Abstract
Accurate forecasting of river flows is essential for effective water resource management, flood risk reduction and environmental protection. The ongoing effects of climate change, in particular the shift in precipitation patterns and the increasing frequency of extreme weather events, necessitate the development of advanced forecasting models. This study investigates the application of long short-term memory (LSTM) neural networks in predicting river runoff in the Velika Morava catchment in Serbia, representing a pioneering application of LSTM in this region. The study uses daily runoff, precipitation and temperature data from 1961 to 2020, interpolated using the inverse distance weighting method. The LSTM model, which was optimized using a trial-and-error approach, showed a high prediction accuracy. For the Velika Morava station, the model showed a mean square error (MSE) of 2936.55 and an R2 of 0.85 in the test phase. The findings highlight the effectiveness of LSTM networks in capturing nonlinear hydrological dynamics, temporal dependencies and regional variations. This study underlines the potential of LSTM models to improve river forecasting and water management strategies in the Western Balkans.
1. Introduction
Accurately predicting the state of rivers is essential to effectively manage water resources, reduce flood risk, facilitate navigation and protect the environment. As climate change continues to alter precipitation patterns [1] and the frequency of extreme weather events increases, the importance of reliable forecasting methods has grown significantly. This need requires the development of sophisticated modeling techniques capable of adapting to these changing conditions, as demonstrated by recent research emphasizing the need for innovative approaches in hydrology [2,3]. Machine learning techniques, in particular long short-term memory (LSTM) networks, have proven to be a powerful tool to improve the accuracy of streamflow predictions under changing climatic conditions [4,5,6,7]. In contrast to conventional hydrological models (e.g., HBV, SWAT), which require extensive calibration of physical parameters and struggle to adapt to non-stationary hydroclimatic conditions, LSTMs autonomously learn complex watershed responses directly from data, bypassing rigid structural assumptions that often limit traditional approaches in data-scarce regions like the Velika Morava catchment [8]. LSTMs have been shown to effectively model complex nonlinear relationships in hydrological data, thereby significantly improving predictive performance compared to traditional methods [9,10,11] This capability is of paramount importance for hydrological applications where understanding historical conditions is essential for making accurate predictions [12,13]. The adaptability of LSTMs to different data types and their ability to model complicated relationships make them a preferred option for hydrological forecasting [14,15,16].
Within the Ems catchment, comparative studies demonstrate that LSTMs outperform conceptual hydrological models like HBV in daily streamflow forecasting, particularly in capturing nonlinear hydrological processes [17]. Studies in Quebec, Canada, show that LSTM-based models can simulate peak streamflow as well as or better than distributed hydrological models, making them suitable for flood frequency analysis. Furthermore, research highlights the potential of using global datasets to improve streamflow prediction using LSTM networks over a large set of catchments worldwide, emphasizing the strengths of LSTM-based modeling in hydrology [18]. These findings underscore the capacity of LSTMs to enhance streamflow forecasting accuracy and reliability, even with limited data, offering a promising avenue for improving water resource management in the region [19,20].
In recent years, LSTMs have undergone rigorous testing in the field of hydrological watershed modeling, demonstrating their potential for predicting hydrological extremes. Kratzert et al. [20], for example, have shown that LSTMs can effectively model the relationships between precipitation and runoff in over 500 watersheds in the United States, significantly outperforming traditional hydrologic models. Gauch et al. [19] further extended this work and showed that LSTMs trained with reanalysis can predict river discharge at arbitrary temporal resolution. Further advances include the integration of LSTMs with physically based routing methods, leading to improved predictions of runoff in different geographical regions [21]. Similarly, Li et al. [22] demonstrated the versatility of LSTMs by integrating them with reduced-order models to represent the spatio-temporal distribution of floods. LSTM networks can effectively predict river flow, with a nonlinear transformation and careful tuning of stack size and cell number balancing learning efficiency and stability [23]. Similarly, Le et al. [24] reported that LSTM-based models outperform feed-forward and convolutional neural networks in predicting river discharge, with simple architectures (one hidden layer) providing highly reliable predictions and minimizing computation time. In addition, Vizi et al. [15] showed that the LSTM model gave the best results in predicting water levels for all time horizons and provided more accurate predictions than the base model, the linear or the multi-layer perceptron model. Cheng et al. [25] have shown that the LSTM model outperforms the ANN model in predicting daily water levels, which is helpful in making strategic water resource management decisions.
In Europe, the use of LSTMs has led to good results. The studies have shown the efficiency of the LSTM model in forecasting both extreme flows and low flows [21,25]. Furthermore, research has demonstrated the effectiveness of LSTM models in effectively capturing the temporal dynamics of river discharge data in a range of climatic conditions [26]. In a more recent study, Hauswirth et al. [27] used five different machine learning models, including LSTMs trained on historical observations of runoff and precipitation, to simulate low-flow events using a threshold approach. In addition, Bărbulescu and Zhen [28] showed that LSTMs are the most accurate and fastest when training and testing the monthly discharges of the Buzău River in Romania. Overall, these studies suggest that LSTMs show adaptability to different environmental conditions and improve prediction accuracy in different hydrological contexts [29,30,31,32,33]. Recent studies emphasize the importance of hybrid forecasting systems, combining traditional physics-based approaches with statistical techniques like LSTMs for improved hydrological predictions [32]. Ding et al. demonstrated the effectiveness of integrating numerical weather prediction systems with LSTM models to forecast runoff, highlighting the potential of hybrid approaches in capturing complex hydrological processes [32]. Graph neural networks are also being used to enhance flood forecasting by considering spatial complexities, such as localized rainfall variations and terrain differences, which are often inadequately addressed in traditional models [33]. Furthermore, deep learning algorithms are being utilized to estimate baseflow in both gauged and ungauged basins, improving water resource modeling and management across diverse hydrological conditions [34].
