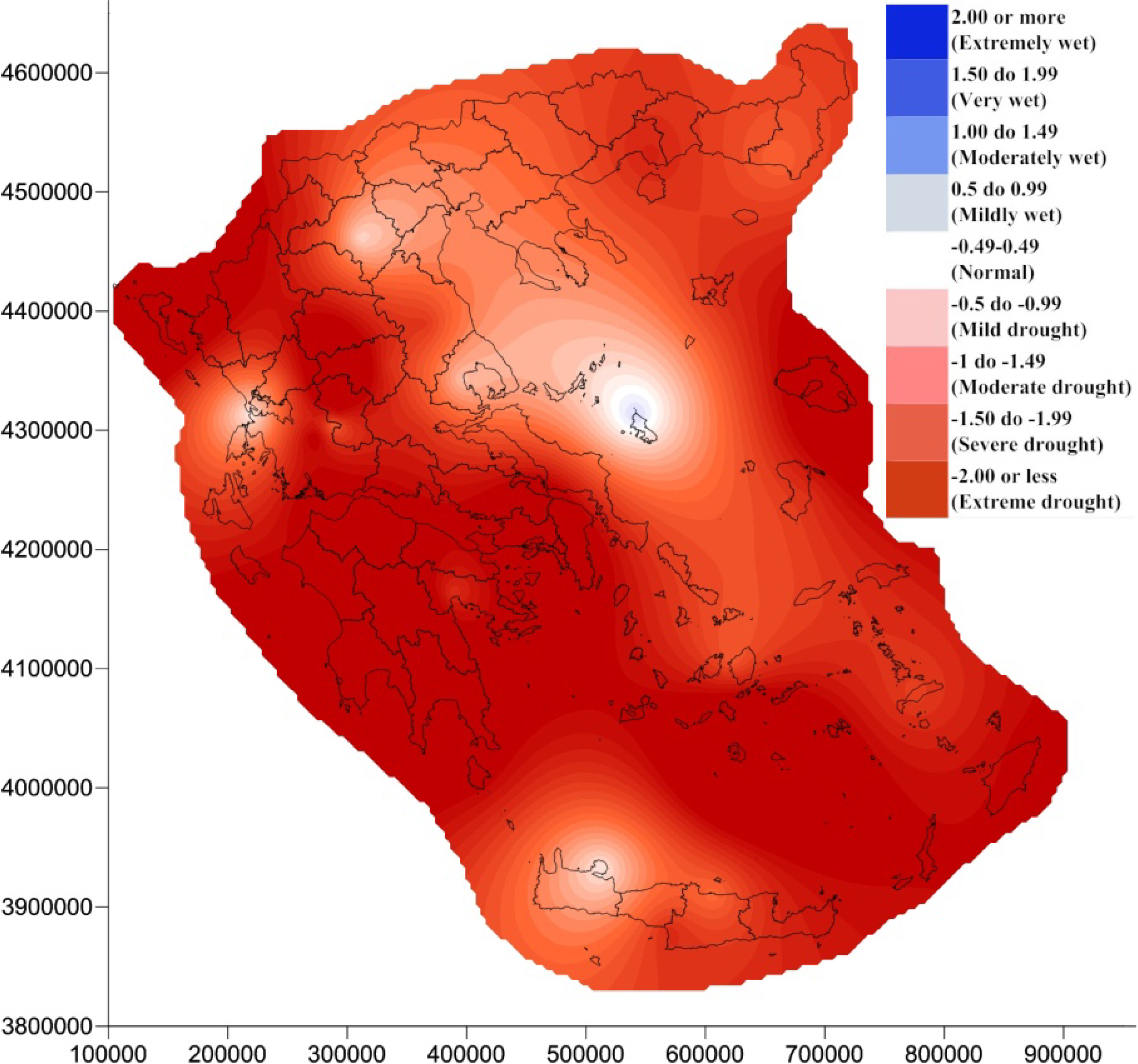
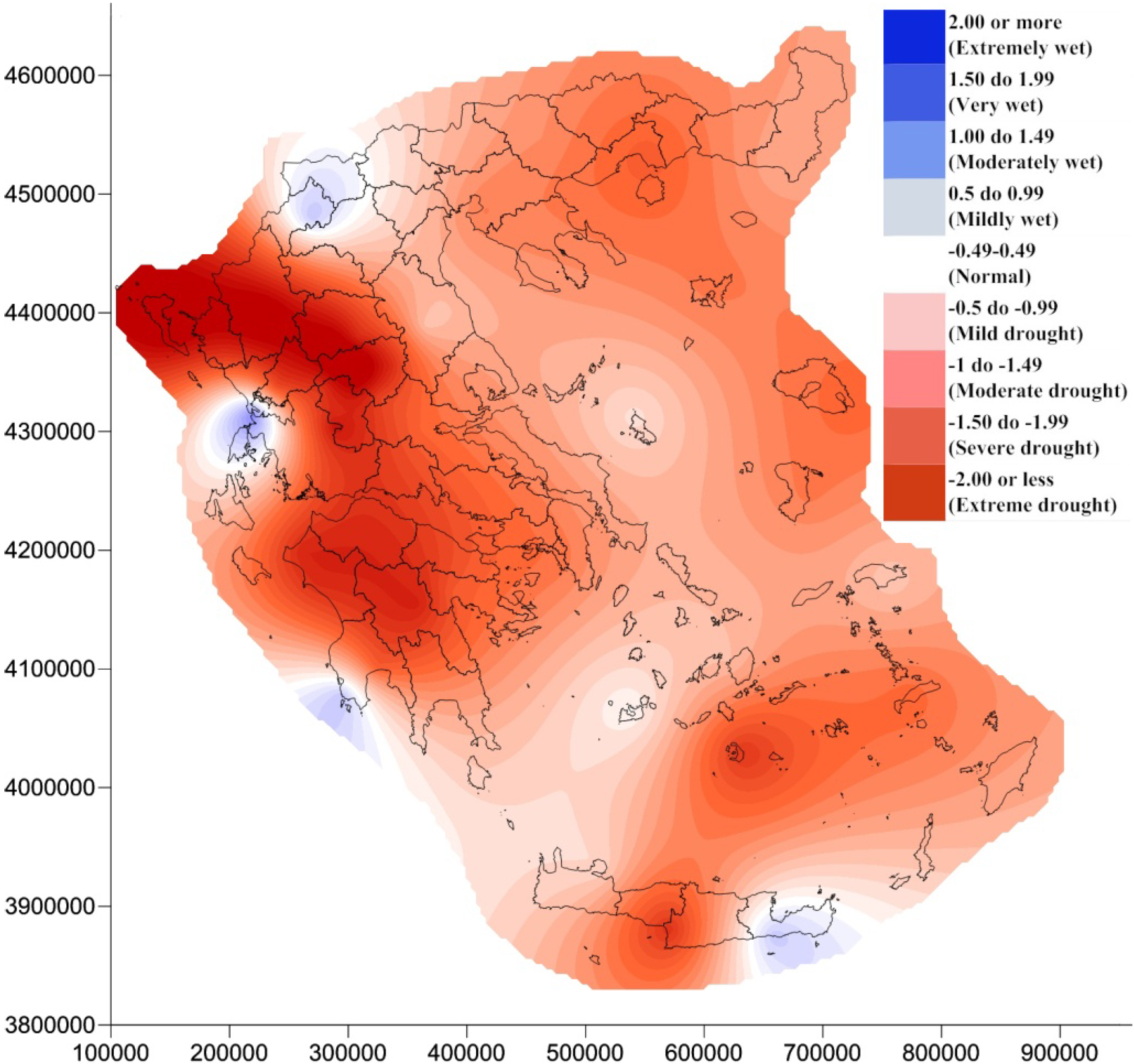
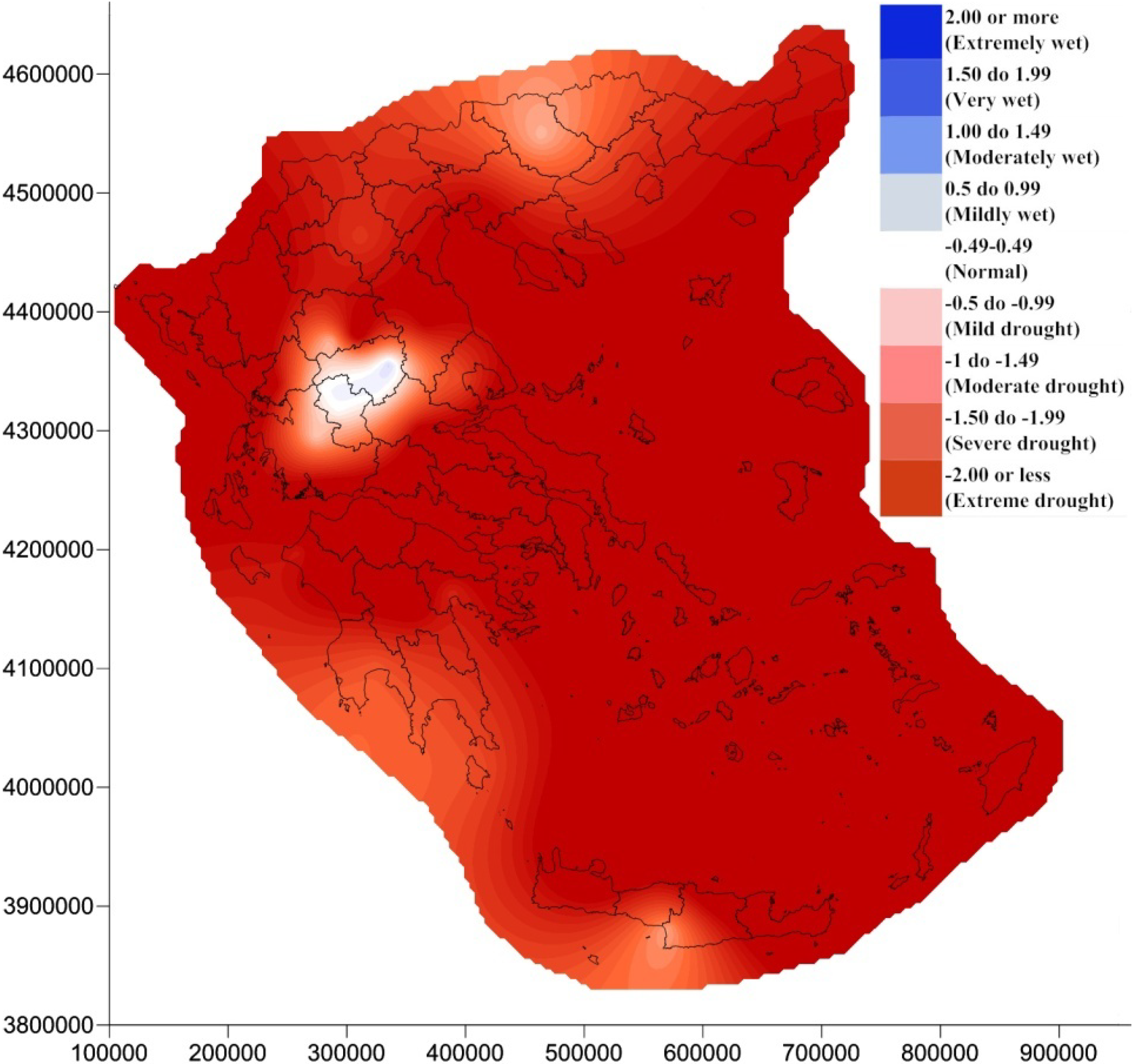
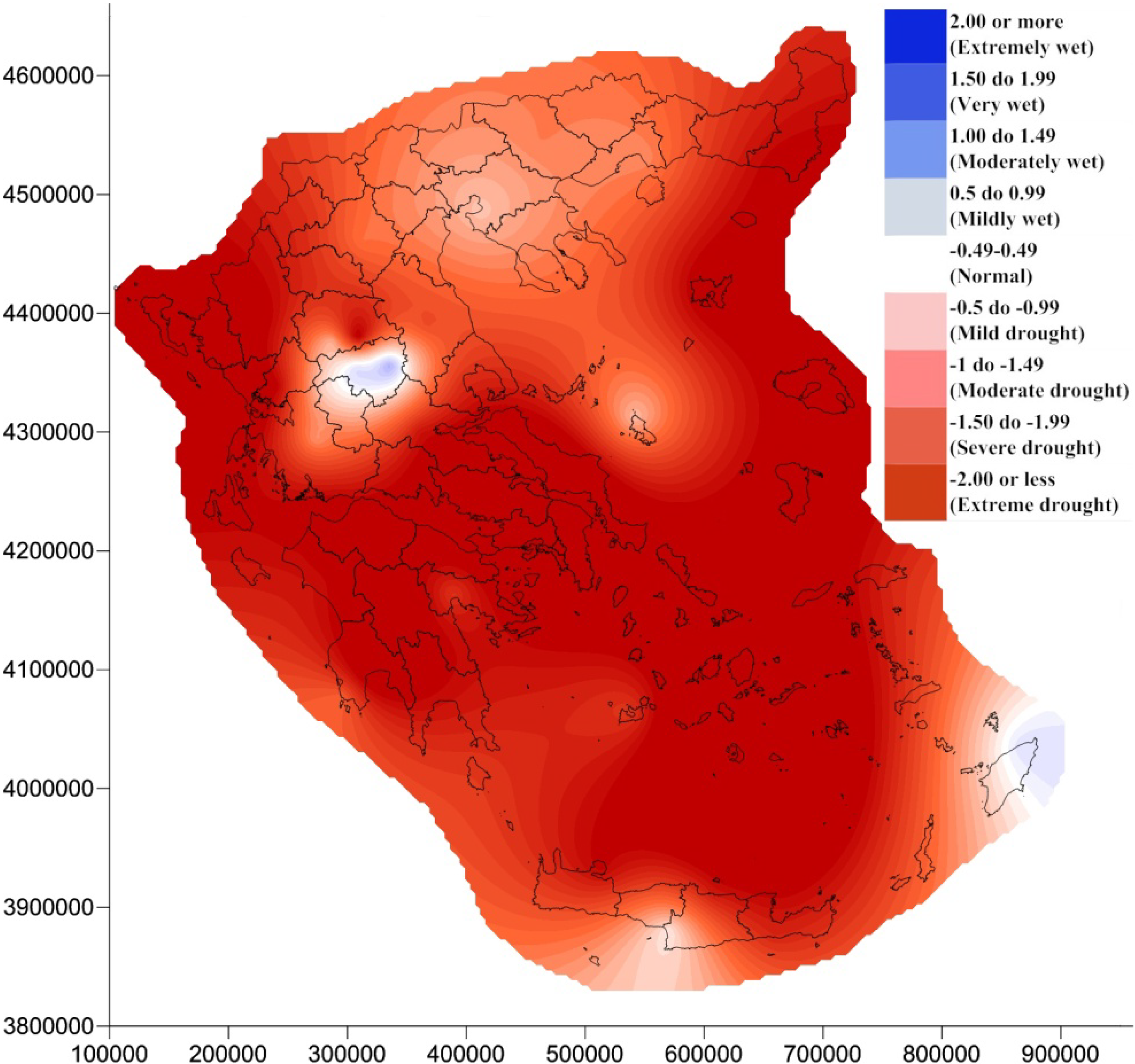

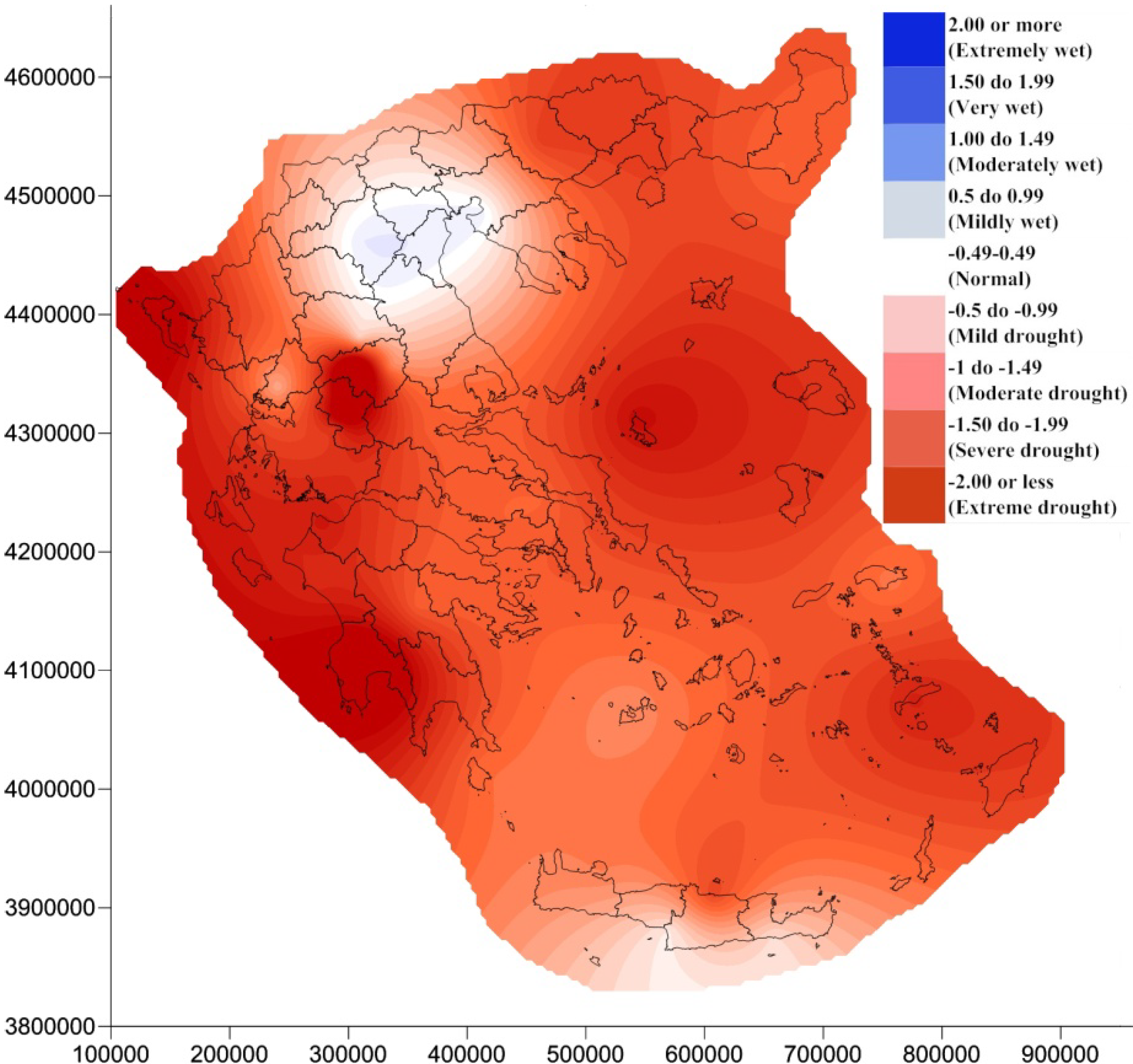
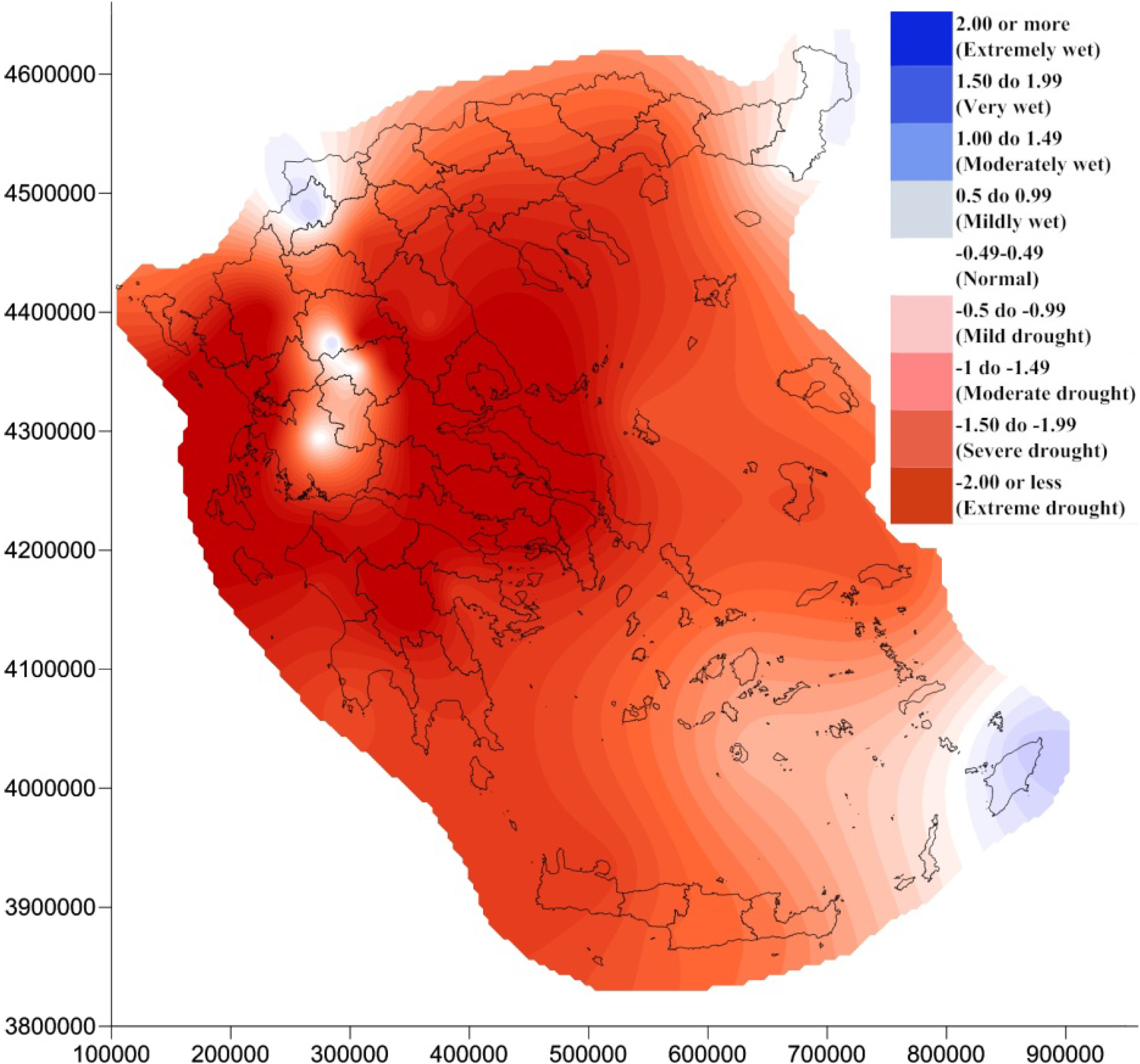

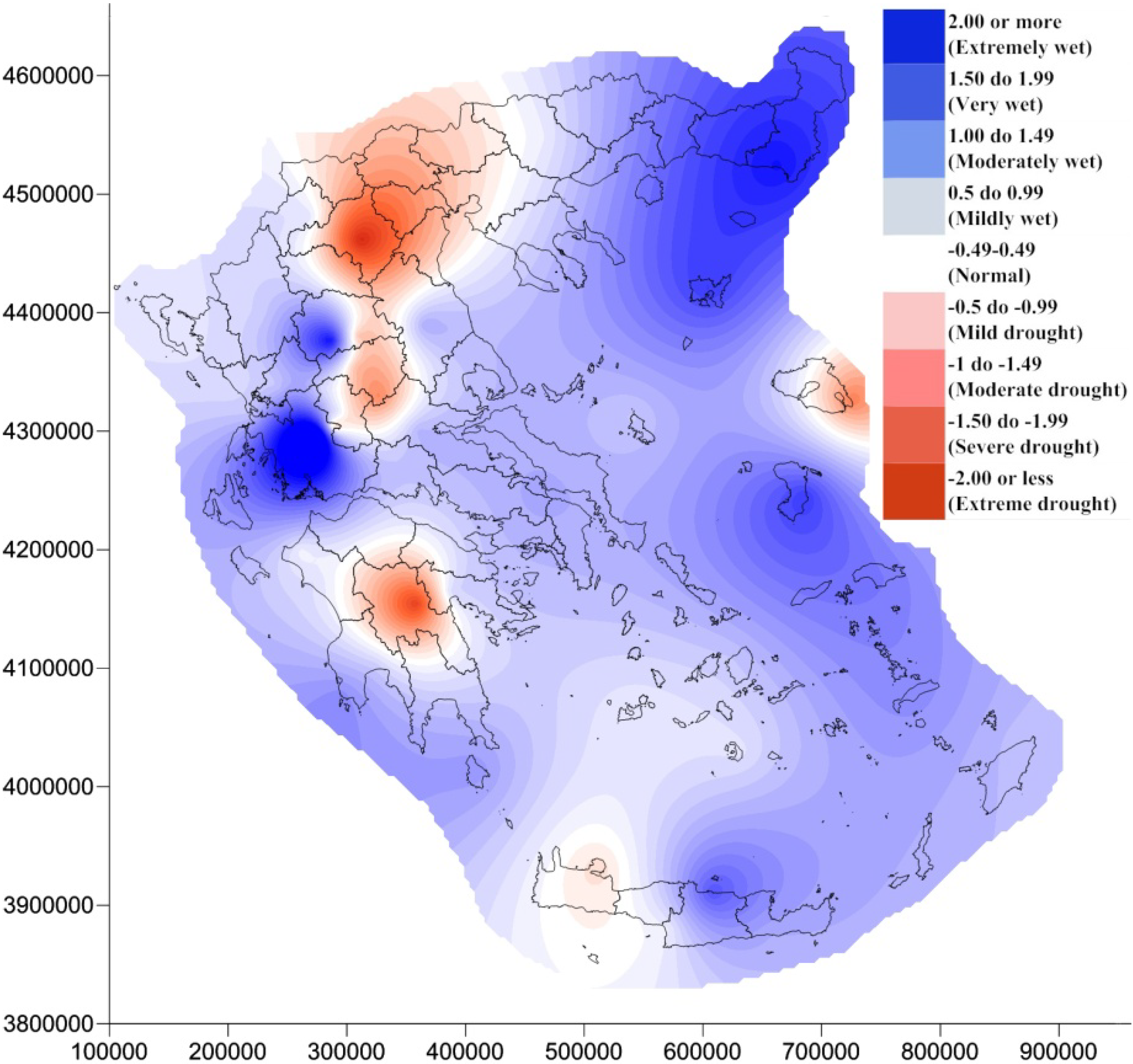
