Planning and Decision Support Tools for the Integrated Water Resources Management in Vietnam
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- -
- The uneven distribution of the river network, the uneven rainfall across Vietnam and the prolonged dry seasons result in water supply problems in some areas.
- -
- Vietnam is a downstream country. Important rivers drain from bordering countries into Vietnam. The quantity and quality of the surface water depends on the water usage in the upstream countries.
- -
- The infrastructure for water supply, wastewater management, flood protection etc. is still deficient and large investments will be required during the coming decades.
- -
- Fast urbanization, industrialization and intensification of agriculture in Vietnam leads to a rapidly increasing water demand and to severe water pollutions. Institutions in Vietnam do not yet have the capacity to efficiently plan water resource usage and control water pollution.
- -
- Water is finite and a vulnerable resource
- -
- IWRM is a participatory approach
- -
- Recognizing women in their central role for the provision, management and safeguarding of water
- -
- Realizing the social and economic value of water
- -
- Integrating economic efficiency in water use, equity, environmental and ecological sustainability
2. Methods and Results
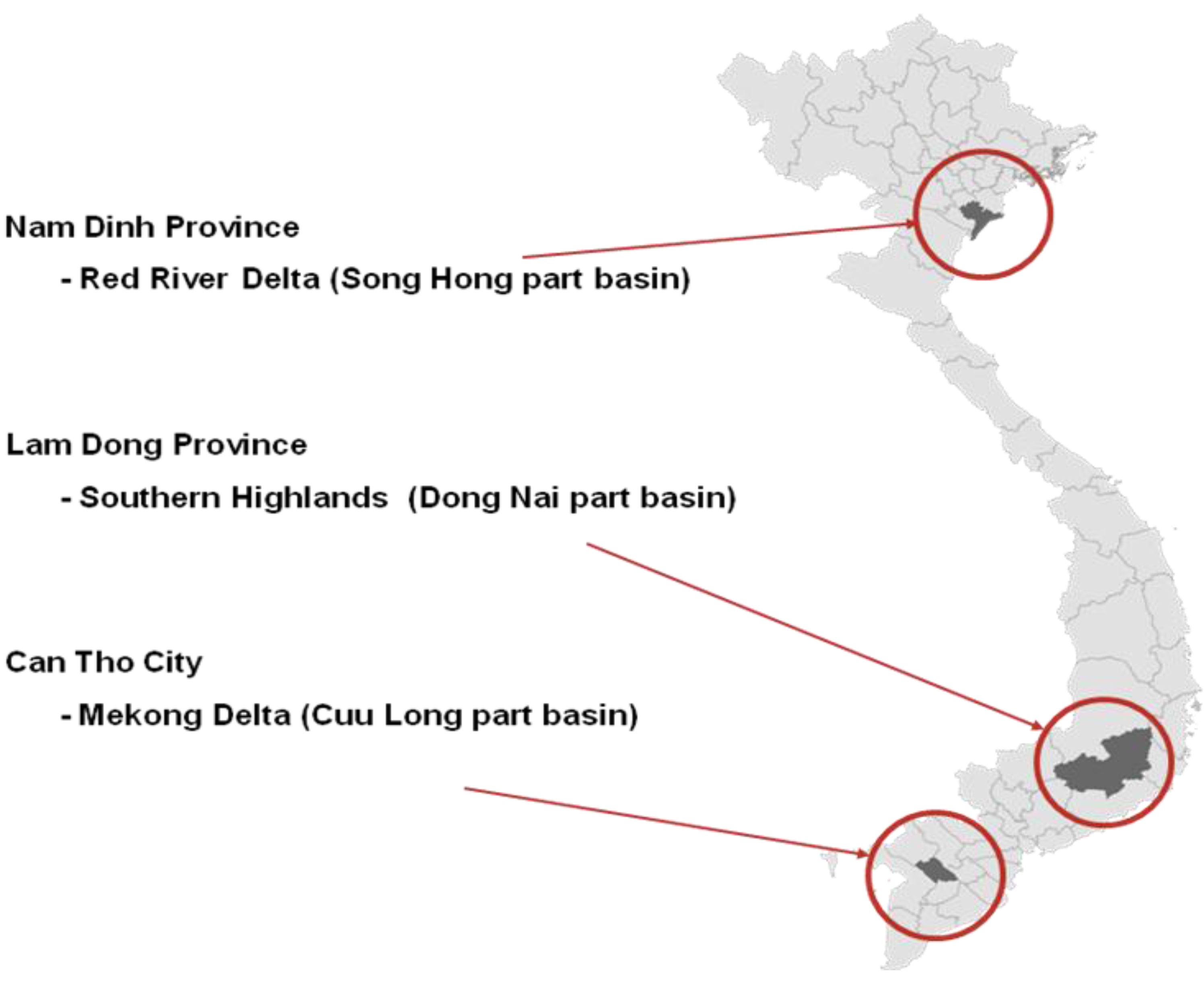
2.1. Research Areas
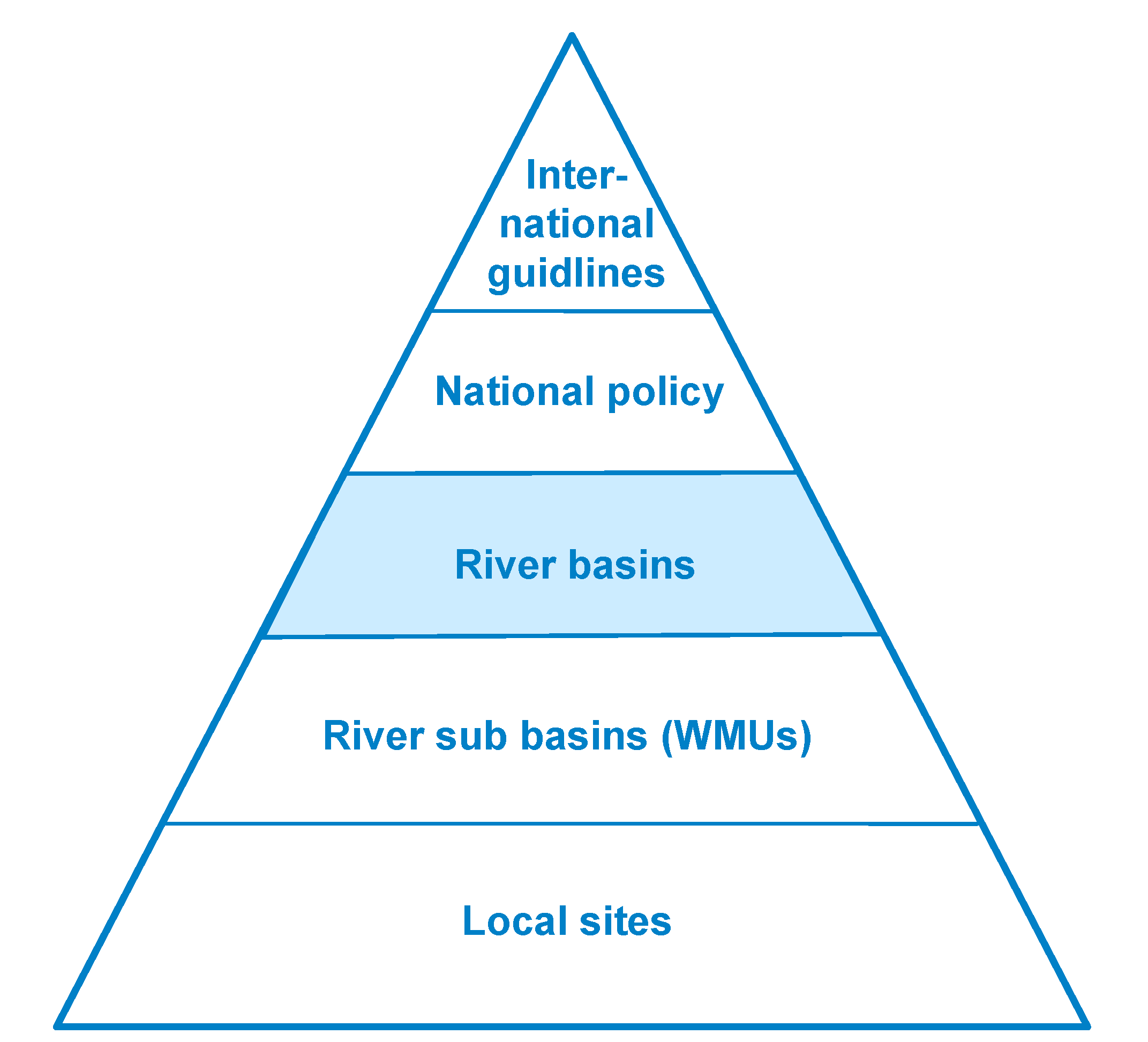
2.2. Concept of the Project
- (1)
- International level (international guidelines: e.g. Global Water Partnership, Agenda 21)
- (2)
- National planning level (national Vietnamese water and environmental policy, national Vietnamese legislation)
- (3)
- River basin planning level
- (4)
- River sub basin planning level (WMUs)
- (5)
- Local sites planning level (local measures)
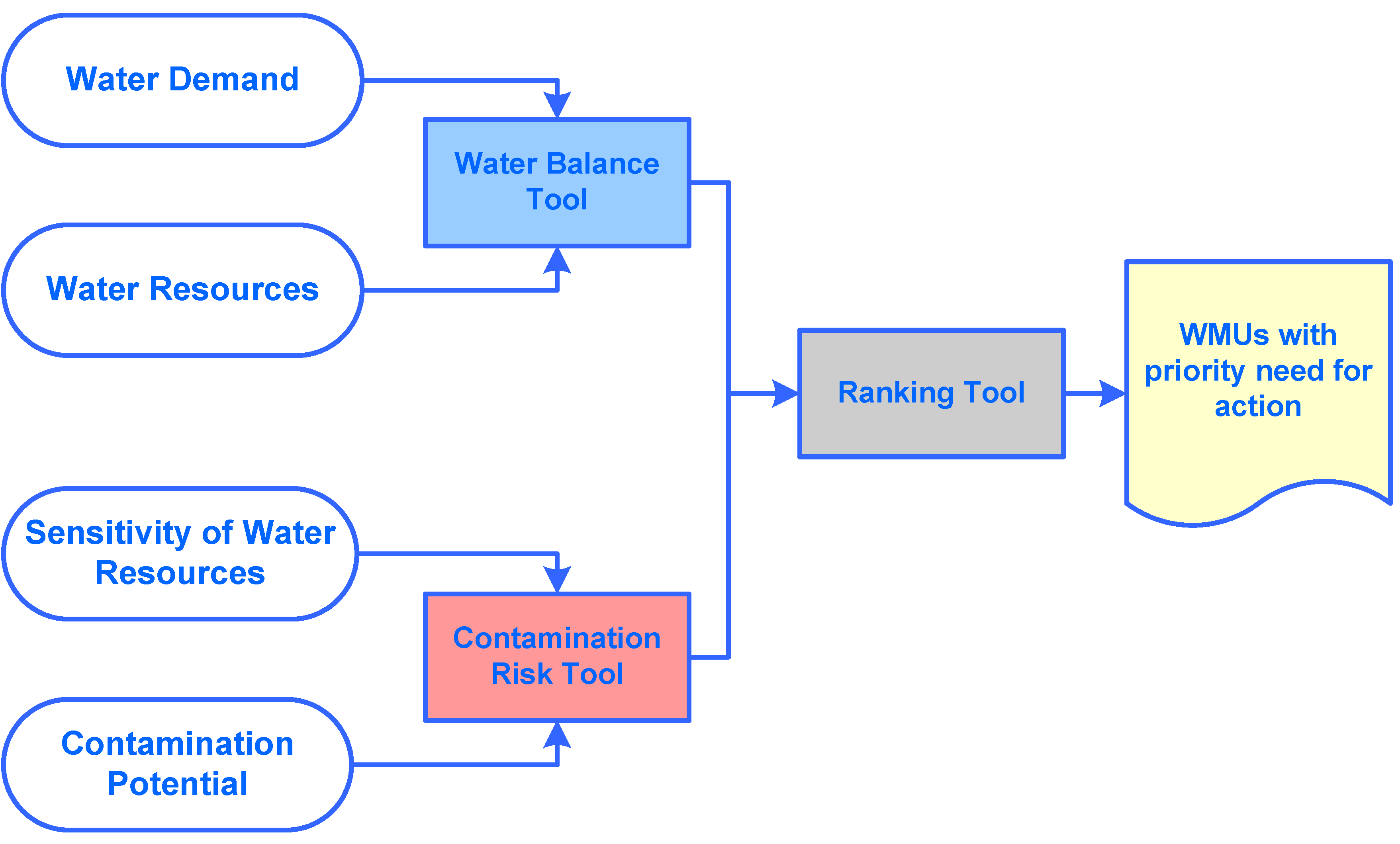
- -
- Water Balance Tool: Evaluation of water demand versus water resources;
- -
- Contamination Risk Tool: Evaluation of sensitivity of water resources versus contamination potential;
- -
- Ranking Tool: Assessment of WMUs with priority need for action.