The present study focuses on the application of LSTM networks for the prediction of river discharge at three hydrological stations in the Velika Morava catchment in Serbia. Significantly, this is the first application of LSTM methods for streamflow forecasting in this region. The study has two aims: First, to fill a significant knowledge gap in the existing literature by providing insights into the applicability of advanced machine learning techniques in regional hydrology. Second, to provide a framework for understanding the unique hydrological characteristics and challenges of the Velika Morava catchment. By improving our understanding of LSTM performance in various hydrologic contexts, this study establishes a foundation for future research efforts aimed at effectively integrating machine learning into water resource management strategies.
2. Study Area
The catchment area of the Velika Morava River covers 37,561 km2, which is 42% of the territory of Serbia [35]. This catchment can be further divided into three hydrographic units: the direct catchment of the Velika Morava (6242 km2), the catchment of the Južna Morava (15,469 km2) and the catchment of the Zapadna Morava (15,850 km2) [36,37] (Figure 1). The Velika Morava River originates from the confluence of the Južna Morava and the Zapadna Morava near the town of Stalać and is the largest national river system in Serbia. The relief of the Velika Morava catchment area is dominated by the mountains of the Serbian–Macedonian massif in the central part, the Dinarides in the west and southwest and the Carpathian–Balkan Mountains in the east and southeast. The northern part consists of the wide valley of the Velika Morava River. The lowest point is 67 m above sea level, at the confluence of the Velika Morava and the Danube, and the highest point is on Hajla Mountain, at 2500 m above sea level [36].
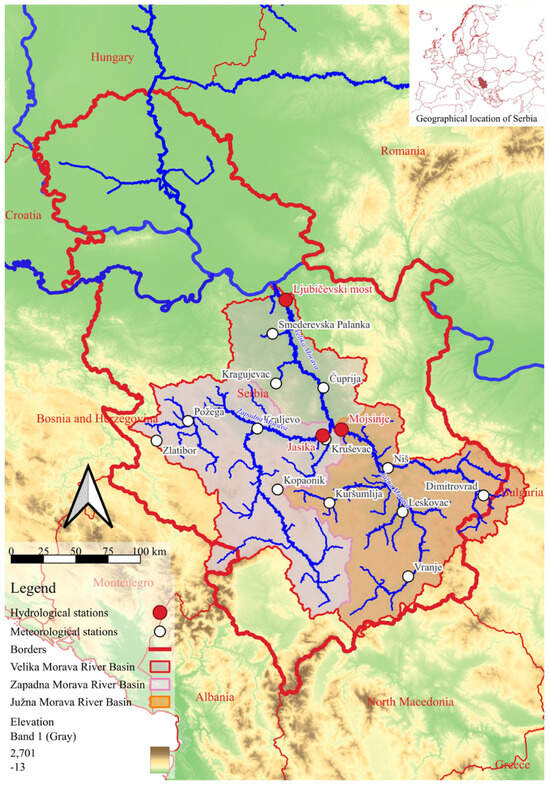
Figure 1.
Velika Morava River basin with hydrological and meteorological stations.
The catchment area of the Velika Morava, the largest river basin in Serbia, covers 42% of the country’s territory. Air temperatures and the precipitation regime have a strong influence on the discharge regime of the rivers. In winter, most of the Velika Morava catchment area is covered with snow [37]. In spring, this snow melts, which coincides with precipitation, especially in the lower regions. The high water levels in spring are therefore caused by rain and snowmelt in the mountains, while the low water levels in summer/autumn are caused by a lack of precipitation and increased evapotranspiration. It can therefore be concluded that the rivers in the Velika Morava basin mostly belong to the pluvio-nival water regime, with high water in spring (March and April) and low water in summer–autumn (August and September) [38].
Land use and human activities significantly influence hydrological processes within the Velika Morava River basin. According to the WRB classification, the basin’s predominant soil types include Eutric Cambisol and Vertisol, with Fluvisol and Fluvisol humic present in alluvial plains and Leptosol in higher elevations [36,37]. Agriculture plays a dominant role, covering 286,866 ha, with 79% classified as arable land. Cereals, particularly corn (49%) and wheat (38%), constitute the primary crops [36]. Despite intensive agriculture, irrigation remains limited due to the river’s relatively low discharge. However, hydrological alterations from dams and reservoirs pose significant challenges. Numerous studies have highlighted the adverse impacts of dams on river discharge, aquatic biodiversity and overall ecosystem health [39,40,41,42].
The amount of precipitation shows a high degree of spatial variation, as the average annual precipitation ranges from 600 mm in the Velika Morava and Južna Morava valleys to 1200 mm in the western and southern mountain regions of the Zapadna Morava catchment area and the mountains in the eastern part of the Južna Morava catchment area [42]. The average annual air temperature in the lowlands is between 10 and 12 °C, while in the highest mountain regions, the average temperature is below 3 °C [43].
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
In this study, daily discharge, precipitation and temperature were used to investigate the influence of these climate variables on river discharge. The discharge values were determined for three stations, while the meteorological data were obtained for a total of 12 stations (Figure 1). The historical data for these variables were obtained from the Republic Hydrometeorological Service of Serbia (RHSS) in Belgrade to ensure high data accuracy and consistency for model development. A visual inspection confirmed that the selected river station records contained no missing observations. RHSS enforces rigorous quality control procedures to ensure the reliability of the collected and maintained hydrological data. The institute adheres to strict standards to guarantee the accuracy and consistency of the dataset used in this study. In addition to following its internal protocols, RHSS also complies with the guidelines set by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO). The period from 1961 to 2020 was chosen to provide a sufficiently long time series, necessary for further analysis of drought deficits and durations through distribution function calculations.
