Abstract
Climate change has increased the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events worldwide. In South Korea, annual precipitation in 2014–2015 was only 50% of the long-term average, resulting in severe drought conditions. This drought extended water residence time in dam reservoirs, enhancing internal nutrient recycling, degrading water quality, and promoting harmful cyanophyta blooms in downstream reservoirs. Using the Standardized Precipitation Index—for drought assessment, and monthly water sampling—for environmental factors and phytoplankton analyses, this study examined the impacts of drought on water quality and phytoplankton communities in a series of interconnected dam reservoirs (Uiam, Cheongpyeong, Sambong-ri, and Paldang Lakes) within the Bukhan River system from 2013 to 2016. The prolonged residence time during drought facilitated nutrient accumulation and recycling within the reservoirs, intensifying eutrophication and water quality deterioration, alongside a pronounced cyanobacterial dominance and harmful algal blooms. These findings suggest that changes in upstream dam discharges directly influence water quality and ecosystem health in downstream reservoirs and that diverse hydrological changes associated with drought pose a significant threat to water source management. These findings may inform the development of integrated water management strategies for maintaining water quality and protecting water sources during droughts and extreme climatic events.
1. Introduction
Extreme weather events, such as drought and heavy rainfall, have become more frequent and intense globally due to climate change. In South Korea, annual precipitation in 2014–2015 was only 50% of the long-term average, with total rainfall below 1000 mm, leading to severe drought conditions [1]. Drought significantly affects the hydrological regimes, water quality, and aquatic ecosystems of dam reservoirs by prolonging water residence time [2,3], which in turn promotes internal eutrophication [4]. Increased water residence time can enhance internal phosphorus recycling, especially in shallow lakes, thereby accelerating eutrophication [5]. Moreover, changes in inflow and outflow due to reduced precipitation not only influence the hydrological regime of downstream reservoirs and river discharge [6] but also alter nutrient concentrations [7]. Additional drought-related impacts on reservoir environments include intensified stratification [4,8], reduced dissolved oxygen levels, and increased internal nutrient cycling, thereby accelerating eutrophication processes [9]. Furthermore, drought-induced sediment resuspension and anoxic conditions can increase internal phosphorus loading, exacerbating eutrophication and cyanobacterial blooms [10,11]. Supporting this, long-term observations in reservoirs have shown that repeated drawdown and refill cycles under drought conditions can elevate phosphorus, dissolved organic carbon, and iron concentrations, reduce water clarity and oxygen levels, and shift ecosystems toward eutrophic states with increased phytoplankton biovolume [12].
The reservoirs in the Bukhan River system are artificial lakes formed by damming rivers, with expanded water surfaces that are highly susceptible to pollutant inputs from surrounding areas. Most of these reservoirs are undergoing eutrophication, which is further exacerbated by population growth and urbanization in adjacent watersheds [13,14]. Due to the monsoonal climate, where 50–60% of the annual precipitation occurs in summer, hydrological conditions (e.g., water residence time) frequently fluctuate between upstream and downstream sections of these reservoirs [15,16]. In the Bukhan River system, upstream dams (e.g., Hwacheon, Chuncheon, and Soyang dams) drain into Uiam Lake, which subsequently connects to downstream reservoirs, such as Cheongpyeong and Paldang Lakes. Consequently, variation in upstream dam discharges directly affects the water residence time and water quality of downstream reservoirs, contributing to nutrient loading and phytoplankton blooms [17,18]. A long-term study of the Andong Reservoir demonstrated that droughts, particularly reduced summer precipitation, increased water residence time, and total phosphorus concentrations, resulted in elevated chlorophyll-a levels and eutrophication risk [19].
In this interconnected dam reservoir ecosystem, environmental changes induced by severe drought not only degrade water quality but also alter freshwater phytoplankton community composition [20,21]. Prolonged droughts, especially when coupled with elevated water temperatures, can trigger extensive cyanobacterial blooms, including harmful species that thrive under warm, nutrient-enriched conditions with extended residence time [22,23,24,25]. A long-term study of the Daecheong Reservoir in South Korea reported that years with reduced monsoon rainfall showed increased dominance of cyanobacteria such as Microcystis and Anabaena, linked to elevated water temperatures and phosphorus levels [26]. These findings highlight the potential for drought-driven phytoplankton regime shifts under climate stress. In addition, cyanobacterial outbreaks in these reservoirs can produce odor-causing compounds, such as 2-methylisoborneol and geosmin, which adversely affect the water supply, particularly in Paldang Lake, South Korea’s largest water source [27,28,29].
Therefore, this study investigated the effects of drought from 2013 to 2016, particularly during the low precipitation period of 2014–2015, on water quality and phytoplankton communities in the interconnected dam reservoirs (Uiam, Cheongpyeong, Sambong-ri, and Paldang Lakes) of the Bukhan River system. The objective was to elucidate how prolonged water residence times and changes in physicochemical parameters influence reservoir ecosystems, thereby informing integrated water quality management and ecosystem conservation strategies during drought conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The creation of Lake Uiam (St. 1) in August 1967 followed the construction of Uiam Dam, a multipurpose facility with a hydroelectric capacity of 45 MW. The dam has a height of 23 m, an embankment length of 273 m, and a total storage capacity of 80 million cubic meters, serving as a reservoir with a basin area of approximately 282.8 km2.
Lake Cheongpyeong (St. 2) was constructed in 1943 for hydroelectric power generation with a capacity of 80 MW. This small artificial reservoir, situated in the lower Bukhan River basin, has a water surface area of 17.6 km2 and a catchment area of 9921 km2. The reservoir exhibits relatively stable water levels throughout the year. The corresponding dam stands 31 m tall, with an embankment length of 470 m and a total storage capacity of 185 million cubic meters.