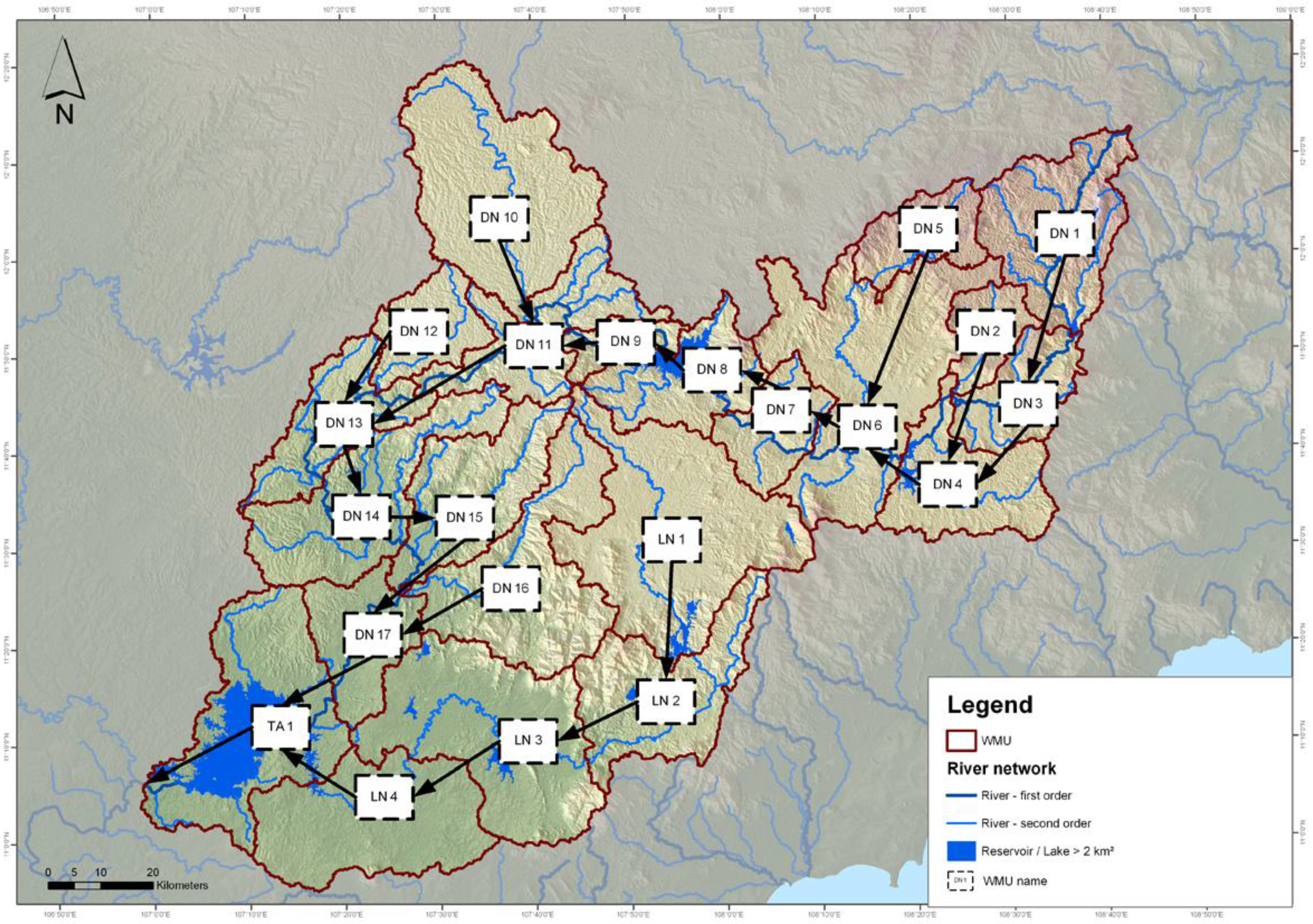
- -
- Basic maps: Water Management Units, administration, population density, land use, orohydrography, natural reserve, geology, soil;
- -
- Water balance: hydrological system, water infrastructure, water resources, water demands, water balance;
- -
- Contamination risk: infiltration into groundwater, diffuse pollution of surface water, direct discharge into surface water.
