A Study on Blue Infrastructure Governance from the Issue-Appeal Divergence Perspective: An Empirical Analysis Based on LDA and BERTopic Models
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
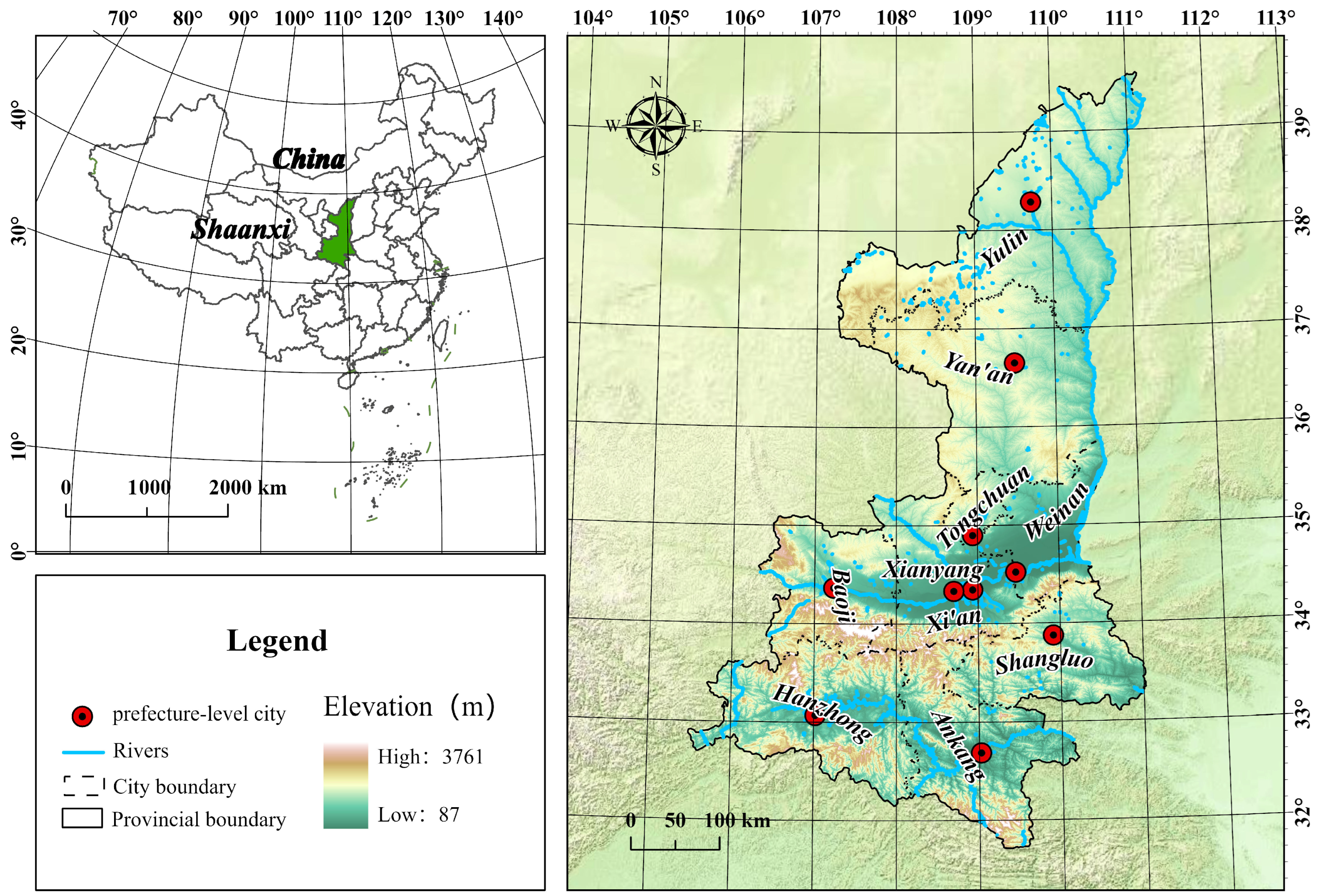
2.1. Study Area
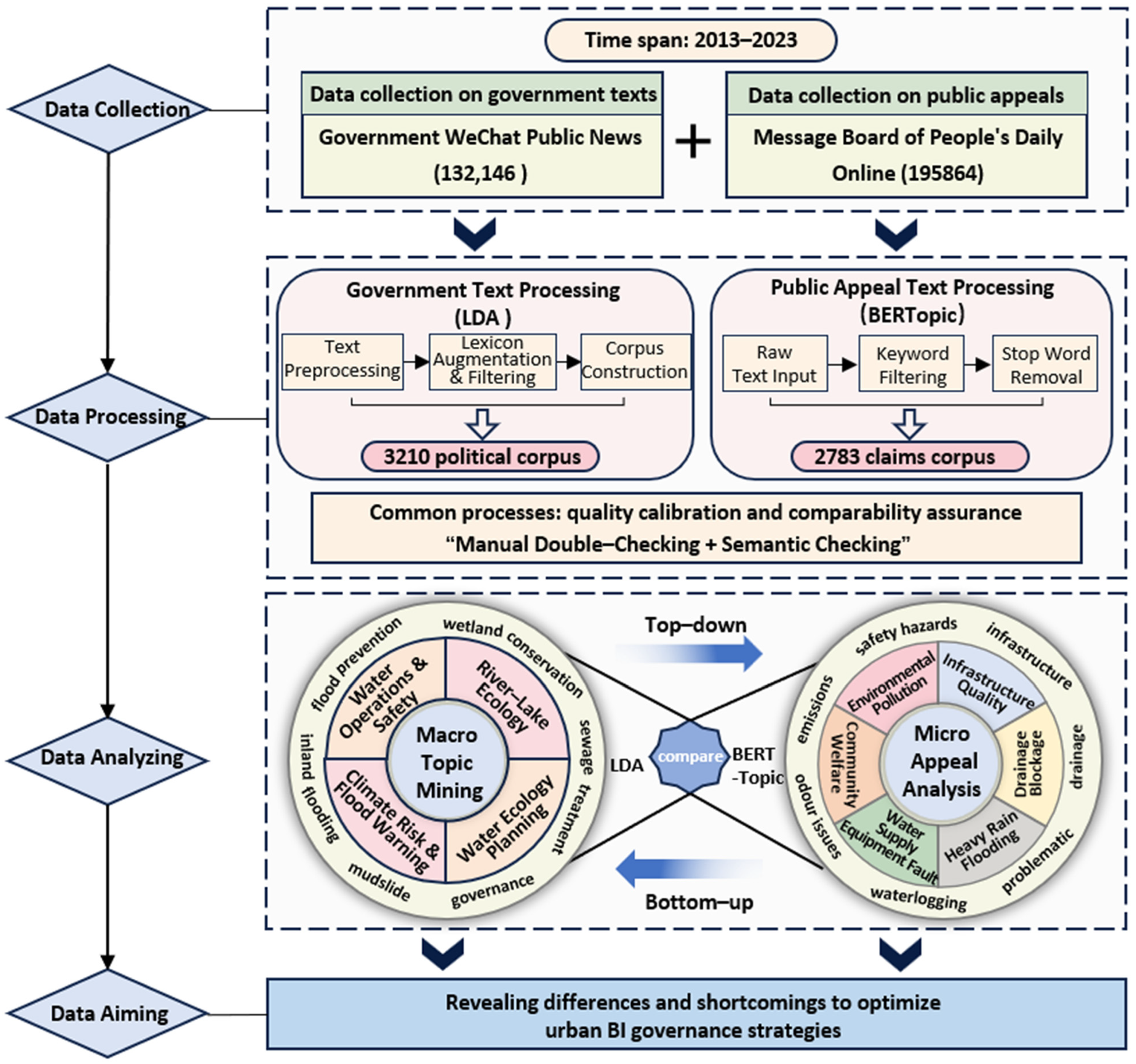
2.2. Research Framework
2.3. Data Collection and Pre-Processing
2.3.1. Government Text Data Processing
2.3.2. Public Appeal Text Data Processing
2.4. Methods
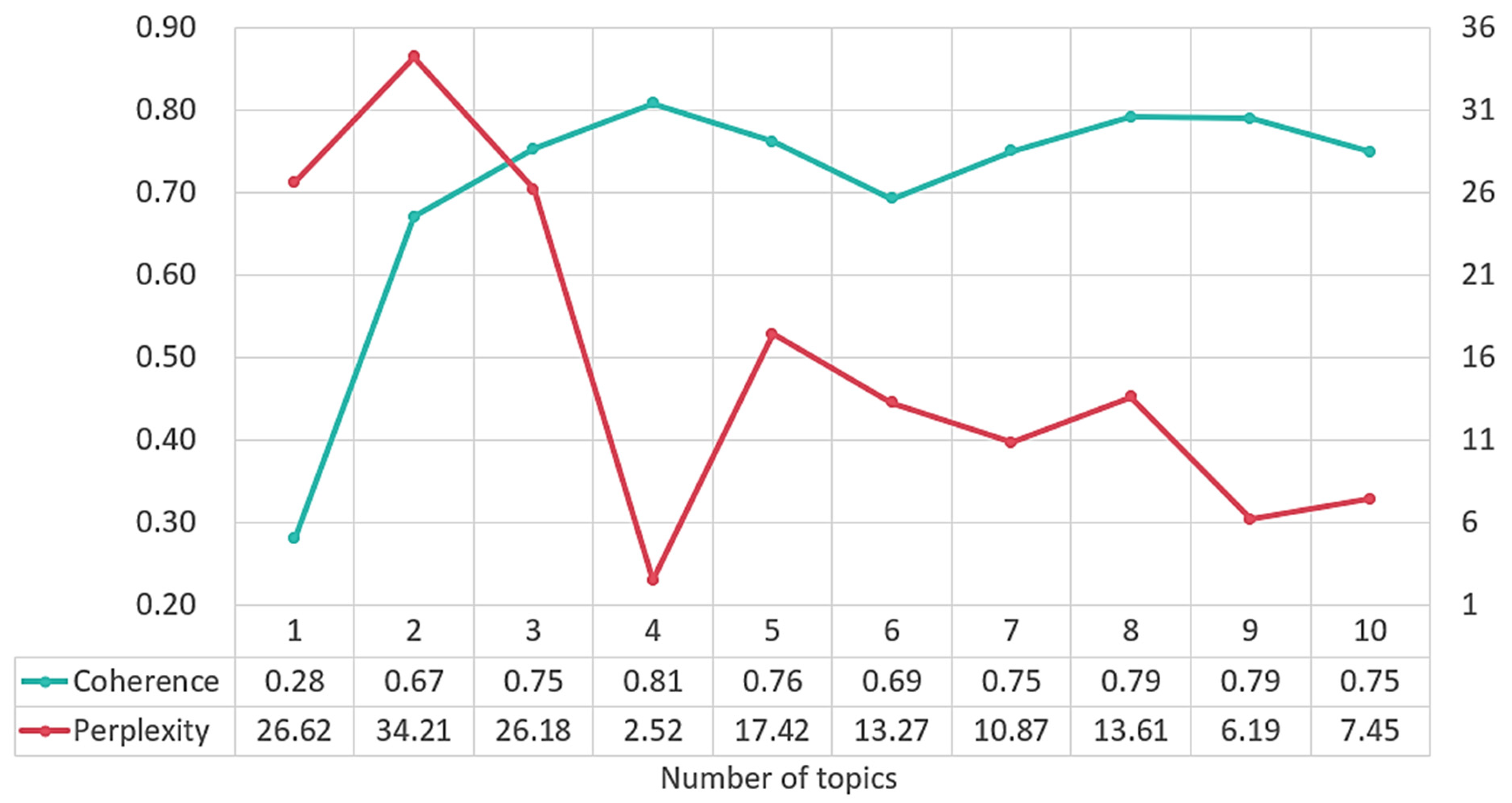
2.4.1. LDA Topic Model
2.4.2. BERTopic
3. Research Results
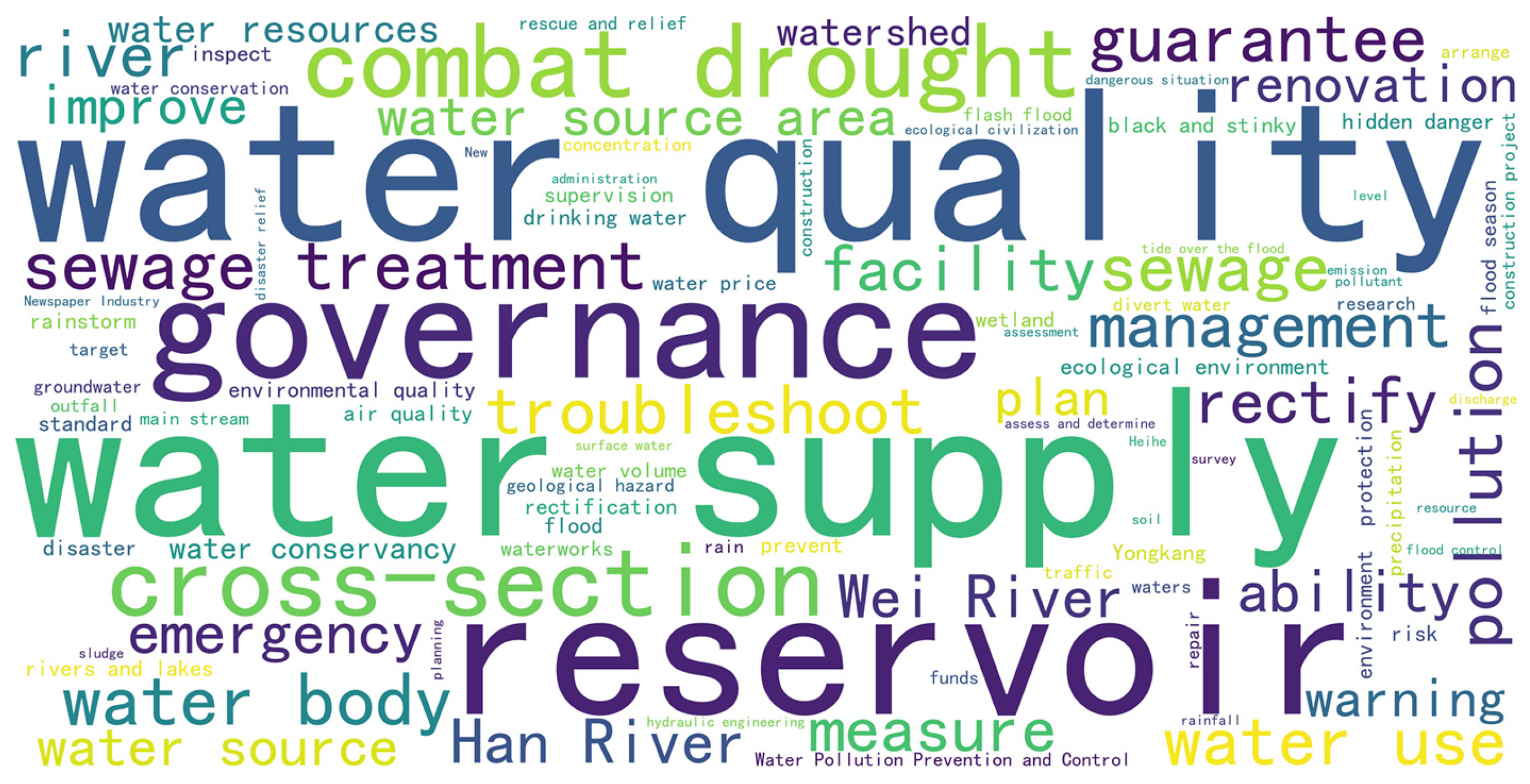
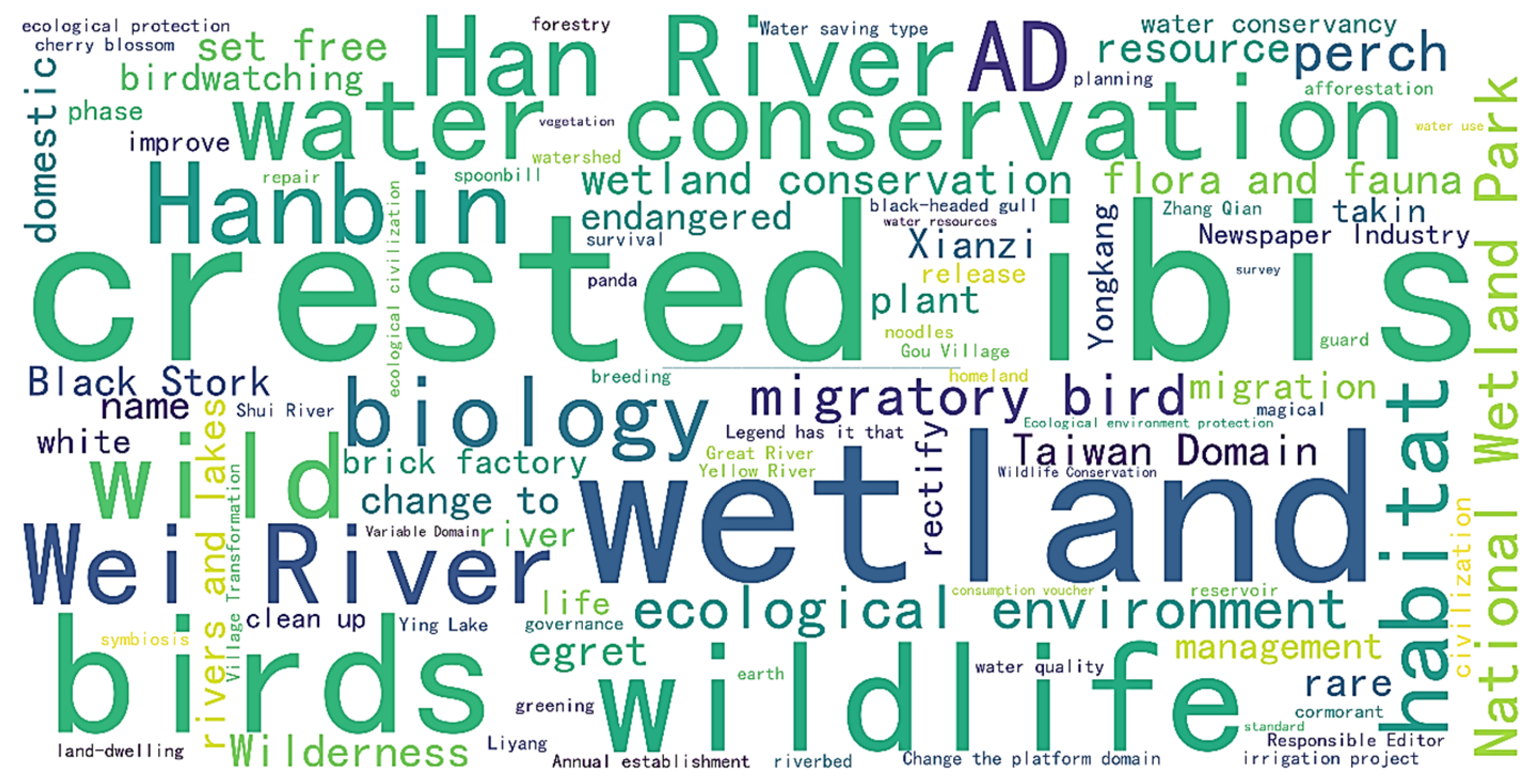
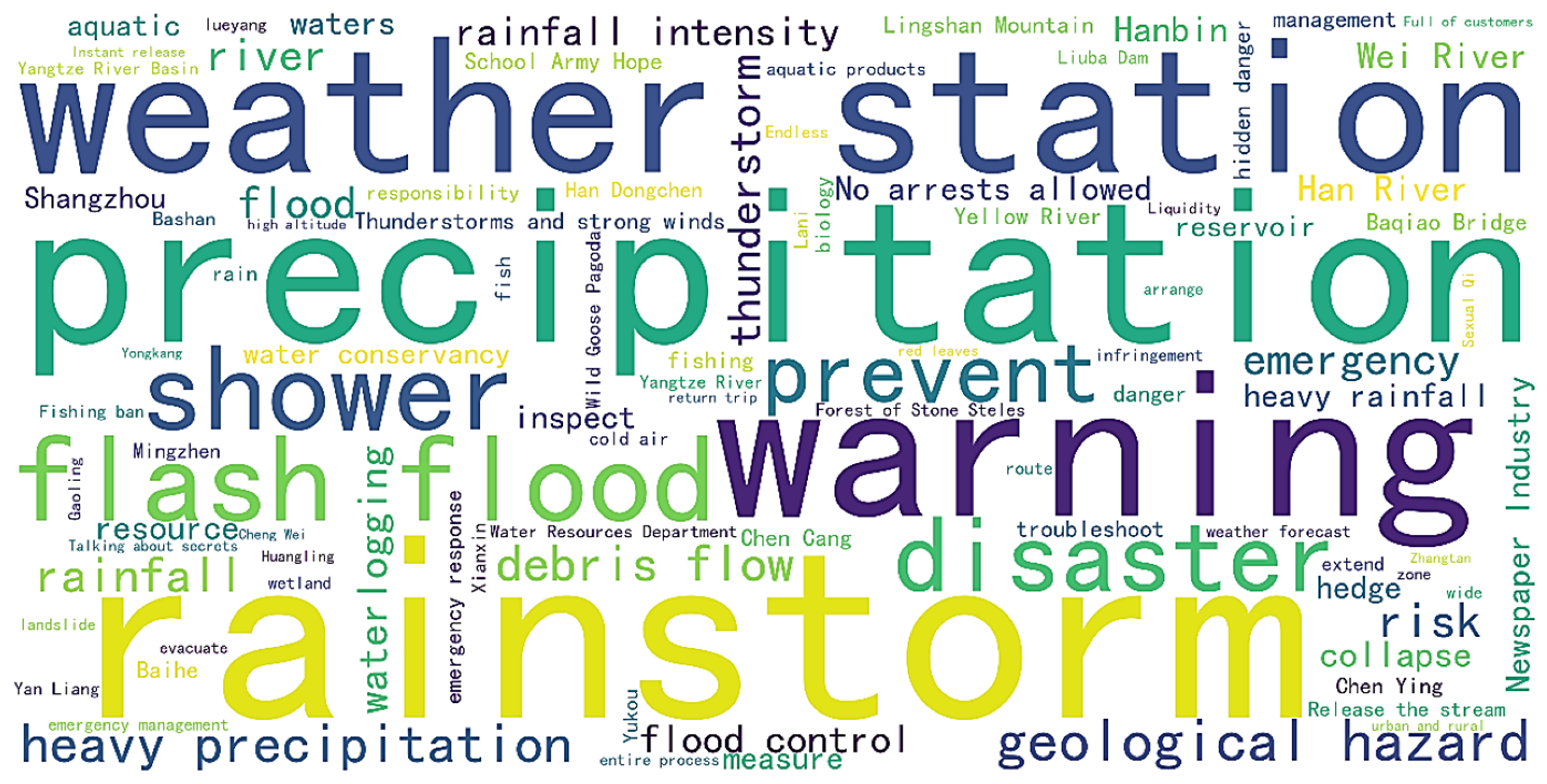
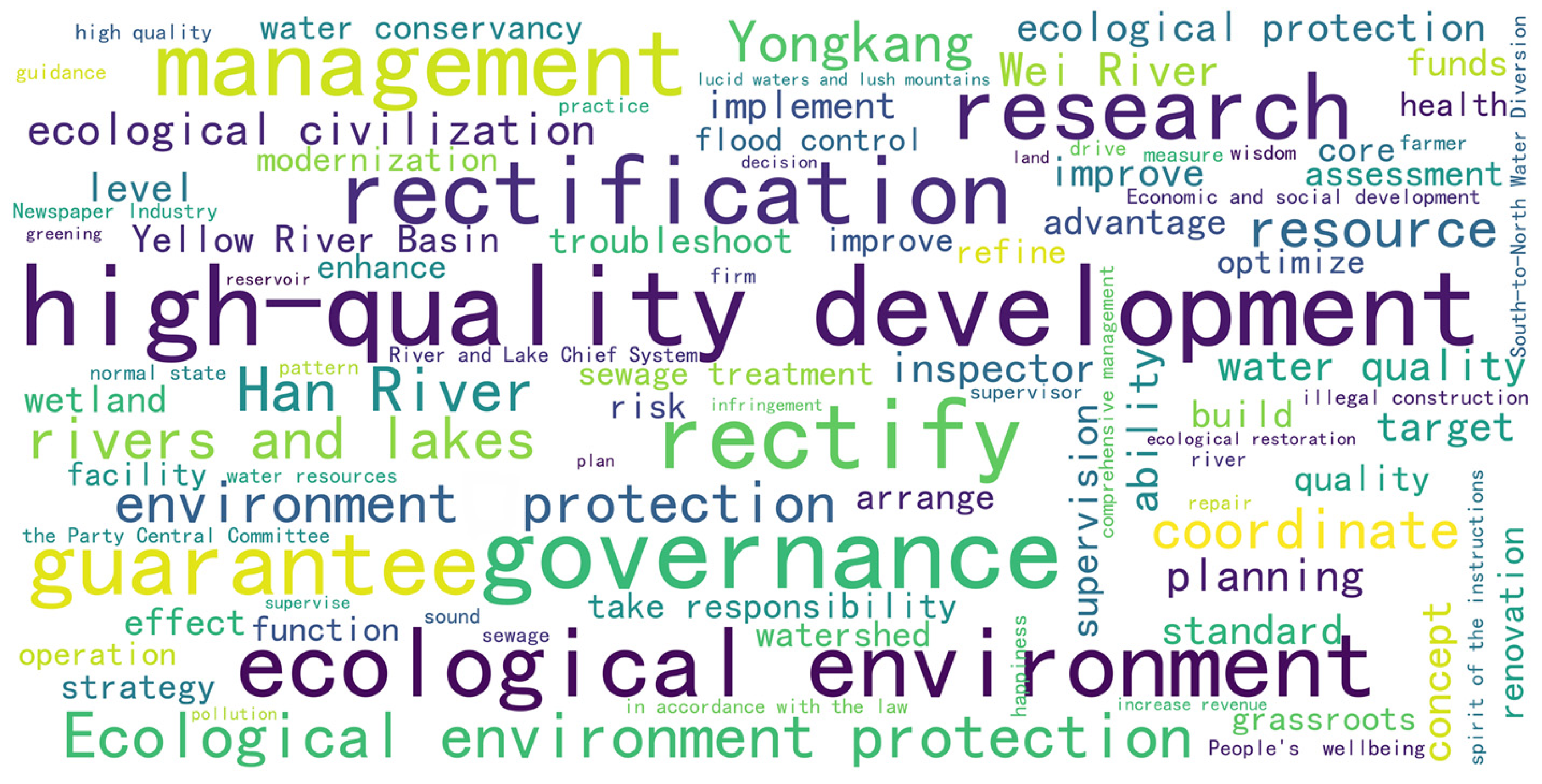
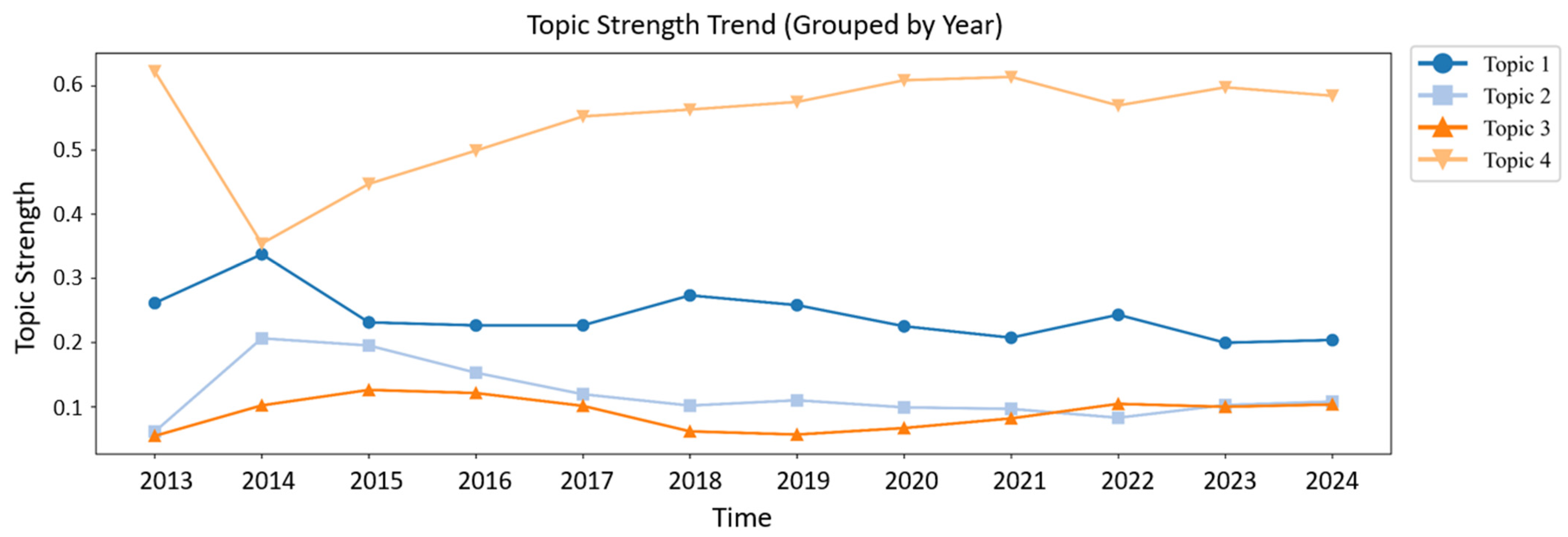
3.1. Identification of BI-Related Government Topics and Spatial Analysis Based on LDA
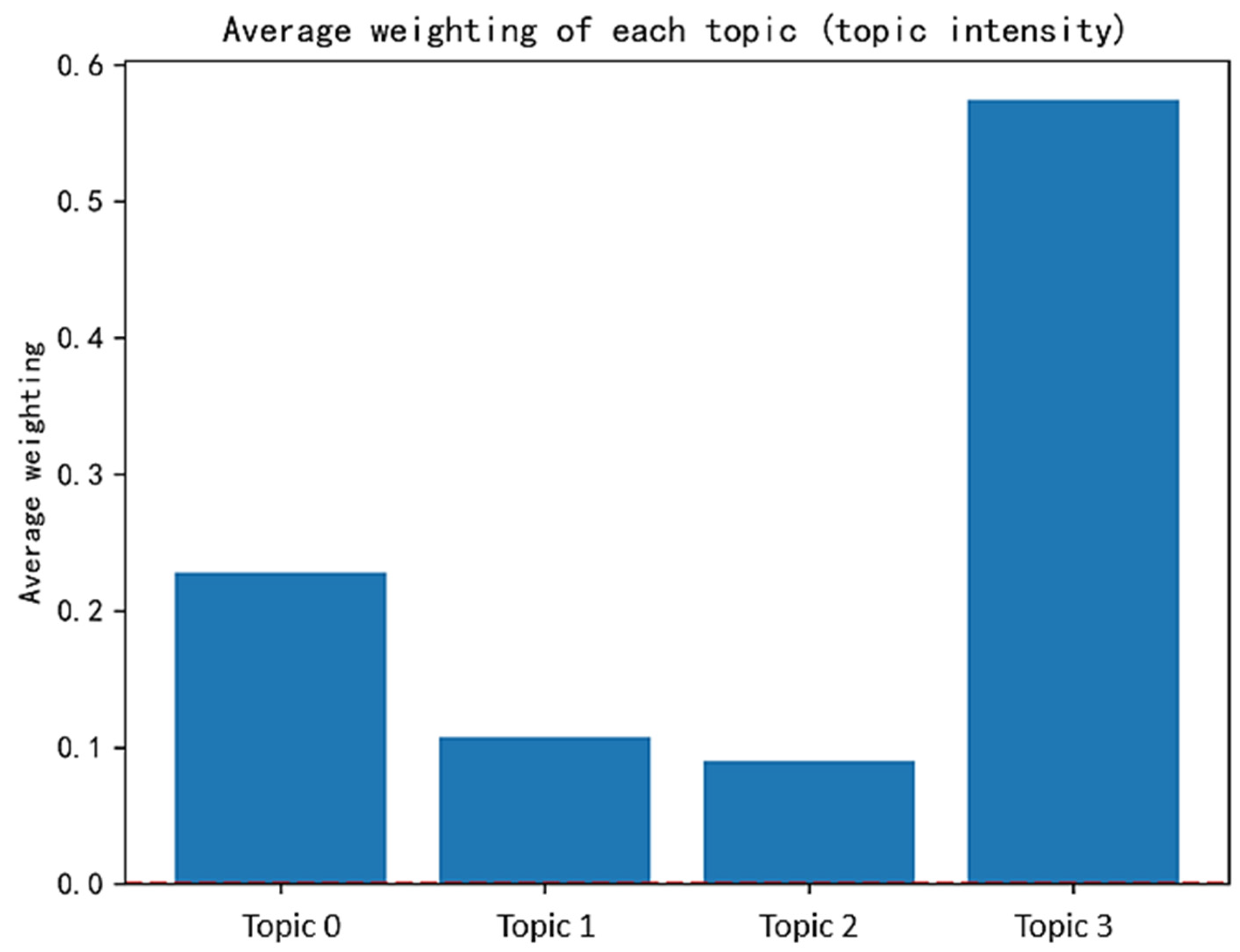