The Namhan, Bukhan, and Gyeongancheon Rivers converge to form Lake Paldang (St. 4), the man-made lake that supports recreation, river upkeep, hydropower production, and water delivery. The Namhan, Bukhan, and Gyeongancheon Rivers provide 60%, 37%, and 3% of the inflow, respectively, into the about 23,800 km2 lake basin. The lake’s high basin-to-reservoir area ratio of 652 and surface area of 36.5 km2 make it especially susceptible to pollutant intrusions. Furthermore, Lake Paldang provides around 80% of the drinking water for the Seoul Metropolitan Area, making it a vital regional water source for the city.
Since the late 1990s, the Bukhan River system has been subject to progressively stringent water quality regulations, as it serves as a major drinking water source for the Seoul metropolitan area. In Cheongpyeong and Soyang Lakes, all cage aquaculture facilities were removed by 1999 under the Ministry of Environment’s directives. In Uiam Lake, fishery and aquaculture activities were also restricted, with full implementation completed by 2016. Lake Paldang, designated as a water source protection zone in 1989, has undergone a series of comprehensive pollution control procedures. The Ministry of Environment launched a full-scale water quality improvement plan in 1998, which included removing fish farms and implementing a Total Maximum Daily Load system. By 2005, infrastructure such as sewage treatment and livestock wastewater facilities were expanded, and fishing activities were further restricted. Consequently, anthropogenic influences on the reservoir system have been substantially reduced.
The following were the study locations: the front of Uiam Dam (St. 1), the front of Cheongpyeong Dam (St. 2), the Bukhan River confluence area at Sambong-ri (St. 3), and the front of Paldang Dam (St. 4) (Figure 1).
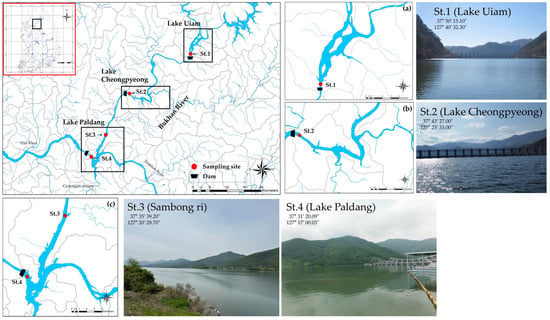
Figure 1.
Locations of study sites in the Bukhan River, South Korea((a): Lake Uiam, (b): Lake Cheongpyeong, (c): Lake Paldang).
2.2. Data Sources for Precipitation and Hydrological Factors
Precipitation data were obtained from the Korea Meteorological Administration (KMA) for stations located within the catchment areas of Lakes Paldang and Sambong-ri (Yangpyeong Meteorological Station), Lake Cheongpyeong (Hongcheon Meteorological Station), and Lake Uiam (Chuncheon Meteorological Station) (http://www.kma.go.kr, accessed on 4 September 2023). Using cumulative or average values, daily hydrological data, including inflow, outflow, and water levels, were retrieved from the Korea Water Resources Management Information System (WAMIS, http://www.wamis.go.kr, accessed on 4 September 2023). All collected baseline data were thoroughly examined for missing values and outliers on a variable-specific basis, and only the validated data were used for subsequent analyses.
2.3. Drought Condition Assessment Using Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI)
In this study, the Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) was used to assess drought conditions in South Korea from 2013 to 2016. SPI is a widely used index that standardizes precipitation variability over a given period to quantify drought occurrence and duration. For this analysis, SPI-6 (6-month accumulation) and SPI-12 (12-month accumulation) were applied to assess seasonal and long-term drought conditions, respectively. SPI-6 captures seasonal fluctuations and medium-term drought patterns, while SPI-12 evaluates long-term precipitation deficits and prolonged drought events.
Drought severity was classified based on the criteria proposed by McKee, et al. [30], where an SPI value of −1.0 or above indicates normal conditions, values between −1.0 and −1.5 indicate moderate drought, values between −1.5 and −2.0 indicate severe drought, and values below −2.0 denote extreme drought. The SPI analysis identified a persistent drought period from late 2014 to 2015. According to SPI-6, drought conditions intensified between May and July 2014, with SPI values decreasing from −1.05 to −2.40, marking the onset of severe drought. Furthermore, from July to October 2015, SPI-6 ranged between −1.78 and −2.78, indicating sustained severe to extreme drought conditions. The SPI-12 analysis also indicated a prolonged drought, with values reaching −1.91 in July 2014, followed by persistent values below −2.0 throughout 2015, classifying this period as an extreme long-term drought (Table S1).
Based on these analyses, the period from 2014 to 2015 was characterized by sustained drought conditions in South Korea, with 2015 exhibiting extreme drought severity according to SPI-12. This study utilized SPI-based classification to determine that 2014–2015 was a period of significant meteorological drought.
2.4. Sample Collection and Water Quality Analysis
At the study sites, water samples were taken every month from January 2013 to December 2016 for phytoplankton and environmental factor analysis. To prevent light-induced reactions in the water samples, brown glass bottles were used during the boat sampling. After collection, the samples were promptly chilled and taken to the lab for examination.
Using a digital multi-parameter sensor (YSI-EXO, YSI Inc., Yellow Springs, OH, USA), the following parameters were monitored in situ: water temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen (DO), and electrical conductivity (EC). The biological oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), total nitrogen (TN), nitrate (NO3-N), ammonia (NH3-N), chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) concentration, total phosphorus (TP), phosphate (PO4-P), suspended solids (SS), and total organic carbon (TOC) were all analyzed in the laboratory following standard procedures described in the Korea Water Quality Standard [31].
2.5. Korean Trophic State Index
The Korean Trophic State Index (TSIKO), developed by the Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Environment, was used to assess the trophic state of the Bukhan River system. The eutrophication evaluation index known as TSIKO takes into account the water quality characteristics of South Korea’s largest lakes and reservoirs. It makes use of metrics like TP and Chl-a as indicators of autochthonous organic matter and TOC as an indicator of allochthonous organic matter [32]. The formulas generated from water quality measurements in domestic lakes and reservoirs are represented by Equations (1) through (3).
Equation (4) was used to construct TSIKO, with a 50% weighting factor for TOC and a 25% weighting factor for Chl-a and TP. Oligotrophic (≤30), mesotrophic (31–50), eutrophic (51–70), and hypertrophic (>71) were the four trophic states into which the computed TSIKO values were divided.
