Enhanced Nitrification of High-Ammonium Reject Water in Lab-Scale Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBRs)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reject Water Chemical Characteristics
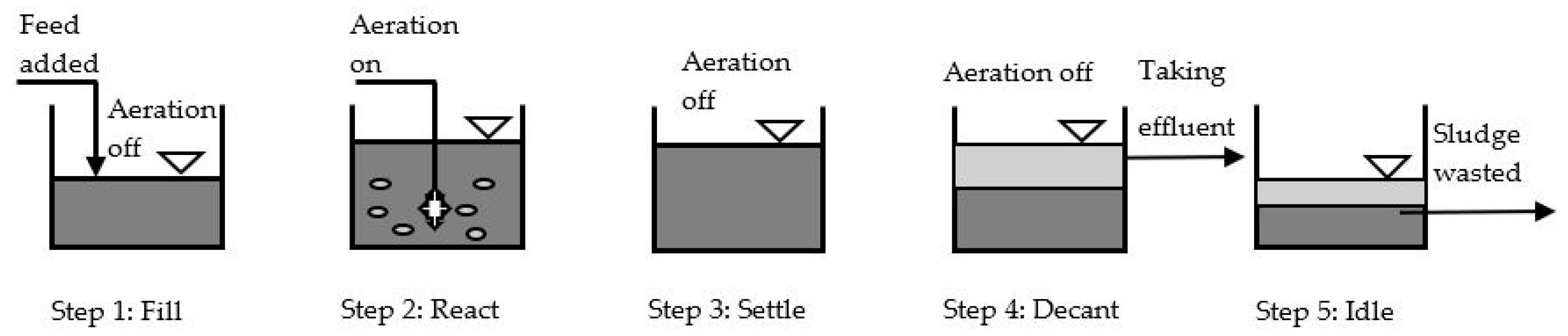
2.2. Nitrification Reactor Configuration and Operating Principle
2.3. Operation of Reactors
2.4. Analytical Procedures
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
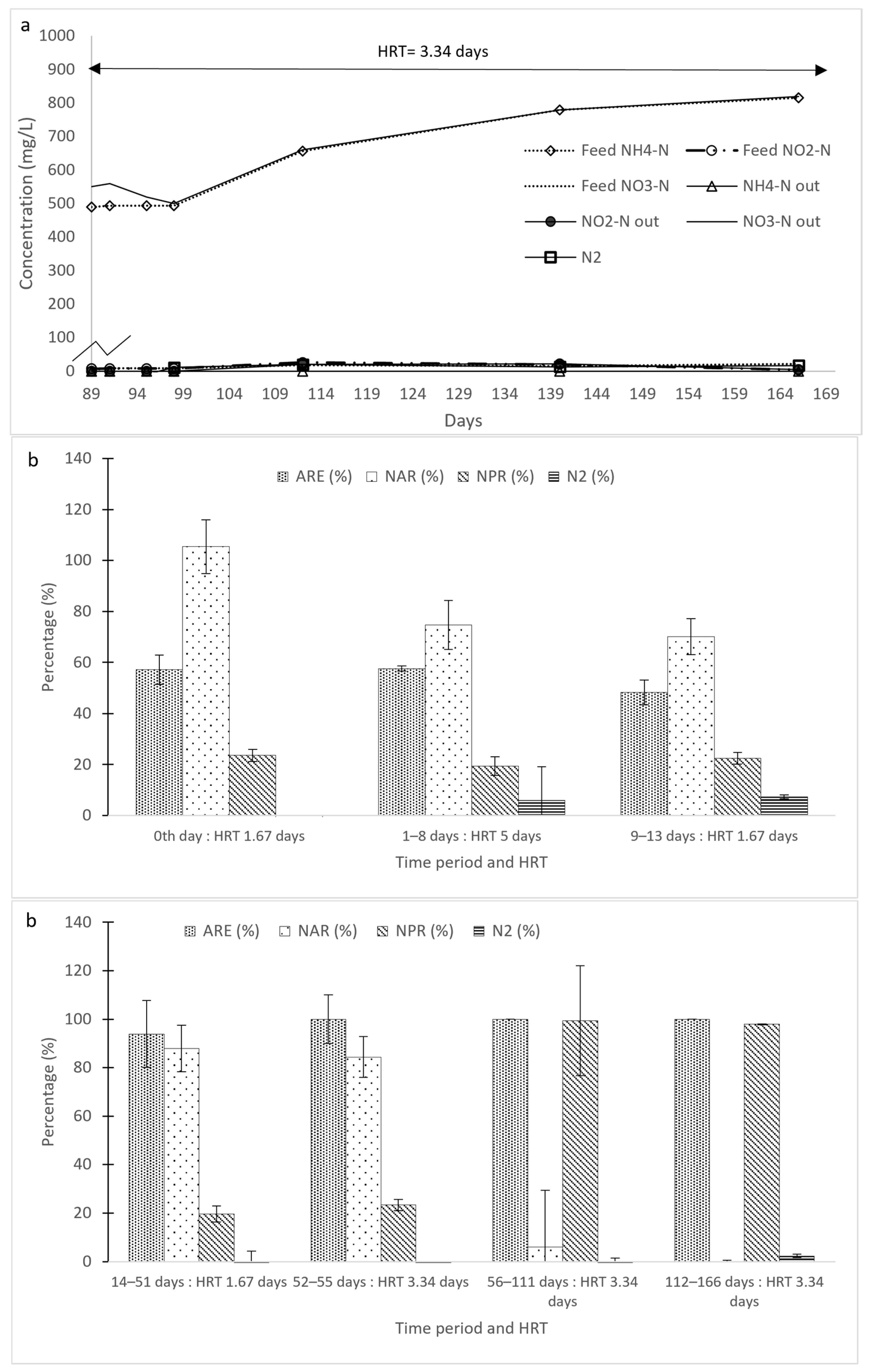
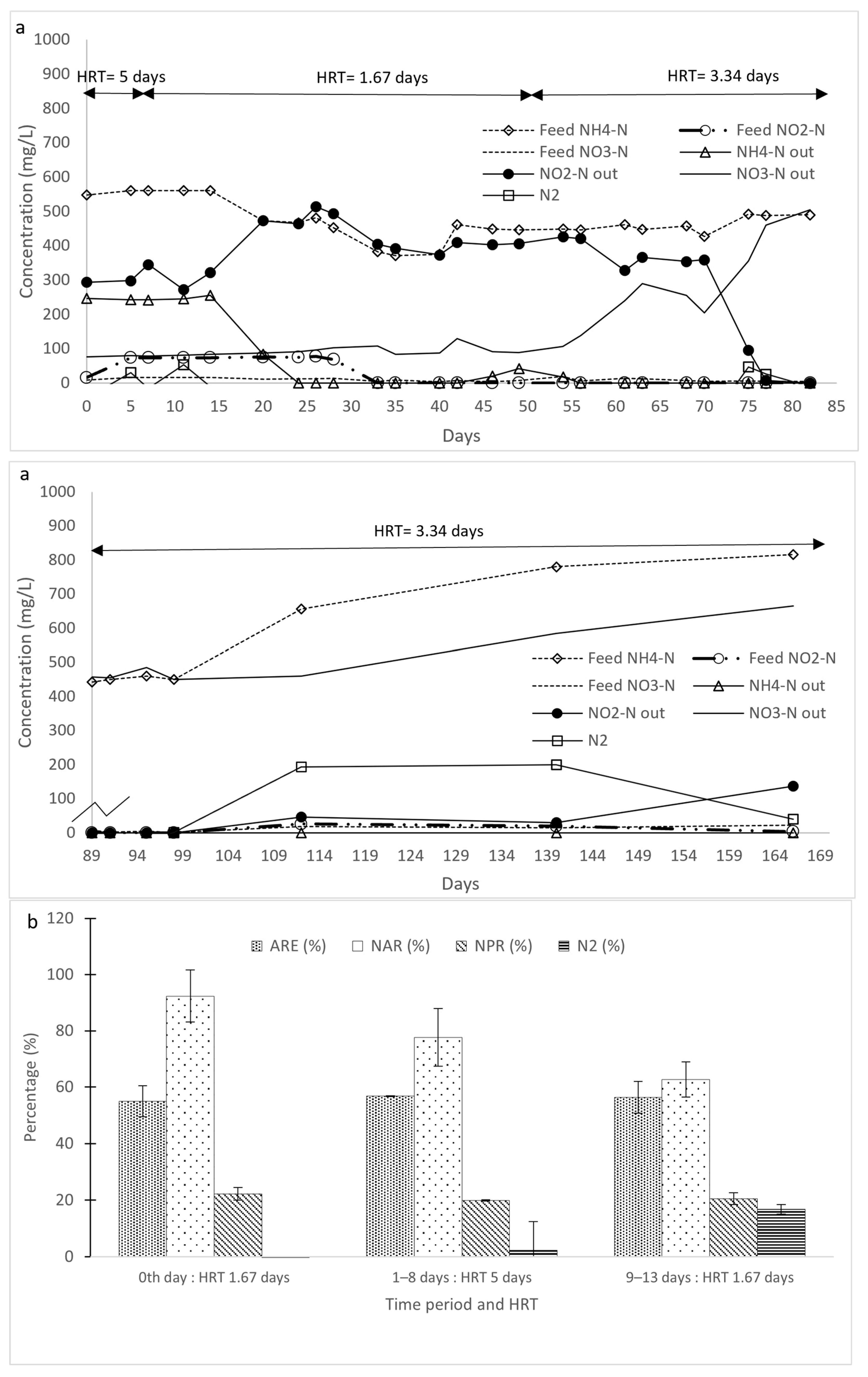
3.1. Initial Ammonium Transformation in Reactors R1 and R2
3.2. Change in Operational Conditions in Reactors R1 and R2
3.2.1. Effect of NLR Reduction
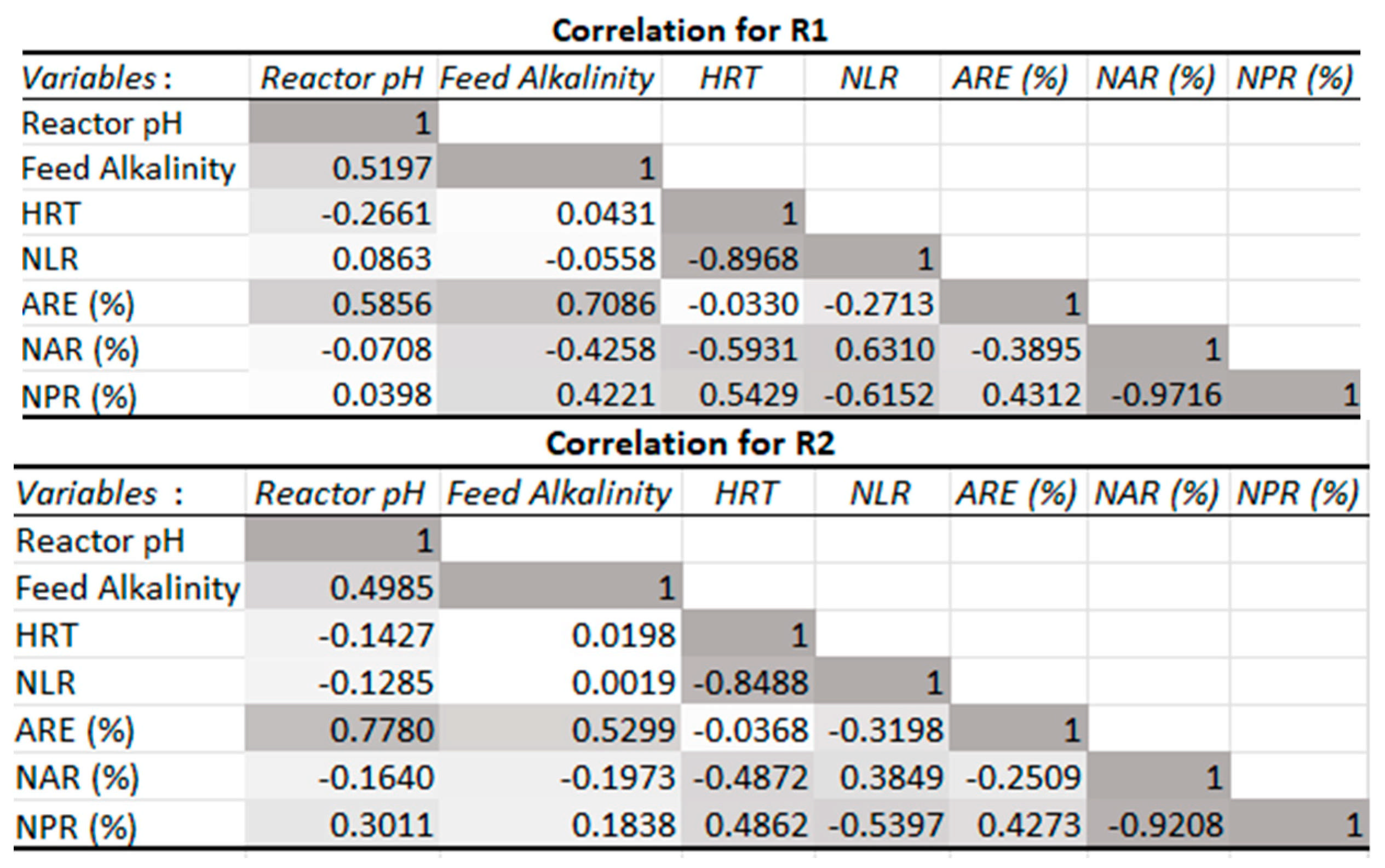
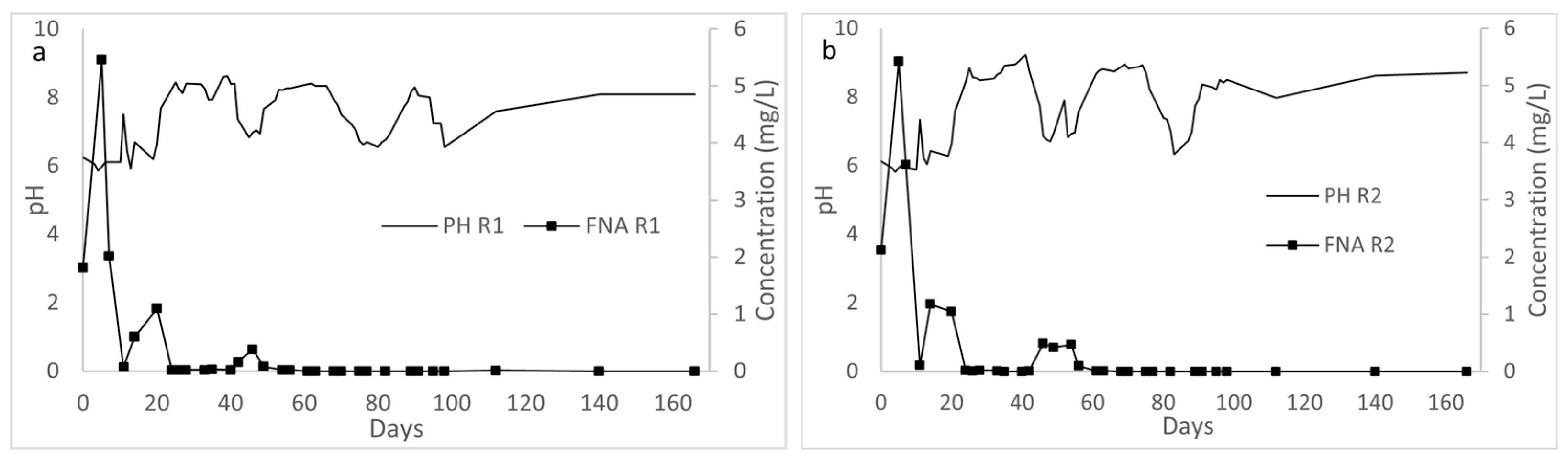
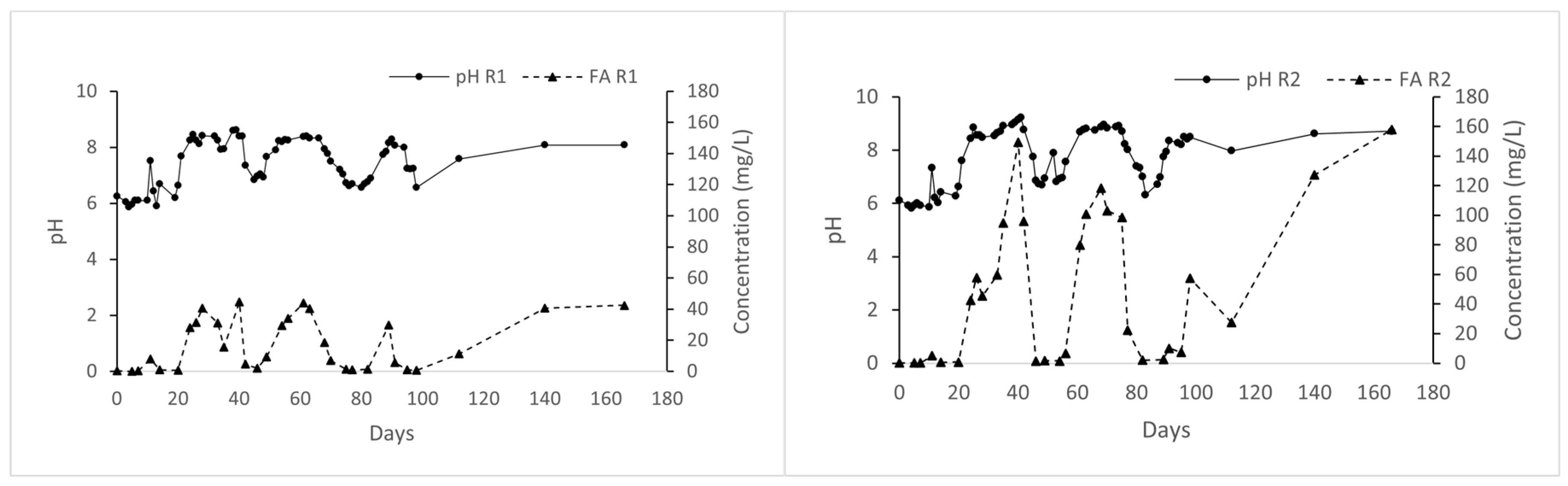
3.2.2. Effect of pH and Alkalinity Concentration
3.2.3. Chemical Oxygen Demand-to-Nitrogen (COD/N) Ratio
3.2.4. Combined Effect of Reduced NLR and Longer HRT