3.1.1. Identification and Characteristic Analysis of Government Topic
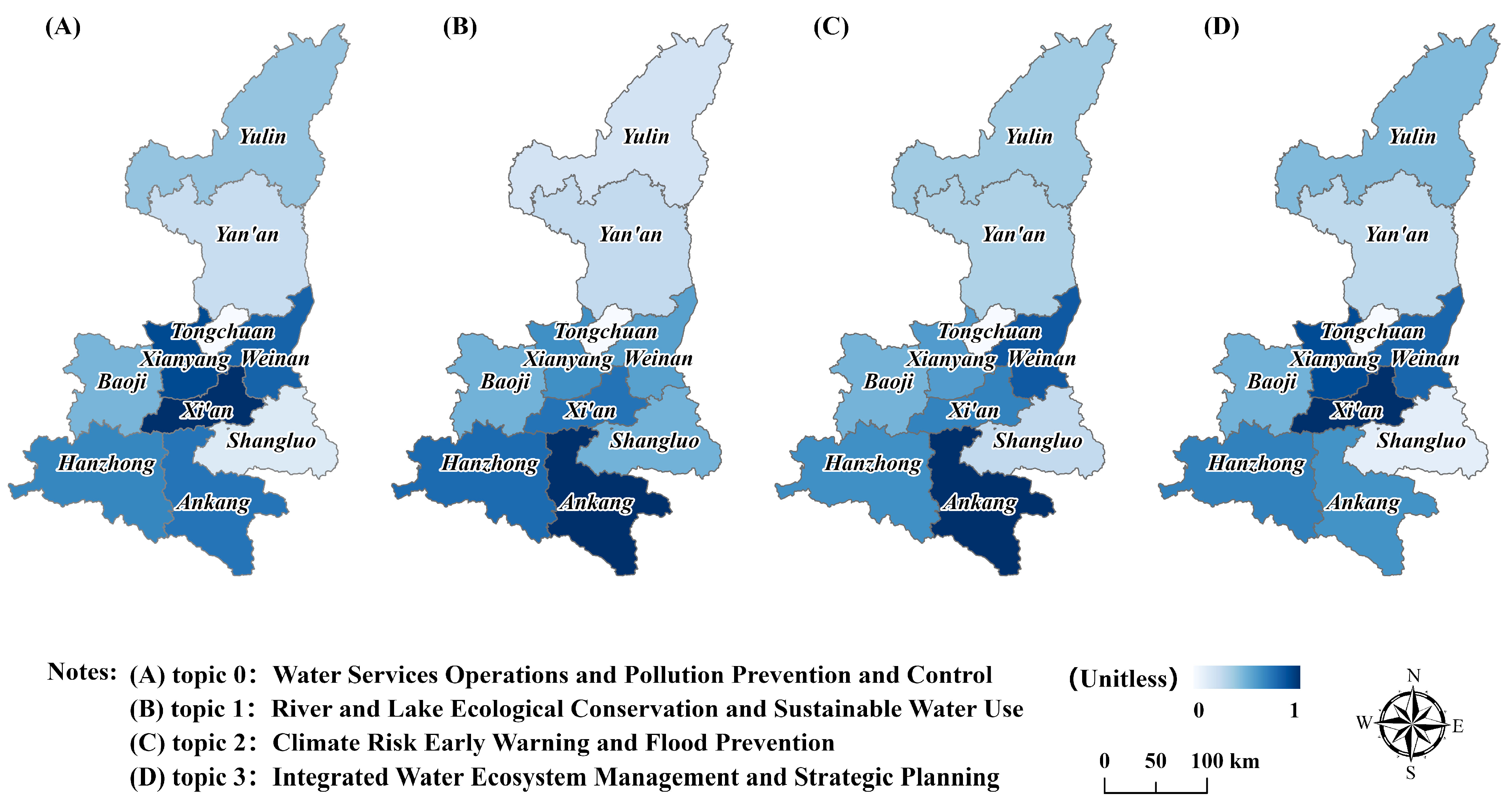
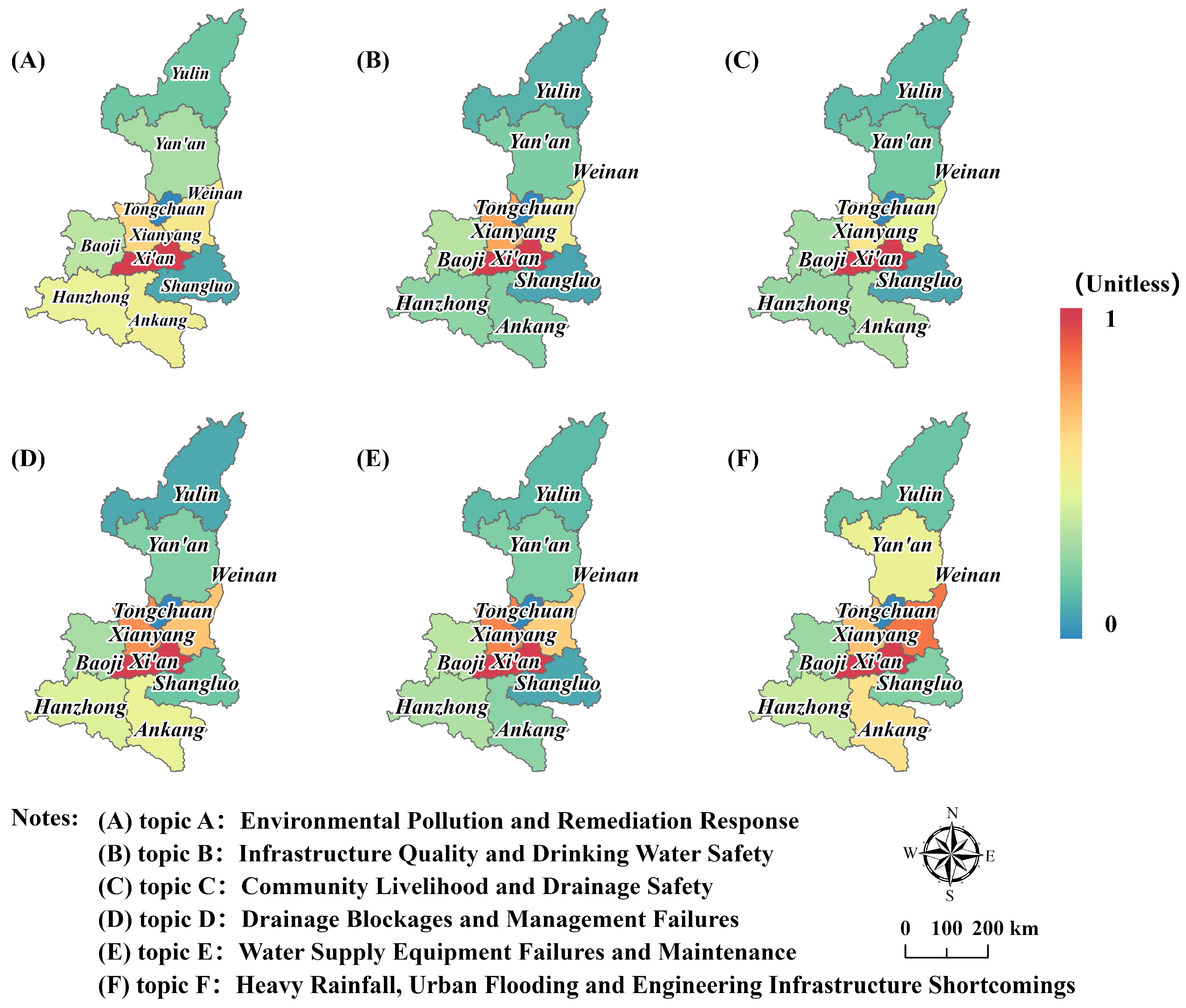
3.1.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Government Topics
3.2. Identification of BI-Related Public Demands and Spatial Analysis Based on BERTopic
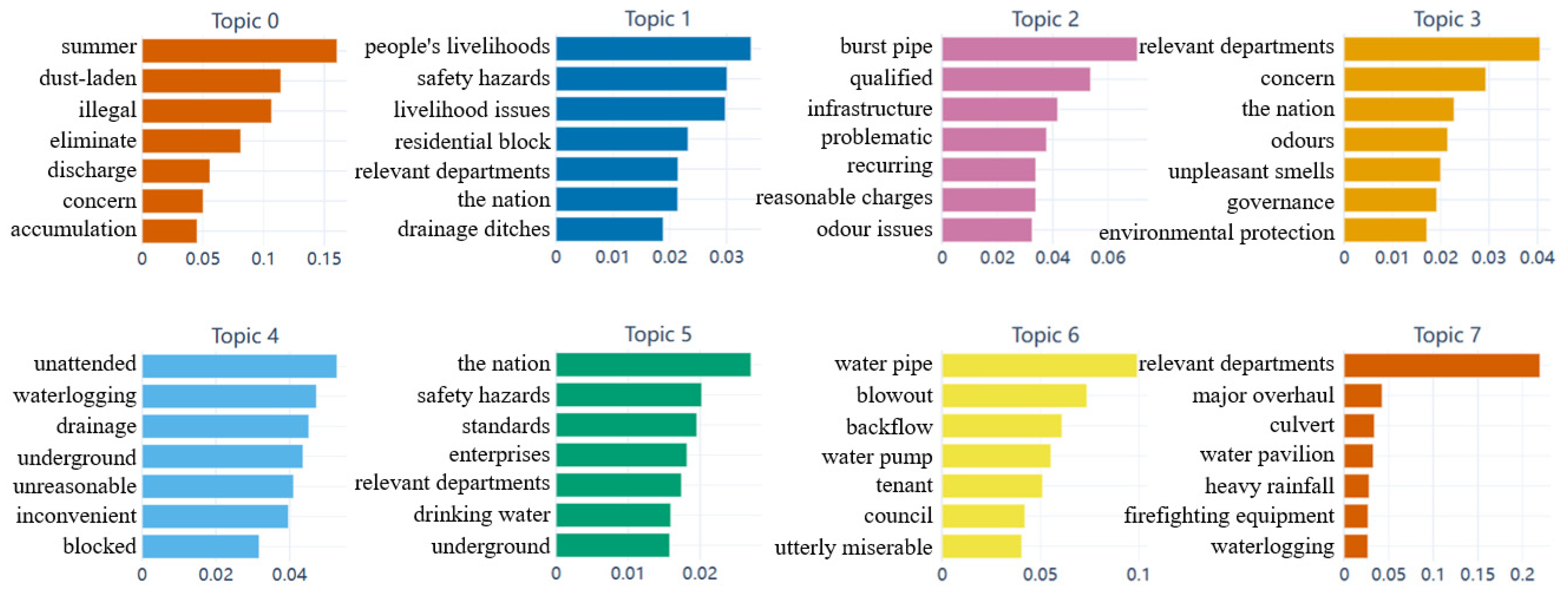
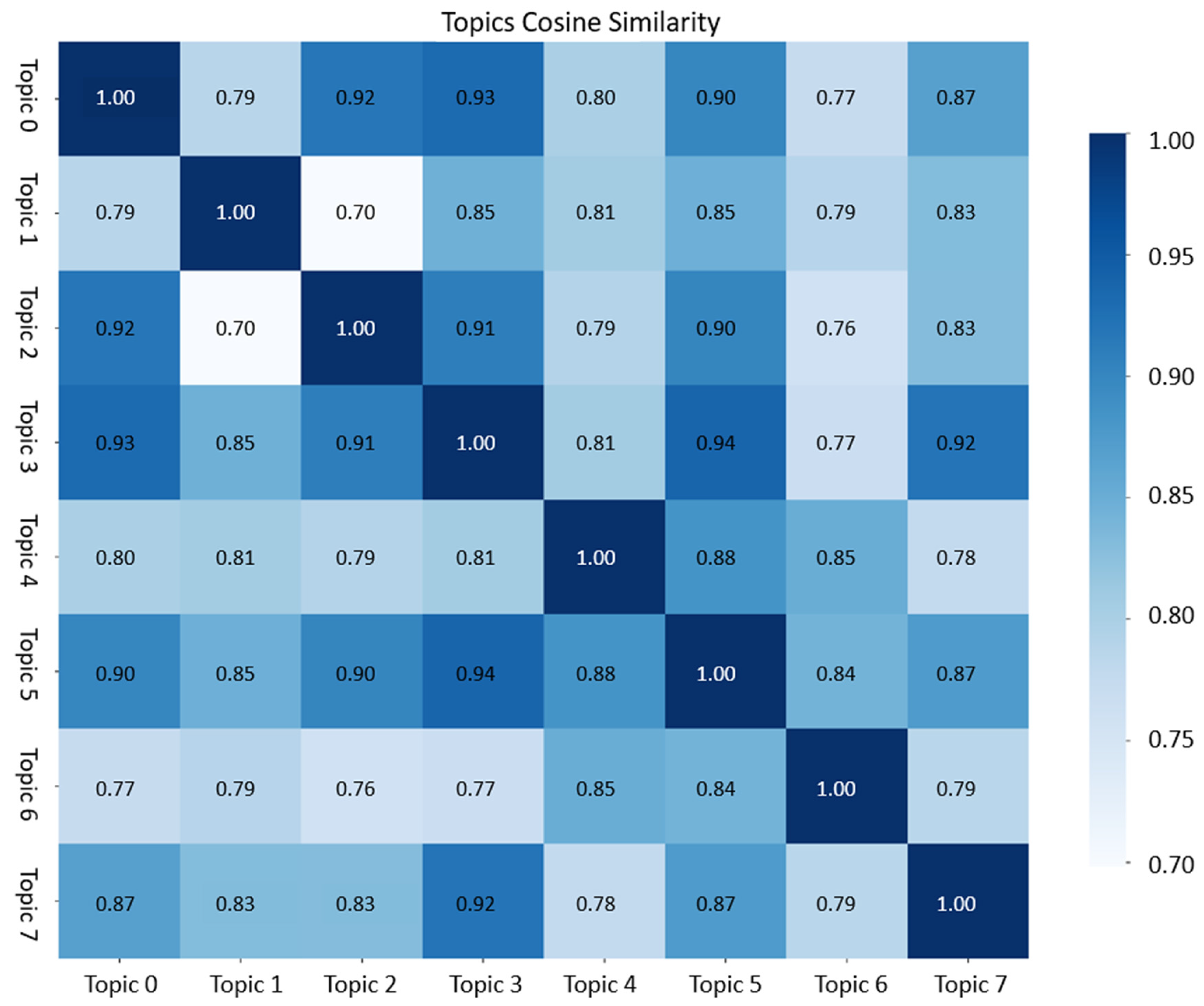
3.2.1. Identification of Public Demands Topics and Semantic Features
The municipal drainage on Century Avenue is blocked, preventing the discharge of domestic wastewater from surrounding residents. Sewage from adjacent residential areas is being forcibly directed into the municipal drainage pipelines, causing odour issues on the streets, severe water accumulation on nearby roads, and even pavement collapse.
