Effective Combination of MOF and MoS2 Layers: A Novel Composite Material Capable of Rapidly Degrading Dyes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Part
2.1. Experimental Test Materials
2.1.1. Chemical Reagents
2.1.2. Experimental Instruments
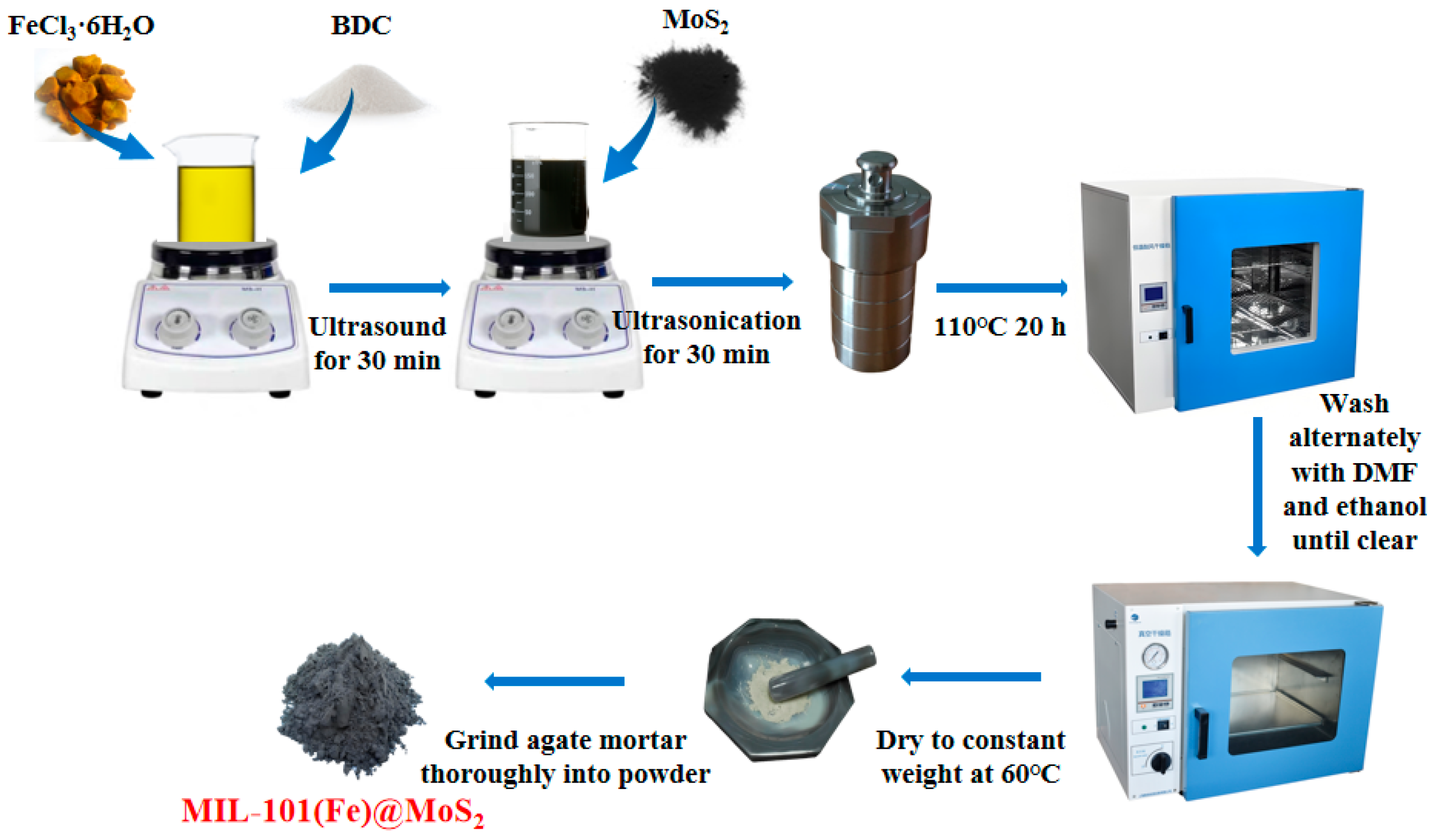
2.2. Catalyst Preparation
2.2.1. Preparation of MIL-101(Fe)
2.2.2. Preparation of MIL-101(Fe)@MoS2
2.3. Analytical Methods
2.3.1. Photo-Fenton Degradation of CR Experiment
2.3.2. Free-Radical-Trapping Experiments
2.3.3. Total Organic Carbon (TOC) Determination and Mineralization Rate Assessment
2.3.4. Catalyst Stability and Reproducibility Testing
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalyst Characterization
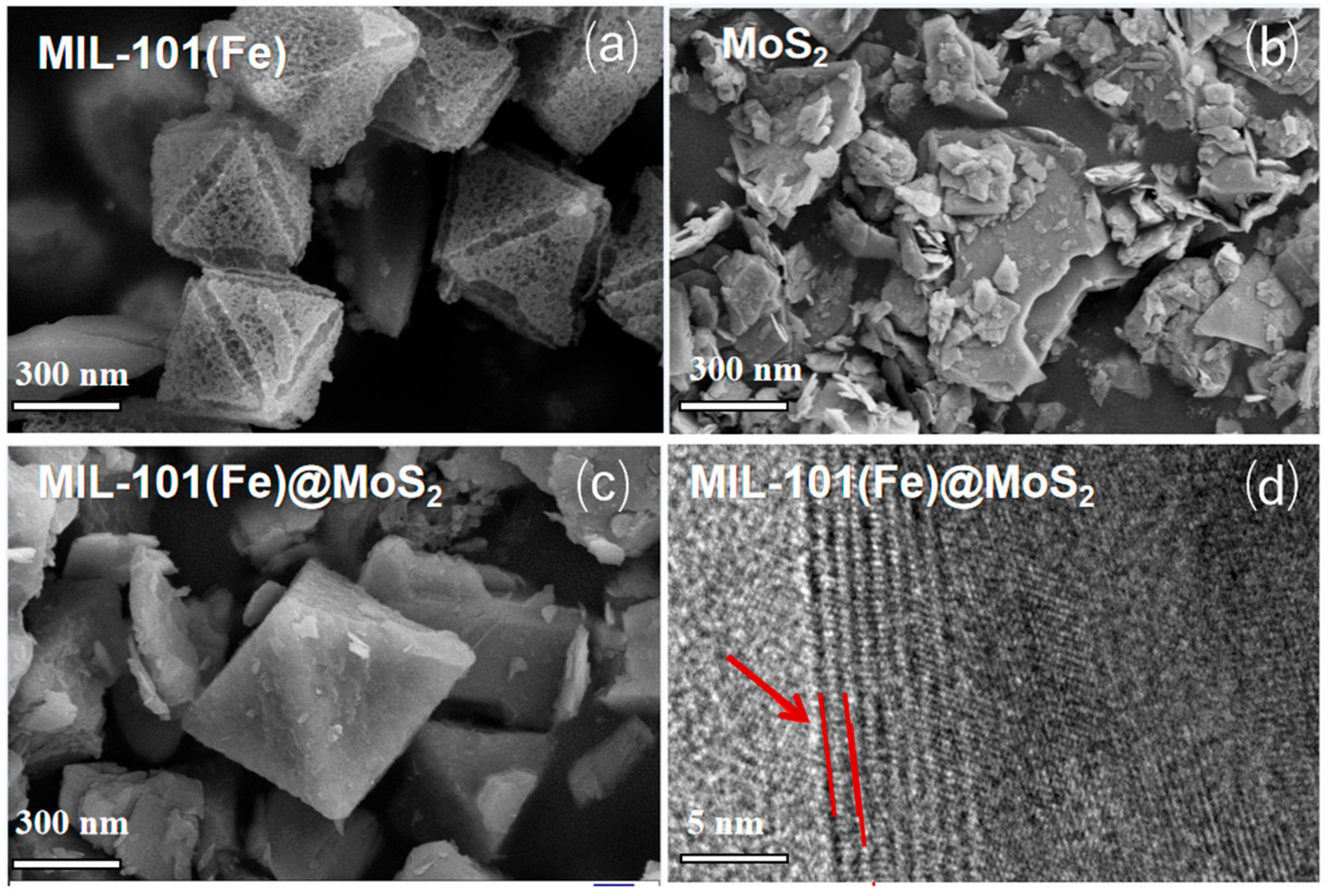
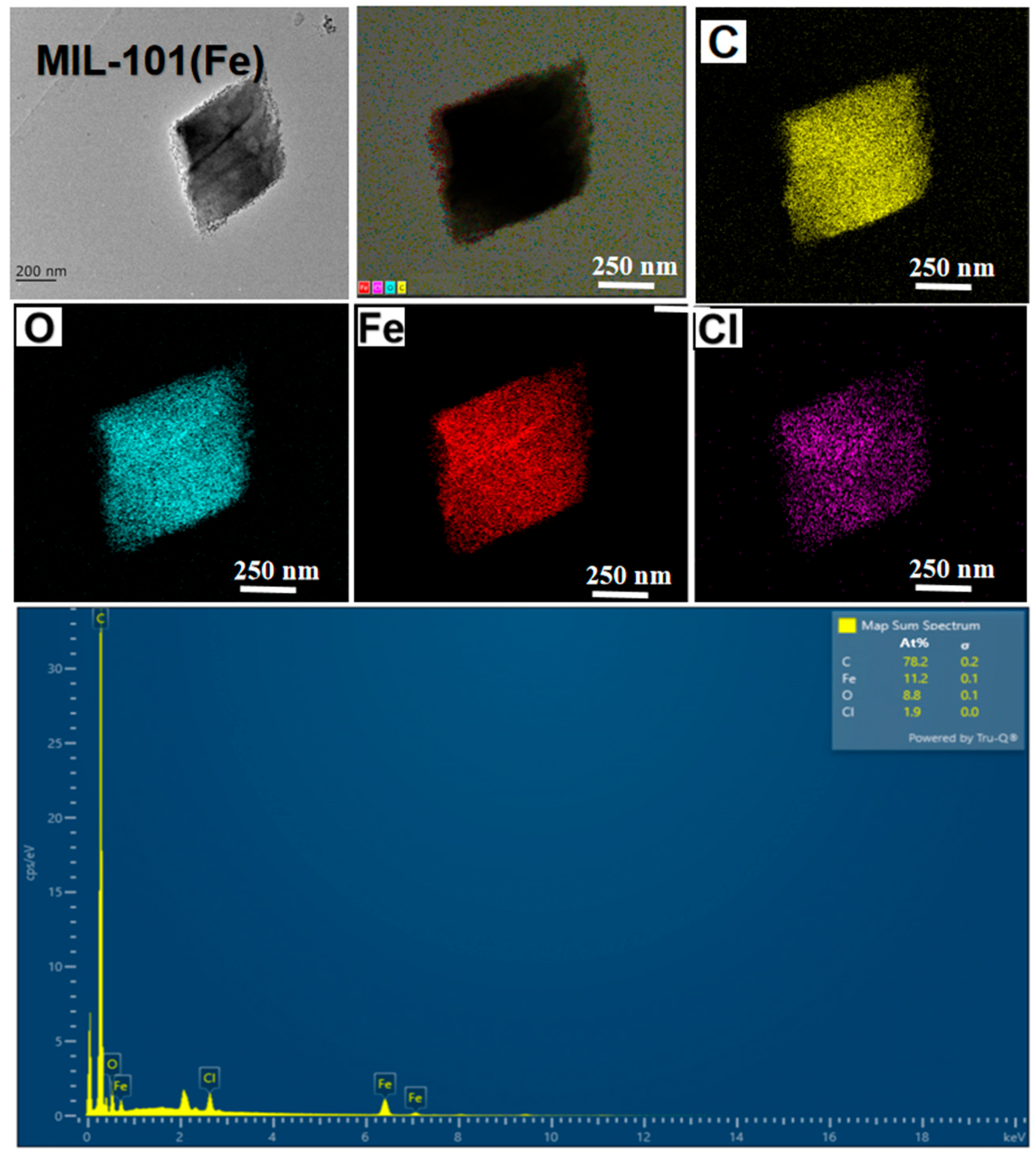
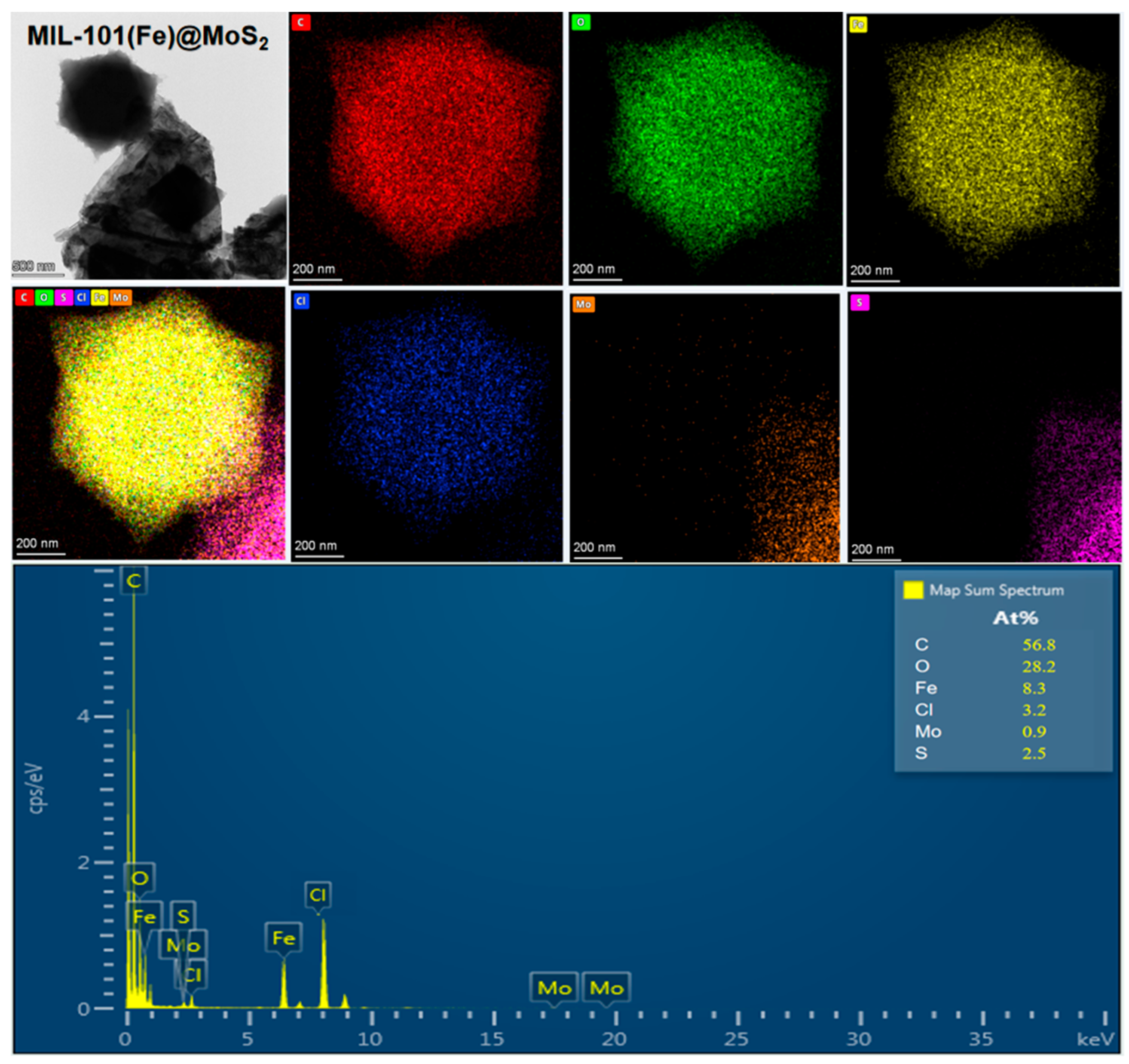
3.1.1. SEM/Energy-Dispersive X-Ray Spectroscopy (EDS) and High-Resolution Transmission Electron Microscopy Analysis
3.1.2. XRD Analysis
3.1.3. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy Analysis
3.2. Analysis of the Photocatalytic Properties
3.2.1. The Effect of Different MoS2 Doping Ratios on the Degradation Efficiency
3.2.2. Effect of H2O2 Dosage on the Degradation Efficiency
3.2.3. Effect of the Initial CR Concentration on the Degradation Efficiency
3.2.4. Effect of the Initial pH Value on Degradation Efficiency
3.3. Degradation Kinetics and Mechanism Analysis
3.3.1. Comparison of the Contribution of MIL-101(Fe)@MoS2 to CR Degradation and Adsorption Under Different Conditions
3.3.2. Radical-Trapping Experiment and Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR) Spectrum Analysis
3.3.3. Analysis of Band Structure and Band Gap Values (Tauc Formula)
3.4. Catalyst Stability
3.4.1. Loop Experiment and Efficiency Retention Rate
3.4.2. Metal-Leaching Quantity Assessment and Environmental Safety
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ozturk, E. Improving water-use efficiency and environmental performances in an integrated woven-knitted fabric printing-dyeing textile mill. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 379, 134805. [Google Scholar]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Dhal, J.P.; Panigrahi, G.K. Magnesium oxide nanoparticles decorated iron oxide nanorods: Synthesis, characterization and remediation of Congo red dye from aqueous media. Compos. Commun. 2020, 22, 100496. [Google Scholar]
- Debnath, S.; Maity, A.; Pillay, K. Impact of process parameters on removal of Congo red by graphene oxide from aqueous solution. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 260–272. [Google Scholar]
- GB8978-1996; Integrated Wastewater Discharge Standard. Ministry of Environmental Protection: Beijing, China, 1996.