2.3. Water Balance Tool
2.3.1. Water Resources
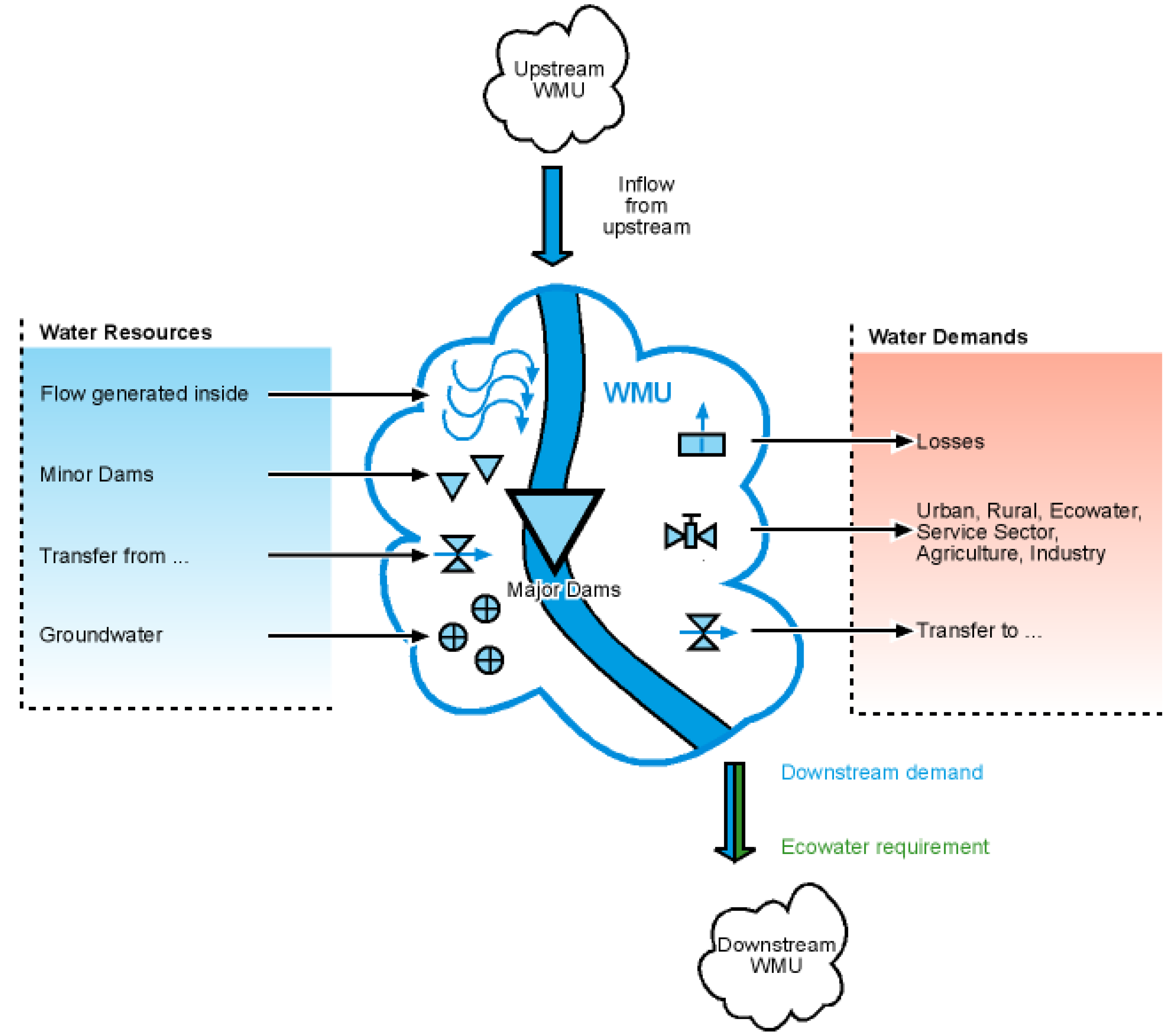
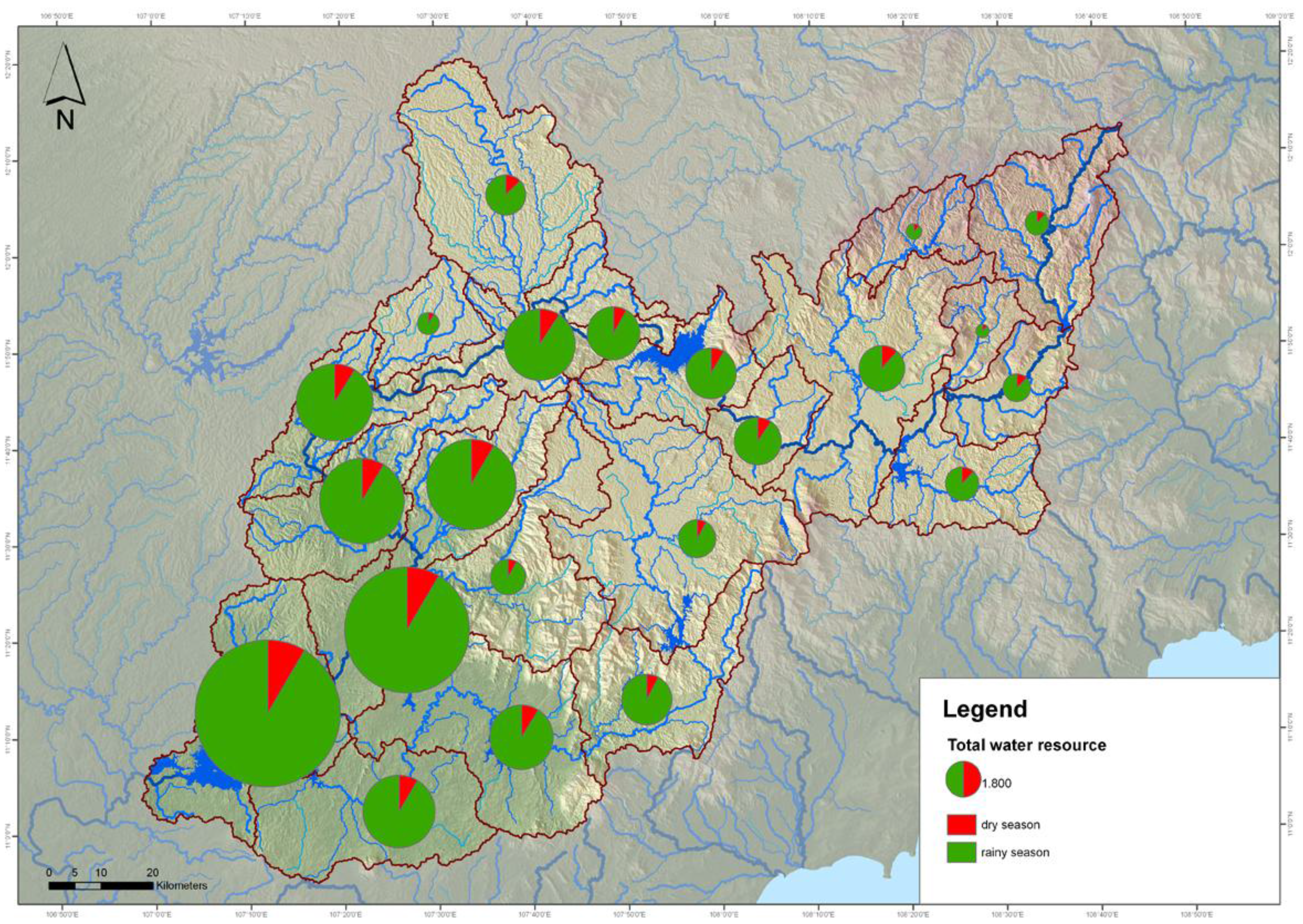
2.3.2. Water Demand
- -
- Population;
- -
- Agriculture;
- -
- Industry;
- -
- Service sector;
- -
- Ecowater requirement.

