1. Introduction
Digital Twin (DT) technology has been increasingly utilized across various sectors to create virtual models of physical systems for monitoring, simulation, and optimization. In the context of maritime communication and environmental monitoring, Digital Twins, particularly Underwater Digital Twins (UDTs), offer a powerful tool to enhance the management and protection of coastal ecosystems.
Virtual representations of real-world habitats, such as undersea ecosystems, are produced in marine surveillance through Digital Twins. The data from sensors installed in Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) is used to create these virtual models, which aid in real-time monitoring and simulation of changes. This real-time virtual model may enhance decision-making, and environmental hazards like pollution or tsunamis can be addressed more quickly. Digital Twins combine information from several sensors into a single model that is updated continuously in response to new sensor data, giving an accurate and dynamic depiction of the surroundings. At the core of Digital Twin systems, especially underwater, sensors gather essential data regarding environmental factors such as water temperature, salinity, current velocity, tide heights, and atmospheric conditions. This information is sent to the Digital Twin, where it is analyzed and utilized to refresh the virtual representation of the marine surroundings. The combination of sensors and Digital Twins offers significant advantages, such as real-time monitoring, for observing swiftly evolving situations in dynamic coastal regions. Moreover, by gathering extensive data, Digital Twins provide improved precision in comprehending environmental conditions, while machine learning techniques, such as CosLU-VS-LSTM, aid in identifying anomalies and producing predictive insights regarding possible risks. To manage large volumes of sensor data and maintain security, methods like Sliding–Huffman Coding (SHC) for compressing data and Twisted Koblitz Curve Cryptography (TKCC) for safeguarding data are used, guaranteeing effective transmission while preserving data integrity. In conclusion, sensors are essential for collecting real-time environmental data for Digital Twin systems. These utilize these data to develop comprehensive virtual models supporting informed maritime surveillance and conservation decision-making. The collaboration between sensors and Digital Twins improves maritime activities, leading to improved risk management and faster responses to irregularities, and aiding in the sustainability of coastal ecosystems. The Coromandel Coast represents the southeastern coastal area of the Indian subcontinent, functioning as a vital corridor for maritime activities [
1]. These activities encompass naval operations, environmental protection, maritime surveillance, fishing, and more [
2,
3]. To ensure both safety and sustainability, there is a pressing need for an advanced maritime communication and monitoring system [
4].
Nevertheless, the intricate underwater environment presents significant challenges for monitoring maritime conditions [
5]. To assess the risks beneath the surface, Digital Twins—a virtual representation—facilitate an information exchange process that supports effective decision-making [
6,
7]. By merging the underwater sensor network with Digital Twins [
8], real-time environmental changes can be accurately detected [
9], and timely risk alerts can be issued, particularly in ecologically sensitive areas such as the Coromandel Coast.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) significantly enhances the functionality of Digital Twins [
10]. Deep Learning models effectively identify and analyze patterns within sensor data [
11]. Furthermore, AI facilitates improved maritime communication by transmitting acoustic signals to the Maritime Alert Command Centre (MACC) [
12].
Syed et al. [
13] reviewed AI techniques in water resource management, identifying gaps in their integration for better prediction and management. They covered methods like ANN, DL, LSTM, ML models, and RF. The authors proposed a novel framework that combines these approaches with a Digital Twin and multi-modal transformer to improve prediction accuracy and efficiency. This sets the foundation for a future detailed model that could enhance water demand forecasting and support global sustainability in water use. Moreover, this work supports our research by proposing a unified AI framework that integrates various techniques to enhance prediction accuracy and operational efficiency in water resource management. This aligns with our goal of improving forecasting methods.
The popularity of Artificial Intelligence and Digital Twins has surged in recent years, leading to their application across various domains for numerous scenarios.
Epiphaniou et al. [
14] assessed the enhancement of cyber resilience in Internet of Things (IoT) applications by implementing Digital Twins within underwater ecosystems. The underwater parameters were optimized using a Genetic Algorithm (GA). Subsequently, anomalies in the sensor data were predicted by employing a Support Vector Machine (SVM). This approach improved cyber security resilience for underwater coastal monitoring; however, the subpar quality of the data resulted in an ineffective resilience strategy.
Bi et al. [
15] focused on the development of Digital Twins to monitor intricate coastal terrains. This study integrated IoT sensor data collected from underwater environments into the Digital Twin framework. The monitoring and early warning systems were established by transmitting these data to a neural network algorithm. This facilitated timely interventions based on the alerts generated. Nonetheless, the integration of multiple sensors introduced complexities to the model. The proposed Underwater Digital Twin (UDT) sensor network offers an innovative maritime communication and monitoring system, distinguishing itself from existing networks and AI frameworks. Its key advantage lies in the advanced AI integration, specifically the Exponential Hyperbolic Crisp Adaptive Network-based Fuzzy Inference System (EHC-ANFIS), which excels in decision-making processes. The system utilizes the CosLU-VS-LSTM method for anomaly detection, surpassing traditional models in precision and accuracy. Epiphaniou et al. [
14] and Bi et al. [
15] struggle with complexity and data handling; this model addresses these challenges through efficient data compression, optimized communication paths, and enhanced security. This ensures reliable and secure communication in the demanding underwater environments of the Coromandel Coast, improving ecosystem monitoring.
Zhou et al. [
16] implemented a tsunami monitoring system in coastal areas utilizing Digital Twins. This system was designed to detect variations in the underwater marine ecosystem. The Wavelet Transform technique was employed to identify waveforms specific to tsunamis. Anomalies in the sensor data were subsequently detected using a threshold-based method. This buoy-based system enabled a quicker response; however, the prevalence of false positives increased due to background marine noise, leading to inaccurate alerts.
