Analysis and Evaluation of Water Resources Status in Dongying Based on Grey Water Footprint Theory
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Overview of the Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Methods
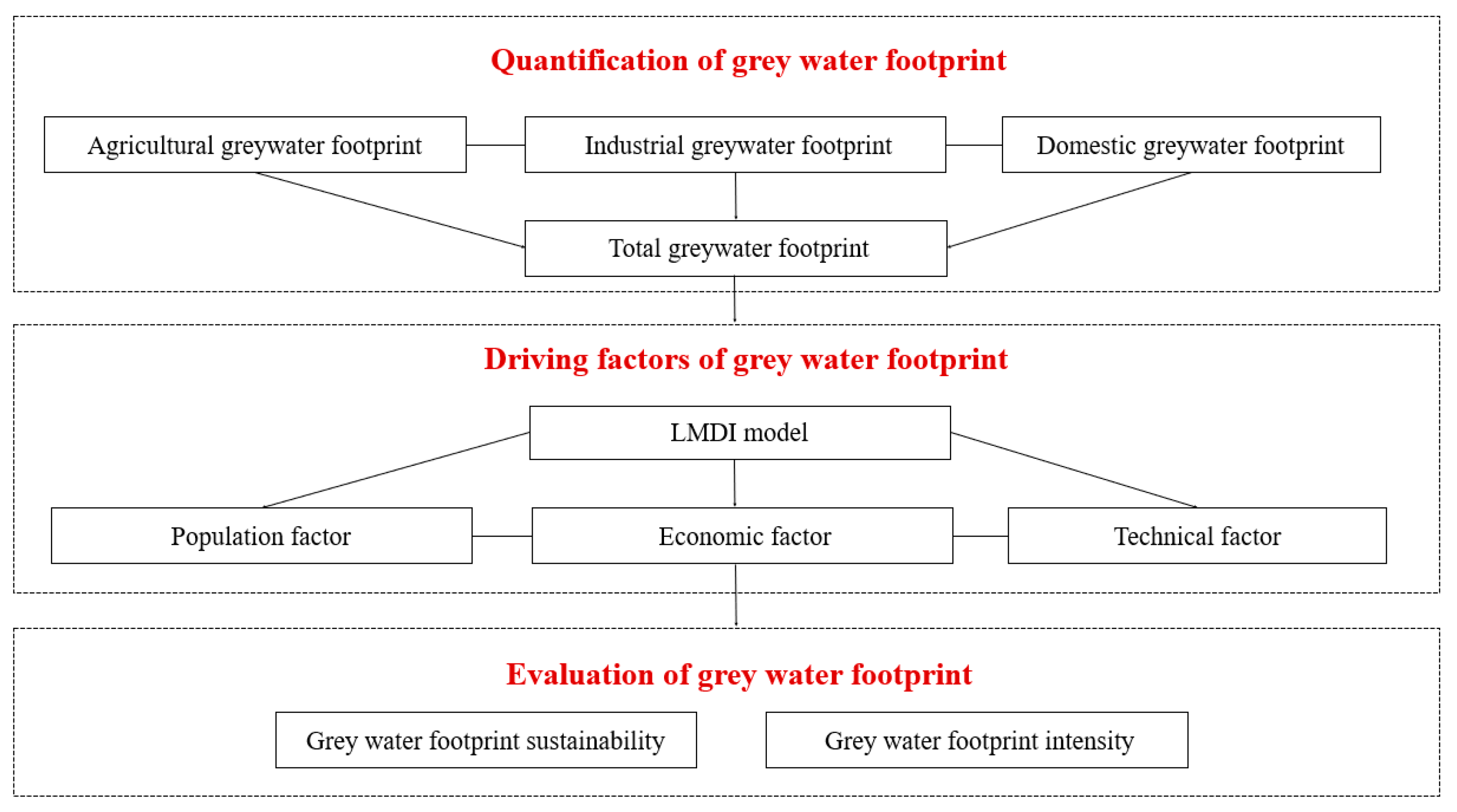
2.3.1. Quantification of Grey Water Footprint
- Agricultural grey water footprint
- 2.
- Industrial grey water footprint
- 3.
