Analytical Description and Evaluation of Soil Infiltration Processes Under Horizontal Moistube Irrigation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Laboratory Experiment
2.2. Feature Analysis and Model Development
3. Results and Analysis
4. Limitations of the Study
5. Conclusions
- (1)
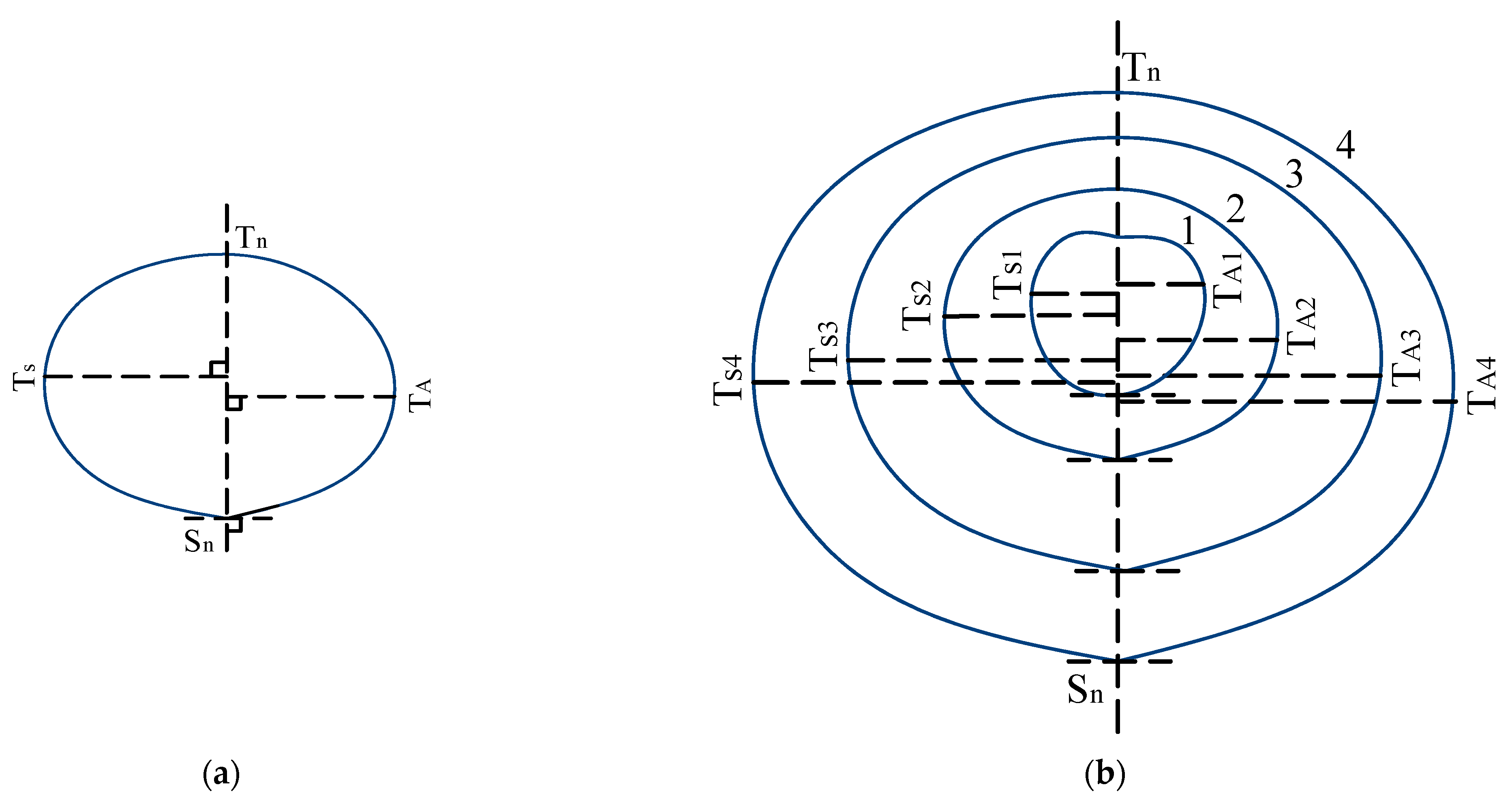
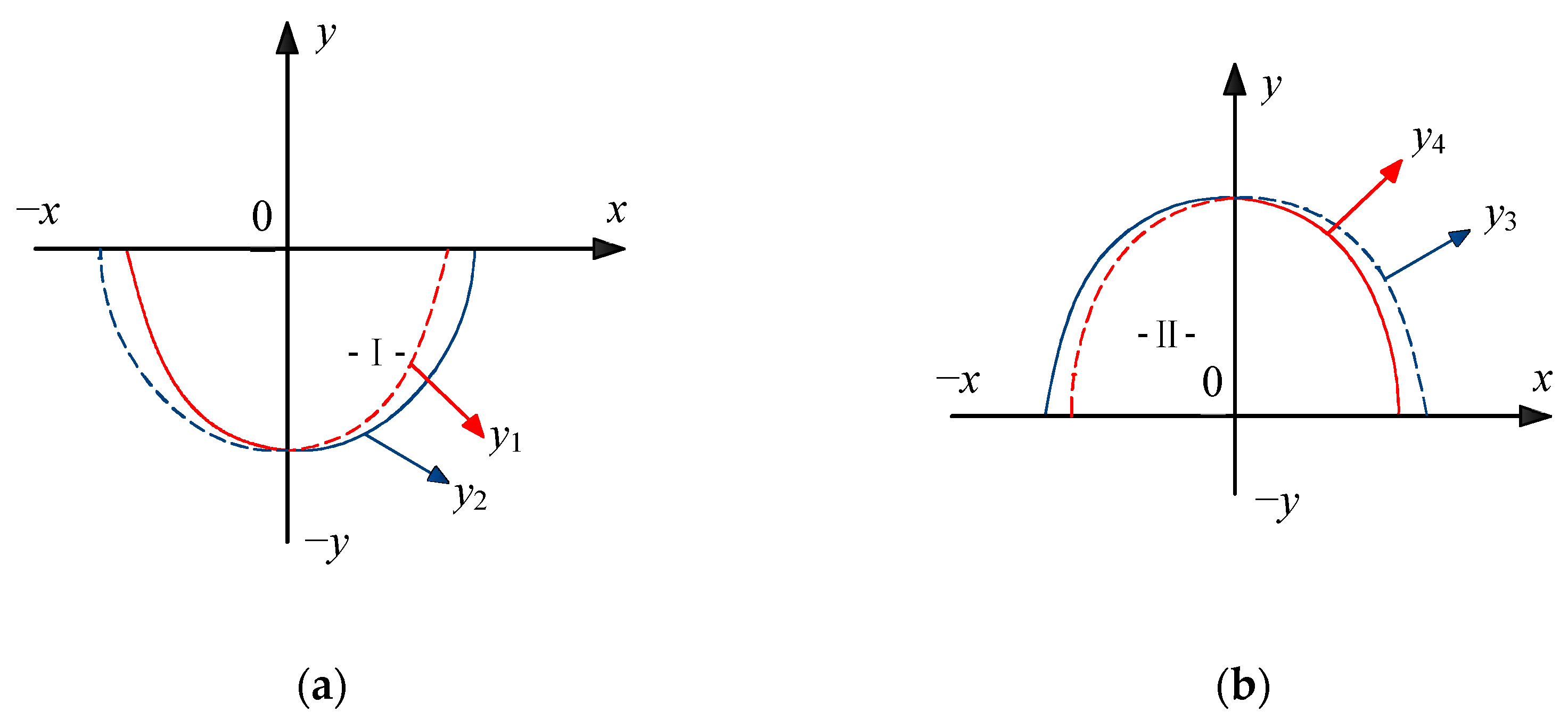
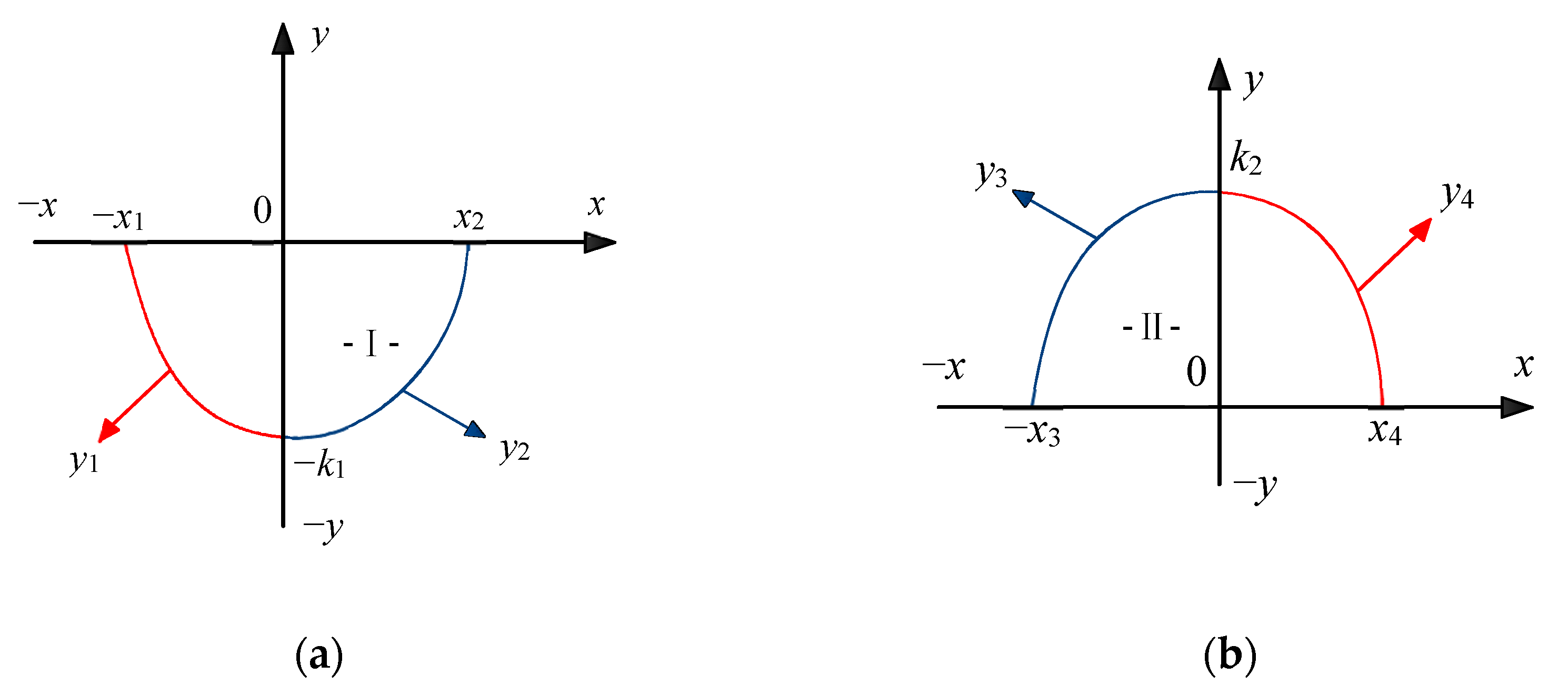
- Experimental data were utilized to determine the values of parameters a and k in the model at each time step. For soil profile I, parameters a1 and a2 were consistently positive (a1 > 0, a2 > 0). Meanwhile, based on the location of the vertex (0, −k1) of the convex parabola on the negative side of the y-axis, the parameter −k1 remained consistently negative (−k1 < 0). For parameters a3 and a4 in the model corresponding to soil profile II, both were assigned negative values (a3 < 0, a4 < 0) in accordance with the concave characteristic of the parabola. Simultaneously, considering the location of the vertex (0, k2) of the concave parabola on the positive side of the y-axis, the parameter k2 was consistently positive (k2 > 0).