Wang et al. [
17] introduced a model for safety management and decision support in port operations and logistics, utilizing a Digital Twin framework. This model integrates a hybrid approach combining Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Long Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks to facilitate decision-making within the Digital Twin paradigm. The framework enhances safety measures, thereby decreasing the probability of accidents. Nonetheless, it faced limitations in managing large datasets.
Zhou et al. [
18] proposed a Digital Twin-based smart maritime logistics maintenance system aligned with Industry 5.0. The initial phase involved the deployment of sensors to collect real-time data. Subsequently, features were extracted from these data and input into neural networks. The deep learning models generated optimal decisions to enhance the reliability of the Digital Twin systems. However, this approach exhibited significant computational complexity.
Charpentier et al. [
19] focused on creating a safer and more efficient maritime industry by implementing 5G and advanced edge computing systems. Their research utilized edge network softwarization and intelligence to develop applications that improve the safety and efficiency of maritime operations. This model streamlined the creation of intricate 5G vertical services and beyond and encouraged collaboration among industry stakeholders, network specialists, and EdgeApp developers. However, deploying this model in challenging maritime environments characterized by saltwater and high humidity proved difficult.
Adityawan et al. [
20] investigated a tsunami early warning system along the coast that utilizes maritime wireless communication. This system integrated communication between vessels at sea and coastal radio stations. The ships involved in this framework were outfitted with Very High Frequency (VHF) radio communication technology. The model effectively transmitted warning messages promptly and did not necessitate ongoing maintenance or monitoring. However, the study identified a restricted communication range, especially in isolated or challenging coastal areas, which resulted in connectivity challenges.
Current research on environmental monitoring in maritime settings has largely neglected data security, impacting coastal area monitoring efficacy. To enhance cybersecurity, data encryption from sensors is vital. Furthermore, existing studies inadequately address the dynamic environmental conditions necessary for risk prediction in coastal systems. Noteworthy shortcomings include the lack of inquiry into coastal ecosystem monitoring in light of variable conditions influenced by Digital Twins, the vulnerability of underwater sensor networks to cyber threats, insufficient analysis of unusual data spikes and unauthorized requests that impede monitoring, bandwidth limitations in underwater communication affecting data processing, and excessive energy use by traditional communication protocols.
Wang et al. [
21] proposed a blind channel estimation method for FBMC/OQAM systems that avoids using preambles, thereby improving spectral efficiency. The technique enhances estimation accuracy by leveraging spatial diversity to introduce data redundancy, especially at high SNRs. Simulation results demonstrate its superior performance over traditional preamble-based methods. However, this work supports our research by offering a highly efficient blind channel estimation approach to enhance the spectral efficiency and accuracy of underwater Digital Twin sensor networks in maritime communication systems using EHC-ANFIS. This reference is relevant to underwater communication channel estimation, offering potential improvements in data transmission for maritime sensor networks. Increasing spectral efficiency and estimation accuracy through blind methods and spatial diversity supports more reliable and efficient communication in challenging underwater environments.
Table 1 presents a comparative analysis of the proposed model against existing studies, highlighting its objectives, benefits, and drawbacks.
The proposed model demonstrated remarkable efficiency in maritime communication and monitoring of the Coromandel Coast, yielding superior results. In contrast, the existing model by Ramírez-Herrera et al. [
22] exhibited a high false alarm rate, while the approach by Pribadi et al. [
23] was burdened with significant initial setup costs. Additionally, the traditional method outlined by Suppasri et al. [
24] proved to be less effective due to its complex system. Furthermore, the models presented by Epiphaniou et al. [
14] and Zhou et al. [
16] achieved only limited performance. Therefore, the proposed framework surpasses the current adopted techniques.
Consequently, a framework is proposed to enhance the Underwater Digital Twins Sensor Network (UDTSN), thereby supporting coastal ecosystems’ sustainable management and protection. The proposed framework offers several significant contributions.
- -
It facilitates the monitoring of the Coromandel Coast through a Digital Twin-based decision-making process that employs the AI-driven EHC-ANFIS technique.
- -
It safeguards the underwater sensor data within the maritime ecosystem by implementing the TKCC method.
- -
It enables the analysis of anomalous patterns during data transmission through the Anomaly Detection System (ADS) model, utilizing the CosLU-VS-LSTM deep learning classifier.
- -
To ensure efficient data transmission within a static bandwidth, data compression is used using the SHC model.
- -
Lastly, it identifies the optimal path for data transmission to enhance communication efficiency by employing the AP-ACO technique.
The remaining paper is arranged as follows:
Section 2 analyzes the existing works,
Section 3 explains the proposed coastal monitoring system,
Section 4 describes the performance of the proposed model, and
Section 3 concludes the research paper with future recommendations.
2. Materials and Methods: Maritime Communication and Monitoring Methodology
This paper addresses the security of underwater sensor data and conducts maritime communication and monitoring in relation to the dynamic environmental conditions of the Coromandel Coast.
