Seasonal Distribution of Nutrient Salts and Microbial Communities in the Pearl River Delta
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Method
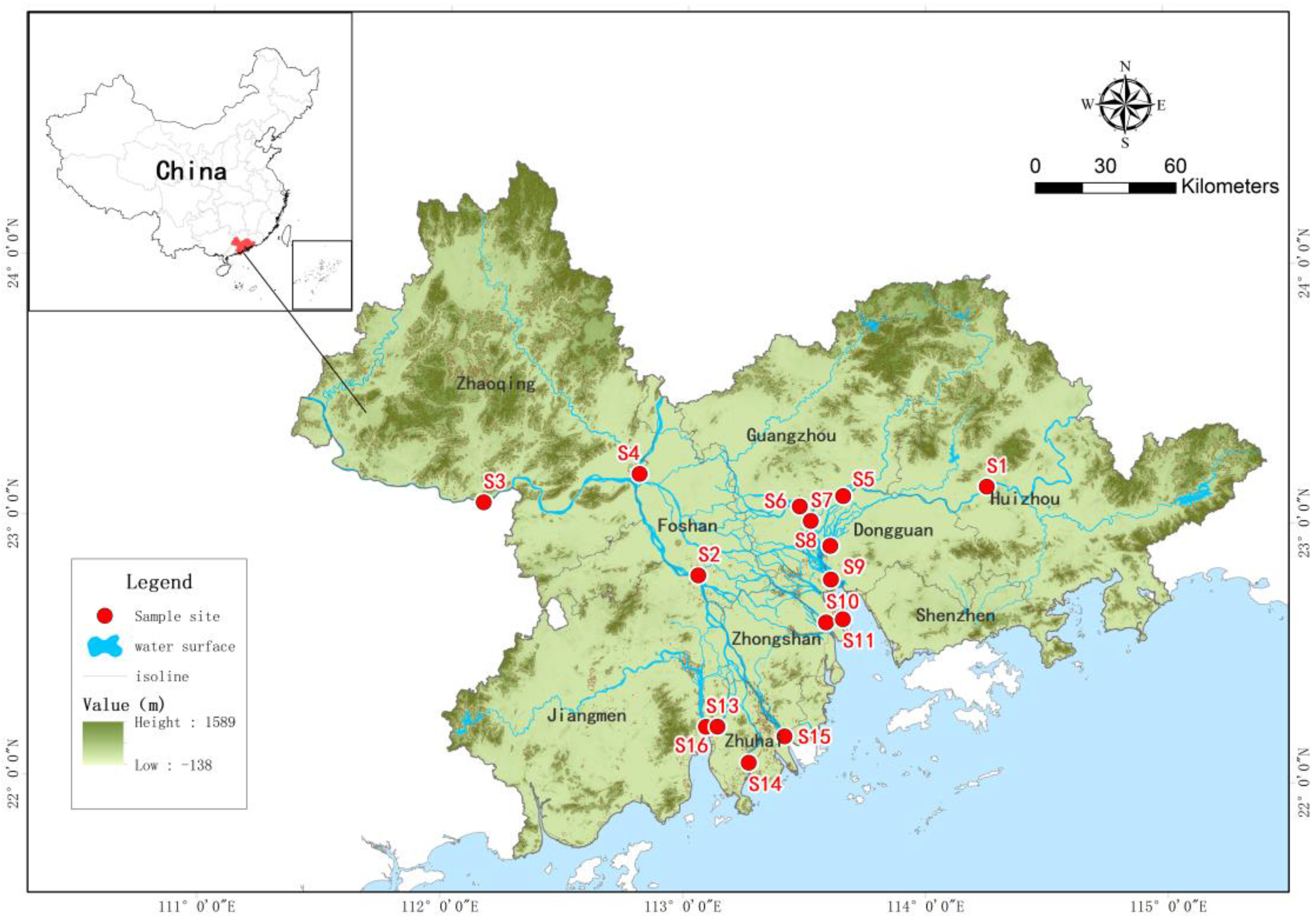
2.1. Study Area and Sample Collection
2.2. Determination of Physico-Chemical Parameters
2.3. DGT Analysis
2.4. Bacterial Community Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
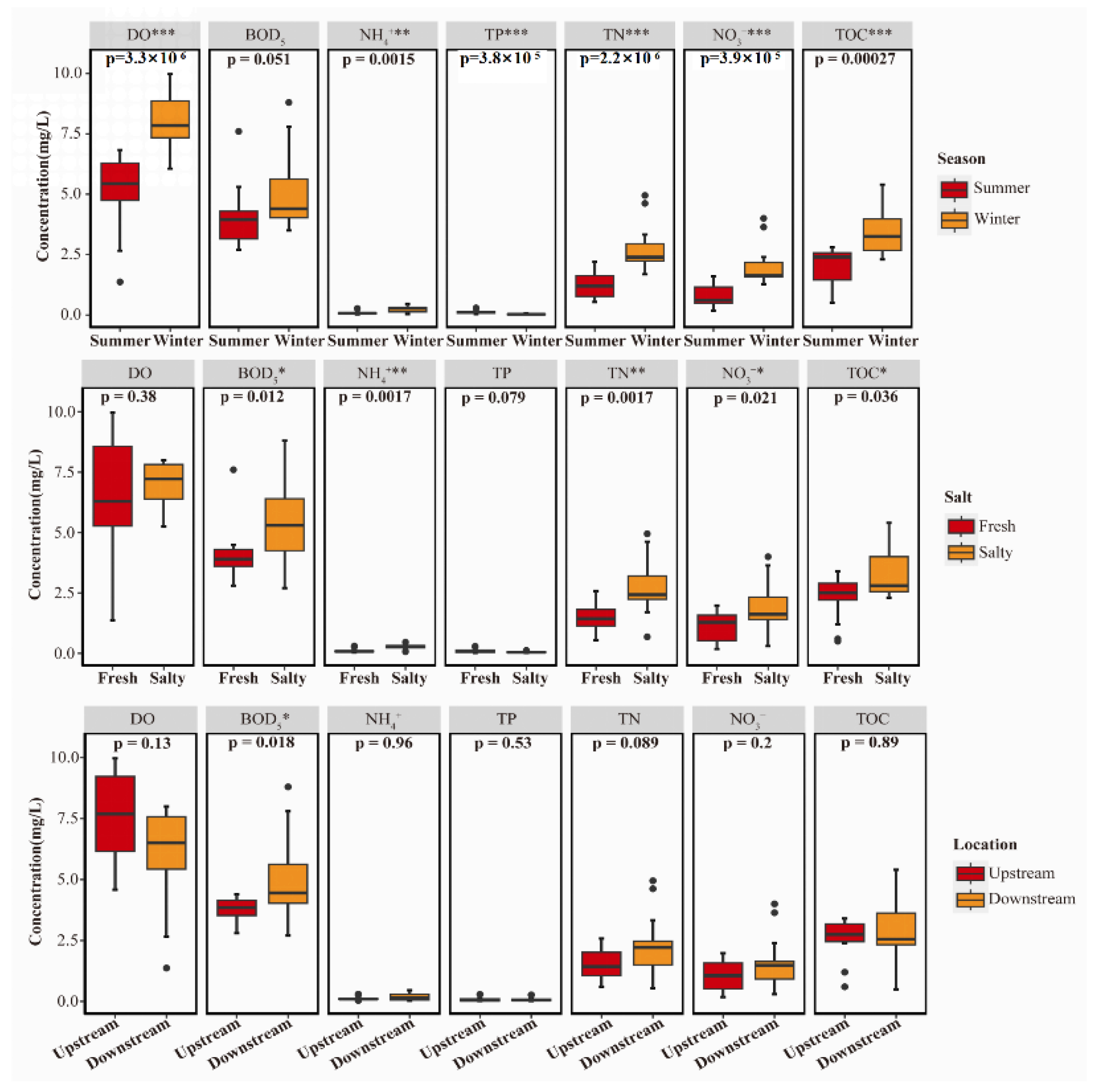
3.1. Spatiotemporal Changes in Water Quality
3.2. Spatiotemporal Changes in Sediment Composition
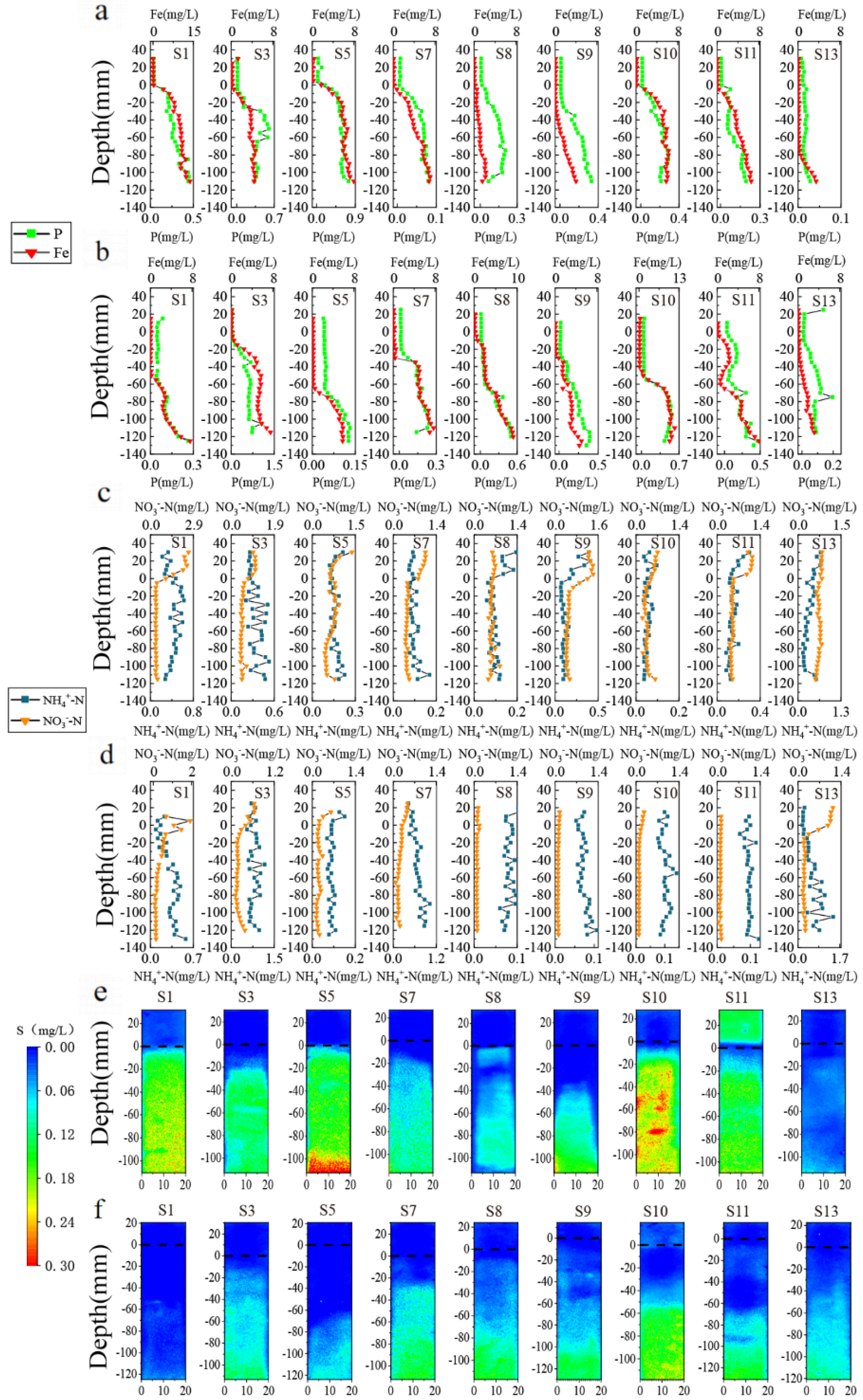
3.3. Vertical Distribution of DGT-P, Fe, S, and N
3.4. Diffusion Fluxes of P, Fe, N, and S at the SWI
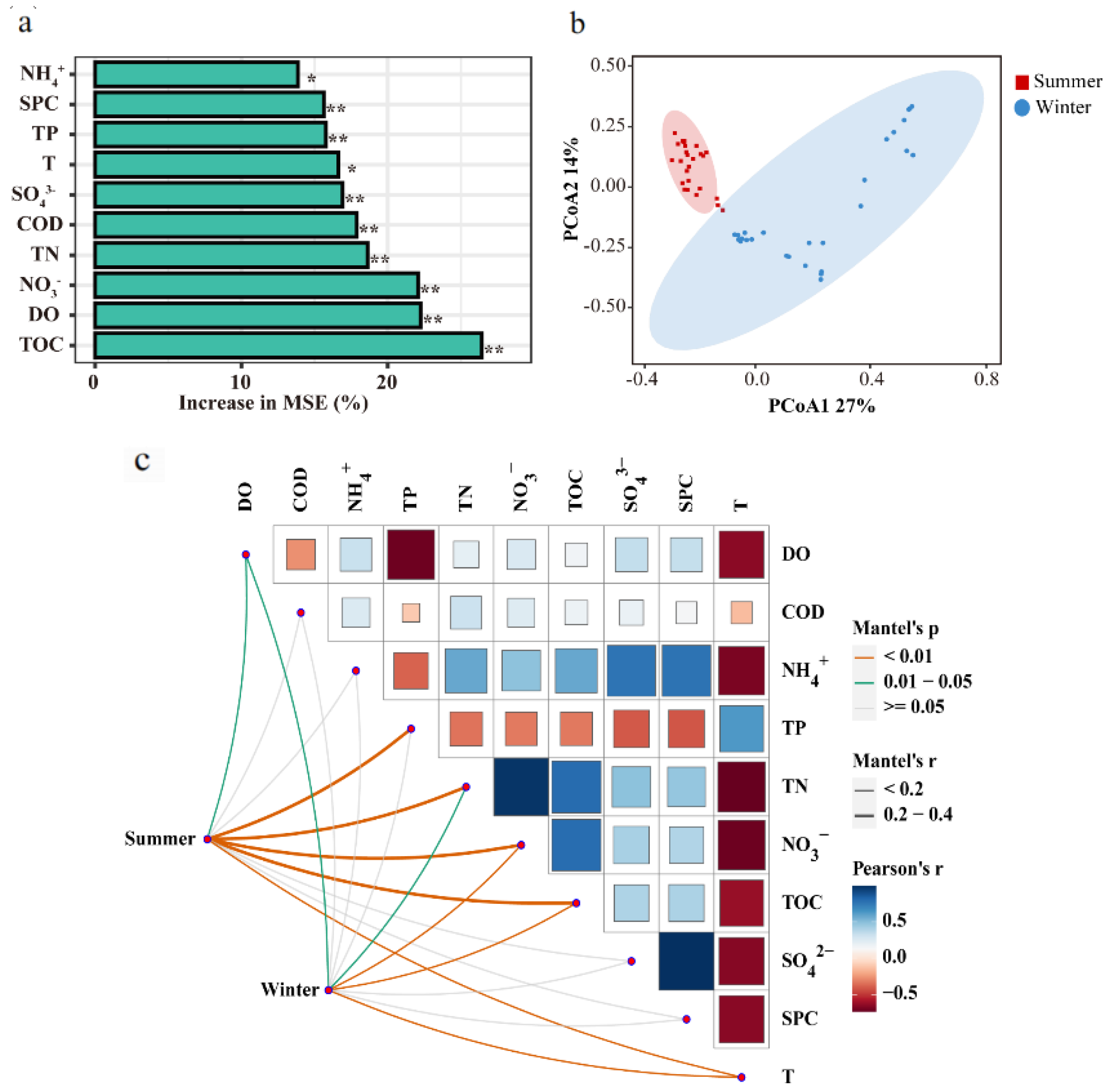
3.5. Spatiotemporal Variations in Diversity of Microbial Communities in Water
3.6. Microbial Participation in P, Fe, N, and S Coupling Processes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Szabo, S.; Brondizio, E.; Renaud, F.G.; Hetrick, S.; Nicholls, R.J.; Matthews, Z.; Tessler, Z.; Tejedor, A.; Sebesvari, Z.; Foufoula-Georgiou, E.; et al. Population dynamics, delta vulnerability and environmental change: Comparison of the Mekong, Ganges–Brahmaputra and Amazon delta regions. Sustain. Sci. 2016, 11, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Cai, S.; Zhan, W.; Li, Y. Changes in the distribution of surface sediment in Pearl River Estuary, 1975–2017, largely due to human activity. Cont. Shelf Res. 2021, 228, 104538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, X.Z. Eutrophication control strategies for highly anthropogenic influenced coastal waters. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 705, 135760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.P.; Huang, L.M.; Yue, W.Z. The characteristics of nutrients and eutrophication in the Pearl River estuary, South China. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2003, 47, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, C.; He, C.; Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Pang, Y.; Shi, Q.; He, D. Characterization of dissolved organic matter processing between surface sediment porewater and overlying bottom water in the Yangtze River Estuary. Water Res. 2022, 215, 118260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Liu, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, X. Effects of pH, Temperature, Dissolved Oxygen, and Flow Rate on Phosphorus Release Processes at the Sediment and Water Interface in Storm Sewer. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2013, 2013, 104316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.J.; Phillips, L.; Longmore, A.; Hayden, H.L.; Heidelberg, K.B.; Tang, C.; Mele, P. Temporal profiling resolves the drivers of microbial nitrogen cycling variability in coastal sediments. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 856, 159057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; He, L.; Yin, K.; Pan, G.; Harrison, P.J. Bacterial distribution and nutrient limitation in relation to different water masses in the coastal and northwestern South China Sea in late summer. Cont. Shelf Res. 2011, 31, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibbons, K.J.; Bridgeman, T.B. Effect of temperature on phosphorus flux from anoxic western Lake Erie sediments. Water Res. 2020, 182, 116022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, N.; Lu, W.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zhang, W.; Lei, P. In situ high-resolution measurement of phosphorus, iron and sulfur by diffusive gradients in thin films in sediments of black-odorous rivers in the Pearl River Delta region, South China. Environ. Res. 2020, 189, 109918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Lou, Y.; Xu, M.; Wu, C.; Meng, J.; Shi, L.; Xia, F.; Xu, Y. Spatial distribution and influencing factors on the variation of bacterial communities in an urban river sediment. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 272, 115984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Chen, H.; Liu, M.; Yang, J.R.; Xiao, P.; Wilkinson, D.M.; Yang, J. Response of the eukaryotic plankton community to the cyanobacterial biomass cycle over 6 years in two subtropical reservoirs. ISME J. 2019, 13, 2196–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Z.; Song, N.; Wang, C.; Jiang, H. Functional potential and assembly of microbes from sediments in a lake bay and adjoining river ecosystem for polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon biodegradation. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 23, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Goncalves, P.; Copeland, E.; Qi, S.S.; Dai, Z.C.; Li, G.L.; Wang, C.Y.; Du, D.L.; Thomas, T. Invasion by the weed Conyza canadensis alters soil nutrient supply and shifts microbiota structure. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2020, 143, 107739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sun, Y.; Yu, M.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, H.; Peng, R.; Li, Z.; Cui, J.; Luo, X. Linking Shifts in Bacterial Community Composition and Function with Changes in the Dissolved Organic Matter Pool in Ice-Covered Baiyangdian Lake, Northern China. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fike, D.A.; Bradley, A.S.; Rose, C.V. Rethinking the Ancient Sulfur Cycle. Annu. Rev. Earth Planet. Sci. 2015, 43, 593–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zhang, L.; Hong, J.; Sun, J.; Jiang, F. Different ferric dosing strategies could result in different control mechanisms of sulfide and methane production in sediments of gravity sewers. Water Res. 2019, 164, 114914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mortimer, C.H. The Exchange of Dissolved Substances Between Mud and Water in Lakes, II. J. Ecol. 1941, 30, 147–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Song, C.-L.; Cao, X.-Y.; Zhou, Y.-Y. The phosphorus release pathways and their mechanisms driven by organic carbon and nitrogen in sediments of eutrophic shallow lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 572, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H. The Evolution of the Pearl River Estuary; China Ocean: Beijing, China, 1990; pp. 116–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Ding, S.; Ren, M.; Li, C.; Xu, S.; Sun, Q.; Xu, L. Enhanced DGT capability for measurements of multiple types of analytes using synergistic effects among different binding agents. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 446–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Sun, Q.; Xu, D.; Jia, F.; He, X.; Zhang, C. High-Resolution Simultaneous Measurements of Dissolved Reactive Phosphorus and Dissolved Sulfide: The First Observation of Their Simultaneous Release in Sediments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 8297–8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavery, P.S.; Oldham, C.E.; Ghisalberti, M. The use of Fick’s First Law for predicting porewater nutrient fluxes under diffusive conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2001, 15, 2435–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lap, B.Q.; Nam, N.H.; Anh, B.T.K.; Linh, T.T.T.; Quang, L.X.; Toan, V.D.; Hang, B.T.T.; Babel, S.; Phan, T.