- (2)
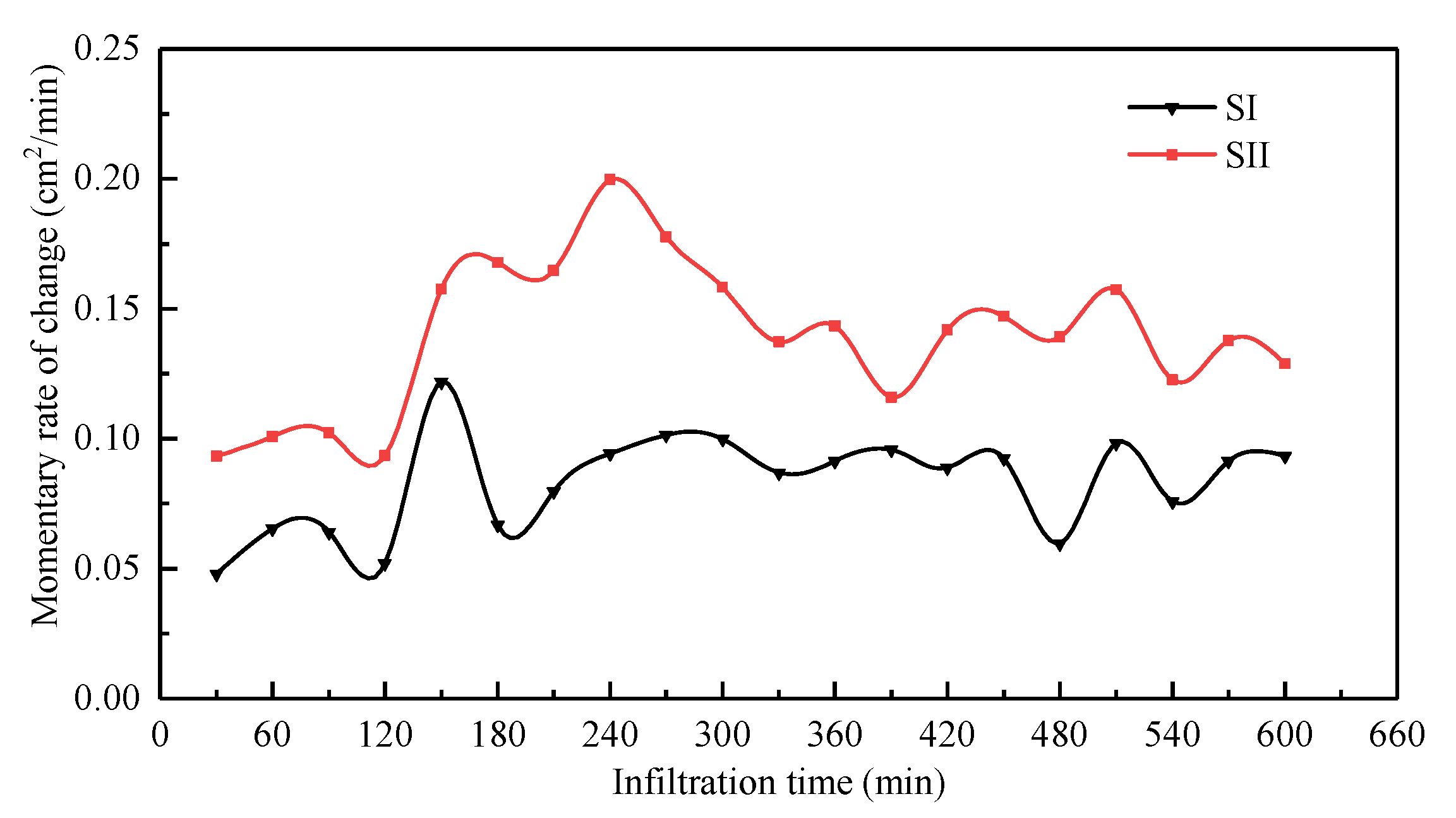
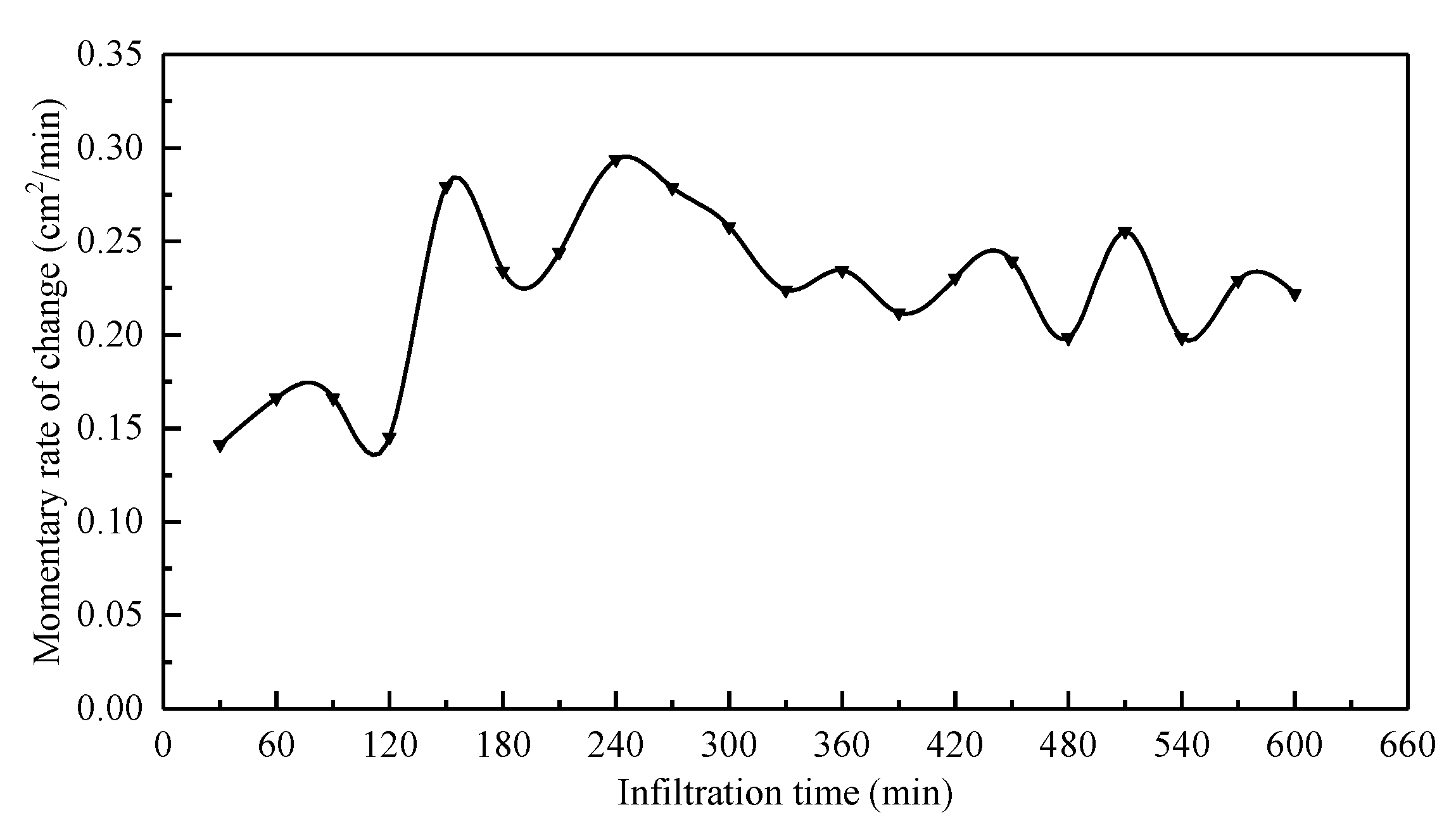
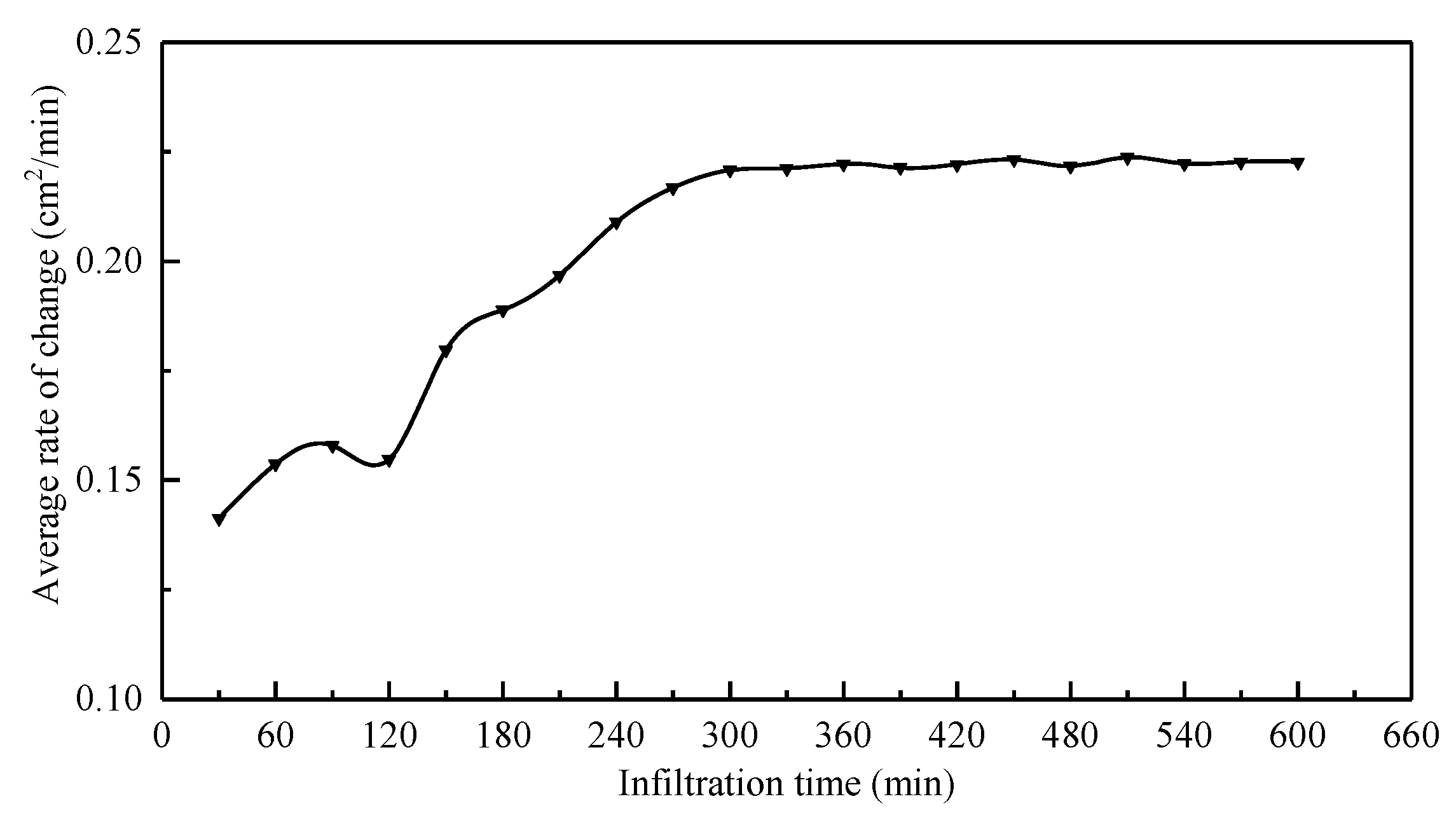
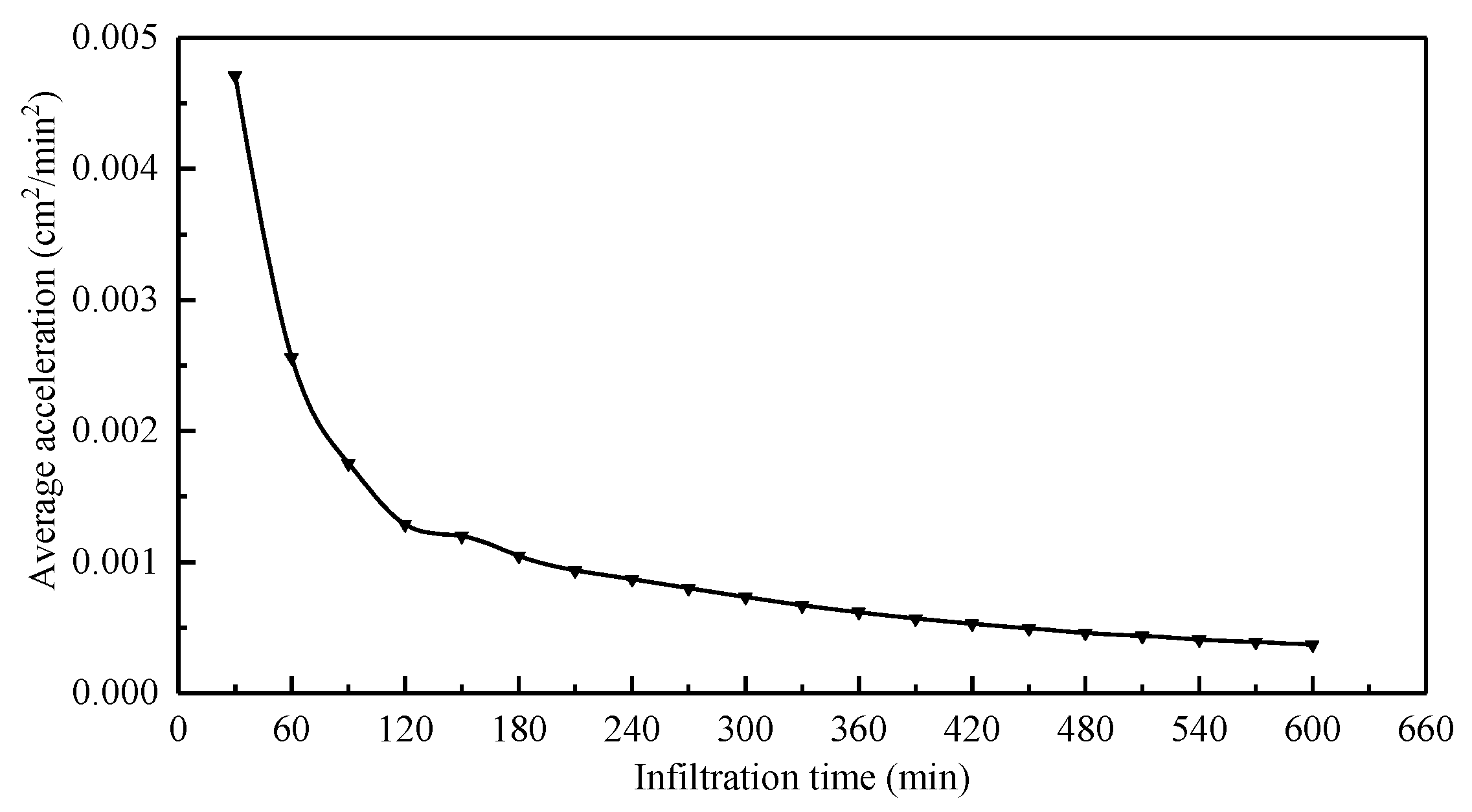
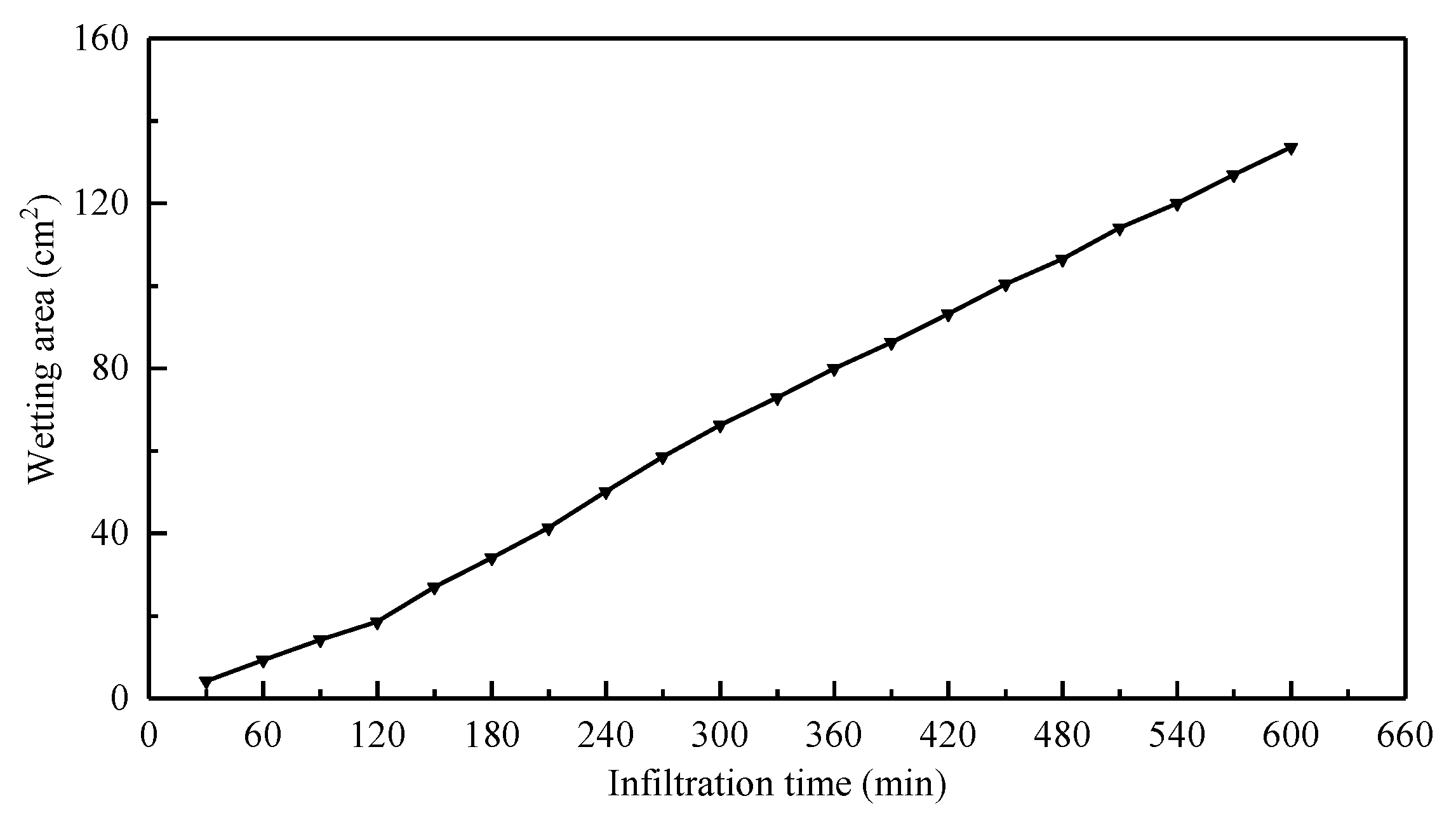
- The instantaneous variation rate of the wetted area within soil profiles exhibits continuous nonlinear changes across both temporal and spatial dimensions. The average acceleration of wetted area variation characterizes the overall spatiotemporal dynamics of soil profiles, with the magnitude of the wetted area increasing as its variation rate decreases.
- (3)
- Moistube irrigation can be implemented in soils with varying textures, under different moistube discharge rates, and under distinct water-use periods. Under these diverse conditions, the maximum wetting distances of the wetted soil profile differ in the horizontal direction, vertical upward direction, and vertical downward direction. However, the key variables and parameters of the proposed model are derived from the primary components of these distinct wetted soil profiles. When the model is operated at any given time step, it generates coordinate values that represent the dimensions and positions of each component within the wetted soil profile. In other words, the primary components of the wetted body in the moistube irrigation system form the basis of the variables and parameters for the model developed in this study. Consequently, to determine the wetted body at any moment during moistube irrigation application under different conditions, it is sufficient to input the values of each component of the wetted soil profile and execute the established model.