- Domestic grey water footprint
2.3.2. Driving Factors of Grey Water Footprint
2.3.3. Evaluation of Grey Water Footprint
- Grey water footprint sustainability
- 2.
- Grey water footprint intensity
3. Results
3.1. Quantification of Grey Water Footprint
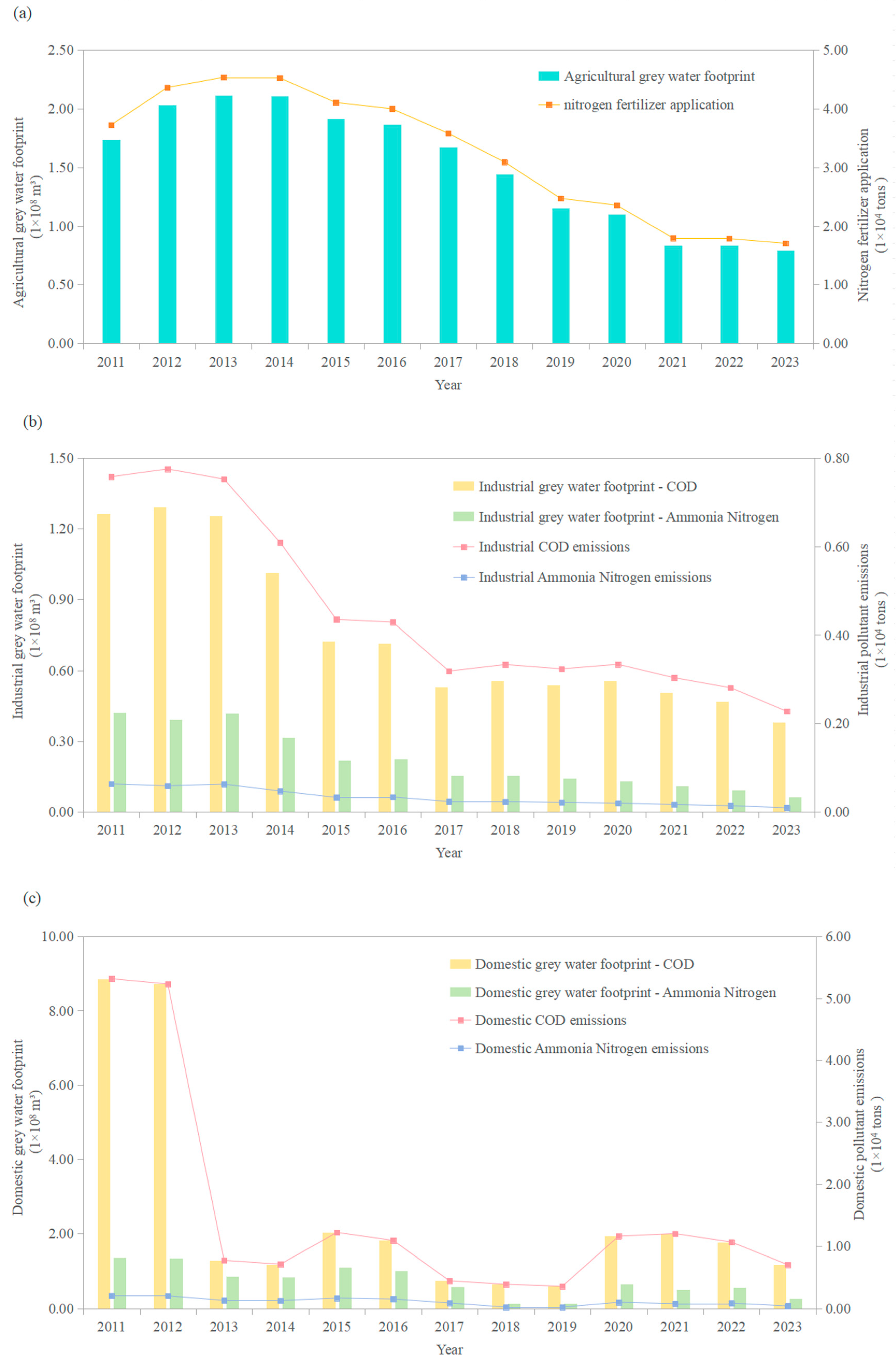
3.1.1. Agricultural, Industrial, and Domestic Greywater Footprint
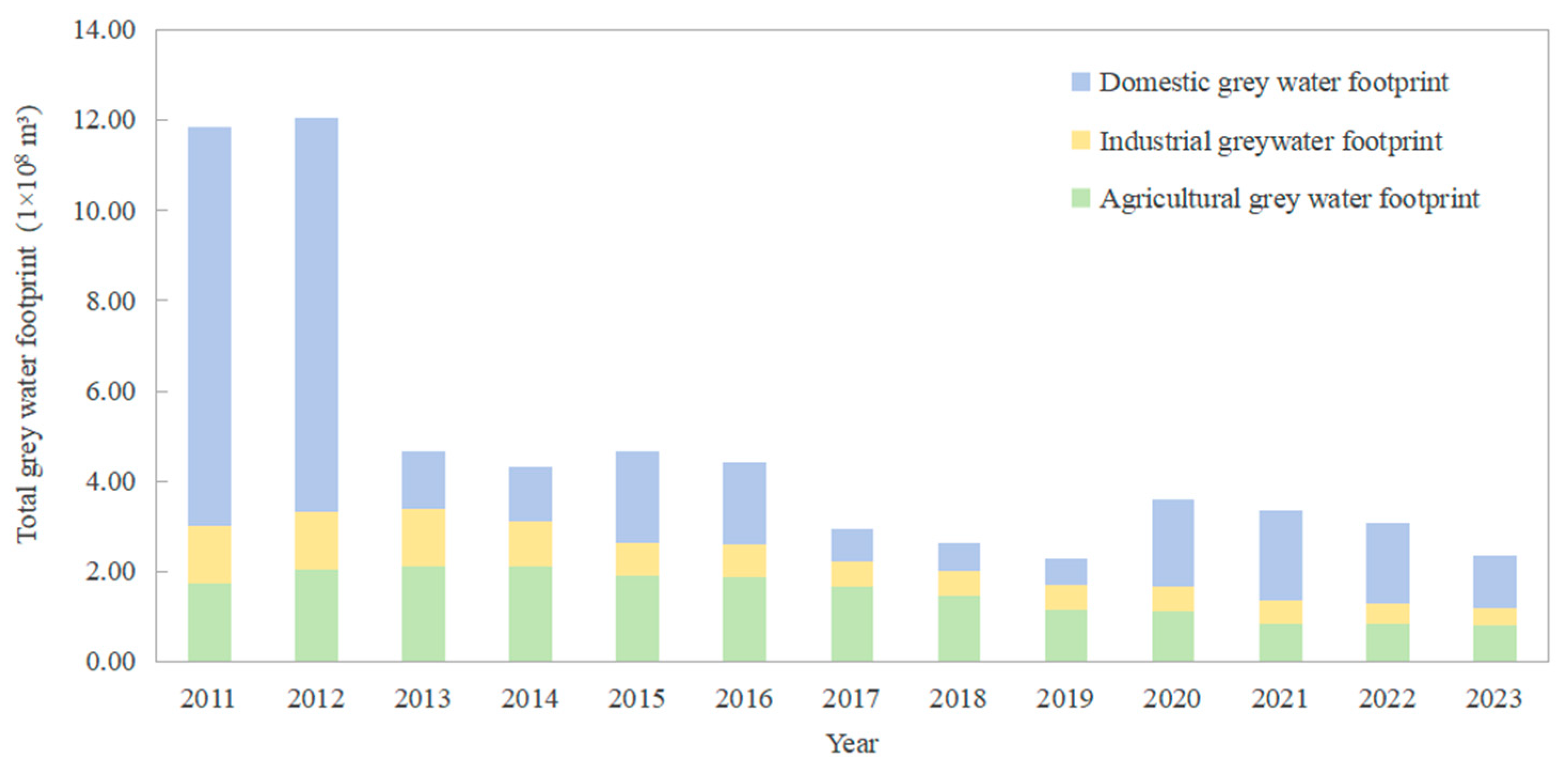
3.1.2. Total Grey Water Footprint
3.2. Driving Factors of Grey Water Footprint
3.3. Evaluation of Grey Water Footprint
4. Discussion
4.1. Quantification and Factor Analysis of Grey Water Footprint
4.2. Evaluation of Grey Water Footprint
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Al-Addous, M.; Bdour, M.; Alnaief, M.; Rabaiah, S.; Schweimanns, N. Water Resources in Jordan: A Review of Current Challenges and Future Opportunities. Water 2023, 15, 3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, J.; Jia, L.; Wang, L. Evaluation of water resource carrying potential and barrier factors in Gansu Province based on game theory combined weighting and improved TOPSIS model. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Y. Study on the nonlinear transition relationship between water resources consumption and economic development in Heilongjiang province based on system dynamics. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2025, 57, 102193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Economic Forum. Global Risks 2015; World Economic Forum: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Central Committee of the Communist Party of China & State Council. Outline of the National Water Network Construction Plan. China Water Resour. 2023, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, P.; Wang, H.; Hu, Q.; Yi, Y.; Fei, L. Research on China’s water-saving policies and practices. Water Resour. Dev. Res. 2025, 25, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, D.; Song, C.; Li, C.; Lei, D.; Song, G.; Yuan, J.; Tong, C.; Cao, L. Analysis of water stress and driving factors based on virtual water flows in China. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2025, 80, 712–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, J.; Tian, C. Research on implied carbon emissions and implied water resource utilization in China’s international trade under the dual carbon goals. Ecol. Econ. 2025, 41, 87–93+144. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, B.; Han, M.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Du, H. An analysis on the trend of sustainable utilization of water resources in Dongying City, China. Water Resour. 