Exploratory Analysis on the Chemical Composition of Aquatic Macrophytes in a Water Reservoir—Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Collection and Analysis
2.2. Statistical and Machine Learning Analysis
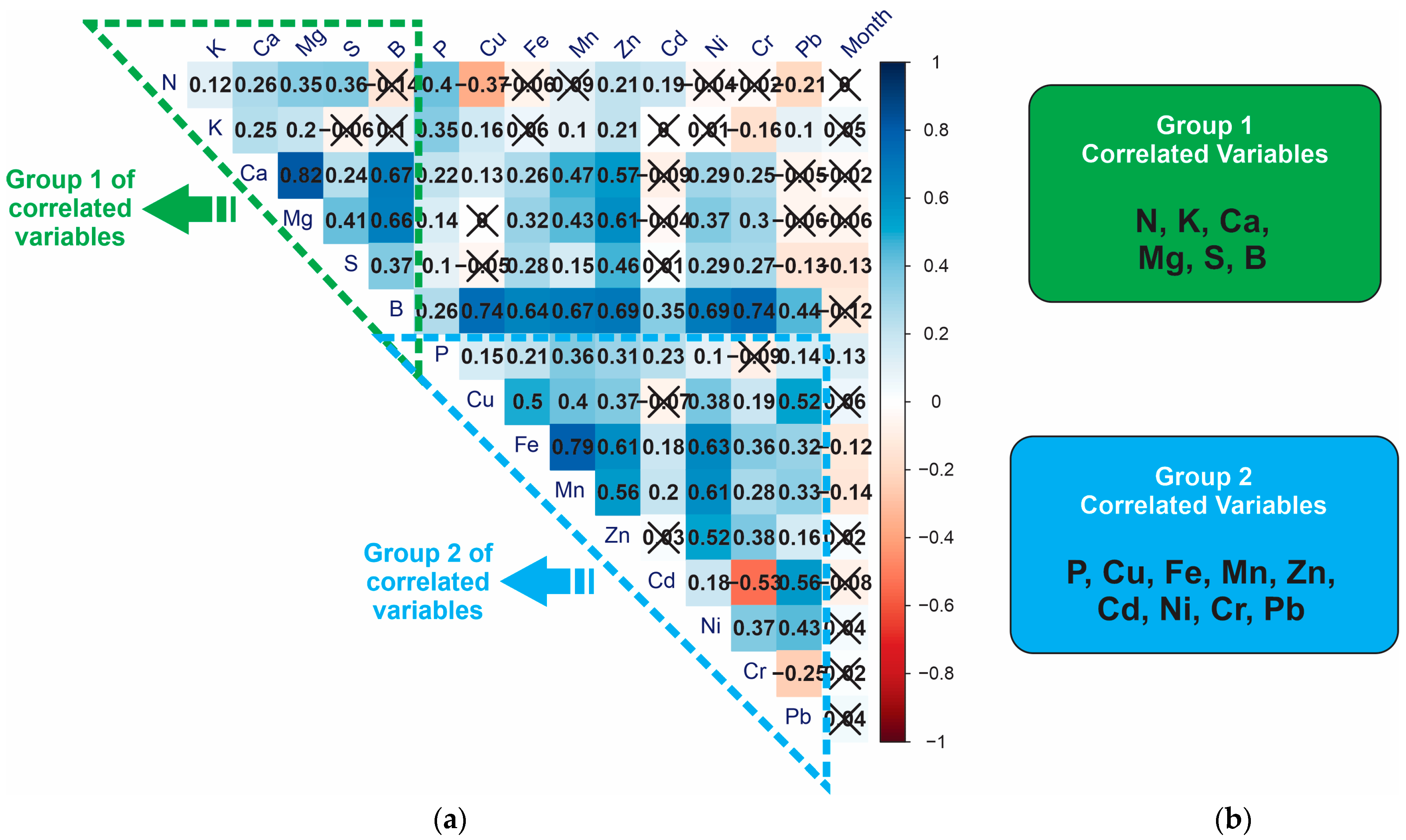
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Species | N (g/kg) | P (g/kg) | K (g/kg) | Ca (g/kg) | Mg (g/kg) | S (g/kg) | B (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRASU | 24.1 ± 7.9 | 2.4 ± 0.8 | 44.3 ± 13.7 | 5.2 ± 3.9 | 2.7 ± 1.4 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 5.5 ± 2 |
| ECHPO | 13.2 ± 4.3 | 1.5 ± 0.6 | 46.6 ± 22.3 | 2.8 ± 1.1 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 2.7 ± 0.8 | * |
| EICAZ | 21.1 ± 7.6 | 2.8 ± 0.9 | 64.3 ± 15.9 | 13.9 ± 4.2 | 3 ± 0.4 | 1.6 ± 0.6 | 18.7 ± 3.1 |
| EICCR | 24.1 ± 5.8 | 2.4 ± 0.9 | 51.1 ± 11.9 | 20.5 ± 2.5 | 6.3 ± 0.7 | 2.6 ± 0.7 | 24.2 ± 5.8 |
| ELDDE | 28.6 ± 6.7 | 4.1 ± 1.5 | 47.9 ± 20.6 | 15.9 ± 9 | 3.3 ± 1.1 | 2.9 ± 1 | 31.9 ± 5.9 |
| ENYAN | 37.8 ± 1.6 | 3.2 ± 0.3 | 56.4 ± 0.7 | 21 ± 2.3 | 6.6 ± 0.8 | 3.2 ± 0.1 | 29 ± 4.7 |
| MYRAQ | 24.5 ± 16.3 | 3.1 ± 1.2 | 44.9 ± 22.2 | 17.7 ± 5.2 | 3.9 ± 0.9 | 1.9 ± 0.7 | * |
| PANRI | 21.5 ± 8.1 | 2.4 ± 1.1 | 29.6 ± 12.7 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | 1.7 ± 0.4 | 2.1 ± 0.6 | 5.9 ± 2.5 |
| PASRE | 24.2 ± 2.6 | 3.6 ± 1 | 76.2 ± 11.2 | 6.5 ± 2 | 3.7 ± 0.7 | 3.1 ± 0.1 | * |
| PIIST | 25.5 ± 5.2 | 2.8 ± 0.7 | 53.9 ± 13.7 | 34.8 ± 12 | 8.2 ± 2 | 2.8 ± 1.1 | 50.9 ± 13.6 |
| POFCO | 20 ± 8.6 | 3.7 ± 1.1 | 49.8 ± 16.1 | 9.1 ± 2.4 | 2.3 ± 0.5 | 1.1 ± 0.2 | * |
| POLFE | 18.8 ± 5.5 | 2.6 ± 0.9 | 35.5 ± 15.2 | 15.5 ± 8.9 | 4.2 ± 1 | 2.2 ± 0.7 | * |
| POLLA | 26.8 ± 8.3 | 2.3 ± 0.9 | 49.3 ± 21.5 | 12.9 ± 4.2 | 4.5 ± 1.4 | 2 ± 0.5 | 24 ± 3.7 |
| SAGMO | 19.1 ± 8.2 | 4.6 ± 1.4 | 66.3 ± 30.5 | 8.8 ± 3.1 | 3.2 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.7 | * |
| SAVAU | 21.7 ± 4.8 | 2.5 ± 0.8 | 20.4 ± 6.8 | 11.4 ± 4.9 | 3.8 ± 0.8 | 2.7 ± 0.5 | 42.2 ± 14.5 |
| TYHDO | 16.7 ± 6 | 2.3 ± 0.8 | 38 ± 20.7 | 11.9 ± 1.9 | 3.3 ± 0.8 | 1.7 ± 0.7 | * |
| Species | Cu (mg/kg) | Fe (mg/kg) | Mn (mg/kg) | Zn (mg/kg) | Cd (mg/kg) | Ni (mg/kg) | Cr (mg/kg) | Pb (mg/kg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BRASU | 14.8 ± 11.7 | 1455.4 ± 1963.9 | 345.3 ± 450.9 | 67.2 ± 25.3 | 9.8 ± 9.7 | 5 ± 2.1 | 3.6 ± 3.5 | 15.5 ± 8.5 |