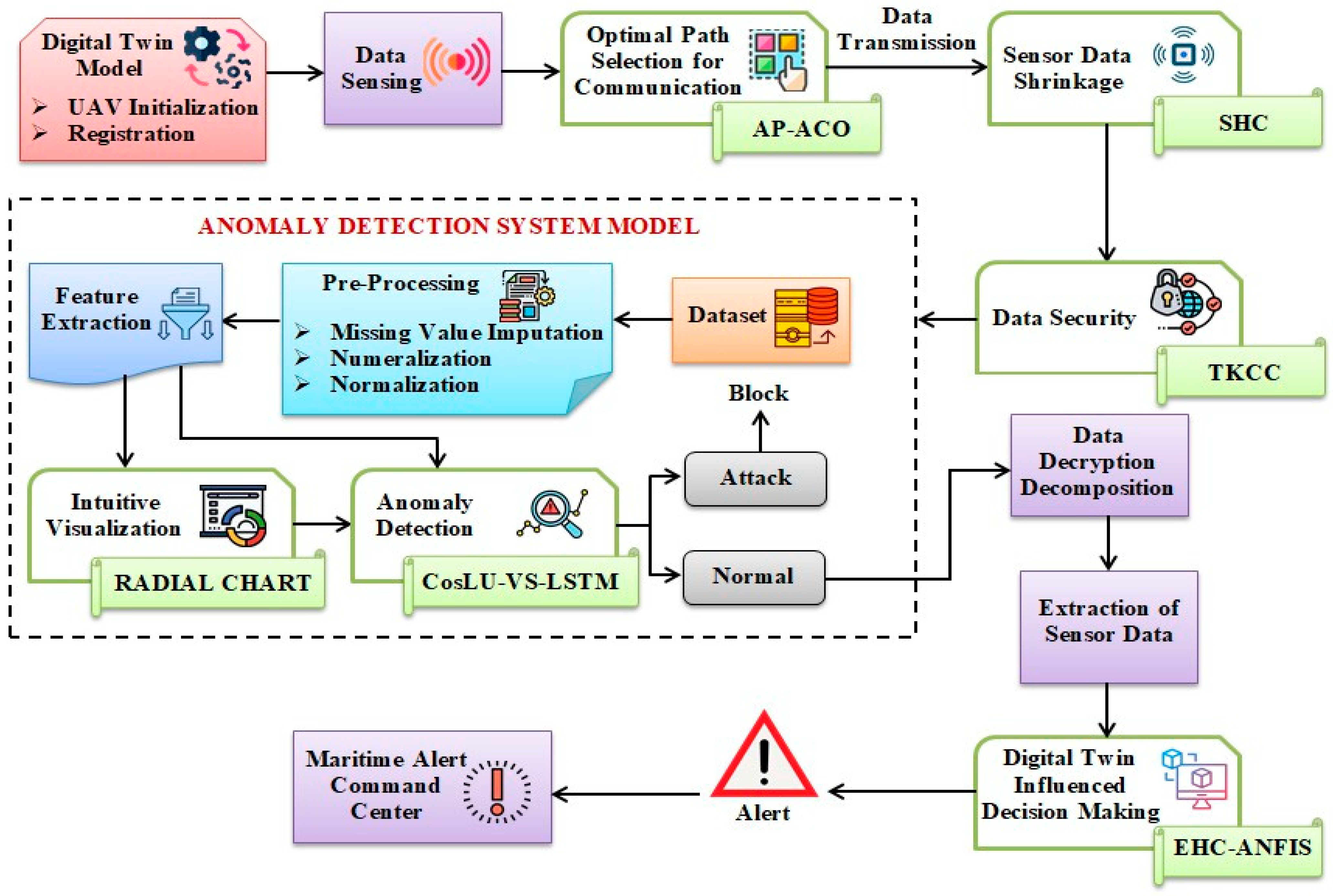
Figure 1 depicts the block diagram representing the proposed work.
2.1. UAV Initialization and Registration
The maritime communication and monitoring of the Coromandel Coast starts with the initialization of the AUV (
B) and is given by the following:
where (
s) is the number of AUVs. Next, AUVs are registered into the UDTSN with the AUV identity number and initial Global Positioning System (GPS) coordinates. After registration, by utilizing Digital Twins, the replica of an AUV is created, which helps in the navigation of AUVs underwater without collision.
2.2. Data Sensing
The underwater sensor data (
H), which includes parameters such as tide level, current speed, wind speed, water temperature, and salinity—collectively referred to as Internet of Things (IoT) data—are acquired by the Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) (
B). Wind speed and other environmental factors, including tide levels, current speed, water temperature, and salinity, are measured by the underwater sensor network, which also includes an Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV). These data are gathered by the sensors and sent to a monitoring system for evaluation and decision-making, including possible notifications for ecosystem monitoring and marine communication. This is represented as follows:
where (
j) is the number of data points sensed using the AUV. The number of data points sensed by the Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV), with “
j” representing the total count of these measurements, such as tide levels, wind speed, and other environmental factors.
2.3. Optimal Path Selection for Communication
To enhance the communication of the Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV) via the Underwater Delay Tolerant Sensor Network (UDTSN) to the Maritime Alert Command Centre (MACC), the optimal transmission path for (H) is determined using Adaptive Pheromone Ant Colony Optimization (AP-ACO).
This method leverages Ant Colony Optimization, which adapts to dynamic environments for real-time pathfinding. However, it is noted that ACO exhibits slow convergence in extensive spaces. Consequently, an Adaptive Pheromone (AP) distribution function is employed during the exploration phase. The Adaptive Pheromone Ant Colony Optimization (AP-ACO) technique, derived from the classical Ant Colony Optimization (ACO) algorithm, is adapted in this study to optimize communication paths within an Underwater Digital Twin Sensor Network (UDTSN). Traditional ACO, inspired by the foraging behavior of ants, is known for pathfinding in large and dynamic spaces. However, the AP-ACO method introduces an Adaptive Pheromone distribution function that adjusts pheromone levels more effectively, improving the convergence speed, which is crucial in underwater sensor networks with fluctuating environmental conditions and bandwidth constraints. The algorithm is tailored to address the unique challenges of real-time ecological monitoring by continuously adjusting pheromone levels during the exploration phase, ensuring efficient identification of optimal communication paths between Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and the Maritime Alert Command Centre (MACC). This adaptation enhances the performance of the ACO algorithm by enabling faster convergence, making it more suitable for underwater networks where traditional ACO might struggle with slow convergence in large, dynamic environments. While the AP-ACO technique itself is not novel, its specific application for underwater communication systems in this study represents a novel use of ACO in a complex and dynamic environment, improving communication efficiency for real-time maritime monitoring systems. The AP-ACO process is elaborated as follows.
