Study on Improving the Purification Function of Constructed Wetlands with Construction Waste Substrates by Acid–Base Substrate Configuration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
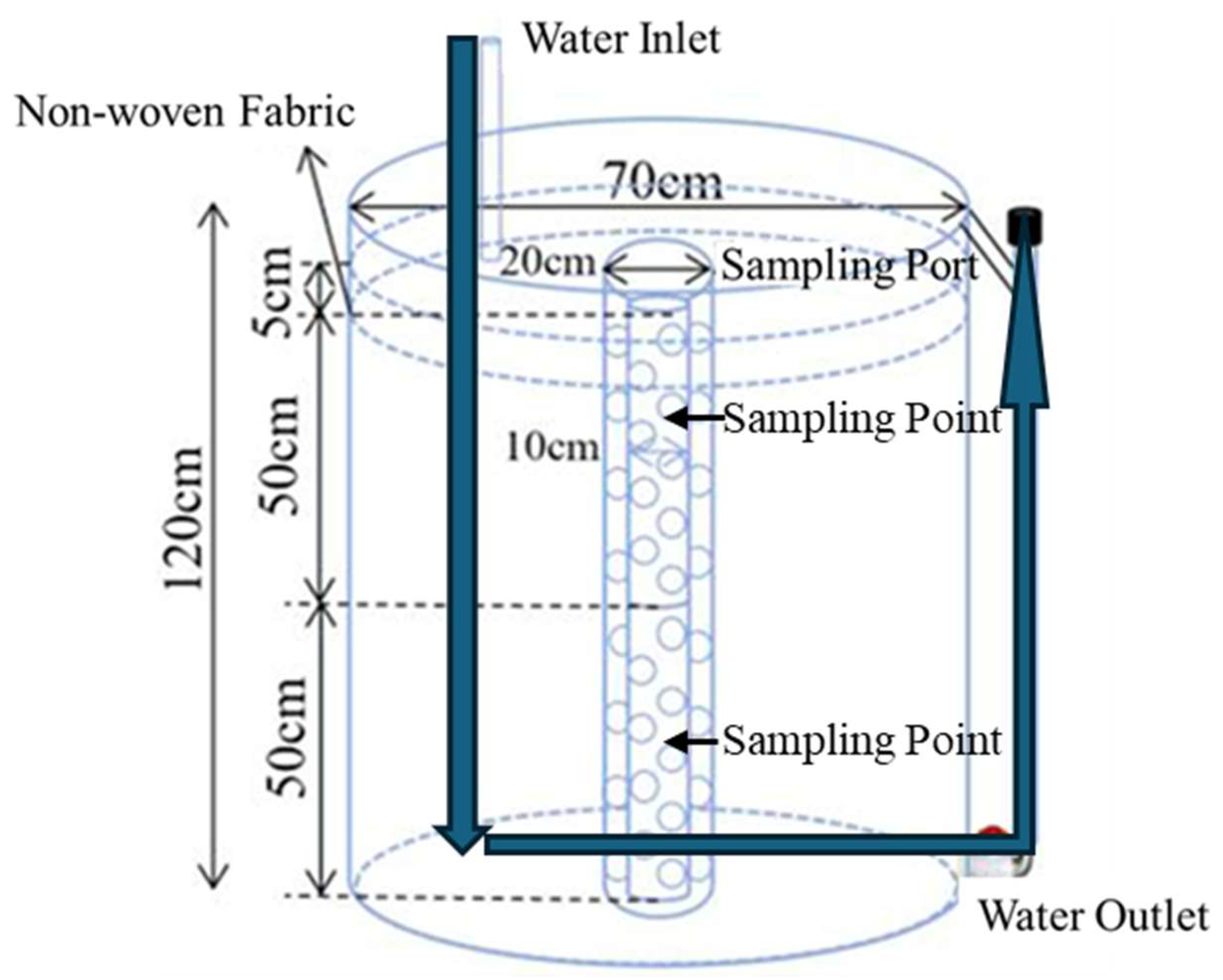
2.1. Experimental Design and Operation
2.2. Sampling and Analysis
3. Results
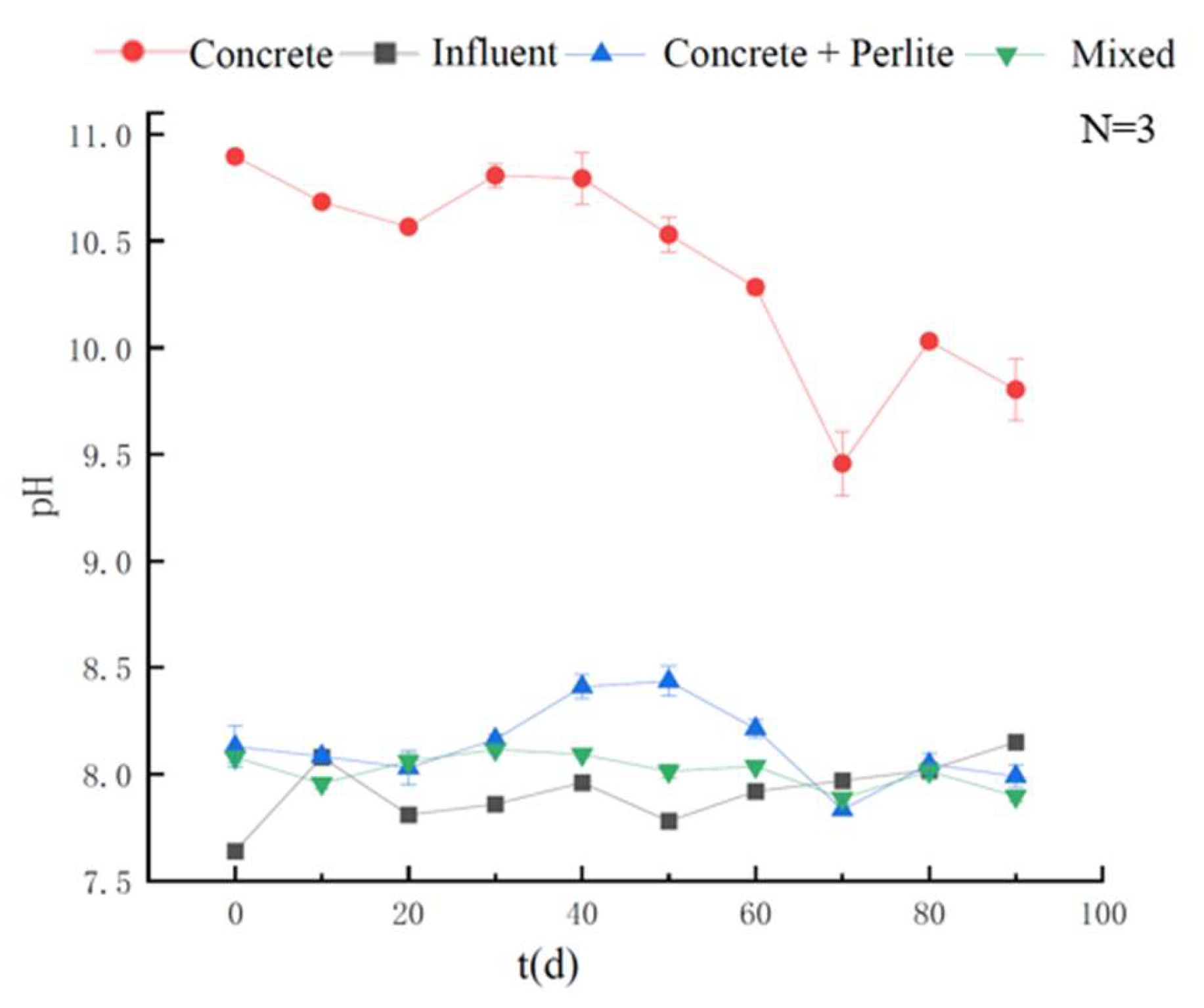
3.1. Regulation of Effluent pH
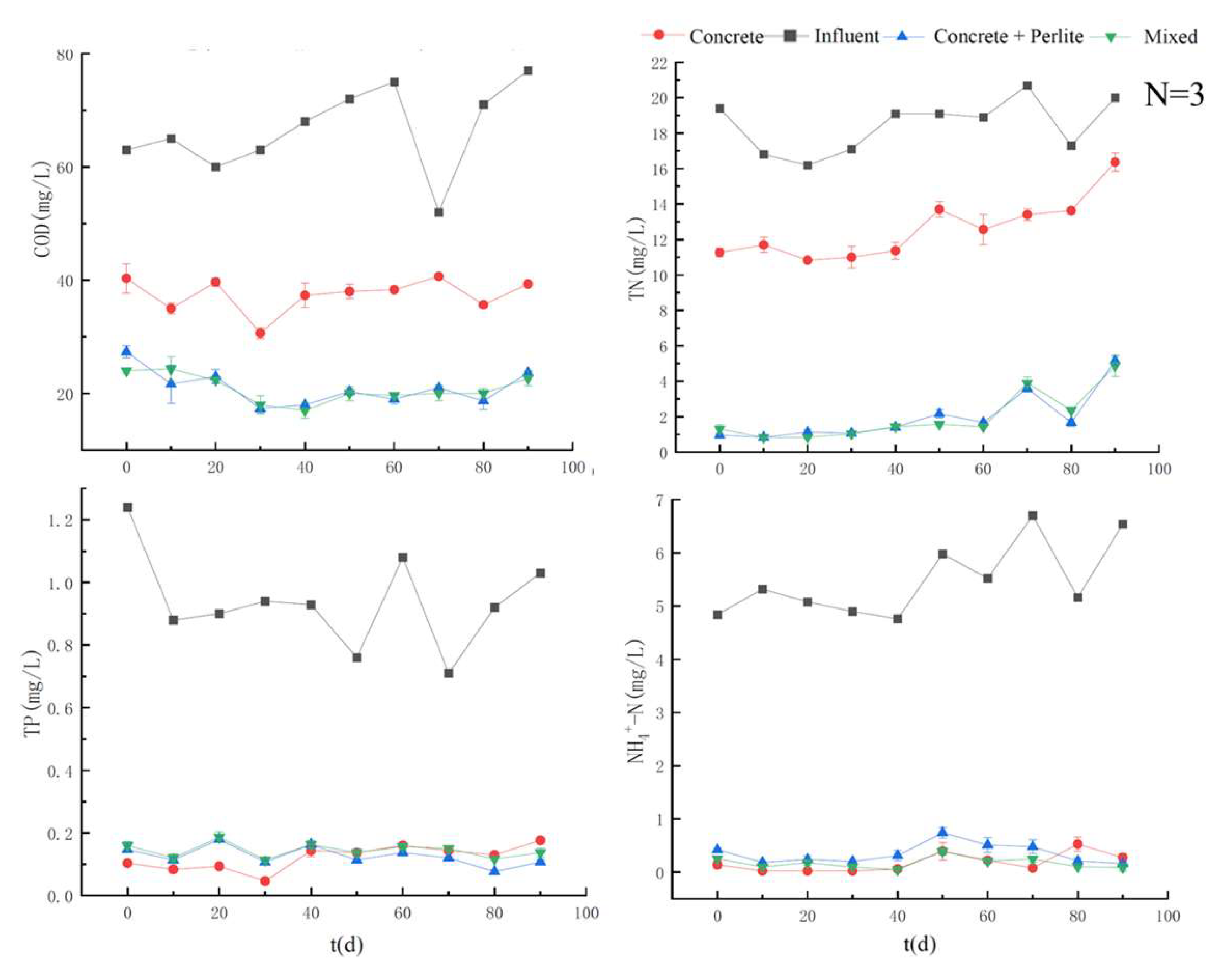
3.2. Pollutant Removal
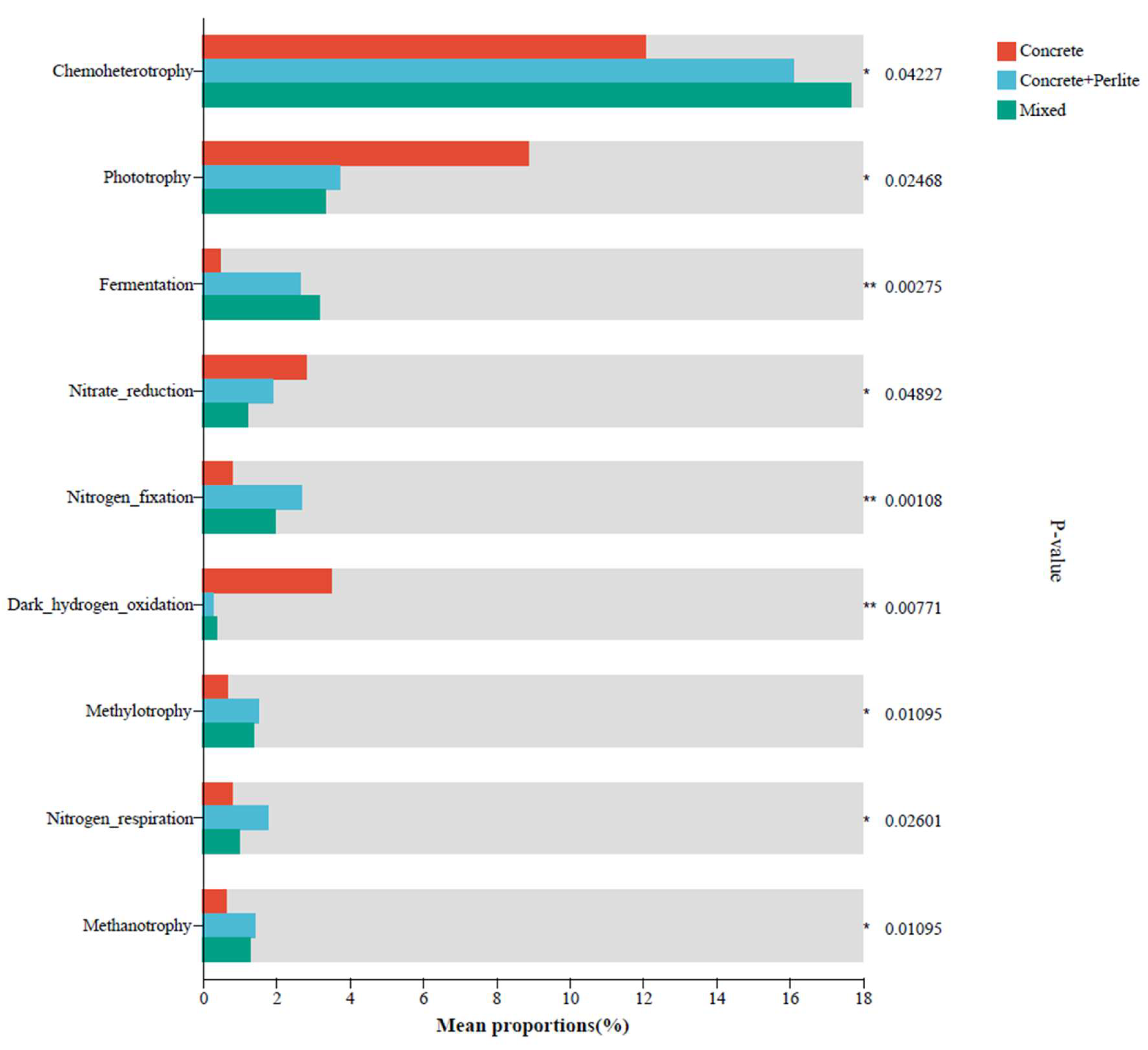
3.3. Microbial Community Characteristics
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CDW | Construction and demolition waste |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| NH4+-N | Ammonium nitrogen |
| pH | Potential of hydrogen |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
References
- Ji, Z.H.; Tang, W.Z.; Pei, Y.S. Constructed wetland substrates: A review on development, function mechanisms, and application in contaminants removal. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Wu, L.Y.; Jin, Y.; Gong, Y.W.; Li, A.Z.; Li, J.X.; Li, F. Recycled aggregates from construction and demolition waste as wetland substrates for pollutant removal. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 311, 127766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsia, D.; Sympikou, T.; Topi, E.; Pappa, F.; Matsoukas, C.; Fountoulakis, M.S. Use of recycled construction and demolition waste as substrate in constructed wetlands for the wastewater treatment of cheese production. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 362, 121324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.F.; Zhu, J.Z.; Gu, X.J.; Zhu, J.J. Current Situation and Control of Agricultural Non-point Source Pollution. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2010, 20, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Z.; Ding, Z.; Zha, X.; Cheng, T.; Ding, Z.; Zha, X.; Cheng, T. Phosphorus Adsorption Characteristics of Different Substrates in Constructed Wetland. China Water Wastewater 2009, 25, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, H.; Chen, R.; Wang, L.; Jiang, L.; Yang, F.; Zheng, S.; Wang, G.; Lin, X. Soil pH, total phosphorus, climate and distance are the major factors influencing microbial activity at a regional spatial scale. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.; Gao, X.F.; Tam, C.M.; Ng, K.M. Physio-chemical reactions in recycle aggregate concrete. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 163, 823–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hube, S.; Zaqout, T.; Ogmundarson, O.; Andradottir, H.O.; Wu, B. Constructed wetlands with recycled concrete for wastewater treatment in cold climate: Performance and life cycle assessment. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 904, 166778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.S.; Zhu, H.Z.; Wu, K.M.; Zhao, X.H.; Wang, F.; Liao, Q.L. Fines isolated from waste concrete as a new material for the treatment of phosphorus wastewater. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 12539–12549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd Roni, N.; Adnan, S.H.; Hamidon, N.; Ismail, T. The vertical recycled concrete aggregate filter for removal of phosphorus in wastewater. In 3rd International Conference on Civil and