TSIKO = 0.5 TSIKO(TOC) + 0.25 TSIKO(TP) + 0.25 TSIKO(Chl-a)
2.6. Phytoplankton Analysis
To preserve the water samples for the analysis of dominant species and phytoplankton community composition, Lugol’s solution was added to achieve a final concentration of 2%. A 1 mL aliquot was subsequently placed in a Sedgwick-Rafter counting chamber and observed under a phase-contrast microscope (Eclipse 80i; Nikon, Tokyo, Japan) at magnifications of ×100 to ×400. For species identification requiring higher resolution, microscopic examination was conducted at ×1000 magnification using a slide glass. Species identification and cell density estimation were conducted with reference to John, et al. [33], Hirose, et al. [34], Krammer [35], Krammer and Lange-Bertalot [36,37,38].
2.7. Statistical Analysis
A one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used to analyze annual variations in physicochemical factors in the Bukhan River system, and post hoc Duncan’s test was applied to identify significant differences across years. Spearman’s correlation analysis was performed to examine the relationships between environmental variables and phytoplankton. Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS 20 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA), with significance level set at p < 0.05. Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) was conducted using PC-ORD5 (Lincoln City, OR, USA) to examine the relationship between phytoplankton communities and environmental factors. Prior to analysis, taxa present in less than 0.4% of total samples were excluded, and all environmental data were normalized using log(1 + x) transformation [39,40].
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Precipitation and Hydrological Characteristics
At the study sites, the average annual precipitation was 1575 mm in 2013, 723 mm in 2014, 766 mm in 2015, and 1079 mm in 2016, with the 2014–2015 period receiving only 45.9% of the 2013 precipitation. Notably, summer precipitation in 2016 reached only 40.5% of the 2013 level, a critical reduction in a monsoonal climate where summer rainfall typically accounts for 50–60% of the annual total, thereby leading to severe drought conditions. In Uiam Lake, located in the mid-upper reaches of the Bukhan River system, the average annual precipitation in 2014–2015 (716 mm) was only 41.2% of that recorded in 2013 (1739 mm), with summer precipitation at merely 29.3%, indicating extreme drought conditions (Figure 2). The reduced water levels observed in the summer of 2014 were attributed to preemptive water releases in anticipation of the monsoon, and the subsequent prolonged drought prevented the recovery of water levels, reducing both inflow and outflow to approximately 30% of normal values. In contrast, Paldang Lake, which serves as a primary water source, maintained a constant full water level with minimal fluctuations due to continuous discharges from the upstream dams of the Bukhan and Namhan Rivers (Figure 2).
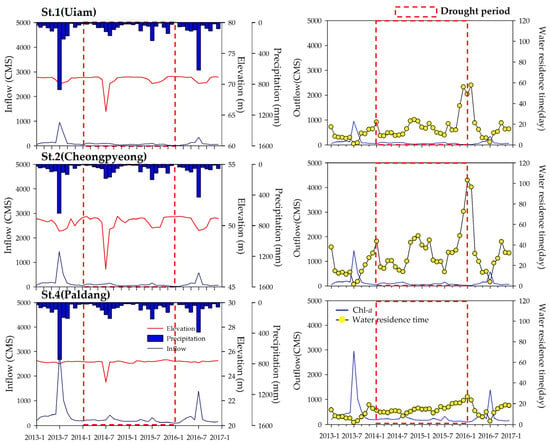
Figure 2.
Annual hydrological factors in Bukhan River.
Water residence times in Uiam Lake, Cheongpyeong Lake, and Paldang Lake were approximately 2.0, 1.9, and 1.7 times higher than normal values, respectively, with differences being statistically significant (p < 0.05) (Figure 2 and Figure 3). During the summer, residence times increased by more than threefold, underscoring the pronounced impact of the drought. Furthermore, as the drought continued, water residence times increased sharply during the winter (October 2015–February 2016). Although prolonged drought in dam reservoirs generally exacerbates downstream drought conditions [6,41], in the Bukhan River system, the downstream Paldang Lake, serving as a key water supply for the metropolitan area, maintained a normal high water level, suggesting that the effects of drought were more pronounced in the upstream dam reservoirs.
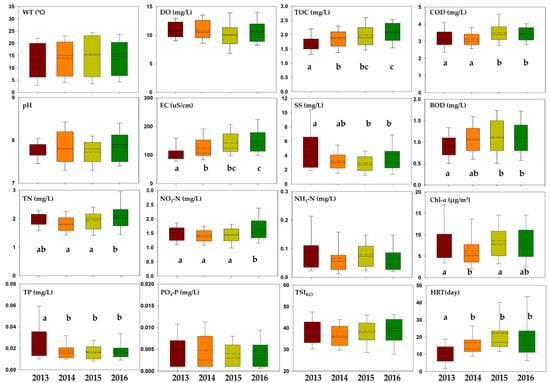
Figure 3.
Changes in environmental variables over time in Bukhan River. There were significant differences among years, as determined using ANOVA. Different small letters (a, b, and c) indicate significant differences determined using Duncan’s test (dashed line: average, straight line: median).
3.2. Water Quality Characteristics
Environmental parameters at the sites are presented in Figure 4 as monthly averages. In 2014, when drought conditions were severe, nutrient concentrations (e.g., TN and TP) and Chl-a decreased temporarily, resulting in improved water quality. However, as the drought persisted beyond 2015, indicators such as TOC, COD, BOD, and TN exhibited a deteriorating trend. TN, for example, showed significant reductions during the extreme drought period of 2014–2015 (p < 0.05) but increased again as precipitation recovered in 2016. This pattern suggests that TP is more influenced by pollutant inputs from rainfall than by water levels [42,43,44] (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Its rapid post-drought increase may be attributed to both pollutant runoff from surrounding areas and nutrient leaching resulting from drying–reflooding cycles [45,46].
