Acute Toxicity Assessment of Textile Wastewater Treated with Pinus patula Biochar Using Daphnia pulex
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals, Reactants, and Textile Wastewater (TWW) Collection
2.2. Pinus patula-Derived Biochar (BC) Production and Characterization
2.3. TWW Characterization and Batch Adsorption Studies
2.4. Acute Toxicity Assessment Using D. pulex
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. P. patula-Derived BC Characterization
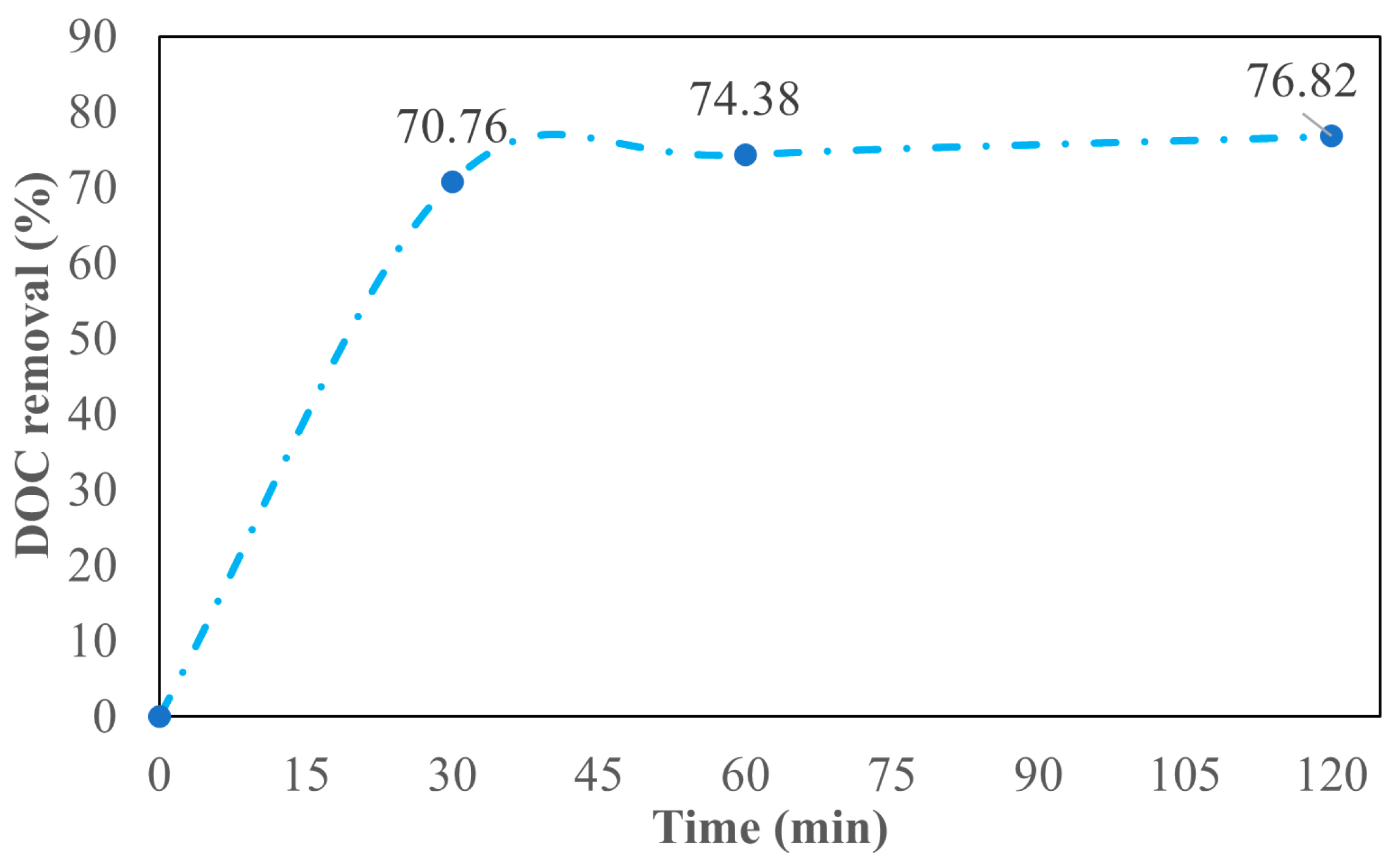
3.2. Efficiency of P. patula-Derived BC in the Removal of DOC from TWW
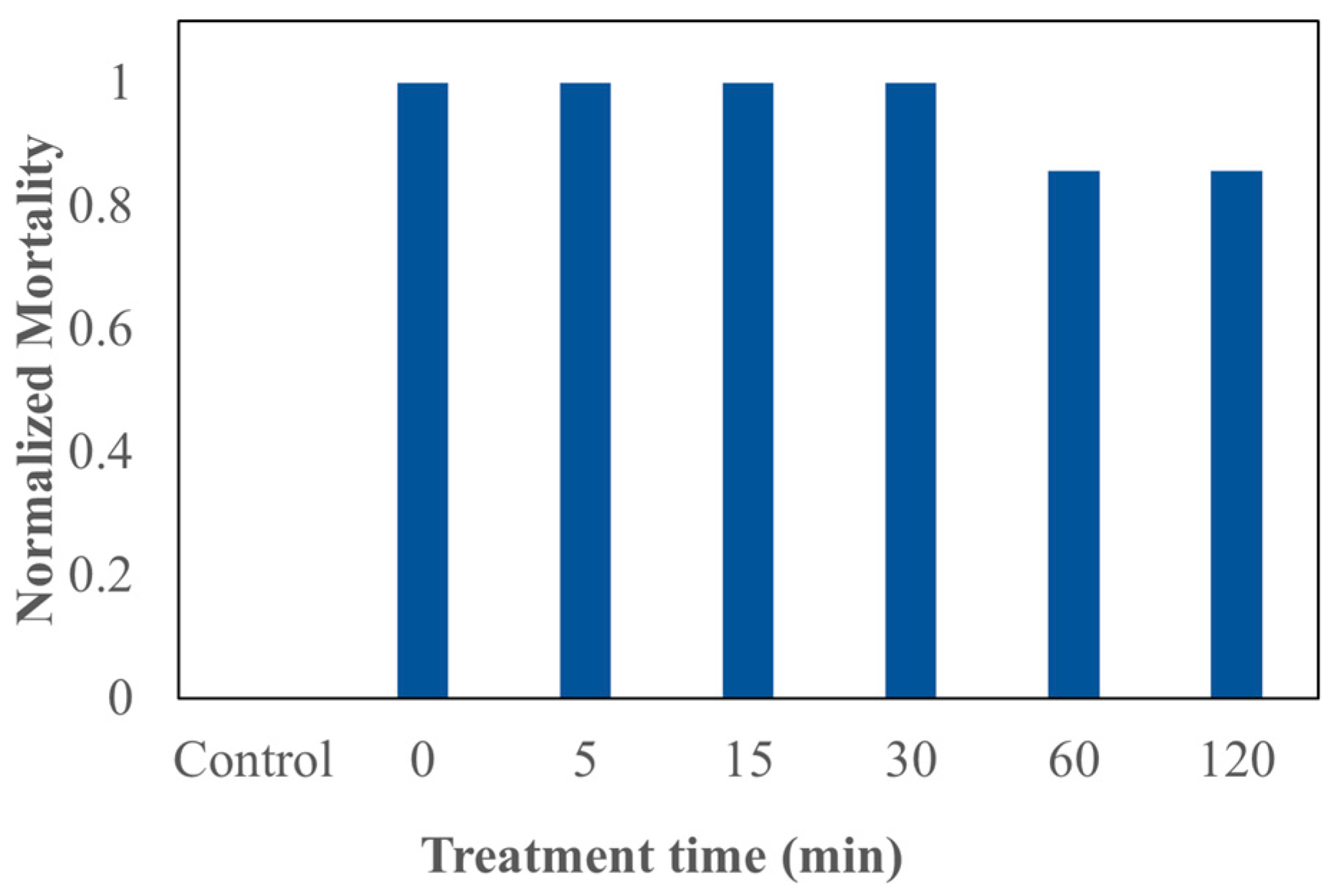
3.3. Acute Toxicity of TWW Treated with P. patula-Derived BC Using D. pulex
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lu, Y.; Duan, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Yin, Y.; Han, Q.; Ou, Z.; Luo, G.; Sun, M.; Li, G.; et al. Generation of H2O2 via Simultaneous Treatment of Cotton and Organic Pollutants in Textile Wastewater. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 355, 129567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Chi, M.; Eygen, G.V.; Guan, K.; Matsuyama, H. Comprehensive Review of Nanofiltration Membranes for Efficient Resource Recovery from Textile Wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 506, 160132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kholy, S.A. Environmentally Benign Freeze-Dried Biopolymer-Based Cryogels for Textile Wastewater Treatments: A Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 276, 133931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragaw, T.A. A Review of Dye Biodegradation in Textile Wastewater, Challenges Due to Wastewater Characteristics, and the Potential of Alkaliphiles. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.; Poler, J.C. Removal and Degradation of Dyes from Textile Industry Wastewater: Benchmarking Recent Advancements, Toxicity Assessment and Cost Analysis of Treatment Processes. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 113754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.B.; Vinayak, A.; Mudgal, G.; Kesari, K.K. Azo Dye Bioremediation: An Interdisciplinary Path to Sustainable Fashion. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristea, M.-E.; Zarnescu, O. Indigo Carmine: Between Necessity and Concern. J. Xenobiot. 2023, 13, 509–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarandona, A.; Salazar, H.; Insausti, M.; Lanceros-Méndez, S.; Zhang, Q. Synergistic Green Degradation of Organic Dyes Using a BiSI Catalyst: Adsorption, Sonocatalysis, and Photocatalysis. J. Water Process Eng. 2024, 58, 104731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalasangi, V.; Mayilswamy, N.; Kandasubramanian, B. Biochar-Derived Adsorbents for Removal of Rhodamine B from Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2024, 28, 101987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Khan, N.A.; Shehata, N.; Singh, J.; Ramamurthy, P.C. Insight into Biochar as Sustainable Biomass: Production Methods, Characteristics, and Environmental Remediation. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 475, 143645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moncada, J.; Cardona, C.A.; Higuita, J.C.; Vélez, J.J.; López-Suarez, F.E. Wood Residue (Pinus patula Bark) as an Alternative Feedstock for Producing Ethanol and Furfural in Colombia: Experimental, Techno-Economic and Environmental Assessments. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2016, 140, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limenih, B.Y.; Stoeckl, N.; O’Reilly-Wapstra, J.; Volker, P. Managing Forest Residues for Biodiversity, Bioenergy, and Smoke Reduction: Insights from a Discrete Choice Experiment in Tasmania, Australia. Energy Policy 2024, 195, 114351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uemura Silva, V.; Nascimento, M.F.; Resende Oliveira, P.; Panzera, T.H.; Rezende, M.O.; Silva, D.A.L.; Borges de Moura Aquino, V.; Rocco Lahr, F.A.; Christoforo, A.L. Circular vs. Linear Economy of Building Materials: A Case Study for Particleboards Made of Recycled Wood and Biopolymer vs. Conventional Particleboards. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 285, 122906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutiérrez, J.; Rubio-Clemente, A.; Pérez, J.F. Effect of Main Solid Biomass Commodities of Patula Pine on Biochar Properties Produced under Gasification Conditions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 160, 113123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, S.K.; Jain, A.; Shrivastava, K. Review on Recent Advancement of Adsorption Potential of Sugarcane Bagasse Biochar in Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2024, 206, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahoor, A.; Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Yi, W.; Sajnani, S.; Tai, L.; Tahir, N.; Abdoulaye, B.; Mahaveer; et al. Agricultural Lignocellulose Biochar Material in Wastewater Treatment: A Critical Review and Sustainability Assessment. Environ. Funct. Mater. 2025; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, J.; Bao, J.; Liu, Y. Removal of Methylene Blue from Simulated Wastewater Based upon Hydrothermal Carbon Activated by Phosphoric Acid. Water 2025, 17, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavali, M.; Hennig, T.B.; Libardi Junior, N.; Kim, B.; Garnier, V.; Benbelkacem, H.; Bayard, R.; Woiciechowski, A.L.; Matias, W.G.; de Castilhos Junior, A.B. Co-Hydrothermal Carbonization of Sawdust and Sewage Sludge: Assessing the Potential of the Hydrochar as an Adsorbent and the Ecotoxicity of the Process Water. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nnadozie, E.C.; Ajibade, P.A. Isotherm, Kinetics, Thermodynamics Studies and Effects of Carbonization Temperature on Adsorption of Indigo Carmine (IC) Dye Using C. odorata Biochar. Chem. Data Collect. 