Abstract
Spoil heaps have become a major source of anthropogenic soil erosion, but the hydrological responses and erosion mechanisms of in situ slopes under rainstorms remain poorly understood. We performed simulated rainfall experiments at real estate (Site A), railway (Site B), and railway station (Site C) construction sites, as well as spoil sites (Site D) in China’s Yangtze River Delta. Rainfall parameters, surface runoff, interflow, vertical soil moisture profiles, and sediment yield were monitored: (1) Hydrological responses differed significantly across the sites due to soil structure complexity; stable erosion after the first rainfall event was not achieved at any site except Site C. Soil erosion was the strongest at Site C, followed by Sites D, B, and A. After the second rainfall event, erosion was stable, increasing, and decreasing at Sites A, B and C, and D, respectively. (2) Runoff and the soil loss rate were positively correlated (R2 > 0.7), and the slopes of the fitted regression lines were highest for Sites B and C, followed by Sites D and A. (3) Soil erodibility values based on field data were 0.0029, 0.1164, 0.1974, and 0.0989 t·hm2·h·hm−2·MJ−1·mm−1 for Sites A, B, C, and D, respectively. (4) The soil bulk density, gravel content, and silt content were key factors contributing to the severe erosion of field spoil heaps. Spoil heaps from different project types exhibited distinct hydrological and erosional behaviors, which necessitates targeted mitigation strategies to reduce severe erosion and landslide risks.
1. Introduction
Urban production and construction activities are vital drivers of economic prosperity and social development, yet they cause extensive surface disturbances, including soil excavation [1], compaction [2], and spoil heaps [3,4]. These disturbances lead to vegetation destruction, terrain alteration, and changes in soil structure and composition, which render surfaces more susceptible to erosion [5,6,7]. Spoil heaps, which are formed by excavation and the deposition of loose materials, feature steep slopes, have exposed surfaces, and comprise heterogeneous materials; they have become a primary source of anthropogenic soil and water loss [8,9,10,11]. Human-altered spoil heap slopes disrupt natural rainfall–runoff processes, resulting in sediment yields tens of times higher than those from bare natural slopes [12,13]. In the Yangtze River Delta, a rapidly urbanizing region in China, frequent construction activities, coupled with monsoon climates and typhoon-induced concentrated rainfall, exacerbate soil erosion from spoil heaps, threatening urban ecosystems and water quality [14,15,16]. Therefore, investigating the hydrological characteristics of in situ project-generated spoil heaps and elucidating their erosion mechanisms are critical for guiding urban soil conservation and environmental protection policies.
Urban construction projects, such as transportation, mining, hydraulic engineering, and urban development, generate spoil heaps with distinct morphologies and soil properties [17]. Common slope shapes include linear, polygonal, and terraced forms [18]. The composition of mining spoil heaps is complex, and the sand content averages 39.24%; linear infrastructure projects produce gravel-dominated debris, and urban construction yields soil-based waste [19]. Soil bulk density and infiltration capacity vary with the deposition duration. Urban projects constrained by land management often involve short-term heaps (days to years), which are temporarily covered with dense nets [20,21]. In contrast, mining heaps accumulate over decades; they, thus, require long-term stabilization measures such as vegetation restoration, soil amendment, or engineering barriers [7,22,23]. Surveys indicate that spoil heap slopes in China’s six major erosion regions range from 21° to 46° and from 1.2 to 19 m in length [24].
Spoil heaps differ markedly from natural soils in their texture, structure, and infiltration capacity, as they often contain gravel and construction debris due to excavation activities [25]. Laboratory simulations show that infiltration rates in sandy loam and purple soil heaps are 1.70–4.07 and 7.02–11.59 times higher, respectively, than those in undisturbed soils [9]. Gravel reduces sediment yield; sediment yield is reduced by 84.2% in Lou soil heaps with gravel [26], by 35.23–76.84% in waste heaps [27], and by 87.0–92.3% in loess heaps [28]. However, gravel decreases erosion in clay heaps but increases erosion in sandy loam heaps [29]. Sediment yield initially rises and then declines with the gravel content, as low gravel concentrations inhibit flow velocity [30]. Erosion severity varies by soil type; sandy loam heaps yield more sediment than purple soil heaps [9]. Aeolian sand heaps erode more readily than red soil or Lou soil heaps [31,32], and sandy heaps erode 3.0 and 2.3 times faster than loam and clay heaps, respectively [33]. Critical slope gradients (e.g., 30° for mining heaps) [34] and lengths (e.g., 22.26 m for Lou soil heaps) [35] exist, below which erosion increases with slope steepness and length [36]. Gravelly heaps exhibit shorter critical slope lengths (3~5 m), with erosion rates decreasing within this range [37]. Slope aspect also influences erosion; southwest-facing heaps in Belgium and northern France experience maximal erosion due to prevailing rain-bearing winds [38].
Rainfall is a key driver of spoil heap erosion, which is affected by the intensity, frequency, and pattern of rainfall. Higher intensities amplify runoff shear stress, stream power, and rill erosion [30], progressively increasing erosion rates [33]. Extreme short-duration rainfall triggers severe erosion, and extensive surface erosion can eventually lead to the formation of gullies [23,37]. Multi-event rainfall elevates runoff but reduces sediment yield [39]. Platform-topped heaps subjected to combined rainfall and upstream inflow exhibit sediment surges of up to 49-fold [40]. Rainfall, inflow, and their interaction contribute 9.24–27.90%, 13.97–69.73%, and 20.72–70.83% to total sediment loss, respectively [41]. Rainfall peak timing exacerbates erosion; early, late, and mid-peak storms increase sediment by 79.7%, 78.2%, and 14.2% compared with uniform rainfall [42]. Simulated scouring experiments confirm that erosion increases with flow discharge [9,41,43].
The current research predominantly employs simplified laboratory spoil heap models to explore factors such as rainfall, flow, gravel content, and soil texture. Although these studies have advanced our understanding of runoff and erosion mechanisms, such models often use homogeneous soils, with short deposition periods and insufficient compaction, which fails to replicate the complexity of field spoil heaps. In addition, the field-scale erosion mechanisms under extreme rainfall remain underexplored. Most studies have focused on single-project heaps (e.g., tunnels, mines, power plants, or real estate), yet comparative analyses of erosion characteristics across project types are lacking.