The initial position (
R) of the communication paths (ant) in UDSTN is initialized as follows:
where (
ubR !
lbR) are the upper bound and lower bound values of (
R), and (α) is the random number. Next, the fitness function (ℑ) that determines the best path is evaluated regarding the minimum response time (
I) as follows:
Now, the position of the ants regarding the search for food using exploration and exploitation is updated. During the exploration phase, the ants release pheromones, which influence the selection of their paths. In this context, the parameter AP (δ), which determines a more effective starting point and enhances convergence, is defined as follows:
where (
g) is the pheromone level, (β) is the pheromone evaporation rate, and (χ) is the heuristic value. Now, the new position (
R′) of ants regarding (δ) is updated as follows:
Next, during the local update (exploitation phase), the ants encourage other ants to choose (δ); thus, the updated position (
) is equated by the following:
Finally, the optimal path for the efficient transmission of maritime sensor data via the UDTSN has been determined based on the fitness (ℑ). The route selected is denoted as (Rbest). This study presents a robust mathematical model integrating Underwater Digital Twins (UDTs) with a sensor network to enhance maritime communication and monitor coastal ecosystems, particularly along the Coromandel Coast. It uses advanced techniques like AP-ACO for optimized data transmission, SHC for data compression, TKCC for encryption, and CosLU-VS-LSTM for anomaly detection. The model, validated using the NSL-KDD dataset, shows superior data accuracy, security, and compression performance. This approach significantly contributes to sustainable marine resource management by improving ecosystem monitoring and hazard detection, although future work could expand to include more coastal ecosystems. Mathematical modeling and validations are important for comprehending marine ecosystems and maintaining ecological balance while enhancing resource management for sustainability. Incorporating technologies such as Underwater Digital Twins, sensor networks, and AI offers creative solutions. The UDT framework generates a digital marine ecosystem model, allowing for real-time observation and knowledgeable decision-making. It employs AI-driven fuzzy logic alongside the EHC-ANFIS for data processing, AP-ACO for enhancing data transmission efficiency, SHC for compressing data, and TKCC for ensuring data security. CosLU-VS-LSTM deep learning detects anomalies for swift environmental threat awareness. Sensor networks gather information on tide levels, salinity, temperature, and currents, transmitting it to the Maritime Alert Command Centre (MACC) for risk management. Metrics like precision, recall, and accuracy assess how effectively the model forecasts. This system improves sustainable resource extraction and risk identification, with future investigations focused on broadening its structure to protect various coastal ecosystems while promoting sustainable management of marine resources.
Table 2 compares underwater sensor networks’ optimization methods, such as AP-ACO, PSO, FMM, Visibility Graph, Potential Fields, and GNN. It highlights each method’s advantages, disadvantages, and relevant recent references (2020–2024). This comparison explains why AP-ACO is preferred for real-time, dynamic underwater environments due to its adaptability and efficiency.
2.4. Sensor Data Shrinkage
In this stage, the transmission of sensor data (H) with a fixed bandwidth is optimized by applying shrinkage techniques utilizing SHC. In this context, Huffman Coding (HC) is employed to compress the data, allowing its reconstruction into the original format without any loss of information.
On the contrary, input that frequently alters could not be updated in the Huffman tree, as the codes are fixed in the tree. Consequently, the Sliding Window technique is employed in Huffman Coding to incorporate the data into the tree.
To create a Huffman tree (
) based on new sensor data, the Sliding Window (
q), which discards the old data and includes the latest data as segments, is included into (
). It is expressed as follows:
where (
d) is the frequency of the symbols (
G). Here, shorter codes are assigned for frequent symbols, and longer ones are allotted to less frequent symbols. The frequency (
d) is updated for each symbol, which helps in compression of the data. The updated frequency (
d*) is equated by the following:
The Huffman tree is rebalanced based on (
d*) to give the compressed sensor data (
) as follows:
Thus, the compressed sensor data are transmitted effectively through the selected path (Rbest) of the Underwater Digital Twins Sensor Network.
2.5. Data Security
Here, to ensure that the data received in the MACC matches the transmitted data, the compressed data are protected using TKCC.
The method employed for securing the data is Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), which offers a high level of security with a reduced key size. Nevertheless, the drawbacks associated with the Elliptic Curve lead to increased computational complexity. The Twisted Koblitz Curve (TKC) is utilized as an alternative to the Elliptic Curve in ECC to address this challenge. The data security process is illustrated below.
