Isolation and Characterization of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterium N.eA1: Insights into Nitrogen Conversion and N2O Emissions in Varied Environmental Conditions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
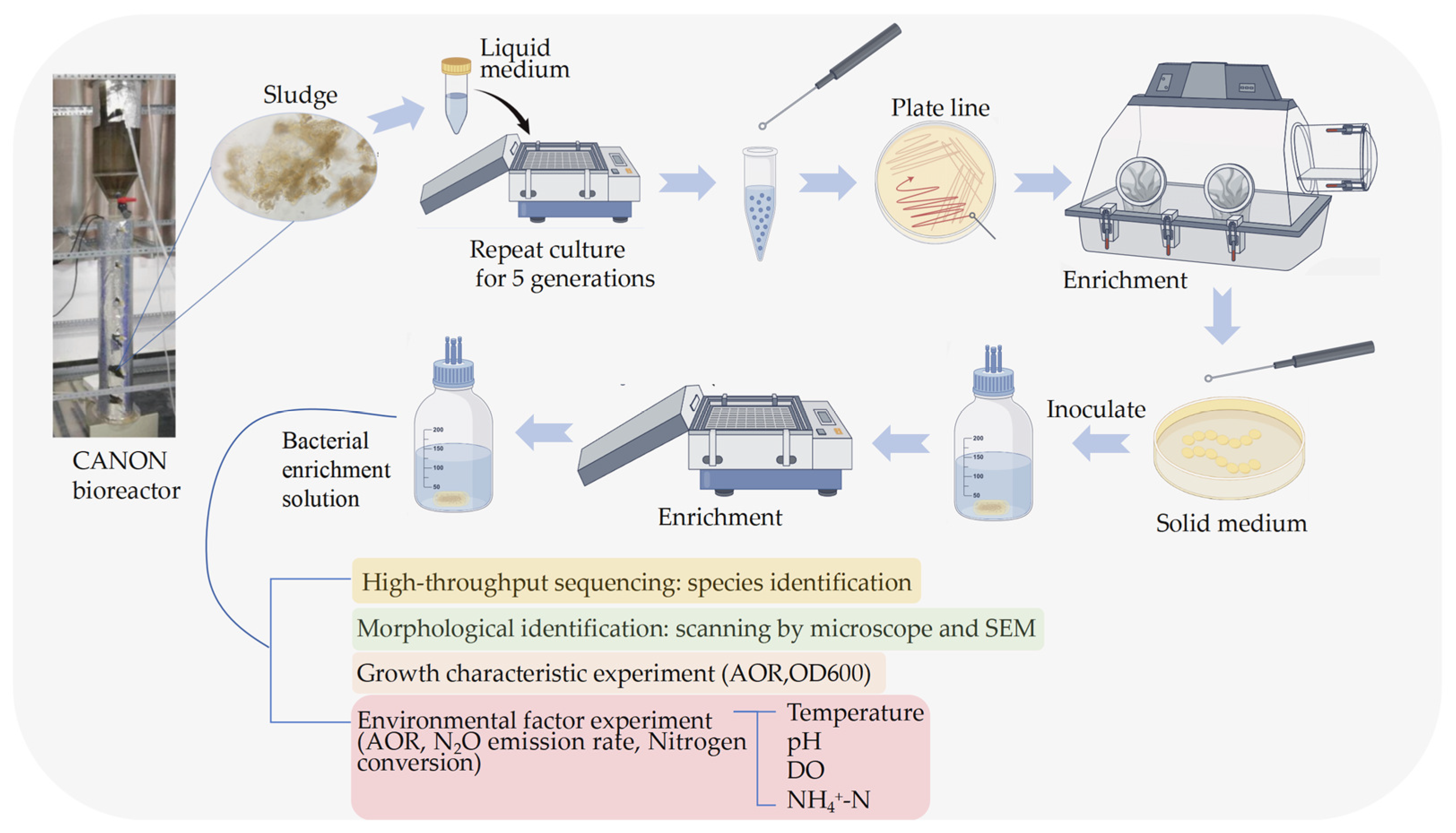
2.1. Separation, Purification and Enrichment Culture
2.2. Growth Characteristic Experiment
2.3. Environmental Factor Experiment
2.4. Bioinfomatics Analysis
2.5. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Growth Characteristics, Genetic Identification and Morphological Analysis
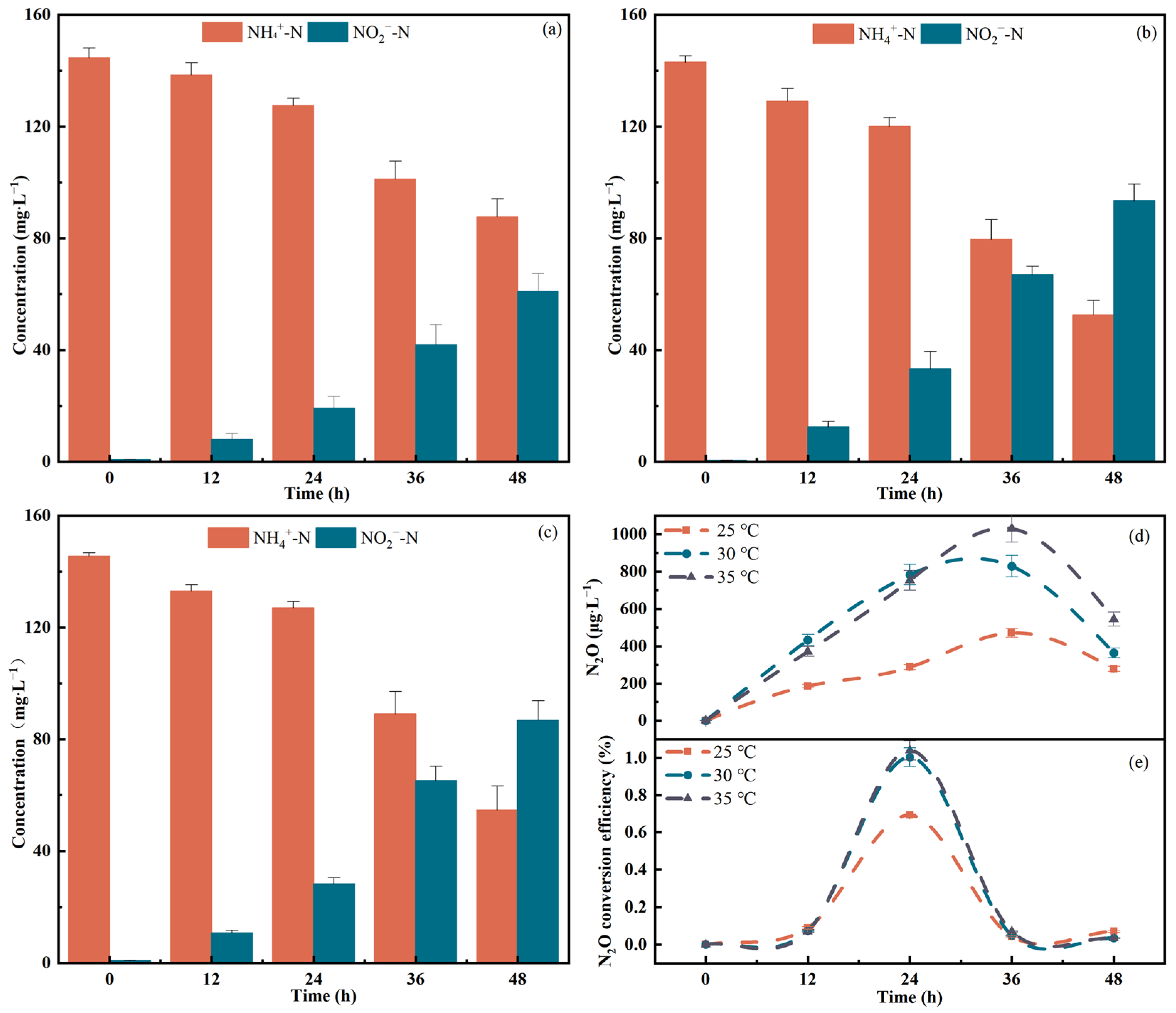
3.2. Effect of Temperature on Strain N.eA1
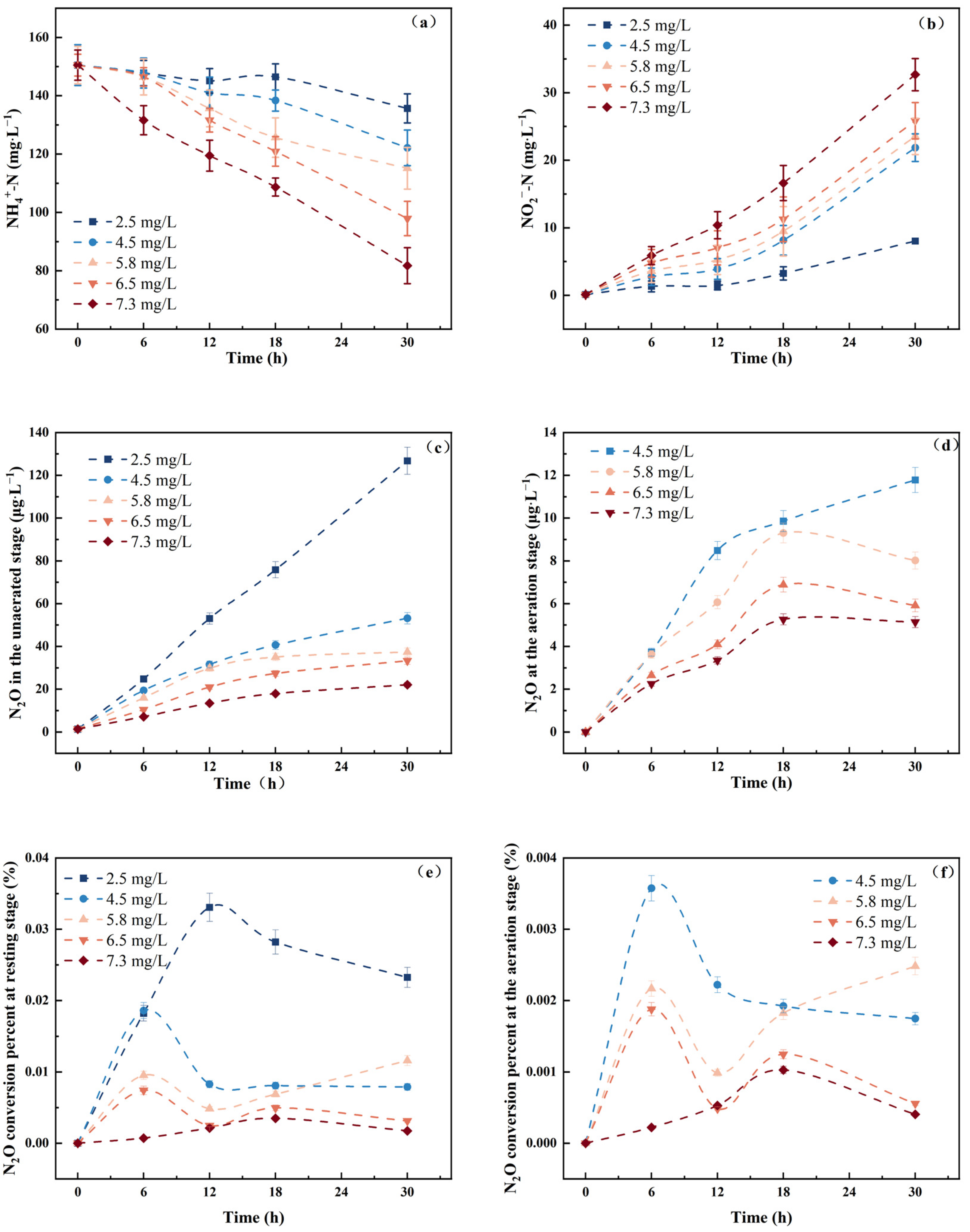
3.3. Effect of DO Concentration on Strain N.eA1
3.4. Effect of pH on Strain N.eA1
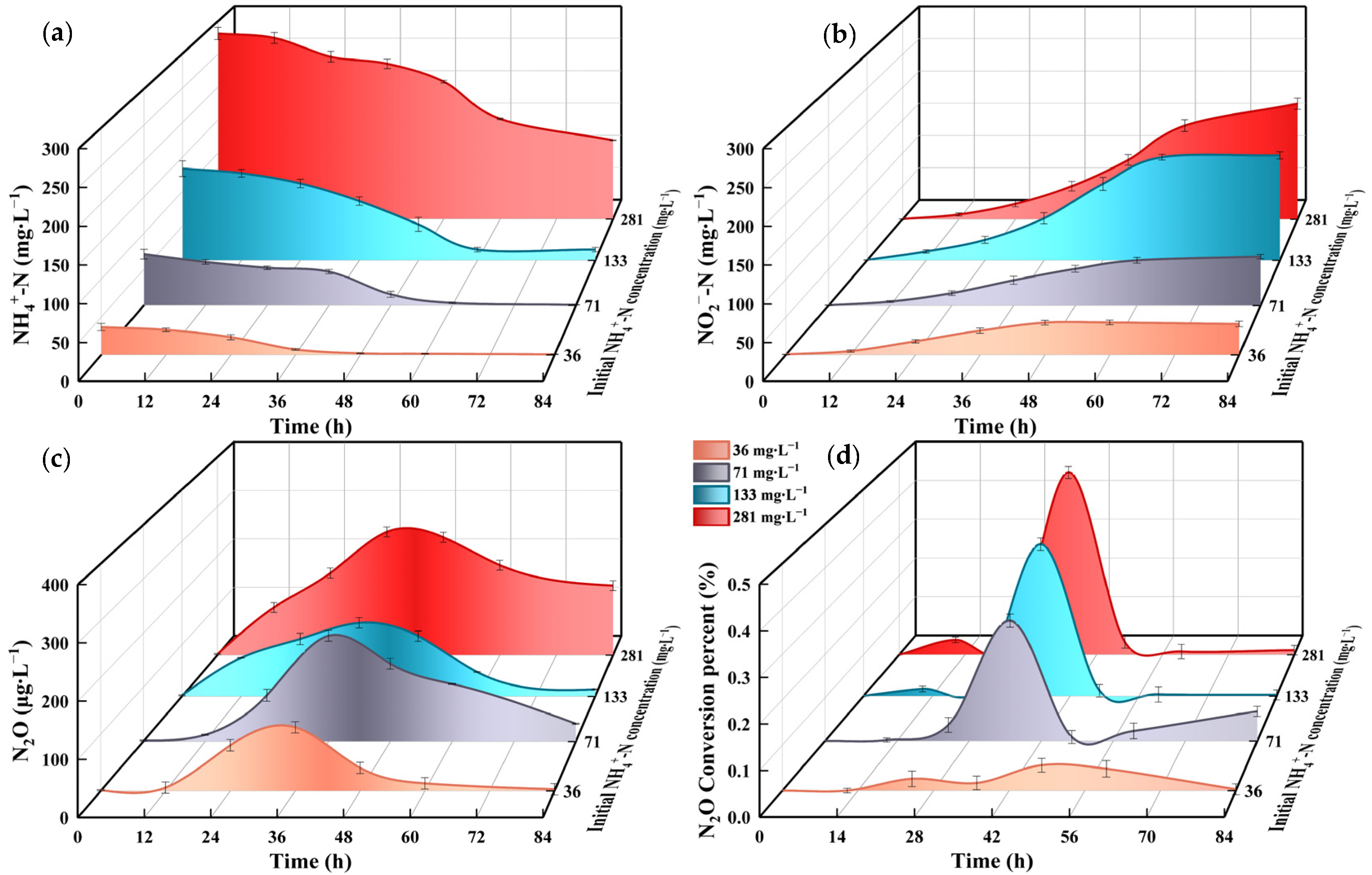
3.5. Effect of NH4+-N Concentration on Strain N.eA1
3.6. Sensitivity Analysis of Environmental Factors to N2O Emission
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CANON | Completely autotrophic nitrogen removal over nitrite |
| AOR | Ammonia oxidation rate |
Appendix A
References
- Cui, Z.; Yue, S.; Wang, G.; Meng, Q.; Wu, L.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Li, S.; Zhang, F.; Chen, X. Closing the yield gap could reduce projected greenhouse gas emissions: A case study of maize production in China. Glob. Change Biol. 2013, 19, 2467–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Chao, Q.; Huang, L. The Core Conclusions and Interpretation of Working Group I Contribution to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Chin. J. Urban Environ. Stud. 2015, 3, 1550003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuang, W.; Gao, X.; Tenuta, M.; Gui, D.; Zeng, F.J.B.; Soils, F.O. Relationship between soil profile accumulation and surface emission of N2O: Effects of soil moisture and fertilizer nitrogen. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2019, 55, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, E.A. The contribution of manure and fertilizer nitrogen to atmospheric nitrous oxide since 1860. Nat. Geosci. 2009, 2, 659–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Ling, N.; Chen, H.; Zhu, C.; Kong, Y.; Wang, M.; Shen, Q.; Guo, S. Distinct drivers of activity, abundance, diversity and composition of ammonia-oxidizers: Evidence from a long-term field experiment. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2017, 115, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Feng, S.; Sun, H.; Wu, S.; Zhuang, G.; Deng, Y.; Bai, Z.; Jing, C.; Zhuang, X. Linking N2O emissions from biofertilizer-amended soil of tea plantations to the abundance and structure of N2O-reducing microbial communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 11338–11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, T.; Ushiki, N.; Fujitani, H.; Tsuneda, S. A rapid collection of yet unknown ammonia oxidizers in pure culture from activated sludge. Water Res. 2017, 108, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wu, J.; Liu, B.; Li, Y.-Y.; Yasui, H. Competitive dynamics of anaerobes during long-term biological sulfate reduction process in a UASB reactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 280, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Q.; Chen, M.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Wu, N.; Chen, K.; Chen, X.; Liu, Y.; Feng, Y.; Ren, G.; et al. The protection of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria (AOB) using PDDA/GO composite materials in high salinity wastewater. J. Water Process Eng. 2022, 49, 102998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepanshi, R.; Anshu, B.; Akshay, K.; Vinod, K.; Gunda, M.; Kashyap, K.D. Applications of autotrophic ammonia oxidizers in bio-geochemical cycles. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 471, 144318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Sun, C.; Lin, H.; Liu, W.; Qin, W.; Chen, T.; Yang, T.; Wen, X. Differences in distributions, assembly mechanisms, and putative interactions of AOB and NOB at a large spatial scale. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2023, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; He, H.; Ding, J.; Zhang, Z.; Leng, Y.; Liao, M.; Xiong, W. Effects of Three Antibiotics on Nitrogen-Cycling Bacteria in Sediment of Aquaculture Water. Water 2024, 16, 1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zajac, O.; Sudol, M.Z.; Godzieba, M.; Ciesielski, S. Changes in Nitrification Kinetics and Diversity of Canonical Nitrifiers and Comammox Bacteria in a Moving Bed Sequencing Batch Biofilm Reactor—A Long-Term Study. Water 2024, 16, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, X.; Baeten, J.E.; Volcke, E.I.P. Effect of operating conditions on N2O emissions from one-stage partial nitritation-anammox reactors. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 143, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wrage, N.; Velthof, G.L.; Van Beusichem, M.L.; Oenema, O. Role of nitrifier denitrification in the production of nitrous oxide. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Burger, M.; Doane, T.A.; Horwath, W.R. Ammonia oxidation pathways and nitrifier denitrification are significant sources of N2O and NO under low oxygen availability. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 6328–6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakata, M.; Takahashi, M.; Zumft, W.; Sakamoto, A.; Morikawa, H. Conversion of the Nitrate Nitrogen and Nitrogen Dioxide to Nitrous Oxides in Plants. Acta Biotechnol. 2003, 23, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Tang, S.; Liao, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, X.; Ji, G. Effect of low temperature on contributions of ammonia oxidizing archaea and bacteria to nitrous oxide in constructed wetlands. Chemosphere 2023, 313, 137585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Cong, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Meng, L.; Liu, M.; Ma, F. Nitrous oxide emission in a laboratory anoxic-oxic process at different influent pHs: Generation pathways and the composition and function of bacterial community. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 328, 124844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathnayake, R.M.L.D.; Oshiki, M.; Ishii, S.; Segawa, T.; Satoh, H.; Okabe, S. Effects of dissolved oxygen and pH on nitrous oxide production rates in autotrophic partial nitrification granules. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 197, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Kazarina, A.; Hansen, P.M.; Ward, K.; Hargreaves, C.; Reese, N.; Ran, Q.; Kessler, W.; de Souza, L.F.; Loecke, T.D.; et al. Metabolism diversification of ammonia-oxidizing archaea and bacteria under different precipitation gradients and land legacies. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2025, 206, 105831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Li, F.; Wang, N.; Peng, H.; Chen, A.; Wu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, H. Relative contribution of ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and denitrifying fungi to N2O production during rice straw composting with biochar and biogas residue amendments. Bioresour. Technol. 2023, 390, 129891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; Cai, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Zheng, P.; Jetten, M.S.; Hu, B. A novel denitrifying methanotroph of the NC10 phylum and its microcolony. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Pei, Z.; Jiao, L. Start-Up and Bacterial Enrichment of an Anammox Reactor with Polyurethane Porous Material: Performance and Microbial Community. Water 2024, 16, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ 535-2009; Water Quality. Determination of Ammonia Nitrogen. Nessler’s Reagent Spectrophotometry. Ministry of Ecology and Environment: Beijing, China, 2009.
- GB/T 11889-1989; Water Quality—Determination of Aniline Compounds—Spectrophotometric Method with N-(1-naphthyl) Ethylenediamine. State Bureau of Technical Supervision of China: Beijing, China, 1989.
- Lan, D. Solid-contact Potentiometric Sensor for the Determination of Total Ammonia Nitrogen in Seawater. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 3296–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Jiang, T.; Wang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Wang, B. Low alkalinity, free ammonia, and free nitrous acid cooperatively stabilize partial nitrification under excessive aeration condition. Chemosphere 2024, 352, 141447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pianosi, F.; Beven, K.; Freer, J.; Hall, J.W.; Rougier, J.; Stephenson, D.B.; Wagener, T. Sensitivity analysis of environmental models: A systematic review with practical workflow. Environ. Model. Softw. 2016, 79, 214–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shengkui, D.; Li, Z.; Ling, H.W. Sensitivity Analysis of Coastal City Tourism and Environmental Systems Based on Coupling Model. Sens. Mater. 2020, 32, 1913–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Neu, T.R.; Nielsen, P.H.; Seviour, T.; Stoodley, P.; Wingender, J.; Wuertz, S. The biofilm matrix: Multitasking in a shared space. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 21, 70–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, G.-P.; Yu, H.-Q.; Li, X.-Y. Extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) of microbial aggregates in biological wastewater treatment systems: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. Int. Rev. J. 2010, 28, 882–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flemming, H.-C.; Wingender, J.; Szewzyk, U.; Steinberg, P.; Rice, S.A.; Kjelleberg, S. Biofilms: An emergent form of bacterial life. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 563–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellicer-Nàcher Carles Smets, F.B. Structure, composition, and strength of nitrifying membrane-aerated biofilms. Water Res. 2014, 57, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, E.; Pérez, J.; Kreft, J.