| ECHPO | 27.4 ± 12.2 | 6433.9 ± 7343 | 575.5 ± 602.3 | 76 ± 18.9 | 8.9 ± 10.1 | 9.7 ± 4.3 | 6.7 ± 6.4 | 27.1 ± 10.5 |
| EICAZ | 25.7 ± 12.9 | 4153.7 ± 6347.1 | 792.8 ± 455.3 | 101 ± 35.1 | 8.7 ± 9 | 7.2 ± 4.2 | 3.6 ± 2.9 | 22.3 ± 9.9 |
| EICCR | 14.9 ± 3.9 | 6062.9 ± 3886.2 | 2437.2 ± 2233.3 | 175 ± 122 | 1.9 ± 0.5 | 11.4 ± 5 | 9.3 ± 4.8 | 11 ± 5.2 |
| ELDDE | 34.6 ± 11 | 9586.5 ± 8775.5 | 7968.7 ± 7291.4 | 454.4 ± 293.7 | 32 ± 45.8 | 19.9 ± 7.9 | 10.4 ± 13 | 29.2 ± 20.5 |
| ENYAN | 21.3 ± 1.4 | 4659.3 ± 1766.9 | 1372.3 ± 480.8 | 240 ± 31.6 | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 15.7 ± 1.8 | 12.8 ± 3.3 | 15.9 ± 1.8 |
| MYRAQ | 30.1 ± 13.3 | 9004.3 ± 14,944.3 | 2039.3 ± 919.5 | 127.5 ± 74.9 | 30.7 ± 57.7 | 12.5 ± 10.2 | 10.4 ± 11.1 | 37.6 ± 28.3 |
| PANRI | 12.8 ± 11.3 | 1477.9 ± 1925 | 255.8 ± 173.7 | 48.3 ± 17.4 | 12.2 ± 16.2 | 5.6 ± 3.2 | 5.8 ± 5.6 | 16.9 ± 11 |
| PASRE | 39.5 ± 8.5 | 8400 ± 1449.6 | 1862.5 ± 506.9 | 135.3 ± 32.5 | 13.8 ± 2.8 | 15.5 ± 2.3 | 2 ± 1.3 | 37.5 ± 8 |
| PIIST | 18.2 ± 8.1 | 7054.2 ± 4021.9 | 1985.6 ± 1087.5 | 183.6 ± 81 | 2.3 ± 2.5 | 14.3 ± 5.6 | 13.7 ± 4 | 15.6 ± 7.7 |
| POFCO | 22.9 ± 10.5 | 1605.8 ± 1301 | 1401.1 ± 465.8 | 43.2 ± 19.8 | 10.7 ± 12.1 | 6.9 ± 4 | 5.2 ± 5.8 | 26.1 ± 17.2 |
| POLFE | 28.4 ± 9.9 | 7857.7 ± 5709.4 | 1331.3 ± 726.9 | 121.2 ± 43.9 | 27.4 ± 37.8 | 8.8 ± 5 | 8.2 ± 7.3 | 23.8 ± 10.3 |
| POLLA | 15.7 ± 11.9 | 1585.9 ± 1911.8 | 729.1 ± 569.2 | 93.8 ± 35.8 | 11.9 ± 20.4 | 5.7 ± 2.8 | 3.2 ± 2.2 | 17.4 ± 13.3 |
| SAGMO | 28.4 ± 10.5 | 12,555.7 ± 12,360.5 | 1211 ± 562.5 | 104.7 ± 40.8 | 15.8 ± 15.7 | 10.6 ± 8 | 5.8 ± 8.7 | 29.1 ± 15.5 |
| SAVAU | 24.2 ± 6.6 | 18,513.7 ± 9903.9 | 2727.2 ± 1640 | 169.8 ± 113.9 | 17.2 ± 34.7 | 18.2 ± 9.4 | 19.7 ± 12.6 | 24.3 ± 24.6 |
| TYHDO | 28.4 ± 11 | 4745.7 ± 7746.7 | 1687.5 ± 1661.8 | 69.8 ± 40.9 | 32.5 ± 44 | 8.9 ± 5.9 | 1.5 ± 0.8 | 29.6 ± 18.8 |
References
- Oliver, S.; Corburn, J.; Ribeiro, H. Challenges Regarding Water Quality of Eutrophic Reservoirs in Urban Landscapes: A Mapping Literature Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitelli, R.A.; Pitelli, R.L.C.M.; Filho, W.R.C.; da Silva Rocha, R.J.; Cruz, F.; Neto, J.J. Avaliação das concentrações de nutrientes e metais pesados nas principais macrófitas aquáticas do reservatório de Santana—RJ no período de três anos. Semioses 2018, 12, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.E.; Consuegra, S.; Börger, L.; Jones, J.; Garcia de Leaniz, C. Impacts of Artificial Barriers on the Connectivity and Dispersal of Vascular Macrophytes in Rivers: A Critical Review. Freshw. Biol. 2020, 65, 1165–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyenje, P.M.; Foppen, J.W.