Here, we investigated four types of project-specific spoil heaps using field-based rainfall simulations in the Yangtze River Delta—a highly urbanized region in eastern China. Our objectives were to (1) analyze the hydrological and sediment yield processes of spoil heaps under rainstorms; (2) estimate soil erodibility (K) using field data and the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE); and (3) characterize the effects of rainfall, flow, gravel content, and soil texture on soil erosion. Our comparison of erosion disparities among heaps in complex environments will aid region-specific ecological protection and erosion control strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Design
Our study focused on spoil heaps for production and construction projects in the Yangtze River Delta, where real estate and transportation activities are common [14,16] (Figure 1a). This area has a subtropical monsoon climate with an annual average temperature of 14–18 °C and 1000–1500 mm of rainfall [44]. Based on a survey in China by Zhao et al. [24], we studied four types of projects, including real estate, railway, and railway station construction sites, as well as a spoil site. We carried out artificial rainfall simulations on typical spoil heaps that reflect the characteristics of the four projects (Figure 1b–e). The basic information for each spoil heap is shown in Table 1.

Figure 1.
The project location and typical spoil heaps in the Yangtze River Delta. Notes: Sites A, B, C, and D correspond to the test plots for real estate, railway, and railway station construction sites, as well as the spoil site, respectively.

Table 1.
Basic information of the sample sites.
We established plots on a relatively flat slope on each spoil heap using a stainless steel frame and default specifications of 2 m × 1 m [7]. At the bottom, we set up a V-shaped collection flume for surface runoff and an L-shaped collection flume for interflow. The installation position should be adjusted based on the actual conditions, such as the presence of large stones or uneven surfaces. Therefore, the actual lengths of the four plots were different, as shown in Table 1. Due to the small scale of the experimental plots, we primarily focused on measuring the interrill erosion of spoil heaps. To ensure the stability of the device, the L-shaped collection flume was installed 10 cm away from the bottom of the plot, which collected water flowing from the 10 cm soil profile. To prevent the rainwater accumulated on the V-shaped collection flume from entering the runoff samples, we connected the outlet of the flume and the sample receiving port with a plastic bag.
To reduce the influence of moisture conditions of the spoil heap itself on the simulation process, surface pre-wetting before the experiment was conducted to make the soil moisture content reach the field capacity [45]. The water supply during the pre-wetting process was derived from the simulated rainfall, which lasted for 15 min. The rainfall intensity was similar to that in the subsequent experiments. After the pre-wetting ended, the slope was left undisturbed for 30 min to allow the gravitational water to fully infiltrate into the lower soil layer.
Field-simulated rainfall is often influenced by wind speed and its direction, which results in an uneven rainfall distribution. Based on actual field conditions, the spacing and angle of three rainfall nozzles were slightly adjusted, and the effective rainfall area was set to 4 m × 4 m to cover the plot to the greatest extent possible. The rainfall uniformity reached 80% to simulate actual rainfall [46]. Additionally, a simple rain gauge was installed on each side of the plot, and the average rainfall from these gauges was used as the actual rainfall amount for each event.
Rainstorm events can cause severe erosion, and 98.6% of severe erosion is caused by summer precipitation based on 72 meteorological stations in the Yangtze River Delta region [47,48,49]. Rainfall simulations were performed based on rainstorm events in our study. Patterns of natural rainfall are complex and include both continuous and intermittent precipitation. In particular, multiple raindrop splashes during intermittent rainfall can break up soil aggregates, and their effect on infiltration performance is stronger than that of continuous rainfall with the same duration [50]. In our study, a total of 11 continuous rainfall events were simulated. Consecutive rainfall events within a day at the same sites were combined to represent intermittent rainfall, with a rain-free interval ranging from 72 to 121 min. The duration of continuous rainfall was either 30 min or 110 min, while that of intermittent rainfall was either 170 min or 220 min. A total of 16 rainfall events were carried out: 7 rainfall events were simulated at Site A, and 3 rainfall events were simulated at each of the other sites. We increased the number of rainfall events at Site A because runoff was the lowest at this site. All the simulated rainfall parameters are shown in Table 2. According to the definition of short-duration storms (>16 mm·h−1 within 6 h), all the simulated events except No. 5 met the storm threshold [51]. Historical data (1980–2010a) indicate that short-duration storms in the Yangtze River Delta typically yield an average rainfall of 35 mm [52]. Most simulated events in this study reached or exceeded this threshold, except for No.1–3 and No.5. Furthermore, 68.75% of the events simulated sudden storms (≥20 mm·h−1 or ≥50 mm·3 h−1) [53], and three events (No.10, 13, and 16) surpassed the regional extreme thresholds (77.90–83.15 mm) [52]. These simulations effectively replicated rainstorms in the Yangtze River Delta.

Table 2.
Parameter values of artificial rainfall simulations.
2.2. Measurements and Methods
2.2.1. Erosion Process Determination
After the rainfall started, all the surface runoff samples were collected every 10 min, and then the runoff volume (mm) was measured. The runoff coefficient was calculated by the runoff volume divided by the precipitation amount. A portion of the runoff samples were sent to the laboratory to determine their sediment content (g·L−1) by the oven drying method, and then the soil loss (Mg·ha−1) was calculated, which was calibrated to the values of unit rainfall amount for analysis. After the rainfall ended, the total interflow samples were collected and measured. The interflow amount (mm) was calibrated to the unit rainfall amount and the plot area.
2.2.2. Soil Sampling and Testing
Before the tests started, we collected 0–10 cm surface soil samples from the plot slope to analyze the soil water content (%); sand, silt, and clay content (%); gravel content (%); soil organic matter (g·kg−1); and soil pH. Soil bulk density (g·cm−3) was determined by the cut ring method. After rainfall at the test sites, soil samples were collected every 10 cm from the 0–40 cm section to analyze the vertical distribution of the soil water content (%). The profile was excavated in the downhill orientation.
2.2.3. Measurement of Soil Erodibility
The soil erodibility (K-value) was generally calculated using the amount of soil loss caused by the unit rainfall erosivity on a standard plot [54,55,56]. Based on field investigations of spoil heaps in the southern red soil region, the standard plot had a slope length of 4.8 m and a slope of 37° [4]. The USLE is a classic erosion mathematical model used to quantify the relationship between soil loss on slopes and its main influencing factors as shown in Equation (1) [57].
where A is the measured soil erosion (t·ha−1); R is the rainfall erosivity (MJ·mm·ha−1·h−1), calculated by Equation (2); K is the soil erodibility (t·ha·h·ha−1·MJ−1·mm−1), which is mainly based on the soil texture, organic matter, and infiltration; and S and L are the slope and length, respectively, which are corrected using the standard plot dimensions (slope 37°, length 4.8 m) by Equation (3). C and P are the vegetation cover and management factor and soil and water conservation measure factor, respectively, which were both set to 1 because the slope was bare without protection.
where E is the total kinetic energy of rainfall (MJ·ha−1); e is the kinetic energy of rainfall per unit rainfall amount (MJ·mm·ha−1).
where λ and θ are the length and slope of the test plot, respectively.