3.3. Cost-Benefit Insights on the Feasibility of Nitrification
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Botheju, D.; Svalheim, O.; Bakke, R. Digestate Nitrification for Nutrient Recovery. Open Waste Manag. J. 2010, 3, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Hoek, J.; Duijff, R.; Reinstra, O. Nitrogen Recovery from Wastewater: Possibilities, Competition with Other Resources, and Adaptation Pathways. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernet, N.; Delgenes, N.; Akunna, J.C.; Delgenès, J.-P.; Moletta, R. Combined Anaerobic–Aerobic SBR for the Treatment of Piggery Wastewater. Water Res. 2000, 34, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, N.; Cesaro, A.; Di Capua, F.; Esposito, G. Exploiting the Nutrient Potential of Anaerobically Digested Sewage Sludge: A Review. Energies 2021, 14, 8149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, T.T.H.; Fettig, J.; Meon, G. Kinetics and Simulation of Nitrification at Various pH Values of a Polluted River in the Tropics. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2019, 19, 54–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindasamy, P.; Muthusamy, S.K.; Bagavathiannan, M.; Mowrer, J.; Jagannadham, P.T.K.; Maity, A.; Halli, H.M.; G.K., S.; Vadivel, R.; T.K., D.; et al. Nitrogen Use Efficiency—A Key to Enhance Crop Productivity under a Changing Climate. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1121073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, C.; Cao, H.; Liang, J.; Pei, S.; Li, Z. Nitrate Absorption and Desorption by Biochar. Agronomy 2023, 13, 2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellali, S.; El-Bassi, L.; Charabi, Y.; Usman, M.; Khiari, B.; Al-Wardy, M.; Jeguirim, M. Recent Advancements on Biochars Enrichment with Ammonium and Nitrates from Wastewaters: A Critical Review on Benefits for Environment and Agriculture. