Adaptive Penetration Unit for Deep-Sea Sediment Cone Penetration Testing Rigs: Dynamic Modeling and Case Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
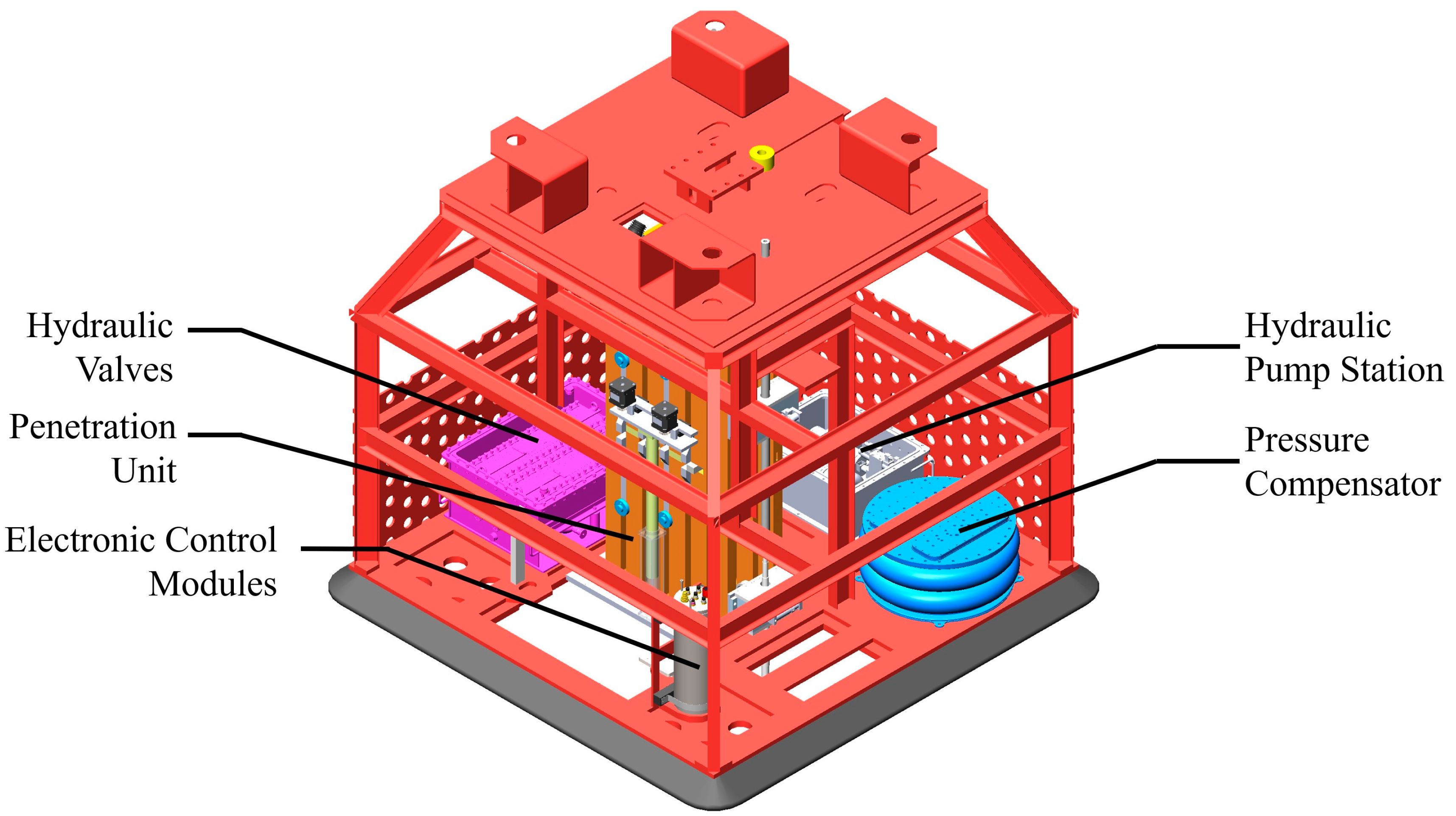
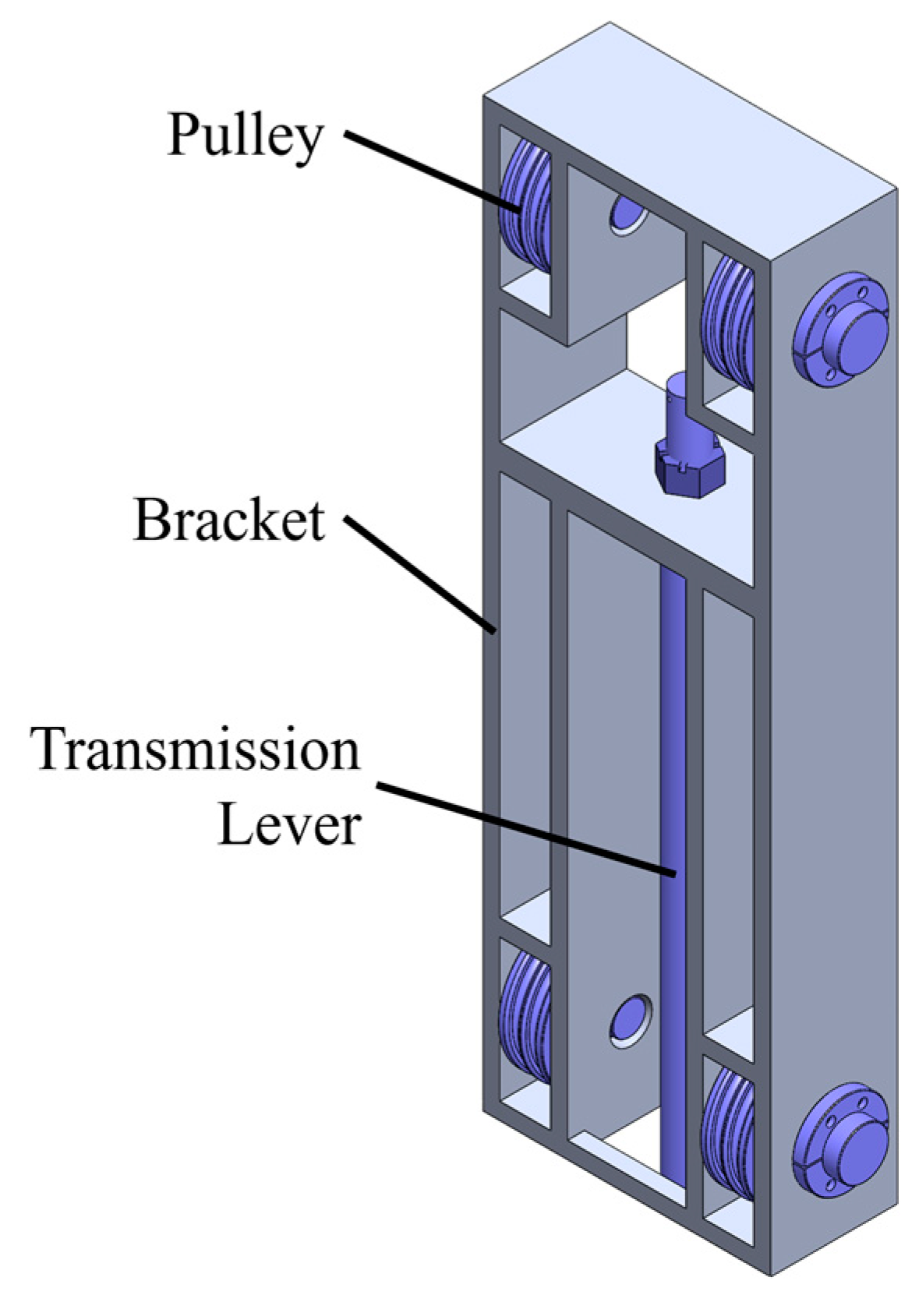
2. Structure of the Load-Adaptive CPT Rig
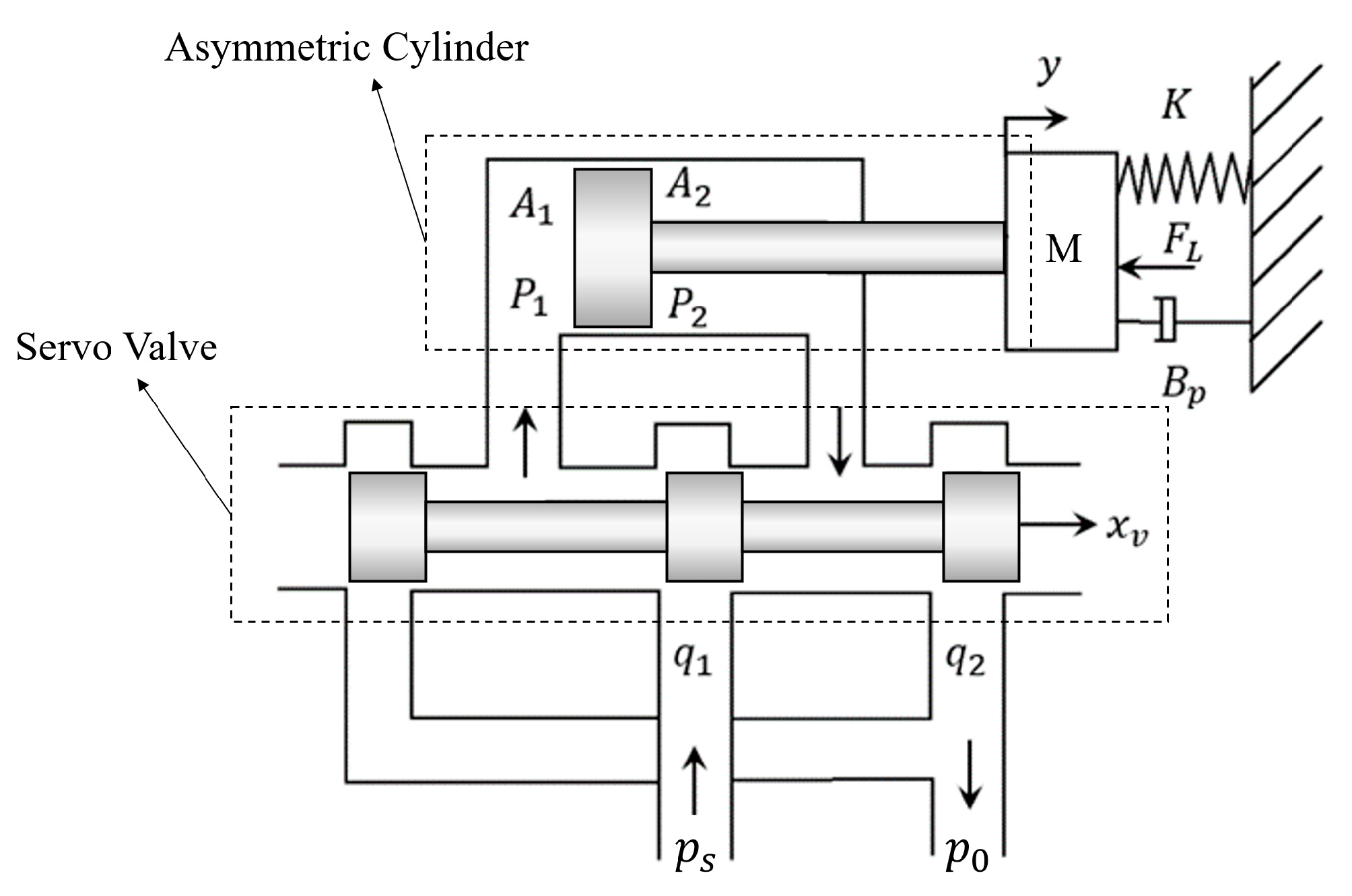
3. Modeling of the Hydraulic Drive System for the Penetration Unit
3.1. Modeling of Servo Valve Mechatronics Subsystem
3.2. Modeling of Asymmetric Cylinder Controlled by Servo Valve Subsystem
3.3. Modeling of Servo Valve Displacement Sensor Subsystem
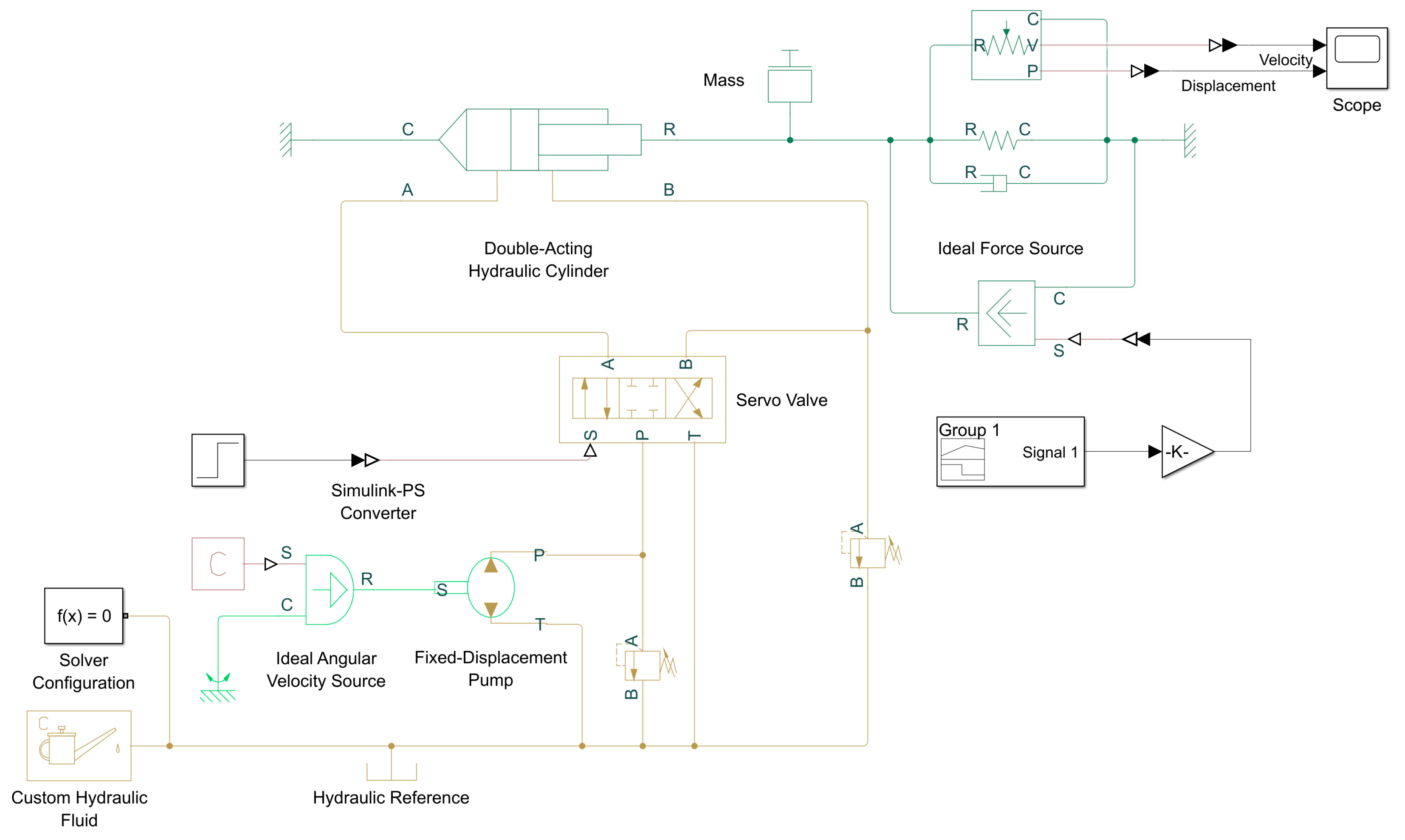
3.4. Modeling of Hydraulic Drive System
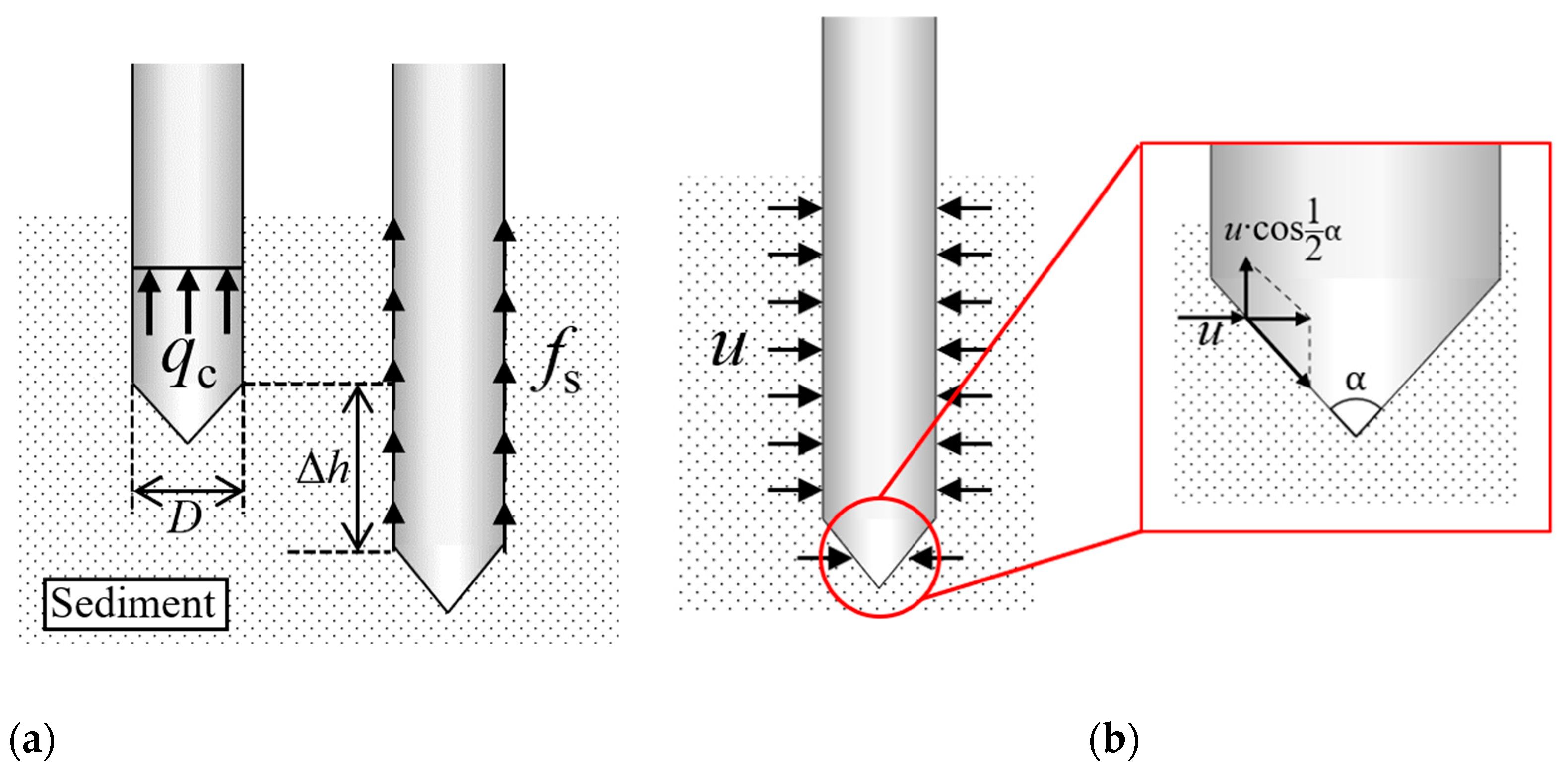
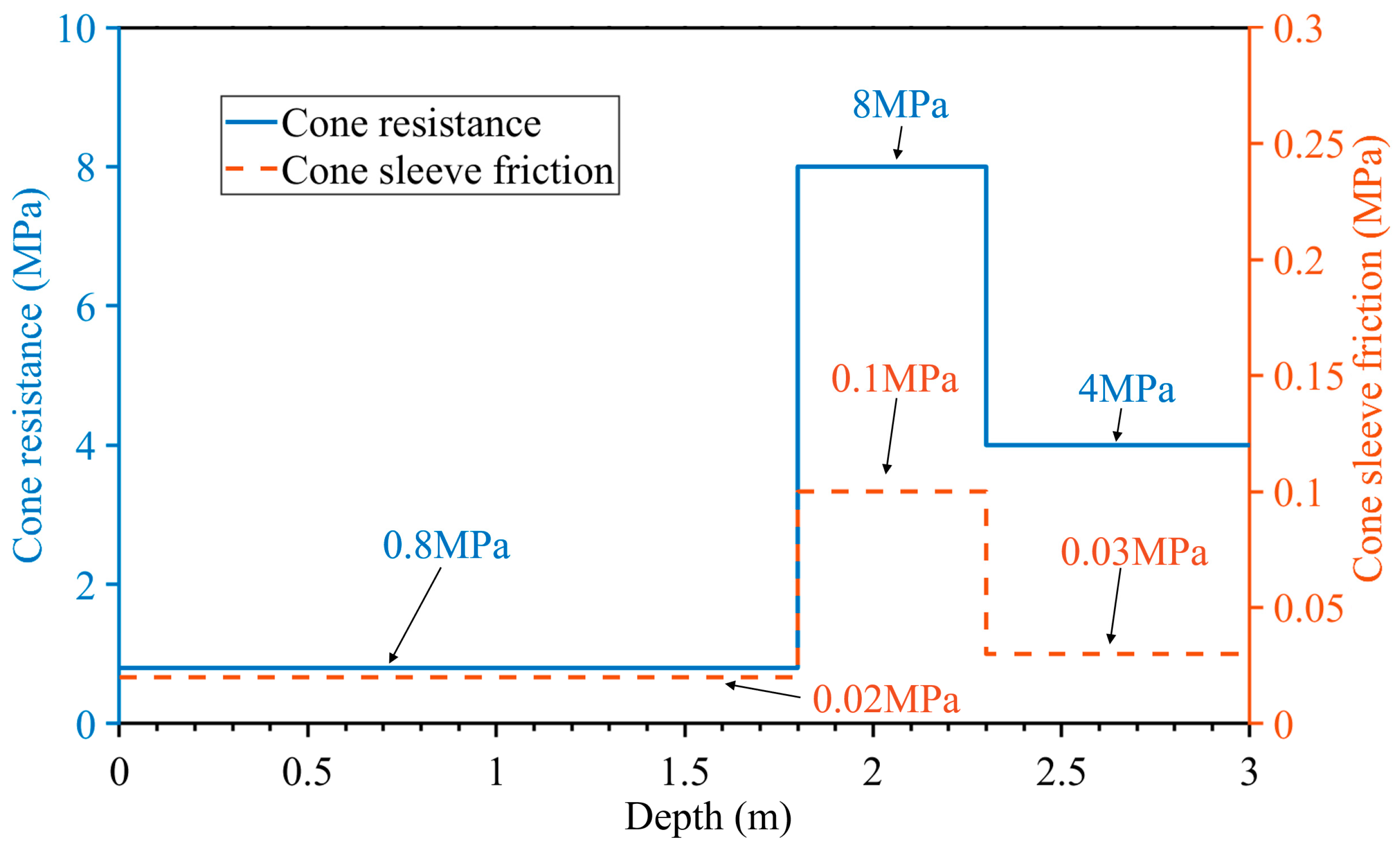
3.5. Determination of System Boundary Conditions
4. Discussion
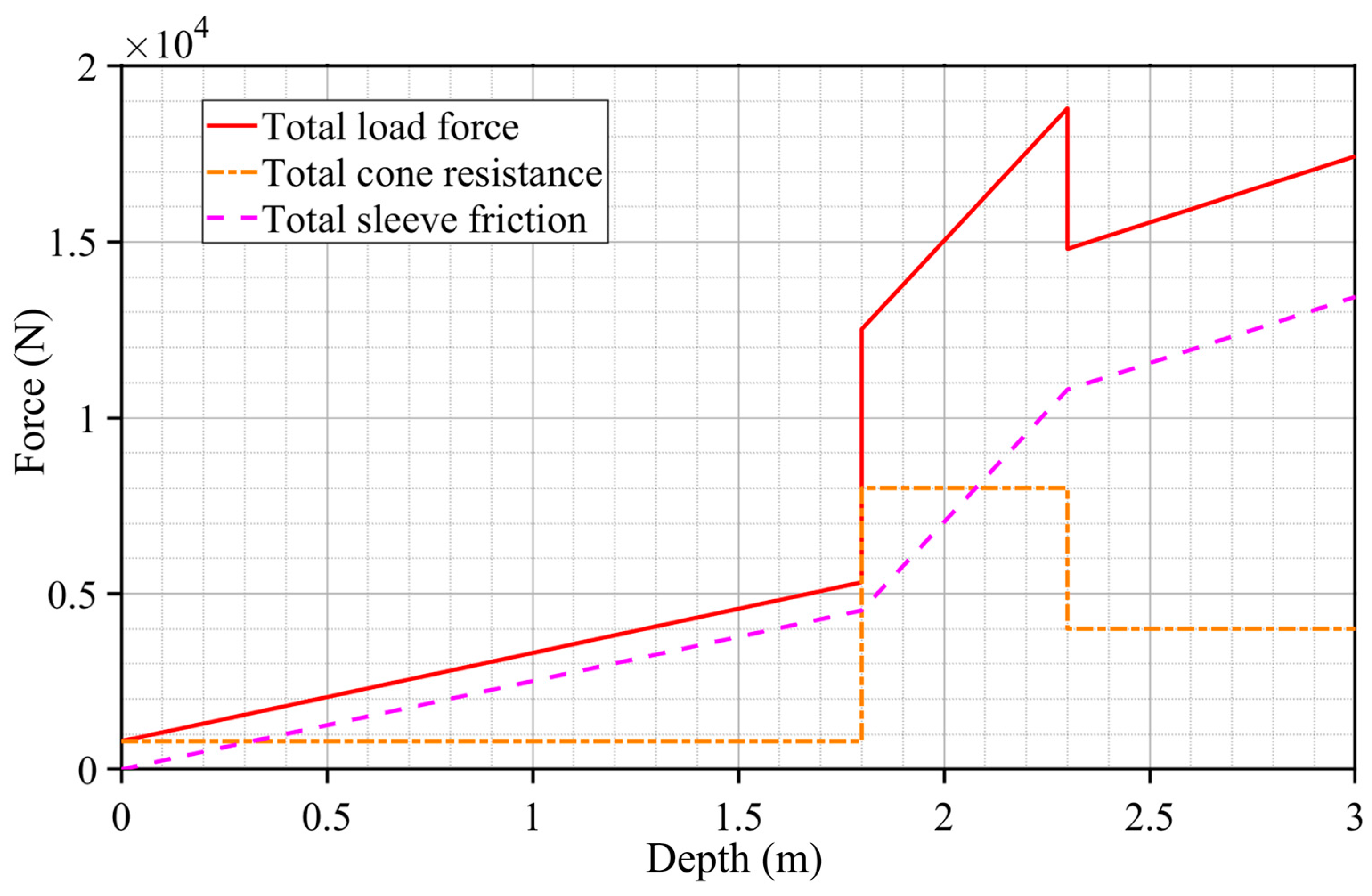
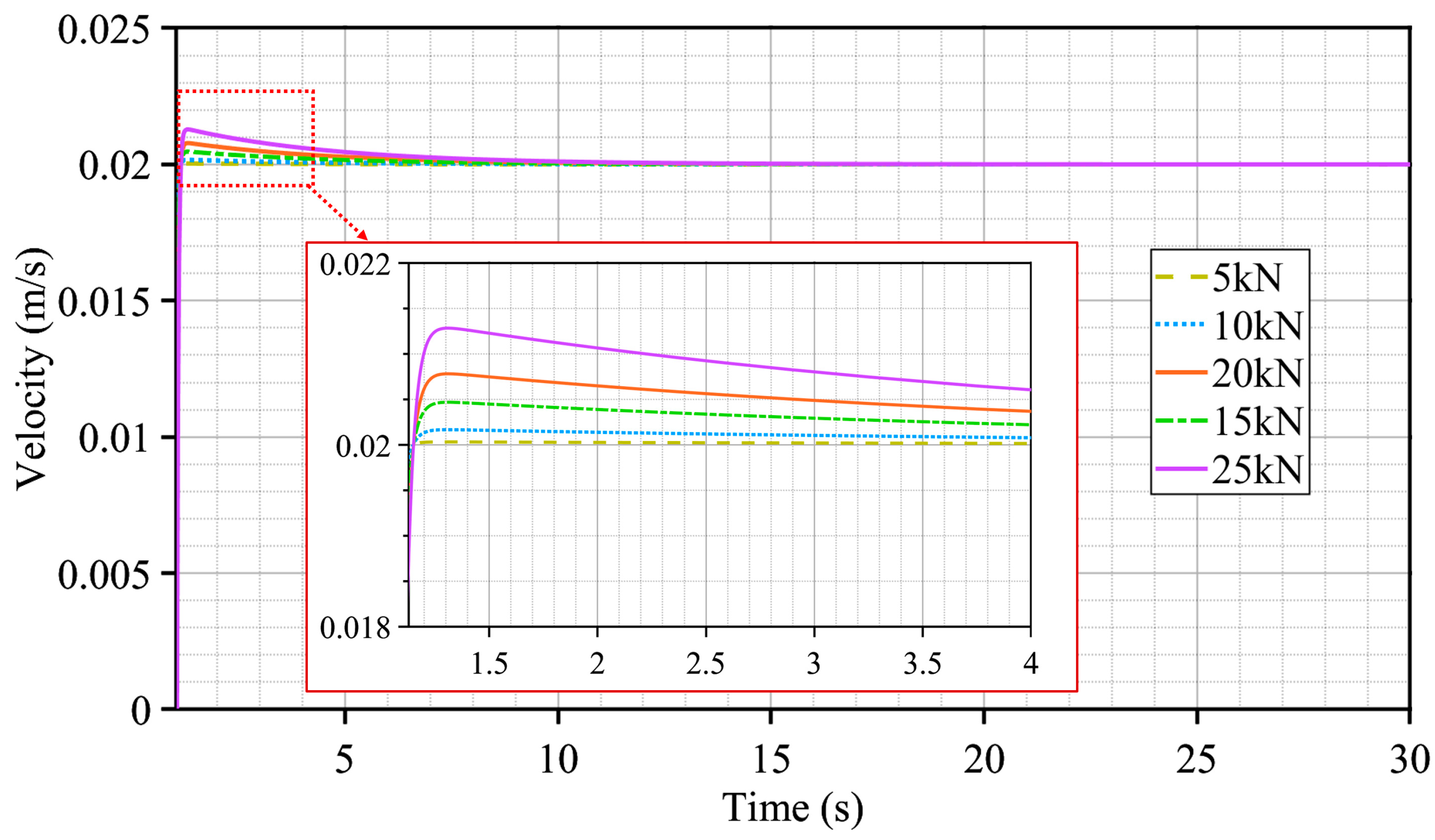
4.1. Calculation of Dynamic Load
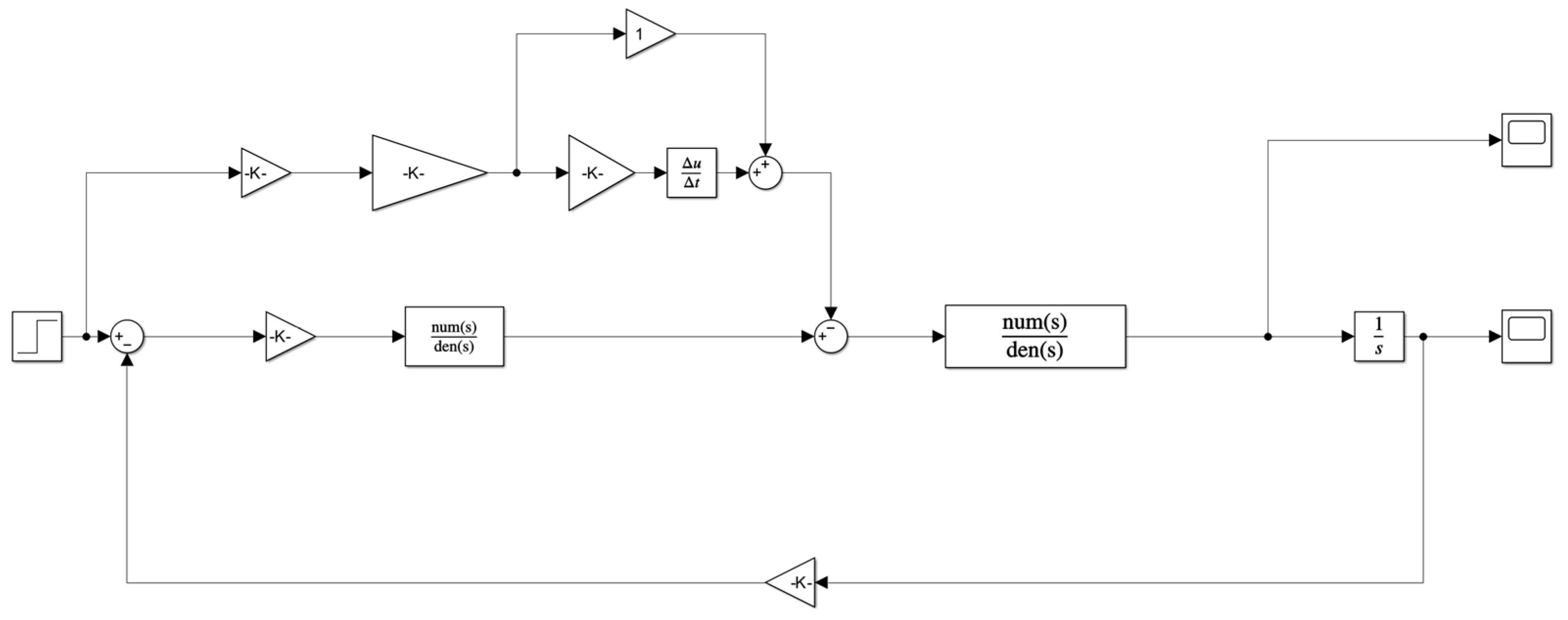
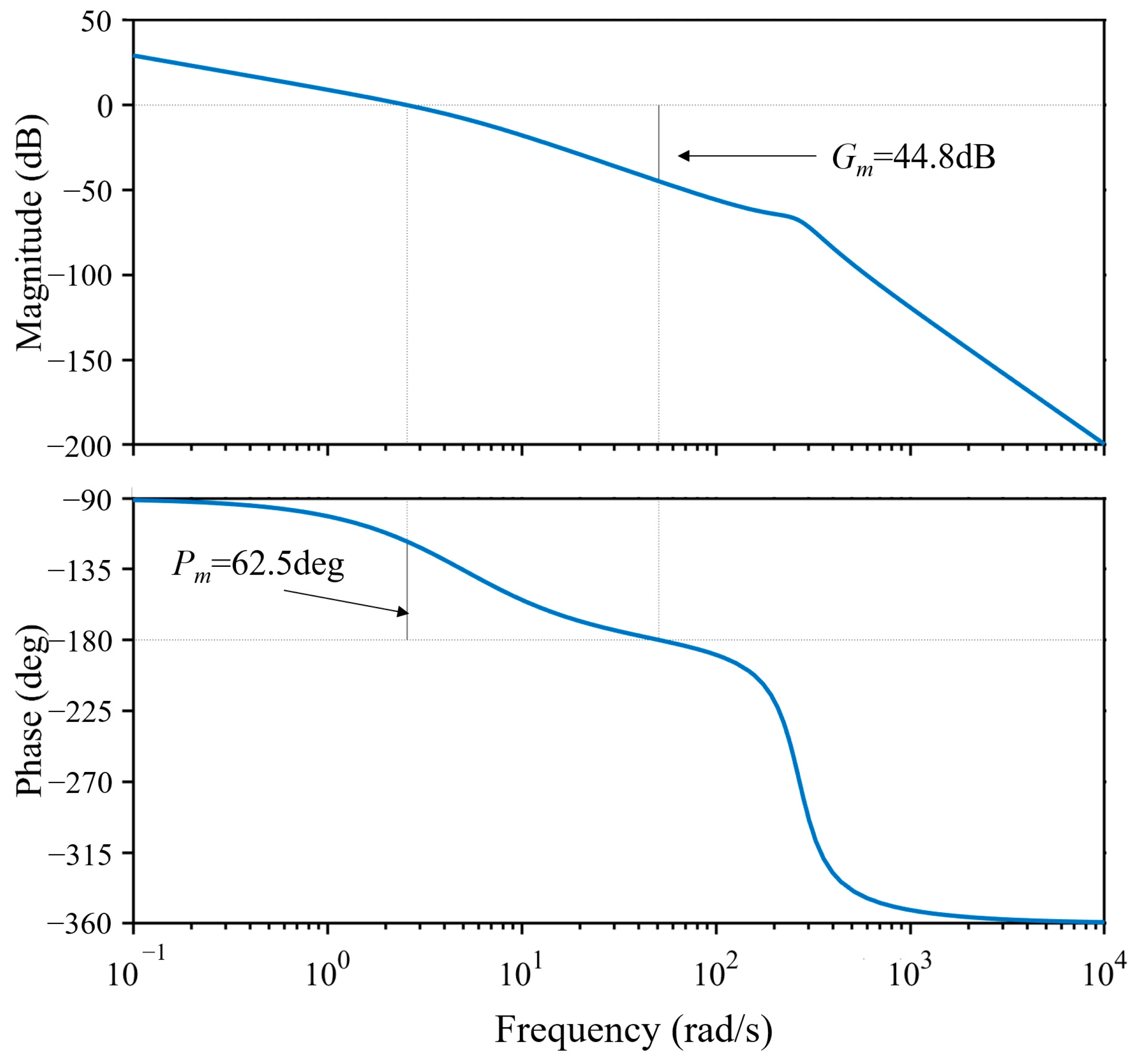
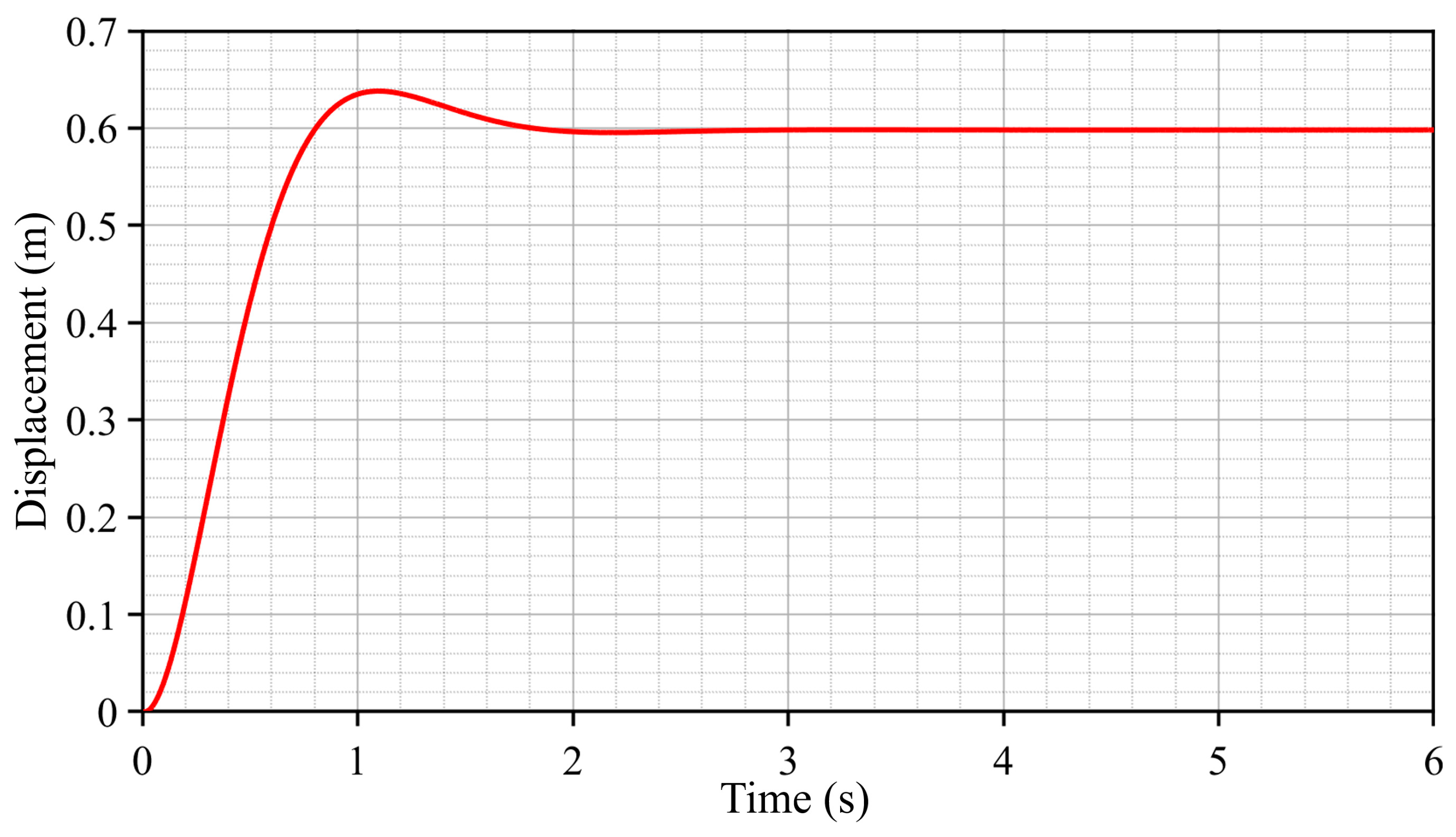
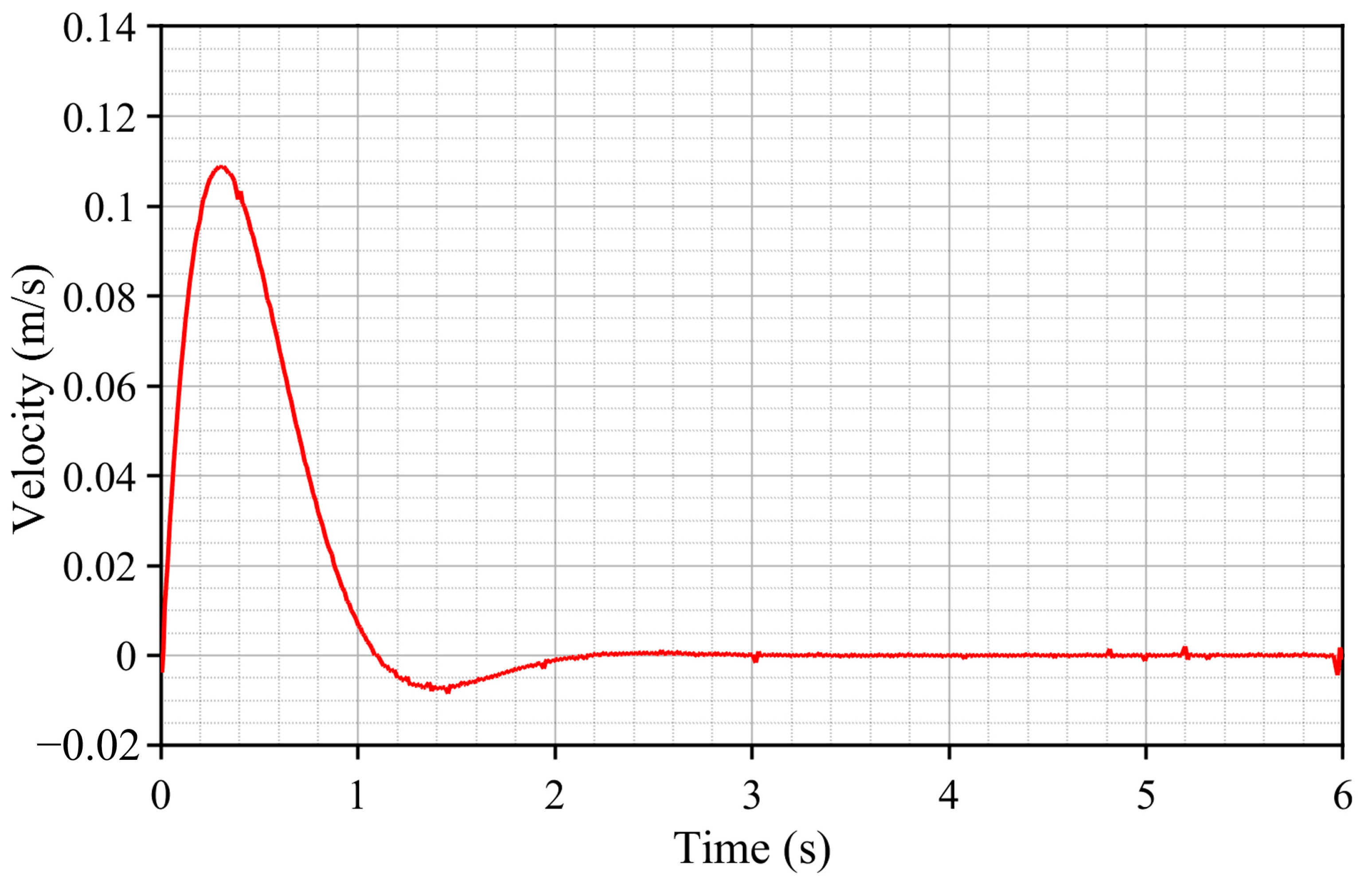
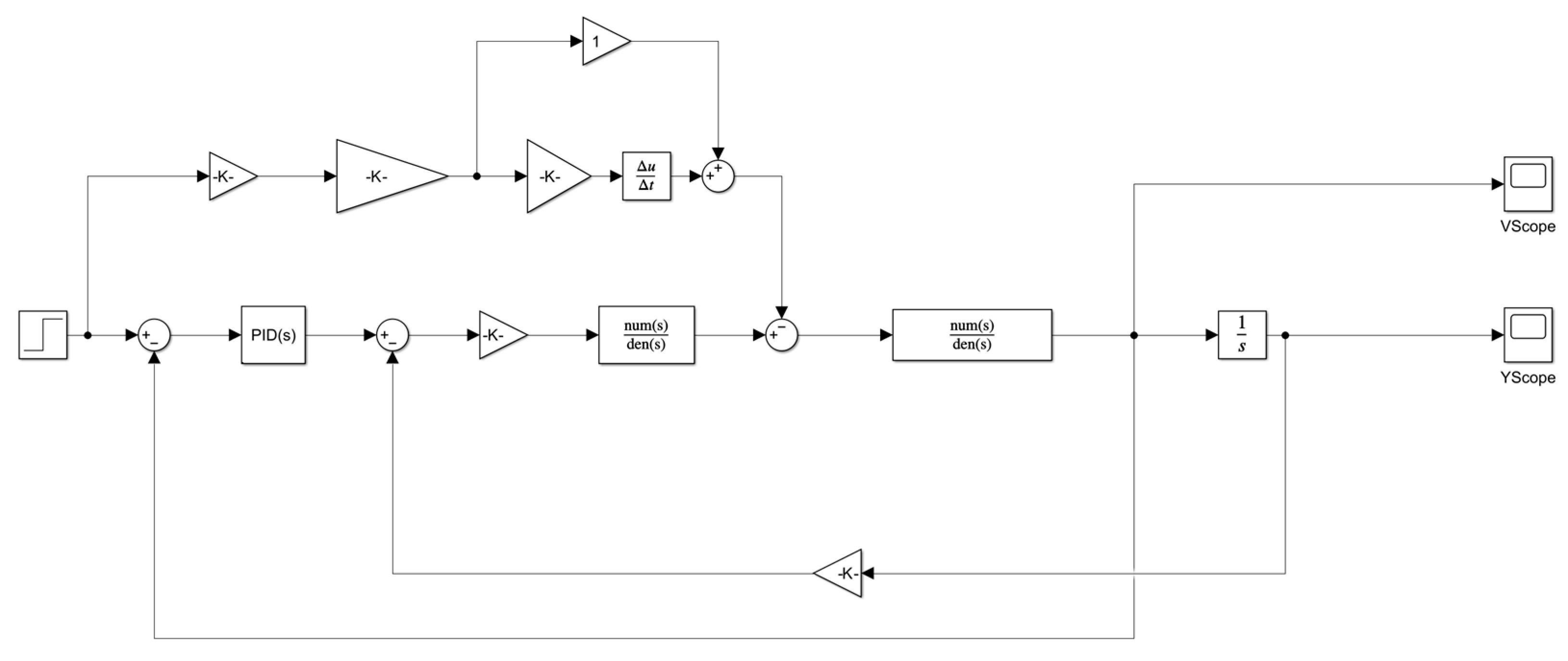
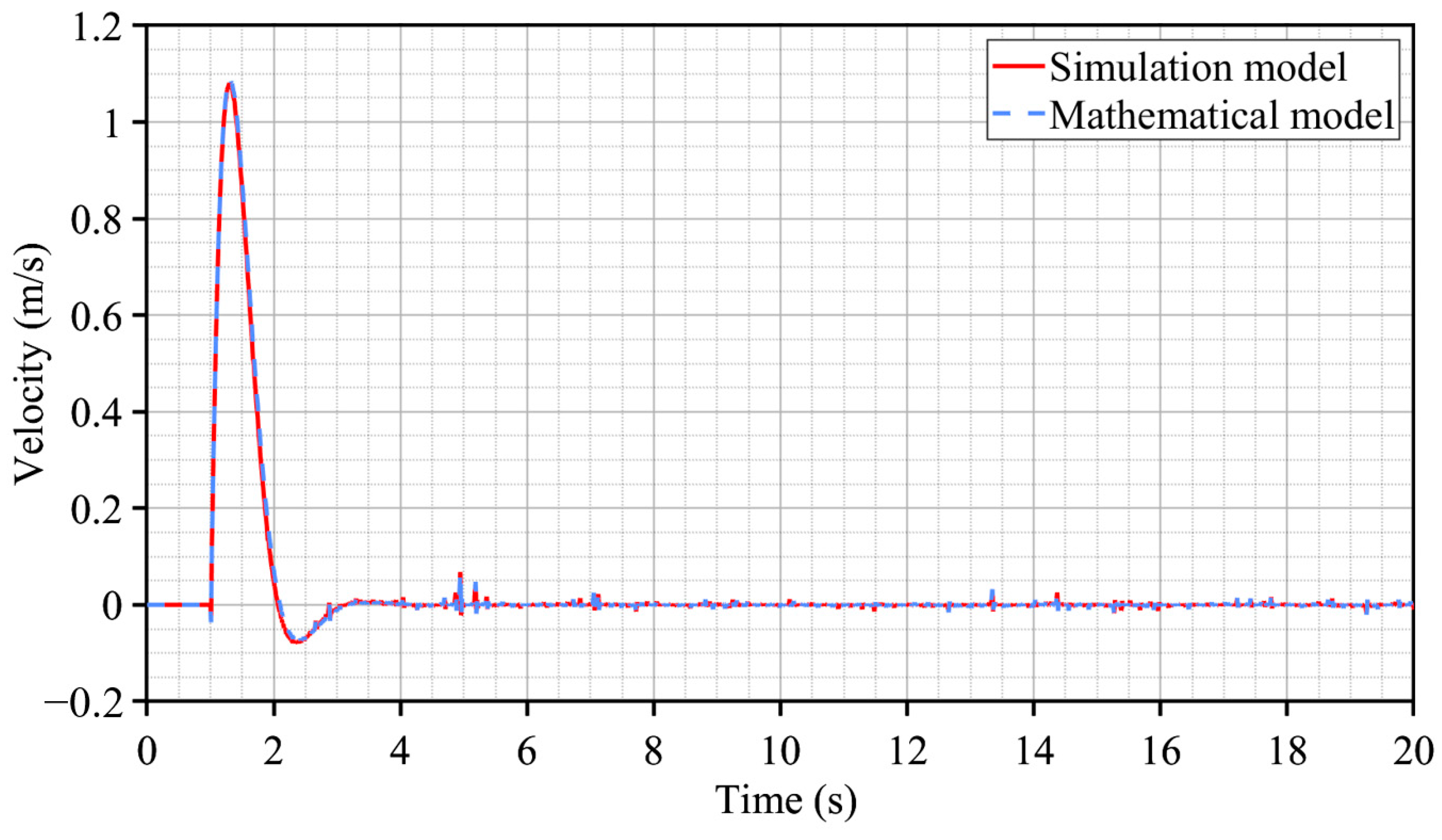
4.2. Model Consistency Validation and Control Logic Design
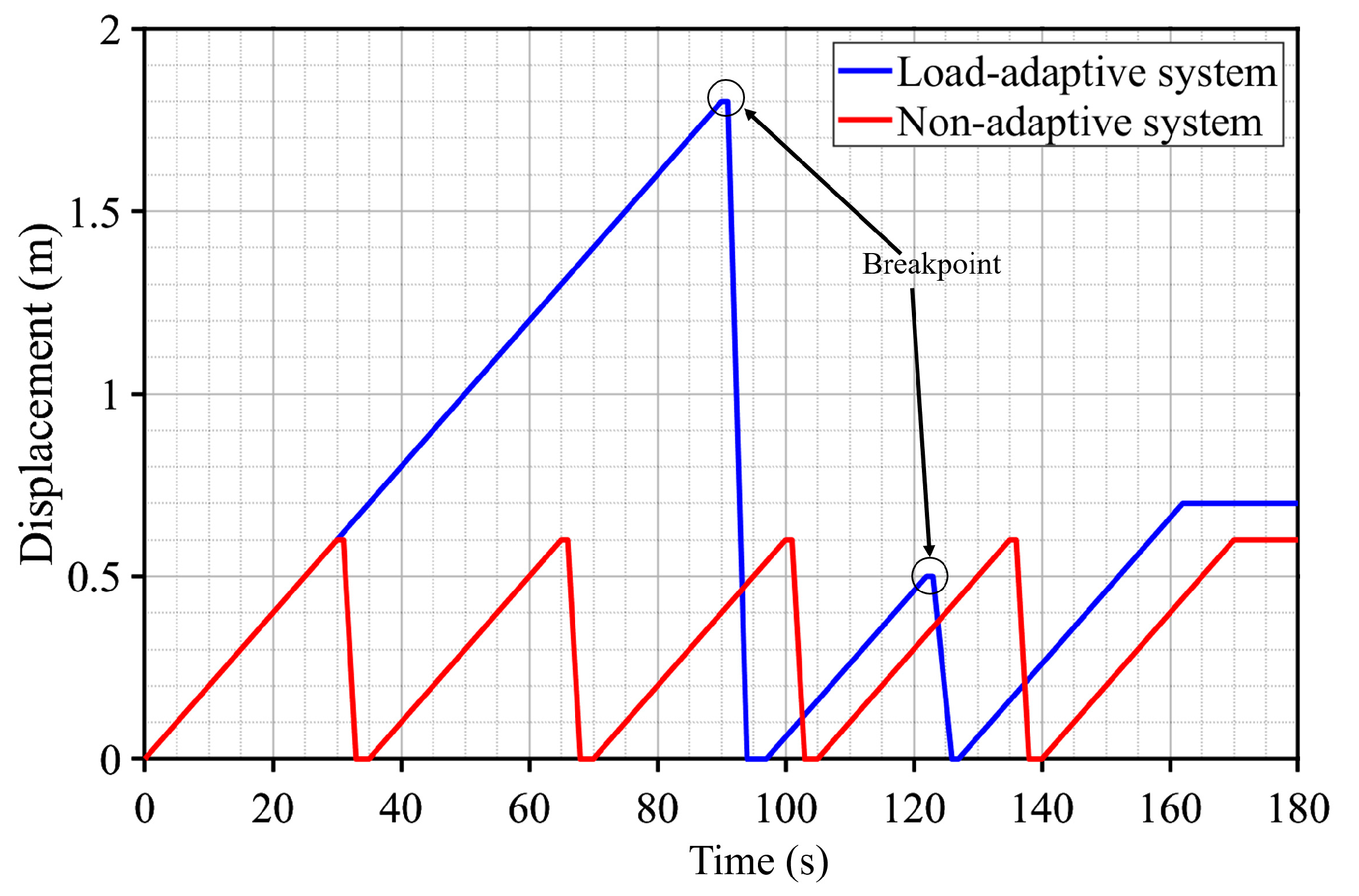
4.3. Static Load Testing
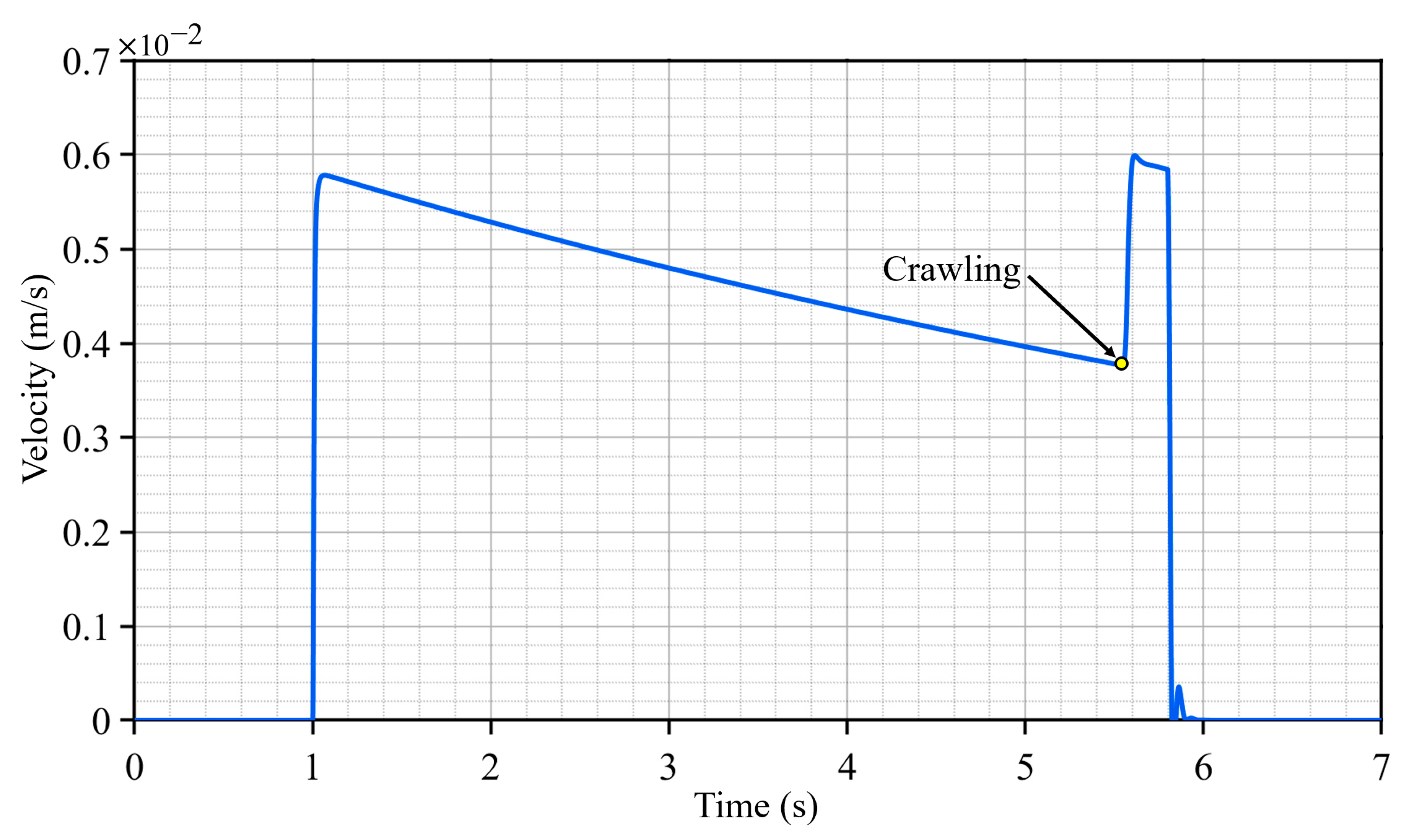
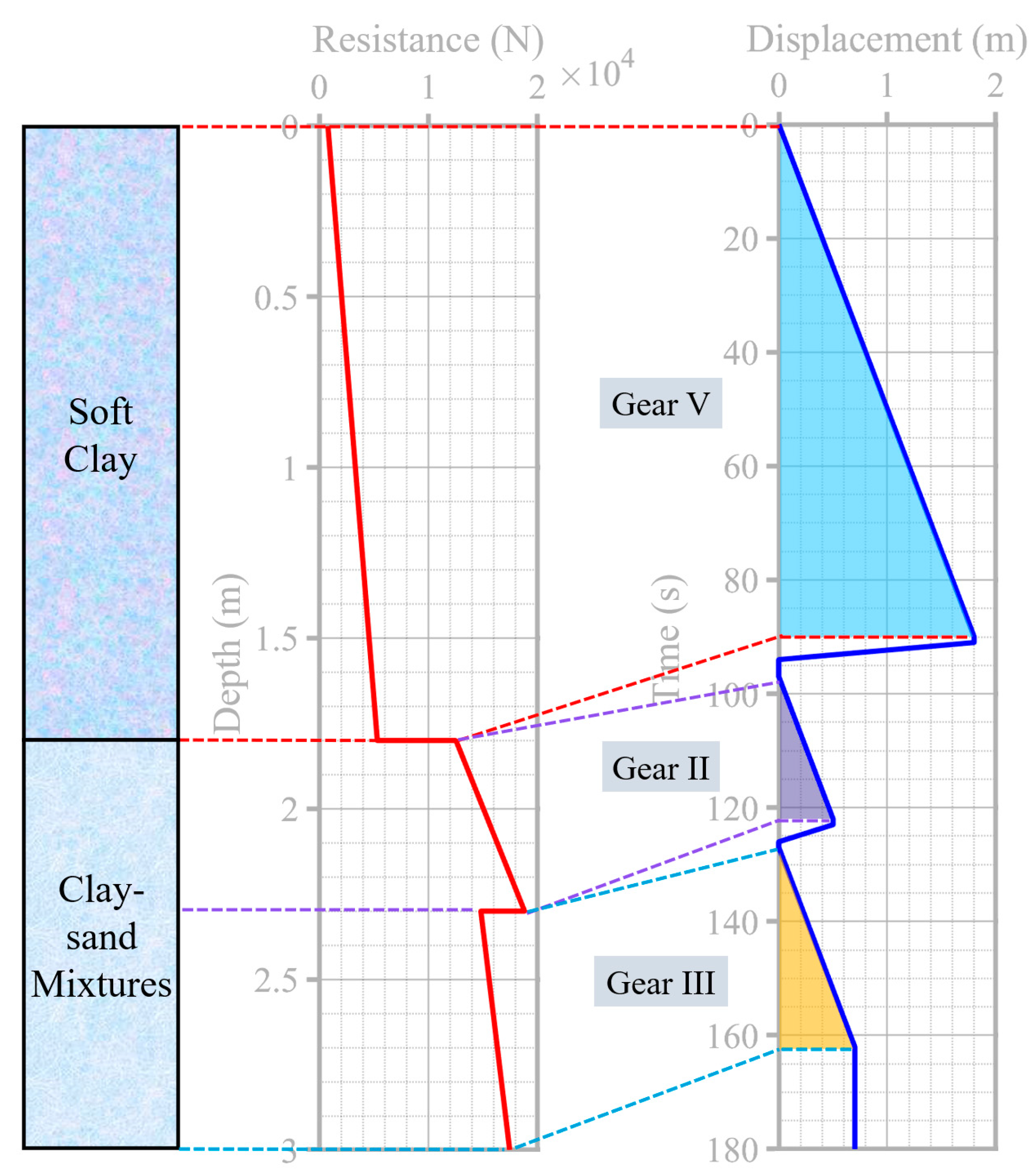
4.4. Dynamic Load Testing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, J.; Tang, G.; Huang, J.X. Analysis and modelling of a novel hydrostatic energy conversion system for seabed cone penetration test rig. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 169, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, B.J. Soil classification using electric cone penetrometer. In Proceedings of the Sympsium on Cone Penetration Testing and Experience, Geo-Technical Engineering Division, ASCE, St. Louis, MO, USA, 26–30 October 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Wahl, D.A.J. Implementation of Variable Rate Cone Penetration Testing: An Experimental Field Study; University of California: Davis, CA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Ghose, R.; Goudswaard, J. Integrating S-wave seismic-reflection data and cone penetration test data using a multiangle multiscale approach. Geophysics 2004, 69, 440–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.J. CPT equipment: Recent advances and future perspectives. Cone Penetration Test. 2022, 2022, 66–80. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, F.D.; Jia, Y.G.; Liu, X.L.; Guo, L.; Zhang, M.S.; Shan, H.X. In situ measurement of the engineering mechanical properties of seafloor sediment. Mar. Geol. Quat. Geol. 2016, 36, 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, T.; Song, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Wu, Z. Triaxial experiments on the mechanical properties of hydrate-bearing marine sediments of South China Sea. Mar. Pet. Geol. 2016, 77, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Zhou, M.; Hu, Y.; Hossain, M.S. Effects of cone tip roughness, in-situ stress anisotropy and strength inhomogeneity on CPT data interpretation in layered marine clays: Numerical study. Eng. Geol. 2017, 227, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunne, T.; Robertson, P.K.; Powell, J.J.M. Cone penetration testing in geotechnical practice. Eng. Geol. 1999, 50, 219–220. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, P.K. Soil classification using the cone penetration test. Can. Geotech. J. 1990, 27, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.S.; Zhang, L.M.; Wang, H.J.; Zou, H.F.; Li, J.H. Marine soil behaviour classification using piezocone penetration test (CPTu) and borehole records. Can. Geotech. J. 2021, 58, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Guo, L.; Jia, L.; Sun, W.; Xue, G.; Yang, X.; Liu, X. Development and application of a 3,000-m Seabed Cone Penetration Test and Sampling System based on a hydraulic drive. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11, 1377405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storteboom, O.; Woollard, M.; Verhagen, J. Efficiency examined of hands-free Cone Penetration Testing using the SingleTwist™ with COSON. In Cone Penetration Testing 2022; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 230–235. [Google Scholar]
- Shoukat, G.; Michel, G.; Coughlan, M.; Malekjafarian, A.; Thusyanthan, I.; Desmond, C.; Pakrashi, V. Generation of Synthetic CPTs with Access to Limited Geotechnical Data for Offshore Sites. Energies 2023, 16, 3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunne, T. The CPT in offshore soil investigations–a historic perspective. JK Mitchell Lecture. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Symposium on the Cone Penetration Test, CPT, Huntington Beach, CA, USA, 9–11 May 2010; p. 10. [Google Scholar]