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Namara, R.E.; Nagar, R.K.; Upadhyay, B. Economics, adoption determinants, and impacts of micro-irrigation technologies: Empirical results from India. Irrig. Sci. 2007, 25, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.S.; Li, Y.F.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, W.X. Microirrigation in China: History, current situation and prospects. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 47, 372–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, W.Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.L.; Xue, W.L.; Zhang, L.T. Effects of Buried Depth and Pressure Head on Water Movement of Wetted Soil during Moistube-irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2013, 44, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, E.K.; Mabhaudhi, T.; Senzanje, A. Hydraulic and clogging characteristics of Moistube irrigation as influenced by water quality. J. Water Supply Res. Technol.—AQUA 2018, 67, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.W.; Zhao, T.; Bai, G.L.; Liu, W.G. HYDRUS-2D simulation of soil wetting pattern with horizontal moistube-irrigation and analysis of its influencing factors. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2018, 34, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.W.; Huang, N.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, T. Simulation of soil wetting pattern of vertical moistube-irrigation. Water 2018, 10, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naglič, B.; Kechavarzi, C.; Coulon, F.; Pintar, M. Numerical investigation of the influence of texture, surface drip emitter discharge rate and initial soil moisture condition on wetting pattern size. Irrig. Sci. 2014, 32, 421–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ogaidi, A.A.; Wayayok, A.; Rowshon, M.K.; Abdullah, A.F. Wetting patterns estimation under drip irrigation systems using an enhanced empirical model. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 176, 203–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.J.; Lin, S.D.; Wang, Q.J.; Wang, K. Influence of Soil Hydraulic Parameters on Soil Wetting Pattern Shape of Point Source Infiltration. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2020, 51, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Cai, H.J.; Guo, Y.C.; Geng, B.J. Experimental Study on Factors Effecting Soil Wetted Volume of Clay Loam Under Drip Irrigation. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2002, 18, 17–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kilic, M. A new analytical method for estimating the 3D volumetric wetting pattern under drip irrigation system. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 228, 105898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Niu, W.Q.; Zhang, L.L.; Shi, L.Y. Experimental study on characters of wetted soil in moistube irrigation. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2012, 10, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.W.; Yang, Z.W.; Hu, W.L. Establishment and validation of wetting pattern model of moistube irrigation in homogeneous soil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabral, P.P.; Pandey, P.K.; Pandey, A.; Singh, K.P.; Singh, M.S. Modelling of wetting pattern under trickle source in sandy soil of Nirjuli, Arunachal Pradesh (India). Irrig. Sci. 2012, 30, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molael, K.M.; Liaghat, A.; Abbasi, F. Estimation of soil moisture pattern in subsurface drip irrigation using dimensional analysis method. Iran. J. Agric. 2008, 39, 371–378. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, W.W.; Ma, X.Y.; Li, J.; Parkes, M. Simulation of point source wetting pattern of subsurface drip irrigation. Irrig. Sci. 2011, 29, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, E.K.; Senzanje, A.; Mabhaudhi, T. Soil water dynamics under Moistube irrigation. Phys. Chem. Earth Parts A/B/C 2020, 115, 102836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorburn, P.J.; Cook, F.J.; Bristow, K.L. Soil-dependent wetting from trickle emitters: Implications for system design and management. Irrig. Sci. 2003, 22, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cook, F.J.; Thorburn, P.J.; Fitch, P.; Bristow, K.L. WetUp: A software tool to display approximate wetting patterns from drippers. Irrig. Sci. 2003, 22, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncef, H.; Khemaies, Z. An analytical approach to predict the moistened bulb volume beneath a surface point source. Agric. Water Manag. 2016, 166, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
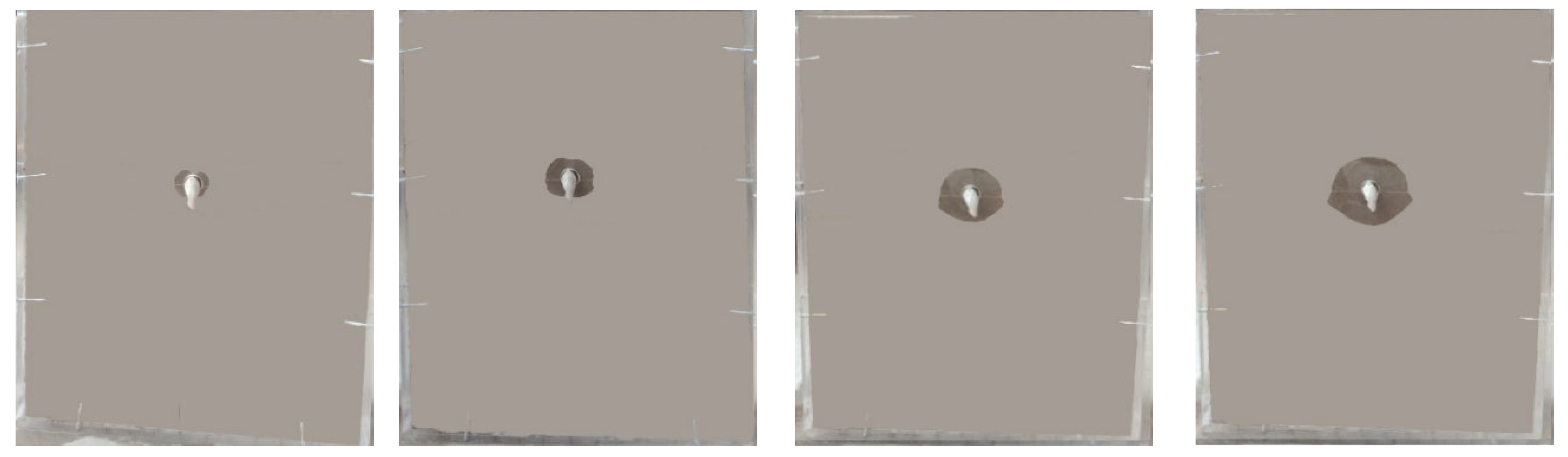

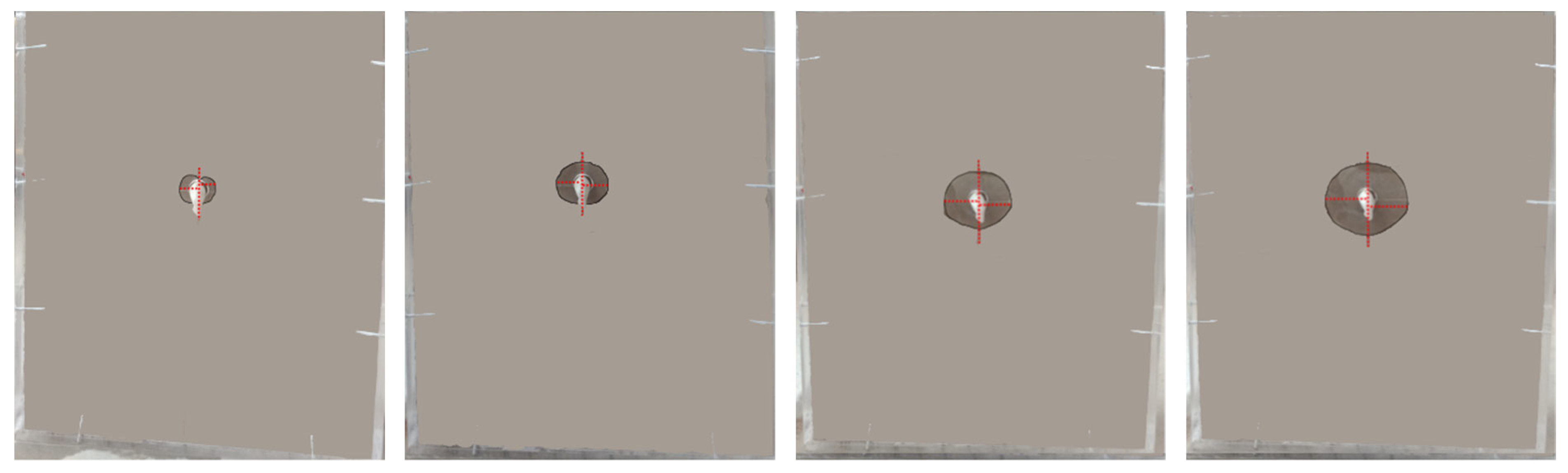
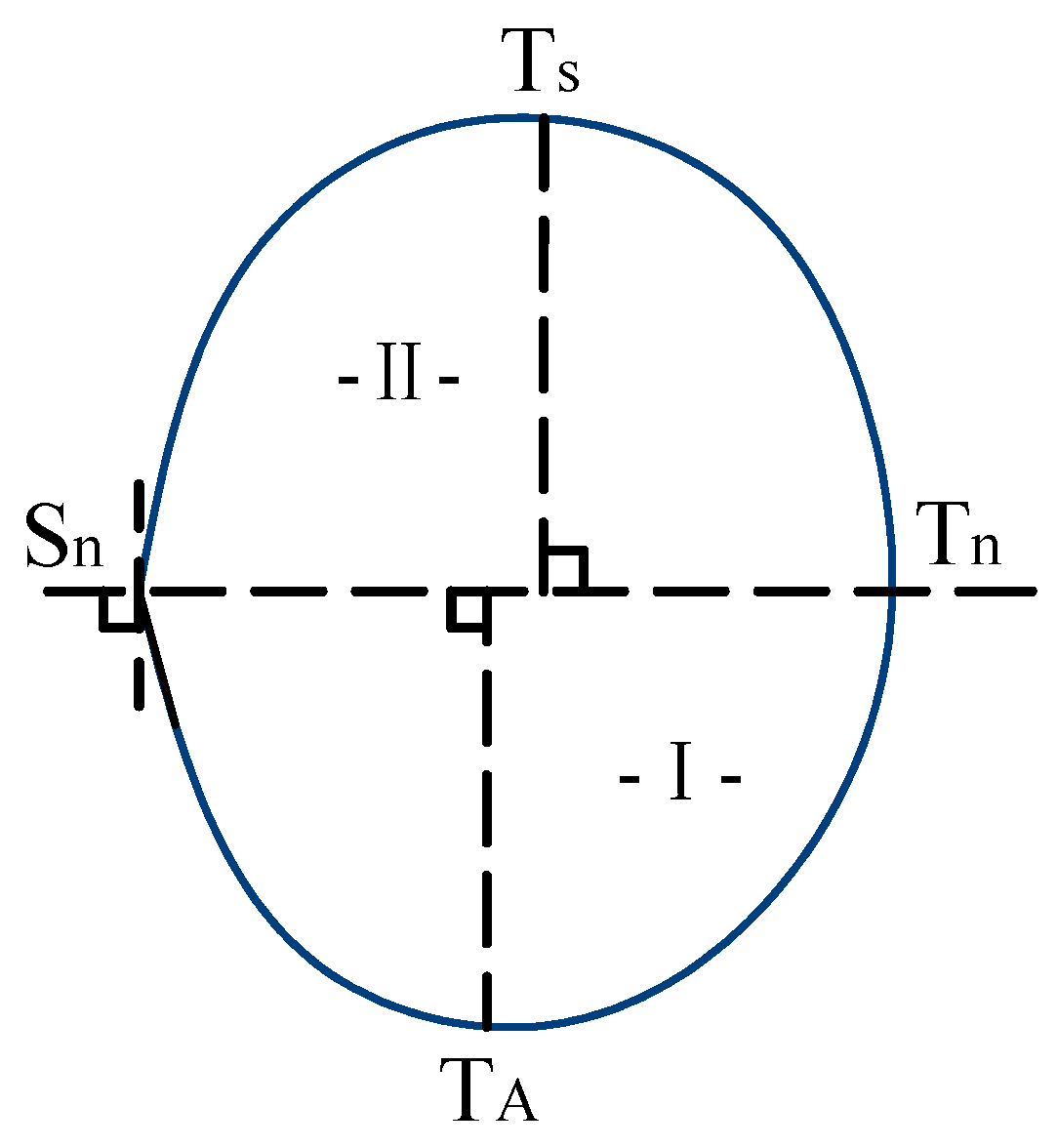
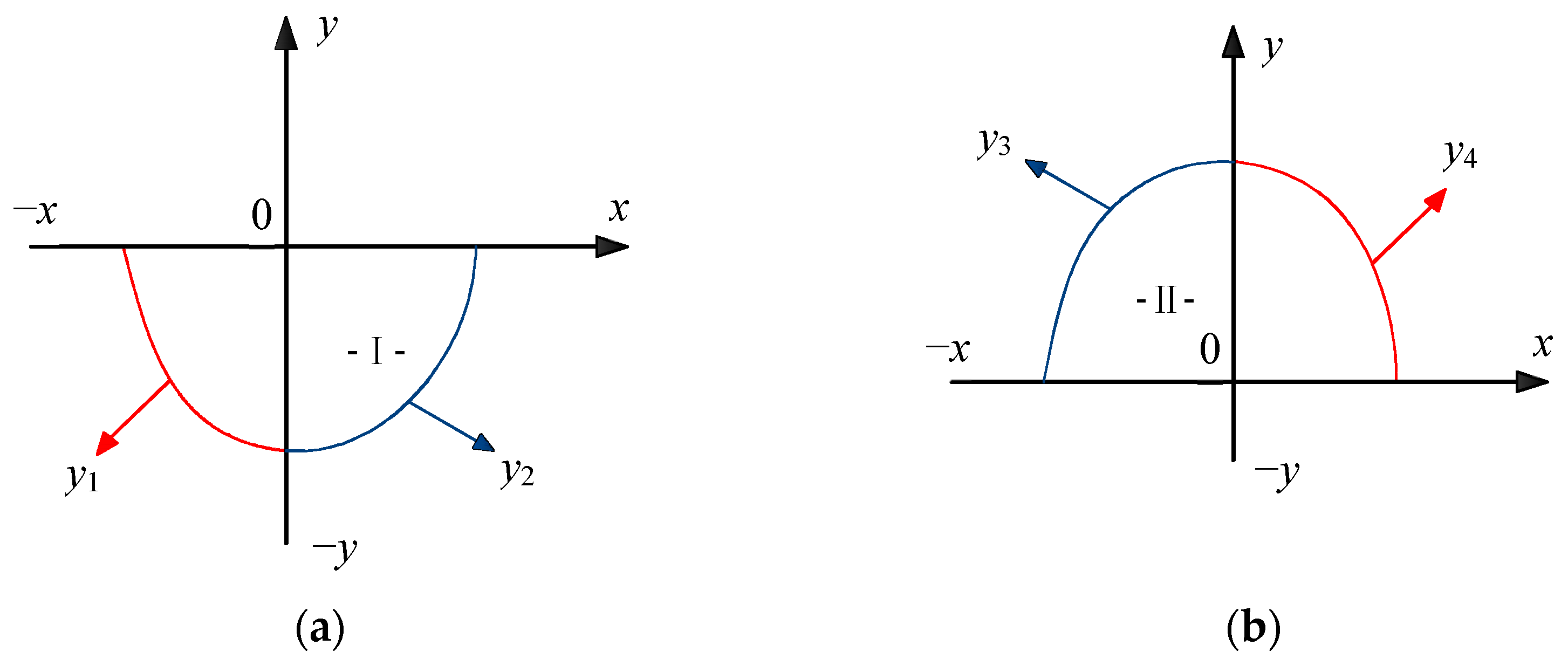
| Soil Texture | Bulk Density γ/(g·cm−3) | Soil Saturated Hydraulic Conductivity Ks/(cm·min−1) | Moistube Burial Depth D/cm | Pressure Head H/cm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Loam | 1.35 | 0.0186 | 30 | 160 |
| Soil Texture | Infiltration Time/min | I | II | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a1 | a2 | −k1 | a3 | a4 | k2 | ||
| Loam | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 | 1.20 | 1.88 | −1.2 | −1.50 | −2.34 | 1.50 | |
| 60 | 0.66 | 0.87 | −1.7 | −0.74 | −0.97 | 1.90 | |
| 90 | 0.53 | 0.65 | −2.1 | −0.58 | −0.71 | 2.30 | |