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 305, 114368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, N.; Kammann, C.I.; Schmidt, H.-P.; Kappler, A.; Behrens, S. Nitrate Capture and Slow Release in Biochar Amended Compost and Soil. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Gu, X.; Liang, R.; Ban, G.; Ma, L.; He, T.; Wang, Z. Comparing Combined Application of Biochar and Nitrogen Fertilizer in Paddy and Upland Soils: Processes, Enhancement Strategies, and Agricultural Implications. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 933, 173160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchobanoglous, G.; Burton, F.L.; Stensel, H.D. Wastewater Engineering: Treatment and Reuse, 4th ed.; Inc. Metcalf & Eddy, Ed.; McGraw-Hill Series in Civil and Environmental Engineering; McGraw-Hill: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; ISBN 978-0-07-041878-3. [Google Scholar]
- Karmann, C.; Mágrová, A.; Jeníček, P.; Bartáček, J.; Kouba, V. Advances in Nitrogen Removal and Recovery Technologies from Reject Water: Economic and Environmental Perspectives. Bioresour. Technol. 2024, 391, 129888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Li, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S.; Wan, Y.; Yu, H. Fast Start-up of Partial Nitrification for High-Ammonia Wastewater Treatment Using Zeolite with in-Situ Bioregeneration. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 59, 105077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive-EU-2024/3019-EN-EUR-Lex. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/dir/2024/3019/oj/eng (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Anthonisen, A.C.; Loehr, R.C.; Prakasam, T.B.S.; Srinath, E.G. Inhibition of Nitrification by Ammonia and Nitrous Acid. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1976, 48, 835–852. [Google Scholar]
- THE 17 GOALS|Sustainable Development. Available online: https://sdgs.un.org/goals (accessed on 13 April 2025).