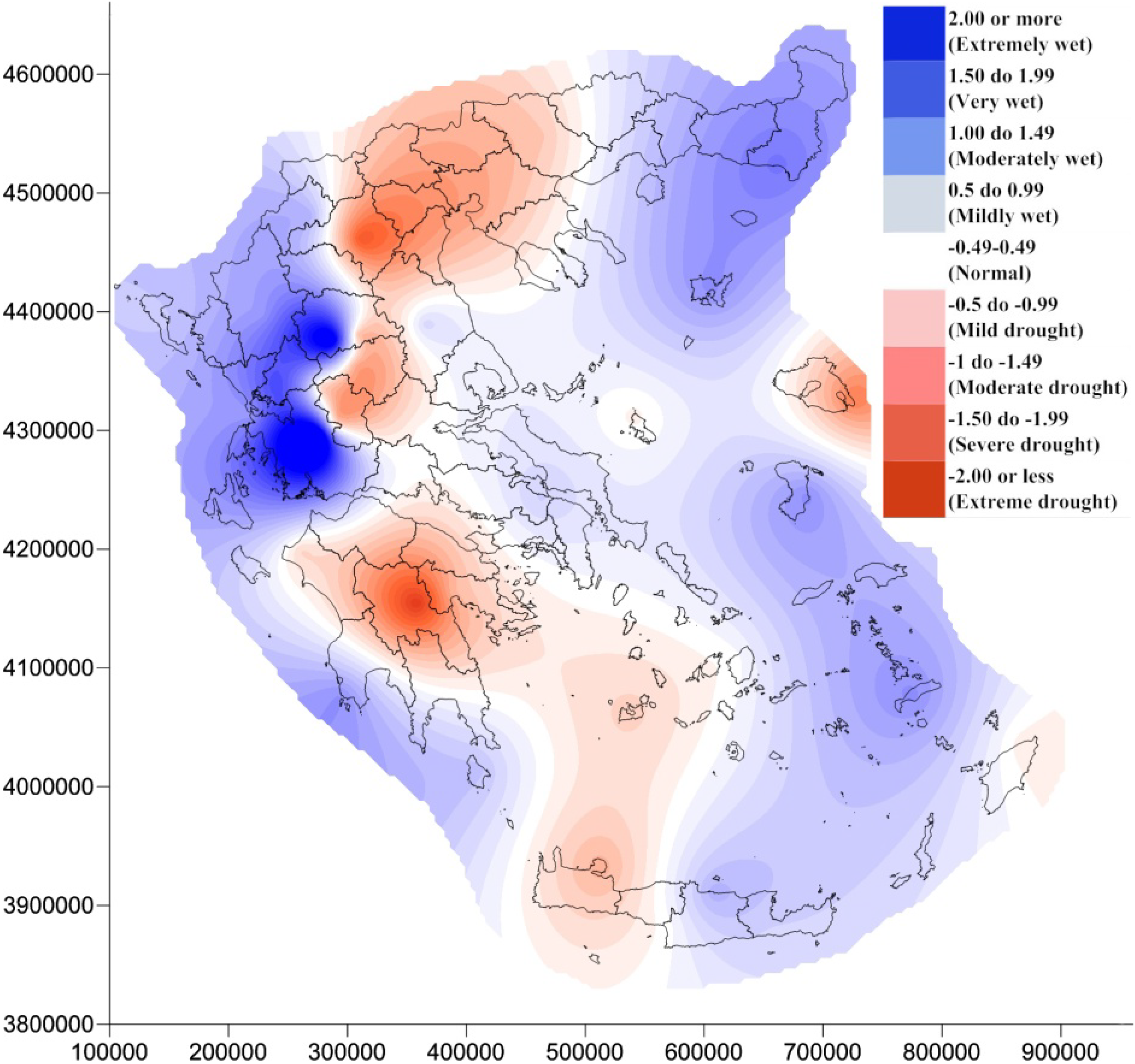
5. Conclusions
References
- Karavitis, C.A. Drought and urban water supplies: The case of Metropolitan Athens. Water Pol. 1998, 1, 505–524. [Google Scholar]
- Karavitis, C.A.; Scientific Co-ordinator. Technical Report on Contract No. 10889/11/07 /2007 with Agricultural University of Athens (AUA); Technical support to the central water agency of greece for the development of a drought master plan for greece and an immediate drought mitigation plan; Department of Natural Resources and Agricultural Engineering, Water Resources Management Sector, Ministry of Planning, Public Works and the Environment: Athens, Greece, 2008. (in Greek)
- Karavitis, C.A. Decision support systems for drought management strategies in Metropolitan Athens. Water Int. 1999, 24, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willeke, G.E.; Hosking, J.R.M.; Wallis, J.R.; Guttman, N.B. The National Drought Atlas; Institute for Water Resources Report 94–NDS–4; U.S. Army Corps of Engineers: Washington, DC, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs, W.J.; Maher, J.V. Rainfall Deciles as Drought Indicators; Bureau of Meteorology: Melbourne, Australia, 1967. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, W.C. Meteorological Drought; U.S. Department of Commerce Weather Bureau: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Shafer, B.A.; Dezman, L.E. Development of a surface water supply index (swsi) to assess the severity of drought conditions in snowpack runoff areas. In Proceedings of the Western Snow Conference, Fort Collins, CO, USA; 1982; pp. 164–175. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Propeedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–184.