A = R·K·L·S·C·P
R = EI30,
E = eP,
e = 0.119 + 0.0873 lg I, I ≤ 76,
e = 0.283, I > 76
E = eP,
e = 0.119 + 0.0873 lg I, I ≤ 76,
e = 0.283, I > 76
LS = (λ/4.8)0.5 × (θ/37)1.25
Based on the above equation, the K-values at each site were measured by establishing a linear relationship between soil erosion (A) and their influencing factors (RLS), which provide a closer approximation to the accurate value compared with when an average value is used [58].
2.3. Statistical Analysis
All the measured data were recorded and calculated in MS Excel (Version 2010). A correlation analysis was conducted to comprehensively explore indexes of spoil heaps and rainfall using the SPSS software (Version 22.0). All the figures were made using Origin (Version 2025) or ArcGIS (Version 10.2.2) software.
3. Results
3.1. Hydrological Responses of Spoil Heaps
Hydrological processes on spoil heap slopes include surface runoff, vertical infiltration, and interflow. As shown in Figure 2a, the maximum runoff coefficient (value of 1.07) occurred at Site C, and the minimum (value of 0.01) was observed at Site A. The average runoff coefficient was highest for Site C, followed by Sites D, B, and A, with average values of 0.90, 0.67, 0.38, and 0.05, respectively.
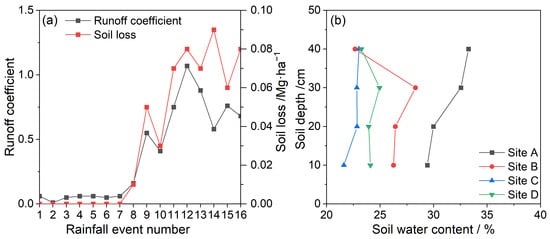
Figure 2.
The runoff coefficient and soil loss (a) and the soil vertical moisture distribution (b). Notes: Sites A, B, C, and D are the test plots in the real estate, railway, and railway station construction sites, as well as the spoil site, respectively.
Runoff dynamics were further analyzed using two continuous rainfall events per site (Figure 3): (1) Site A: The runoff rate rose continuously during the first event but declined 10 min before rainfall cessation. In the second event, runoff was initiated after 10 min, followed by fluctuating increases and slowed growth 30 min prior to rainfall cessation. The stable runoff rate was slightly higher than the highest runoff rate in the first rainfall event. (2) Site B: The runoff rates showed sustained increases in the first rainfall event and a stable increasing pattern in the second rainfall event. The stable runoff rate in the second rainfall event was 70% of the peak runoff rate in the first rainfall event, and it stabilized within 30 min. (3) Site C: The runoff rates increased with rainfall, and both stabilized after 50 min. The runoff rate at the stable state in the second rainfall event was 48% higher than that in the first rainfall event. (4) Site D: Rising runoff rates were observed for both events, and rapid runoff initiation (within 10 min) was observed with the second rainfall event and a 45% peak rate increase.
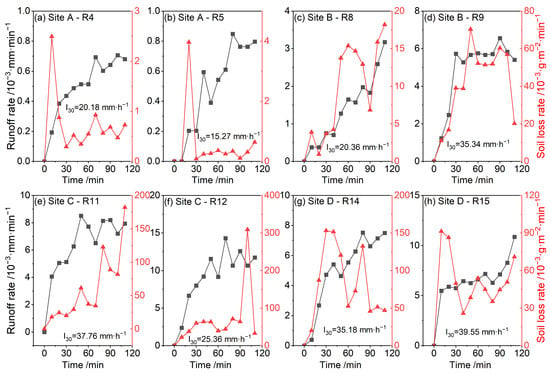
Figure 3.
Runoff rate and soil loss rate in the slope erosion process. Notes: Sites A, B, C, and D are the test plots in the real estate, railway, and railway station construction sites, as well as a spoil site, respectively. R4–R15 correspond to rainfall events. I30, maximum rainfall intensity in 30 min.
Soil moisture profiles (0–40 cm depth) revealed infiltration patterns (Table 1, Figure 2b). Site A had the highest pre- and post-rainfall moisture (minimal change: 1.1%), with water accumulation below 20–30 cm and outflow observed at the slope bases. Site B had the lowest initial moisture but the largest post-rainfall increase (19.4%), with a wetting front at 30–40 cm. Sites C and D had intermediate moisture changes (C: 5.3%; D: 10.2%). Site D exhibited deeper infiltration (>40 cm), while Site C showed a uniform moisture distribution (0–40 cm).
Interflow, which is horizontal water movement at a depth of 10 cm, varied significantly: 4.8 × 10−3 and 3.9 × 10−3, 0 and 0, 11.4 × 10−3 and 9.2 × 10−3, and 6.1 × 10−3 and 13.7 × 10−3 mm for the first and second rainfall events at Sites A, B, C, and D, respectively; the proportion of interflow derived from the runoff volume was 8.1% and 7.1%, 0% and 0%, 1.5% and 0.9%, and 1.1% and 1.8%, respectively. Interflow decreased with repeated rainfall at Sites A and C but increased at Site D, which reflected divergent subsurface flow dynamics.
3.2. Erosion Process of Spoil Heaps
Spoil heaps undergo severe soil erosion under continuous storm events [59]. Soil loss per rainfall amount was highest for Site D, followed by Sites C, B, and A, with average values of 7.60 × 10−2, 7.49 × 10−2, 3.05 × 10−2, and 0.06 × 10−2 Mg·ha−1, and average sediment content of 11.6, 8.5, 7.8, and 1.3 g·L−1, respectively (Figure 2). As the number of rainfall events increased, the soil loss at Site A remained stable; at Sites B and C, the soil loss increased by 3.24- and 0.15-fold, respectively. In contrast, soil loss decreased by 0.37-fold at Site D.
Erosion dynamics were further analyzed based on the soil loss rate changes from two continuous rainfall events per site (Figure 3). At Site A, the soil loss rates spiked abruptly, declined, and then increased in a fluctuating manner, and the soil loss rates were slightly lower after the second rainfall event compared with the first rainfall event. At Site B, the soil loss rate increased in a fluctuating manner after the first rainfall event, and a stable increasing trend followed by a decrease was observed after the second rainfall event, which resulted in a 3-fold increase in the peak rate of soil loss. At Site C, a fluctuating increase was observed after the first rainfall event; after the second rainfall event, a stable increasing trend followed by fluctuations was observed. The stabilized soil loss rate was 35% of the peak rate in the previous rainfall event. At Site D, fluctuations were observed after the first event and stabilized after 90 min of rainfall. The second event featured similar fluctuations, but a 50% peak increase was observed late during the rainfall period. These results underscore the significant variability in erosion dynamics among spoil heaps under sequential storms.
