Assessing the Risk of Internal Loading of Phosphorus from Drinking Reservoir Sediments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites
2.2. Sediment Composition
2.3. Phosphate Absorption Capacity
2.4. Orthophosphate in Overlying Water
3. Results
3.1. Sediment Composition
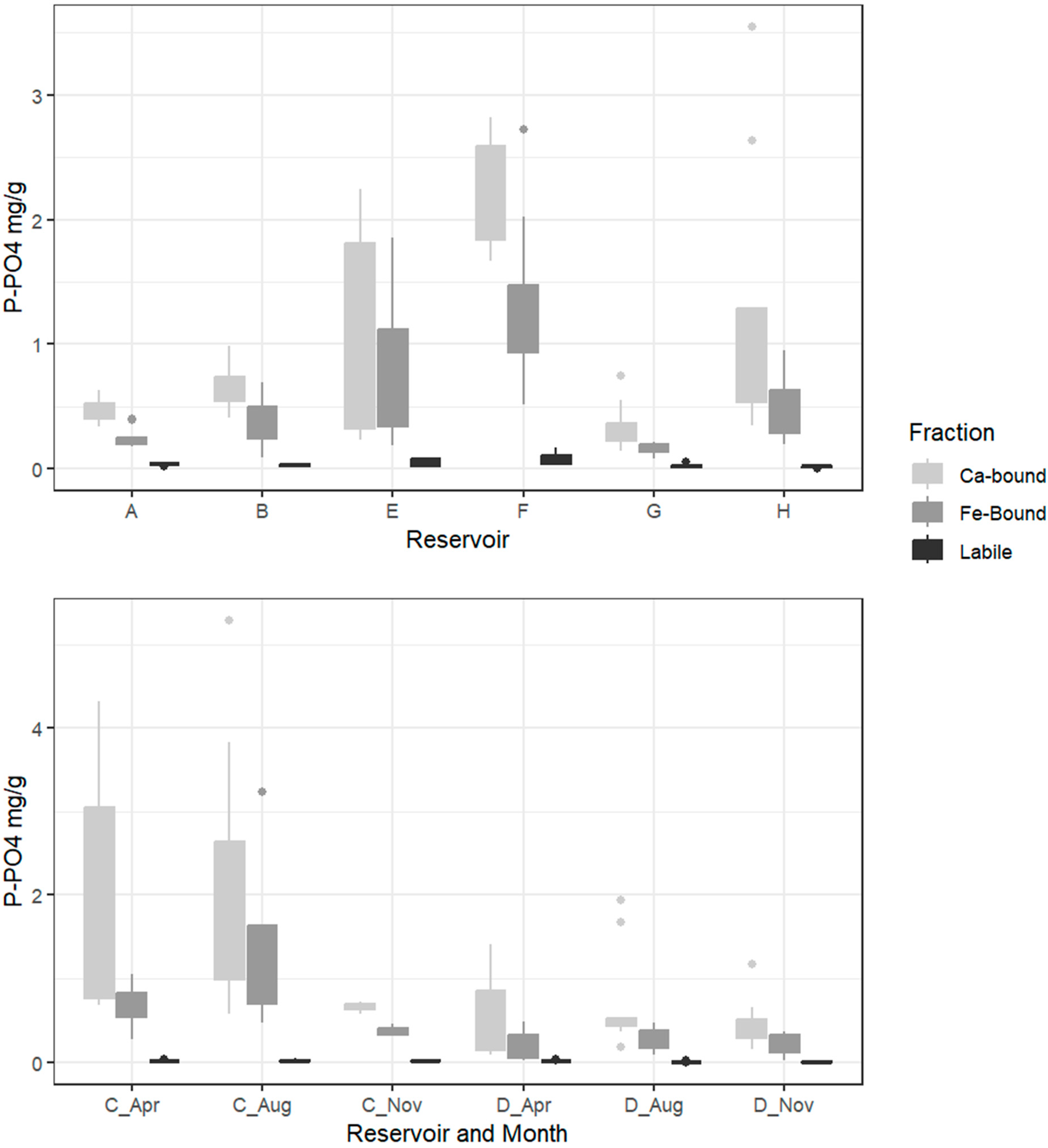
3.2. Phosphorus Fractions
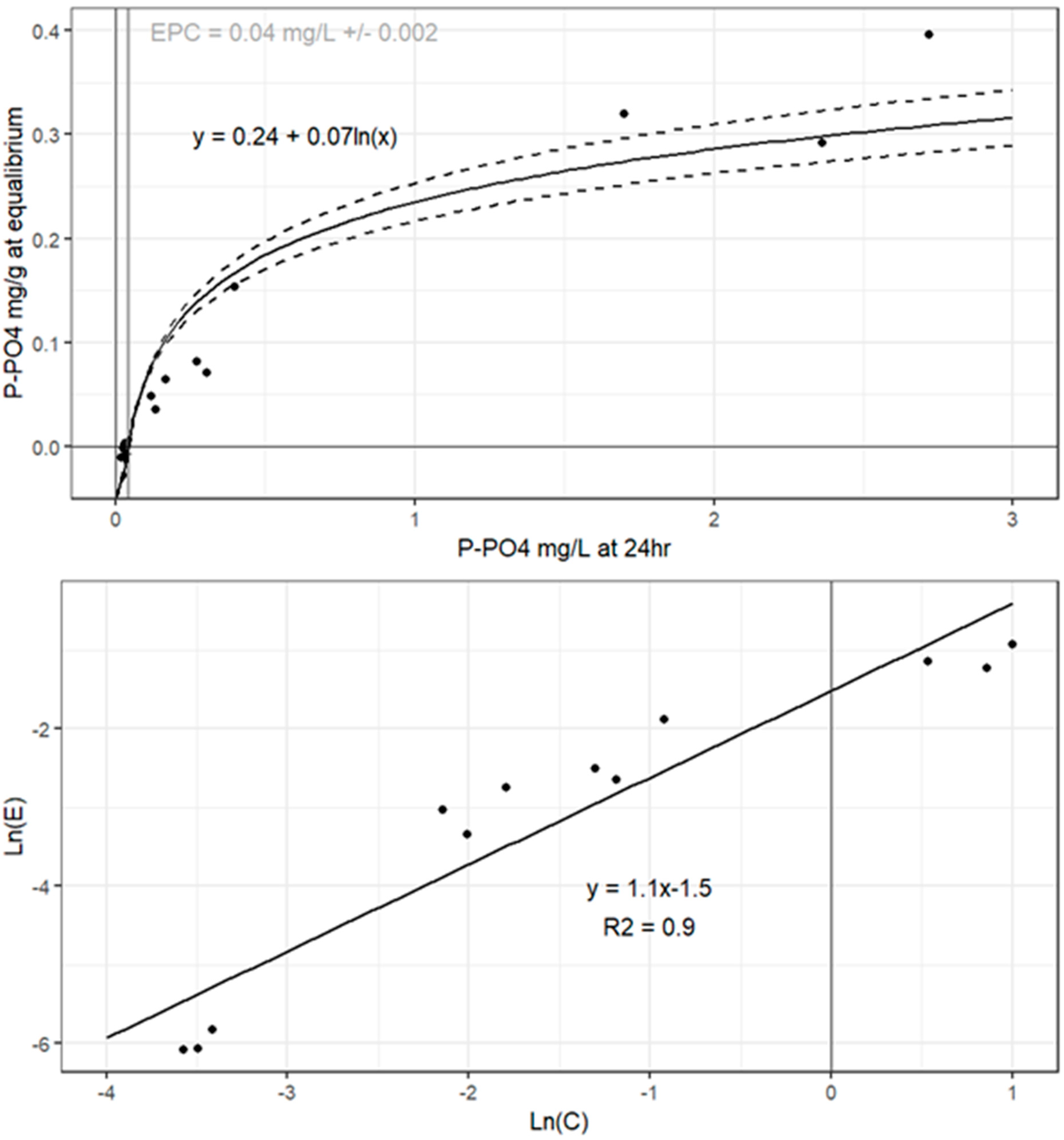
3.3. Phosphorus Absorption Capacity (PAC)
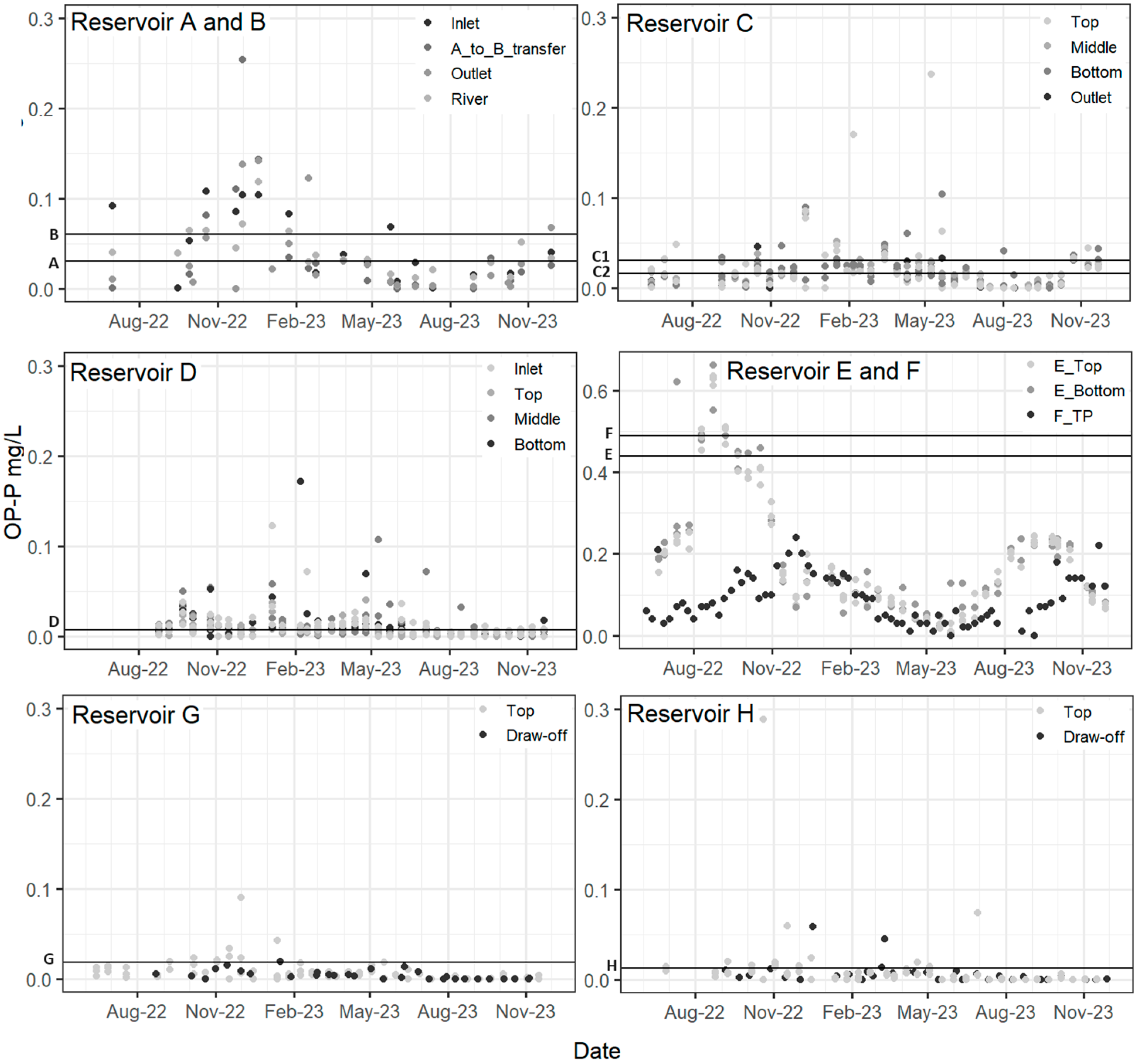
3.4. Orthophosphate (OP) and EPC
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Oliveira, M.; Machado, A.V. The Role of Phosphorus on Eutrophication: A Historical Review and Future Perspectives. Environ. Technol. Rev. 2013, 2, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnes, P.J.; Louise Heathwaite, A.; Spears, B.M.; Brownlie, W.J.; Elser, J.J.; Haygarth, P.M.; Macintosh, K.A.; Withers, P.J.A. Phosphorus