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Kulabako, R.; Muwanga, A. Eutrophication and Nutrient Release in Urban Areas of Sub-Saharan Africa—A Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytyqi, P.; Czikkely, M.; Shala-Abazi, A.; Fetoshi, O.; Ismaili, M.; Hyseni-Spahiu, M.; Ymeri, P.; Kabashi-Kastrati, E.; Millaku, F. Macrophytes as Biological Indicators of Organic Pollution in the Lepenci River Basin in Kosovo. J. Freshw. Ecol. 2020, 35, 105–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomaz, S.M.; da Cunha, E.R. The Role of Macrophytes in Habitat Structuring in Aquatic Ecosystems: Methods of Measurement, Causes and Consequences on Animal Assemblages’ Composition and Biodiversity. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2010, 22, 218–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- do Nascimento Filho, S.L.; Gama, W.A.; do Nascimento Moura, A. Effect of the Structural Complexity of Aquatic Macrophytes on Epiphytic Algal, Macroinvertebrates, and Their Interspecific Relationships. Aquat. Sci. 2021, 83, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, A.K.; Sharma, M.; Navneet, S. A Review on Impact of Water Pollution on Aquatic Ecosystem. In Current Research and Innovations in Life Sciences; JPS Scientific Publications: Olaipadi, India, 2021; pp. 129–145. ISBN 978-81-950475-3-6. [Google Scholar]
- Dhir, B.; Sharmila, P.; Saradhi, P.P. Potential of Aquatic Macrophytes for Removing Contaminants from the Environment. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 754–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herath, I.; Vithanage, M. Phytoremediation in Constructed Wetlands. In Phytoremediation: Management of Environmental Contaminants; Ansari, A.A., Gill, S.S., Gill, R., Lanza, G.R., Newman, L., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 2, pp. 243–263. ISBN 978-3-319-10969-5. [Google Scholar]