- Randolph, M.F. New tools and directions in offshore site investigation. Aust. Geomech. J. 2016, 51, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, P.K. Cone penetration test (CPT)-based soil behaviour type (SBT) classification system—An update. Can. Geotech. J. 2016, 53, 1910–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Duan, Z.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, X.; Luo, S. Offshore cone penetration test and its application in full water-depth geological surveys. In IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2020; Volume 570, p. 042008. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, H.; Liu, L.; He, H.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Peng, P. The practice and development of T-bar penetrometer tests in offshore engineering investigation: A comprehensive review. J. Mar. Sci. Eng. 2023, 11, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCALLUMA, A. Cone penetration testing (CPT) in Antarctic firn: An introduction to interpretation. J. Glaciol. 2014, 60, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCALLUMA, A. A brief introduction to cone penetration testing (CPT) in frozen geomaterials. Ann. Glaciol. 2014, 55, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanizadeh, A.R.; Aziminejad, A.; Asteris, P.G.; Armaghani, D.J. Soft Computing to predict earthquake-induced soil liquefaction via CPT results. Infrastructures 2023, 8, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, T.; Yang, Z.; Ling, X.; Yang, X.; Lu, K.; Xue, G. Development and application of the 3000 m-level multiparameter CPTu in-situ integrated test system. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2023, 41, 400–411. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, P.K.; Cabal, K.L. Guide to Cone Penetration Testing for Geotechnical Engineering; Gregg Drilling & Testing: Signal Hill, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zou, H.; Zhang, L.; Cai, G.; Liu, S. Evaluation of CPTU-based soil classification charts for offshore sediments in Pearl River Delta, China. In Proceedings of the Geo-Congress 2020, Minneapolis, Minnesota, 25–28 February 2020; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2020; pp. 633–639. [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi, A.; Martinez, A.; DeJong, J.T. Discrete element model (DEM) simulations of cone penetration test (CPT) measurements and soil classification. Can. Geotech. J. 2020, 57, 1369–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, R.; Hino, T.; Chai, J.; Yoshimura, M. Interpretation of density profile of seabed sediment from nuclear density cone penetration test results. Soils Found. 2013, 53, 671–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudong, J.; Yonggang, J.; Xiaolei, L. Development and application of new offshore CPT equipment. Coast. Eng. 2016, 35, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Krage, C.P.; DeJong, J.T.; Schnaid, F. Estimation of the coefficient of consolidation from incomplete cone penetration test dissipation tests? J. Geotech. Geoenvironmental Eng. 2015, 141, 06014016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lange, D.A.; van Duinen, T.A.; Peters, D.J. Large diameter cone penetrometers: What is an appropriate location for the transition to the rod diameter. In Cone Penetration Testing 2022; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Niazi, F.S.; Mayne, P.W. Cone penetration test based direct methods for evaluating static axial capacity of single piles. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2013, 31, 979–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, S.; Minav, T. Control and performance analysis of variable speed pump-controlled asymmetric cylinder systems under four-quadrant operation. Actuators 2020, 9, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Gu, L.C.; Xu, Y.G.; Shi, L.C.; Wang, H.T. Research on control strategy of asymmetric electro-hydraulic servo system based on improved PSO algorithm. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2022, 14, 16878132221096226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, V.; Seshadri, V. Model reduction using the Routh stability criterion. IEEE Trans. Autom. Control. 1978, 23, 729–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.D.; Cho, H.S.; Lee, C.O. Stability analysis of a load-sensing hydraulic system. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part A Power Process Eng. 1988, 202, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margolis, D.L.; Hennings, C. Stability of hydraulic motion control systems. ASME. J. Dyn. Sys., Meas., Control. 1997, 119, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, W.; Congress, S.S.C.; Cai, G.; Puppala, A.J.; Dong, X.; Du, Y. Empirical correlations of soil parameters based on piezocone penetration tests (CPTU) for Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macau Bridge (HZMB) project. Transp. Geotech. 2021, 30, 100605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Li, Y.; Pei, W. The effect of natural water content on the penetration resistance of seabed sediment. Hydrogr. Surv. Charting 2005, 6, 51–53. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, G.; Liu, Y.; Guo, L.; Liu, B. Optimization on motion-robust and energy-saving controller for hydraulic penetration system of seabed equipment. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part M J. Eng. Marit. Environ. 2021, 235, 792–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

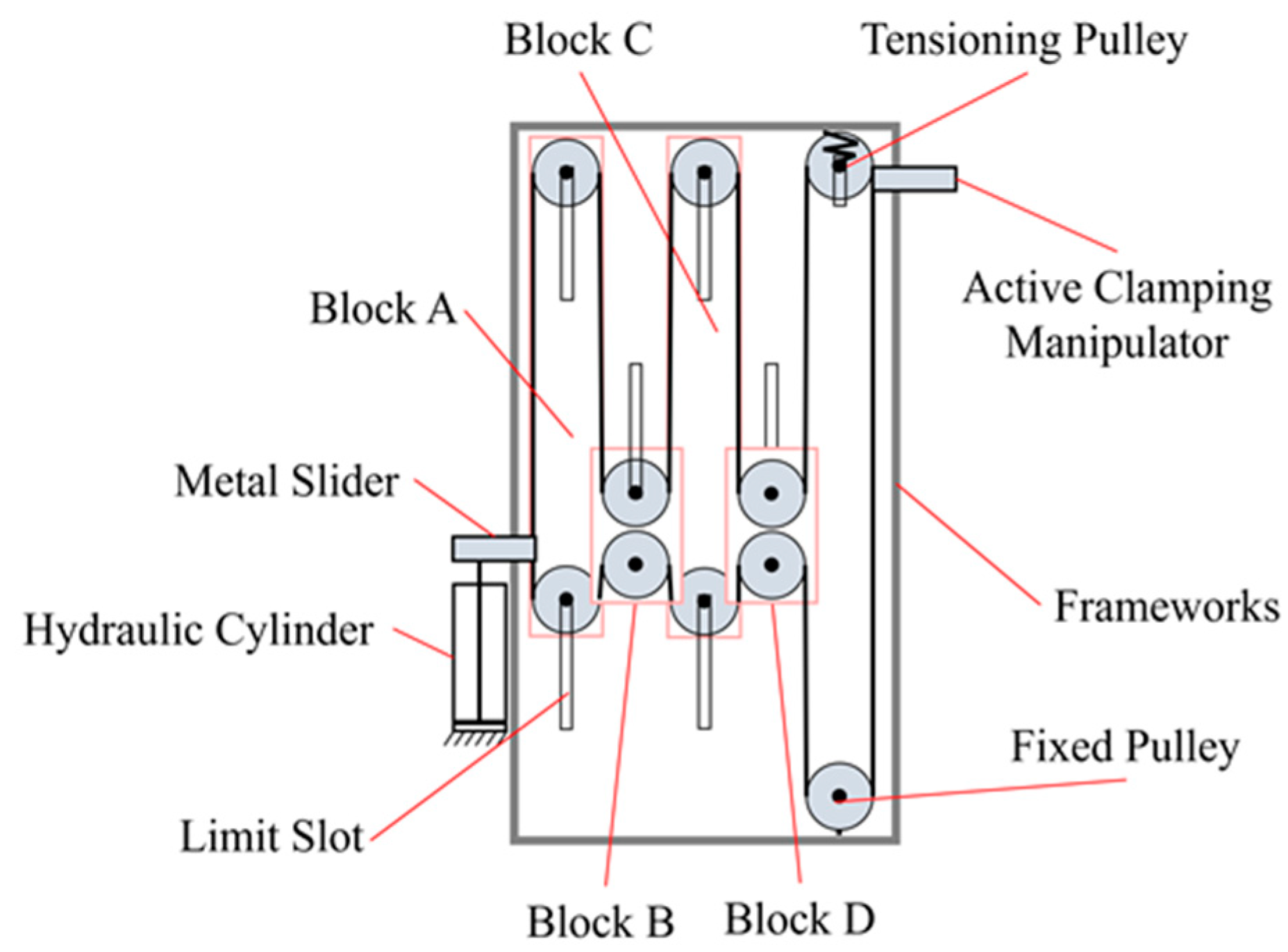
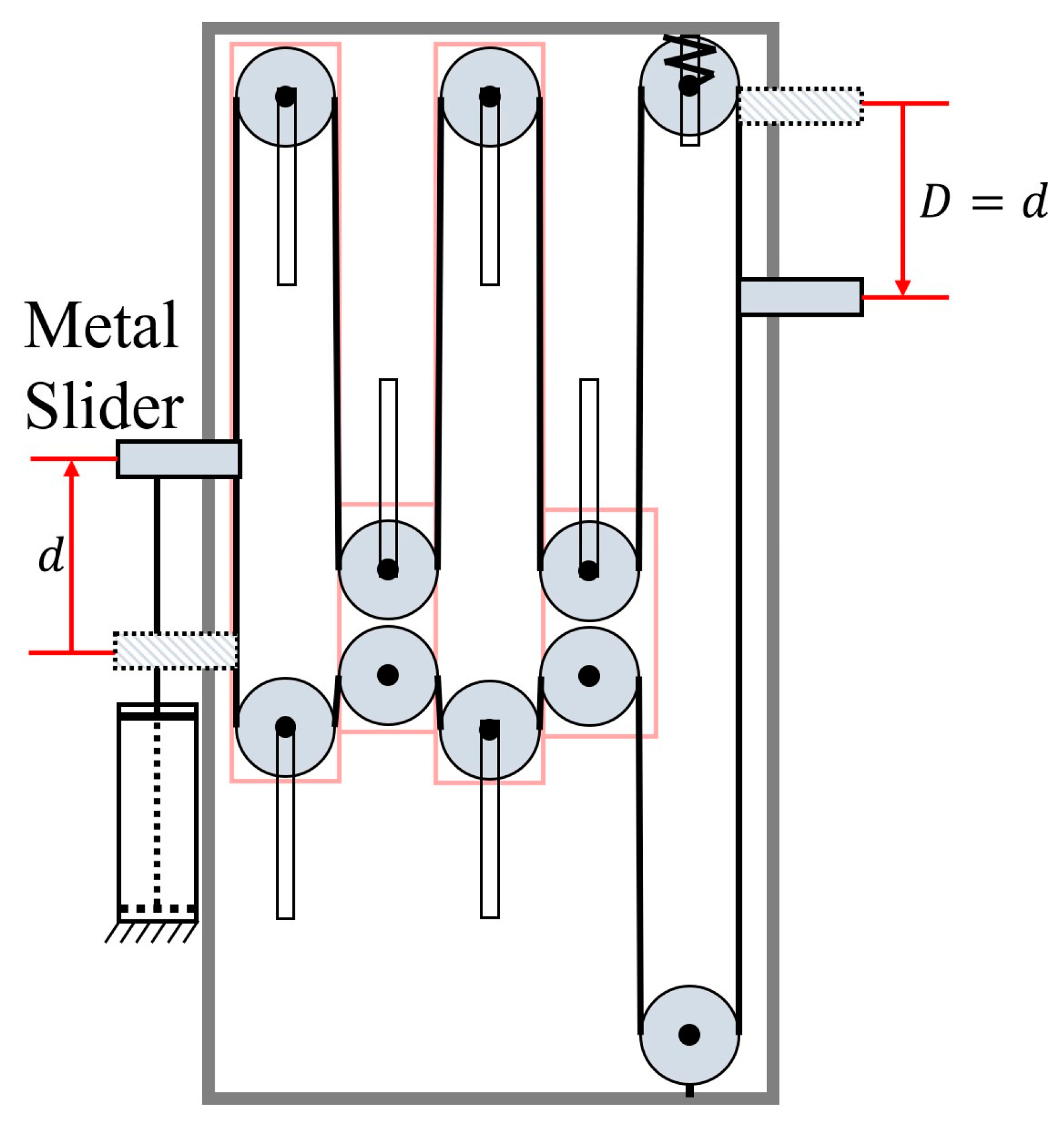

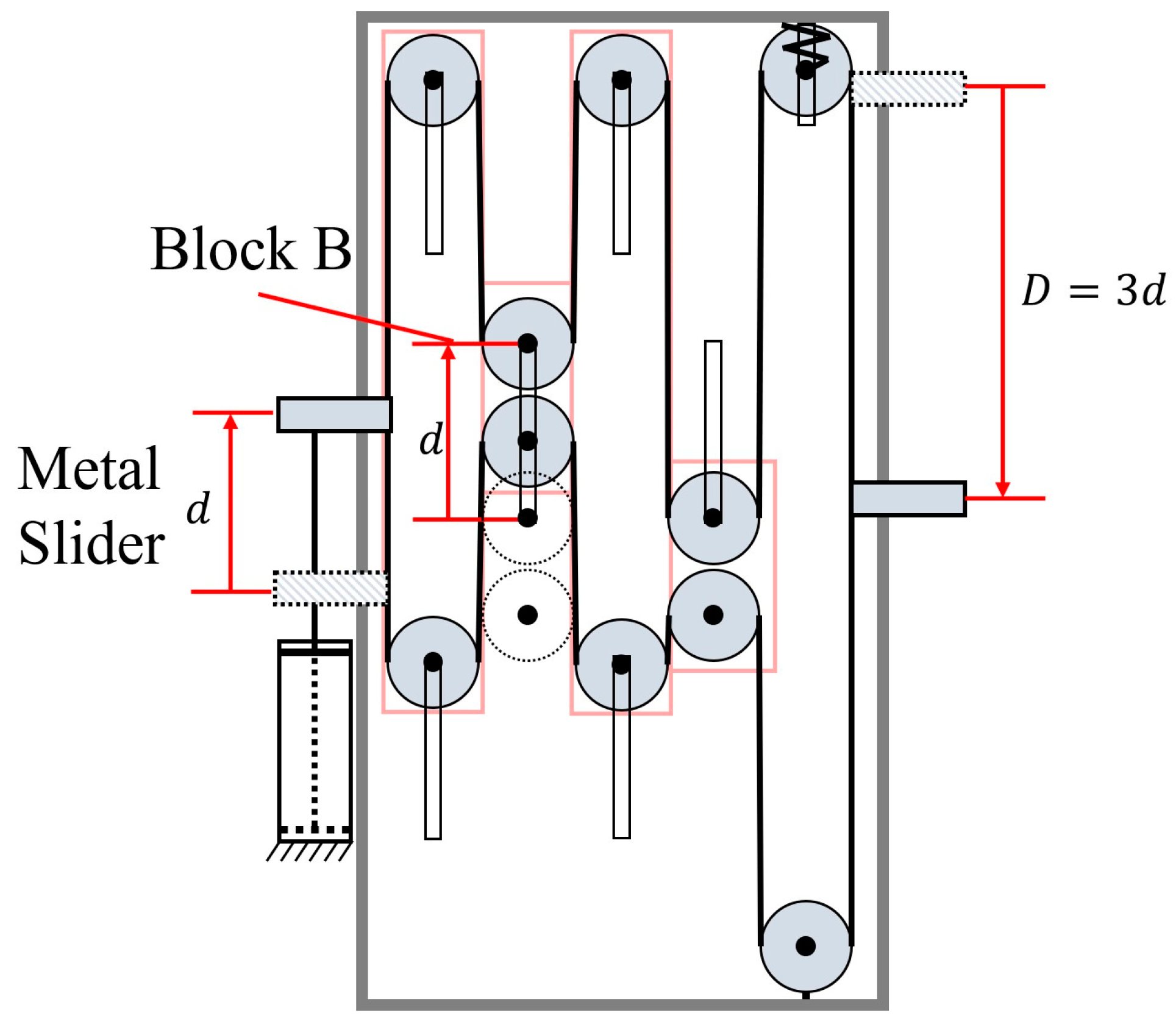



| Gear I | Gear II | Gear III | Gear IV | Gear V | Gear VI | Gear VII | Gear VIII | Gear IX | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pulley Block A | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Pulley Block B | ╳ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Pulley Block C | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ↓ | ↓ |
| Pulley Block D | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ╳ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ | ↑ |
| Stroke Amplification | 0 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 4 | 6 | 6 | 8 | 8 |
| Metal Slider | ↑ | ╳ | ↑ | ╳ | ↑ | ╳ | ↑ | ╳ | ↑ |
| Total Stroke Amplification | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
| Penetration Force | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F | F |
| Hydraulic Cylinder Speed | 2 cm/s | 1 cm/s | 0.67 cm/s | 0.5 cm/s | 0.4 cm/s | 0.33 cm/s | 0.29 cm/s | 0.25 cm/s | 0.22 cm/s |
| Penetration Speed | 2 cm/s | ||||||||
| Parameters | Symbol (Unit) | Values |
|---|---|---|
| Flow-pressure coefficient | ||
| Internal leakage coefficient | ||