To account for the spatial variability of precipitation and temperature, we used inverse distance weighting (IDW), a widely used spatial interpolation technique. IDW estimates values at unsampled locations based on the proximity and influence of nearby observed data points [44]. This method is particularly suitable for hydrological variables like precipitation, which exhibit strong local spatial dependence, as IDW leverages the first law of geography by assigning greater weight to observations closer to the target location [45]. We optimized the power parameter (p = 2) and search radius through cross-validation, ensuring minimal bias in capturing orographic precipitation gradients and temperature lapse rates, an approach validated in similar mountainous basins [46,47]. This method was used to regionalize meteorological data to determine the influence of climate parameters (mainly air temperatures and precipitations) on streamflow at selected hydrological stations. Since precipitation and temperature are spatially heterogeneous and crucial for river dynamics, an accurate interpolation of these variables was essential. Data from several meteorological stations were interpolated to generate spatially representative inputs for each hydrological station. IDW assigns a weighting to the observations that is inversely proportional to their distance from the target location. This ensures that closer stations have a greater influence on the interpolated values. The simplicity, computational efficiency and effectiveness of IDW in capturing local spatial variability made it the ideal choice for this study. The resulting interpolated meteorological data were then used as input to a long short-term memory (LSTM) model, which is capable of capturing temporal dependencies and nonlinear relationships between climatic variables and river discharge. By combining IDW with LSTM, this study effectively integrates spatial heterogeneity with temporal dynamics and provides a robust framework for modeling the complex interactions between climate variables and hydrological responses.
3.2. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Model
A long short-term memory (LSTM) neural network was used to predict runoff based on historical observations of runoff and meteorological variables such as precipitation, temperature and evapotranspiration. The LSTM model was trained separately for each of the three catchments using data from the corresponding gauging stations. The dataset was split into 80% for training and 20% for testing to ensure a reliable assessment of model performance. The LSTM model was built using the Keras package, a high-level neural network API written in Python 3.13. The model architecture and hyperparameters were optimized through a process of trial and error, where different configurations were evaluated to determine the optimal setup. The final model architecture consisted of a single LSTM layer with four units, followed by a dense output layer. This initial, hands-on exploration allowed us to develop crucial intuition regarding the interaction between hyperparameters and model performance, particularly in capturing the non-linear dynamics of streamflow in our study area [48]. Given the computational expense of exhaustive grid searches and the limited availability of high-quality, long-term data for robust training, this initial exploration guided a subsequent, more focused refinement strategy, concentrating on the most influential hyperparameters within a narrowed parameter space, a pragmatic approach often necessitated in data-scarce hydrological applications [49]. The model was then compiled using the Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 0.001 and the mean squared error (MSE) was chosen as the loss function. LSTM models have proven successful in predicting time series, especially in the context of seasonal data. Accordingly, the model was trained to recognize historical patterns both in the target variable (discharge) and in the meteorological data from neighboring stations. The choice of model configuration took into account previous studies [13], which guided the selection of hyperparameters, including the MSE loss function and the learning rate of 0.001. The architecture of the model included a single LSTM layer with 4 units, carefully chosen to balance model complexity and performance. The number of epochs and batch sizes for training were determined based on the results of the evaluation metrics. Epoch values of 16, 32, 64 and 128 were tested, and batch sizes ranged from 1 to 50. The model was trained with the optimal configuration for each station, with no dropout applied during training. Several verification metrics were used to evaluate the performance of the model; these included mean squared error (MSE), coefficient R-squared (R2), Nash-Sutcliffe efficiency (NSE) and mean percentage error (MPE). These metrics were used to assess the accuracy of the model during both the training and testing phases, providing a comprehensive understanding of the model’s ability to predict streamflow accurately.
To quantify overfitting, we employed 5-fold cross-validation [50,51]. This method involves partitioning the dataset into five equally sized subsets, where the model is trained on four subsets and tested on the remaining one. This process is repeated five times, each time using a different subset for testing, ensuring that every data point is used for both training and testing. The performance metrics, including MSE, R2, NSE and MPE, were calculated for each fold [52], and the average results were analyzed to evaluate the model’s generalization ability and detect any overfitting tendencies across different sub-basins of the Morava River.
4. Results and Discussion
The results presented in this section offer a statistical summary of the river discharge, precipitation and temperature data for the Velika Morava, Južna Morava and Zapadna Morava rivers. The subsequent table emphasizes salient metrics, including mean, standard deviation, minimum, maximum, skewness and kurtosis for each variable across the three rivers (Table 1).

Table 1.
Statistical summary of hydrological and meteorological variables for study area.
The following table provides an overview of the discharge, precipitation and temperature data for three river basins: Velika Morava, Južna Morava and Zapadna Morava. The statistics presented include the mean, standard deviation, minimum, maximum, skewness and kurtosis for each variable. As expected, the Velika Morava River has the highest mean discharge (225.12 m3/s), followed by Zapadna Morava (102.92 m3/s) and Južna Morava (90.31 m3/s). The standard deviation of the discharge is also highest in Velika Morava (213.776 m3/s), while Južna Morava has the lowest (102.47 m3/s). The maximum discharge is observed in Velika Morava (2338.0 m3/s), while the minimum discharge is measured in Južna Morava (6.18 m3/s). The precipitation values show considerable fluctuations, with the Zapadna Morava catchment having the highest mean value (1.79 mm) and the Velika Morava catchment just behind (1.77 mm). The Velika Morava basin also had the highest skewness (5.934) and kurtosis (66.60), suggesting a propensity for more extreme precipitation events. Temperature variation is minimal, with mean temperatures of 11.6 °C in Velika Morava, 12.4 °C in Južna Morava and 11.4 °C in Zapadna Morava basins. The skewness and kurtosis for temperature are near zero, reflecting a fairly symmetrical temperature distribution.