| 120 | 0.50 | 0.54 | −2.4 | −0.56 | −0.61 | 2.70 | |
| 150 | 0.46 | 0.50 | −3.1 | −0.47 | −0.51 | 3.20 | |
| 180 | 0.37 | 0.45 | −3.3 | −0.41 | −0.51 | 3.70 | |
| 210 | 0.29 | 0.42 | −3.5 | −0.33 | −0.48 | 4.00 | |
| 240 | 0.22 | 0.39 | −3.7 | −0.26 | −0.45 | 4.30 | |
| 270 | 0.20 | 0.37 | −4.0 | −0.23 | −0.42 | 4.60 | |
| 300 | 0.19 | 0.33 | −4.3 | −0.22 | −0.38 | 4.90 | |
| 330 | 0.19 | 0.30 | −4.5 | −0.21 | −0.34 | 5.10 | |
| 360 | 0.18 | 0.27 | −4.7 | −0.20 | −0.30 | 5.30 | |
| 390 | 0.17 | 0.24 | −4.9 | −0.19 | −0.27 | 5.40 | |
| 420 | 0.17 | 0.23 | −5.1 | −0.19 | −0.25 | 5.60 | |
| 450 | 0.16 | 0.22 | −5.3 | −0.18 | −0.24 | 5.80 | |
| 480 | 0.16 | 0.22 | −5.4 | −0.17 | −0.24 | 6.00 | |
| 510 | 0.15 | 0.21 | −5.6 | −0.17 | −0.23 | 6.20 | |
| 540 | 0.14 | 0.20 | −5.7 | −0.16 | −0.22 | 6.30 | |
| 570 | 0.14 | 0.19 | −5.9 | −0.16 | −0.21 | 6.50 | |
| 600 | 0.14 | 0.17 | −6.0 | −0.16 | −0.18 | 6.60 | |
| Soil Texture | Infiltration Time/min | I | II | S | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | SI | S3 | S4 | SII | |||
| Loam | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 30 | 0.80 | 0.64 | 1.44 | 2.00 | 0.80 | 2.80 | 4.24 | |
| 60 | 1.81 | 1.59 | 3.40 | 4.05 | 1.77 | 5.83 | 9.23 | |
| 90 | 2.80 | 2.52 | 5.32 | 6.13 | 2.76 | 8.89 | 14.21 | |
| 120 | 3.52 | 3.36 | 6.88 | 7.92 | 3.78 | 11.70 | 18.58 | |
| 150 | 5.37 | 5.17 | 10.54 | 11.09 | 5.33 | 16.43 | 26.97 | |
| 180 | 6.60 | 5.94 | 12.54 | 14.80 | 6.66 | 21.46 | 34.00 | |
| 210 | 8.17 | 6.77 | 14.93 | 18.67 | 7.73 | 26.40 | 41.33 | |
| 240 | 10.11 | 7.65 | 17.76 | 23.51 | 8.89 | 32.39 | 50.15 | |
| 270 | 12.00 | 8.80 | 20.80 | 27.60 | 10.12 | 37.72 | 58.52 | |
| 300 | 13.47 | 10.32 | 23.79 | 30.71 | 11.76 | 42.47 | 66.26 | |
| 330 | 14.70 | 11.70 | 26.40 | 33.32 | 13.26 | 46.58 | 72.98 | |