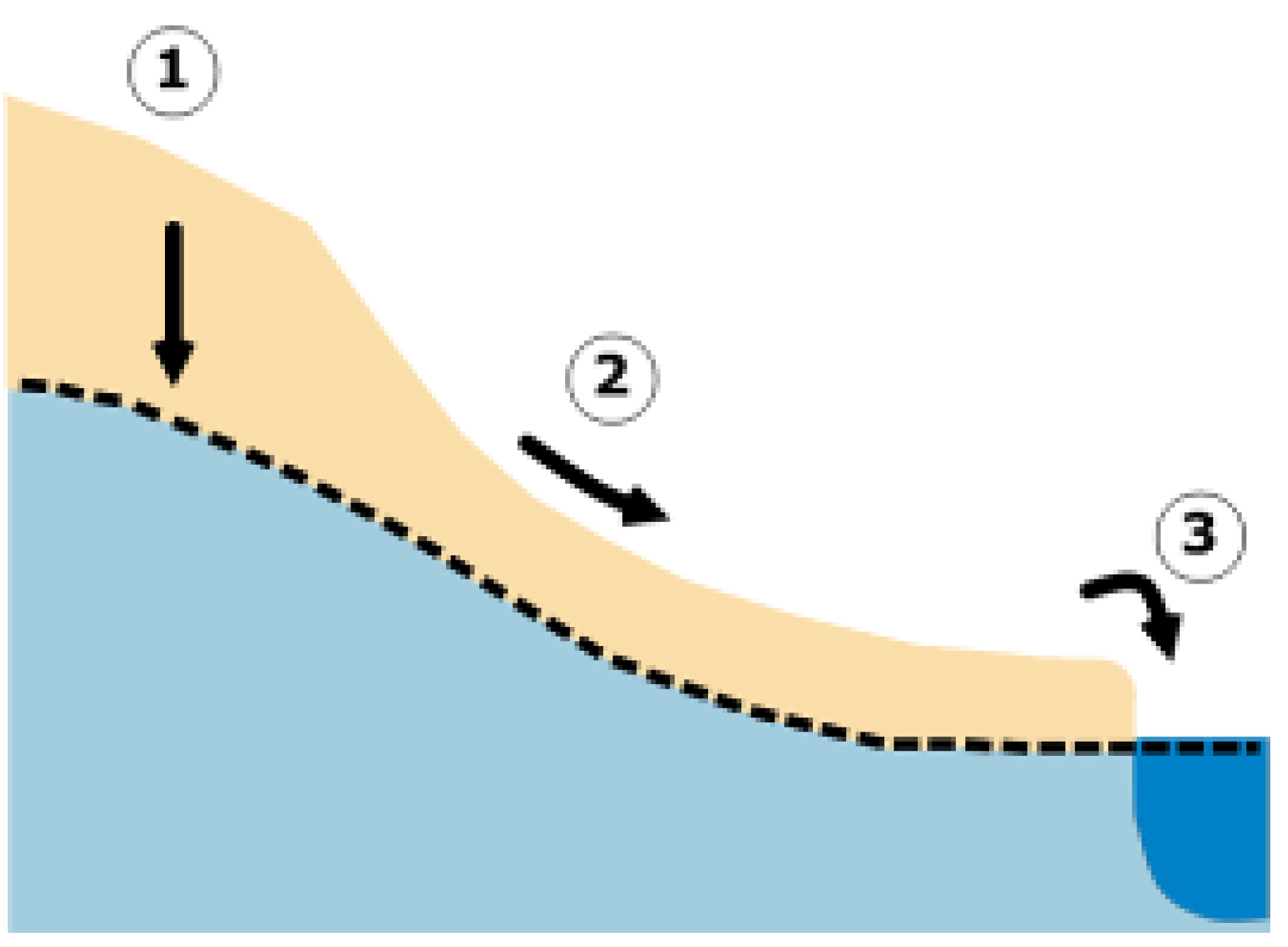
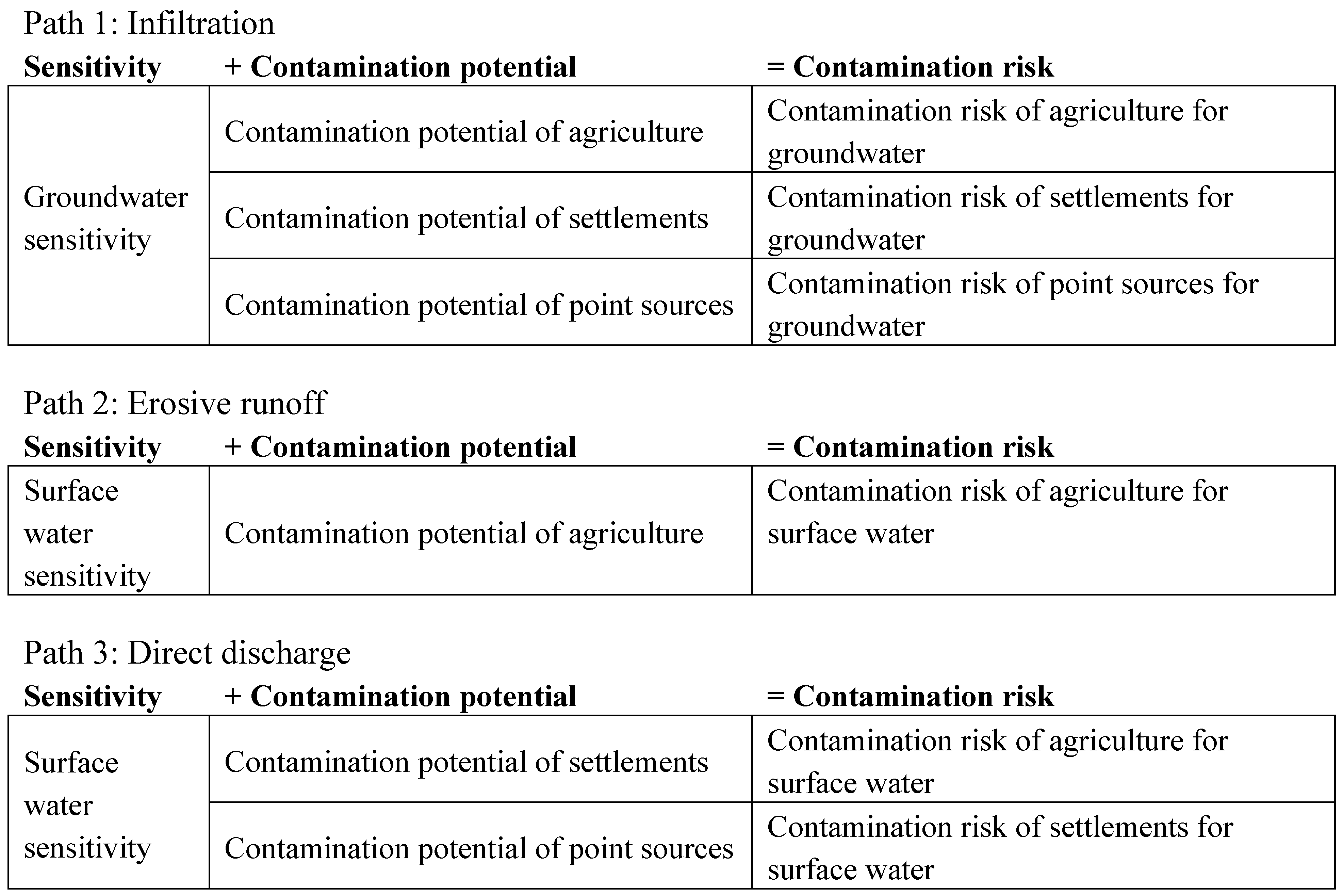
2.4. Contamination Risk Tool
- Infiltration of solute pollutants from diffuse and point sources into groundwater
- Transport of pollutants from diffuse sources by erosive runoff into surface water
- Direct discharge of pollutants from point sources into surface water
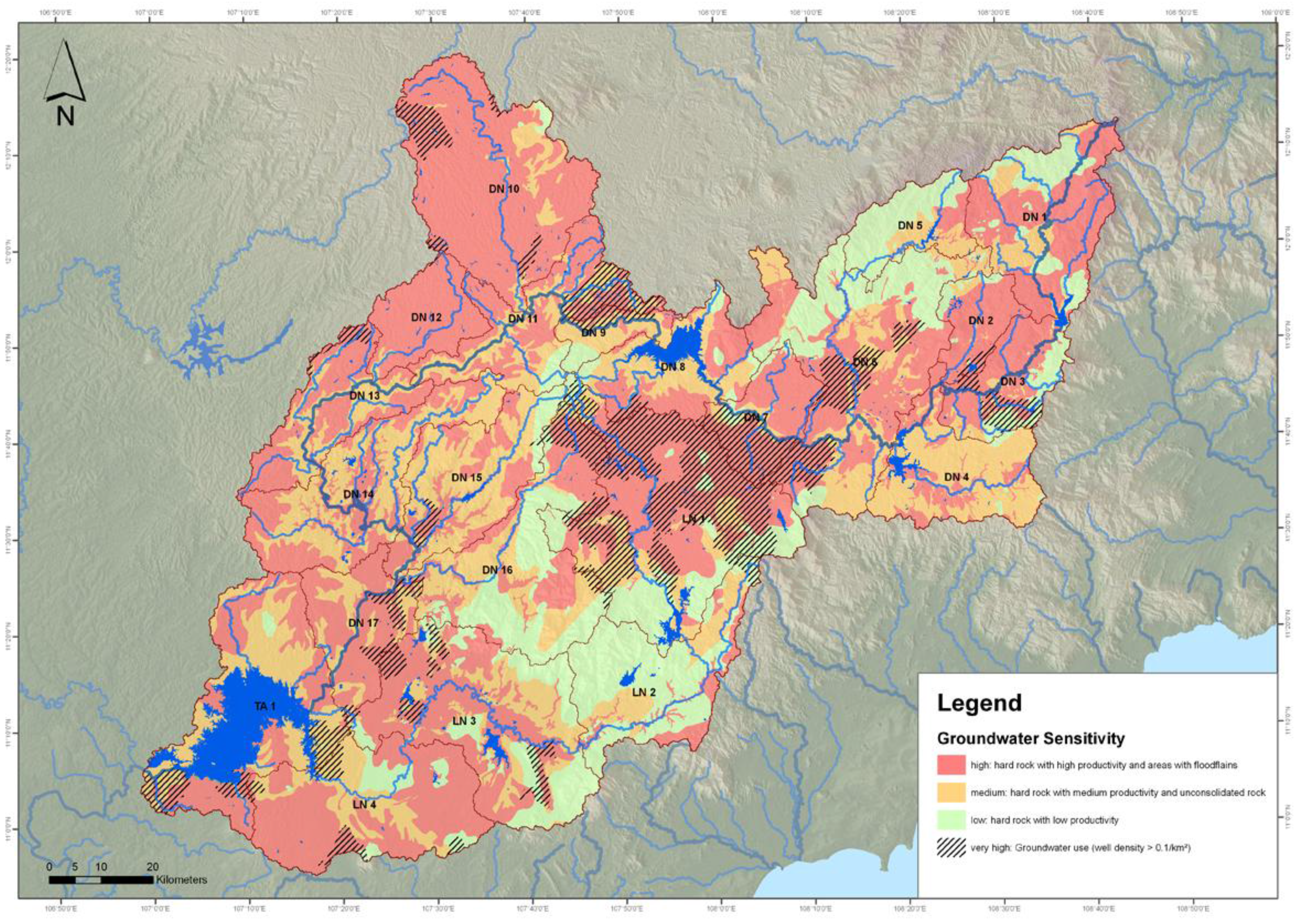
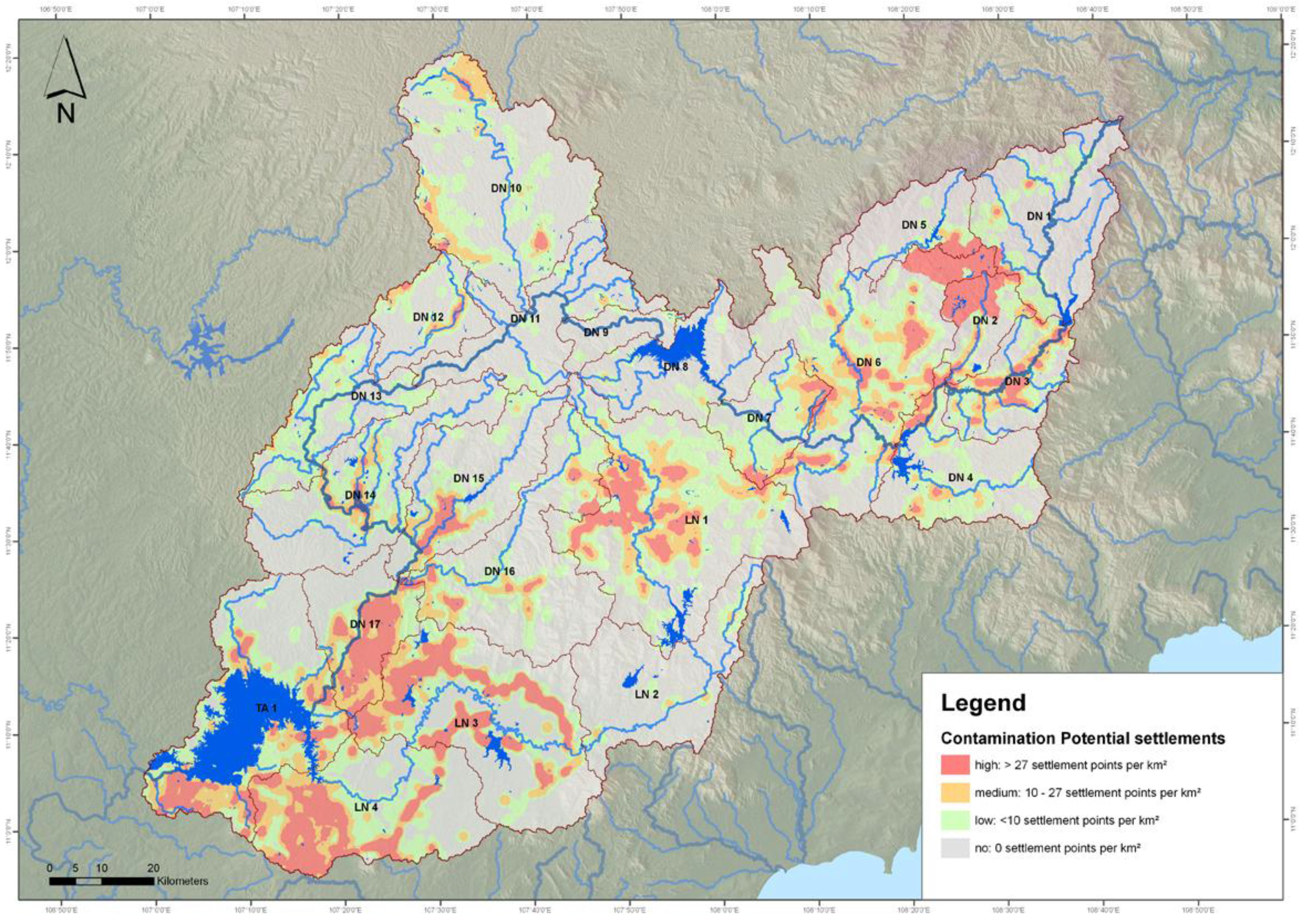
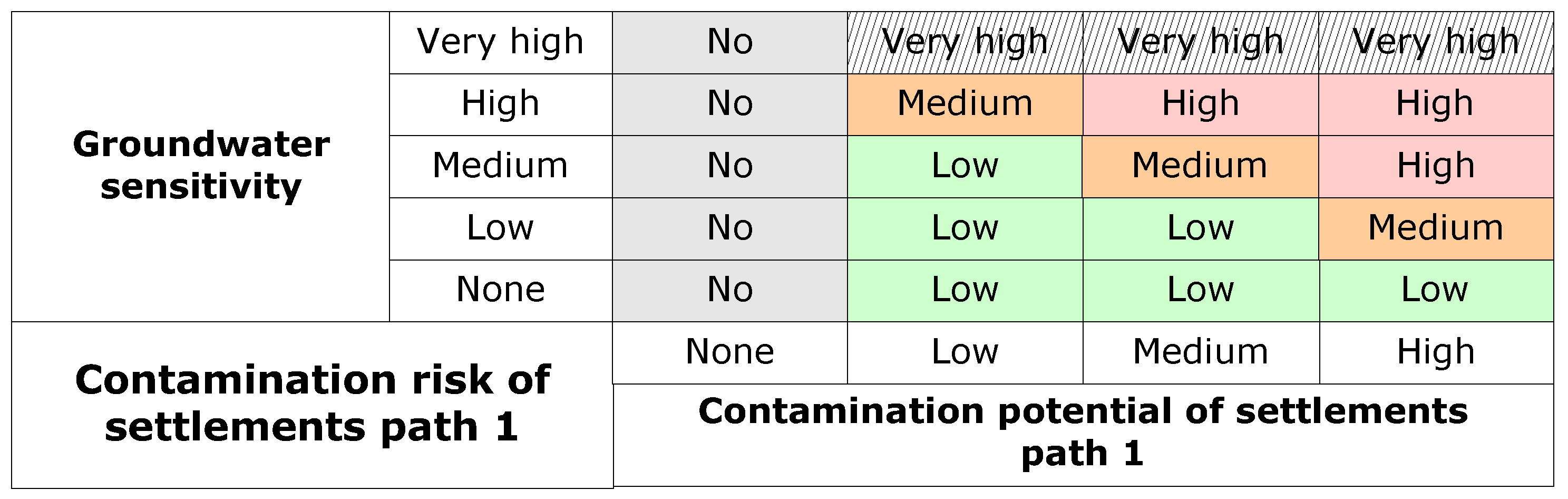
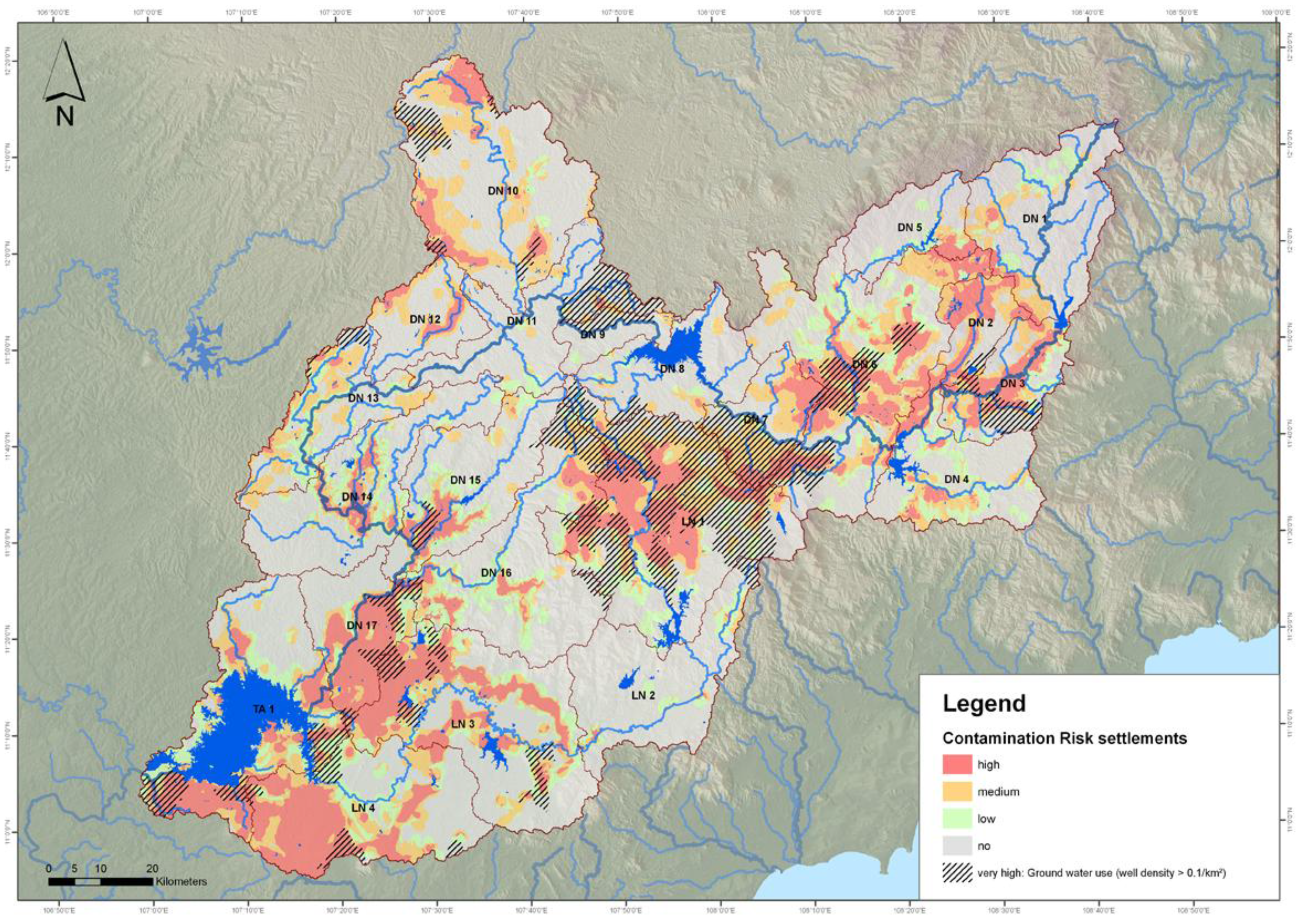
2.5 Ranking Tool
3. Implementation and Changing Institutional Set-Up—Awareness Raising, Cooperation, Capacity Development
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgements
References