2021, 33, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pessôa, T.S.; Ferreira, L.E.d.L.; da Silva, M.P.; Pereira Neto, L.M.; do Nascimento, B.F.; Fraga, T.J.M.; Jaguaribe, E.F.; Cavalcanti, J.V.; da Motta Sobrinho, M.A. Açaí Waste Beneficing by Gasification Process and Its Employment in the Treatment of Synthetic and Raw Textile Wastewater. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 240, 118047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokay Yılmaz, F.G.; Tekin, G.; Ersöz, G.; Atalay, S. Reclamation of Real Textile Wastewater by Sequential Advanced Oxidation and Adsorption Processes Using Corn-Cob Based Materials. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 335, 122196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trivedi, Y.; Sharma, M.; Mishra, R.K.; Sharma, A.; Joshi, J.; Gupta, A.B.; Achintya, B.; Shah, K.; Vuppaladadiyamd, A.K. Biochar Potential for Pollutant Removal during Wastewater Treatment: A Comprehensive Review of Separation Mechanisms, Technological Integration, and Process Analysis. Desalination 2025, 600, 118509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabry, H.A.; Salaah, S.M.; El-Naggar, M.M.; Ali, E.H.A.; Khalil, M.T.; Ibrahim, A.A.E.; Mostafa, A.B. Nanocomposite Treatment of Hospital Wastewater; Prophylaxis Toxicity in the Freshwater Crayfish Muscles and Hepatopancreas. Sci. Afr. 2025, 27, e02567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanighias, T.; Umar, A.; Abdullahi, M.; Abdallah, M.A.-E.; Orsini, L. Combined Toxicity of Perfluoroalkyl Substances and Microplastics on the Sentinel Species Daphnia magna: Implications for Freshwater Ecosystems. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 363, 125133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.J.; Lassiter, M.G. Chapter 26—Environmental Toxicology: Aquatic. In Information Resources in Toxicology, 5th ed.; Wexler, P., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikuda, O.; Roubeau Dumont, E.; Chen, Q.; Macairan, J.-R.; Robinson, S.A.; Berk, D.; Tufenkji, N. Toxicity of Microplastics and Nanoplastics to Daphnia magna: Current Status, Knowledge Gaps and Future Directions. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark-Wolf, T.J.; Holt, K.A.; Johansson, E.; Nisi, A.C.; Rafiq, K.; West, L.; Boersma, P.D.; Hazen, E.L.; Moore, S.E.; Abrahms, B. The Capacity of Sentinel Species to Detect Changes in Environmental Conditions and Ecosystem Structure. J. Appl. Ecol. 2024, 61, 1638–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancel, S.; Cachot, J.; Bon, C.; Rochard, É.; Geffard, O. A Critical Review of Pollution Active Biomonitoring Using Sentinel Fish: Challenges and Opportunities. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 360, 124661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foudhaili, T.; Jaidi, R.; Neculita, C.M.; Rosa, E.; Triffault-Bouchet, G.; Veilleux, É.; Coudert, L.; Lefebvre, O. Effect of the Electrocoagulation Process on the Toxicity of Gold Mine Effluents: A Comparative Assessment of Daphnia magna and Daphnia pulex. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 708, 134739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Daphnia as a Versatile Model System in Ecology and Evolution. EvoDevo 2022, 13, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, T.; Wang, B.; Gao, B.; Cheng, N.; Feng, Q.; Chen, M.; Wang, S. Degradation of Organic Pollutants from Water by Biochar-Assisted Advanced Oxidation Processes: Mechanisms and Applications. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 442, 130075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubio-Clemente, A.; Gutiérrez, J.; Henao, H.; Melo, A.M.; Pérez, J.F.; Chica, E. Adsorption Capacity of the Biochar Obtained from Pinus patula Wood Micro-Gasification for the Treatment of Polluted Water Containing Malachite Green Dye. J. King Saud Univ. Eng. Sci. 2021, 35, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego-Ramírez, C.; Chica, E.; Rubio-Clemente, A. Elimination of Indigo Carmine in Water by Pinus patula Biochar: Adsorption Process Optimization, Kinetics and Isotherms. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 112425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dendy, D.; Lestari, W.W.; Anshori, I.; Surawijaya, A.; Handayani, M.; Wahyuningsih, S.; Saraswati, T.E.; Ridho Suharbiansah, R.S. Enhanced Indigo Carmine Adsorption Using Ethylenediamine-Modified MIL-101(Cr) Materials. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 334, 130465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EPA. Whole Effluent Toxicity Methods; Reports and Assessments. 2025. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/cwa-methods/whole-effluent-toxicity-methods (accessed on 3 April 2024).
- Shao, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, Q.; Guo, G. Acute Toxicity of Binary and Ternary Mixtures of La, Ce and Dy on Daphnia magna: Toxicity Patterns Depend on the Ratios of the Components and the Concentration Gradient. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 956, 177305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Méndez-Hernández, J.E.; Ramírez-Vives, F.; Sobrino-Figueroa, A.S.; Garza-López, P.M.; Loera, O. Ecotoxicological Evaluation and Treatment of a Denim-Laundry Wastewater. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2022, 233, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuzer, B.; Guida, M.; Ciner, F.; Aktan, B.; Aydin, M.I.; Meric, S.; Selcuk, H. A Multifaceted Aggregation and Toxicity Assessment Study of Sol–Gel-Based TiO2 Nanoparticles during Textile Wastewater Treatment. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 4966–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saghir, S.; Pu, C.; Fu, E.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, Z. Synthesis of High Surface Area Porous Biochar Obtained from Pistachio Shells for the Efficient Adsorption of Organic Dyes from Polluted Water. Surf. Interfaces 2022, 34, 102357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Ul Haq Khan, Z.; Sabahat, S.; Aftab, M.; Sun, J.; Samad Shah, N.; Rahim, A.; Abdullah, M.M.S.; Imran, M. Synergistic Degradation of Toxic Azo Dyes Using Mn-CuO@Biochar: An Efficient Adsorptive and Photocatalytic Approach for Wastewater Treatment. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2025, 302, 120844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.P.; Ashworth, D.J.; Celis, N.; Ibekwe, A.M. Optimizing Date Palm Leaf and Pistachio Shell Biochar Properties for Antibiotic Adsorption by Varying Pyrolysis Temperature. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2023, 21, 101325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, F.; Ji, G.; Irfan, M.; Gao, Y.; Shafiq, F.; Sun, Y.; Ain, Q.U.; Li, A. Adsorption Performance and Mechanism of Cationic and Anionic Dyes by KOH Activated Biochar Derived from Medical Waste Pyrolysis. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 314, 120271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.-L.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.-H.; Song, M.; Kwon, E.E. Low-Temperature Biochar Production from Torrefaction for Wastewater Treatment: A Review. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 387, 129588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Yuan, X.; Li, X.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H. Burgeoning Prospects of Biochar and Its Composite in Persulfate-Advanced Oxidation Process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 409, 124893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Olsen, M.N.P.; Moni, C.; Dieguez-Alonso, A.; de la Rosa, J.M.; Stenrød, M.; Liu, X.; Mao, L. Comparison of Properties of Biochar Produced from Different Types of Lignocellulosic Biomass by Slow Pyrolysis at 600 °C. Appl. Energy Combust. Sci. 2022, 12, 100090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimm, A.; Conrad, S.; Gentili, F.G.; Mikkola, J.-P.; Hu, T.; Lassi, U.; Silva, L.F.O.; Lima, E.C.; dos Reis, G.S. Highly Efficient Boron/Sulfur-Modified Activated Biochar for Removal of Reactive Dyes from Water: Kinetics, Isotherms, Thermodynamics, and Regeneration Studies. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2025, 713, 136486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.K.C.; Truong, T.T.T.; Le, A.L.; Do, D.A.M.; Nguyen, T.G.; Tran, T.D.; Pham, T.D. Synthesis, Characterization of Novel Protein-Modified Rice Husk Biochar and Their Applications for Highly Adsorptive Removal Azo Dye in Water. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 37, 104037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Yu, Z.; Chen, L.; Du, J.; Li, J.; Yuan, W.; Li, X.; Lin, J. Thin-Film Composite Electro-Nanofiltration Membrane for One-Step and Efficient Fractionation of Dyes and Salts in High-Salinity Textile Wastewater. Desalination 2024, 591, 118056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GilPavas, E.; Correa-Sánchez, S. Optimization of the Heterogeneous Electro-Fenton Process Assisted by Scrap Zero-Valent Iron for Treating Textile Wastewater: Assessment of Toxicity and Biodegradability. J. Water Process Eng. 2019, 32, 100924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego Ramírez, C.; Chica, E.; Rubio-Clemente, A. Study of the Feasibility of Pinus patula Biochar: Regeneration of the Indigo Carmine-Loaded Biochar and Efficiency for Real Textile Wastewater Treatment. Processes 2024, 12, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Ángeles, M.J.; González-Nava, V.J.; Castro-Fernández, J.A.; García-Estrada, R.; Espejel-Ayala, F.; Reyes-Vidal, Y.; Rivera-Iturbe, F.F.; Cárdenas, J.; Bustos, E. Textile-Washing Wastewater Treatment Using Ozonolysis, Electro-Coagulation, and Electro-Oxidation. Electrochim. Acta 2025, 512, 145473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, M.F.; Khandaker, S.; Sarker, F.; Islam, A.; Rahman, M.T.; Awual, M.R. Current Treatment Technologies and Mechanisms for Removal of Indigo Carmine Dyes from Wastewater: A Review. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 318, 114061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Panicker, T.F.; Kumar Mishra, R.; Srinivas Kini, M. A Comprehensive Review of Production and Characterization of Biochar for Removal of Organic Pollutants from Water and Wastewater. Water-Energy Nexus 2024, 7, 243–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Kammah, M.; Elkhatib, E.; Gouveia, S.; Cameselle, C.; Aboukila, E. Enhanced Removal of Indigo Carmine Dye from Textile Effluent Using Green Cost-Efficient Nanomaterial: Adsorption, Kinetics, Thermodynamics and Mechanisms. Sustain. Chem. Pharm. 2022, 29, 100753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plentz Gomes Vasconcelos, L.; Almeida Albuquerque, A.; Roberta Cabral Ribeiro, K.; Beatriz Oliveira Palmeira, M.; Thalis Vaz da Costa Capistrano, R.; Inácio Soletti, J.; Helena Vieira Carvalho, S.; Daltro Bispo, M. Comparison of Adsorption Potential of Methylene Blue and 17β-Stradiol on Biochar, Activated Biochar and Catalytic Biochar from Lignocellulosic Waste. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2025, 144, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali Alshehri, M.; Pugazhendhi, A. Biochar for Wastewater Treatment: Addressing Contaminants and Enhancing Sustainability: Challenges and Solutions. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2024, 16, 100504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foong, S.Y.; Chin, B.L.F.; Lock, S.S.M.; Yiin, C.L.; Tan, Y.H.; Zheng, G.; Ge, S.; Liew, R.K.; Lam, S.S. Enhancing Wastewater Treatment with Engineered Biochar from Microwave-Assisted Approach—A Comprehensive Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2024, 36, 103835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Yue, Y. Phosphate Adsorption from Phosphorus-Polluted Wastewater by Peanut Hull-Derived Biochar Functionalized with Eggshell-Based Calcium Chloride: Preparation, Adsorption Performance and Mechanism. Desalination Water Treat. 2024, 320, 100880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayaz, M.; Khan, A.H.A.; Song, K.; Ali, A.; Yousaf, S.; Kazmi, A.; Rashid, A. Integration of Physio-Biological Methods for Remediation of Dyes and Toxic Metals from Textile Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. Rep. 2025, 29, 102044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GilPavas, E.; Dobrosz-Gómez, I.; Gómez-García, M.-Á. Efficient Treatment for Textile Wastewater through Sequential Electrocoagulation, Electrochemical Oxidation and Adsorption Processes: Optimization and Toxicity Assessment. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 878, 114578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Methneni, N.; Morales-González, J.A.; Jaziri, A.; Mansour, H.B.; Fernandez-Serrano, M. Persistent Organic and Inorganic Pollutants in the Effluents from the Textile Dyeing Industries: Ecotoxicology Appraisal via a Battery of Biotests. Environ. Res. 2021, 196, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, R.; Mirzaei, F.; Ghanbari, F.; Feizi, R.; Mehdipour, F. Real Textile Wastewater Treatment by a Sulfate Radicals-Advanced Oxidation Process: Peroxydisulfate Decomposition Using Copper Oxide (CuO) Supported onto Activated Carbon. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.M.; Nogueira, V.; Lopes, I.; Rocha-Santos, T.; Pereira, R. Evaluation of the Potential Toxicity of Effluents from the Textile Industry before and after Treatment. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Alkimin, G.D.; Paisio, C.; Agostini, E.; Nunes, B. Phytoremediation Processes of Domestic and Textile Effluents: Evaluation of the Efficacy and Toxicological Effects in Lemna minor and Daphnia magna. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 4423–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, J.-H.; Kang, J.-K.; Park, S.-J.; Lee, C.-G. Application of Magnetic Biochar Derived from Food Waste in Heterogeneous Sono-Fenton-like Process for Removal of Organic Dyes from Aqueous Solution. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 37, 101455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, D. Ecology, Epidemiology, and Evolution of Parasitism in Daphnia; National Center for Biotechnology Information (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2005.