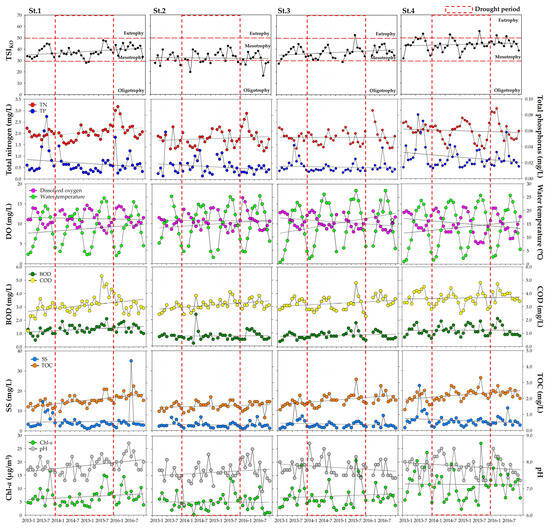
Figure 4.
Annual physicochemical factors in Bukhan River.
TOC and COD also displayed statistically significant differences during the drought period (p < 0.05) (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Specifically, episodic rainfall following drought can lead to a sudden increase in TOC due to the flush of accumulated organic matter from surrounding soils [47], while reduced water levels during drought can result in higher concentrations of organic matter, thereby elevating TOC [48]. The TSIKO (Korean Trophic State Index) also tended to deteriorate significantly between years (p < 0.05) (Figure 3 and Figure 4). Notably, at downstream sites St. 3 (Sambong-ri) and St. 4 (Paldang Lake), TOC, Chl-a, and TP levels were high, whereas TN concentrations were low. This is attributed to the increased water residence time in downstream reservoirs during prolonged drought, which enhances internal nutrient recycling [49,50]. The increased residence time also promotes stratification, leading to enhanced algal growth and denitrification, which significantly reduces TN concentrations during drought (p < 0.05). Furthermore, decreased DO in the hypolimnion due to stratification can increase nutrient release from sediments, elevating TP concentrations and further exacerbating eutrophication [51]. These changes likely contribute to the development of algal blooms in downstream dam reservoirs.
3.3. Annual Variation in Phytoplankton Abundance and Characteristics
During the investigation period, phytoplankton cell densities at the sampling sites were as follows: St. 1, 480–5523 cells/mL (average 3502 cells/mL); St. 2, 450–7362 cells/mL (2389 cells/mL); St. 3, 520–7521 cells/mL (3086 cells/mL); and St. 4, 690–21,541 cells/mL (5260 cells/mL). The density was highest at the downstream site St. 4. The mean phytoplankton cell density for the entire Bukhan River system peaked in 2016 (3775 cells/mL), with values of 3418, 3527, and 3657 cells/mL in 2013, 2014, and 2015, respectively, with no significant differences among the years (Figure 5).
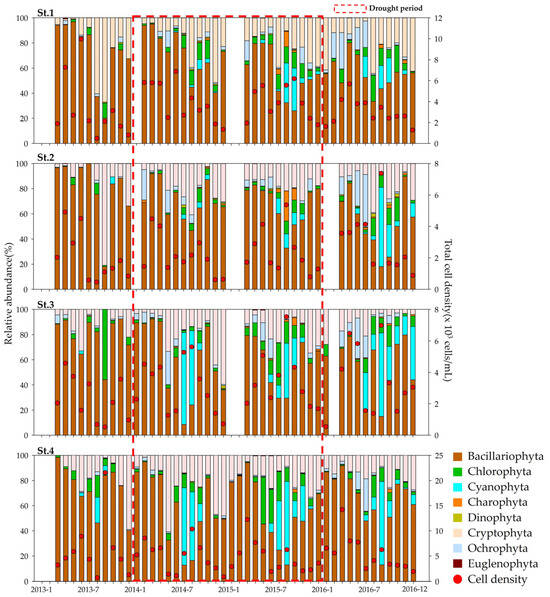
Figure 5.
Annual variation in phytoplankton relative abundance and cell density in Bukhan River.
Regarding the overall relative abundance of phytoplankton groups, the Bukhan River system was dominated by Bacillariophyta, accounting for 64.7% of the total population at all sites, followed by Cryptophyta (17.8%), Cyanophyta (6.7%), Chlorophyta (5.9%), Ochrophyta (3.9%), Charophyta (0.7%), Dinophyta (0.3%), and Euglenophyta (0.02%) (Figure 5).
Comparisons between the reference years (2013 and 2016) and drought years (2014–2015) revealed that while the relative abundances of phytoplankton groups at the upstream sites (St. 1 and St. 2) remained relatively stable, the confluence sites (St. 3 and St. 4) exhibited an increase of over 5% in the relative abundance of Cryptophyta. Rhodomonas, a representative taxon within Cryptophyta, is known for its high adaptability to low water temperatures [52,53] and its insensitivity to low nutrient concentrations and light levels, likely explaining its dominance in environments with prolonged water residence times [54] (Table 1). Moreover, during the summer months (June–August), while little change was observed at upstream sites (St. 1 and St. 2), the relative dominance of Cyanophyta at the downstream sites St. 3 and St. 4 increased sharply to 14.0% and 21.2%, respectively (Figure 6). This suggests that discharge from upstream dams during drought conditions, which increases nutrient concentrations in downstream reservoirs, plays a key role in promoting cyanobacterial blooms, potentially intensifying summer cyanobacterial outbreaks [24,55].

Table 1.
List of major phytoplankton species in Bukhan River.
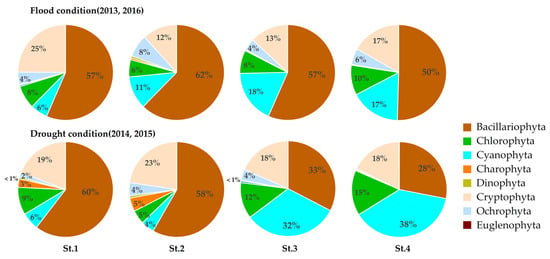
Figure 6.
Annual changes in phytoplankton communities and relative abundances in the Bukhan River during summer (June–August) under flood conditions (2013, 2016) and drought conditions (2014, 2015).