A linear relationship between the runoff rate and soil loss rate was observed after excluding outliers (e.g., abrupt shifts and unstable fluctuations across 11 observation intervals), which yielded strong fits (R2 > 0.7; Figure 4). The slope coefficients of the regression equations reflect sediment transport efficiency. With the exception of the first rainfall event at Site D, sediment yield rates increased linearly with runoff rates, indicating a “more water, more sediment” trend. For the first rainfall event, the slopes were highest for Site C, followed by Sites B and A. For the second rainfall event, the slopes were highest for Site B, followed by Sites D, C, and A. As the number of rainfall events increased, the slope at Site B increased, and the slopes at Sites A and C decreased, which is related to changes in rainfall intensity. This is because high rainfall intensity is characterized by high erosion kinetic energy.
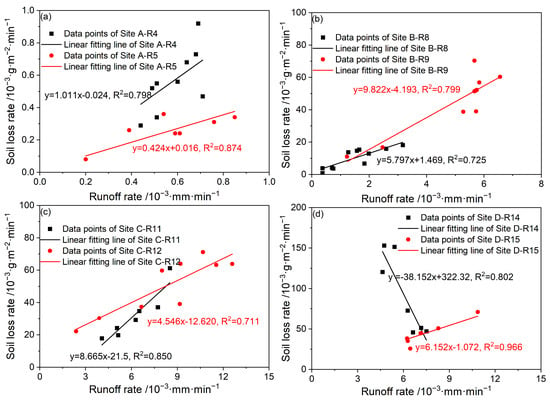
Figure 4.
The linear relationships between the runoff rate and soil loss rate. Notes: R4–R15 correspond to rainfall events. (a) real estate construction site; (b) railway construction site; (c) railway station construction site; (d) a spoil site.
In addition, it should be noted that there was a negative correlation at Site D during the first rainfall event (R14). As shown in Figure 3, within 40 min after the start of rainfall, runoff promoted soil loss, but the pattern was completely reversed thereafter. This might be because the soil sealing phenomenon reduced the ability of runoff to detach soil. Our on-site observations showed that there were many reticular rills on the slope. The rills were smooth inside and had obvious water flow, which was caused by the blockage of soil pores by fine soil particles. During the second rainfall event (R15), the fitting coefficient at Site D was similar to that at Sites B and C during the first rainfall events (R8 and R11). Moreover, the correlation coefficient of the runoff rate and soil loss rate at Site D within the first 40 min of the first rainfall event was even significantly higher than that at Sites B and C during the second rainfall event (R9 and R12). This indicates that the surface scouring at Site D was extremely intense. However, the soil sealing phenomenon at Site D affected subsequent erosion. That is, after 40 min of the first rainfall event and during the erosion process of the second rainfall event, the soil loss rate was relatively low. However, in the latter stage, the runoff rate was higher, and the soil loss rate was lower, which was due to enhanced soil sealing.
3.3. Soil Erodibility Estimation of Spoil Heaps
Soil erodibility, an intrinsic soil property, can be calculated using empirical data [55,56]. The USLE, a widely used empirical model, estimates the soil erodibility factor (K) by establishing a linear relationship between erosion and its driving forces [60]. K factor values derived from multiple rainfall events are presented in Table 3. Rainfall erosivity (R factor) varied significantly across events, ranging from 35.83 to 1311.82 MJ mm·ha−1·h−1, which mainly stems from different rainfall conditions with I30 ranging from 17.73 to 39.55 mm·h−1. Due to slope differences among sites, the product of the slope and its length (L × S factor), calibrated to the standard slope, ranged from 0.37 to 0.71. The soil erosion (A), observed in the field, ranges from 0.01 to 103.15 t·ha−1. The average values at Sites A, B, C, and D were 0.24, 22.98, 57.25, and 68.77 t·ha−1, respectively. According to the linear fits of the above parameters, the K-values for Sites A, B, C, and D were 0.0029, 0.1164, 0.1974, and 0.0989 t·ha1·h·ha−1·MJ−1·mm−1, respectively.

Table 3.
Parameter values in the USLE.
3.4. Correlation Analysis
The correlation analysis results among the above indicators are presented in Table 4. Slope indicators (i.e., runoff coefficient, soil loss, interflow, and K) were significantly positively correlated. Among the rainfall parameters, significant positive correlations were observed between P and T, I30, and R; between T and R; and between I30, I, and R. Specifically, slope indicators were strongly correlated with the rainfall parameters P, I, I30, and R (except for an insignificant correlation between interflow and I), but not with T. The field simulations revealed that the K factor was significantly correlated only with I30, indicating that high rainfall intensity exacerbates soil erodibility.

Table 4.
Correlation analysis.
4. Discussion
4.1. Hydrological Response Characteristics of Spoil Heaps
During the initial rainfall event with continuous heavy rainfall (lasting nearly 2 h), continuous increases in runoff rates on the spoil heaps from construction sites and the spoil site were observed, and steady-state runoff was not reached, except at Site C, where a stable state was achieved 50 min after the rainfall began. This was because the soil bulk density at Site C was high, and spoil heaps can retain less water, which makes it easier to reach a stable infiltration state. Stable runoff was achieved at Site A and B after 80 and 30 min of the second rainfall event, respectively. A stable state failed to be achieved at Site D until the two rainfall events ended. The precipitation needed to achieve a stable runoff rate for Site A, B, and C was 38 mm, 55 mm, and 31 mm, respectively. The soil water content and soil bulk density were low at Site B. The numerous large pores in the soil allow the infiltration of a large amount of rainwater; consequently, the amount of rainfall required for stable runoff generation was highest for Site B. The amounts of rainfall required at Site A and C were similar, but their runoff generation characteristics significantly differed. Site A has a long stable period, which may be related to the lower rainfall intensity and lower runoff rate. However, the soil water content at Site A was the highest, with a large amount of water infiltrating into the lower layers. The amount of rainfall required for stable runoff generation was slightly higher for Site A than for Site C because of Site A’s lower soil bulk density and higher soil water retention capacity. Site C had the highest bulk density and the lowest soil profile water content, which resulted in the fastest generation of stable runoff. Stable runoff generation was never reached for Site D, which was related to the soil sealing phenomenon. The runoff rate increased as the gully developed.