2021, 48, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, R.; Zheng, P. Modeling and evaluating land-use/land-cover change for urban planning and sustainability: A case study of Dongying city, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 172, 1529–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Hung, P.Q. Virtual water trade: A quantification of virtual water flows between nations in relation to international crop trade. Water Sci. Technol. 2002, 49, 203–209. [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra, A.Y.; Chapagain, A.K.; Aldaya, M.M.; Mekonnen, M.M. The Water Footprint Assessment Manual: Setting the Global Standard; Earthscan: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, X. Study on Water Footprint of Coastal Cities in Shandong Peninsula. Master’s Thesis, Ludong University, Yantai, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Depeng, Z.; Yiqing, B.; Yonghui, S.; Zongxue, X.; Guoqiang, W.; Guangwen, M.; Karim, C.A.; Hong, Y. The response of non-point source pollution to land use change and risk assessment based on model simulation and grey water footprint theory in an agricultural river basin of Yangtze River, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaez, R.M.; Ali, D.; Shervin, J.; Mohamadreza, Y. A multi-pollutant pilot study to evaluate the grey water footprint of irrigated paddy rice. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 282, 108291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changxin, X.; Yu, L.; Tianbo, F. Spatial-temporal evolution and driving factors of grey water footprint efficiency in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 844, 156930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, M.; Jian, L.; Jun, W.; Zhenhua, Z.; Liwei, C. Quantification and evaluation of grey water footprint in Yantai. Water 2022, 14, 1893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and derived crop products. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2011, 8, 763–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zeng, W.; Chen, H.; Zhao, Y. Grey water footprint combined with ecological network analysis for assessing regional water quality metabolism. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 3138–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, C.; Guo, X.; Zhao, D.; Liu, K.; Guo, C. Assessment of grey water footprint pressure in the Yangtze River basin and its relationship with water quality. Ecol. Front. 