-T.-H. Monitoring Water Quality in Lien Son Irrigation System of Vietnam and Identification of Potential Pollution Sources by Using Multivariate Analysis. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2021, 232, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, K.; Lin, Z.; Ke, Z. Temporal and spatial distribution of dissolved oxygen in the Pearl River Estuary and adjacent coastal waters. Cont. Shelf Res. 2004, 24, 1935–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Jin, X.; Bu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Wu, F. Effects of particle size, organic matter and ionic strength on the phosphate sorption in different trophic lake sediments. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 128, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassink, J. The capacity of soils to preserve organic C and N by their association with clay and silt particles. Plant Soil 1997, 191, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raats, P.A.C.; Dewilligen, P.; Gerritse, R.G. Transport and fixation of phosphate in acid, homogeneous soils I. Physico-mathematical model. Agric. Environ. 1982, 7, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, P.; Hu, S.; Cai, H.; Yang, Q. Tidal regime shift in Lingdingyang Bay, the Pearl River Delta: An identification and assessment of driving factors. Hydrol. Process. 2020, 34, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Yu, R.; Liu, X.; Cao, Z.; Li, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhuang, S.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, L.; et al. Drivers of spatial and seasonal variations of CO2 and CH4 fluxes at the sediment water interface in a shallow eutrophic lake. Water Res. 2022, 222, 118916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Lin, W.; Wang, S.; Zhou, C. Spatial gradients and molecular transformations of DOM, DON and DOS in human impacted estuarine sediments. Environ. Int. 2024, 185, 108518. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, M.Y.; Dafforn, K.A.; Brown, M.V.; Johnston, E.L. Bacterial communities are sensitive indicators of contaminant stress. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 1029–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondergaard, M.; Jensen, P.J.; Jeppesen, E. Retention and Internal Loading of Phosphorus in Shallow, Eutrophic Lakes. Sci. World J. 2001, 1, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Dong, X.; Wang, M.; Wang, G. Sulfur cycling in freshwater sediments: A cryptic driving force of iron deposition and phosphorus mobilization. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 657, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Wang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, B.; Yu, J.; Cai, Y.; Yang, Z.; Liu, E.; Li, Q.; Yin, H. Water-level fluctuations regulate the availability and diffusion kinetics process of phosphorus at lake water–sediment interface. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Lu, Z.; Tobias, C.R.; Wang, Y.; Xiao, K.; Yu, Q.; Lin, J.; Huang, G.; Chen, N. Salt marsh expansion into estuarine mangrove mudflats reduces nitrogen removal capacity. CATENA 2023, 232, 107459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Lu, S.; Deng, Y.; Feng, C.; Chen, N.; Guo, H. Different forms of phosphorous transformation and release prediction with environment factor in sediments from Lake Dongting, China. Desalination Water Treat. 2021, 214, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, C.; Ding, S.; Yao, L.; Shen, Q.; Zhu, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, D. Dynamics of phosphorus–iron–sulfur at the sediment–water interface influenced by algae blooms decomposition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 300, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsev, S.; Tsandev, I.; Heureux, I.L.; Rancourt, D.G. Factors controlling long-term phosphorus efflux from lake sediments: Exploratory reactive-transport modeling. Chem. Geol. 2006, 234, 127–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Jia, J.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Bai, J. Seasonality and assembly of soil microbial communities in coastal salt marshes invaded by a perennial grass. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 331, 117247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Chen, W.; Sun, J.; Liu, L.; Huang, X. Spatial Variation in Bacterioplankton Communities in the Pearl River, South China: Impacts of Land Use and Physicochemical Factors. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, G.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Chen, S.; Deng, H.; Annalisa, O.-H. High sulfide production induced by algae decomposition and its potential stimulation to phosphorus mobility in sediment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 650, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Simon, P.N.; Liu, J.; Liu, L.; Dai, X.; Zhang, X.; Kuang, J.; Igarashi, Y.; Pan, X.; et al. Distinct Network Interactions in Particle-Associated and Free-Living Bacterial Communities during a Microcystis aeruginosa Bloom in a Plateau Lake. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freeman, E.C.; Creed, I.F.; Jones, B.; Bergström, A.-K. Global changes may be promoting a rise in select cyanobacteria in nutrient-poor northern lakes. Glob. Change Biol. 2020, 26, 4966–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smucker, N.J.; Beaulieu, J.J.; Nietch, C.T.; Young, J.L. Increasingly severe cyanobacterial blooms and deep water hypoxia coincide with warming water temperatures in reservoirs. Glob. Change Biol. 2021, 27, 2507–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.X.; Yu, P.; Li, R.W.; Huang, J.; Zhou, Z.; Hu, S.; Wang, Y.C.; Qiu, G.S. Plankton diversity and community characteristics in Danjiangkou Reservoir based on environmental DNA metabarcoding. J. Lake Sci. 2021, 33, 1650–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernhard, A.E.; Debbie, C.; James, M.M.; Field, K.G. Microbial community dynamics based on 16S rRNA gene profiles in a Pacific Northwest estuary and its tributaries. Fems Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 1, 115–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Jiao, N.; Cottrell, M.; Kirchman, D. Contribution of major bacterial groups to bacterial biomass production along a salinity gradient in the South China Sea. Aquat. Microb. Ecol. 2006, 43, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, M.; Lifang, W.; Guo, X.; Zhai, W.; Li, Q.; He, B.; Kao, S.