We request the Mayor to urge the relevant departments to address these issues, particularly the water problems caused by sand mining. Additionally, attention should be given to the pollution of the Ru River from mining activities in Yangxie, and timely governance measures should be implemented.
The water supply pipes in our residential community are severely aged. This week alone, burst pipe incidents have required repairs three times, resulting in intermittent water supply and unstable water pressure. The frequent failure of infrastructure significantly disrupts daily life and poses safety hazards concerning drinking water. The property management company only performs temporary fixes. Relevant departments such as the District Government and the Municipal Water Authority should supervise and fund a complete overhaul of the pipeline network, rather than merely providing emergency responses.
Following the heavy rainfall in Yan’an a few days ago, a landslide occurred on the hillside above the residential building where we live. A large amount of collapsed soil flowed into the drainage ditch behind our stone cave dwellings, causing it to become blocked and accumulate water. This has resulted in water leakage through the rear walls of all the stone caves, creating significant safety hazards. Currently, because the obstructing soil cannot be cleared, proper drainage from the residential building is impossible.
As previously reported to Secretary Yan, the drainage system at the entrance of Yangou has repeatedly become blocked, causing sewage to overflow. Although the issue was raised before, it would only be cleared temporarily before becoming blocked again, failing to address the root cause of the problem. Now that the weather has turned cold, the sewage on the roads is freezing.
…I am a tenant living in the … Recently, water pipes in the community have frequently burst, and power outages occur regularly. The property management never provides advance notice, making life here utterly miserable for residents. We hope the relevant departments will look into the water and electricity situation in our community…
On the eastern side of the contiguous area between Fuping and Pucheng in the western part of Luyang Lake, a large expanse of beach and low-lying land suffers from perennial water accumulation due to poor drainage of the alkali drainage ditches, resulting in waterlogging. A solution is urgently needed.
Every rainy season during heavy downpours, the railway culvert near Shizuitou on Baoguang Road inevitably experiences severe water accumulation, often exceeding half a metre in depth, completely blocking passage for both vehicles and pedestrians. It is hoped that a major overhaul of the culvert’s drainage pipes can be conducted, rather than relying on temporary water pumping measures every year.