2025, 45, 154–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, J.; Zheng, Z. Analysis of the regional equilibrium of grey water footprint in Shandong Province. Water Sav. Irrig. 2022, 3, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Xian, C.; Pan, X.; Zhen, Q.; Han, B.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Ouyang, Z. Integrated assessments of nitrogen pollution footprints and grey water footprints in the urban ecosystem. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2019, 39, 985–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Liu, X.; Li, Z. Assessment of sustainability of water resource utilization on the northern slope of Tianshan Mountains based on grey water footprint. South-to-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2025, 23, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xian, C.; Ouyang, Z. Integrated assessment of sustainability in urban water resources utilization in China based on grey water footprint. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2021, 41, 2983–2995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Q.; Wu, X.; Shi, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, A.; Yin, D.; Feng, Q.; Ji, W.; Kang, S. Constraints and coordinated allocation strategies of water and land resources for sustainable use of coastal saline-alkali land in the Yellow River Delta. Strateg. Study CAE 2023, 25, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Ding, W.; Li, W.; Liu, X. Study on Evaluation of Water Resources Carrying Capacity and Obstacle Factors in the Yellow River Basin. Yellow River 2021, 43, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Du, X.; Yu, S. Discussions on collaborative development of comprehensive governance of Yellow River Estuary and ecological protection. China Water Resour. 2025, 7, 7–13+62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, F. Analysis of water ecological security and water resources intensive utilization strategies in Dongying. J. Party Sch. Shengli Oilfield 2023, 36, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, L.; Dou, S.; Wang, G.; Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Ji, Y.; Fan, Y. Study of the coordination relationship between the water capacity and the distribution of productive forces in the Yellow River Delta. China Water Resour. 2022, 16, 10–13. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Dong, B.; Liu, J. Current Status Evaluation and Protection Countermeasures of Groundwater Resources in Dongying City. Shandong Water Resour. 