As Figure 2 shows, the performance of the model is evaluated on three different datasets, namely Velika Morava, Južna Morava and Zapadna Morava, using four key metrics: MSE, R2, NSE and MPE, for both the training and testing phases. For the MSE metric, the Velika Morava dataset shows significantly higher values in the test phase (2936.55) than in the training phase (1970.66), indicating a degree of overfitting. In contrast, the Južna Morava and Zapadna Morava datasets show more balanced MSE values between training and testing and have comparatively smaller discrepancies. This observation is consistent with the findings of Arpit et al. [52], who reported that models showing lower variance between training and testing phases indicate better generalization ability. This result indicates that these models have a better generalization ability. In terms of R2 and NSE, all datasets show robust performance, with test values approaching or matching the training values, especially in Velika Morava, where both R2 and NSE are above 0.90 for both phases, indicating high predictive accuracy and minimal bias. The importance of achieving high R2 and NSE values is well documented in the hydrological literature as an indicator of model reliability [53,54]. The MPE values remain minimal, with Velika Morava having the lowest values, indicating accurate predictions. The Zapadna Morava dataset shows slightly better MPE results compared to Južna Morava, as it shows less bias in both the training and test datasets. The figure as a whole shows the effectiveness of the models in all three datasets, with a certain degree of overfitting observed in Velika Morava, while the other models show a strong generalization, particularly with respect to R2, NSE and MPE metrics. This finding aligns with recent evaluations that underscore the necessity of employing an array of performance metrics to comprehensively appraise model efficacy [55,56].
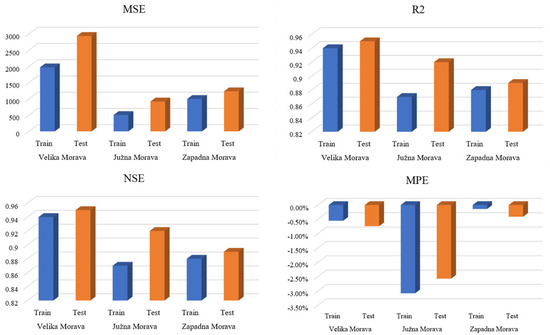
Figure 2.
Validation metric results.
The model performance was assessed using 5-fold cross-validation across three Morava River sub-basins: Južna Morava, Velika Morava and Zapadna Morava. Results show strong predictive performance, with varying generalization across the sub-basins. For Južna Morava, the training MSE was 321.36 ± 19.47, while the test MSE was 714.17 ± 33.96, resulting in a generalization gap of 542.81. The NSE values were 0.84 (train) and 0.72 (test), indicating reasonable predictive accuracy but some overfitting. Velika Morava showed similar trends, with a training MSE of 350.43 ± 20.14 and a test MSE of 457.72 ± 57.03, leading to a generalization gap of 607.29. The NSE values of 0.92 (train) and 0.77 (test) reflect robust performance and better generalization than Južna Morava. In contrast, Zapadna Morava had the lowest generalization gap (290.50), with balanced MSE and NSE values, suggesting a well-fitted model. Improvements in generalization could further enhance accuracy for Južna Morava and Velika Morava.
Figure 3 shows a strong correlation between the observed and predicted values for all three rivers, indicating the effectiveness of the model in predicting river discharge. Recent studies have shown that high correlation coefficients between observed and predicted values are an important indicator of the reliability of the model in hydrological predictions [57]. The visual alignment of the training and test data along the red dashed line indicates that the model generalizes well across both datasets. This result is consistent with the conclusions of studies highlighting the importance of visualizing model outputs for effective assessment of generalization abilities [58]. For Velika Morava (upper panel) and Zapadna Morava (lower panel) in particular, the predicted values closely follow the observed discharges, demonstrating the effectiveness of the model in capturing the dynamics of these catchments. The ability of models to accurately represent hydrological dynamics is essential for effective water resources management, as emphasized in recent literature [55]. A similar observation can be made for the Južna Morava River (middle panel), which shows a remarkable predictive ability by exhibiting a slight deviation from the one-to-one line but still showing a satisfactory fit. Such deviations are often attributed to the inherent variability of hydrological processes and underline the need for robust modeling approaches. The results underline the resilience of the model in different river catchments and demonstrate its ability to produce reliable runoff forecasts for the study area.
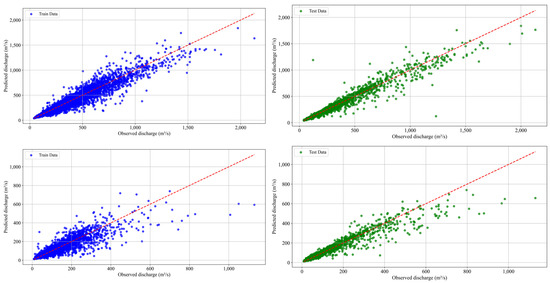
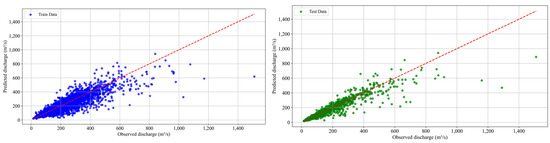
Figure 3.
Comparison of observed and predicted discharge. (upper) Velika Morava River; (middle) Južna Morava River, (lower) Zapadna Morava River; blue—train data; green—test data.