-U. Why is metabolic labour divided in nitrification? Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sedlacek, C.J.; Giguere, A.T.; Dobie, M.D.; Mellbye, B.L.; Ferrell, R.V.; Woebken, D.; Sayavedra-Soto, L.A.; Bottomley, P.J.; Daims, H.; Wagner, M. Transcriptomic Response of Nitrosomonas europaea Transitioned from Ammonia- to Oxygen-Limited Steady-State Growth. mSystems 2020, 5, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamori, Y.; Wu, X.-L.; Mizuochi, M. N2O producing capability of Nitrosomonas europaea, Nitrobacter winogradskyi and Alcaligenes faecalis. Water Sci. Technol. 1997, 36, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhongjun, J.; Ralf, C. Bacteria rather than Archaea dominate microbial ammonia oxidation in an agricultural soil. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1658–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arp, D.J.; Chain, P.S.G.; Klotz, M.G. The Impact of Genome Analyses on Our Understanding of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacteria. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2007, 61, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackbune, R.; Vadivelu, V.M.; Yuan, Z.; Keller, J. Determination of growth rate and yield of nitrifying bacteria by measuring carbon dioxide uptake rate. Water Environ. Res. A Res. Publ. Water Environ. Fed. 2007, 79, 2437–2445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, L.Y.; Klotz, M.G. The nitrogen cycle. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, R94–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, W.; Villez, K.; Kipf, M.; Wunderlin, P.; Siegrist, H.; Vogt, L.; Joss, A. N2O emission in full-scale wastewater treatment: Proposing a refined monitoring strategy. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 699, 134157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Ulanov, A.V.; Nobu, M.; Liu, W.-T. Global metabolomic responses of Nitrosomonas europaea 19718 to cold stress and altered ammonia feeding patterns. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 1843–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulle, S.W.H.V.; Vandeweyer, H.J.P.; Meesschaert, B.D.; Vanrolleghem, P.A.; Dejans, P.; Dumoulin, A. Engineering aspects and practical application of autotrophic nitrogen removal from nitrogen rich streams. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 162, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijuan, M.; Zhao, Y. Full-Scale Source, Mechanisms and Factors Affecting Nitrous Oxide Emissions; IWA Publishing: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kampschreur, M.J.; Kleerebezem, R.; de Vet, W.W.; van Loosdrecht, M.C. Reduced iron induced nitric oxide and nitrous oxide emission. Water Res. 2011, 45, 5945–5952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.-D.; Noguera, D.R. Evaluating the effect of dissolved oxygen on ammonia-oxidizing bacterial communities in activated sludge. Water Res. 2004, 38, 3275–3286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, Y.; Ni, B.-J.; Lant, P.; Yuan, Z. N2O production rate of an enriched ammonia-oxidising bacteria culture exponentially correlates to its ammonia oxidation rate. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3409–3419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fux, C.; Siegrist, H. Nitrogen removal from sludge digester liquids by nitrification/denitrification or partial nitritation/anammox: Environmental and economical considerations. Water Sci. Technol. A J. Int. Assoc. Water Pollut. Res. 2004, 50, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampschreur, M.J.; vand der Star, W.R.L.; Wieldiers, H.A.; Mulder, J.W.; Jetten, M.S.M.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Dynamics of nitric oxide and nitrous oxide emission during full-scale reject water treatment. Water Res. 2008, 42, 812–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunming, F.; Yihao, B.; Fan, Y.; Jian, X.; Fuguo, Q. Achieving partial nitrification: A strategy for washing NOB out under high DO condition. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 347, 119186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, J.M.; Su, Q.; Ma, Y.; Valverde-Pérez, B.; Domingo-Félez, C.; Jensen, M.M.; Smets, B.F. The pH dependency of N-converting enzymatic processes, pathways and microbes: Effect on net N2O production. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 1623–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorelsky, S.I.; Ghosh, S.; Solomon, E.I. Mechanism of N2O reduction by the μ4-S tetranuclear CuZ cluster of nitrous oxide reductase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 278–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, W.