- Agarwal, A.; delos Angeles, M. Integrated Water Resources Management, 1st ed.; Global Water Partnership: Stockholm, Sweden, 2000. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Neitsch, S.L.; Arnold, J.G.; Kiniry, J.R.; Williams, J.R.; King, K.W. Soil and Water Assessment Tool. In Theoretical Documentation Version 2000; Grassland, Soil & Water Research Laboratory, GSWRL Report 02-01, Blackland Research and Extension Center, BRC Report 02-05: Temple, Texas, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Provincial Statistical Offices (Ed.) Statistical Yearbook Lam Dong, Dong Nai, Binh Tuan, Binh Phuoc, Dak Nong, Dalat, Dong Nai, Phan Thiet, Dong Xoai; Gia Nghia, Vietnam, 2007. [Green Version]
- Richard, G.; Luis, S. Crop Evapotranspiration—Guidelines for Computing Crop Water Requirements; FAO Irrigation and drainage paper 56; FAO: Rome, Italy, 1998. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Legel, S. Nutztiere der Tropen. In Band II und III, 1st ed.; Hirzel: Stuttgart, Germany, 1990. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- MONRE. National Water Resources Strategy towards the Year 2020, 1st ed.Ministry of Natural Resources and Environment: Hanoi, Vietnam, 2006. [Green Version]
- Cuddihy, W.; Frederiksen, H. Viet Nam Water Resources Sector Review, 1st ed.; World Bank: Washington D.C., USA, 1996. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
© 2010 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Jolk, C.; Greassidis, S.; Jaschinski, S.; Stolpe, H.; Zindler, B. Planning and Decision Support Tools for the Integrated Water Resources Management in Vietnam. Water 2010, 2, 711-725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2040711
Jolk C, Greassidis S, Jaschinski S, Stolpe H, Zindler B. Planning and Decision Support Tools for the Integrated Water Resources Management in Vietnam. Water. 2010; 2(4):711-725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2040711
Chicago/Turabian StyleJolk, Christian, Sandra Greassidis, Sylvia Jaschinski, Harro Stolpe, and Björn Zindler. 2010. "Planning and Decision Support Tools for the Integrated Water Resources Management in Vietnam" Water 2, no. 4: 711-725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2040711
APA StyleJolk, C., Greassidis, S., Jaschinski, S., Stolpe, H., & Zindler, B. (2010). Planning and Decision Support Tools for the Integrated Water Resources Management in Vietnam. Water, 2(4), 711-725. https://doi.org/10.3390/w2040711