- Grochowska, J. Assessment of Water Buffer Capacity of Two Morphometrically Different, Degraded, Urban Lakes. Water 2020, 12, 1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GilPavas, E.; Dobrosz-Gómez, I.; Gómez-García, M.-Á. Optimization and Toxicity Assessment of a Combined Electrocoagulation, H2O2/Fe2+/UV and Activated Carbon Adsorption for Textile Wastewater Treatment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 651, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Liu, G.; Wang, C. A Review of the Conversion of Wood Biomass into High-Performance Bulk Biochar: Pretreatment, Modification, Characterization, and Wastewater Application. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2025, 361, 131448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhila, H.; Bhapkar, A.; Bhame, S. Metal Oxide/Biochar Hybrid Nanocomposites for Adsorption and Photocatalytic Degradation of Textile Dye Effluents: A Review. Desalination Water Treat. 2025, 321, 101004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, T.; Debnath, A.; Manna, M.S. Adsorption of Malachite Green by Aegle Marmelos-Derived Activated Biochar: Novelty Assessment through Phytotoxicity Tests and Economic Analysis. J. Indian Chem. Soc. 2024, 101, 101219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Units | Wood Pellets | BC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface area (BET) | m2/g | 1.16 | 367.33 |
| Pore volume | cm3/g | 0.0006 | 0.20 |
| N | wt% | 0.02 | 0.19 |
| O | wt% | 47.28 | 0.9 |
| H | wt% | 5.69 | 0.97 |
| C | wt% | 47.01 | 97.94 |
| H/C | - | 1.45 | 0.12 |
| O/C | - | 0.75 | 0.01 |
| Volatile material (VM) | wt% | 84.64 | 20.59 |
| pHpzc | - | - | 6 |
| Parameter | Unit | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical oxygen demand (COD) | mgO2/L | 630.3 |
| 5 d biochemical oxygen demand (BOD5) | mgO2/L | 222.2 |
| BOD5/COD | - | 0.35 |
| Temperature | °C | 24.9 |
| True colour | Pt-Co | 201 |
| Apparent colour | Pt-Co | >90 |
| Total organic carbon (TOC) | mgC/L | 217.9 |
| Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) | mgC/L | 124.5 |
| Conductivity | mS/cm | 2.4 |
| pH | pH units | 6.4 |
| Species | Experimental Conditions | Results | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| D. magna | t = 48 h Number of neonates per sample = 5 Photoperiod: 12:12 T = 25 °C Dilutions of the TWW were performed with reconstituted water |
| [37] |
| D. magna | t = 24 h Number of neonates per sample = 5 Photoperiod: 12:12 T = 25 °C Dilutions of the TWW were performed with reconstituted water (100, 50, 25, 12.5, 6.2, and 3.1%) |
| [61] |
| D. magna | t = 48 h Number of neonates per sample = 10 Photoperiod: 16:8 Dilutions of the TWW were performed with reconstituted water |
| [62] |
| D. magna | t = 48 h Number of neonates per sample = 5 Photoperiod: 16:8 Dilutions of the TWW were performed with reconstituted water (100, 66.67, 44.44, 29.63, 19.75, 13.17, and 8.78%) |
| [63] |
| D. magna | t = 48 h Number of neonates per sample = 5 Photoperiod: 16:8 T = 20 °C Dilutions of the TWW were performed with reconstituted water (100–1%) |
| [64] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gallego-Ramírez, C.; García-Zapata, Y.; Aguirre, N.; Chica, E.; Rubio-Clemente, A. Acute Toxicity Assessment of Textile Wastewater Treated with Pinus patula Biochar Using Daphnia pulex. Water 2025, 17, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081143
Gallego-Ramírez C, García-Zapata Y, Aguirre N, Chica E, Rubio-Clemente A. Acute Toxicity Assessment of Textile Wastewater Treated with Pinus patula Biochar Using Daphnia pulex. Water. 2025; 17(8):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081143
Chicago/Turabian StyleGallego-Ramírez, Carolina, Yuri García-Zapata, Néstor Aguirre, Edwin Chica, and Ainhoa Rubio-Clemente. 2025. "Acute Toxicity Assessment of Textile Wastewater Treated with Pinus patula Biochar Using Daphnia pulex" Water 17, no. 8: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081143
APA StyleGallego-Ramírez, C., García-Zapata, Y., Aguirre, N., Chica, E., & Rubio-Clemente, A. (2025). Acute Toxicity Assessment of Textile Wastewater Treated with Pinus patula Biochar Using Daphnia pulex. Water, 17(8), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17081143