| External leakage coefficient | 0 | |
| Equivalent leakage coefficient | ||
| Additional leakage coefficient | 3.55 | |
| Natural frequency | Wh (rad/s) | 268 |
| Flow gain | Ksv (m3/s ∙ A) | 4.38 |
| Bandwidth of servo valve | ωsv (rad/s) | 0.03 |
| Damping ratio of servo valve | ξsv | 0.6 |
| Parameters | Symbol (Unit) | Values |
|---|---|---|
| External load equivalent mass | 400 | |
| Flow rate | 0.61 | |
| Total flow-pressure coefficient | ||
| Hydraulic damping ratio | 0.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, X.; Fei, Z.; Guo, L.; Xue, G.; Liu, Y. Adaptive Penetration Unit for Deep-Sea Sediment Cone Penetration Testing Rigs: Dynamic Modeling and Case Study. Water 2025, 17, 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081159
Zhu Y, Zhang Z, Yang X, Fei Z, Guo L, Xue G, Liu Y. Adaptive Penetration Unit for Deep-Sea Sediment Cone Penetration Testing Rigs: Dynamic Modeling and Case Study. Water. 2025; 17(8):1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081159
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yusen, Zhiqiang Zhang, Xiuqing Yang, Zihang Fei, Lei Guo, Gang Xue, and Yanjun Liu. 2025. "Adaptive Penetration Unit for Deep-Sea Sediment Cone Penetration Testing Rigs: Dynamic Modeling and Case Study" Water 17, no. 8: 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081159
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhang, Z., Yang, X., Fei, Z., Guo, L., Xue, G., & Liu, Y. (2025). Adaptive Penetration Unit for Deep-Sea Sediment Cone Penetration Testing Rigs: Dynamic Modeling and Case Study. Water, 17(8), 1159. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081159