Environmental Engineering; Izhar, T., Ibrahim, N., Dahalan, F.A., Saad, F., Ghani, A.A., Ibrahim, N.M., Yusof, S.Y., Bawadi, N.F., AnudaiAnuar, S., Eds.; Science Publishing Group: New York, NY, USA, 2021; Volume 646. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.M.; Ma, Y.; Chen, J.; Cai, Y.; Lu, Q.Q.; Yu, Q.; Duan, X.T.; Zhao, D.H.; An, S.Q. The negative effect of the high pH of waste concrete in constructed wetlands on COD and N removal. J. Water Process. Eng. 2023, 51, 103356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Wang, J.P.; Lin, X.C.; Wang, H.; Li, H.E.; Li, J.K. Purification effects of recycled aggregates from construction waste as constructed wetland filler. J. Water Process. Eng. 2022, 50, 103335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staunton, J.; Williams, C.D.; Morrison, L.; Henry, T.; Fleming, G.; Gormally, M.J. Spatio-temporal distribution of construction and demolition (C&D) waste disposal on wetlands: A case study. Land Use Policy 2015, 49, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saavedra, R.; Etxeberria, M. Carbonation Treatments for Durable Low-Carbon Recycled Aggregate Concrete. Materials 2025, 18, 4168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.J.; Yin, J.; Xu, W.X.; Liu, S.Z.; Liu, X.F. Alkalinity Regulation and Optimization of Cementitious Materials Used in Ecological Porous Concrete. Materials 2024, 17, 1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radevic, A.; Despotovic, I.; Zakic, D.; Oreskovic, M.; Jevtic, D. Influence of acid treatment and carbonation on the properties of recycled concrete aggregate. Chem. Ind. Chem. Eng. Q. 2018, 24, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetene, Y.; Addis, T. Adsorptive Removal of Phosphate From Wastewater Using Ethiopian Rift Pumice: Batch Experiment. Air Soil Water Res. 2020, 13, 1178622120969658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 18918-2002; Discharge Standard of Pollutants for Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plant. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2002.
- GB 3838-2002; Environmental Quality Standards for Surface Water. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2002.