and Water Quality. In Our Phosphorus Future; Brownlie, W.J., Sutton, M.A., Heal, K.V., Reay, D.S., Spears, B.M., Eds.; UK Centre for Ecology & Hydrology: Edinburgh, UK, 2022; pp. 1–23. [Google Scholar]
- Rittmann, B.E.; Mayer, B.; Westerhoff, P.; Edwards, M. Capturing the Lost Phosphorus. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 846–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordell, D.; Drangert, J.O.; White, S. The Story of Phosphorus: Global Food Security and Food for Thought. Glob. Environ. Change 2009, 19, 292–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, K.; Cordell, D.; Mavinic, D. A Brief History of Phosphorus: From the Philosopher’s Stone to Nutrient Recovery and Reuse. Chemosphere 2011, 84, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powers, S.M.; Tank, J.L.; Robertson, D.M. Control of Nitrogen and Phosphorus Transport by Reservoirs in Agricultural Landscapes. Biogeochemistry 2015, 124, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Wang, S.; Jin, X. Phosphorus Release in Response to PH Variation in the Lake Sediments with Different Ratios of Iron-Bound P to Calcium-Bound P. Chem. Speciat. Bioavailab. 2005, 17, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Choi, M.; Tanentzap, A.J.; Liu, J.; Jang, K.S.; Lennon, J.T.; Liu, Y.; Soininen, J.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Ecological Networks of Dissolved Organic Matter and Microorganisms under Global Change. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WFD UKTAG River Phosphorus UKTAG Method Statement; Water Framework Directive (WFD) United Kingdom Technical Advisory Group (UKTAG): Stirling, UK, 2013.