3.4. CCA of the Phytoplankton Community and Environmental Factors
CCA was performed at both the group and species levels to evaluate the relationships between environmental factors and phytoplankton communities in the Bukhan River system. Axis 1 and Axis 2 explained 12.7% and 3.9% of the variation in the relationships between phytoplankton and environmental factors, respectively (Figure 7).
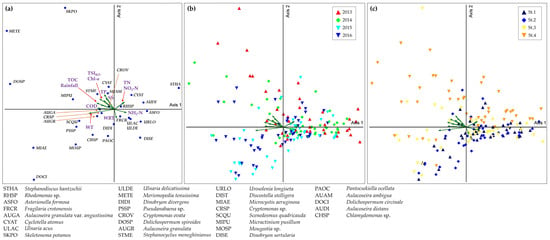
Figure 7.
Annual variation in canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) results for relationships between environmental parameters and phytoplankton in Bukhan River (a). Ordination diagrams showing differences with respect to year (b) and study site (c).
CCA results revealed that Bacillariophyta, including Ulnaria spp., Asterionella formosa, and Fragilaria crotonensis, were negatively correlated with water temperature, TP, and TOC while showing positive correlations with water residence time (Figure 7). A. formosa and Ulnaria spp., which are typically abundant in temperate lakes during the spring [56,57], demonstrate a relatively high tolerance to low water temperatures, an adaptation that favors their growth during cooler periods [58,59,60]. Fragilaria crotonensis is frequently observed under low-nutrient and silicate-deficient conditions, suggesting its competitive advantage in oligotrophic environments [61,62] (Table 1).
Cryptomonas spp. and Rhodomonas sp. were positively correlated with Chl-a and nutrient concentrations. Correlation analyses showed significant positive relationships between these taxa and TN (r = 0.334, p < 0.01), TP (r = 0.293, p < 0.01), and Chl-a (r = 0.347, p < 0.01), indicating their contribution to increased Chl-a concentrations in upstream reservoirs during spring, autumn, and drought periods (Table 2). Although Rhodomonas and Cryptomonas are abundant in the spring under low water temperatures [63,64], their ability to thrive under low temperatures, limited light, and low nutrient availability [54,65,66,67] suggest that they have high adaptability and can maintain year-round dominance despite environmental fluctuations due to upstream dam releases and summer monsoon events.

Table 2.
Correlation coefficients for relationships between various taxa and environmental factors in Bukhan River.
Cyanophyta (Dolichospermum, Microcystis, Pseudanabaena, and Merismopedia) abundances were positively correlated with water temperature, TOC, TP, precipitation, and TSIKO, indicating that nutrient inputs from precipitation promote cyanobacterial dominance. A correlation analysis further revealed strong positive associations between Cyanophyta and TOC, COD, and TSIKO, as well as a positive relationship with precipitation. In addition, precipitation showed a significant positive correlation with TP (r = 0.308, p < 0.01), suggesting that reduced rainfall during drought conditions enhances nutrient inputs and stimulates cyanobacterial blooms in downstream reservoirs (Table 2).
These findings imply that limited precipitation during summer droughts increases nutrient inputs in downstream dam reservoirs, favoring the proliferation of cyanobacteria. Buoyancy regulation enables cyanobacteria to thrive under favorable surface conditions, such as higher temperatures, light availability, and enhanced nutrient uptake, providing a competitive advantage over other algal groups [68,69,70,71]. Furthermore, the buoyancy control in cyanobacteria facilitates their vertical migration in the water column, allowing them to remain near the surface where optimal conditions for growth and photosynthesis are maintained while avoiding excessive light exposure, which further enhances nutrient uptake [72,73,74].
In particular, Dolichospermum circinale and Microcystis aeruginosa, which are managed as harmful algae in Korea, showed positive correlations with the water residence time. This suggests that prolonged drought conditions promote the proliferation of toxic cyanobacteria in downstream reservoirs, such as Paldang Lake (Table 1, Figure 7). These results are consistent with previous findings showing that extended drought enhances the growth of toxic cyanobacterial species [24,75]. Moreover, the increased abundance of Pseudanabaena sp. during extended drought may trigger episodes of musty odor events, adversely affecting water supply management in downstream regions [27,28,29].
4. Conclusions
Despite being the largest watershed and water source in Korea, studies on aquatic ecosystem changes related to climate change in the Han River basin are scarce, despite its importance. This study comprehensively analyzed the impacts of severe drought conditions in the Bukhan River system on hydrological characteristics, water quality, and phytoplankton communities. During the drought, a marked reduction in precipitation led to declines in water levels as well as inflow and outflow, resulting in prolonged water residence times in upstream dam reservoirs and enhanced internal nutrient recycling. Initially, water quality improved slightly due to temporary decreases in nutrient concentrations and Chl-a levels; however, as the drought continued, water quality deteriorated, as evidenced by increased levels of TOC, COD, BOD, and TN. These changes could be attributed to the large-scale flush of organic matter accumulated in soils following rainfall after a drought and concentration in the water body during drought periods.
There were significant differences in the distribution and dominant phytoplankton species between upstream and downstream sites, with downstream areas exhibiting a pronounced dominance of cyanobacteria. Moreover, an increase in harmful cyanobacterial species was observed, suggesting that changes in upstream dam discharges and prolonged water residence times in downstream reservoirs contribute significantly to nutrient enrichment and subsequent harmful algal blooms.
