Removal of Indicator Micropollutants Included in Directive (EU) 2024/3019 Using Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Selection and Characteristics of Membranes
2.2. Chemicals and Consumables
2.3. Preparation of the Synthetic Matrix
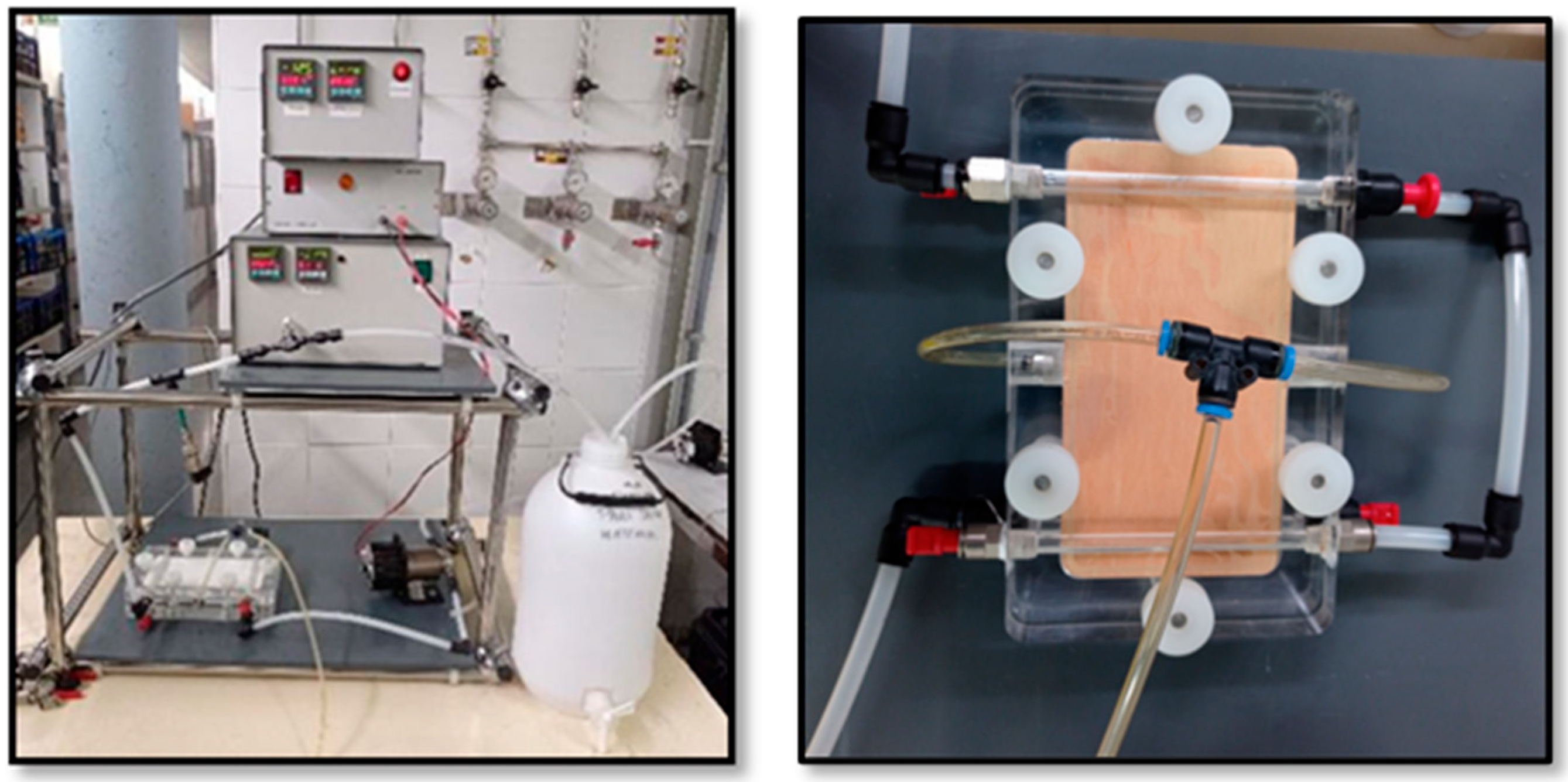
2.4. Experimental Design and Set-Up
2.5. CEC Analysis
2.6. Method Validation
2.7. Calculation of Removal Percentage
3. Results and Discussion
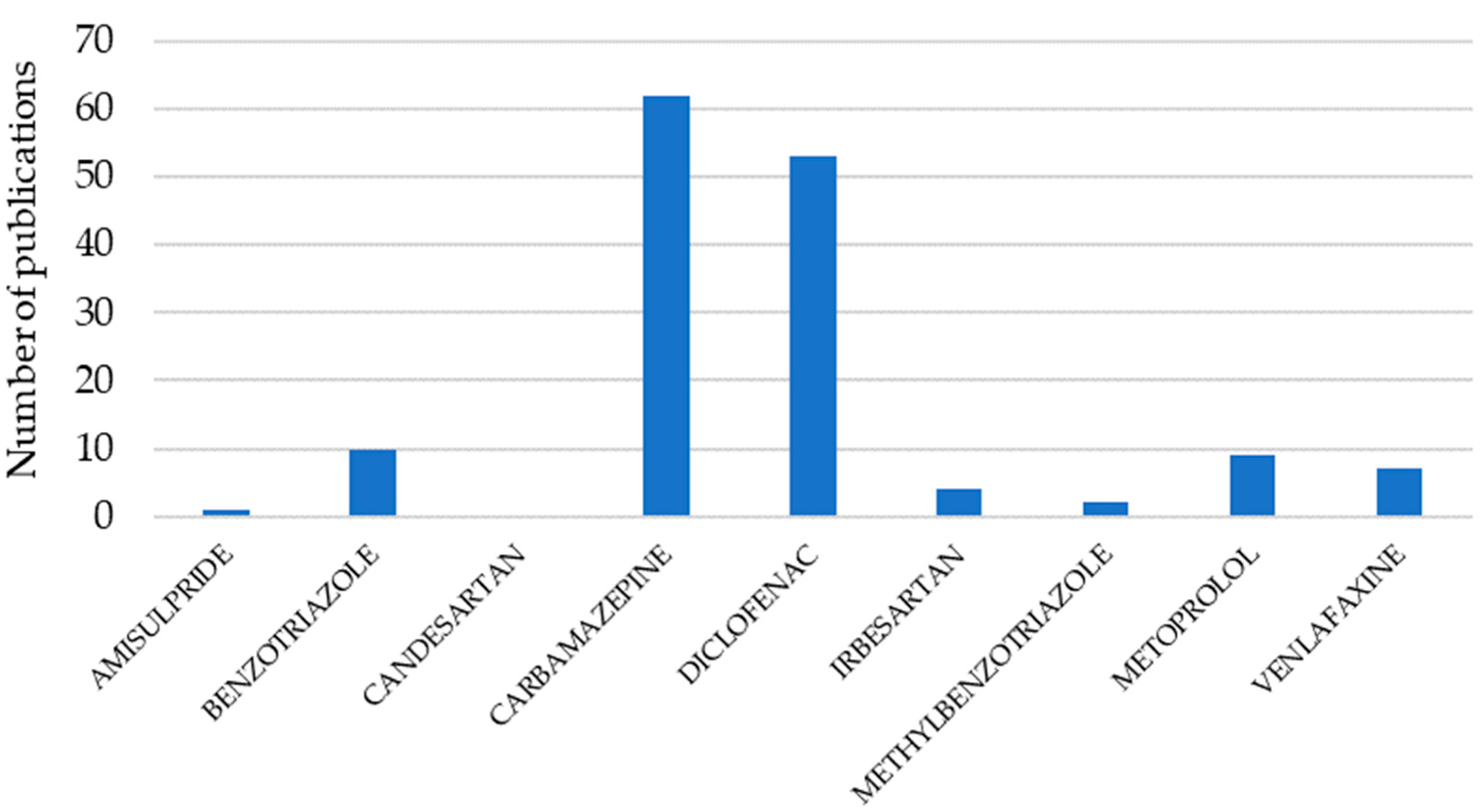
3.1. Elimination of CECs
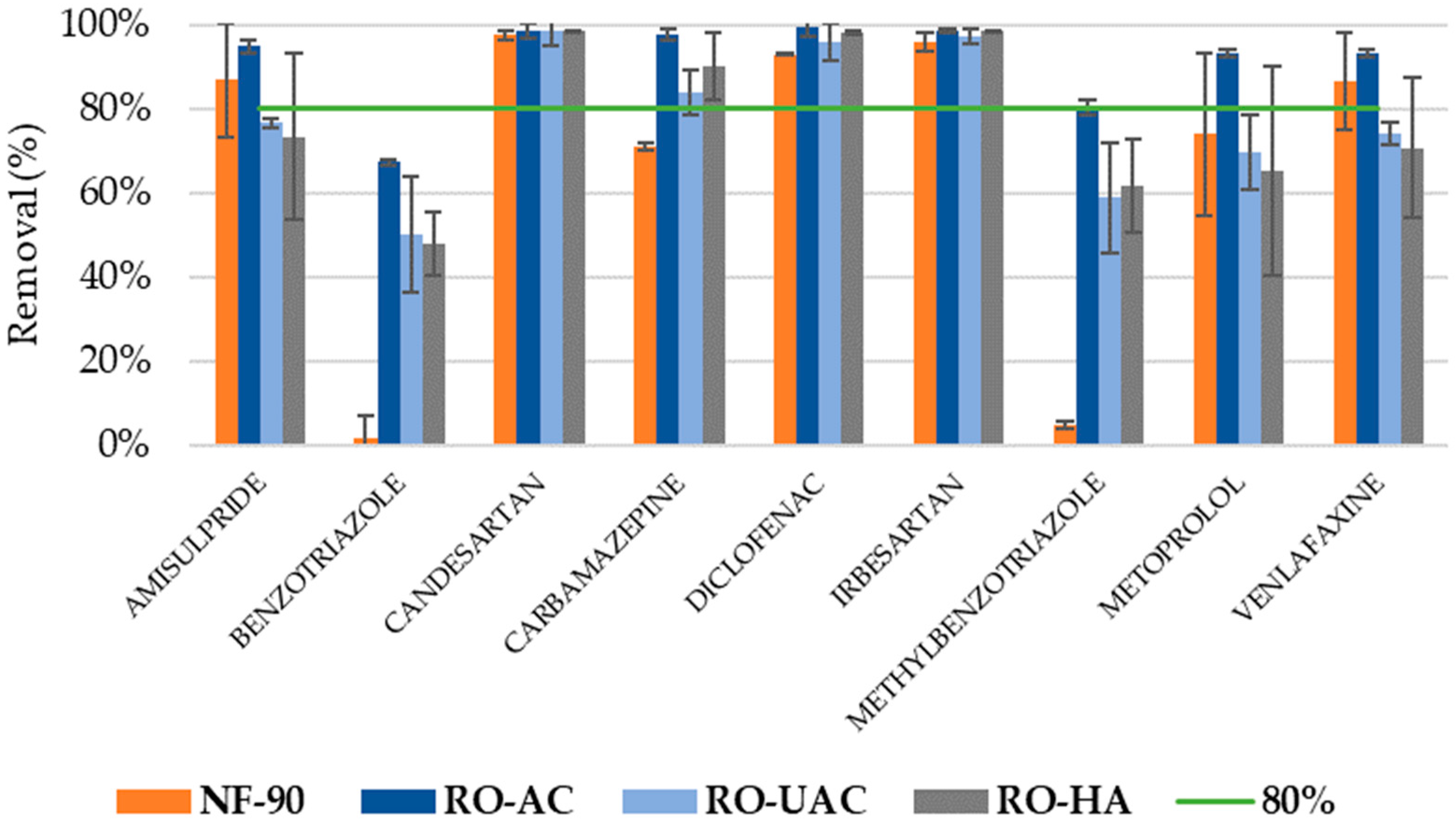
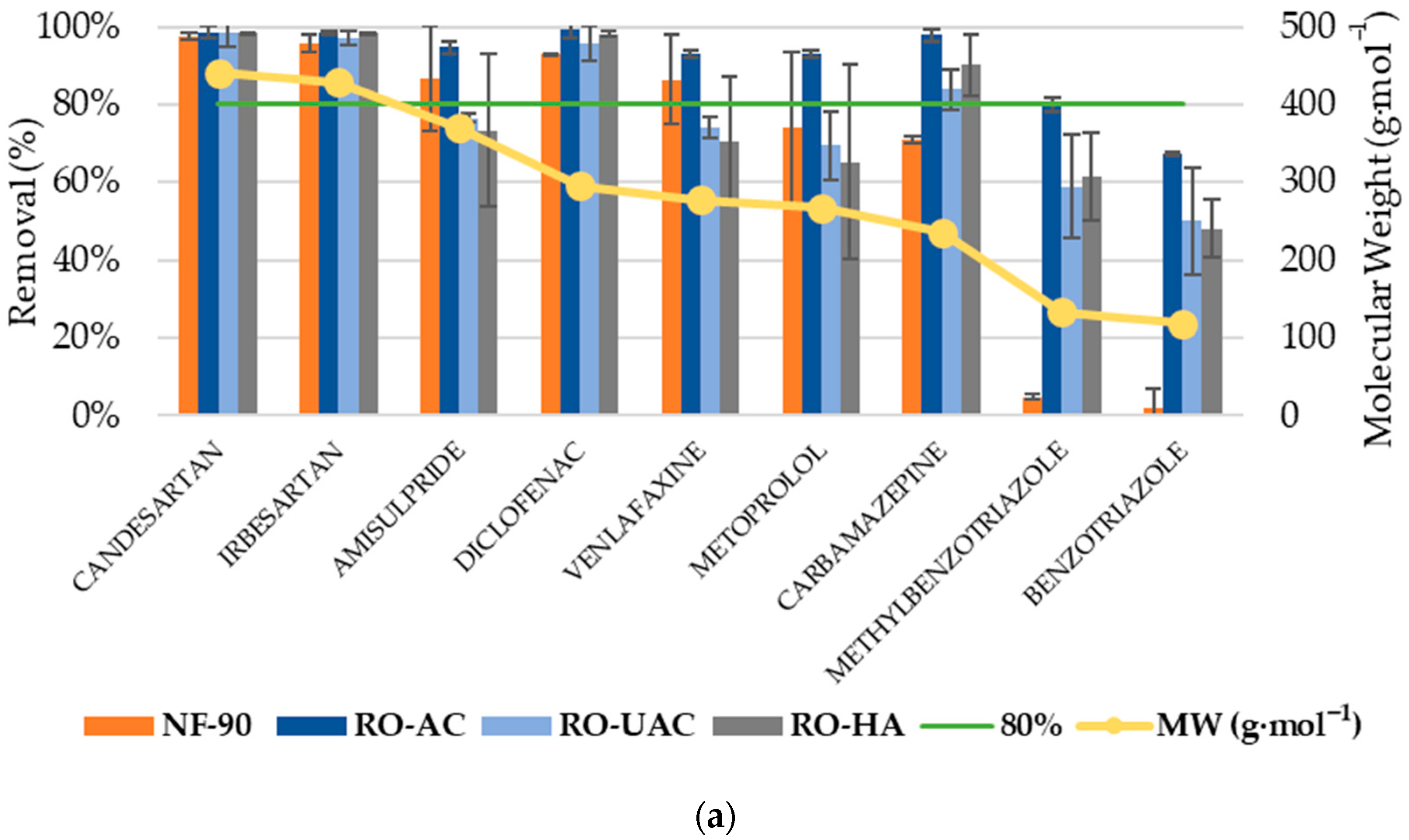