- Sivalingam, V.; Ahmadi, V.; Babafemi, O.; Dinamarca, C. Integrating Syngas Fermentation into a Single-Cell Microbial Electrosynthesis (MES) Reactor. Catalysts 2020, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dohare, E.D.; Bochare, E.P. Sequential Batch Reactors: Taking Packaged Wastewater Treatment to New Heights—A Review. Int. J. Civ. Eng. Technol. IJCIET 2014, 5, 131–138. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Eaton, A.D., Franson, M.A.H., Eds.; APHA-AWWA-WEF: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0-87553-047-5. [Google Scholar]
- Analytical Procedures and Appendices Spectroquant Prove 300. Available online: https://chem.eng.psu.ac.th/new_chem/upload/manual/144/SQ%20Prove%20300%20-%20Analytical%20Procedures%20and%20Appendices%202017-07%20(1).pdf (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Wu, J.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y.; Su, H.; Hu, X.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wen, G. Impact of Organic Carbons Addition on the Enrichment Culture of Nitrifying Biofloc from Aquaculture Water: Process, Efficiency, and Microbial Community. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janka, E.; Pathak, S.; Rasti, A.; Gyawali, S.; Wang, S. Simultaneous Heterotrophic Nitrification and Aerobic Denitrification of Water after Sludge Dewatering in Two Sequential Moving Bed Biofilm Reactors (MBBR). Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdolvand, Y.; Sadeghiamirshahidi, M.; Keenum, I. Denitrification Processes, Inhibitors, and Their Implications in Ground Improvement. Biogeotechnics 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, S.; Han, X.; Gan, Y.; Wu, C.; Peng, Y. Evaluating the Effects of Nitrogen Loading Rate and Substrate Inhibitions on Partial Nitrification with FISH Analysis. Water Sci. Technol. 2012, 65, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, O.; Bernet, N.; Delgenès, J.-P. Effect of Dissolved Oxygen Concentration on Nitrite Accumulation in Nitrifying Sequencing Batch Reactor. Water Environ. Res. 2007, 79, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusof, N.; Hassan, M.; Phang, L.-Y.; Tabatabaei, M.; Othman, M.R.; Mori, M.; Wakisaka, M.; Sakai, K.; Shirai, Y. Nitrification of Ammonium-Rich Sanitary Landfill Leachate. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) Nitrification. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/nitrification_1.pdf (accessed on 3 March 2025).