The results at the field sites contrast with those of the laboratory studies, which report stable runoff within 10 min for simplified spoil heaps made of sandy loam, purple soil, coal mine tailings, or silty clay [9,10,26,29]. Typically, runoff initiation is delayed during early rainfall due to high infiltration rates in dry surface soils. As soils saturate, infiltration decreases, and runoff rates rise rapidly and become stable [61]. However, field spoil heaps have a low gravel content (<4%) and thick water-absorbing layers (e.g., 20–30 cm at Site A, 30–40 cm at Site B and D, and over 40 cm at Site C), with prolonged infiltration phases, which delays the achievement of steady runoff. These deep storage layers increase water retention, which increases landslide risks when soil moisture exceeds critical thresholds. Thus, the gravel content and the hydrological conditions of the subsurface soil must be prioritized in spoil heap management to mitigate rainfall-triggered disasters. The fluctuations in runoff, which were more pronounced than those in laboratory studies and included sudden surges and drops, were caused by heterogeneous internal structures (such as cracks and water-retaining layers) and intermittent blockages by debris. This emphasizes the necessity of in situ monitoring [62]. Moreover, the platform–steep slope system of field spoil heaps introduces dual drivers of erosion: direct rainfall and upstream inflow. This interaction amplifies runoff by 86–629% and intensifies flow turbulence; rainfall has a dominant effect when discharge is low, and the effect of inflow becomes dominant as discharge increases [40,41]. These coupled mechanisms will be explored in future studies to further improve stabilization strategies.
4.2. Erosion Mechanisms of Spoil Heaps
All spoil heaps except those from the real estate construction site (Site A) exhibited severe erosion; this mainly stemmed from the high rainfall volume and intensity. The soil at Site A has a high content of sand particles, organic matter, and moisture. This site is not prone to soil loss because of the stability of the soil structure and the weak hydrodynamic force. There was a positive synergistic relationship between the sediment yield rate and runoff rate, which is often described as “more water, more sediment”. As the runoff increases, it enhances the scouring capacity of the soil and shortens the development time of rills, thus accelerating the erosion process [9]. The erosion process usually starts with sheet erosion (the uniform removal of soil from the surface by rainfall and runoff); it then transitions to discontinuous rills, and finally to continuous rills. This process is mainly driven by hydraulic forces, with occasional gravitational collapses [10]. While laboratory studies have reported that sediment yield stabilizes after an initial peak [61], the field spoil heaps in this study did not show steady-state erosion under storms. Instead, the sediment rates increased across successive rainfall events. This accelerated erosion is a result of the continuous increase in runoff capacity and the continuous supply of loose material, as observed at Sites B and C. However, the soil properties of the accumulations at these two sites, as well as their erosion characteristics, differed greatly. The soil at Site B had a low bulk density and low water content. Rainfall mainly wets the underlying soil through infiltration, so the surface hydrodynamic force of water was relatively weak. When the rainfall intensity and duration increased, soil erosion increased rapidly and reached a stable erosion state during the second rainfall event. The soil at Site C had a high bulk density and a relatively high gravel content, which resulted in a strong surface hydrodynamic force of water and a large amount of soil erosion. As the rainfall intensity decreases and the rainfall continues, the erosive capacity of runoff decreases, but the total amount of erosion increases significantly. In contrast, in the laboratory models, the stabilized runoff leads to a reduction in sediment yields over time because the surface material becomes depleted [61]. The spoil heaps from real estate projects (Site A) showed minimal fluctuations in sediment yield, and the spoil heap at Site D experienced an abrupt decline in sediment yield (70.20%) during the middle of the rainfall event. This decrease is related to the soil sealing of the erosion gullies caused by the clogging of pores by fine soil particles. The soil bulk density and organic matter content at Site D were very low, and the soil texture was extremely loose. Before the formation of soil seals, severe erosion occurred on the slope surface, which was more serious at Site D than at Sites B and C.
The dynamics of sediment are significantly affected by the composition of spoil heaps. Fine-grained soils are the main sources of erosion. Soil-based slopes have detachment rates that are 1.1 to 3.3 times higher than those of gravel-mixed slopes because the flow on such slopes is faster and more turbulent [9,63]. However, in karst regions, limestone gravel can enhance both infiltration and sediment yield [64]. Rill erosion generates fluctuating sediment rates. In the early stage, headcut collapses contribute to these fluctuations; in the later stage, sidewall failures play a role, which results in multiple peaks and troughs in sediment rates [10,65]. The field heaps in this study showed intense fluctuations, including sudden 2.6-fold surges or decreases of 70.20% (Figure 3c,h). These fluctuations were exacerbated by gravitational erosion under high rainfall intensities [66]. Extreme storms with a rainfall intensity greater than 90 mm·h−1 can further amplify these effects. Under such conditions, the erosion rates of spoil heaps can increase to 630 times those of natural slopes [60], and gravel, rather than having a protective role, can actually promote erosion [67]. For example, the relatively high gravel content at Site C may have exacerbated soil erosion. Heavy rainfall can disrupt the cohesion between soil and gravel, increase surface roughness, and concentrate the flow networks, which may trigger landslides [68,69]. These findings emphasize the urgent need for targeted mitigation strategies during extreme rainfall events to reduce the potential hazards caused by spoil heaps.
4.3. Soil Erodibility of Spoil Heaps
Field measurements of spoil heaps in the Yangtze River Delta revealed soil erodibility (K) values ranging from 0.0029 to 0.1974 t·hm2·h·hm−2·MJ−1·mm−1, which were lower than those from laboratory-based simulations. For example, the K-values were 0.0300–0.0728, 0.0091–0.0259, and 0.0096–0.0201 for sandy, loamy, and clayey heaps, respectively [11]. In the loess area, the K-value was 0.0074–0.0224 [58]. Anthropogenic disturbances during construction significantly alter soil properties, topography, and surface cover, resulting in highly variable K-values. The K-values of the four studied heaps were −0.93 to 4.16 times those of natural soils, and coefficients of variation were markedly higher for the four studied heaps (66.55% > 3.26%) [70].
Deposition duration, which ranged from 1 to 5 months in this study, had no clear effect on K. However, prior research has indicated that the K-value decreases as soils stabilize over time. Specifically, the K-values during the phase in which soil is disturbed were 2.03 times higher than those during the phase in which soils are stable [1]. This suggests that the K-value could potentially decline as the deposition duration is prolonged, but further validation is needed to confirm this relationship.