- Chen, H.; Wang, K.; She, S.Q.; Yu, X.; Yu, L.Y.; Xue, G.; Li, X. Insight into dissolved organic nitrogen transformation and characteristics: Focus on printing and dyeing wastewater treatment process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131086. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, C.K.; Xiang, Z.Q.; Huang, J.C.; Liu, G.B.; Yu, X.M.; Liu, W.J.; Cao, H.J. Efficient adsorptive removal of Sb (Ⅲ) and Sb (V) from printing and dyeing wastewater by TiCl4. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 493, 152858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Guo, J.; Yao, Q.; Zhang, S.; Feng, S.; Guan, F.C.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; He, J.H. Self-cleaning and multi-active sites amphoteric composite sponges: Efficient removal, selective adsorption and photocatalyst substrates of dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 494, 152865. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.K.; Chen, T.Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, R.Q.; Zhu, N.L.; Li, L.X.Y.; Zhao, L.X.; Li, Z.G.; Wang, Y.W.; Jiang, G.B. Occurrence and ecological risk assessment of highly toxic halogenated byproducts during chlorination decolorization of textile printing and dyeing wastewater. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 17970–17978. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, N.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fan, Y.; Li, Q.; Xu, L.; Jiang, J.; Gao, J.; Shi, J.; Wang, H.; et al. TiO2/CMWCNT/CaAlg composite membrane used for dye desalination and its rapid cleaning under ultraviolet light and advanced oxidation activated by monopersulfate. Compos. Commun. 2024, 48, 101921. [Google Scholar]
- Solayman, H.M.; Hossen, M.A.; Aziz, A.A.; Yahya, N.Y.; Leong, K.H.; Sim, L.C.; Monir, M.U.; Zoh, K.D. Performance evaluation of dye wastewater treatment technologies: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 109610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Fan, X.; Liang, A.; Zhang, S.; Wang, W.; Qu, S.; Li, C. Electron-rich CNTs modified FeOCl/Fe2O3 with improved Fenton catalytic performance. Compos. Commun. 2021, 27, 100811. [Google Scholar]
- Kakavandi, B.; Salmasi, M.Z.; Ahmadi, M.; Naderi, A.; Roccara, P.; Bedía, J.; Farzood, M.H.; Kalantary, R.R. Spinel cobalt ferrite-based porous activated carbon in conjunction with UV light irradiation for boosting peroxymonosulfate oxidation of bisphenol A. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118242. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, N.; Madani, Z.; Giannakis, S.; Isari, A.A.; Arjmand, M.; Hasanvandian, F.; Noorisephir, M.; Kakavandi, B. Peroxymonosulfate assisted pesticide breakdown: Unveiling the potential of a novel S-scheme ZnO@CoFe2O4 photo-catalyst, anchored on activated carbon. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 334, 122059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosio, G.N.; Einschlag, F.S.G.; Carlos, L.; Mártire, D.O. Recent advances in the development of novel Iron-Copper bimetallic photo fenton catalysts. Catalysts 2023, 13, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, J.; Guo, S.; Chen, Y.A.; Shahzad, A.; Ullah, M.W.; Chen, F.X. Metal sulfides as emerging materials for advanced oxidation of wastewater: Recent developments, challenges, and prospects. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 509, 215765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.Y.; Deng, B.X.; Xu, L.F.; Tang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Hu, T.F.; Chen, Y.; Deng, L.F.; Bai, Y.J.; Du, K. Enhanced removal of organic dyes by piezoelectric-Fenton-like treatment with Fe-MOF@MoS2 catalysts. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1007, 176474. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Yue, D.; Li, R.; Song, H. Facile synthesis of NH2-MIL-53 (Al)@ BiOBr@ CQDs ternary heterostructure photocatalyst for degradation of ciprofloxacin in water. Compos. Commun. 2024, 50, 102028. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Q.; Zheng, S.; Ma, W.; Qian, J.; Huang, L.; Deng, H.; Zhou, Q.; Zheng, S.; Li, S.; Du, H.; et al. Facile synthesis of direct Z-scheme PPy/NH2-UiO-66heterojunction for enhanced photocatalytic Cr (VI) reduction, industrialelectroplating wastewater treatment, and tetracycline degradation. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2024, 344, 123669. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.C.; Hu, B.C.; Shang, L.M.; Ma, T.; Li, C.; Liang, H.W.; Yu, S.H. General synthesis and solution processing of metal-organic framework nanofibers. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2202504. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.; Huang, C.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, R.; Wang, Y.; An, P.; Zhang, J.; Qiu, M.; Zhou, L.; et al. Dynamic Restructuring of Coordinatively Unsaturated Copper Paddle Wheel Clusters to Boost Electrochemical CO2 Reduction to Hydrocarbons. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202112116. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, J.; Liang, Z.; Zou, R.; Zhao, Y. Heterogeneous catalysis in zeolites, mesoporous silica, and metal-organic frameworks. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1701139. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, N.Y.; Zheng, Y.T.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z.Y.; Huang, C.Z.; Xu, Q. Reticular framework materials for photocatalytic organic reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2023, 52, 7949–8004. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Huang, G.; Guan, Q.; Dong, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, S.H.; Jiang, H.L. Integration of Pd nanoparticles with engineered pore walls in MOFs for enhanced catalysis. Chem 2021, 7, 686–698. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, J.; Qin, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Long, C.; Zhao, M.; Tang, Z. Metal-organic frameworks as catalytic selectivity regulators for organic transformations. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 5366–5396. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.J.; Wang, C.C.; Dong, K.X.; Zhang, P.; Chen, X.B.; Li, X. Study on degradation of orange G by modified Fe-based metal-organic frameworks activated persulfate. Chin. J. Catalys. 2023, 51, 101–112. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Z.J.; Zhou, R.; Liu, W.; Liao, S.; Liu, Z.N. Preparation of MIL/MoS2 and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. Ind. Water Wast. 2023, 54, 39–43. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadijokani, F.; Ghaffarkhah, A.; Molavi, H.; Dutta, S.; Lu, Y.; Wuttke, S.; Kamkar, M.; Rojas, O.J.; Arjmand, M. COF and MOF hybrids: Advanced materials for wastewater treatment. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 34, 2305507. [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson, T.; Zhi, L.; Olsen, B.; Mitlin, D. Lithium ion battery applications of molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) nanocomposites. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 7, 209–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dharman, R.K.; Francis, B.M.; Ponraj, J.S.; Muthuvijayan, S.; Manavalan, R.K.; Harisingh, S.; Balasubramanian, S.; Dhanabalan, S.C. Realization of Ti MOF/MoS2 hybrid nanostructure and their catalytic activity towards 4-nitrophenol reduction. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 17, 1760–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, R.; Sun, Q.; Chen, Z.; Du, H. Embedding of ultra-dispersed MoS2 nanosheets in N, O heteroatom-modified carbon nanofibers for improved adsorption of Hg2+. Compos. Commun. 2022, 31, 101106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, C.Q.; Ye, D.Q.; Hu, Y. The mechanism of effective photocatalytic degradation of toluene by Zr/Ti bimetallic metal-organic framework derivatives loaded with TiO2. Appl. Catal. B 2025, 361, 124635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, Y.; Huo, D.; Liu, H.; Cheng, S.; Ding, M.; Jiang, B.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, G. An Investigation of PPy@1T/2H MoS2 Composites with Durable Photothermal-Promoted Effect in Photo-Fenton Degradation of Methylene Blue and in Water Evaporation. Polymers 2023, 15, 3900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Yuan, X.; Sun, M.; Wang, Z.; Cao, G.; Gao, K.; Yang, C.; Zhang, F.; Dang, F.; Wang, W. Oxidation of tetracycline hydrochloride with a photoenhanced MIL-101(Fe)/g-C3N4/PMS system: Synergistic effects and radical/nonradical pathways. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 251, 114524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.W.; Zhu, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.H.; Jiang, Q.K.; Zhao, Z.Y.; Liang, X.Y.; Hu, C. Unraveling the high-activity origin of single-atom iron catalysts for organic pollutant oxidation via peroxymonosulfate activation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2021, 55, 8318–8328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhu, K.; Qin, W.L.; Gan, Y.P.; Huang, Y.Z.; Jiang, Z.W.; Chen, Y.W.; Li, X.; Yan, K. Acceleration of Fe3+/Fe2+ cycle in garland-like MIL-101(Fe)/MoS2 nanosheets to promote peroxymonosulfate activation for sulfamethoxazole degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 470, 144190. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, Y.J.; Nie, H.D.; Wei, K.Q.; Cao, J.J.; Huang, H.; Shao, M.W.; Liu, Y.; Kang, Z.H. Interface photo-charge kinetics regulation by carbon dots for efficient hydrogen peroxide production. J. Mater. Chem. A 2021, 9, 515–522. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, H.; Sun, X.H.; Zhang, S.; Shi, W.L.; Chin, F.G. Achieving high-efficient photocatalytic persulfate-activated degradation of tetracycline via carbon dots modified MIL-101(Fe) octahedrons. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 66, 298–309. [Google Scholar]