In conclusion, this study demonstrates that severe drought conditions extend beyond a mere meteorological phenomenon to cause water quality degradation and ecosystem alterations, with substantial implications for the management of major water sources. Consequently, the development of integrated strategies that consider the multifaceted environmental changes and their interactions during drought conditions is essential for effective water resource management and conservation.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/w17071023/s1, Table S1: Annual Standardized Precipitation Index (SPI) in Bukhan River (≥−1.0: Normal conditions, −1.5 ≤ SPI < −1.0: Moderate drought, −2.0 ≤ SPI < −1.5: Severe drought, SPI < −2.0: Extreme drought).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.B.S., J.K.I. and S.-J.H.; methodology, Y.B.S. and J.K.I.; software, Y.B.S. and J.K.I.; validation, Y.B.S. and J.K.I.; formal analysis, Y.B.S. and J.K.I.; investigation, Y.B.S., J.K.I., J.H.B., C.H.P. and S.-J.H.; resources, J.K.I., Y.B.S. and S.-J.H.; data curation, Y.B.S. and J.K.I.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.B.S. and J.K.I.; writing—review and editing, Y.B.S., J.K.I., J.H.B., C.H.P. and S.-J.H.; visualization, Y.B.S., J.K.I. and J.H.B.; supervision, J.K.I. and S.-J.H.; project administration, J.K.I. and S.-J.H.; funding acquisition, J.K.I. and S.-J.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Korea Environment Industry & Technology Institute (KEITI) through the “Development of the polluted sediment dredging technology containing Akinete equipped with a state-of-the-art ultra-short baseline acoustic positioning ROV robot Program” (2480000243) and the National Institute of Environmental Research (NIER) [grant number NIER-2024-01-01-053] funded by the Korea Ministry of Environment (MOE).
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding authors.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| BOD | Biological oxygen demand |
| CCA | Canonical correspondence analysis |
| Chl-a | Chlorophyll-a |
| COD | Chemical oxygen demand |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| EC | Electrical conductivity |
| DO | Dissolved oxygen |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| NO3-N | Nitrate |
| NH3-N | Ammonia |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| PO4-P | Phosphate |
| TSIKO | Korean Trophic State Index |
| SS | Suspended solids |
| WRT | Water residence time |
References
- Mun, Y.-S.; Nam, W.-H.; Jeon, M.-G.; Kim, T.; Hong, E.-M.; Hayes, M.J.; Tsegaye, T. Application of meteorological drought index using Climate Hazards Group InfraRed Precipitation with Station (CHIRPS) based on global satellite-assisted precipitation products in Korea. J. Korean Soc. Agric. Eng. 2019, 61, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mosley, L.M. Drought impacts on the water quality of freshwater systems; review and integration. Earth Sci. Rev. 2015, 140, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, P.S. Drought and Aquatic Ecosystems: Effects and Responses; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Srifa, A.; Phlips, E.J.; Cichra, M.F.; Hendrickson, J.C. Phytoplankton dynamics in a subtropical lake dominated by cyanobacteria: Cyanobacteria ‘Like it Hot’ and sometimes dry. Aquat. Ecol. 2016, 50, 163–174. [Google Scholar]
- Jeppesen, E.; Søndergaard, M.; Jensen, J.P.; Havens, K.E.; Anneville, O.; Carvalho, L.; Coveney, M.F.; Deneke, R.; Dokulil, M.T.; Foy, B. Lake responses to reduced nutrient loading–an analysis of contemporary long-term data from 35 case studies. Freshw. Biol. 2005, 50, 1747–1771. [Google Scholar]
- Marcinkowski, P.; Grygoruk, M. Long-term downstream effects of a dam on a lowland river flow regime: Case study of the Upper Narew. Water 2017, 9, 783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingole, N.P.; An, K.-G. Modifications of nutrient regime, chlorophyll-a, and trophic state relations in Daechung Reservoir after the construction of an upper dam. J. Ecol. Environ. 2016, 40, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Olsson, F.; Mackay, E.B.; Moore, T.; Barker, P.; Davies, S.; Hall, R.; Spears, B.; Wilkinson, J.; Jones, I.D. Annual water residence time effects on thermal structure: A potential lake restoration measure? J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 314, 115082. [Google Scholar]
- Rocha, M.A.M.; Barros, M.U.; Costa, A.C.; de Assis de Souza Filho, F.; Lima Neto, I.E. Understanding the water quality dynamics in a large tropical reservoir under hydrological drought conditions. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 76. [Google Scholar]
- Bloesch, J. Mechanisms, measurement and importance of sediment resuspension in lakes. Mar. Freshw. Res. 1995, 46, 295–304. [Google Scholar]
- Orihel, D.M.; Baulch, H.M.; Casson, N.J.; North, R.L.; Parsons, C.T.; Seckar, D.C.; Venkiteswaran, J.J. Internal phosphorus loading in Canadian fresh waters: A critical review and data analysis. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2017, 74, 2005–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luong, H.A.; Rohlfs, A.-M.; Facey, J.A.; Colville, A.; Mitrovic, S.M. Long-term study of phytoplankton dynamics in a supply reservoir reveals signs of trophic state shift linked to changes in hydrodynamics associated with flow management and extreme events. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.C.; Park, J.H.; Hwana, G.S.; Choi, K.S. Eutrophication of large freshwater ecosystems in Korea. Korean J. Limnol. 1997, 30, 512–517. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, J.-K.; Kang, C.-K.; Kim, H.-S.; Hwang, S.-J. Limnological characteristics of the river-type Paltang Reservoir, Korea: Hydrological and environmental factors. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2003, 36, 242–256. [Google Scholar]