The gravel content significantly modifies soil properties. Multiple factors related to gravel, such as particle size, geometry, embedding patterns, coverage, and proportion, influence surface roughness, crust formation, raindrop splash, infiltration, runoff processes, flow velocity, and rill erosion. These effects may be potentially linked to excavation depth and engineering characteristics [4]. Gravel-related parameters are crucial predictors of the K-values for spoil heaps. Ma et al. [4] introduced the index of the total surface area of rock in a unit volume of the soil–rock mixture (Cs) into the soil and rock factor (Tr) and formulated a function that relates Tr to the soil erodibility factor K: Tr = K − 0.0145Cs + 0.0024. Subsequently, Li et al. [60] developed a soil–rock K-value estimation model (Ki) based on the gravel content (Pi) and the pure soil K-value (K0): Ki = K0 − 0.047Pi + 0.0016. In this study, the variability in K across the four sites, which was lowest for Site A (real estate), followed by Site B (railway), Site D (spoil site), and Site C (railway station), was strongly correlated with the gravel content and soil properties. Site C, which had the highest gravel content (including bricks and foam debris), bulk density, and K-value (0.1974), was in contrast to Site A, which had minimal gravel, superior water retention, and the lowest K-value (0.0029). Even though the gravel content in this study was less than 4%, which is lower compared with the 10–30% typically observed in laboratory studies, its effect on the K-value remained significant [4,58].
An accurate estimation of the K-value is essential for predicting soil erosion. However, sufficient field validation is lacking, and this results in large discrepancies between the predicted and measured values [70,71,72,73,74]. However, in some cases, the predicted K-values could be off by a significant margin from the actual measured values in the field [70]. Spoil heap-specific models also face similar challenges, and their applicability is limited. The preliminary field data from this study, which covered only four sites, highlights the need for expanded monitoring efforts. Future collaborations will be needed to establish a comprehensive and robust dataset in the Yangtze River Delta region. This will help refine the K-value models and enable more precise management of urban soil erosion.
5. Conclusions
We performed field-based simulated rainfall experiments to monitor the hydrological and soil erosion processes of four types of disturbed spoil heaps, which revealed the unique response mechanisms under extreme rainfall conditions. Significant spatial heterogeneity in erosion characteristics was observed. Specifically, adjacent sites exhibited nearly 70-fold differences in sediment yield, a disparity that is difficult to achieve in homogenized laboratory models.
Real estate spoil heaps (Site A) showed the lowest sediment loss. Although their runoff scouring capacity decreased over time, they still retained a large amount of water, which poses latent risks of delayed landslides. Transportation-related spoil heaps showed severe erosion and had similar runoff–sediment relationships. However, the soil erodibility of railway station heaps (Site C, K = 0.1974) was 79% higher than that of railway heaps (Site B, K = 0.1164), which is related to their higher gravel content and bulk density. The spoil heap at Site D exhibited anomalous sediment dynamics. Specifically, the soil loss rates decreased as the runoff rates increased, which is likely attributed to soil sealing.
In summary, these results highlight the diverse erosion characteristics and mechanisms among different types of disturbed spoil heaps. One limitation of this study worth noting is that the simulated rainfall conditions at the different sites were inconsistent, which limits the comparison of the erosion results. Although we standardized the data using rainfall amount and rainfall intensity, long-term monitoring data under natural rainfall conditions are needed, and soil erodibility estimation models should be developed to enhance regulatory strategies for construction-related soil and water conservation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.H.; data curation, Y.H.; formal analysis, Y.H.; funding acquisition, J.D., Z.G. and J.N.; investigation, Y.H. and Y.L.; methodology, Y.H.; project administration, J.W., G.L. and M.Z.; resources, J.D. and Y.L.; software, Y.H. and J.W.; supervision, J.D., Z.G. and J.N.; validation, Y.H.; writing—original draft, Y.H.; writing—review and editing, Y.H. and Z.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, grant number 32371966 and Monitoring, Analysis and Evaluation of Soil Erosion in the Yangtze River Delta Integrated Demonstration Zone, grant number [2024]ZX265.
Data Availability Statement
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Yisi Liu, Pulong Yan, and Yuanzheng Gu for helping with our laboratory work, and Quanman Lin, Mingming Ye and the project builders for help with our fieldwork.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Guo, Q.K.; Qin, W.; Ning, D.H.; Shan, Z.J.; Yin, Z.; Du, P.F. Enhancement coefficient of soil erodibility factor for general disturbed land surface. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 17, 85–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, E.; Eu, S.; Li, Q.W. Assessment of soil erosion potential from the disturbed surface of skid trails in small shovel harvesting system. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 756848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, M.X.; Xie, Y.S.; Zhao, X.; Suo, G.D.; Liu, N.; Chen, L. Runoff and soil loss modeling on spoilbank with soilstone mixture. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 27, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.C.; Xie, Y.S.; Zhao, X.; Wu, Y.Y.; Ding, X.H.; Rong, Y.B. Defining of spoil heaps unit plot and improvement of spoil heaps erodibility factor. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 10, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Amundson, R.; Berhe, A.A.; Hopmans, J.W.; Olson, C.; Sztein, E.; Sparks, D.L. Soil and human security in the 21st century. Science 2015, 348, 1261071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, P.J.; Yu, S. Mechanisms of nature–and human–Driven soil erosion by water. J. Fujian Agric. For. Univ. Nat. Sci. Ed. 2022, 51, 433–450. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.Z.; Tian, Z.Y.; Gu, Z.J.; Wu, B.X.; Yin, L. Controlling soil erosion of tailings from rare earth mines with Paspalum wettsteinii and soil amendments. Land Degrad. Dev. 2024, 35, 5533–5548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.Y.; He, J.L.; Li, J.R.; Xing, E.D.; Wen, A.S.; Liu, Y.P.; Yang, G.Y. Effects of different measures on water erosion control of dump slope at opencast coal mine in typical steppey. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 296–303. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, D.M.; Jiang, G.Y.; Peng, X.D.; Wang, S.S.; Li, Y.X.; Jiang, P. Runoff erosion process on slope of engineering accumulation with different soil–rock ratio. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 152–161. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, W.B.; Shi, D.M.; He, W.J.; Jiang, G.Y.; Jiang, P.; Li, Y.X. Hydrodynamic characteristics of engineering accumulation erosion under side slope runoff erosion process in field scouring experiment. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 153–161. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.L.; Li, J.M.; Kang, H.L.; Guo, M.M.; Li, H.W. Soil erosion prediction model for spoil heaps in production and construction projects. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 27–34+42. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, H.; Gan, Z.M. Erosion and sediment yielding process of soil dumped by people in urbanizing construction area. J. Shaanxi Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 1998, 26, 95–98. [Google Scholar]