- Gyawali, G.; Jeong, H.K. Size Effects of MoS2 on Hydrogen and Oxygen Evolution Reaction. J. Electrochem. Sci. Technol. 2022, 13, 120–127. [Google Scholar]
- Moradi-Bieranvand, M.; Farhadi, S.; Zabadrasti, A.; Mahmoudi, F. Construction of magnetic MoS2/NiFe2O4/MIL-101(Fe) hybrid nanostructures for separation of dyes and antibiotics from aqueous media. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 11037–11056. [Google Scholar]
- Vall’es-García, C.; Gkaniatsou, E.; Santiago-Portillo, A.; Gim, M.; Greneche, J.-M.; Steunou, N.; Sicard, C.; Naval, S.; Serre, C.; García, H. Design of stable mixed-metal MIL-101(Cr/Fe) materials with enhanced catalyticactivity for the Prins reaction. J. Mater. Chem. A 2020, 8, 17002–17011. [Google Scholar]
- Ioelovich, M. Preparation, Characterization and Application of Amorphized Cellulose—A Review. Polymers 2021, 13, 4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, F.; Liu, Y.; Hammouda, S.B.; Doshi, B.; Guijarro, N.; Min, X.; Tang, C.J.; Sillanpää, M.; Sivula, K.; Wang, S. MIL-101(Fe)/g-C3N4 for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalysistoward simultaneous reduction of Cr(VI) and oxidation of bisphenol A in aqueous media. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 272, 119033. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.H.; Liu, C.R.; Li, D.J.; Liu, Y. In situ-generated H2O2 with NCQDs/MIL-101(Fe) by activating O2: A dual effect of photocatalysis and photo-Fenton for efficient removal of tetracycline at natural pH. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 592, 153312. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, Z.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Li, N.; Xu, H.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Pang, H. Design principle and synthetic strategy for metal-organic framework composites. Compos. Commun. 2024, 48, 101933. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.S.; Siddique, M.S.; Yang, Y.K.; Wu, M.; Kang, L.; Yang, H.P. Facile and scalable synthesis of Fe-based metal organic frameworks for highly efficient photo-Fenton degradation of organic contaminants. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 374, 134033. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Song, Z.; Liu, B. Active-passive synergistic alleviation of membrane scaling from groundwater by grafting charged positive monomers on the surface of nanofiltration membranes. Desalination 2025, 599, 118436. [Google Scholar]
- Reichhardt, C.; Jacobson, A.N.; Maher, M.C.; Uang, J.; McCrate, O.A.; Eckart, M.; Cegelski, L. Congo Red Interactions with Curli-Producing E. coli and Native Curli Amyloid Fibers. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0140388. [Google Scholar]
- Kustanovich, I.; Poupko, R.; Zimmermann, H.; Luz, Z.; Labes, M.M. Lyomesophases of the diethylammonium flufenamate-water system studied by deuterium NMR spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 3494–3501. [Google Scholar]