The Figure 4 shows a detailed comparison of the observed discharge values with the model predictions for three hydrological stations: Ljubičevski most, Mojsinje and Jasike. The observed discharge data show the natural variability and patterns of river discharge over time, with significant fluctuations likely related to seasonal and extreme events such as floods and droughts. Recent studies emphasize the importance of understanding these fluctuations for effective water resource management and flood risk assessment [59]. Although the model predictions capture many of these fluctuations, they show slight discrepancies, especially during periods of extreme runoff values. This discrepancy is particularly evident at the Mojsinje station, where the model appears to have difficulty accurately predicting some of the higher peaks. This indicates that certain extreme runoff events may not be fully captured by the model. These challenges in predicting runoff peaks have been documented in various hydrological studies and emphasize the need to calibrate models specifically for extreme events [21,57,60]. A similar observation was made at the Ljubičevski most and Jasike stations, where the model showed a satisfactory fit during non-peak periods, but showed some deviation during flood events. This suggests that improving the model’s ability to accurately capture extreme discharge fluctuations could be a fruitful area of research. Results of this study show robust performance with strong predictive accuracy, particularly for the Velika Morava sub-basin, where both R2 and NSE values exceed 0.90. This result contrasts with the Lim River (Southwest part of Serbia) study [60], where the machine learning models temporal Kolmogorov–Arnold networks (TKANs), long short-term memory (LSTM) and temporal convolutional networks (TCNs) were compared. In this study, the TCNs, showed slightly smaller residuals and better performance in capturing extreme events, with NSE values reaching 0.961. While both studies highlight the challenge of predicting extreme events, our results for the Morava River indicate a more consistent model performance across different sub-basins, compared to the Lim River study where the models showed a significant underprediction for extreme flow events. This comparison further underscores the inherent difficulty of predicting extreme hydrological events and suggests that there are differences in model sensitivity and calibration across various regions.
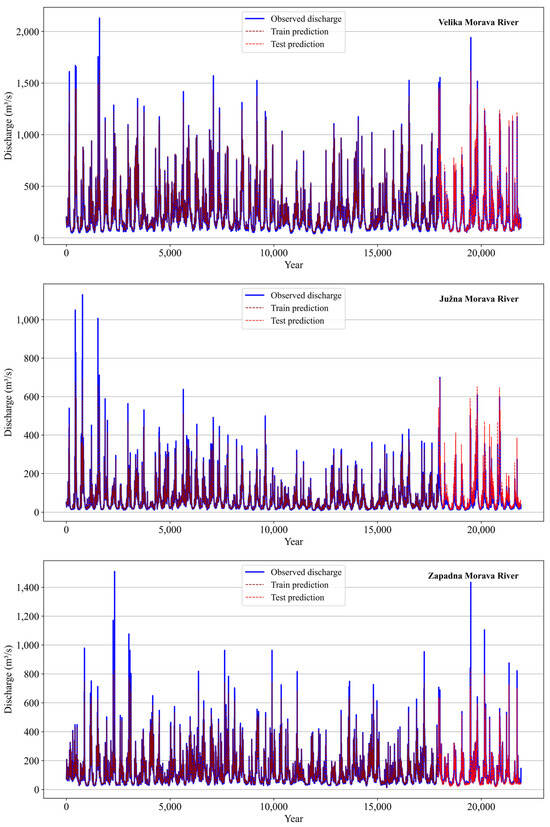
Figure 4.
Time series of observed and predicted discharge.
The observed discrepancies in the predictions, especially in times of flood events, can be attributed to the sensitivity of the model to the training data and the inherent unpredictability of extreme hydrological events [61,62,63]. A detailed analysis of flood conditions (flows ≥ 95th percentile as defined by Kupfer et al. [63]) reveals a significant divergence in model performance during these extreme events compared to baseline validation conditions. Specifically, for Velika Morava, the test values during flood events were lower than the observed values by 37%, while for Južna Morava and Zapadna Morava, the reductions were 31.8% and 38.4%, respectively. These results indicate that the model struggles to accurately predict peak flows during flood conditions, as reflected by the considerable underestimation of flood magnitudes. This discrepancy underscores the limitations of the model in capturing the complexity of flood dynamics, particularly during extreme hydrological events. Research suggests that incorporating different datasets and meteorological inputs can improve model performance in such events [62,63], which is something that will be carried out in future research. It is conceivable that further refinement of the generalizability of the model to rare or extreme events may require additional data sources or adjustments to the calibration. The inclusion of alternative data sources such as radar precipitation estimates or real-time monitoring systems has been shown to significantly improve hydrological forecasts [64]. The collective results suggest that while the model represents the general dynamics of runoff well, its performance needs to be improved for extreme runoff events. Future research could focus on improving the resilience of the model to such events by investigating alternative architectures, data inputs or training strategies. Studies have shown that the use of machine learning and ensemble modeling techniques can lead to improved prediction accuracy under variable hydrological conditions. Subsequent studies could focus on improving the resilience of the model to these events by investigating alternative architectures, data inputs or training strategies, such as including a wider range of extreme weather events in the training set.
5. Conclusions
This study demonstrates the application of long short-term memory (LSTM) networks for the prediction of river discharge in the Velika Morava catchment, the largest river basin in Serbia. The inclusion of historical runoff data and spatially interpolated meteorological data, including precipitation and temperature, enabled the LSTM models to accurately capture the non-linear and temporal dynamics of runoff. The analysis of the three different catchments (Velika Morava, Južna Morava and Zapadna Morava) demonstrated the effectiveness of the LSTM models, as evidenced by the application of various evaluation metrics, including MSE, R2, NSE and MPE. Although some degree of overfitting was observed in the Velika Morava dataset, the overall prediction accuracy remained robust, with R2 and NSE values above 0.90 in both the training and test phases. This result underlines the effectiveness of LSTM networks as reliable tools for hydrological forecasting, especially in regions characterized by complicated water regimes in snowmelt-influenced basins like the Velika Morava.