- Ricks, M.D.; Wilson, W.T.; Zech, W.C.; Fang, X.; Donald, W.N. Evaluation of hydromulches as an erosion control measure using laboratory—Scale experiments. Water 2020, 12, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.Y.; Yang, S.; Yin, S.G.; Xu, H.Z.Y. Spatial—Temporal dynamic characteristics and its driving mechanism of urban built—Up area in Yangtze River Delta based on GTWR model. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2021, 30, 2594–2606. [Google Scholar]
- Fazekašová, D.; Petrovič, F.; Fazekaš, J.; Štofejová, L.; Baláž, I.; Tulis, F.; Tóth, T. Soil Contamination in the Problem Areas of Agrarian Slovakia. Land 2021, 10, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.P.; Yang, S.; Liu, Y.H.; Zhu, Y.H.; Cai, A.N. The urban population agglomeration capacity and its impact on economic efficiency in the Yangtze River Delta Urban Agglomeration. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 13739–13768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wu, S.X.; Wang, C.; Du, M.Q.; Wu, Y.; Liu, S.J.; Zhang, B. Research progress on slope erosion of accumulation bodies in production and construction engineering. Subtrop. Soil Water Conserv. 2018, 30, 31–36. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Cao, B.Z.; Wang, J.; Ren, Y. Study on soil erosion effect of different stacking methods of engineering accumulation based on WEPP model. J. Nat. Disasters 2022, 31, 261–270. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.Z.; Jiang, D.; Jiang, G.Y.; Wang, S.S.; Shi, D.M. Physical Property changes and classification of types in spoil sites of production and construction projects. Technol. Soil Water Conserv. 2014, 6, 32–35. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.H.; Nie, W.T.; Xu, W.S.; Huang, J.Q.; Li, L.; Li, J.M.; Zhang, W.J.; Liu, J.G. Effects of runoff and sediment reduction on engineering accumulation slopes under different soil and water conservation temporary measures. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 141–150. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Sun, Y.R.; Cao, B.Z.; Guang, H.B.; Feng, R.K.; Zhang, Y.R.; Wang, J. Influence of rainfall duration dynamic changes on flow reduction and sediment reduction benefits of fine mesh net on construction spoil deposits. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 37, 8–16+30. [Google Scholar]
- Rydgren, K.; Halvorsen, R.; Odland, A.; Skjerdal, G. Restoration of alpine spoil heaps: Successional rates predict vegetation recovery in 50 years. Ecol. Eng. 2011, 37, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.M.V.; Wrana, A.; Rajwa, S.; Różański, Z.; Frączek, R. Slope stability numerical analysis and landslide prevention of coal mine waste dump under the impact of rainfall—A case study of Janina mine, Poland. Energies 2022, 15, 8311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.S.; Jing, M.X.; Liu, X.Y.; Xu, J. Types and characteristies of spoilbank in development construction project. Sci. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 11, 88–94. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.Z.; Tian, Z.Y.; Ma, R.; Liang, Y.; Zhu, X.C.; Qu, L.L. Effects of superabsorbent polymers (SAPs) incorporated with organic and inorganic fertilizer on the water and nutrient retention of soil in rare earth mine tailing areas. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 3384–3395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.D.; Wang, W.L.; Lou, Y.B.; Bai, Y.; Kang, H.L.; Cui, Z.Q.; Lu, Z.J. Effects of gravel content on runoff and sediment yield on Lou soil engineering accumulation slopes under simulated rainfall conditions. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 33, 3027–3036. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.R.; Luo, H.; Xie, Y.S. Effects of rock fragment content, size and cover on soil erosion dynamics of spoil heaps through multiple rainfall events. Catena 2019, 172, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.Z.; Kang, H.L.; Yu, X.; Wang, W.L.; Tian, P. Influences of rock fragments on the hydraulics and erosion of concentrated runoff in steep spoil heaps on the Loess Plateau of China. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2022, 37, 553–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.R.; Luo, H.; Hu, J.S.; Xie, Y.S. The effects of rock fragment content on the erosion processes of spoil heaps: A laboratory scouring experiment with two soils. J. Soils Sediments 2019, 19, 2089–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Wang, X.W.; Luo, H.; Zhang, J.Y. Relationship among runoff, soil erosion, and rill morphology on slopes of overburdened stockpiles under simulated rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2024, 633, 130991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, H.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Guo, M.M.; Kang, H.L.; Li, J.M.; Bai, Y. Runoff—Sediment relationship and erosion dynamic characteristics for two types of engineering deposits under rainfall condition. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 3141–3153. [Google Scholar]
- Sha, X.Y.; Wang, W.L.; Lou, Y.B.; Kang, H.L. The dynamic difference of runoff erosion on slope surface of different soil engineering accumulation bodies. J. Nat. Disasters 2022, 31, 191–199. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.M.; Niu, J.; Wang, W.L.; Zhang, P.C.; Cheng, D.B.; Wang, Y.F.; Zhang, G.H.; Guo, M.M. Differences in characteristics of runoff and sediment yielding from spoil heaps with different soil textures. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2016, 32, 187–194. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, T.T.; Wang, D.M.; Zhang, Z.Z.; Zhang, P.; Liu, X.Y. Characteristics of runoff, sediment and nitrogen and phosphorus output of steep slope of abandoned soil deposits under scouring flow. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 101–109+117. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, P.L.; Wang, W.L.; Li, J.M.; Kang, H.L.; Lou, Y.B.; Wei, S.H. Responses of runoff and sediment yield to slope length and gravel content of Lou soil engineering accumulation slope in Guanzhong region, Northwest China. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 35, 749–758. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.Q.; Lou, Y.C.; Qi, X.Y.; Gao, Z.L.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, S. Influence of flow intensity, slope and soil particle fractal dimension on slope erosion of engineering accumulation body. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 35, 127–134. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Wang, W.L.; Li, J.M. Response of velocity and sediment production characteristics of spoil heaps to slope length and gravel action. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2023, 37, 48–56+102. [Google Scholar]