2021, 2, 75–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Li, C. A novel multidimensional framework for bridging conservation gaps and optimizing the system of natural reserves for biodiversity: A case study of Dongying, China. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 170, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y. Spatiotemporal Evolution of Land Subsidence and Mechanism Discussion in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ph.D. Thesis, Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Science, Qingdao, China, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, M. Study on the Protection and Utilization of Agricultural Heritage in Dongying City Under the Background of the Construction of Yellow River National Cultural Park. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University of Art & Design, Jinan, China, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Z.; Xing, L. Study on Dynamic Change Features of Wetlands in Dongying City Based on RS. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinfeng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Shiyi, Z.; Fenzhen, S. Coastal wetland degradation and ecosystem service value change in the Yellow River Delta, China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 44, e02501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y. Analysis of development trends in Shandong’s Dongying integration into the provincial capital economic circle. China Natl. Cond. Strength 2021, 5, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H. Research on the Transformation Path of Dongying’s Resource-Based City from the Perspective of Life Cycle Theory. Master’s Thesis, Shandong University, Jinan, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xia, J.; Zuo, Q.; Wu, Q. Research framework, key issues and prospects of the Human-Water Relationship in the Yellow River Basin. Yellow River 2025, 47, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; He, F.; He, G.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; Chang, H.; Zhu, Y. Review the phenomenon of Yellow River cutoff from a whole perspective and identification of current water shortage. Yellow River 2020, 42, 42–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Z.; Ma, Y.; Ren, G.; Zhang, H.; Wang, A.; Liu, Y.; Xu, M.; Hu, Y.; et al. Challenges to the ecological conservation and high-quality development of the Yellow River Delta and countermeasures for scientific and technological support. Mar. Sci. 2023, 47, 79–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. State Environmental Protection Agency of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 1997.