The TKC (
Z), responsible for managing the coordinates within the finite field and providing a non-zero variable, is expressed as follows:
where (
L,
M) are the horizontal and vertical axes of (
Z), and (
u,
v) are the coordinate values. Now, the public key (ϕ) and the private key (γ) of the TKCC are calculated for securing the input data.
where (
e) is the randomly generated coordinate of the TKC. Finally,
is secured using (ϕ) and (γ) to make sure that the data security persists during data transmission in the complex acoustic environment of the Coromandel Coast. The secured data (
X) is equated as follows:
The pseudo-code of TKCC is explained in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1. Pseudo-code for TKCC |
| Input: Compressed sensor data |
| Output: Secured data (X) |
| Begin |
| Initialize coordinate parameters (u, v) |
| Create TKC |
| Z →M2 = L3 + (u ∗ L2) + v |
| For |
| While [(L,M) ∈ Z] |
| Calculate the public key using (u, v) |
| ϕ = (u + v) ∗ Z(e) |
| Generate private key regarding (ϕ) |
| γ = ϕ ∗ Z(e) |
| Encrypt sensor data |
| |
| Continue data transmission |
| End while |
| End for |
| Obtain Secured sensor data (X) |
| End |
Thus, the sensitive sensor data are encrypted and sent for further processing.
2.6. Anomaly Detection System Model
In this stage, the Anomaly Detection System (ADS) model is trained to safeguard the integrity of sensitive maritime data transmitted via the Underwater Digital Twins Sensor Network. The details of the ADS model training are outlined below.
2.6.1. Dataset
Initially, to train the ADS model regarding anomaly detection during sensor data transmission, the NSL-KDD dataset is collected. The data (
U) present in the NSL-KDD dataset are given by the following:
where (
ƒ) represents the number of (
U).
2.6.2. Pre-Processing
Next, to structure the data for effective anomaly detection, the pre-processing steps, such as Missing Value Imputation (MVI), numeralization, and normalization are implemented.
- ✓
Missing Value Imputation
Here, the missing values in (
U) are added based on the median of the neighboring data. The imputation of the values is evaluated as follows:
where (
U‴) represents the imputed data for the missing value of (
ƒ).
- ✓
Numeralization
Following MVI, the string data in (
U‴) are transformed in numerical values, facilitating the processing of Artificial Intelligence (AI). The numeralization of (
U‴) is given below.
where
is the numeralized data, and (
k) is the binary vector.
- ❖
Normalization
Finally,
is normalized using the min-max technique. Here, the data are scaled to fall in the range of (0 to 1). Consequently, all data points that exist on varying scales undergo scalar transformation. The normalization process is represented as follows:
where (
) is the normalized data, which are the final pre-processed output, and
are the minimum and maximum values of
.
2.6.3. Feature Extraction
Here, from (
), various features are extracted, including duration, protocol_type, service, flag, src_bytes, dst_bytes, wrong_fragment, urgent, dst_host_srv_count, count, num_compromised, num_access_files, serror_rate, dst_host_count, dst_host_srv_rerror_rate, and are represented as follows:
where (
T) is the feature extracted, and (
y) is the number of (
T).
2.6.4. Intuitive Visualization
To analyze the differences and similarities in (
T), the Radial Chart is employed, as it effectively captures patterns in the input, particularly when examining the features over time. It is expressed as
where (
F) is the intuitive visualization of (
T), (λ) is the axes of the Radial Chart, and (
c) is the circular format of the chart.
2.6.5. Anomaly Detection
In this stage, identification of anomalies within the data packets is conducted through the application of the CosLU-VS-LSTM Artificial Intelligence methodology. This approach employs Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, which address the vanishing gradient issue and facilitate more efficient training on extensive sequences of IoT sensor data for the purpose of anomaly detection. However, LSTM networks are susceptible to overfitting, and using the sigmoid activation function can hinder the classification speed. Variational Shake-drop (VS) regularization is implemented to mitigate the overfitting concern. At the same time, the Cosinu-sigmoidal Linear Unit (CosLU) function is adopted in place of the sigmoid activation function to enhance the speed of the anomaly detection process. The architecture of the proposed classifier is illustrated in
Figure 2.
The following sections detail the method of CosLU-VS-LSTM, which incorporates elements such as forget date, input gate, output gate, cell state, and memory.
- ↱
Regularization
The proposed classifier’s input is denoted as (T), and (F) is represented together as (A).
To address the overfitting issue, the vs. regularization technique is employed, which facilitates the learning of a robust representation within the data and appropriately scales the data. This technique is indicated by the following:
where (
A*) is the regularized data, (
p) is the weight value, and (κ) is the skip connection factor.
- ↱
Activation Function
Next, the CosLU function (μ), which combines linear and cosine components to capture complex patterns, and the hyperbolic tangent (tanh) activation function (ε) that maps the patterns effectively, are calculated as follows:
where (θ) is the scaling hyperparameter, and (exp) is the exponential factor.
- ↱
Forget Gate
Here, the data that are not necessary for detecting anomaly are removed. The previous hidden layer (
Dm−1), with time (
m), previous memory (
Jm−1), and the input (
A*), is added and activated using (μ). This is expressed as follows:
where (
S) is the output of the forget gate, and (
n) the bias value.
- ↱
Input gate
Here, the information is added to the present memory (
Jm). Here, the inputs are activated using (μ) and (ε) simultaneously as follows:
where (
K) is the output of the input gate.