- Environment Agency. Phosphorus and Freshwater Eutrophication Pressure Narrative; Environment Agency: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rippey, B.; Campbell, J.; McElarney, Y.; Thompson, J.; Gallagher, M. Timescale of Reduction of Long-Term Phosphorus Release from Sediment in Lakes. Water Res. 2021, 200, 117283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Molen, D.T.; Boers, P.C.M. Influence of Internal Loading on Phosphorus Concentration in Shallow Lakes before and after Reduction of the External Loading. Hydrobiologia 1994, 275–276, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boström, B.; Andersen, J.M.; Fleischer, S.; Jansson, M. Exchange of Phosphorus across the Sediment-Water Interface. Hydrobiologia 1988, 170, 229–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penn, M.R.; Auer, M.T.; Doerr, S.M.; Driscoll, C.T.; Brooks, C.M.; Effler, S.W. Seasonality in Phosphorus Release Rates from the Sediments of a Hypereutrophic Lake under a Matrix of PH and Redox Conditions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, A.; Reddy, K.R. Role of Eh and PH on Phosphorus Geochemistry in Sediments of Lake Okeechobee, Florida. J. Environ. Qual. 1994, 23, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, O.; Nürnberg, G.; Horppila, J.; Haldna, M.; Niemistö, J. Redox-Related Release of Phosphorus from Sediments in Large and Shallow Lake Peipsi: Evidence from Sediment Studies and Long-Term Monitoring Data. J. Great Lakes Res. 2020, 46, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, R.G.; Underwood, G.J.C. The Potential for Phosphorus Release across the Sediment-Water Interface in an Eutrophic Reservoir Dosed with Ferric Sulphate. Water Res. 2001, 35, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Redshaw, C.J.; Mason, C.F.; Hayes, C.R.; Roberts, R.D. Factors Influencing Phosphate Exchange across the Sediment-Water Interface of Eutrophic Reservoirs. Hydrobiologia 1990, 192, 233–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Sun, L.; Qin, B.; Wu, T.; Shen, X.; Wang, Y. Characteristics of Sediment Resuspension in Lake Taihu, China: A Wave Flume Study. J. Hydrol. 2018, 561, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.C.; Rydin, E. Lake Trophic Status Can Be Determined by the Depth Distribution of Sediment Phosphorus. Limnol. Ocean. 2011, 56, 2051–2063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Yang, P.; Geng, J.; Yin, H.; Chen, K. Sediment Internal Nutrient Loading in the Most Polluted Area of a Shallow Eutrophic Lake (Lake Chaohu, China) and Its Contribution to Lake Eutrophication. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 262, 114292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Xu, X.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, P.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Lu, X.; Zhang, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Seasonal Pattern of Nutrient Limitation in a Eutrophic Lake and Quantitative Analysis of the Impacts from Internal Nutrient Cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2019, 53, 13675–13686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, S.E.; Taylor, C.H.; Bell, V.; Bellamy, T.R.; Hooper, A.S.; Taylor, H.; Jouault, M.; Kille, P.; Perkins, R.G. Impact of Copper Sulphate Treatment on Cyanobacterial Blooms and Subsequent Water Quality Risks. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 366, 121828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.; Baird, R.; Eaton, A.; Clesceri, L. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Water Environment Federation: Alexandria, VA, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hwang, C.P.; Lackie, T.H.; Huang, P.M. Adsorption of Inorganic Phosphorus by Lake Sediments. J. Water Pollut. Control Fed. 1976, 26, 2754–2760. [Google Scholar]