- Kochi, L.Y.; Freitas, P.L.; Maranho, L.T.; Juneau, P.; Gomes, M.P. Aquatic Macrophytes in Constructed Wetlands: A Fight against Water Pollution. Sustainability 2020, 12, 9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Espinosa, C.; Sauvage, S.; Al Bitar, A.; Green, P.A.; Vörösmarty, C.J.; Sánchez-Pérez, J.M. Denitrification in Wetlands: A Review towards a Quantification at Global Scale. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivaisi, A.K. The Potential for Constructed Wetlands for Wastewater Treatment and Reuse in Developing Countries: A Review. Ecol. Eng. 2001, 16, 545–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, A.C.D.; dos Santos, A.M.; dos Santos, F.S.; Pereira, A.C.C.; Sobrinho, N.M.B.A. Mecanismos de Respostas das Plantas à Poluição por Metais Pesados: Possibilidade de Uso de Macrófitas para Remediação de Ambientes Aquáticos Contaminados. Rev. Virtual Química 2016, 8, 262–276. [Google Scholar]
- Poveda, J. The Use of Freshwater Macrophytes as a Resource in Sustainable Agriculture. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 369, 133247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, S.B.; Ahmad, A.; Said, N.S.M.; Imron, M.F.; Abdullah, S.R.S.; Othman, A.R.; Purwanti, I.F.; Hasan, H.A. Macrophytes as Wastewater Treatment Agents: Nutrient Uptake and Potential of Produced Biomass Utilization toward Circular Economy Initiatives. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 790, 148219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayanthan, S.; Hasan, H.A.; Abdullah, S.R.S. Floating Aquatic Macrophytes in Wastewater Treatment: Toward a Circular Economy. Water 2024, 16, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naiman, R.J.; Décamps, H.; UNESCO. The Ecology and Management of Aquatic-Terrestrial Ecotones; Naiman, R.J., Décamps, H., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1990; ISBN 978-92-3-102668-3. [Google Scholar]
- Pitelli, R.L.C.M.; Ferraudo, A.S.; Pitelli, A.M.C.M.; Pitelli, R.A.; Velini, E.D. Utilização de análise multivariada e redes neurais artificiais na determinação do comportamento de colonização de populações de macrófitas aquáticas no reservatório de Santana. Planta Daninha 2009, 27, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witten, I.H.; Frank, E.; Hall, M.A.; Pal, C.J. Data Mining: Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques, 4th ed.; Morgan Kaufmann: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016; ISBN 978-0-12-804291-5. [Google Scholar]
- Fox, J.; Marquez, M.M.; Bouchet-Valat, M. Rcmdr: R. Commander. Available online: https://github.com/RCmdr-Project/rcmdr (accessed on 10 February 2005).