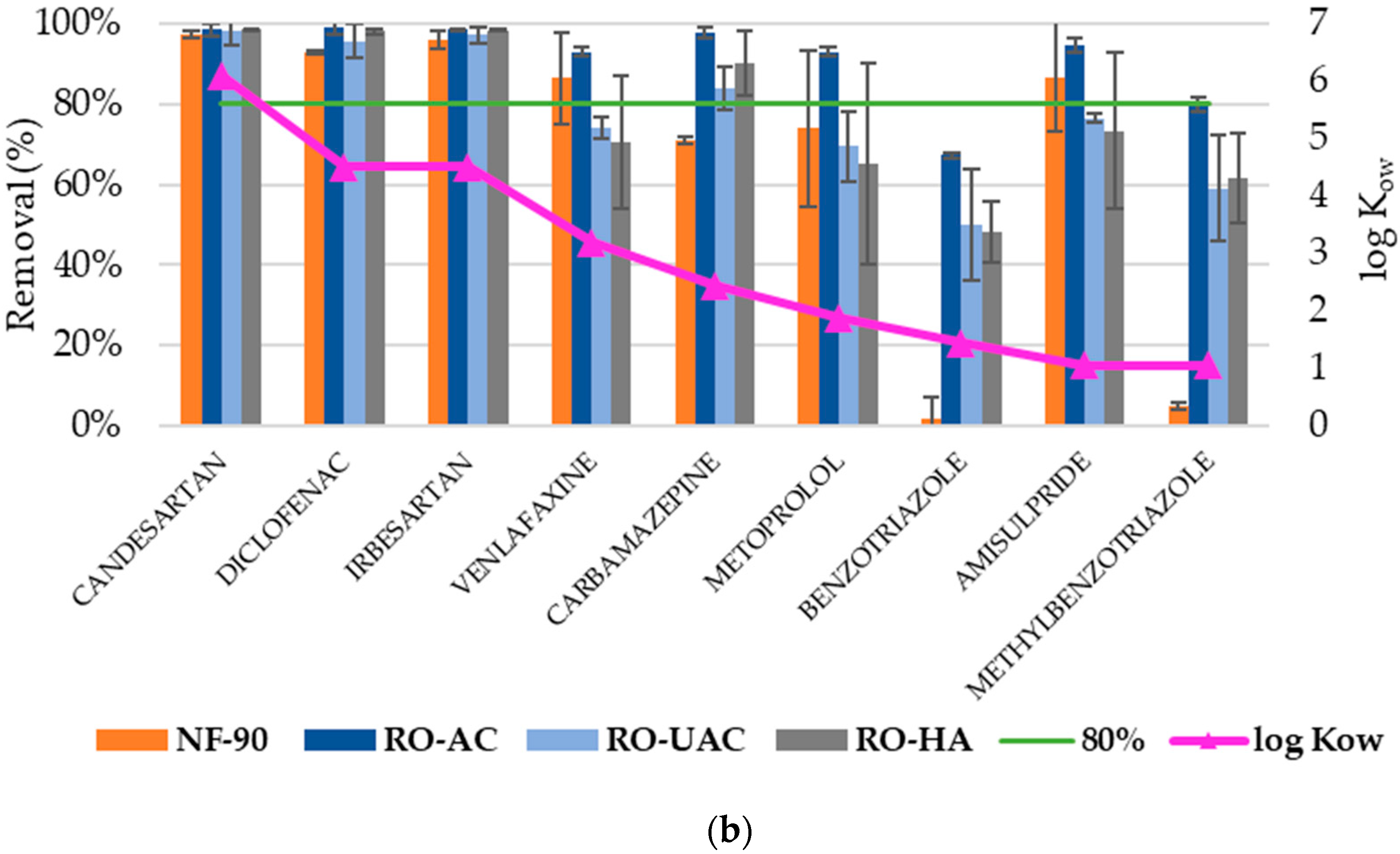
3.2. Analysis of CEC Rejection
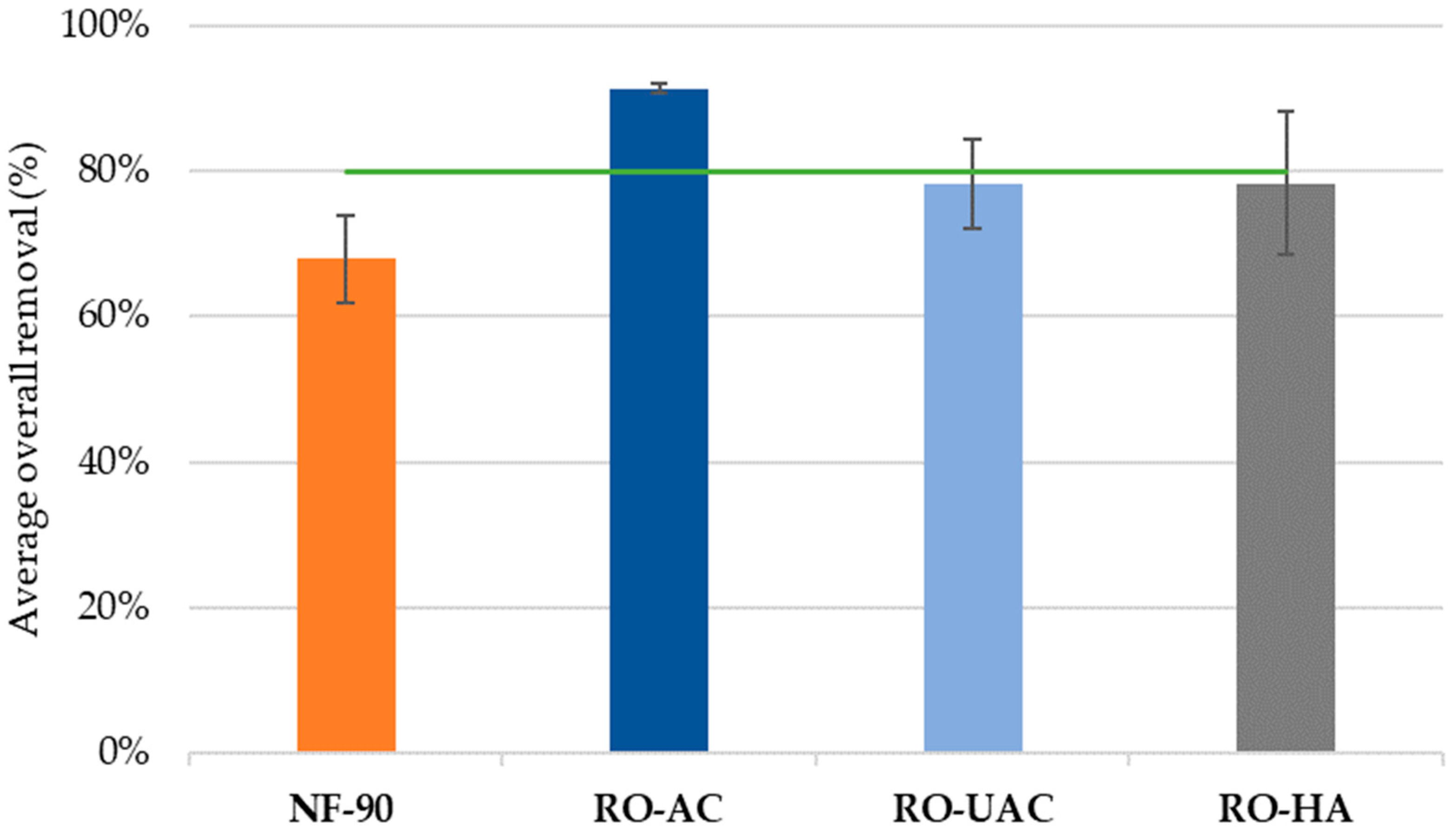
3.3. Global Removal of CECs
3.4. Challenges in the Treatment of Real Effluents and the Influence of TDS on Membrane Treatment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- UN World Water Development Report 2024|UN-Water. Available online: https://www.unwater.org/publications/un-world-water-development-report-2024 (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Wada, Y.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Sustainability of global water use: Past reconstruction and future projections. Environ. Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 104003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, E.R.; Van Vliet, M.T.H.; Qadir, M.; Bierkens, M.F.P. Country-level and gridded estimates of wastewater production, collection, treatment and reuse. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, C.; Jiang, J.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yuan, C.; Bai, L.; Meng, S.; Cao, G. Removal of antibiotics and estrogens by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes. J. Hazard Mater. 2024, 461, 132628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggen, R.I.L.; Hollender, J.; Joss, A.; Schärer, M.; Stamm, C. Reducing the discharge of micropollutants in the aquatic environment: The benefits of upgrading wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 7683–7689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurke, R.; Rößler, M.; Marx, C.; Diamond, S.; Schubert, S.; Oertel, R.; Fauler, J. Occurrence and removal of frequently prescribed pharmaceuticals and corresponding metabolites in wastewater of a sewage treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 532, 762–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolaou, A.; Meric, S.; Fatta, D. Occurrence patterns of pharmaceuticals in water and wastewater environments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2007, 387, 1225–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.T.; Bouwer, E.J.; Coelhan, M. Occurrence and biodegradability studies of selected pharmaceuticals and personal care products in sewage effluent. Agric. Water Manag. 2006, 86, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, “The Norman Network”. Available online: https://www.norman-network.net/ (accessed on 13 January 2025).