- ↱
Memory
The output of the forget gate (
S) and the input gate (
K) are added to update the present memory (
Jm) as follows:
- ↱
Output gate
Finally, depending on (
Jm), and (
A*), the output gate value (
W), which extracts the most important information and helps in identifying the anomaly, is calculated as follows:
where (
W*) is the overall anomaly detected output,
W (
z) shows the presence of anomaly when (
W = 1), and
W (
z) is the normal class when (
W = 0). The pseudo-code for CosLU-VS-LSTM is explained in Algorithm 2.
| Algorithm 2. Pseudo-code for CosLU-VS-LSTM |
| Input: Features (T), Intuitive representation (F)
|
| Output: Anomaly detected output (W*)
|
| Begin |
| Initialize (p), (n)
|
| Regularize input
|
| A* = (A × p) + [(1 − p)A * κ]
|
| For (A*)
|
| Calculate activation function
|
| μ = A* + {θ ∗ 1 − cos(A*)⌈}
|
| ε = [exp A* − exp −A*]/[exp A* + exp −A*]
|
| While (μ,ε)
|
| For (time = m)
|
| Evaluate forget gate
|
| S = ⌊{A*, Dm−1, Jm−[1 ∗ p} + n⌋ ⊗ μ]
|
| Determine input gate
|
| K = S ⊗ 〈{[(A*, Dm−1) ∗ p] + n} ∗ ε〉
|
| Update memory
|
| Jm = S ⊕ K |
| Calculate output gate
|
| W = J m ∗ ε ⊗ {μ ∗ ⌈A*, Dm⌉−1}⌈
|
| Attain classified output |
| End if |
| End for |
| Return (W*) |
| End |
The proposed framework enhances underwater communication and monitoring for the Coromandel Coast by integrating advanced technologies. It uses Underwater Digital Twin (UDT) technology for real-time environmental monitoring, with decision-making powered by an AI-driven Exponential Hyperbolic Crisp Adaptive Network-based Fuzzy Inference System (EHC-ANFIS). Data security is ensured through Twisted Koblitz Curve Cryptography (TKCC), while an Anomaly Detection System (ADS) with CosLU-VS-LSTM identifies irregularities in sensor data. To optimize bandwidth, Sliding–Huffman Coding (SHC) compresses the data, and Adaptive Pheromone Ant Colony Optimization (AP-ACO) selects the optimal communication path. These innovations collectively improve the efficiency of maritime communication and monitoring, contributing to the sustainable management of coastal ecosystems.
Upon completion of the ADS model training, any detected anomalies during the real-time transmission of data (X) will result in the blocking of that transmission, while data transmission for the normal class will proceed uninterrupted within the UDTSN.
2.7. Data Decryption and Decomposition
For
W (
z), the data (
X) are transmitted along the Underwater Digital Twins Sensor Network. To further process the data for the monitoring purpose of the Coromandel Coast, decryption is performed using the keys (ϕ) and (γ) generated by the TKCC method as explained in the following sections.
where (
Y) is the decrypted data. Next, (
Y) is decomposed using (
) to obtain the exact file and is given by the following:
where (
Q) is the decomposed data.
2.8. Extraction of Sensor Data
Here, the original sensor data (H) passing through the UDTSN are extracted from (Q). These data are further used to monitor the Coromandel Coast for varying complex environmental changes and conditions.
2.9. Digital Twin-Influenced Decision-Making
The final decision-making process concerning the monitoring level of the Coromandel Coast is conducted through the EHC-ANFIS (AI-IoT) hybrid approach. The data (H), collected via the Underwater Digital Twins Sensor Network, serve as the input for the EHC-ANFIS system. This system employs the Adaptive Network-based Fuzzy Inference System, which evaluates the IoT sensor data obtained from Autonomous Underwater Vehicles (AUVs) and modifies parameters in response to updated climatic information, thereby facilitating decisions related to the monitoring of the Coromandel Coast. Optimizing fuzzy rules and threshold settings in a maritime monitoring system based on Underwater Digital Twins (UDTs) using the Exponential Hyperbolic Crisp Adaptive Network-based Fuzzy Inference System (EHC-ANFIS). It starts with defining fuzzy rules based on environmental parameters like tide level, current speed, wind speed, water temperature, and salinity, with an “if-then” structure, such as “If tide level = low, then risk = low”. The data collected from the sensors are fuzzified using the EHC membership function, which improves the handling of crisp inputs, making it easier for the system to manage uncertainty. These fuzzified inputs are then evaluated by the ANFIS, which applies fuzzy logic to assess relationships between input variables and determines the appropriate risk level, such as issuing a “green”, “yellow”, or “red” alert. Threshold values, such as “high tide > 5 m”, are optimized to maximize detection accuracy and minimize false alerts by adjusting boundaries based on historical or real-time data. After the fuzzy rules and thresholds are applied, the output is defuzzified to generate a crisp decision, such as a specific alert level. The EHC-ANFIS hybrid model refines the system by dynamically adjusting fuzzy rules and thresholds based on incoming sensor data, ensuring optimal decision-making efficiency. This continuous optimization enhances the system’s performance, providing accurate and timely alerts and responses based on varying environmental conditions. It is important to note that the ANFIS framework necessitates specialized knowledge and expertise to accurately define fuzzy sets, membership functions, and rule bases. The Exponential Hyperbolic Crisp (EHC) membership function is implemented to improve the decision-making process. The subsequent steps involved in the decision-making process are outlined below.