3.2.2. Spatial Distribution Characteristics of Public Demands
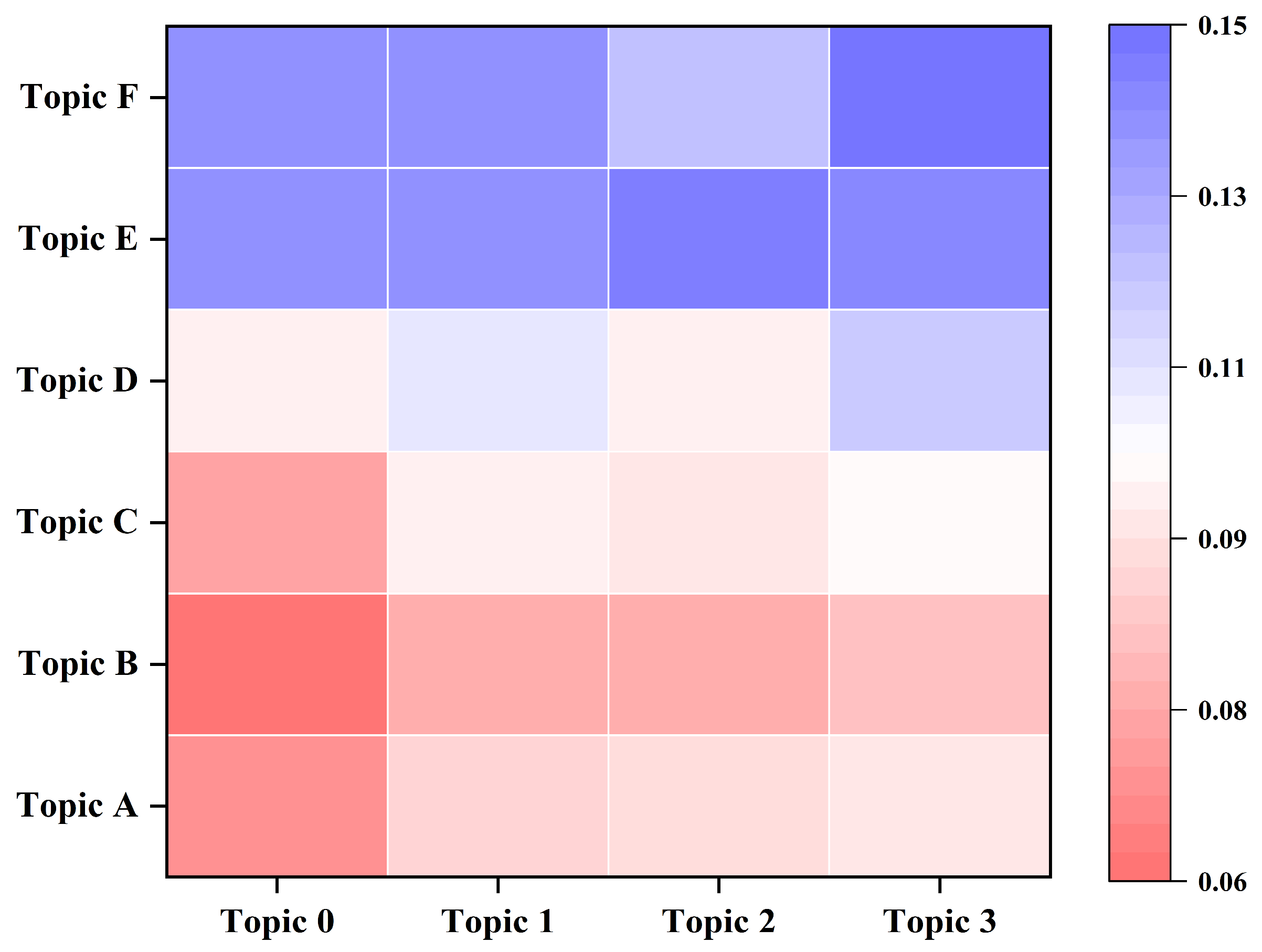
3.3. Mapping Analysis of Social Demands and Political Concerns
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings: Structural Features and the Semantic Gap in BI Provision and Demand in Shaanxi Province
4.2. Spatial Comparison and Analysis: From Semantic Gap to Geographical Mismatch
4.2.1. “Risk-Driven” Alignment: Consensual Attention Under Natural Constraints
4.2.2. “System-Lag” Mismatch: Governance Priority Deviation in Urbanization
4.3. Dialogue with Existing Research: Validation, Deepening and Advancement
4.3.1. Empirical Support for the Existing Consensus
4.3.2. Further Elaboration of the “Mismatch” Mechanism
4.3.3. Novelty and Contribution Beyond Literature
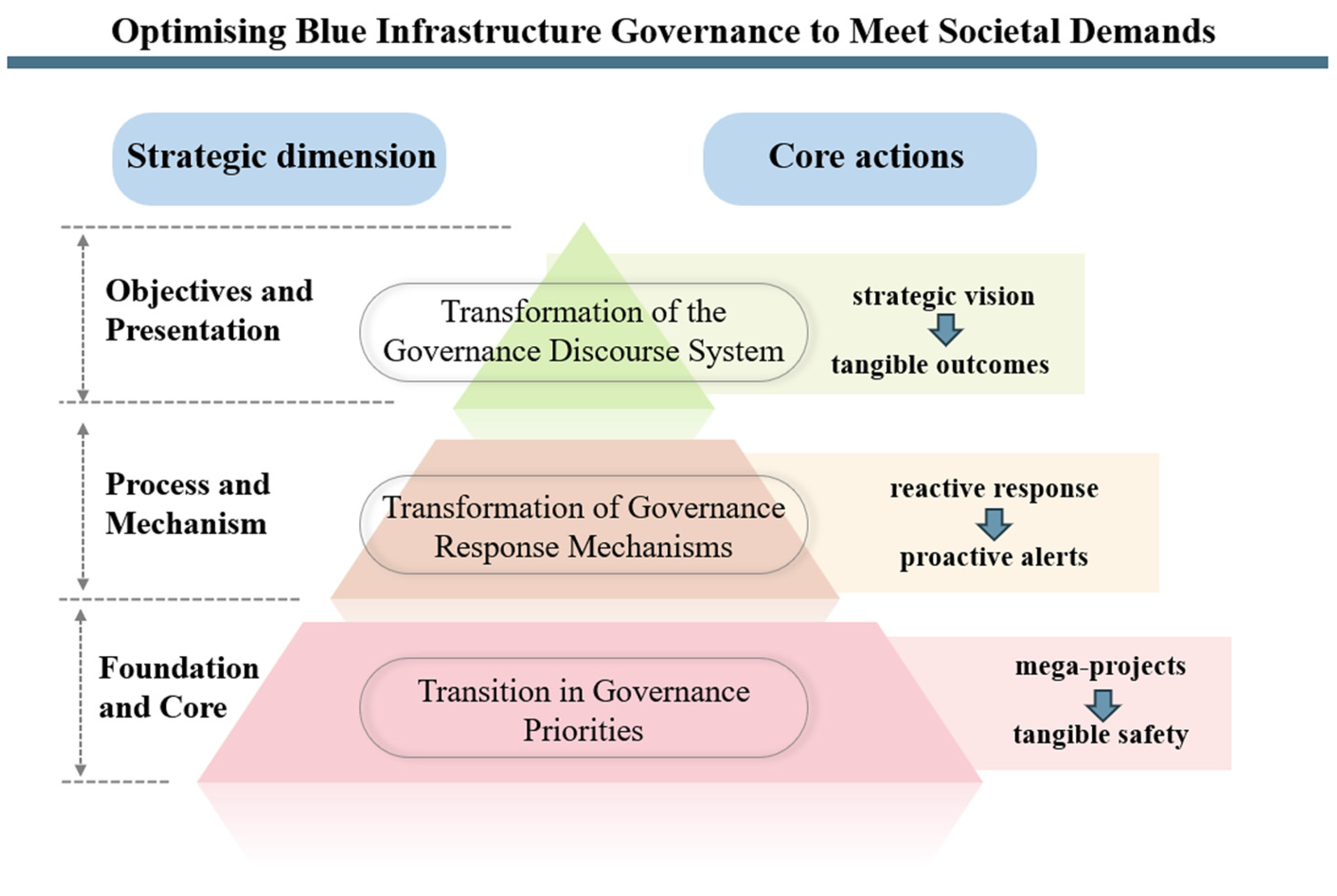
4.4. Research Implications
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
5.1. Findings
5.2. Recommendations
5.3. Research Limitations and Outlooks
5.3.1. Limitations of the Study
5.3.2. Research Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Serial Number | Stopwords | Serial Number | Stopwords | Serial Number | Stopwords |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Hello | 13 | Phase 1 | 25 | West Road |
| 2 | Leader | 14 | Phase 2 | 26 | North China |
| 3 | Secretary | 15 | Xinglong | 27 | Lan Hu |
| 4 | Hi | 16 | Hanzhong | 28 | Xi’an City |
| 5 | Qujiang | 17 | None | 29 | Xianyang |
| 6 | New district | 18 | Baihua | 30 | North China |
| 7 | Myself | 19 | Driver | 31 | Zi Jun |
| 8 | May I ask | 20 | Taiyicheng | 32 | Contemporary |
| 9 | South road | 21 | Now | 33 | Approximately |
| 10 | Shaanxi | 22 | To date | 34 | West Third Ring Road |
| 11 | Thank you | 23 | Western | 35 | North–South |
| 12 | Respected | 24 | Xixian | 36 | Northern District |
References
- United Nations Environment Programme. Integrated Approaches in Action: A Companion to the International Good Practice Principles for Sustainable Infrastructure; United Nations Environment Programme: Nairobi, Kenya, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, K.; Littlewood, S. From green belts to green infrastructure? Theevolution of a new concept in the emerging soft governance of spatial strategies. Plan. Pract. Res. 2010, 25, 203–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almaaitah, T.; Appleby, M.; Rosenblat, H.; Drake, J.; Joksimovic, D. The potential of blue-green infrastructure as a climate change adaptation strategy: A systematic literature review. Blue-Green Syst. 2021, 1, 223–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiano Flores, C.; Vikolainen, V.; Crompvoets, J. Governance assessment of a blue-green infrastructure project in a small size city in belgium. The potential of herentals for a leapfrog to water sensitive. Cities 2021, 117, 103331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsson, S.; Bäcklin, O.; Friberg, J.; Eriksson, S.F.; Haghighatafshar, S.; Konarska, J.; Kotze, S.; Lindberg, F.; Malmberg, C.; Rayner, D.; et al. A framework for integrated assessment of blue-green infrastructure: A decision support tool for evaluating climate adaptation and social benefits in relation to construction and maintenance costs. Cities 2025, 166, 106239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Willems, P. Assessing blue-green infrastructures for urban flood and drought mitigation under changing climate scenarios. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 62, 102798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Water Framework Directive. Available online: https://environment.ec.europa.eu/topics/water/water-framework-directive_en (accessed on 11 October 2025).