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Q.; Ma, B. The inhibitory effects of free ammonia on ammonia oxidizing bacteria and nitrite oxidizing bacteria under anaerobic condition. J. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 1247–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehtovirta-Morley, L.E. Ammonia oxidation: Ecology, physiology, biochemistry and why they must all come together. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2018, 365, fny058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Porro, J.; Nopens, I. Quantification and Modelling of Fugitive Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Urban Water Systems; IWA publishing: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Poghosyan, L.; Lehtovirta-Morley, L.E. Investigating microbial and environmental drivers of nitrification in alkaline forest soil. ISME Commun. 2024, 4, ycae093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mastroleo, F.; Arnau, C.; Verbeelen, T.; Mysara, M.; Gòdia, F.; Leys, N.; Van Houdt, R. Metaproteomics, Heterotrophic Growth, and Distribution of Nitrosomonas europaea and Nitrobacter winogradskyi after Long-Term Operation of an Autotrophic Nitrifying Biofilm Reactor. Appl. Microbiol. 2022, 2, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, K.; Stein, L.Y.; Klotz, M.G.; Van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Nitrous oxide production by lithotrophic ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and implications for engineered nitrogen-removal systems. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1832–1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kool, D.M.; Wrage, N.; Zechmeister-Boltenstern, S.; Pfeffer, M.; Brus, D.; Oenema, O.; Van Groenigen, J. Nitrifier denitrification can be a source of N2O from soil: A revised approach to the dual-isotope labelling method. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 759–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peleg, M.; Normand, M.D.; Corradini, M.G. The Arrhenius equation revisited. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2012, 52, 830–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho-Silva, V.H.; Coutinho, N.D.; Aquilanti, V. Temperature dependence of rate processes beyond Arrhenius and Eyring: Activation and Transitivity. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Serial Number | Reagent | Addition Amount (μg∙L−1) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | NaCl | 300 |
| 2 | MgSO4·7H2O | 140 |
| 3 | FeSO4·7H2O | 30 |
| 4 | KH2PO4 | 20 |
| 5 | NH4HCO3 | 282 |