- An, K.-G.; Jones, J.R. Factors regulating bluegreen dominance in a reservoir directly influenced by the Asian monsoon. Hydrobiologia 2000, 432, 37–48. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, S.; Shin, M.; Kim, J.; Eum, J.; Lee, Y.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; You, K.; Owen, J.; Kim, B. The effects of Asian summer monsoons on algal blooms in reservoirs. Inland Waters 2016, 6, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Kim, Y.; Kim, B. Simulation of eutrophication in a reservoir by CE-QUAL-W2 for the evaluation of the importance of point sources and summer monsoon. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2019, 35, 64–76. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, H.-W.; Choi, J.-W.; An, K.-G. Spatio-temporal water quality variations at various streams of Han-River watershed and empirical models of serial impoundment reservoirs. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2012, 45, 378–391. [Google Scholar]
- Mamun, M.; Atique, U.; Kim, J.Y.; An, K.-G. Seasonal water quality and algal responses to monsoon-mediated nutrient enrichment, flow regime, drought, and flood in a drinking water reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 10714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaver, J.R.; Casamatta, D.A.; East, T.L.; Havens, K.E.; Rodusky, A.J.; James, R.T.; Tausz, C.E.; Buccier, K.M. Extreme weather events influence the phytoplankton community structure in a large lowland subtropical lake (Lake Okeechobee, Florida, USA). Hydrobiologia 2013, 709, 213–226. [Google Scholar]
- Williamson, C.E.; Saros, J.E.; Vincent, W.F.; Smol, J.P. Lakes and reservoirs as sentinels, integrators, and regulators of climate change. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2009, 54, 2273–2282. [Google Scholar]
- Jang, M.T.G.; Alcântara, E.; Rodrigues, T.; Park, E.; Ogashawara, I.; Marengo, J.A. Increased chlorophyll-a concentration in Barra Bonita reservoir during extreme drought periods. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 843, 157106. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, A.S.; Milewski, A.M. Spatiotemporal relationships of phytoplankton blooms, drought, and rainstorms in freshwater reservoirs. Water 2020, 12, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabowska, M.; Mazur-Marzec, H.; Więcko, A. How Extreme Droughts Change the Impact of Eutrophic Reservoir on Its Outflow, with Special References to Planktonic Cyanobacteria and Their Secondary Metabolites? Water 2025, 17, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindler, D.W. Recent advances in the understanding and management of eutrophication. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2006, 51, 356–363. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.Y.; Atique, U.; Mamun, M.; An, K.-G. Long-term interannual and seasonal links between the nutrient regime, sestonic chlorophyll and dominant bluegreen algae under the varying intensity of monsoon precipitation in a drinking water reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, S.J.; Im, J.K.; Byeon, M.-S.; Yu, S.J. Characteristics of cyanobacteria and odorous compounds production in lake uiam and lower gonji stream. J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2019, 35, 99–104. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, J.-H.; Yu, M.; Lee, E.; Yoo, S.-J.; Kim, B.-H.; Byun, M.-S. Temporal and spatial distribution of microbial community and odor compounds in the Bukhan river system. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2018, 51, 299–310. [Google Scholar]
- Byun, J.-H.; Hwang, S.J.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.R.; Lee, J.K.; Lim, B.J. Relationship between a Dense Population of Cyanobacteria and Odorous Compounds in the North Han River System in 2014 and 2015. Korean J. Ecol. Environ. 2015, 48, 263–271. [Google Scholar]
- McKee, T.B.; Doesken, N.J.; Kleist, J. The relationship of drought frequency and duration to time scales. In Proceedings of the 8th Conference on Applied Climatology, Anaheim, CA, USA, 17–22 January 1993; pp. 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- MOE. Standard Methods for the Examination Water Quality; The Korean Ministry of Environment: Sejong, Republic of Korea, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, B.; Kong, D. Examination of the Applicability of TOC to Korean Trophic State Index (TSI KO). J. Korean Soc. Water Environ. 2019, 35, 271–277. [Google Scholar]
- John, D.M.; Whitton, B.A.; Brook, A.J. The Freshwater Algal Flora of the British Isles: An Identification Guide to Freshwater and Terrestrial Algae; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hirose, H.; Yamagishi, T.; Akiyama, M. Illustrations of the Japanese Freshwater Algae; Uchidarokakuho Publ. Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Bacillariophyceae. Naviculaceae. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1986; Volume 1, p. 876. Available online: http://link.springer.com/book/9783827426154 (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd 2/2. Bacillariophyceae. 2. Teil: Bacillariaceae, Epithemiaceae, Surirellaceae; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 02/3: Bacillariophyceae: Teil 3: Centrales, Fragilariaceae, Eunotiaceae; Gustav Fischer Verlag: Stuttgart, Germany, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Krammer, K.; Lange-Bertalot, H. Süßwasserflora von Mitteleuropa, Bd. 02/4: Bacillariophyceae: Teil 4: Achnanthaceae, Kritische Ergänzungen zu Achnanthes sl, Navicula s. Str., Gomphonema, Gesamtliteraturverzeichnis Teil 1–4, Ergänzter Nachdruck, 2004; Spektrum Akademischer Verlag: Heidelberg, Germany, 1999; Available online: http://link.springer.com/book/9783827408389 (accessed on 4 September 2023).