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development. Wang Menghui: Implementing the Urban Renewal Initiative. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/xinwen/2020-12/29/content_5574417.htm (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- General Office of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China. Opinion of the General Office of the State Council on Sustaining the Urban Renewal Initiative. Available online: https://www.gov.cn/zhengce/202505/content_7023882.htm (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- Gao, X.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Kou, C. Achieving urban ecosystem resilience: Static and dynamic attack simulation and cascading failure analysis of urban blue-green infrastructure networks. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 179, 114205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Li, Y. Building urban resilience: Lessons from the COVID-19 pandemic for future-proofing city infrastructure. Urban Manag. 2025, 14, 913–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Foley, K. Promoting climate-resilient cities: Developing an attitudinal analytical framework for understanding the relationship between humans and blue-green infrastructure. Environ. Sci. Policy 2023, 146, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hysa, A.; Löwe, R.; Geist, J. Waterfront usage trends across german metropolitan areas: A social-ecological perspective to urban blue-green infrastructure connectivity. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 260, 105369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambily, P.; Chithra, N.R.; Firoz, C.M. A novel framework for prioritization and spatial suitability assessment of blue-green infrastructure for urban pluvial flood resilience. J. Hydrol. 2025, 655, 132976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poggioli, M.; Cavadini, G.B.; Zheng, Z.; Rodriguez, M.; Mutzner, L. The impact of blue-green infrastructure on trace contaminants: A catchment-wide assessment. Water Res. X 2024, 25, 100261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iojă, C.I.; Badiu, D.L.; Haase, D.; Hossu, A.C.; Niță, M.R. How about water? Urban blue infrastructure management in romania. Cities 2021, 110, 103084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Zhai, W.; He, Z.; Shi, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, C. How does blue-green infrastructure affect the urban thermal environment across various functional zones? Urban For. Urban Green. 2025, 105, 128698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Ni, Z.; Xia, B.; Qiu, R. New perspective to evaluate the carbon offsetting by urban blue-green infrastructure: Direct carbon sequestration and indirect carbon reduction. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 12966–12975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Wen, C.; Xu, M. International lessons for green infrastructure planning in global maritime centres under the guiding principle of safety resilience. Int. Urban Plan. 2025, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Chang, J. The impact of national sponge city construction on urban water ecological environment quality. J. Nat. Resour. 2024, 39, 2721–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nóblega-Carriquiry, A.; March, H.; Sauri, D.; Hack, J. Neighbour perspectives on cultural ecosystem services of blue-green infrastructures: The ecovillage hannover, germany. Ecosyst. Serv. 2025, 72, 101701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Włodarczyk-Marciniak, R.; Krauze, K.; Kretek-Kamińska, A.; Krzewińska, A. Can we rely on people’s choices when envisioning retrofit of semi-public courtyards using blue-green infrastructure? Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 123076. [Google Scholar]
- Lamond, J.; Everett, G. Sustainable blue-green infrastructure: A social practice approach to understanding community preferences and stewardship. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2019, 191, 103639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Hu, H.; Shu, T. A study on the variations in blue-green space quality among different types of urban communities based on activity spaces. Hum. Geogr. 2023, 38, 44–55. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Y.; Ye, S.; Zhong, W.; Guo, R. Collaborative governance in urban water area conservation: Strategies for mitigating blue space encroachment. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 62, 102862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, Y.; Du, F.; Li, X.; Kong, Y. Mechanisms of Healing Task Landscape Formation in Urban Blue-Green Spaces and Development of a Measurement Scale. Adv. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 44, 1036–1049. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, F.K.S.; Lu, L.; Zhu, Y.; Balzan, M.V.; Pezzoli, A.; Johnson, M.; Zhu, F.; Ruan, T.; Luo, G.; Li, G.; et al. Exploring community perceptions and engagement of nature-based solutions: The case of ningbo, a chinese coastal sponge city. Nat. Based Solut. 2023, 4, 100093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, R.; Yang, D. Multidimensional characterisation and empirical study of urban street networks from a holistic street perspective: An analytical framework integrating transport, social and natural dimensions. J. Urban Plan. 2024, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horanyi, A.M.; Thorn, J.P.R. Spatial distribution, determinants, and implementation barriers of green-blue-grey infrastructure-based urban heat island mitigation strategies in budapest, hungary. Urban For. Urban Green. 2025, 113, 129092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deely, J.; Hynes, S. Blue-green or grey, how much is the public willing to pay? Landsc. Urban Plan. 2020, 203, 103909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wang, K. Policy synergy analysis on coordinating reduction of pollution and carbon emissions in china: Insights from text mining and network analysis. Environ. Manag. 2024, 372, 123389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Luo, Y.; Qian, X.; Dong, L. Understanding the dynamics of urban just transitions: An interdisciplinary analysis with latent dirichlet allocation (LDA). Urban Manag. 2025, 14, 485–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Guo, B.; Zhao, W.; He, Y.; Wang, X. Making smart cities human-centric: A framework for dynamic resident demand identification and forecasting. Sustainability 2025, 17, 9423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, C.; Yang, Y. A multi-modal social media data analysis framework: Exploring the complex relationships among urban environment, public activity, and public perception—A case study of xi’an, china. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Shi, C. Digital administrative burden: The generation and evolution of governance-citizen interaction costs in the digital sphere—An analysis based on the public welfare supervision information platform in province a. Public Adm. Policy Rev. 2025, 14, 127–143. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Yang, Z.; Guo, Y. Employment structural effects in corporate digital transformation: An empirical analysis based on text mining of annual reports from listed manufacturing enterprises. China Soft Sci. 2023, 4, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, Y.; Yang, F.; Guo, J. Thematic mining and content analysis of domestic government data openness research based on the bertopic model. Libr. Sci. Res. 2025, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grootendorst, M. BERTopic: Neural Topic Modeling with a Class-Based TF-IDF Procedure. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2203.05794. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, H.; Long, R.; Chen, H.; Sun, K.; Sun, Q.; Li, Q. Examining public attitudes and perceptions of waste sorting in china through an urban heterogeneity lens: A social media analysis. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2023, 199, 107233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X. Cultural ecosystem services in china’s national parks and their impact on public online engagement − analysis of douyin short videos data based on BERTopic modeling. Nat. Conserv. 2025, 87, 126969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lam, W.W.T.; Yuan, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, Q. Shaping sustainable healthy diets discourse on facebook: A multi-region investigation of urban stakeholders’ communication, social networks and public engagement. Cities 2025, 162, 105944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, H.; Park, Y.E. Agenda-setting effects for COVID-19 vaccination: Insights from 10 million textual data from social media and news articles using BERTopic. Int. Inf. Manag. 2025, 83, 102907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokcimen, T.; Das, B. Exploring climate change discourse on social media and blogs using a topic modeling analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, B.; Li, S.; Jiang, B.; Wang, X.; Lu, W.; Hu, Y.; Wen, T.; Feng, Y. Actual supply-demand of the urban green space in a populous and highly developed city: Evidence based on mobile signal data in guangzhou. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 169, 112839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Zhao, M.; Tang, X.; Wu, C. Ecological restoration zoning and strategy based on ecosystem service supply and demand relationships: A case study of the yellow river basin. J. Nat. Conserv. 2025, 84, 126837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Bao, C. Unraveling supply-demand relationship of urban agglomeration’s ecosystem services for spatial management zoning: Insights from threshold effects. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2025, 121, 106239. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.Y.; Mistur, E.; Kim, D.; Mo, Y.; Hoefer, R. Toward human-centric urban infrastructure: Text mining for social media data to identify the public perception of COVID-19 policy in transportation hubs. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Sun, X.; Zhou, H. A study on the dynamic evolution of public perception based on big data text mining: The case of Heilong Jiang province’s business environment. Manag. Rev. 2025, 37, 222–236. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Zhou, Y. From social demands to policy responses: A text mining-based study on autonomous driving technology development strategies. Intell. Theory Pract. 2025, 48, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Cong, J.; Proverbs, D.; Zhang, L. An evaluation of urban resilience to flooding. Water 2021, 13, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, M.; Ferguson, J.; Khan, A.; Liu, G.; Skoyles, A.; Drescher, M. Synthesizing the evidence on green and blue infrastructure for urban temperature mitigation in canada. Environ. Rev. 2025, 33, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehnert, M.; Brabec, M.; Jurek, M.; Tokar, V.; Geletič, J. The role of blue and green infrastructure in thermal sensation in public urban areas: A case study of summer days in four czech cities. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 66, 102683. [Google Scholar]
- Vishwakarma, R.K.; Joshi, H.; Goonetilleke, A. Sustainability evaluation of the stormwater drainage system in six indian cities. Sustainability 2023, 15, 14906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, G.; Shanthi Priya, R. Blue green infrastructure: A panacea for urban environmental challenges. Case study: Thiruvananthapuram city, kerala, india. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 68, 2646–2652. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, A.; Liu, S.; Shi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Research on green space health check mechanisms and zonal management for urban protective spaces under the concept of “urban dual restoration”. Geogr. Res. 2025, 44, 3322–3340. [Google Scholar]
- Shaanxi’s Urbanisation Rate Reaches 66.14%: Since the Commencement of the 14th Five-Year Plan Period, It Has Increased by an Average of 0.8 Percentage Points Annually, Achieving the Planned Target Two Years Ahead of Schedule. Available online: https://www.shaanxi.gov.cn/xw/sxyw/202503/t20250325_3465999.html (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- The People’s Leaders’ Message Board. Available online: https://liuyan.people.com.cn/ (accessed on 14 December 2025).
- Han, C.; Chen, Z. Promoting green development through balancing: Does regional coordination favouring the west facilitate pollutant reduction? Econ. Q. 2023, 23, 948–964. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Zhu, H.; Quan, D. Research on heritage conservation and cultural tourism development strategies in the post-pandemic era: A case study of the shaanxi section of the yellow river basin. China Soft Sci. 2020, S1, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Geomorphology and Climate of Shaanxi Province. Available online: https://www.shaanxi.gov.cn/sq/sxgk/dmqh/202011/t20201120_2046831.html (accessed on 25 December 2025).
- Notice Concerning the Issuance of the Shaanxi Province Climate Change Adaptation Action Plan. Available online: https://sthjt.shaanxi.gov.cn/xxgk/fdnr/zcwj/shf/202401/t20240102_2989044.html (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- Shaanxi Has Experienced Its Second Most Severe Prolonged Period of Continuous Rainfall Since 1961. Available online: https://shaanxi.china.com/m/news/20000876/20251013/25977780.html (accessed on 11 December 2025).
- Western China Network: Shaanxi Experiences Heaviest Rainfall Since 1961, Breaking Multiple Historical Records! Available online: https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_14849903 (accessed on 12 December 2025).
- 2024 Shaanxi Land Greening Bulletin. Available online: https://lyj.shaanxi.gov.cn/zwxx/lydt/202504/t20250422_3499644.html (accessed on 9 September 2025).
- Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. A grounded theory approach to classifying “g-lef” composite greenways. Planners 2022, 38, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Ao, Y.; Ni, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ding, Z.; Huang, F.; Li, M. Spatial-temporal evolution characteristics and driving mechanisms of green spaces in shaanxi province from an ecological resilience perspective. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2025, 34, 1866–1878. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, K.; Su, J.; Bao, H. Practical pathways and intrinsic mechanisms of multi-stakeholder collaborative governance in urban renewal: An exploratory case study based on Hangzhou. Acta Nat. Resur. Sin. 2025, 40, 1451–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Si, M.; Pan, B. Mechanisms, obstacles and pathways for the characteristic development of small towns in zhejiang province: An extended model and application for sustainable development. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Foley, K. Preference and perception of individuals for blue-green infrastructure in the promotion of climate-resilient cities: A visual experiment in ireland and china. Urban For. Urban Green. 2025, 106, 128730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Shi, Y.; Ni, Z.; Sun, X. Empowering government decision-making with social demand data: An analytical framework based on the integration of four diagnostic approaches. Mod. Intell. 2024, 44, 80–89. [Google Scholar]
- Tencent Holdings Limited. WeChat. Available online: https://www.wechat.com (accessed on 26 December 2025).