- Wu, C.; Spongberg, A.L.; Witter, J.D.; Fang, M.; Czajkowski, K.P. Uptake of pharmaceutical and personal care products by soybean plants from soils applied with biosolids and irrigated with contaminated water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 6157–6161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossberger, A.; Hadar, Y.; Borch, T.; Chefetz, B. Biodegradability of pharmaceutical compounds in agricultural soils irrigated with treated wastewater. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 185, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.W.; Wen, Z.D. Phthalate esters in the environment: A critical review of their occurrence, biodegradation, and removal during wastewater treatment processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 986–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baken, K.A.; Sjerps, R.M.A.; Schriks, M.; van Wezel, A.P. Toxicological risk assessment and prioritization of drinking water relevant contaminants of emerging concern. Environ. Int. 2018, 118, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertová, D. Recast of the Urban Wastewater Treatment Directive brings new challenges not only in the water management sector. Vodohospodářské Tech.-Ekon. Inf. 2024, 66, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2020/2184 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2020 on the Quality of Water Intended for Human Consumption. 2020. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/dir/2020/2184/oj (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- European Union. Regulation (EU) 2020/741 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 25 May 2020 on Minimum Requirements for Water Reuse. 2020. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/reg/2020/741/oj (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- European Union. Directive (EU) 2024/3019 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 27 November 2024 Concerning Urban Wastewater Treatment. 2024. Available online: http://data.europa.eu/eli/C/2023/250/oj (accessed on 14 February 2025).
- Bui, X.T.; Vo, T.P.T.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W.S.; Nguyen, T.T. Multicriteria assessment of advanced treatment technologies for micropollutants removal at large-scale applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 563–564, 1050–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, L.; Malato, S.; Antakyali, D.; Beretsou, V.G.; Đolić, M.B.; Gernjak, W.; Heath, E.; Ivancev-Tumbas, I.; Karaolia, P.; Ribeiro, A.R.L.; et al. Consolidated vs new advanced treatment methods for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern from urban wastewater. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 655, 986–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Yao, Z.; Mei, Y.; Peng, L.E.; Yang, Z.; Shao, S.; Tang, C.Y. Nanofiltration for Drinking Water Treatment: A Review. Front. Chem. Sci. Eng. 2021, 16, 681–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.Y.; Yang, Z.; Guo, H.; Wen, J.J.; Nghiem, L.D.; Cornelissen, E. Potable Water Reuse through Advanced Membrane Technology. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10215–10223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Feng, Z.; Rui, X.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z. A review on reverse osmosis and nanofiltration membranes for water purification. Polymers 2019, 11, 1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, A.; Sodiq, A.; Giwa, A.; Eke, J.; Pikuda, O.; De Luca, G.; Di Salvo, J.L.; Chakraborty, S. A review of emerging trends in membrane science and technology for sustainable water treatment. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 266, 121867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yangali-Quintanilla, V.; Maeng, S.K.; Fujioka, T.; Kennedy, M.; Amy, G. Proposing nanofiltration as acceptable barrier for organic contaminants in water reuse. J. Memb. Sci. 2010, 362, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doederer, K.; Farré, M.J.; Pidou, M.; Weinberg, H.S.; Gernjak, W. Rejection of disinfection by-products by RO and NF membranes: Influence of solute properties and operational parameters. J. Memb. Sci. 2014, 467, 195–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Chu, K.H.; Al-Hamadani, Y.A.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Kim, D.-H.; Yu, M.; Heo, J.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by membranes in water and wastewater: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 335, 896–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellona, C.; Drewes, J.E.; Xu, P.; Amy, G. Factors affecting the rejection of organic solutes during NF/RO treatment—A literature review. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2795–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Toshima, S.; Amy, G.; Watanabe, Y. Rejection of neutral endocrine disrupting compounds (EDCs) and pharmaceutical active compounds (PhACs) by RO membranes. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 245, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.M.; Li, B.; Zhang, T.; Li, X.Y. Performance of nanofiltration membrane in rejecting trace organic compounds: Experiment and model prediction. Desalination 2015, 370, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FilmTecTM NF90-400/34i. Available online: https://www.dupont.com/products/filmtecnf9040034i.html (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- Toray RO|Toray Membrane|TORAY. Available online: https://www.water.toray/products/ro/#brackish-water (accessed on 14 January 2025).
- DIN 38412-26; German Standard Methods for the Examination of Water, Wastewater and Sludge—Group L: Biotets (L26)—Testing of the Biodegradability of Water-Soluble Sulfactants Using and Activated Sludge Model. Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN): Berlin, Germany, 1994. Available online: https://tienda.aenor.com/norma-din-38412-26-1994-05-2288704 (accessed on 23 November 2024).