| 360 | 15.98 | 13.16 | 29.14 | 36.04 | 14.84 | 50.88 | 80.02 | |
| 390 | 17.31 | 14.70 | 32.01 | 38.16 | 16.20 | 54.36 | 86.37 | |
| 420 | 18.70 | 15.98 | 34.68 | 41.07 | 17.55 | 58.61 | 93.29 | |
| 450 | 20.14 | 17.31 | 37.45 | 44.08 | 18.95 | 63.03 | 100.48 | |
| 480 | 21.24 | 18.00 | 39.24 | 47.20 | 20.00 | 67.20 | 106.44 | |
| 510 | 22.77 | 19.41 | 42.19 | 50.43 | 21.49 | 71.92 | 114.11 | |
| 540 | 23.94 | 20.52 | 44.46 | 52.92 | 22.68 | 75.60 | 120.06 | |
| 570 | 25.17 | 22.03 | 47.20 | 55.47 | 24.27 | 79.73 | 126.93 | |
| 600 | 26.00 | 24.00 | 50.00 | 57.20 | 26.40 | 83.60 | 133.60 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Liu, D.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, T. Analytical Description and Evaluation of Soil Infiltration Processes Under Horizontal Moistube Irrigation. Water 2026, 18, 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010035
Liu D, Yang Z, Huang Y, Wang X, Liu X, Zhang G, Liu T. Analytical Description and Evaluation of Soil Infiltration Processes Under Horizontal Moistube Irrigation. Water. 2026; 18(1):35. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010035
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Di, Zhiwei Yang, Yongting Huang, Xiongshi Wang, Xingrong Liu, Guoxin Zhang, and Tao Liu. 2026. "Analytical Description and Evaluation of Soil Infiltration Processes Under Horizontal Moistube Irrigation" Water 18, no. 1: 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010035
APA StyleLiu, D., Yang, Z., Huang, Y., Wang, X., Liu, X., Zhang, G., & Liu, T. (2026). Analytical Description and Evaluation of Soil Infiltration Processes Under Horizontal Moistube Irrigation. Water, 18(1), 35. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010035