- Manning, C.D.; Prabhakar Raghavan, G.; Schütze, H.U. Introduction to Information Retrieval; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2008; p. 506. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Cai, D.; Huang, C.; Kit, C. Chinese word segmentation: Another decade review. arXiv 2007, arXiv:1901.06079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Hu, Z.; Li, S.; Wu, H.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, G. More Than Text: Multi-Modal Chinese Word Segmentation; Association for Computational Linguistics: Stroudsburg, PA, USA, 2021; pp. 550–557. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, L. Topic analysis of chinese documents based on key phrases and latent dirichlet allocation model. In Proceedings of the 2024 9th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing (ICSP), Xi’an, China, 19–21 April 2024; pp. 665–670. [Google Scholar]
- Häffner, S.; Hofer, M.; Nagl, M.; Walterskirchen, J. Introducing an interpretable deep learning approach to domain-specific dictionary creation: A use case for conflict prediction. Polit. Anal. 2023, 31, 481–499. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, B.J. Automated dictionary generation for political eventcoding. Polit. Sci. Res. Methods 2019, 1, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blei, D.M.; Ng, A.Y.; Jordan, M.I. Latent dirichlet allocation. J. Mach. Learn. 2003, 3, 993–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Barnes, S.J.; Jia, Q. Mining meaning from online ratings and reviews: Tourist satisfaction analysis using latent dirichlet allocation. Tour. Manag. 2017, 59, 467–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzayed, A.; Al-Khalifa, H. BERT for arabic topic modeling: An experimental study on BERTopic technique. Procedia Comput. Sci. 2021, 189, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, E.; Yoon, N.; Sohn, S.Y. Exploring new digital therapeutics technologies for psychiatric disorders using BERTopic and PatentSBERTa. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Chang. 2023, 186, 122130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. In Proceedings of the 2019 Conference of the North American Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics Human Language Technologies (NAACL HLT 2019), Minneapolis, MN, USA, 2–7 June 2019; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Lu, W.; Wu, L. Calculation of time lags in multi-source scientific literature for detecting emerging themes in disciplines: Implications from the agricultural field. J. Inf. Sci. 2021, 40, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Li, G.; Jia, F. Fiscal hierarchy reform and the reconstruction of tax collection incentives: A study using the provincial-directly-administered counties reform as a natural experiment. Manag. World 2020, 36, 32–50. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.; Russo, A. Exploring the role of public participation in delivering inclusive, quality, and resilient green infrastructure for climate adaptation in the UK. Cities 2024, 148, 104879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Serial Number | Shaanxi Province Mnici-Palities | Official Government WeChat Account Name | WeChat Official ID |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Xi’an | Xi’an Release | xianfabu |
| 2 | Weinan | Weinan Release | Weinangovweb |
| 3 | Tongchuan | Tongchuan Release | tcfb_wx |
| 4 | Hanzhong | Hanzhong Release | hanzhongfabu |
| 5 | Ankang | Ankang Release | ankang_gov |
| 6 | Shangluo | Shangluo Government Release | shangluozhengwufabu |
| 7 | Yulin | Yulin Daily | ylrbwx |
| 8 | Baoji | Baoji Release | bjfb0917 |
| 9 | Xianyang | Xianyang Release | xianyangfabunews |
| 10 | Yan’an | Yan’an Release | yananfabu |
| Statistics on High Frequency Words in Government Texts | People’s Internet Message Board High Frequency Words Statistics | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Serial Number | Key Words | Frequency | Serial Number | Key Words | Frequency |
| 1 | Governance | 2076 | 1 | Water supply interruption | 2216 |
| 2 | High-quality development | 1848 | 2 | Water usage | 501 |
| 3 | Management | 1737 | 3 | Water supply | 447 |
| 4 | Rectification | 1644 | 4 | Problem resolution | 328 |
| 5 | Flood prevention | 1578 | 5 | Water pipes | 276 |
| 6 | Water quality | 1560 | 6 | Residence | 262 |
| 7 | Guarantee | 1550 | 7 | Management | 253 |
| 8 | Ecological environment | 1542 | 8 | Water Charges | 252 |
| 9 | Correction | 1400 | 9 | Relevant Departments | 236 |
| 10 | Han River | 1386 | 10 | Refurbishment | 228 |
| 11 | Research | 1309 | 11 | Costs | 205 |
| 12 | Wei River | 1197 | 12 | Wastewater | 203 |
| 13 | Measures | 1141 | 13 | Services | 199 |
| 14 | Wetland | 1104 | 14 | Construction work | 191 |
| 15 | Water supply | 1102 | 15 | Rainfall | 190 |
| 16 | Ecological and environmental protection | 1097 | 16 | Water consumption | 185 |
| 17 | Rivers and lakes | 1063 | 17 | Repair | 183 |
| 18 | Reservoir | 1047 | 18 | No water | 180 |
| 19 | Resources | 1037 | 19 | Charge | 178 |
| 20 | Environmental protection | 1014 | 20 | Water pressure | 178 |
| Serial Number | Subject Name | Weighting | Keywords and Weights |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topic 0 | Water Services Operations and Pollution Prevention and Control | 16.35% | flood prevention, water bodies, water quality, water supply, reservoirs, inspection, sewage treatment, wastewater, water conservancy, drought resistance, rivers, pollution, cross-sections, black and odorous water, facilities, water sources |
| Topic 1 | River and Lake Ecological Conservation and Sustainable Water Use | 5.59% | rivers and lakes, wetlands, water conservation, unauthorized structures, greening, wildlife, crested ibis, birds, biology, Wei River, wild, Yellow River, clearing, afforestation, water-efficient, wetland conservation |
| Topic 2 | Climate Risk Early Warning and Flood Prevention | 5.15% | torrential rain, precipitation, showers, meteorological observatory, early warning, mountain torrents, prevention, disasters, geological hazards, floods, rainfall, heavy rainfall, urban waterlogging, mudslides, landslides, thunderstorms |
| Topic 3 | Integrated Water Ecosystem Management and Strategic Planning | 72.91% | high-quality development, rectification, ecological and environmental protection, research, governance, remediation, planning, supervision, coordination, ecological conservation, resources, Yellow River basin, water management, environmental conservation, ecological environment, objectives |
| Subject Number | Subject Name | Core Characteristic Word | Number of Documents |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topic 0 | Summer_Dust-Laden_ Illegal | summer, dust-laden, illegal, eliminate, discharge, concern, accumulation, household waste, emissions, mosquitoes | 117 |
| Topic 1 | People’s Livelihoods_Safety Hazards_Public Welfare Issues | people’s livelihoods, safety hazards, livelihood issues, residential block, relevant departments, the nation, drainage ditches, waterlogging, inconvenience, water shortage | 518 |
| Topic 2 | Burst Pipe_Qualified_ Infrastructure | burst pipe, qualified, infrastructure, problematic, recurring, reasonable charges, odour issues, building management, registration, supporting facilities | 258 |
| Topic 3 | Relevant Departments_ Concern_The Nation | relevant departments, concern, the nation, odours, unpleasant smells, governance, environmental protection, safety hazards, malodorous, emissions | 468 |
| Topic 4 | Unattended_Waterlogging_Drainage | unattended, waterlogging, drainage, underground, unreasonable, inconvenient, blocked, unsolvable, neglected, drainpipe | 358 |
| Topic 5 | The Nation_Safety Hazards_Standards | the nation, safety hazards, standards, enterprises, relevant departments, drinking water, underground, sewage, blockage, hardening | 521 |
| Topic 6 | Water Pipe_Blowout_Backwater | water pipe, blowout, backflow, water pump, tenant, council, utterly miserable, drinking water, filling with water, draining wate | 134 |
| Topic 7 | Relevant Departments_ Major Overhaul_Culvert | relevant departments, major overhaul, culvert, water pavilion, heavy rainfall, firefighting equipment, waterlogging, verification, unauthorized structures, waterfront | 146 |
| New Topic Number | New Theme Name | Method of Handling | Original Topic |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topic A | Environmental Pollution and Remediation Response | Merge | Topic 0 + Topic 3 |
| Topic B | Infrastructure Quality and Drinking Water Safety | Merge | Topic 2 + Topic 5 |
| Topic C | Community Livelihood and Drainage Safety | Reserve | Topic 1 |
| Topic D | Drainage Blockages and Management Failures | Reserve | Topic 4 |
| Topic E | Water Supply Equipment Failures and Maintenance | Reserve | Topic 6 |
| Topic F | Heavy Rainfall, Urban Flooding and Engineering Infrastructure Shortcomings | Reserve | Topic 7 |
| Subject Number | Policy Provisions Topics Collection Y | Topic 0 | Topic 1 | Topic 2 | Topic 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Public Demands Topics Collection X | Water Services Operations and Pollution Prevention and Control | River and Lake Ecological Conservation and Sustainable Water Use | Climate Risk Early Warning and Flood Prevention | Integrated Water Ecosystem Management and Strategic Planning | |
| Topic A | Environmental Pollution and Remediation Response | 6.93% | 9.13% | 9.25% | 9.75% |
| Topic B | Infrastructure Quality and Drinking Water Safety | 6.05% | 7.99% | 7.81% | 8.39% |
| Topic C | Community Livelihood and Drainage Safety | 7.63% | 9.88% | 9.50% | 10.05% |
| Topic D | Drainage Blockages and Management Failures | 9.83% | 11.10% | 9.88% | 11.84% |
| Topic E | Water Supply Equipment Failures and Maintenance | 13.65% | 13.54% | 14.05% | 13.88% |
| Topic F | Heavy Rainfall, Urban Flooding and Engineering Infrastructure Shortcomings | 13.52% | 13.54% | 12.24% | 14.62% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2026 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Guo, B.; Wang, X.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, W.; Yang, B.; Shi, Y. A Study on Blue Infrastructure Governance from the Issue-Appeal Divergence Perspective: An Empirical Analysis Based on LDA and BERTopic Models. Water 2026, 18, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020148
Guo B, Wang X, Hou Y, Zhang W, Yang B, Shi Y. A Study on Blue Infrastructure Governance from the Issue-Appeal Divergence Perspective: An Empirical Analysis Based on LDA and BERTopic Models. Water. 2026; 18(2):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020148
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuo, Bin, Xinyu Wang, Yitong Hou, Wen Zhang, Bo Yang, and Yuanyuan Shi. 2026. "A Study on Blue Infrastructure Governance from the Issue-Appeal Divergence Perspective: An Empirical Analysis Based on LDA and BERTopic Models" Water 18, no. 2: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020148
APA StyleGuo, B., Wang, X., Hou, Y., Zhang, W., Yang, B., & Shi, Y. (2026). A Study on Blue Infrastructure Governance from the Issue-Appeal Divergence Perspective: An Empirical Analysis Based on LDA and BERTopic Models. Water, 18(2), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18020148