- Wang, S.; Lin, Y. Spatial evolution and its drivers of regional agro-ecological efficiency in China from the perspective of water footprint and grey water footprint. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2021, 41, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, M.; Tang, Z. Study on ecological compensation standards of water resources based on grey water footprint: A case of the Yangtze River economic belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 2553–2563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Z.K.H. Factorizing changes in energy and environmental indicators through decomposition. Energy 1998, 23, 489–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hou, B.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Wang, X. Evaluation of water resources utilization based on water footprint theory in Beijing. South-to-North Water Transf. Water Sci. Technol. 2021, 19, 680–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P. Virtual Water and Water Footprint; Higher Education Press: Beijing, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, L. Study on spatial convergence of grey water footprint intensity on provincial scale in China. J. Liaoning Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2017, 40, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Sun, C. Regional inequality and factor decomposition of the per capita grey water footprint in China. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2018, 38, 6314–6325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Wang, P.; Cao, W.; Fu, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Guo, J.; Huang, Z.; Chen, X. Long-term assessment of soil salinization patterns in the Yellow River Delta using landsat imagery from 2003 to 2021. Land 2024, 14, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiantian, C.; Jiahua, Z.; Sha, Z.; Yun, B.; Jingwen, W.; Shuaishuai, L.; Tehseen, J.; Xianglei, M.; Pangali, S.T.P. Monitoring soil salinization and its spatiotemporal variation at different depths across the Yellow River Delta based on remote sensing data with multi-parameter optimization. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 29, 24269–24285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Working Committee of Agricultural High-Tech Industry Demonstration Area of the Yellow River Delta of Shandong Province. Promoting high-quality development of agricultural high-tech industry demonstration area of the Yellow River Delta. Bull. Chin. Acad. Sci. 2020, 35, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yinshuai, L.; Chunyan, C.; Zhuoran, W.; Gengxing, Z. Upscaling remote sensing inversion and dynamic monitoring of soil salinization in the Yellow River Delta, China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 148, 110087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W. Study on the Influence of Modern Agricultural Industrial Structure Adjustment on Agricultural Economic Growth in Dongying City, Shandong Province. Master’s Thesis, Yangtze University, Jingzhou, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zeng, G. Spatial Organization of Innovation in the Oil Equipment Manufacturing Industry: Case of Dongying, China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2019, 30, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Zhi, X.; Meng, X.; Song, M. Path exploration and practical innovation for building a water-saving society in Dongying city. In Proceedings of the 2025 (9th) Conference on Efficient Water Use and Water-Saving Technologies in China, Yiwu, China, 27–29 May 2025; p. 5. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, P.; Sun, M.; Song, X. Study on the spatial and temporal dynamic evolution and driving factors of grey water footprint in China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2024, 33, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M. Decoupling Analysis of Water Resources and Economic Growth in Shanghai Based on Water Footprint. Master’s Thesis, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Q.; Sun, X.; Tang, L. Design of clay core wall weathered dam considering the deterioration of soft rock. Water Conserv. Constr. Manag. 2024, 44, 61–68+73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

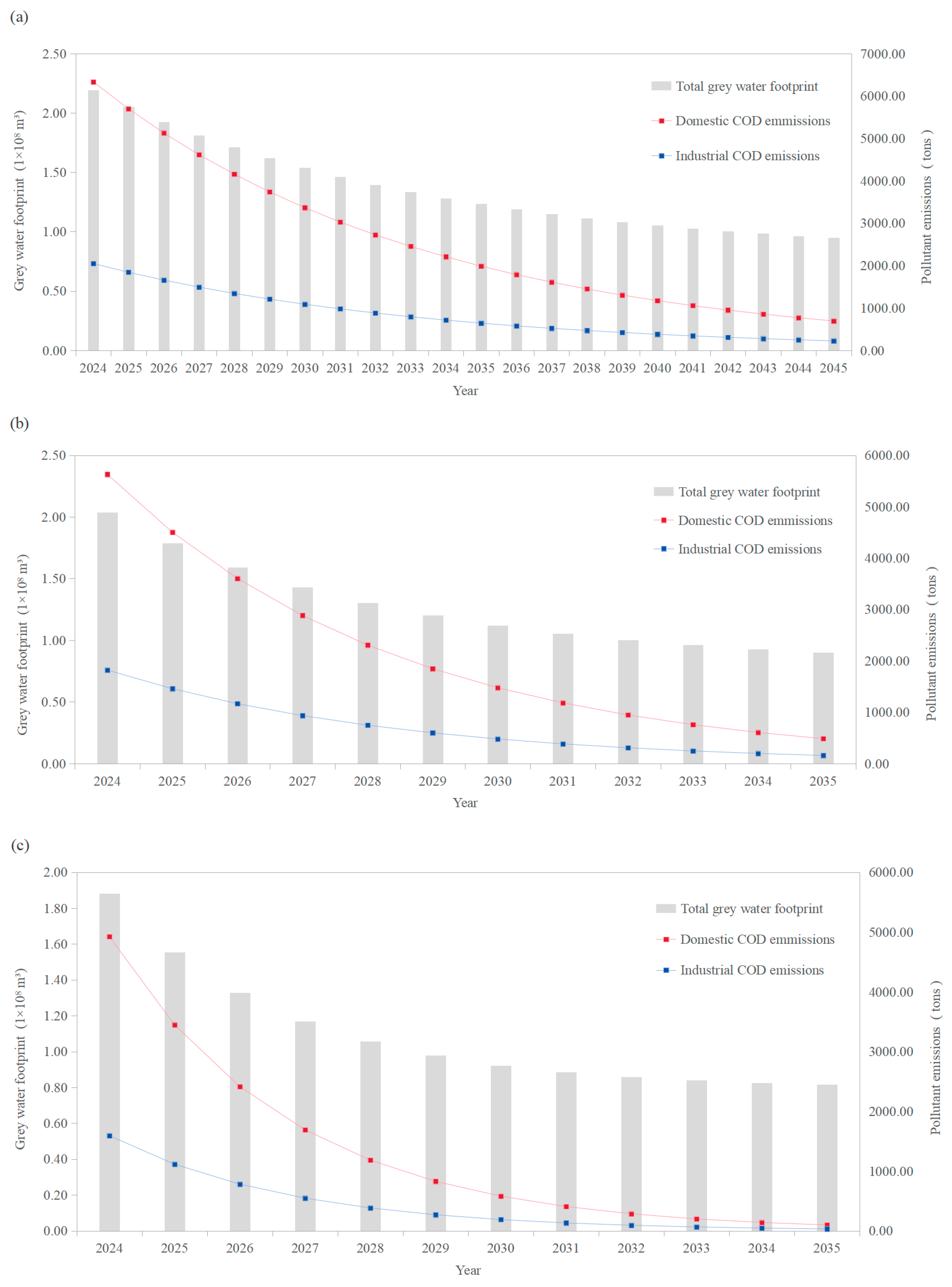
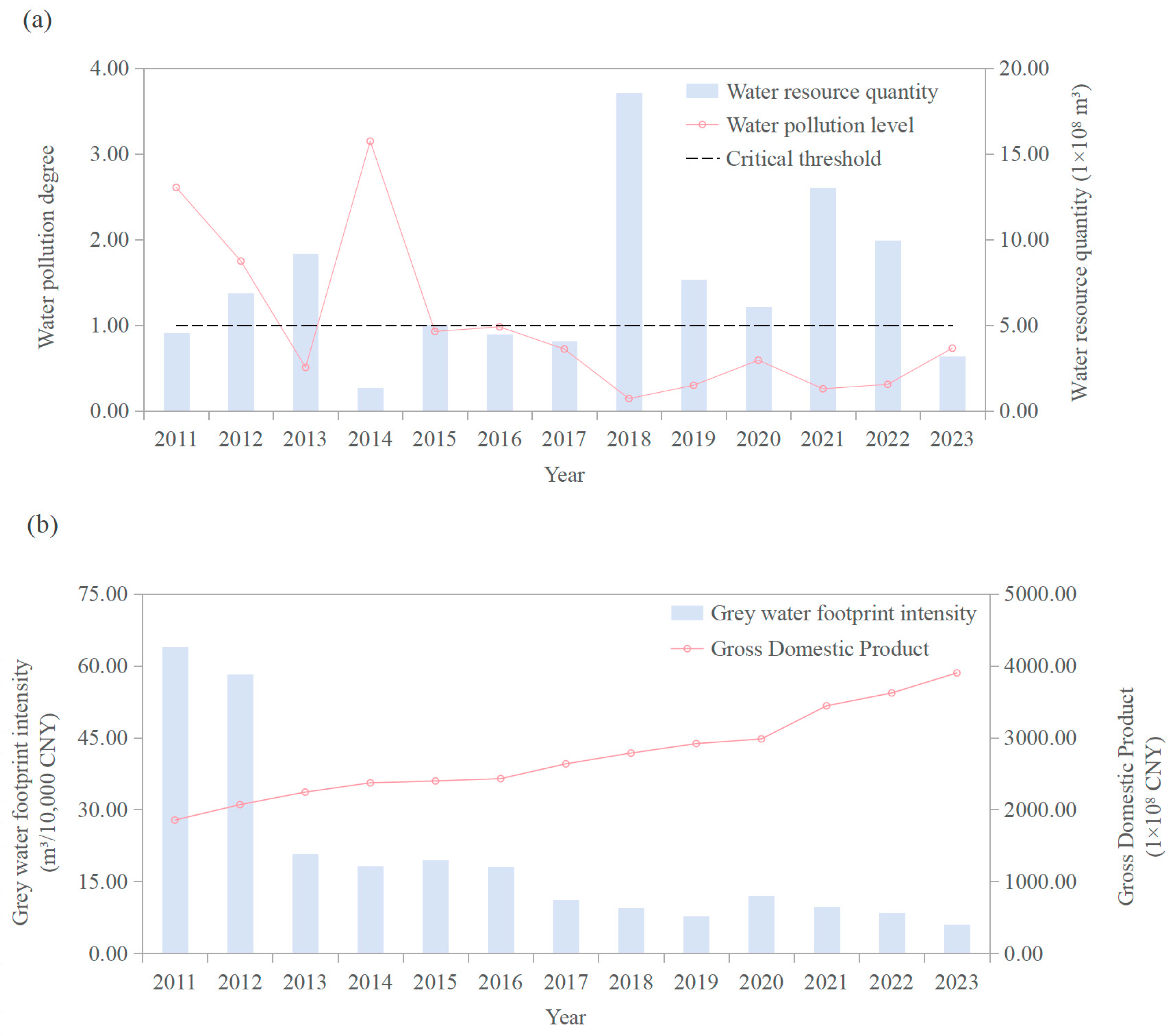