- ✓
Rule
The fuzzy rule (
C) based on the if–then condition is initially set for making adequate decisions to monitor the coastal ecosystem. It is equated as follows:
where the tide level (
a) is recorded in meters, the current speed (
b) is expressed in meters per second, the wind speed (
i) is indicated in kilometers per hour, the water temperature (
t) is measured in Celsius degrees, and salinity (
r) is quantified using the Practical Salinity Unit (PSU). Additionally, (
l) denotes the sound velocity, influencing the acoustic sensor performance, while (
x) represents the sensor battery level. In this context, the decision-making (
E) related to the monitoring of the coast is categorized as follows: (
E1) signifies a green alert indicating low risk, (
E2) denotes a yellow alert representing moderate risk, (
E3) indicates a red alert for high risk, (
E4) refers to a red alert for critical hazards, (
E5) is a special alert for disruption in acoustic propagation, (
E6) represents the yellow alert with pre-emptive early warning for incoming storms, and (
E7) is a multi-factor red alert that combines risks from environmental factors and system failures. In order to monitor the coastal ecology, the Autonomous Underwater Vehicle (AUV)’s sensors gather various environmental data. Water temperature (in Celsius degrees), salinity (measured in Practical Salinity Units, PSUs), wind speed (in kilometers per hour), tide level (in meters), and current speed (in meters per second) are among the particular characteristics. The AUV gathers these characteristics, Internet of Things (IoT) data, for subsequent processing in the underwater sensor network.
- ✓
Membership Function
Now, the EHC membership function (ψ) that identifies the parameters effectively, is used. It is equated as
where (
o1,
o2) are the scaling parameters of the input (
H). Regression analysis models the relationship between a dependent variable (ground truth) and independent variables (predictions from various models). Techniques like Linear Regression are useful for simple, linear relationships, while Polynomial Regression captures non-linear patterns. Ridge and Lasso Regression add regularization to prevent overfitting, with Lasso also performing feature selection. Support Vector Regression (SVR) handles non-linear data, and Random Forest Regression uses multiple decision trees to reduce overfitting. Neural Networks and Gradient Boosting Machines (GBMs) like XGBoost are used for complex, high-performance models, with GBMs improving weak models through sequential decision trees. The choice of method depends on data complexity and model performance needs.
- ✓
Fuzzification
Here, the input (
H) is converted into fuzzy data (
) so that the AI method can learn the input data precisely. It is given by
The input is multiplied by the membership function to assess the extent of the relationship between the data.
- ✓
Defuzzification
The fuzzy data () are derived using the rule (C) and subsequently defuzzified to obtain the final output as shown below.
Thus, (E) represents the decision-making in monitoring the Coromandel Coast.
2.10. Alert to Maritime Alert Command Centre
According to the obtained (E), an alert is sent to the MACC. Consequently, the proposed framework’s implementation enhances maritime communication and surveillance of the Coromandel Coast. The effectiveness of the proposed initiative is detailed below.
3. Results and Discussions
This section presents the performance evaluation and comparative analysis of the proposed model alongside existing techniques to demonstrate the reliability of the proposed model. Additionally, the implementation of the proposed model is carried out on the PYTHON working platform.
3.1. Dataset Description
The framework presented utilizes the “NSL-KDD” dataset to evaluate the proposed model. The NSL-KDD dataset is an improved version of the KDD Cup 1999 dataset for evaluating intrusion detection systems. It contains labeled network traffic data, categorized into normal and attack types, and is commonly used in research. The dataset includes features like connection statistics and service types, which are essential for detecting malicious network activities. It is available publicly on platforms like Kaggle. This dataset has been sourced from publicly accessible materials, with the corresponding link provided in the References section. It comprises a total of 125,973 data entries. Of this total, 80%, equating to 100,778 entries, is allocated for training, while the remaining 20%, amounting to 25,195 entries, is designated for testing purposes.
3.2. Performance Assessment
The evaluation of the proposed method alongside existing techniques is conducted to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed model.
Figure 3 illustrates the graphical comparison between the proposed EHC-ANFIS and existing methodologies regarding fuzzification, defuzzification, and rule generation times. The EHC-ANFIS model exhibited significantly lower times of 21,045 ms for fuzzification, 45,012 ms for defuzzification, and 51,452 ms for rule generation, attributed to implementing the Exponential Hyperbolic Crisp Membership Function. In contrast, the conventional techniques, including ANFIS, Fuzzy, Rule-Based Prediction (RBP), and Trapezoidal Fuzzy Logic System (Trapezoidal FLS), recorded higher average times of 71,422.25 ms, 80,329.5 ms, and 89,144.75 ms for fuzzification, defuzzification, and rule generation, respectively. This highlights the superior performance of the proposed model.
The figure compares the processing times (in milliseconds) for fuzzification, defuzzification, and rule generation across different fuzzy inference systems: the proposed EHC-ANFIS, ANFIS, Fuzzy, RBP, and Trapezoidal FLS. It shows that the proposed EHC-ANFIS model has significantly lower processing times for each of the three phases compared to the other systems, indicating better efficiency. This chart does not represent convergence time but illustrates the performance of each system in completing these specific tasks. Convergence time alone does not reflect a model’s total quality because it simply counts how quickly it achieves a solution and ignores characteristics such as solution correctness, generalization ability, resilience, and interpretability. A model may converge rapidly yet generate inferior results, be sensitive to hyperparameters, or consume too many resources. To assess a model’s performance, it is critical to examine not just convergence time but also accuracy, generalization, efficiency, and stability.
The performance validation of the proposed CosLU-VS-LSTM model, along with existing techniques such as LSTM, Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs), and Deep Neural Networks (DNNs), is illustrated in
Figure 4a,b. The proposed CosLU-VS-LSTM demonstrated impressive metrics, achieving precision, recall, F-Measure, accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity values of 98.35%, 99.15%, 99.00%, 98.62%, 99.15%, and 98.31%, respectively. Additionally, it recorded a low False Positive Rate (FPR) of 0.0268776 and a False Negative Rate (FNR) of 0.008653. In contrast, the existing models—LSTM, CNN, RNN, and DNN—exhibited lower precision rates of 95.13%, 93.75%, 90.87%, and 88.15%, respectively. These established techniques also showed diminished accuracy, recall, F-measure, sensitivity, and specificity. Notably, the existing DNN model had a significantly high FPR of 0.1786746 and an FNR of 0.119243. To address the overfitting problem, the Variational Shake Drop Regularization technique was adapted within the CosLU-VS-LSTM framework. Consequently, the results indicate that the proposed model outperformed the existing methodologies.