- Palfai, I. Description and forecasting of droughts in hungary. In Proceedings of the 14th Congress on Irrigation and Drainage (ICID), Rio de Janario, Brazil; 1990; Volume 1-C, pp. 151–158. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D.; Hayes, M.J. Understanding the complex impacts of drought: A key to enhancing drought mitigation and preparedness. Water Resour. Manag. 2007, 21, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chortaria, C.; Karavitis, C.A.; Alexandris, S. Development of the SPI drought index for Greece using geo-statistical methods. In Proceedings of BALWOIS 2010 Int. Conference, Ohrid, FYROM, 25–29 May 2010.
- Yevjevich, V.; da Cuncha, L.; Vlachos, E.C. Coping with Droughts; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Grigg, N.S.; Vlachos, E.C. Drought and water-supply management: Roles and responsibilities. J. Water Resour. Plann. Manag. 1993, 119, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, M.J.; Svoboda, M.D.; Wilhite, D.A.; Vanyarkho, O.V. Monitoring the 1996 drought using the standardized precipitation index. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1999, 80, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, N.B. Accepting the standardized precipitation index: A calculation algorithm. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1999, 35, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hayes, M.J.; Wilhite, D.A.; Svoboda, M.D. The effect of the length of record on the standardized precipitation index calculation. Int. J. Climatol. 2005, 25, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lana, X.; Serra, C.; Burgueño, A. Patterns of monthly rainfall shortage and excess in terms of the standardized precipitation index for Catalonia (NE Spain). Int. J. Climatol. 2001, 21, 1669–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lloyd-Hughes, B.; Saunders, M.A. A drought climatology for Europe. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 1571–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiris, G.; Vangelis, H. Towards a drought watch system based on spatial SPI. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livada, I.; Assimakopoulos, V.D. Spatial and temporal analysis of drought in greece using the standardized precipitation index (SPI). Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2007, 89, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sönmez, F.K.; Kömüscü, A.Ü.; Erkan, A.; Turgu, E. An analysis of spatial and temporal dimension of drought vulnerability in turkey using the standardized precipitation index. Nat. Hazards 2005, 35, 243–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loukas, A.; Vasiliades, L.; Tzabiras, J. Evaluation of climate change on drought impulses in Thessaly, Greece. Eur. Water 2007, 17/18, 17–28. [Google Scholar]
- Vasiliades, L.; Loukas, A.; Patsonas, G. Evaluation of a statistical downscaling procedure for the estimation of climate change impacts on droughts. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 9, 879–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPI software. Drought Management Centre for South Eastern Europe (DMCSEE) Project, European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2009. Available online: http://www.dmcsee.org/en/events/ (accessed on 7 September 2010).
- Hosking, J.R.M.; Wallis, J.R. Regional Frequency Analysis: An approach Based on L-moments; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Sprent, P.; Smeeton, N.C. Applied Nonparametric Statistical Methods, 3rd ed.; Chapman & Hall/CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Yevjevich, V. Probability and Statistics in Hydrology; Water Resources Publications: Littleton, CO, USA, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Thom, H.C.S. A note on the gamma distribution. Mon. Weather Rev. 1958, 86, 117–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosking, J.R.M. On the characterization of distributions by their L-moments. J. Stat. Plann. Infer. 2006, 136, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramowitz, M.; Stegun, I.A. Handbook of Mathematical Functions with Formulas, Graphs, and Mathematical Tables; Dover Publications, INC.: New York, NY, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Athanasopoulos, G. Application of the SPI in Greece. Master Thesis, Department of Chemical Engineering, National Technical University of Athens, Athens, Greece, 2011. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Karavitis, C.A.; Alexandris, S.; Tsesmelis, D.E.; Athanasopoulos, G. Application of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in Greece. Water 2011, 3, 787-805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w3030787
Karavitis CA, Alexandris S, Tsesmelis DE, Athanasopoulos G. Application of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in Greece. Water. 2011; 3(3):787-805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w3030787
Chicago/Turabian StyleKaravitis, Christos A., Stavros Alexandris, Demetrios E. Tsesmelis, and George Athanasopoulos. 2011. "Application of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in Greece" Water 3, no. 3: 787-805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w3030787
APA StyleKaravitis, C. A., Alexandris, S., Tsesmelis, D. E., & Athanasopoulos, G. (2011). Application of the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in Greece. Water, 3(3), 787-805. https://doi.org/10.3390/w3030787