- Balseviciute, A.; Patiño-Cantero, I.; Carrillo-Abad, J.; Giner-Sanz, J.; García-Gabaldón, M.; Pérez-Herranz, V.; Martí-Calatayud, M. Degradation of multicomponent pharmaceutical mixtures by electrochemical oxidation: Insights about the process evolution at varying applied currents and concentrations of organics and supporting electrolyte. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 362, 131697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiavola, A.; Di Marcantonio, C.; Porretti, A.N.; Scagnetti, S.; Ciuchi, V.; Boni, M.R.; Micoli, S.; Lazzazzara, M.; Leoni, S.; Frugis, A.; et al. Application of adsorption and ozonation as quaternary treatment of WWTP effluent for the removal of contaminants of emerging concern: Results from laboratory scale experiments. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada-Vásquez, M.A.; Simarro-Gimeno, C.; Vidal-Barreiro, I.; Cardona-Gallo, S.A.; Pitarch, E.; Hernández, F.; Torres-Palma, R.A.; Chica, A.; Navarro-Laboulais, J. Application of catalytic ozonation using Y zeolite in the elimination of pharmaceuticals in effluents from municipal wastewater treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues-Silva, F.; Santos, C.S.; Marrero, J.A.; Montes, R.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodil, R.; Nunes, O.C.; Starling, M.C.V.; Amorim, C.C.; Gomes, A.I.; et al. Continuous UV-C/H2O2 and UV-C/Chlorine applied to municipal secondary effluent and nanofiltration retentate: Removal of contaminants of emerging concern, ecotoxicity, and reuse potential. Chemosphere 2024, 361, 142355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LMarino; Gagliano, E.; Santoro, D.; Roccaro, P. Fluorescence sensor enabled control of contaminants of emerging concern in reclaimed wastewater using ozone-based treatment processes. Water Res. 2025, 268, 122616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marcantonio, C.; Chiavola, A.; Gioia, V.; Leoni, S.; Cecchini, G.; Frugis, A.; Ceci, C.; Spizzirri, M.; Boni, M.R. A step forward on site-specific environmental risk assessment and insight into the main influencing factors of CECs removal from wastewater. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Ray, N.M.; Wan, J.; Khan, A.; Chakraborty, T.; Ray, M.B. Micropollutants in Wastewater: Fate and Removal Processes. In Physico-Chemical Wastewater Treatment and Resource Recovery; InTech: Chennai, India, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robles-Molina, J.; Gilbert-López, B.; García-Reyes, J.F.; Molina-Díaz, A. Monitoring of selected priority and emerging contaminants in the Guadalquivir River and other related surface waters in the province of Jaén, South East Spain. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 247–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moya-Llamas, M.J.; Bernal, M.A.; Vásquez, E.; Trapote, A.; López, C.M.; Prats, D. Combined UASB+MBR system for biological removal of emerging contaminants, organic matter and nutrients in urban waste water. In Proceedings of the 20th International Congress on Project Management and Engineering, Cartagena, Colombia, 13–15 July 2016; pp. 1385–1397. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, E.D.V.; Llamas, M.J.M.; Del Hombre Bueno, M.A.B.-R.; Trapote, A.; Rico, D.P. Eliminación/Degradación de Triazinas Mediante Biorreactor de Membrana con Post-Tratamiento de Ozonización. KnE Eng. 2018, 3, 597–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio, S.C.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Spruijt, E.; Dykstra, J.E.; van der Wal, A. Modeling micropollutant removal by nanofiltration and reverse osmosis membranes: Considerations and challenges. Water Res. 2022, 225, 119130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Cao, T.; Dykstra, J.E.; Porada, S.; Biesheuvel, P.M.; Elimelech, M. Salt and Water Transport in Reverse Osmosis Membranes: Beyond the Solution-Diffusion Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 16665–16675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; He, J.; Heiranian, M.; Fan, H.; Song, L.; Li, Y.; Elimelech, M. Water transport in reverse osmosis membranes is governed by pore flow, not a solution-diffusion mechanism. Sci. Adv. 2023, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nure, J.F.; Nkambule, T.T.I. The recent advances in adsorption and membrane separation and their hybrid technologies for micropollutants removal from wastewater. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2023, 126, 92–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.; Heiranian, M.; Elimelech, M. The solution-diffusion model for water transport in reverse osmosis: What went wrong? Desalination 2024, 580, 117575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijmans, J.G.; Baker, R.W. The solution-diffusion model: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 1995, 107, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.R. Reformulation of the solution-diffusion theory of reverse osmosis. J. Memb. Sci. 2004, 241, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ojajuni, O.; Saroj, D.; Cavalli, G. Removal of organic micropollutants using membrane-assisted processes: A review of recent progress. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2015, 4, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanzada, N.K.; Farid, M.U.; Kharraz, J.A.; Choi, J.; Tang, C.Y.; Nghiem, L.D.; Jang, A.; An, A.K. Removal of organic micropollutants using advanced membrane-based water and wastewater treatment: A review. J. Memb. Sci. 2020, 598, 117672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wu, W.; Ma, M.; Hu, Y.; Li, R. Occurrence and distribution of emerging contaminants in wastewater treatment plants: A globally review over the past two decades. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 951, 175664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.L.; Zhang, Z.L.; Banks, E.; Grover, D.; Jiang, J.Q. Pharmaceutical residues in wastewater treatment works effluents and their impact on receiving river water. J. Hazard Mater. 2009, 166, 655–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onesios, K.M.; Yu, J.T.; Bouwer, E.J. Biodegradation and removal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products in treatment systems: A review. Biodegradation 2009, 20, 441–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OJones, A.H.; Voulvoulis, N.; Lester, J.N. Human Pharmaceuticals in the Aquatic Environment a Review. Environ. Technol. 2001, 22, 1383–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barceló, L.D.; de Alda, M.J.L. Contaminación y Calidad Química del Agua: El Problema de los Contaminantes Emergentes. Barcelona. 2008. Available online: https://fnca.eu/phocadownload/P.CIENTIFICO/inf_contaminacion.pdf (accessed on 12 February 2025).