- Mekidiche, M.; Khaldi, K.; Lerari-Zinai, D.; Bachari, K. Montmorillonite-supported Cu-tripeptide complex for efficient Congo red degradation. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 339, 130640. [Google Scholar]
- Mansour, D.; Albawi, E. Abdulmohsen Khalaf Dhahi Alsukaibi, Basmah Al Shamari, Removal of Congo red dye by electrochemical advanced oxidation process: Optimization, degradation pathways, and mineralization. Sustain. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeed, M.; Asghar, H.; Khan, I.; Akram, N.; Usman, M. Synthesis of TiO2-g-C3N4 for efficient photocatalytic degradation of Congo Red dye. Catal. Today 2024, 447, 115154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatima, R.; Afridi, M.N.; Mohdeb, I.; Madhusudan, P.; Hwang, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of Congo red using RGO-modified MIL-125 (Ti) under visible light. J. Water Process Eng. 2025, 69, 106893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, K.; Yang, J. Preparation and photocatalytic performance of ultrathin oxygen-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets. Fine Chem. 2023, 40, 1925–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Shen, Y.; Yang, Z. Preparation of Fe-doped BiOBr hollow microspheres for efficient degradation of Congo red under visible light. Min. Metall. Eng. 2023, 43, 154–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudhaik, A.; Kumar, R.; Sharma, S.; Sharma, A.; Devi, S.; Raizada, P.; Le, Q.V.; Ahamad, T.; Nguyen, V.-H.; Singh, P. Structural design of dual Z-scheme GCN/CdO/CaFe2O4 ternary heterojunction with high visible light activity: Photocatalytic performance and mechanism in the degradation of Congo red dye. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2025, 172, 113697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Lv, Z.Q.; Xue, Y.C.; Xu, L.; Qiu, W.H.; Zheng, C.M.; Chen, W.Q.; Wu, M.H. MIL-53 (Fe) incorporated in the lamellar BiOBr: Promoting the visible-light catalytic capability on the degradation of rhodamine B and carbamazepine. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 374, 975–982. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.X.; Yang, S.Y.; Wang, K.; Lou, L.P. Role of primary active species and TiO2 surface characteristics in UV-illuminated photodegradation of Acid Orange 7. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2005, 172, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, K.; Xu, Y.M. Effects of polyoxometalate and fluoride on adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of organic dye X3B on TiO2: The difference in the production of reactive species. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 6204–6212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.Y. Design of Polymeric Carbon Nitride and Their Performance and Mechanism in Catalytic Degradation of Antibiotic Contaminants in Water Under Visible Light. Ph.D. Thesis, Hunan University, Changsha, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Olfatmehr, N.; Kakavandi, B.; Khezri, S.M. Peroxydisulfate activation by enhanced catalytic activity of CoFe2O4 anchored on activated carbon: A new sulfate radical-based oxidation study on the Cefixime degradation. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2022, 302, 121991. [Google Scholar]