Table 3 displays the UDT-EHC-ANFIS model outperforming existing maritime surveillance systems in several areas. It is faster in computational complexity, with processing times of 21,045 ms for fuzzification and 45,012 ms for defuzzification, compared to ANFIS (71,422 ms) and RBP (80,329.5 ms). In security, it achieves 98.01% protection with TKCC, using less memory than traditional methods like ECC. The model excels in anomaly detection, with 98.35% precision and 99.15% recall, surpassing LSTM and DNN. It also compresses data efficiently with SHC in 140,758 ms, outperforming Huffman Coding. Lastly, it achieves superior compression quality with an MSE of 0.00954 and entropy of 32.56, beating traditional methods. This study detects false predictions through the Anomaly Detection System (ADS), which warrants the integrity of maritime sensor data transmitted via the Underwater Digital Twins Sensor Network (UDTSN). The process begins with data preprocessing, which includes Missing Value Imputation (MVI) to fill in missing values, numeralization to convert string data into numerical values, and normalization to scale the data consistently. Next, relevant features are extracted to help in identifying anomalies. The core of anomaly detection uses the CosLU-VS-LSTM model. This deep learning approach combines a Cosine-sigmoidal Linear Unit (CosLU) activation function with Variational Shake-drop Regularization to prevent overfitting. At the same time, the Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network effectively handles time-series data. The model then monitors incoming data, flagging any significant deviations as anomalies (false predictions). The output gate of the LSTM model classifies the data as either normal (0) or anomalous (1). If an abnormality is noticed, the exaggerated data are blocked from transmission to the Maritime Alert Command Centre (MACC), confirming that only valid data are sent. This method has been authenticated with impressive accuracy, precision, and recall metrics, demonstrating its effectiveness in minimizing false predictions and improving the system’s reliability.
Table 4 illustrates the evaluation of the True Positive Rate (TPR) and True Negative Rate (TNR) for the proposed CosLU-VS-LSTM model compared to existing methodologies. The CosLU-VS-LSTM model utilizes the Variational Shake Drop Regularization technique and the CosLU function to identify anomalies effectively. This model achieved impressive TPR and TNR values of 98.72% and 98.31%, respectively. In contrast, traditional techniques such as LSTM, CNN, RNN, and DNN demonstrated a lower average TPR and TNR, recorded at 93.11% and 89.93%, respectively. Therefore, the reliability of the proposed model is substantiated.
Figure 5a–c illustrate the comparative graphical analysis of the proposed model against traditional methods regarding memory consumption during encryption and decryption processes, as well as their respective security and attack levels. The proposed Twisted Koblitz Curve Cryptography (TKCC) utilized 147,245,452 KB of memory for encryption and 149,456,981 KB for decryption. In addition, the TKCC demonstrated a commendable security level of 98.01% and a minimal attack level of 1.99%, outperforming conventional methods. In contrast, traditional techniques such as Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), Rivest–Shamir–Adleman (RSA), Data Encryption Standard (DES), and ElGamal required significantly more memory for both encryption and decryption. Furthermore, these existing methods exhibited inferior security and attack levels. The implementation of the Twisted Koblitz Curve serves to enhance data security.
Table 5 presents the analysis of compression times for the proposed SHC and existing techniques. The proposed SHC achieved a notably low compression time of 140,758 ms, in contrast to the conventional methods: Huffman Coding (HC) at 198,563 ms, Lempel-Ziv (LZ) at 253,564 ms, Run-Length Encoding (RLE) at 314,748 ms, and Arithmetic Coding (AC) at 398,756 ms. Consequently, the proposed SHC demonstrates superior efficiency in sensor data compression.
Figure 6 illustrates the comparative evaluation of the proposed SHC against established methods, including HC, LZ, RLE, and AC. This analysis has enhanced the sliding window with SHC to mitigate inefficiencies. The proposed SHC demonstrated a low Mean Squared Error (MSE) of 0.00954 and a high entropy value of 32.56. In contrast, the existing techniques, such as HC, LZ, RLE, and AC, recorded a higher average MSE of 0.06942 and a lower average entropy of 21.73. Therefore, the proposed model outperforms the current techniques.
The performance validation of the proposed AP-ACO compared to existing techniques concerning response time and process time is illustrated in
Figure 7. The proposed AP-ACO demonstrated a significantly reduced response time of 8701 ms and a processing time of 5117 ms, attributed to its ability to identify optimal solutions adaptively. In contrast, the existing algorithms, including ACO, Dingo Optimization Algorithm (DOA), Osprey Optimization Algorithm (OOA), and Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO), exhibited higher response and process times. Consequently, the findings confirm that the proposed model exhibits lower time complexities.
Table 6 compares Twisted Koblitz Curve Cryptography (TKCC) with traditional security models like ECC, RSA, DES, and ElGamal. TKCC excels in security, efficiency, and low resource usage, making it ideal for real-time maritime applications with low bandwidth and memory constraints. It offers better security (98.01%) and lower attack levels (1.99%) than other models. TKCC is computationally efficient and integrates well with anomaly detection systems, making it the best choice for underwater sensor networks and real-time communication. In contrast, models like ECC and RSA are more computationally expensive and less suitable for resource-constrained environments.