- Fox, J. Using the R Commander: A Point-and-Click Interface for R; Chapman and Hall/CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Lê, S.; Josse, J.; Husson, F. FactoMineR: An R Package for Multivariate Analysis. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 25, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paoletti, M.; Camiciottoli, G.; Meoni, E.; Bigazzi, F.; Cestelli, L.; Pistolesi, M.; Marchesi, C. Explorative Data Analysis Techniques and Unsupervised Clustering Methods to Support Clinical Assessment of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) Phenotypes. J. Biomed. Inform. 2009, 42, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delimiro Visbal-Cadavid, A.M.-M. Use of Factorial Analysis of Mixed Data (FAMD) and Hierarchical Cluster Analysis on Principal Component (HCPC) for Multivariate Analysis of Academic Performance of Industrial Engineering Programs. J. Southwest. Jiaotong Univ. 2020, 55, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, C.R.; Millman, K.J.; van der Walt, S.J.; Gommers, R.; Virtanen, P.; Cournapeau, D.; Wieser, E.; Taylor, J.; Berg, S.; Smith, N.J.; et al. Array Programming with NumPy. Nature 2020, 585, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karim, A.A.; Kumar, M.; Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Kumar, S.; Ray, A.; Dhal, N.K. Enrichment of Primary Macronutrients in Biochar for Sustainable Agriculture: A Review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 52, 1449–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidhuber, J.; Sur, P.; Fay, K.; Huntley, B.; Salama, J.; Lee, A.; Cornaby, L.; Horino, M.; Murray, C.; Afshin, A. The Global Nutrient Database: Availability of Macronutrients and Micronutrients in 195 Countries from 1980 to 2013. Lancet Planet. Health 2018, 2, E353–E368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quilliam, R.S.; van Niekerk, M.A.; Chadwick, D.R.; Cross, P.; Hanley, N.; Jones, D.L.; Vinten, A.J.A.; Willby, N.; Oliver, D.M. Can Macrophyte Harvesting from Eutrophic Water Close the Loop on Nutrient Loss from Agricultural Land? J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 152, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Liu, W.-H.; Liu, C.-X.; Sun, P.; Zeng, Y.-P.; Gao, Y.-Y.; Wang, H.-F.; Zeng, R.J. Enhancing Waste Management and Nutrient Recovery: Preparation of Adsorption-Type Sludge-Biochar Value-Added Fertilizer from Sewage Sludge and Pistia stratiotes. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 429, 139642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matache, A.; Vanghele, N.A.; Matache, M.G.; Petre, A.A. Valorization on the Energy Potential of Pistia Stratiotes in Sustainable Agriculture-Review. E3S Web Conf. 2021, 286, 02002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, M.W.; Sholihah, A.; Sugianto, A. Pistia Stratiotes Utilization to Improve the Straw Compost Quality. J. Ecol. Eng. 2022, 23, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dantzig, G.B. The Diet Problem. Interfaces 1990, 20, 1–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahourag, A.; El Moutaouakil, K.; Cheggour, M.; Chellak, S.; Baizri, H. Multiobjective Optimization to Optimal Moroccan Diet Using Genetic Algorithm. Int. J. Eng. Model. 2023, 36, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munford, A.G. The Use of Iterative Linear Programming in Practical Applications of Animal Diet Formulation. Math. Comput. Simul. 1996, 42, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, K.H.; Shiker, M.A.K. Using a Linear Programming Approach for Modeling the Optimal Diet Problem to Help Treat Hypertension. J. Surv. Fish. Sci. 2023, 10, 668–675. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Han, R.; Song, K.; Zhou, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, Q. Eutrophication Triggers the Shift of Nutrient Absorption Pathway of Submerged Macrophytes: Implications for the Phytoremediation of Eutrophic Waters. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 239, 376–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carignan, R.; Kalff, J. Phosphorus Sources for Aquatic Weeds: Water or Sediments? Science 1980, 207, 987–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mgobozi, V.; Afolayan, A.J.; Otunola, G.A. Heavy Metal Uptake Potential of Egeria densa (Plach) Casp. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 103, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, F.G.; Mielke, K.C.; da Silva Brochado, M.G.; Mendes, K.F.; Tornisielo, V.L. Potential of Egeria densa and Pistia stratiotes for the Phytoremediation of Water Contaminated with Saflufenacil. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2021, 56, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo Páez, A.C.; Narváez-Flórez, S.; Mosquera Vivas, E.S.; Calvo Saad, M.J. Evaluation of the Biostability of Elodea (Egeria densa) and Orange Peel as Bioadsorbent Materials for Pb (II) and Cr (III) in Solution. Ing. E Investig. 2023, 43, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.-L.; Li, J.; Chen, M.; An, R.-D. Comparative Study on the Bioaccumulation of Lead, Cadmium and Nickel and Their Toxic Effects on the Growth and Enzyme Defence Strategies of a Heavy Metal Accumulator, Hydrilla verticillata (L.f.) Royle. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 9853–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Bharti, S.K.; Kumar, S.; Barman, S.C.; Kumar, N. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals and Pesticides Present in Water Using Aquatic Macrophytes. In Phyto and Rhizo Remediation; Arora, N.K., Kumar, N., Eds.; Microorganisms for Sustainability; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 89–119. ISBN 978-981-329-664-0. [Google Scholar]
- Abdallah, M.A.M. Phytoremediation of Heavy Metals from Aqueous Solutions by Two Aquatic Macrophytes, Ceratophyllum demersum and Lemna gibba L. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 1609–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şentürk, İ.; Eyceyurt Divarcı, N.S.; Öztürk, M. Phytoremediation of Nickel and Chromium-Containing Industrial Wastewaters by Water Lettuce (Pistia stratiotes). Int. J. Phytorem. 2023, 25, 550–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnik, P.M.; Zubenko, I.B. Role of Bottom Sediments in the Secondary Pollution of Aquatic Environments by Heavy-Metal Compounds. Lakes Reserv. Sci. Policy Manag. Sustain. Use 2000, 5, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torso, K.; Scofield, B.D.; Chess, D.W. Variations in Aquatic Macrophyte Phenology across Three Temperate Lakes in the Coeur d’Alene Basin. Aquat. Bot. 2020, 162, 103209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnoee, A.B.; Levi, P.S.; Baattrup-Pedersen, A.; Riis, T. Macrophytes Enhance Reach-Scale Metabolism on a Daily, Seasonal and Annual Basis in Agricultural Lowland Streams. Aquat. Sci. 2020, 83, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.; Zhou, Y.; Jeppesen, E.; Shi, K.; Qin, B. Response of Community Composition and Biomass of Submerged Macrophytes to Variation in Underwater Light, Wind and Trophic Status in a Large Eutrophic Shallow Lake. J. Environ. Sci. 2021, 103, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, N.A.; Pandit, A.K.; Ganai, B.A. Factors Affecting the Distribution Patterns of Aquatic Macrophytes. Limnol. Rev. 2014, 14, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rejmankova, E. The Role of Macrophytes in Wetland Ecosystems. J. Ecol. Environ. 