- Spears, B.M.; Meis, S.; Anderson, A.; Kellou, M. Comparison of Phosphorus (P) Removal Properties of Materials Proposed for the Control of Sediment p Release in UK Lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 442, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, A.; Tang, H.; Wang, D. Phosphorus Adsorption on Natural Sediments: Modeling and Effects of PH and Sediment Composition. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1245–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Gunten, K.; Trew, D.; Smerdon, B.; Alessi, D.S. Natural Controls on Phosphorus Concentrations in Small Lakes in Central Alberta, Canada. Can. Water Resour. J. 2023, 48, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.S.; Barthod, B.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zastepa, A.; Liu, X.; Dittrich, M. Geochemical Controls on Internal Phosphorus Loading in Lake of the Woods. Chem. Geol. 2020, 558, 119873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moss, B.; Stansfield, J.; Irvine, K.; Perrow, M.; Phillips, G. Progressive Restoration of a Shallow Lake: A 12-Year Experiment in Isolation, Sediment Removal and Biomanipulation. J. Appl. Ecol. 1996, 33, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, D.I.; Shapiro, J. Nutrient Reduction by Biomanipulation: An Unexpected Phenomenon and Its Possible Cause. SIL Proc. 1922–2010 1984, 22, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, A.; Kubečka, J. Land/Water Ecotone Effects in Reservoirs on the Fish Fauna. Hydrobiologia 1995, 303, 11–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, L.D.; Brockbank, N.; Austin, D. To Mix or Not to Mix? A Holistic Approach to Stratification-Preserving and Destratification Aeration of Drinking-Water Supply Reservoirs. Water Res. 2024, 261, 121974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavin, E.I.; Wain, D.J.; Bryant, L.D.; Amani, M.; Perkins, R.G.; Blenkinsopp, C.; Simoncelli, S.; Hurley, S. The Effects of Surface Mixers on Stratification, Dissolved Oxygen, and Cyanobacteria in a Shallow Eutrophic Reservoir. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehman, J.T. Understanding the Role of Induced Mixing for Management of Nuisance Algal Blooms in an Urbanized Reservoir. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2014, 30, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santschi, P.; Höhener, P.; Benoit, G.; Buchholtz-ten Brink, M. Chemical Processes at the Sediment-Water Interface. Mar. Chem. 1990, 30, 269–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, T.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. Pollutant Removal Performance and Microbial Enhancement Mechanism by Water-Lifting and Aeration Technology in a Drinking Water Reservoir Ecosystem. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 709, 135848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Austin, D.; Scharf, R.; Chen, C.F.; Bode, J. Hypolimnetic Oxygenation and Aeration in Two Midwestern USA Reservoirs. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2019, 35, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Huang, T.; Mao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, K.; Wen, G.; Lv, X.; Deng, L. Controlling Reduced Iron and Manganese in a Drinking Water Reservoir by Hypolimnetic Aeration and Artificial Destratification. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 685, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirol, A.P.; Morales-Williams, A.M.; Braun, D.C.; Marti, C.L.; Pierson, O.E.; Wagner, K.J.; Schroth, A.W. Linking Sediment and Water Column Phosphorus Dynamics to Oxygen, Temperature, and Aeration in Shallow Eutrophic Lakes. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR034813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavoni, E.; Floreani, F.; Petranich, E.; Crosera, M.; Marussi, G.; Acquavita, A.; Pisoni, C.; Klun, K.; Faganeli, J.; Covelli, S. Effect of Forced Aeration on the Biogeochemical Cycle of Nutrients and Metal (Loid) s as a Remedy for Hypoxia in a Permanently Stratified Estuary (Gulf of Trieste, Northern Adriatic Sea). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2024, 205, 116632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammeorg, O.; Nürnberg, G.; Niemistö, J.; Haldna, M.; Horppila, J. Internal Phosphorus Loading Due to Sediment Anoxia in Shallow Areas: Implications for Lake Aeration Treatments. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 82, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, B.; Bryant, L.D.; Matzinger, A.; Wüest, A. Hypolimnetic Oxygen Depletion in Eutrophic Lakes. Env. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9964–9971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albay, M.; Akcaalan, R.; Aykulu, G.; Tufekci, H.; Beattie, K.A.; Codd, G.A. Occurrence of Toxic Cyanobacteria before and after Copper Sulphate Treatment in a Water Reservoir, Istanbul, Turkey. Arch. Hydrobiol. Suppl. Algol. Stud. 2009, 109, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Jeune, A.H.; Charpin, M.; Deluchat, V.; Briand, J.F.; Lenain, J.F.; Baudu, M.; Amblard, C. Effect of Copper Sulphate Treatment on Natural Phytoplanktonic Communities. Aquat. Toxicol. 2006, 80, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, N.; Ma, B.; Liu, X.; Niu, L.; Yang, F.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Effects of Copper Sulfate Algaecide on the Cell Growth, Physiological Characteristics, the Metabolic Activity of Microcystis Aeruginosa and Raw Water Application. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 445, 130604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Water Company | Reservoir | Sediment Sampling Dates | Water Column Sampling Depth, m |
|---|---|---|---|
| Company 1 | Reservoir A | February 24 | 1.4–1.8 |
| Company 1 | Reservoir B | February 24 | 5.9–6.0 |
| Company 1 | Reservoir C | April, August, November 23 | 7.0–14.0 |
| Company 2 | Reservoir D | April, August, November 23 | 8.5–11.5 |
| Company 3 | Reservoir E | May 23 | 4.0–10.0 |
| Company 3 | Reservoir F | May 23 | 4.0–16.0 |
| Company 4 | Reservoir G | June 23 | 9.0–23.0 |
| Company 4 | Reservoir H | June 23 | 12.0–24.0 |
| Reservoir | Fe, mg/kg, ±se | Water Content, %w/w, ±se |
|---|---|---|
| Reservoir A | 6600 ± 1200 | 65 ± 0.66 |
| Reservoir B | Not measured | 62 ± 2.71 |
| Reservoir C | 35,700 ± 1500 | 80 ± 1.28 |
| Reservoir D | 33,400 ± 2050 | 83 ± 1.41 |
| Reservoir E | 52,700 ± 1550 | 82 ± 0.31 |
| Reservoir F | 27,200 ± 2100 | 86 ± 0.34 |
| Reservoir G | 27,950 ± 1950 | 81 ± 0.44 |
| Reservoir H | 36,450 ± 2650 | 77 ± 0.20 |
| Reservoir | Month | EPC, mg P-PO4/L ± se | Freundlich, E | Freundlich, r2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reservoir A | February | 0.03 ± 0.002 | 0.13C0.89 | 0.88 |
| Reservoir B | February | 0.06 ± 0.002 | 0.09C1.09 | 0.80 |
| Reservoir C | April | 0.03 ± 0.001 | 0.22C0.95 | 0.78 |
| Reservoir C | August | 0.016 ± 0.003 | 0.94C1.04 | 0.63 |
| Reservoir C | November | 0.03 ± 0.001 | 0.22C1.10 | 0.90 |
| Reservoir D | April | 0.007 ± 0.0004 | 0.37C0.81 | 0.46 |
| Reservoir D | August | Not well defined | 0.59C0.47 | 0.22 |
| Reservoir D | November | 0.007 ± 0.00005 | 0.79C0.82 | 0.52 |
| Reservoir E | May | 0.44 ± 0.02 | 0.03C0.99 | 0.67 |
| Reservoir F | May | 0.49 ± 0.02 | 0.07C1.11 | 0.68 |
| Reservoir G | June | 0.018 ± 0.003 | 0.095C0.62 | 0.86 |
| Reservoir H | June | 0.013 ± 0.0006 | 0.28C0.72 | 0.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Watson, S.E.; Bell, V.; Kille, P.; Rand, J.M.; Bryant, L.D.; Perkins, R.G. Assessing the Risk of Internal Loading of Phosphorus from Drinking Reservoir Sediments. Water 2025, 17, 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060799
Watson SE, Bell V, Kille P, Rand JM, Bryant LD, Perkins RG. Assessing the Risk of Internal Loading of Phosphorus from Drinking Reservoir Sediments. Water. 2025; 17(6):799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060799
Chicago/Turabian StyleWatson, Sophie E., Veronica Bell, Peter Kille, James M. Rand, Lee D. Bryant, and Rupert G. Perkins. 2025. "Assessing the Risk of Internal Loading of Phosphorus from Drinking Reservoir Sediments" Water 17, no. 6: 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060799
APA StyleWatson, S. E., Bell, V., Kille, P., Rand, J. M., Bryant, L. D., & Perkins, R. G. (2025). Assessing the Risk of Internal Loading of Phosphorus from Drinking Reservoir Sediments. Water, 17(6), 799. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17060799