- Naderi, A.; Firooz, M.H.; Gharibzadeh, F.; Giannakis, S.; Ahmadi, M.; Kalantary, R.R.; Kakavandi, B. Anchoring ZnO on spinel cobalt ferrite for highly synergic sono-photo-catalytic, surfactant-assisted PAH degradation from soil washing solutions. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 326, 116584. [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy, B.D.; Beiler, A.M.; Johnson, B.A.; Liseev, T.; Castner, A.T.; Ott, S. Analysis of electrocatalytic metal-organic frameworks. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2020, 406, 213137. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, X.W.; Wang, F.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, P.; Fu, H.; Zhao, C. Photocatalysis activation of peroxodisulfate over the supported Fe3O4 catalyst derived from MIL-88A(Fe) for efficient tetracycline hydrochloride degradation. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 426, 131927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


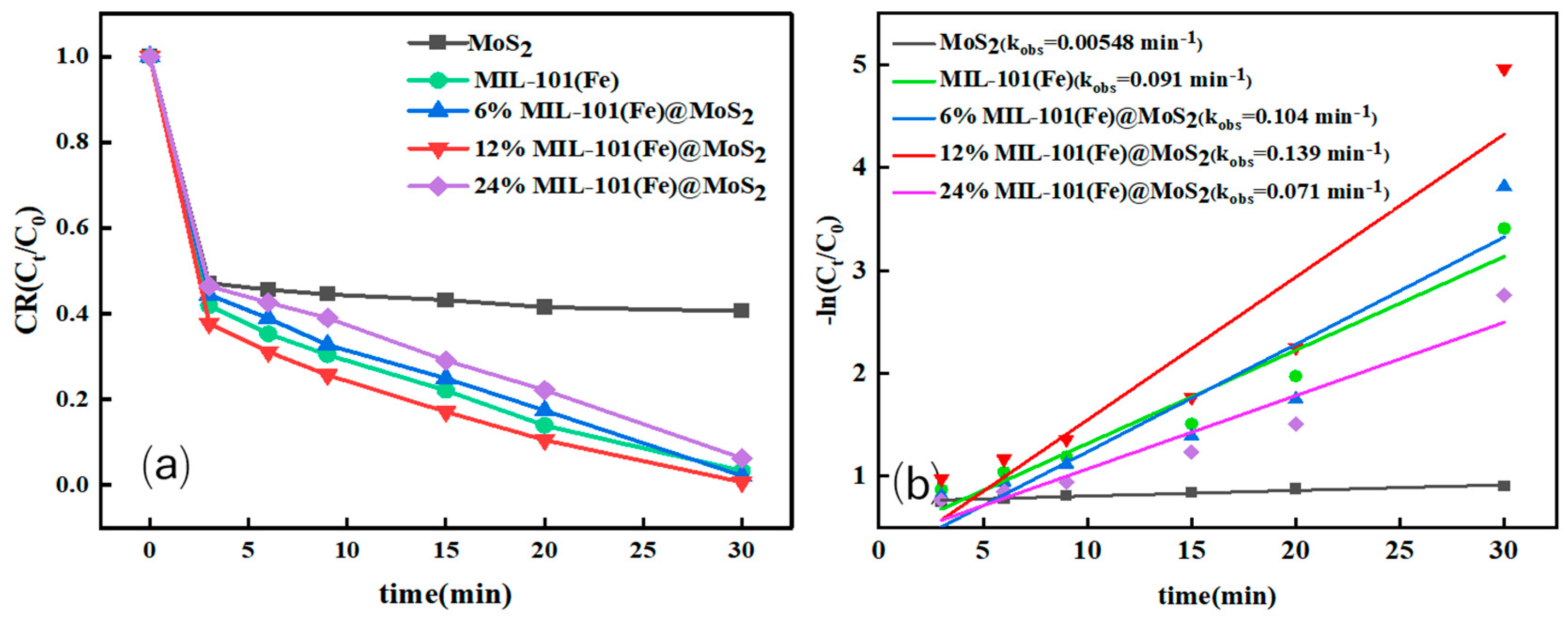
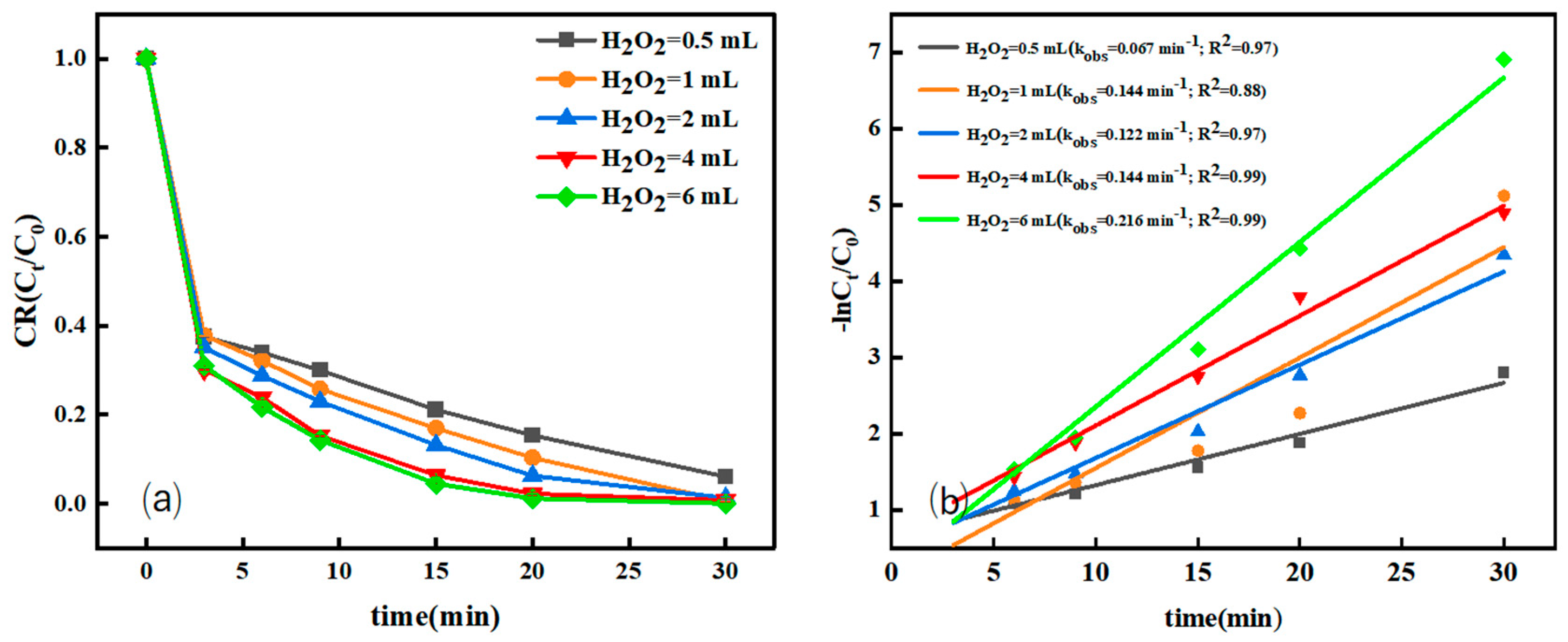
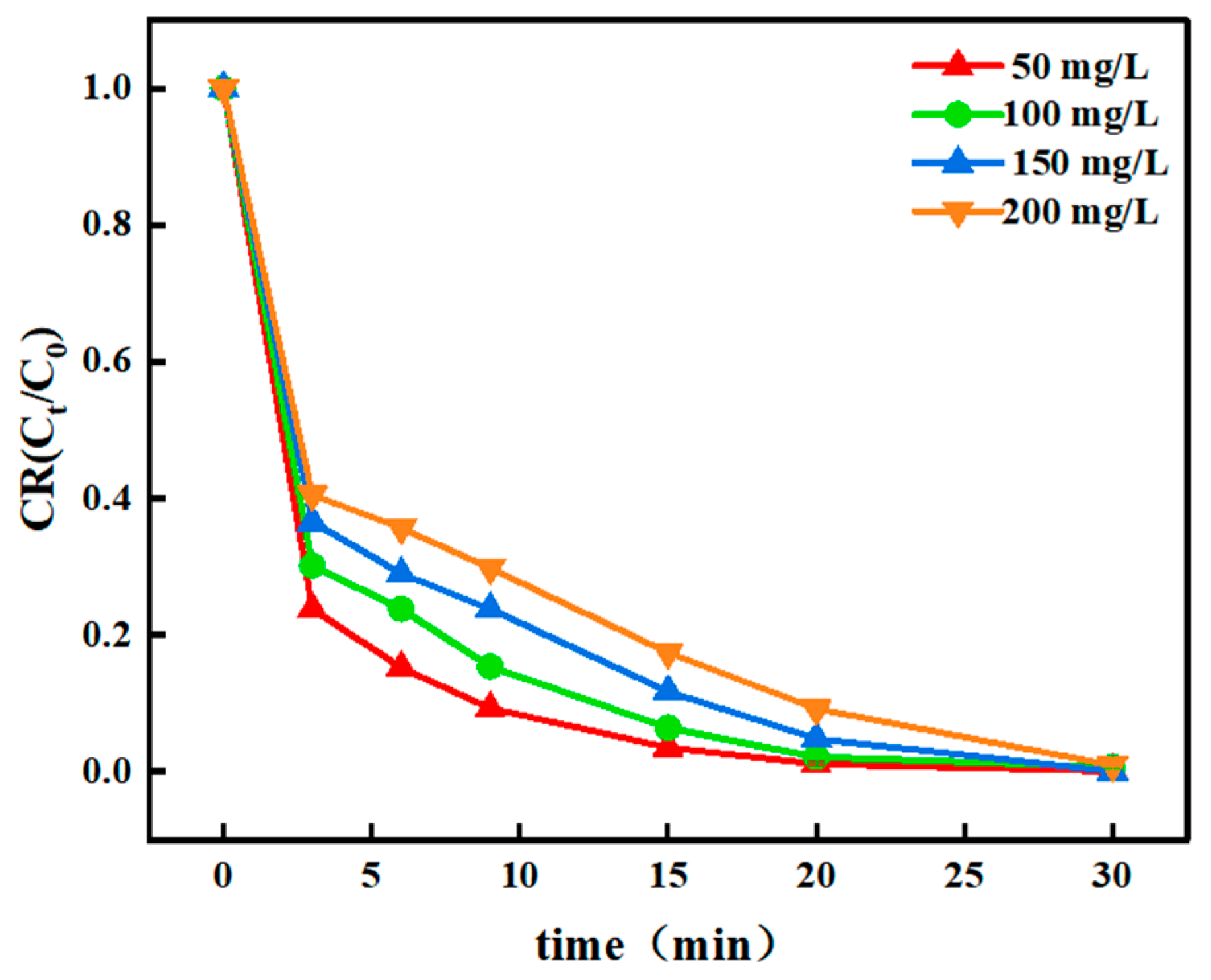

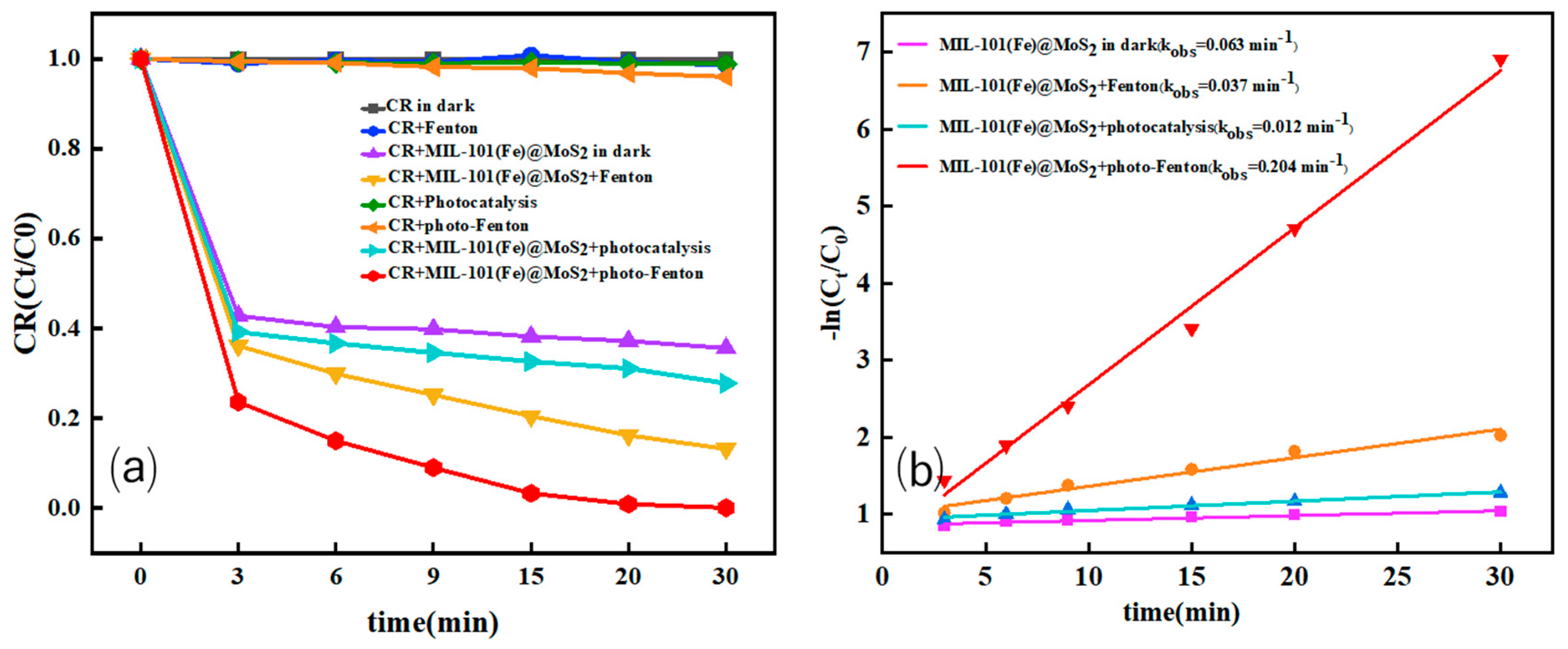
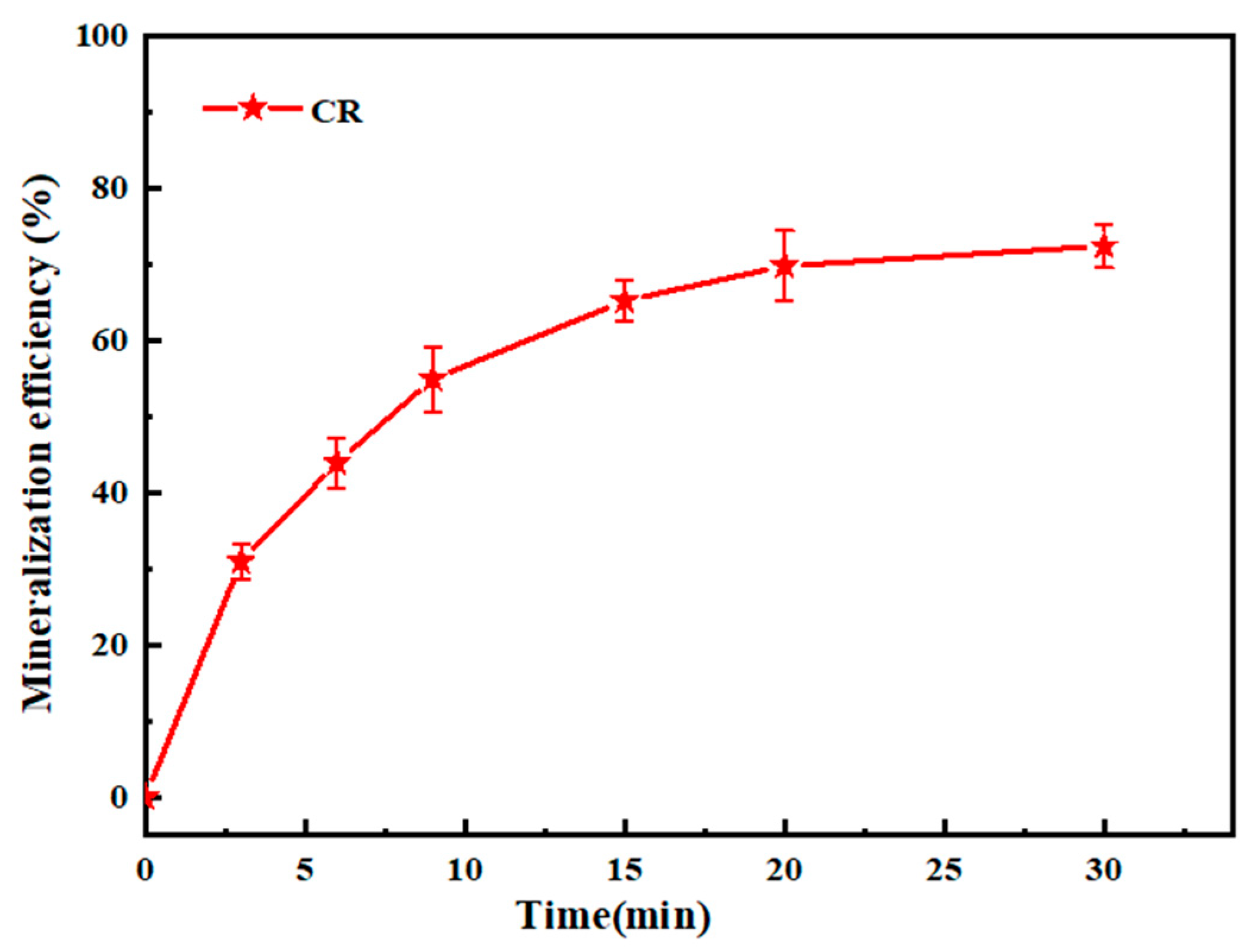
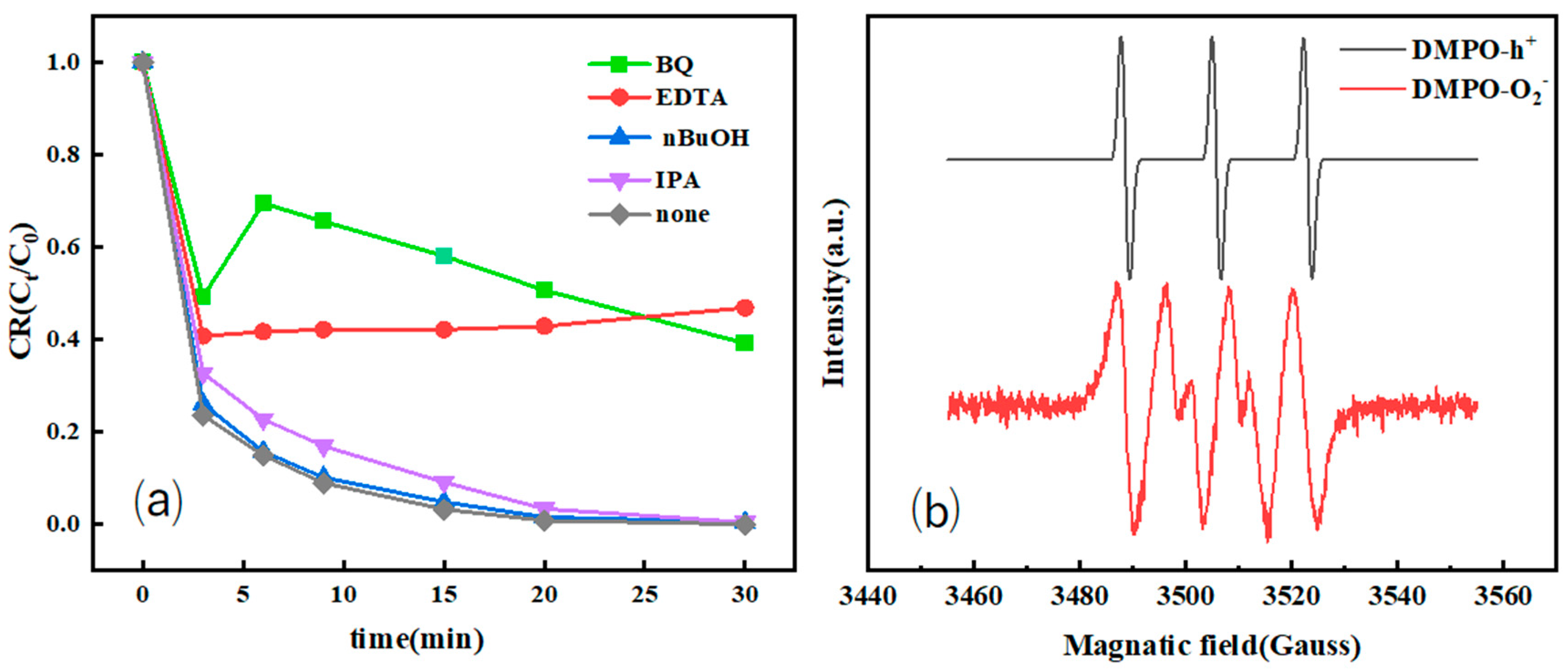

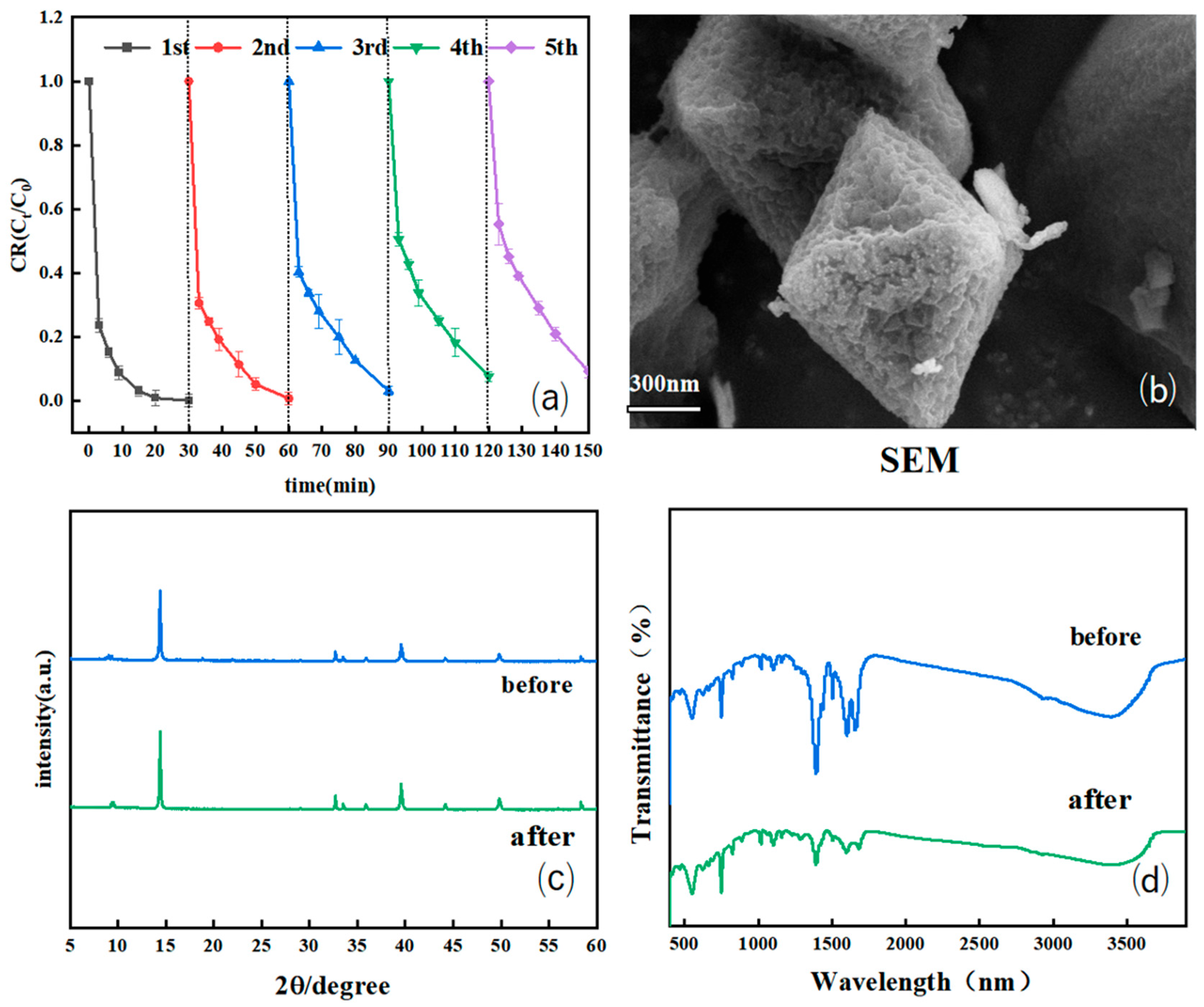
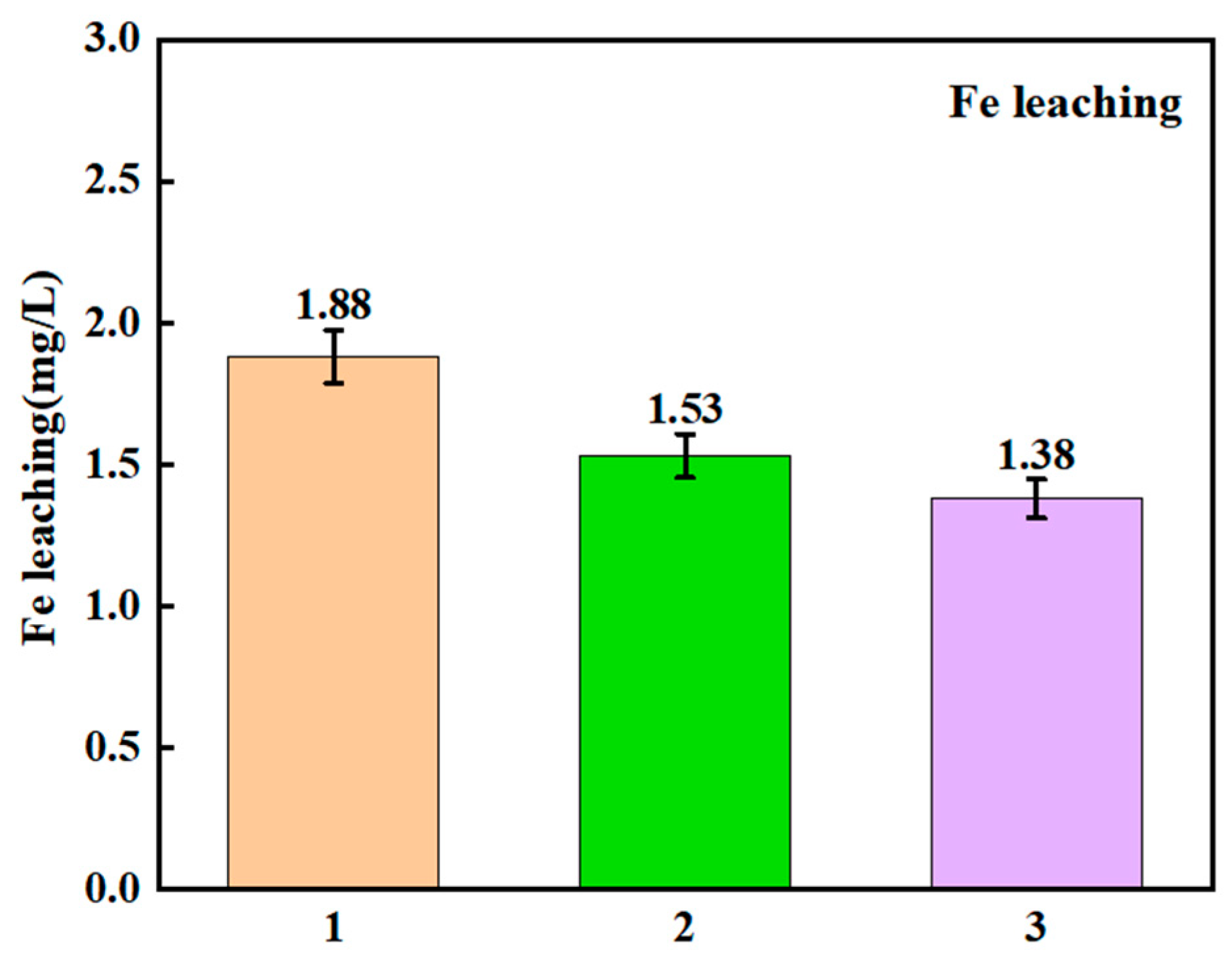
| Catalyst Type | Pollutants (Concentration) | Degradation Time | Degradation Efficiency | Reaction Rate Constant min−1 | Repeatability Stability | Literature Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TiO2-g-C3N4-10 | Congo red (100 mg/L) | 180 min | 100% | 0.0104 | After five cycles: 83.7% | [51] |
| RGO-modified MIL-125 (Ti) | Congo red (10 mg/L) | 180 min | 92.60% | 0.012 | After four cycles: 65.2% | [52] |
| Ultrathin oxygen-doped g-C3N4 nanosheets | Congo red (20 mg/L) | 120 min | 83.10% | 0.0131 | - | [53] |
| Fe-doped BiOBr hollow spheres (7% Fe) | Congo red (50 mg/L) | 180 min | 89.66% | 0.00935 | - | [54] |
| GCN/CdO/CaFe2O4 ternary heterojunction | Congo red (5 × 10−6 M) | 60 min | 88% | - | After five cycles: 80% | [55] |
| MIL-101(Fe)@MoS2 | Congo red (50 mg/L) | 30 min | 100% | 0.204 | After five cycles: 90.8% | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, S.; Yuan, Z.; Zhao, H.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Meng, L. Effective Combination of MOF and MoS2 Layers: A Novel Composite Material Capable of Rapidly Degrading Dyes. Water 2025, 17, 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070980
Zheng S, Yuan Z, Zhao H, Xu Y, Jiang N, Meng L. Effective Combination of MOF and MoS2 Layers: A Novel Composite Material Capable of Rapidly Degrading Dyes. Water. 2025; 17(7):980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070980
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Shengyang, Zhixiu Yuan, Haitao Zhao, Yaping Xu, Nan Jiang, and Lijun Meng. 2025. "Effective Combination of MOF and MoS2 Layers: A Novel Composite Material Capable of Rapidly Degrading Dyes" Water 17, no. 7: 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070980
APA StyleZheng, S., Yuan, Z., Zhao, H., Xu, Y., Jiang, N., & Meng, L. (2025). Effective Combination of MOF and MoS2 Layers: A Novel Composite Material Capable of Rapidly Degrading Dyes. Water, 17(7), 980. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17070980