- Beullens, J.; Van de Velde, D.; Nyssen, J. Impact of slope aspect on hydrological rainfall and on the magnitude of rill erosion in Belgium and northern France. Catena 2014, 114, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Gao, Z.L.; Li, Y.H.; Sun, G.F.; Lou, Y.C.; Yang, S.Y.; Wu, T. Soil erosion characteristics of engineering deposits under continuous runoff scouring. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 42, 61–67. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, Y.B.; Wu, X.; Ciao, Z.L.; Li, Y.H. Characteristics of soil erosion on engineering accumulation slope under the rainfall and inflow conditions. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2020, 36, 69–77. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.C.; Wu, T.; Sun, G.F.; Cen, Y.F.; Su, B.N.; Gao, Z.L. Effect of combined rainfall and inflow on soil erosion of spoil tips. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 2229–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.T.; Gao, Z.L.; Li, Z.B.; Tian, H.W. Downslope runoff and erosion response of typical engineered landform to variable inflow rate patterns from upslope. Nat. Hazards 2016, 80, 775–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.J.; Gao, Z.L.; Li, Y.H.; Zhang, L.T.; Liu, Z.Z. Study on characteristics of runoff and sediment yield on steep slope of engineering accumulation body. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2016, 30, 107–110. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.F.; Xu, Y.P.; Tabari, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Song, S.; Hu, Z.L. Innovative trend analysis of annual and seasonal rainfall in the Yangtze River Delta, Eastern China. Atmos. Res. 2020, 231, 104673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Zhao, L.S.; Fan, C.H.; Li, K.F.; Fang, F.Y.; Qian, X.H. Influencing factors of rainwater transformation and soil erosion in thin soil hillslope of rock desertification regions. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2022, 38, 88–97. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Zhao, T.N.; Peng, X.F.; Guo, Y.; Liang, C. Effectiveness of soil and water conservation of greening mulch of roadside slope. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2013, 29, 63–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Xu, Y.P.; Wang, Q.; Xu, Y.; Gao, B. Evolution and non stationary characteristics of summer precipitation structure over the Yangtze River Delta. Adv. Water Sci. 2022, 33, 730–742. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, B.; Ma, X.W.; Jiao, J.Y.; Zhao, W.T.; Ling, Q.; Li, J.J.; Zhang, X.H. Magnitude and hotspots of soil erosion types during heavy rainstorm events on the Loess Plateau: Implications for watershed management. Catena 2024, 246, 108365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Liu, Y.H.; Dong, Y.Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Jidai, J.Q.; Jiao, J.Y.; Liu, B.Y.; Chen, H.; Han, J.Q. Regional difference and prevention strategy of farmland erosion induced by extreme rainstorms in the Loess area and Rocky mountain area of Northern China. Earth Surf. Process. Landforms 2024, 49, 2704–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.Q.; Zhang, X.R.; Jiao, F.X.; Li, G.L. The relationship between soil crust and infiltration under simulated continuous and intermittent precipitation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 38, 64–72+81. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, R.C.; Yuan, W.H.; Li, J. The asymmetry of rainfall process. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 1850–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.R.; Yao, R.; Zhu, Z.Z.; Jin, H.X.; Zhang, S.L. Spatiotemporal evolution of population exposure to multi—Scenario rainstorms in the Yangtze River delta urban agglomeration. J. Geogr. Sci. 2024, 4, 654–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.R.X.; Wang, X.F.; Huang, L.; Luo, Y.L. Spatial and temporal characteristics of abrupt heavy rainfall events over Southwest China during 1981–2017. Int. J. Climatol. 2021, 41, 3286–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsen, T.C.; Wischmeier, W.H. Soil erodibility evaluations for soils on the runoff and erosion stations. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1963, 27, 590–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, K.L.; Xie, Y. An Empirical Soil Loss Equation. In Proceedings of the 12th ISCO Conference, Process of Erosion and its Environmental Effects, Beijing, China, 26 May 2002; Volume l, pp. 21–25. [Google Scholar]
- Palmira, B.H.; Seidou, O. Empirical and physical modelling of soil erosion in agricultural hillslopes. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2024, 72, 279–291. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Department of Agriculture Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978; p. 537. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.W.; Wang, W.L.; Huang, P.F.; Bai, Y. Experimental study of soil erodibility fator of earth–ock engineering accumulation in loess areas. J. Sediment. Res. 2014, 2, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- García-Ruiz, J.M. The effects of land uses on soil erosion in Spain: A review. Catena 2010, 81, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.M.; Wang, W.L.; Huang, P.F.; Li, H.W. Impact on erosion and sediment yield by gravel in pile body of development on struction in Loess Area. J. Sediment. Res. 2014, 4, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.T.; Gao, Z.L.; Yang, S.W.; Li, Y.H.; Tian, H.W. Dynamic processes of soil erosion by runoff on engineered landforms derived from expressway construction: A case study of typical steep spoil heap. Catena 2015, 128, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Wei, Y.C.; Li, Z.; Luo, H.; Xie, Y.S. Response of runoff and sediment yield to gravel content in engineered deposit slopes under continuous rainfall conditions. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 44, 91–100. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.J.; Wang, W.L.; Kang, H.L.; Zhao, M.; Guo, M.M.; Bai, Y.; Su, H.; Nie, H.Y. Differences in hydraulic erosion processes of the earth and earth–rock Lou soil engineering accumulation in the Loess Region. Chin. J. Appl. Ecol. 2020, 31, 1587–1598. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, T.H.; Zhou, W.; Liu, T.; Yang, Y.C.; Mo, B. Characteristics sediment yield and runoff on the slope surface of gravel accumulation in Karst area under continuous simulated rainfall. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2020, 34, 55–60. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, X.D.; Shi, D.M.; Jiang, D.; Wang, S.S.; Li, Y.X. Runoff erosion process on different underlying surfaces from disturbed soils in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area, China. Catena 2014, 123, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, H.L.; Wang, W.L.; Xue, Z.D.; Guo, M.M.; Li, J.M.; Bai, Y.; Deng, L.Q.; Li, Y.F. Experimental study on runoff and sediment yield from engineering deposition with gravel in the northern windy–sandy region, Shaanxi. Adv. Water Sci. 2016, 27, 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Rui, M.G.; Zhou, Y.C. Study on the dynamic hydrodynamic characteristics of runoff on the slope of red soil engineering accumulation. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2024, 31, 143–152+159. [Google Scholar]
- Lv, J.R.; Xie, Y.S.; Luo, H. Erosion process and temporal variations in the soil surface roughness of spoil heaps under multi–day rainfall simulation. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.K.; Lv, J.R.; Luo, H.; Xie, Y.S. Evolution of surface drainage network for spoil heaps under simulated rainfall. Water 2021, 13, 3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Z.Y.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.X.; Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y. Assessing the declining trend in soil erodibility across China: A comparison of conventional and digital K–factor maps. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2025, 13, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.L.; Peng, W.Y.; Yang, H.L. Soil erodibility and its estimation for agricultural soil in china. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2007, 44, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Shi, X.Z. Soil erodiable K in east hillyfields of the southern Yangtze River. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 1999, 6, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Y.; Liu, X.C.; Cao, L.X.; Zheng, F.L.; Zhang, P.C.; Shi, M.C.; Cao, Q.Y.; Yuan, J.Q. Soil erodibility factor (K) calculation and distribution on water erosion areas in China. Chin. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2013, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Guo, Q.K.; Wang, A.J.; Liu, B.Y.; Zhang, M.N.; Chang, Q.Q. Calculation of soil erodibility factor under different soil types based on runoff plot data. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2019, 39, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).