| 6 | NaHCO3 | 1600 |
| 7 | CuSO4·5H2O * | 0.075 |
| 8 | ZnSO47H2O * | 0.03 |
| 9 | CoCl2 6H2O * | 0.375 |
| 10 | MnCl2·2H2O * | 0.3 |
| 11 | H3BO4 * | 0.014 |
| 12 | EDTA * | 0.5 |
| 13 | NaMoO4·2H2O * | 0.22 |
| Serial Number | Factors | Level | Cultivation Conditions | Measuring Time Interval |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Temperature | 25 °C | 120 rpm; in dark | 12 h |
| 2 | 30 °C | |||
| 3 | 35 °C | |||
| 4 | pH | 6.5 | 120 rpm; in dark | 12 h |
| 5 | 8.0 | |||
| 6 | 9.5 | |||
| 7 | DO concentration | 2.5 ± 0.5 mg∙L−1 | 120 rpm; in dark | 6 h |
| 8 | 4.5 ± 0.2 mg∙L−1 | |||
| 9 | 5.8 ± 0.2 mg∙L−1 | |||
| 10 | 6.5 ± 0.2 mg∙L−1 | |||
| 11 | 7.3 ± 0.2 mg∙L−1 | |||
| 12 | NH4+-N concentration | 36.5 ± 0.5 mg∙L−1 | 120 rpm; in dark | 12 h |
| 13 | 71.0 ± 0.5 mg∙L−1 | |||
| 14 | 133.0 ± 0.5 mg∙L−1 | |||
| 15 | 281.0 ± 0.5 mg∙L−1 |
| Serial Number | Environmental Factor | Standardized Regression Coefficient (SRC) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Temperature | 0.62 |
| 2 | pH | 0.30 |
| 3 | DO | 0.85 |
| 4 | NH4+-N | 0.45 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Li, K.; Yan, Z.; Ren, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, H. Isolation and Characterization of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterium N.eA1: Insights into Nitrogen Conversion and N2O Emissions in Varied Environmental Conditions. Water 2025, 17, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071027
Liu Y, Li K, Yan Z, Ren Z, Li X, Yang H. Isolation and Characterization of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterium N.eA1: Insights into Nitrogen Conversion and N2O Emissions in Varied Environmental Conditions. Water. 2025; 17(7):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071027
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yuhang, Kai Li, Zhiyao Yan, Zhijun Ren, Xueying Li, and Haobin Yang. 2025. "Isolation and Characterization of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterium N.eA1: Insights into Nitrogen Conversion and N2O Emissions in Varied Environmental Conditions" Water 17, no. 7: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071027
APA StyleLiu, Y., Li, K., Yan, Z., Ren, Z., Li, X., & Yang, H. (2025). Isolation and Characterization of Ammonia-Oxidizing Bacterium N.eA1: Insights into Nitrogen Conversion and N2O Emissions in Varied Environmental Conditions. Water, 17(7), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17071027