The integration of inverse distance weighting (IDW) for spatial interpolation and LSTM for time series modeling has proven to be a robust framework for incorporating spatial heterogeneity and temporal variability in river forecasting. This approach addresses the challenges posed by spatially variable climatic inputs while leveraging the ability of LSTM to model long-term dependencies and complex relationships in hydrological data. The integration of inverse distance weighting (IDW) for spatial interpolation and LSTM for time series modeling has proven to be a robust framework for accounting for spatial heterogeneity and temporal variability in river flow prediction. This approach addresses the challenges posed by spatially variable climatic inputs while taking advantage of LSTM’s ability to model long-term dependencies and complex relationships in hydrologic data.
Significantly, this research represents the first implementation of LSTM models for streamflow forecasting in the Velika Morava catchment, providing a significant advancement in hydrological modeling for this region, where machine learning techniques for river discharge prediction are not widely used. This way we contributed by filling a significant gap in the existing literature. The results underline the potential of machine learning approaches to complement traditional hydrological models, especially in regions where climate change and increasing hydrological extremes require more adaptive and accurate forecasting tools. Future studies could investigate the integration of additional input variables such as soil moisture, evapotranspiration and remote sensing data to further improve the performance of the model.
Providing accurate and reliable runoff predictions is an important contribution of this study, which is expected to improve water resource management, flood risk mitigation and environmental sustainability in the region. The performance of LSTM models demonstrated in this study suggests a wider application in operational hydrological forecasting systems. To facilitate the practical implementation of these models, water management agencies should consider incorporating LSTM-based forecasting tools into their decision-making frameworks, ensuring real-time monitoring and adaptive management strategies. This in turn paves the way for more robust and adaptive water resource management strategies in the face of changing climatic conditions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, I.L. and M.T.; methodology, I.L. and M.T.; software, I.L. and M.T.; validation, I.L., M.T. and Z.B.; formal analysis, M.T.; investigation, I.L. and M.T.; resources, I.L. and P.P.; data curation, I.L.; writing—original draft preparation, I.L.; writing—review and editing, M.T., P.M. and P.P.; visualization, I.L.; supervision, I.L.; project administration, I.L.; funding acquisition, I.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the “Streamflow Drought Through Time” project funded by the EU NextGenerationEU through the Recovery and Resilience Plan of the Slovak Republic within the framework of project no. 09I03-03-V04-00186.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be provided upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Leščešen, I.; Basarin, B.; Podraščanin, Z.; Mesaroš, M. Changes in Annual and Seasonal Extreme Precipitation over Southeastern Europe. Environ. Sci. Proc. 2023, 26, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Chen, F.; Wang, Y.; Long, A.; He, X. Flood Frequency Analysis of Manas River Basin in China under Non-Stationary Condition. J. Flood Risk Manag. 2021, 14, e12745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, B.B.; Jha, R.; Singh, A.; Kumar, D. Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Recurrent Neural Network for Low-Flow Hydrological Time Series Forecasting. Acta Geophys. 2019, 67, 1471–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Tolson, B.A.; Shen, H.; Han, M.; Mai, J.; Lin, J. Enhancing Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM)-Based Streamflow Prediction with a Spatially Distributed Approach. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 2107–2122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshkalam, Y.; Rousseau, A.N.; Rahmani, F.; Shen, C.; Abbasnezhadi, K. Applying Transfer Learning Techniques to Enhance the Accuracy of Streamflow Prediction Produced by Long Short-Term Memory Networks with Data Integration. J. Hydrol. 2023, 622, 129682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, P.; Liu, X.; Xie, J. Simulating Runoff under Changing Climatic Conditions: A Comparison of the Long Short-Term Memory Network with Two Conceptual Hydrologic Models. J. Hydrol. 2021, 592, 125779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Kim, Y. Improving Streamflow Prediction in the WRF-Hydro Model with LSTM Networks. J. Hydrol. 2022, 605, 127297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nifa, K.; Boudhar, A.; Ouatiki, H.; Elyoussfi, H.; Bargam, B.; Chehbouni, A. Deep Learning Approach with LSTM for Daily Streamflow Prediction in a Semi-Arid Area: A Case Study of Oum Er-Rbia River Basin, Morocco. Water 2023, 15, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, C.; Hu, C.; Niu, C.; Li, R.; Li, M.; Xu, Y.; Tian, L. Application of a Hybrid Algorithm of LSTM and Transformer Based on Random Search Optimization for Improving Rainfall-Runoff Simulation. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 11184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Humphries, U.W. A Critical Review of RNN and LSTM Variants in Hydrological Time Series Predictions. MethodsX 2024, 13, 102946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabzevari, T.; Petroselli, A.; Haghighi, A.T.; Babaali, H.R. Comparison of Saturation Models in Complex Hillslopes. Acta Hydrol. Slovaca 2023, 24, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Ding, H.; Wu, M.; Zhang, N.; Shi, M.; Chen, F.; Li, Y. Effects of Different Types of Drought on Vegetation in Huang-Huai-Hai River Basin, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 144, 109428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bo, Y.; Zhang, C.; Fang, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, C.; An, M.; Peng, Y.; Lu, Y. Application of HP-LSTM Models for Groundwater Level Prediction in Karst Regions: A Case Study in Qingzhen City. Water 2025, 17, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.; Alam, M.S.B.; Hassan, M.; Rozbu, M.R.; Ishtiak, T.; Rafa, N.; Mofijur, M.; Shawkat Ali, A.B.M.; Gandomi, A.H. Deep Learning Modelling Techniques: Current Progress, Applications, Advantages, and Challenges. Artif. Intell. Rev. 2023, 56, 13521–13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizi, Z.; Batki, B.; Rátki, L.; Szalánczi, S.; Fehérváry, I.; Kozák, P.; Kiss, T. Water Level Prediction Using Long Short-Term Memory Neural Network Model for a Lowland River: A Case Study on the Tisza River, Central Europe. Env. Sci. Eur. 2023, 35, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Hossni, Y. A Comparative Analysis of LSTM Models Aided with Attention and Squeeze and Excitation Blocks for Activity Recognition. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 3858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, A.; Bormann, H.; Casper, M. Intercomparing LSTM and RNN to a Conceptual Hydrological Model for a Low-Land River with a Focus on the Flow Duration Curve. Water 2023, 15, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martel, J.-L.; Arsenault, R.; Turcotte, R.; Castañeda-Gonzalez, M.; Brissette, F.; Armstrong, W.; Mailhot, E.; Pelletier-Dumont, J.; Lachance-Cloutier, S.; Rondeau-Genesse, G.; et al. Exploring the Ability of LSTM-Based Hydrological Models to Simulate Streamflow Time Series for Flood Frequency Analysis. preprint, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauch, M.; Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Nearing, G.; Lin, J.; Hochreiter, S. Rainfall-Runoff Prediction at Multiple Timescales with a Single Long Short-Term Memory Network. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 25, 2045–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Brenner, C.; Schulz, K.; Herrnegger, M. Rainfall-Runoff Modelling Using Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 6005–6022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frame, J.M.; Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Gauch, M.; Shelev, G.; Gilon, O.; Qualls, L.M.; Gupta, H.V.; Nearing, G.S. Deep Learning Rainfall-Runoff Predictions of Extreme Events. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 3377–3392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, C.; Xu, Y.; Niu, C.; Li, R.; Li, M.; Caihong, H.; Tian, L. An Interpretable Hybrid Deep Learning Model for Flood Forecasting Based on Transformer and LSTM. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 54, 101873. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhang, R.; Fu, G. Using Long Short-Term Memory Networks for River Flow Prediction. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 51, 1358–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, X.H.; Nguyen, D.H.; Jung, S.; Yeon, M.; Lee, G. Comparison of Deep Learning Techniques for River Streamflow Forecasting. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 71805–71820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, M.; Fang, F.; Kinouchi, T.; Navon, I.M.; Pain, C.C. Long Lead-Time Daily and Monthly Streamflow Forecasting Using Machine Learning Methods. J. Hydrol. 2020, 590, 125376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanhapour, M.; Soltani, J.; Shakibian, H.; Malekmohammadi, B.; Hlavcova, K.; Kohnova, S. Development of a Multi-Objective Optimal Operation Model of a Dam Using Meteorological Ensemble Forecasts for Flood Control. Water Resour. Manag. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauswirth, S.M.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Beijk, V.; Wanders, N. The Suitability of a Seasonal Ensemble Hybrid Framework Including Data-Driven Approaches for Hydrological Forecasting. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 501–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bărbulescu, A.; Zhen, L. Forecasting the River Water Discharge by Artificial Intelligence Methods. Water 2024, 16, 1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashemi, R.; Brigode, P.; Garambois, P.; Javelle, P. How Can We Benefit from Regime Information to Make More Effective Use of Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Runoff Models? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 5793–5816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyo, J.C.; Pachepsky, Y.; Kim, S.; Abbas, A.; Kim, M.; Kwon, Y.S.; Ligaray, M.; Cho, K.H. Long Short-Term Memory Models of Water Quality in Inland Water Environments. Water Res. X 2023, 21, 100207. [Google Scholar]
- Lees, T.; Reece, S.; Kratzert, F.; Klotz, D.; Gauch, M.; De Bruijn, J.; Kumar Sahu, R.; Greve, P.; Slater, L.; Dadson, S.J. Hydrological Concept Formation inside Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Networks. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 3079–3101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunt, K.M.R.; Matthews, G.R.; Pappenberger, F.; Prudhomme, C. Using a Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) Neural Network to Boost River Streamflow Forecasts over the Western United States. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 5449–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roudbari, N.S.; Punekar, S.R.; Patterson, Z.; Eicker, U.; Poullis, C. From Data to Action in Flood Forecasting Leveraging Graph Neural Networks and Digital Twin Visualization. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 18571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaneei, P.; Moradkhani, H. DeepBase: A Deep Learning-Based Daily Baseflow Dataset across the United States. Sci. Data 2025, 12, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urosev, M.; Dolinaj, D.; Strbac, D. At-Site Hydrological Drought Analysis: Case Study of Velika Morava River at Ljubicevski Most (Serbia). J. Geogr. Inst. Jovan Cvijic SASA 2016, 66, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srejić, T.; Manojlović, S.; Sibinović, M.; Bajat, B.; Novković, I.; Milošević, M.V.; Carević, I.; Todosijević, M.; Sedlak, M.G. Agricultural Land Use Changes as a Driving Force of Soil Erosion in the Velika Morava River Basin, Serbia. Agriculture 2023, 13, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trifković, M.; Marinković, G.; Ilić, B.; Pejičić, G.; Lazić, J. Land Consolidation and Irrigation, Case Study, Municipality of Velika Plana. Arch. Tech. Sci. 2016, 1, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Urošev, M.; Dolinaj, D.; Leščešen, I. Hydrological Droughts in the Južna Morava River Basin (Serbia). Geogr. Pannonica 2016, 20, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatun, R.; Pal, S. Effects