- Ding, J.; Shu, Q. Application of Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2000, 5, 320–321. [Google Scholar]
- Bárcenas-Moreno, G.; Bååth, E.; Rousk, J. Functional implications of the pH-trait distribution of the microbial community in a re-inoculation experiment across a pH gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2016, 93, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakar, K.; Pandey, A. Wide pH range tolerance in extremophiles: Towards understanding an important phenomenon for future biotechnology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 2499–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskuil, M.I.; Covey, C.R.; Walter, N.D. Antibiotic Lethality and Membrane Bioenergetics. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2018, 73, 77–122. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, Q.; Wang, Q.-Q.; Wu, L.; Cai, A.-D.; Wang, C.-J.; Zhang, W.-J.; Xu, M.-G. Fertilization impacts on soil microbial communities and enzyme activities across China’s croplands: A meta-analysis. J. Plant Nutr. Fertil. 2018, 24, 1598–1609. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Zhao, Y.G.; Ma, R.; Yang, P.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, D.J.; Sun, F.J.; Zhang, F.H. Effects of Microbial Fertilizers on Soil Improvement and Bacterial Communities in Saline-alkali Soils of Lycium barbarum. J. Agric. Biotechnol. 2020, 28, 1499–1510. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, J.; Hu, X.B.; Chen, M.L.; Zhang, J.M.; Guo, F.C.; Vymazal, J.; Chen, Y. Meta-analysis of the removal of trace organic contaminants from constructed wetlands: Conditions, parameters, and mechanisms. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 178, 106596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, T.; Zhang, L.; Quan, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, F. Study on Adsorption and Bio-degradability of Aged-refuse-based Bioreactor. Environ. Eng. 2007, 6, 34–36. [Google Scholar]
- Zhengwei, L.; Xishu, H.; Xuan, C.; Yongtao, L.; Xudong, W. Effect of pH values on shortcut denitrification and nitrous oxide emission. J. Xi’an Univ. Archit. Technol. 2019, 51, 605–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D.R.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, M. Biotransformation of nitrogen- and sulfur-containing pollutants during coking wastewater treatment: Correspondence of performance to microbial community functional structure. Water Res. 2017, 121, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albina, P.; Durban, N.; Bertron, A.; Albrecht, A.; Robinet, J.C.; Erable, B. Influence of Hydrogen Electron Donor, Alkaline pH, and High Nitrate Concentrations on Microbial Denitrification: A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, S.S.; Hu, Q.L.; Cheng, Y.Q.; Bai, L.Y.; Liu, Z.H.; Xiao, W.J.; Gong, Z.H.; Wu, Y.N.; Feng, K.; Deng, Y.; et al. Application of organic fertilizer improves microbial community diversity and alters microbial network structure in tea (Camellia sinensis) plantation soils. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 195, 104356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Concrete | Concrete + Perlite | Mixed | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chao | 858 b | 2966 a | 2921 a |
| Sobs | 534 b | 2196 a | 2141 a |
| Shannon | 2.50 b | 6.13 a | 6.12 a |
| Simpson | 0.236 a | 0.0071 b | 0.0056 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Cai, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Wei, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhao, D. Study on Improving the Purification Function of Constructed Wetlands with Construction Waste Substrates by Acid–Base Substrate Configuration. Water 2026, 18, 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010069
Cai Y, Gu Y, Zhang M, Wei Y, Zhou R, Zhao D. Study on Improving the Purification Function of Constructed Wetlands with Construction Waste Substrates by Acid–Base Substrate Configuration. Water. 2026; 18(1):69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010069
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Ying, Yumei Gu, Miao Zhang, Ying Wei, Rixiu Zhou, and Dehua Zhao. 2026. "Study on Improving the Purification Function of Constructed Wetlands with Construction Waste Substrates by Acid–Base Substrate Configuration" Water 18, no. 1: 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010069
APA StyleCai, Y., Gu, Y., Zhang, M., Wei, Y., Zhou, R., & Zhao, D. (2026). Study on Improving the Purification Function of Constructed Wetlands with Construction Waste Substrates by Acid–Base Substrate Configuration. Water, 18(1), 69. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010069