-J. Nitrification and inorganic nitrogen distribution in a large perturbed river/estuarine system: The Pearl River Estuary, China. Biogeosciences 2008, 5, 1227–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mino, T.; Arun, V.; Tsuzuki, Y.; Matsuo, T. Effect of phosphorus accumulation on acetate metabolism in the biological phosphorus removal process. Biol. Phosphate Remov. Wastewaters 1987, 12, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De-Bashan, L.E.; Bashan, Y. Recent advances in removing phosphorus from wastewater and its future use as fertilizer (1997–2003). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4222–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Han, F.; Chen, S.; Zhou, W. Integrated application of phosphorus-accumulating bacteria and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria to achieve sustainable phosphorus management in saline soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 885, 163971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, B.; Strous, M.; Tegetmeyer, H.E. Microbial nitrate respiration—Genes, enzymes and environmental distribution. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 155, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, W.; Yang, A.; Mao, Y.; Gu, Y.; Zeng, L.; Du, H.; Shi, L.; Fang, H. Seasonal Distribution of Nutrient Salts and Microbial Communities in the Pearl River Delta. Water 2025, 17, 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060798
Huang Z, Wang J, Li W, Yang A, Mao Y, Gu Y, Zeng L, Du H, Shi L, Fang H. Seasonal Distribution of Nutrient Salts and Microbial Communities in the Pearl River Delta. Water. 2025; 17(6):798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060798
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Zhiwei, Jie Wang, Weijie Li, Aixiu Yang, Yupeng Mao, Yangliang Gu, Luping Zeng, Hongwei Du, Lei Shi, and Huaiyang Fang. 2025. "Seasonal Distribution of Nutrient Salts and Microbial Communities in the Pearl River Delta" Water 17, no. 6: 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060798
APA StyleHuang, Z., Wang, J., Li, W., Yang, A., Mao, Y., Gu, Y., Zeng, L., Du, H., Shi, L., & Fang, H. (2025). Seasonal Distribution of Nutrient Salts and Microbial Communities in the Pearl River Delta. Water, 17(6), 798. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060798