- Morabito, G.; Oggioni, A.; Caravati, E.; Panzani, P. Seasonal morphological plasticity of phytoplankton in Lago Maggiore (N. Italy). Hydrobiologia 2007, 578, 47–57. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, R.; Han, B.; Naselli-Flores, L. Comparing biological classifications of freshwater phytoplankton: A case study from South China. Hydrobiologia 2013, 701, 219–233. [Google Scholar]
- Schilstra, M.; Wang, W.; van Oel, P.R.; Wang, J.; Cheng, H. The effects of reservoir storage and water use on the upstream–downstream drought propagation. J. Hydrol. 2024, 631, 130668. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.-I.; Pan, S.-Y.; Chang, H.-H.; Yu, M.-S.; Lin, W.-L. Will extreme drought impact the reservoir water quality? A 30-year observational study. Agric. Water Manag. 2023, 289, 108574. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, Y.-E.; Kim, H.-S. Inter-Annual and seasonal variations of water quality and trophic status of a reservoir with fluctuating monsoon precipitation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 8499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HaRa, J.; Atique, U.; An, K.-G. Multiyear links between water chemistry, algal chlorophyll, drought-flood regime, and nutrient enrichment in a morphologically complex reservoir. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez, F.; Monicelli, F.; Cavalcante, H.; Becker, V. Effects of prolonged drought on water quality after drying of a semiarid tropical reservoir, Brazil. Limnologica 2022, 93, 125959. [Google Scholar]
- Dieter, D.; Herzog, C.; Hupfer, M. Effects of drying on phosphorus uptake in re-flooded lake sediments. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17065–17081. [Google Scholar]
- Worrall, F.; Burt, T. Trends in DOC concentration in Great Britain. J. Hydrol. 2007, 346, 81–92. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.-H.; Kam, J. Spatiotemporal patterns of water volume and total organic carbon concentration of agricultural reservoirs over South Korea. Water Res. 2024, 256, 121610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winton, R.S.; Calamita, E.; Wehrli, B. Reviews and syntheses: Dams, water quality and tropical reservoir stratification. Biogeosciences 2019, 16, 1657–1671. [Google Scholar]
- Maavara, T.; Chen, Q.; Van Meter, K.; Brown, L.E.; Zhang, J.; Ni, J.; Zarfl, C. River dam impacts on biogeochemical cycling. Nat. Rev. Earth Environ. 2020, 1, 103–116. [Google Scholar]
- Nakulopa, F.; Bärlund, I.; Borchardt, D. How a reservoir modulates downstream water quality under declining upstream loading and progressing climate change. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 912, 169460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilabert, J. Seasonal plankton dynamics in a Mediterranean hypersaline coastal lagoon: The Mar Menor. J. Plankton Res. 2001, 23, 207–218. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-K. The use of winter water temperature and food composition by the copepod Cyclops vicinus (Uljanin, 1875) to provide a temporal refuge from fish predation. Biology 2021, 10, 393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lafarga-De la Cruz, F.; Valenzuela-Espinoza, E.; Millán-Núnez, R.; Trees, C.C.; Santamaría-del-Ángel, E.; Núnez-Cebrero, F. Nutrient uptake, chlorophyll a and carbon fixation by Rhodomonas sp.(Cryptophyceae) cultured at different irradiance and nutrient concentrations. Aquacult. Eng. 2006, 35, 51–60. [Google Scholar]
- Nowicka-Krawczyk, P.; Żelazna-Wieczorek, J.; Skrobek, I.; Ziułkiewicz, M.; Adamski, M.; Kaminski, A.; Żmudzki, P. Persistent cyanobacteria blooms in artificial water bodies—An effect of environmental conditions or the result of anthropogenic change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 6990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krivtsov, V.; Bellinger, E.; Sigee, D. Changes in the elemental composition of Asterionella formosa during the diatom spring bloom. J. Plankton Res. 2000, 22, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, C.S.; Huszar, V.; Kruk, C.; Naselli-Flores, L.; Melo, S. Towards a functional classification of the freshwater phytoplankton. J. Plankton Res. 2002, 24, 417–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gsell, A.S.; de Senerpont Domis, L.N.; Przytulska-Bartosiewicz, A.; Mooij, W.M.; van Donk, E.; Ibelings, B.W. Genotype-by-temperature interactions may help to maintain clonal diversity in Asterionella formosa (Bacillariophyceae). J. Phycol. 2012, 48, 1197–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, V.M. Species composition and dynamics of the phytoplankton in a recently-commissioned reservoir (Azibo-Portugal). Arch. Hydrobiol. 1991, 121, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bondarenko, N.; Guselnikova, N.Y. Studies on Synedra acus Kutz. var. radians (Kutz.) Hust.(Bacillariophyta) in culture. Int. J. Algae 2002, 4, 85–95. [Google Scholar]
- Michel, T.J.; Saros, J.E.; Interlandi, S.J.; Wolfe, A.P. Resource requirements of four freshwater diatom taxa determined by in situ growth bioassays using natural populations from alpine lakes. Hydrobiologia 2006, 568, 235–243. [Google Scholar]
- Bailey-Watts, A. The ecology of planktonic diatoms, especially Fragilaria crotonensis, associated with artificial mixing of a small Scottish loch in summer. Diatom Res. 1986, 1, 153–168. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, A.J.; Wetzel, R.G. Cryptophytes and other microflagellates as couplers in planktonic community dynamics. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1986, 106, 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, U.; Gliwicz, Z.M.; Lampert, W.; Duncan, A. The PEG-model of seasonal succession of planktonic events in fresh waters. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1986, 106, 433–471. [Google Scholar]
- Hammer, A.; Schumann, R.; Schubert, H. Light and temperature acclimation of Rhodomonas salina (Cryptophyceae): Photosynthetic performance. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 29, 287–296. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, J.-G.; Kim, E.-J. Trophic states and phytoplankton compositions of Dam Lakes in Korea. Algae 2002, 17, 275–281. [Google Scholar]
- Im, J.-K.; Sim, Y.-B.; Hwang, S.-J.; Byeon, M.-S.; Kang, T.-G. Temporal and seasonal variations in a phytoplankton community structure in artificial Lake Uiam, South Korea. Water 2023, 15, 4118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsby, A. Gas vesicles. Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 58, 94–144. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.; Fulton, R., III. Ecology of harmful cyanobacteria. In Ecology of Harmful Algae; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2006; pp. 95–109. [Google Scholar]
- Agostoni, M.; Waters, C.M.; Montgomery, B.L. Regulation of biofilm formation and cellular buoyancy through modulating intracellular cyclic di-GMP levels in engineered cyanobacteria. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2016, 113, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Akbar, S.; Sun, Y.; Gu, L.; Zhang, L.; Lyu, K.; Huang, Y.; Yang, Z. Cyanobacterial dominance and succession: Factors, mechanisms, predictions, and managements. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 297, 113281. [Google Scholar]
- Kromkamp, J.; Konopka, A.; Mur, L.R. Buoyancy Regulation in a Strain of Aphaniz. omenon flos-aquae (Cyanophyceae): The Importance of Carbohydrate Accumulation and Gas Vesicle Collapse. Microbiology 1986, 132, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar]
- Tashiro, Y.; Monson, R.E.; Ramsay, J.P.; Salmond, G.P. Molecular genetic and physical analysis of gas vesicles in buoyant enterobacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 18, 1264–1276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, K.; Amano, Y.; Machida, M.; Asukabe, H.; Harada, K.-i. Effects of light and potassium ion on buoyancy regulation with gas vesicle in a Cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa NIES-843. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2018, 229, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Gámez, T.E.; Benton, L.; Manning, S.R. Observations of two reservoirs during a drought in central Texas, USA: Strategies for detecting harmful algal blooms. Ecol. Indic. 2019, 104, 588–593. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).