- Tran, N.H.; Reinhard, M.; Gin, K.Y.H. Occurrence and fate of emerging contaminants in municipal wastewater treatment plants from different geographical regions-a review. Water Res. 2018, 133, 182–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heberer, T. Occurrence, fate, and removal of pharmaceutical residues in the aquatic environment: A review of recent research data. Toxicol. Lett. 2002, 131, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aldana, J.C.; Pedrosa, M.; Silva, A.M.T.; Faria, J.L.; Acero, J.L.; Álvarez, P.M. Nanocomposite PVDF/TiO2 Photocatalytic Membranes for Micropollutant Removal in Secondary Effluent. Catalysts 2024, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhussaini, M.A.; Souza-Chaves, B.M.; Felix, V.; Achilli, A. Comparative analysis of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration for the removal of dissolved contaminants in water reuse applications. Desalination 2024, 586, 117822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, H.; Dhupper, R.; Shrivastava, A.; Kumari, M. Enhancing groundwater remediation efficiency through advanced membrane and nano-enabled processes: A comparative study. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 2023, 23, 100975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Mrabet, H.; Elazhar, F.; Kitanou, S.; Elazhar, M.; Mokhtari, A.; Taky, M.; Elmidaoui, A. Comparison of diverse direct and hybrid membrane processes for nitrate removal from brackish water. Desalination Water Treat. 2022, 273, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasharin, D.V. Increasing Efficiency of Water and Energy Supply Systems in Southern Region Environment of Russian Federation. Lect. Notes Electr. Eng. 2020, 641, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferre, M.; Moya-Llamas, M.J.; Dominguez, E.; Ortuño, N.; Prats, D. Advanced Oxidation Processes and Adsorption Technologies for the Removal of Organic Azo Compounds: UV, H2O2, and GAC. Water 2025, 17, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jun, B.-M.; Jung, B.; Park, C.M.; Jang, M.; Nam, S.-N.; Yoon, Y. Removal of contaminants of emerging concern by membranes in water and wastewater: An updated review. Environ. Eng. Res. 2024, 30, 240103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Membrane | Nanofiltration | Reverse Osmosis | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | NF90-400/34i | 73AC | 73UAC | 73HA |
| Manufacturer | FilmTecTM (DuPont) | Toray Industries | ||
| Type | High removal of nitrates, iron, and organic compounds; low energy consumption | High rejection, chlorine resistant | High rejection, low energy | Extra-low energy |
| Molecular weight cut-off (MWCO) (Da) | 200–400 | 200 | N/A | N/A |
| Salt rejection (%) | 98.7 | 99.8 | 99.5 | 99.3 |
| Maximum operating temperature (°C) | 45 | 45 | 45 | 45 |
| Maximum operating pressure (bar) | 41.4 | 41 | 41 | 25 |
| Maximum pressure drop (bar) | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| pH range in continuous operation | 2–11 | 2–11 | 2–11 | 2–11 |
| Compound | Concentration (g·L−1) |
|---|---|
| peptone | 2.6 × 10−2 |
| meat extract | 1.8 × 10−2 |
| urea | 4.9 × 10−3 |
| MgSO4 7H2O | 3.3 × 10−4 |
| KH2PO4 | 4.6 × 10−3 |
| CaCl2 2H2O | 6.6 × 10−4 |
| NaCl | 1.2 × 10−3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Domínguez, E.; Ferre, M.; Moya-Llamas, M.J.; Ortuño, N.; Prats, D. Removal of Indicator Micropollutants Included in Directive (EU) 2024/3019 Using Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis. Water 2025, 17, 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091269
Domínguez E, Ferre M, Moya-Llamas MJ, Ortuño N, Prats D. Removal of Indicator Micropollutants Included in Directive (EU) 2024/3019 Using Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis. Water. 2025; 17(9):1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091269
Chicago/Turabian StyleDomínguez, Elizabeta, Marta Ferre, María José Moya-Llamas, Nuria Ortuño, and Daniel Prats. 2025. "Removal of Indicator Micropollutants Included in Directive (EU) 2024/3019 Using Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis" Water 17, no. 9: 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091269
APA StyleDomínguez, E., Ferre, M., Moya-Llamas, M. J., Ortuño, N., & Prats, D. (2025). Removal of Indicator Micropollutants Included in Directive (EU) 2024/3019 Using Nanofiltration and Reverse Osmosis. Water, 17(9), 1269. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17091269