of Hydrological Modification on Fish Habitability in Riparian Flood Plain River Basin. Ecol. Inf. 2021, 65, 101398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, R.G.C.; de Freitas, H.C.P.; Zacardi, D.M.; Faria-Junior, C.H. Effects of River Dams on the Fish Guilds in the Northwest Region of the Brazilian Amazon. Fish. Res. 2021, 243, 106091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, V.; Bănăduc, D.; Curtean-Bănăduc, A.; Petrović, A.; Veličković, T.; Stojković-Piperac, M.; Simić, S. Assessment of the Ecological Sustainability of River Basins Based on the Modified the ESHIPPOfish Model on the Example of the Velika Morava Basin (Serbia, Central Balkans). Front. Env. Sci. 2022, 10, 952692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojlović, S.; Srejić, T.; Sibinović, M.; Milošević, M.V.; Bajat, B.; Kostadinov, S. Impact of Precipitation and Human Activities on Suspended Sediment Transport Load in the Velika Morava River Basin (Serbia). Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajat, B.; Blagojević, D.; Kilibarda, M.; Luković, J.; Tošić, I. Spatial Analysis of the Temperature Trends in Serbia during the Period 1961–2010. Theor Appl Clim. 2015, 121, 289–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical Approaches for Incorporating Elevation into the Spatial Interpolation of Rainfall. J. Hydrol. 2000, 228, 113–129. [Google Scholar]
- Carrera-Hernández, J.J.; Gaskin, S.J. Spatio Temporal Analysis of Daily Precipitation and Temperature in the Basin of Mexico. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 231–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moral, F.J. Comparison of Different Geostatistical Approaches to Map Climate Variables: Application to Precipitation. Int. J. Climatol. 2010, 30, 620–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumarasamy, K.; Belmont, P. Calibration Parameter Selection and Watershed Hydrology Model Evaluation in Time and Frequency Domains. Water 2018, 10, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, X.; Jin, Y. Calibration of a Distributed Hydrological Model in a Data-Scarce Basin Based on GLEAM Datasets. Water 2020, 12, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, K.; Decesari, S.; Paglione, M.; Becagli, S.; Rinaldi, M. Nested Cross-Validation Gaussian Process to Model Dimethylsulfide Mesoscale Variations in Warm Oligotrophic Mediterranean Seawater. NPJ Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghomlaghi, A.; Nasseri, M.; Bayat, B. How to Enhance the Inverse Distance Weighting Method to Detect the Precipitation Pattern in a Large-Scale Watershed. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2022, 67, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xie, X.; Zuo, J.; Xing, X.; Liu, B.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, Y. Coupling Random Forest and Inverse Distance Weighting to Generate Climate Surfaces of Precipitation and Temperature with Multiple-Covariates. J. Hydrol. 2021, 598, 126270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpit, D.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, C. Ensemble of Averages: Improving Model Selection and Boosting Performance in Domain Generalization. arXiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Chen, B. Evaluating Uncertainty Estimates in Distributed Hydrological Modeling for the Wenjing River Watershed in China by GLUE, SUFI-2, and ParaSol Methods. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 76, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blöschl, G.; Bierkens, M.F.P.; Chambel, A.; Cudennec, C.; Destouni, G.; Fiori, A.; Kirchner, J.W.; McDonnell, J.J.; Savenije, H.H.G.; Sivapalan, M.; et al. Twenty-Three Unsolved Problems in Hydrology (UPH)–a Community Perspective. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2019, 64, 1141–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyutha, C. Pros and Cons of Various Efficiency Criteria for Hydrological Model Performance Evaluation. Proc. Int. Assoc. Hydrol. Sci. 2024, 385, 181–187. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Huang, H. Short Term Real-Time Rolling Forecast of Urban River Water Levels Based on Lstm: A Case Study in Fuzhou City, China. Int. J. Env. Res. Public. Health 2021, 18, 9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höge, M.; Scheidegger, A.; Baity-Jesi, M.; Albert, C.; Fenicia, F. Improving Hydrologic Models for Predictions and Process Understanding Using Neural ODEs. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2022, 26, 5085–5102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Creutin, J.D.; Blanchet, J.; Reverdy, A.; Brochet, A.; Lutoff, C.; Robert, Y. Reported Occurrence of Multiscale Flooding in an Alpine Conurbation over the Long Run (1850–2019). Water 2022, 14, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahrendt, S.; Horner-Devine, A.R.; Collins, B.D.; Morgan, J.A.; Istanbulluoglu, E. Channel Conveyance Variability Can Influence Flood Risk as Much as Streamflow Variability in Western Washington State. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR031890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinokić, L.; Dotlić, M.; Prodanović, V.; Kolaković, S.; Simonovic, S.P.; Stojković, M. Effectiveness of Three Machine Learning Models for Prediction of Daily Streamflow and Uncertainty Assessment. Water Res. X 2025, 27, 100297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagemann, M.; Park, M.H. Capacity of Semi-Parametric Regression Models to Predict Extreme-Event Water Quality in the Northeastern US. J. Hydrol. 2017, 547, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liang, Z.; Qian, M.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, B. Analysis of Flood Streamflow Sensitivity to Precipitation Using the WRF-Hydro Model in a Humid Environment. Hydrol. Res. 2024, 55, 728–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kupfer, S.; MacPherson, L.R.; Hinkel, J.; Arns, A.; Vafeidis, A.T. A Comprehensive Probabilistic Flood Assessment Accounting for Hydrograph Variability of ESL Events. J. Geophys. Res. Ocean. 2024, 129, e2023JC019886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, F.; Yang, Q.; Yang, J.; Luo, Z.; Shao, J.; Wang, G. Incorporating Multiple Grid-Based Data in CNN-LSTM Hybrid Model for Daily Runoff Prediction in the Source Region of the Yellow River Basin. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 51, 101652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).