2011, 34, 333–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polechońska, L.; Klink, A. Macrophytes as Passive Bioindicators of Trace Element Pollution in the Aquatic Environment. WIREs Water 2023, 10, e1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ijoma, G.N.; Lopes, T.; Mannie, T.; Mhlongo, T.N. Exploring Macrophytes’ Microbial Populations Dynamics to Enhance Bioremediation in Constructed Wetlands for Industrial Pollutants Removal in Sustainable Wastewater Treatment. Symbiosis 2024, 92, 323–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strotmann, U.; Durand, M.-J.; Thouand, G.; Eberlein, C.; Heipieper, H.J.; Gartiser, S.; Pagga, U. Microbiological Toxicity Tests Using Standardized ISO/OECD Methods—Current State and Outlook. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brisson, J.; Chazarenc, F. Maximizing Pollutant Removal in Constructed Wetlands: Should We Pay More Attention to Macrophyte Species Selection? Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3923–3930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Characteristics | Details |
|---|---|
| Number of Instances | 445: Samples collected between 06/1998 and 01/2018 |
| Number of Attributes | 17 |
| Attribute Types | Macrophyte species: qualitative (nominal) Collection date: date N (g/kg): numeric P (g/kg): numeric K+ (g/kg): numeric Ca2+ (g/kg): numeric Mg2+ (g/kg): numeric S (g/kg): numeric B (mg/kg): numeric Cu2+ (mg/kg): numeric Fe2+ (mg/kg): numeric Zn2+ (mg/kg): numeric Mn2+ (mg/kg): numeric Cd2+ (mg/kg): numeric Ni2+ (mg/kg): numeric Cr3+ (mg/kg): numeric Pb2+ (mg/kg): numeric |
| Alkaline Metallic, Alkaline Earth, and Non-Metallic Elements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | ANOVA p-Value | Clusterspecies1 | Clusterspecies2 | Clusterspeciesi |
| N | 0.002 * | a | b | a |
| K+ | 0.015 * | a | b | a |
| Ca2+ | <0.001 * | a | c | b |
| Mg2+ | <0.001 * | a | c | b |
| S | <0.001 * | a | c | b |
| B | <0.001 * | a | b | b |
| Transition and Post-Transition Metallic Elements | ||||
| Element | ANOVA p-Value | Clusterspecies1 | Clusterspecies2 | Clusterspecies3 |
| P | <0.001 * | a | a | b |
| Cu2+ | <0.001 * | a | a | b |
| Fe2+ | <0.001 * | a | b | c |
| Mn2+ | <0.001 * | a | b | c |
| Zn2+ | <0.001 * | a | b | b |
| Cd2+ | <0.001 * | a | b | c |
| Ni2+ | <0.001 * | a | b | b |
| Cr3+ | <0.001 * | a | b | b |
| Pb2+ | <0.001 * | b | a | c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pitelli, R.A.; Simões, R.P.; Pitelli, R.L.; Rocha, R.J.d.S.; Merenda, A.M.P.; da Cruz, F.P.; Lameirão, A.M.M.d.S.; Oliveira Júnior, A.J.d.; Gomes, R.H.M. Exploratory Analysis on the Chemical Composition of Aquatic Macrophytes in a Water Reservoir—Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Water 2025, 17, 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040582
Pitelli RA, Simões RP, Pitelli RL, Rocha RJdS, Merenda AMP, da Cruz FP, Lameirão AMMdS, Oliveira Júnior AJd, Gomes RHM. Exploratory Analysis on the Chemical Composition of Aquatic Macrophytes in a Water Reservoir—Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Water. 2025; 17(4):582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040582
Chicago/Turabian StylePitelli, Robinson Antonio, Rafael Plana Simões, Robinson Luiz Pitelli, Rinaldo José da Silva Rocha, Angélica Maria Pitelli Merenda, Felipe Pinheiro da Cruz, Antônio Manoel Matta dos Santos Lameirão, Arilson José de Oliveira Júnior, and Ramon Hernany Martins Gomes. 2025. "Exploratory Analysis on the Chemical Composition of Aquatic Macrophytes in a Water Reservoir—Rio de Janeiro, Brazil" Water 17, no. 4: 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040582
APA StylePitelli, R. A., Simões, R. P., Pitelli, R. L., Rocha, R. J. d. S., Merenda, A. M. P., da Cruz, F. P., Lameirão, A. M. M. d. S., Oliveira Júnior, A. J. d., & Gomes, R. H. M. (2025). Exploratory Analysis on the Chemical Composition of Aquatic Macrophytes in a Water Reservoir—Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. Water, 17(4), 582. https://doi.org/10.3390/w17040582