- Biesterfeld, S.; Farmer, G.; Russell, P.; Figueroa, L. Effect of Alkalinity Type and Concentration on Nitrifying Biofilm Activity. Water Environ. Res. 2003, 75, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Liu, S.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Z. Analysis of Nitrification Efficiency and Microbial Community in a Membrane Bioreactor Fed with Low COD/N-Ratio Wastewater. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phanwilai, S.; Noophan, P.; Li, C.-W.; Choo, K.-H. Effect of COD:N Ratio on Biological Nitrogen Removal Using Full-Scale Step-Feed in Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants. Sustain. Environ. Res. 2020, 30, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Peng, D.-C. Nitrite Oxidizing Bacteria (NOB) Dominating in Nitrifying Community in Full-Scale Biological Nutrient Removal Wastewater Treatment Plants. AMB Express 2017, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, Z.; Guan, Q. Effect of Free Ammonia Inhibition on NOB Activity in High Nitrifying Performance of Sludge. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 31987–31995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqeel, H.; Liss, S.N. Autotrophic Fixed-Film Systems Treating High Strength Ammonia Wastewater. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 551925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Yang, T.; Zhang, M.; Li, A.; Huang, D.; Xing, Z. Effect of HRT on Nitrogen Removal from Low Carbon Source Wastewater Enhanced by Slurry and Its Mechanism. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 477, 147159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzioli, F.; Bertasini, D.; Bolzonella, D.; Frison, N.; Battista, F. A Critical Review on the Techno-Economic Feasibility of Nutrients Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate in the Agricultural Sector. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2023, 306, 122690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhelal, I.I.; Loetscher, L.H.; Sharvelle, S.; Reardon, K.F. Nitrogen Recovery from Anaerobic Digestate via Ammonia Stripping and Absorbing with a Nitrified Solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 107826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, I.-T.; Lee, Y.-E.; Jeong, Y.; Yoo, Y.-S. A Novel Method to Remove Nitrogen from Reject Water in Wastewater Treatment Plants Using a Methane- and Methanol-Dependent Bacterial Consortium. Water Res. 2020, 172, 115512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Parameter | Value | Units |
|---|---|---|
| Total chemical oxygen demand (tCOD) | 3000 (±545) | mg/L |
| Soluble chemical oxygen demand (sCOD) | 1940 (±375) | mg/L |
| pH | 7.6 (±0.1) | |
| NH4-N | 520 (±55) | mg/L |
| Alkalinity | 2220 (±305) | mg CaCO3/L |
| Vitamin Constituent (g/L) | Mineral Constituent (g/L) |
|---|---|
| Nicotinic acid: 0.05 | H3BO3: 0.05 |
| Pantothenic acid: 0.05 | FeSO4·7H2O: 2.7 |
| Biotin: 0.02 | ZnSO4·7H2O: 0.088 |
| Riboflavin: 0.05 | CuSO4·5H2O: 0.055 |
| Thioctic acid: 0.05 | MnSO4·H2O: 0.04 |
| Pyridoxine hydrochloride: 0.1 | CoCl2·6H2O: 0.05 |
| p-aminobenzoic acid: 0.05 | NiCl2·6H2O: 0.1 |
| Vitamin B12: 0.001 | - |
| Folic acid: 0.02 | - |
| Thiamine: 0.05 | - |
| Parameters | R1 | R2 | Units |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor volume | 2.1 | 0.96 | L |
| Internal diameter | 4.2 | 3 | cm |
| Height | 151.5 | 136.5 | cm |
| Working volume | 1.47 | 0.68 | L |
| Parameters | Operation Period in Days | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 1–8 | 9–13 | 14–51 | 52–111 | 112–166 | |
| Feeding rate (%) | 20 | 20 | 30 | 30 | 30 | 30 |
| Feeding/day | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| HRT (day) | 1.67 | 5 | 1.67 | 1.67 | 3.34 | 3.34 |
| NLR (kg/m3·d) | 0.33 | 0.11 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.03 | 0.28 ± 0.01 | 0.14 ± 0.01 | 0.23 ± 0.03 |
| Alkalinity (mg CaCO3/L) | 1920 | 1980 ± 200 | 1980 ± 200 | 3200 ± 125 | 3190 ± 210 | 5215 ± 465 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gyawali, S.; Janka, E.; Dinamarca, C. Enhanced Nitrification of High-Ammonium Reject Water in Lab-Scale Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBRs). Water 2025, 17, 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091344
Gyawali S, Janka E, Dinamarca C. Enhanced Nitrification of High-Ammonium Reject Water in Lab-Scale Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBRs). Water. 2025; 17(9):1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091344
Chicago/Turabian StyleGyawali, Sandeep, Eshetu Janka, and Carlos Dinamarca. 2025. "Enhanced Nitrification of High-Ammonium Reject Water in Lab-Scale Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBRs)" Water 17, no. 9: 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091344
APA StyleGyawali, S., Janka, E., & Dinamarca, C. (2025). Enhanced Nitrification of High-Ammonium Reject Water in Lab-Scale Sequencing Batch Reactors (SBRs). Water, 17(9), 1344. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091344