| Indicator | Correlation Coefficient (r) |
|---|---|
| Agricultural grey water footprint | 0.50 |
| Industrial grey water footprint | 0.82 ** |
| Domestic grey water footprint | 0.98 ** |
| Year | Population Effect | Economic Effect | Technical Effect | Total Effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2011–2012 | 0.10 | 1.21 | −1.13 | 0.18 |
| 2012–2013 | 0.05 | 0.58 | −8.01 | −7.39 |
| 2013–2014 | 0.03 | 0.22 | −0.60 | −0.35 |
| 2014–2015 | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.31 | 0.36 |
| 2015–2016 | 0.05 | 0.01 | −0.33 | −0.27 |
| 2016–2017 | 0.04 | 0.26 | −1.75 | −1.46 |
| 2017–2018 | 0.02 | 0.13 | −0.45 | −0.30 |
| 2018–2019 | 0.01 | 0.10 | −0.47 | −0.36 |
| 2019–2020 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 1.24 | 1.30 |
| 2020–2021 | 0.002 | 0.50 | −0.74 | −0.24 |
| 2021–2022 | 0.02 | 0.14 | −0.43 | −0.26 |
| 2022–2023 | −0.004 | 0.20 | −0.93 | −0.73 |
| Mean value | 0.03 | 0.29 | −1.11 | −0.79 |
| Standard deviation | 0.03 | 0.33 | 2.20 | 2.08 |
| Variation coefficient | 0.89 | 1.14 | −1.98 | −2.63 |
| Proportion | 2.08% | 20.08% | 77.84% | 100.00% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Meng, X.; Wu, J.; Lu, J.; Dou, W.; Chen, J.; Su, G.; Lin, J.; An, J. Analysis and Evaluation of Water Resources Status in Dongying Based on Grey Water Footprint Theory. Water 2026, 18, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010003
Meng X, Wu J, Lu J, Dou W, Chen J, Su G, Lin J, An J. Analysis and Evaluation of Water Resources Status in Dongying Based on Grey Water Footprint Theory. Water. 2026; 18(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleMeng, Xue, Jun Wu, Jian Lu, Wenjun Dou, Jie Chen, Guangyue Su, Jiazhou Lin, and Jianhao An. 2026. "Analysis and Evaluation of Water Resources Status in Dongying Based on Grey Water Footprint Theory" Water 18, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010003
APA StyleMeng, X., Wu, J., Lu, J., Dou, W., Chen, J., Su, G., Lin, J., & An, J. (2026). Analysis and Evaluation of Water Resources Status in Dongying Based on Grey Water Footprint Theory. Water, 18(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/w18010003







